Abstract
C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 16.304(2) Å, b = 11.1675(15) Å, c = 14.1041(16) Å, β = 109.322(4)°, V = 2423.3(5) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.0802, wR ref(F 2) = 0.1769, T = 150.0 K.
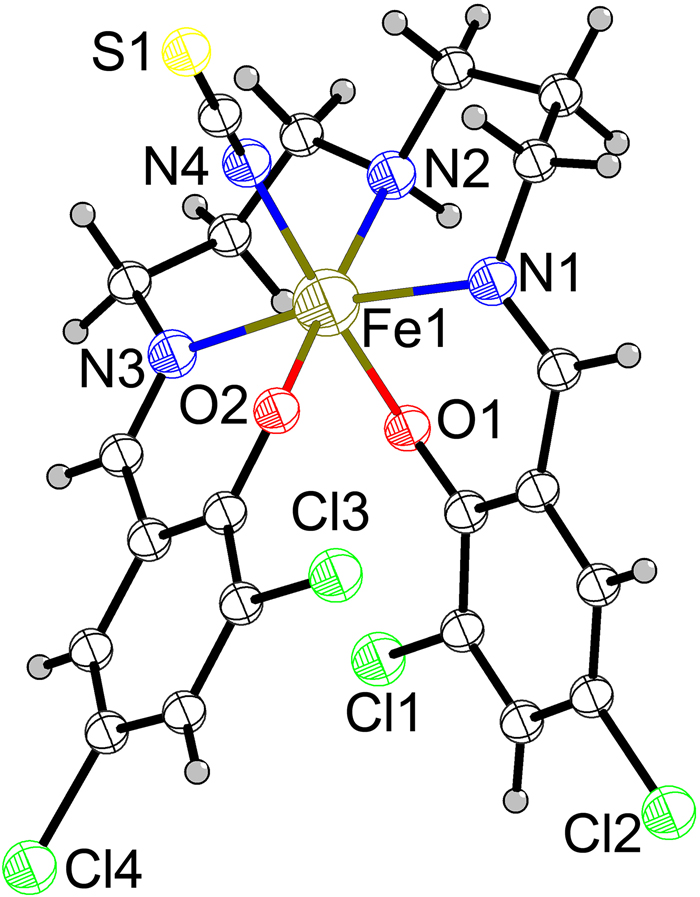
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Red block |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.16 × 0.12 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.18 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.0°, 97% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 16,085, 4167, 0.092 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 3042 |
| N(param)refined: | 298 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], Olex2 [2], SHELX [3, 4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe1 | 0.68685 (7) | 0.16998 (11) | 0.38499 (8) | 0.0288 (3) |
| Cl1 | 0.97872 (13) | 0.27064 (18) | 0.45449 (15) | 0.0336 (5) |
| Cl2 | 0.88176 (14) | 0.70500 (18) | 0.28935 (16) | 0.0364 (5) |
| Cl3 | 0.68504 (15) | 0.5748 (2) | 0.47682 (17) | 0.0439 (6) |
| Cl4 | 0.96799 (14) | 0.5130 (2) | 0.80399 (16) | 0.0372 (5) |
| S1 | 0.41465 (14) | 0.1760 (2) | 0.42112 (18) | 0.0459 (6) |
| O1 | 0.7954 (3) | 0.2115 (5) | 0.3599 (4) | 0.0283 (13) |
| O2 | 0.6895 (3) | 0.3138 (5) | 0.4630 (4) | 0.0314 (13) |
| N1 | 0.6265 (4) | 0.2661 (7) | 0.2511 (5) | 0.0336 (17) |
| N2 | 0.6763 (4) | 0.0139 (6) | 0.2881 (5) | 0.0340 (17) |
| H2 | 0.7164 | 0.0265 | 0.2551 | 0.041* |
| N3 | 0.7697 (4) | 0.0874 (6) | 0.5188 (5) | 0.0266 (15) |
| N4 | 0.5740 (5) | 0.1154 (7) | 0.4038 (5) | 0.0406 (19) |
| C00M | 0.5070 (5) | 0.1392 (7) | 0.4120 (6) | 0.0301 (19) |
| C1 | 0.7479 (5) | 0.4028 (7) | 0.2838 (6) | 0.0291 (19) |
| C2 | 0.8123 (5) | 0.3220 (7) | 0.3432 (6) | 0.0264 (18) |
| C3 | 0.8980 (5) | 0.3675 (7) | 0.3837 (6) | 0.0280 (18) |
| C4 | 0.9194 (5) | 0.4828 (7) | 0.3689 (6) | 0.0291 (19) |
| H4 | 0.9772 | 0.5111 | 0.3984 | 0.035* |
| C5 | 0.8541 (5) | 0.5580 (7) | 0.3093 (6) | 0.0299 (19) |
| C6 | 0.7705 (6) | 0.5211 (8) | 0.2690 (6) | 0.033 (2) |
| H6 | 0.7272 | 0.5752 | 0.2308 | 0.039* |
| C7 | 0.6609 (5) | 0.3594 (8) | 0.2286 (6) | 0.034 (2) |
| H7 | 0.6274 | 0.4040 | 0.1716 | 0.040* |
| C8 | 0.5449 (5) | 0.2205 (9) | 0.1791 (7) | 0.044 (2) |
| H8A | 0.5206 | 0.2799 | 0.1250 | 0.053* |
| H8B | 0.5018 | 0.2070 | 0.2137 | 0.053* |
| C9 | 0.5631 (6) | 0.1027 (9) | 0.1342 (7) | 0.046 (2) |
| H9A | 0.5100 | 0.0792 | 0.0789 | 0.056* |
| H9B | 0.6094 | 0.1171 | 0.1046 | 0.056* |
| C10 | 0.5904 (6) | −0.0011 (9) | 0.2068 (6) | 0.042 (2) |
| H10A | 0.5452 | −0.0136 | 0.2385 | 0.050* |
| H10B | 0.5927 | −0.0744 | 0.1682 | 0.050* |
| C11 | 0.7015 (6) | −0.1031 (8) | 0.3424 (7) | 0.041 (2) |
| H11A | 0.7064 | −0.1645 | 0.2939 | 0.049* |
| H11B | 0.6545 | −0.1284 | 0.3680 | 0.049* |
| C12 | 0.7865 (5) | −0.0986 (7) | 0.4297 (6) | 0.034 (2) |
| H12A | 0.8089 | −0.1813 | 0.4450 | 0.041* |
| H12B | 0.8294 | −0.0528 | 0.4085 | 0.041* |
| C13 | 0.7805 (6) | −0.0429 (7) | 0.5255 (6) | 0.033 (2) |
| H13A | 0.7306 | −0.0786 | 0.5407 | 0.040* |
| H13B | 0.8339 | −0.0623 | 0.5819 | 0.040* |
| C14 | 0.8191 (5) | 0.1512 (7) | 0.5922 (6) | 0.0265 (18) |
| H14 | 0.8595 | 0.1088 | 0.6460 | 0.032* |
| C15 | 0.8191 (5) | 0.2810 (7) | 0.6011 (5) | 0.0241 (17) |
| C16 | 0.8850 (5) | 0.3316 (8) | 0.6824 (6) | 0.0290 (19) |
| H16 | 0.9282 | 0.2812 | 0.7259 | 0.035* |
| C17 | 0.8881 (5) | 0.4510 (7) | 0.6998 (6) | 0.0284 (18) |
| C18 | 0.8274 (5) | 0.5294 (8) | 0.6359 (6) | 0.032 (2) |
| H18 | 0.8316 | 0.6134 | 0.6471 | 0.039* |
| C19 | 0.7613 (5) | 0.4811 (7) | 0.5560 (6) | 0.0290 (18) |
| C20 | 0.7547 (5) | 0.3548 (7) | 0.5363 (6) | 0.0273 (18) |
Source of material
A sample of 0.191 g of the powdered 3,5-dichromosalicylaldehyde (1 mmol) was placed in a conical flask containing 50 ml ethanol, than 0.131 g 3,3′-diaminodipropylamine 0.5 mmol was added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. Then 0.20 g Fe(NO3)3·9H2O (0.5 mmol) was added to the above mixture under stirring and the solution was gradually turned into purple-black. The obtained filtrate was kept undisturbed for two weeks. Black crystal suitable for single crystal diffraction analysis appeared at the bottom of the container.
Experimental details
The structure was solved with the Olex2 program [2] as an interface together with the SHELXT and SHELXL programs [3, 4]. All H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and refined using a riding model, with C–H = 0.98 (methylene), 0.95 Å (benzene), and with U iso(H) = 1.2 U eq(C) for H atoms.
Comment
The introduction of multidentate Schiff-base ligands that can both chelate and bridge metal ions, representing a promising route for the isolation of novel metallic complexes. So far, a number of complexes with unexpected geometries and properties have been synthesized via the combination of different multidentate Schiff-base ligands and 3d/4f metal ions. However, related research on halogenated multidentate ligands is still at an early stage. As a part of our current research interest on the exploration of the regulating effect of Schiff base ligands on transition metal complexes [5], [6], [7], [8], we report herein a new iron complex constructed by a halogenated multidentate ligand.
The asymmetric unit of the title structure consist of a mononuclear complex with the Fe(III) center showing octahedral coordination by tree nitrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms from halogenated ligand L2-, and one nitrogen atom from the SCN- ligand. The bond lengths distributions for Fe–O and Fe–N are in the range of 1.939(5) and 2.187(7) Å. The average bond length of Fe–N is slight longer than that of Fe–O. The bond angles of the Fe(III) centers range from 84.3(2)° to 175.8(2)°. These values match with the previously reported Fe(III) Schiff-base compounds [9]. Intermolecular interaction analysis shows that, beside the neighboring monomers create C–H⋯π interactions, the substituted chlorine atoms formed halogen bonding play an important part in linking the neighboring molecules to form one-dimensional helical supramolecular chain (Cl2⋯Cl1 i , D⋯A = 3.419(12) Å, Cl4⋯ Cl2ii, D⋯A = 3.427(3) Å symmetry code: (i): 2−x, 1−y, 1−z; x, 3/2−y, 1/2+z; Cl4⋯Cl2ii, D⋯A = 3.785(3) Å; symmetry code: (ii): x, 1/2−y, 1/2+z).
Funding source: Fund for Less Developed National Nature Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 31760257
Award Identifier / Grant number: 21761017
Funding source: Yunnan Provincial Undergraduate Universities
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2017FH001-002
Funding source: Innovative Research Team (in Science and Technology) in Universities of Yunnan Province
Funding source: Recruitment Program of Yunnan Province Experts Provincial Young Talents
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2019HB098
Funding source: Ten-Thousand Talents Program of Yunnan Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: YNWR-QNBJ-2018-273
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by Fund for Less Developed National Nature Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31760257, 21761017) as well as the Joint Basic Research Program (partial) of Yunnan Provincial Undergraduate Universities (2017FH001-002), the Program for Innovative Research Team (in Science and Technology) in Universities of Yunnan Province (IRTSTYN), the ment Program of Yunnan Province Experts Provincial Young Talents (2019HB098) and the Ten-Thousand Talents Program of Yunnan Province (YNWR-QNBJ-2018-273).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Agilent Technologies. CrysAlisPRO Software system; Agilent Technologies UK Ltd: Oxford, UK, 2015.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Buchwald, J. R., Kal, S., Civic, M. R., deJoode, I. M., Filatov, A. S., Dinolfo, P. H. Spin modulation and electrochemical behavior of a five-coordinate cobalt(III) salen complex. J. Coord. Chem. 2016, 69, 1695–1708; https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2016.1175001.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Sain, S., Saha, R., Mostafa, G., Fleck, M., Bandyopadhyay, D. Synthesis and crystal structure of three new copper(II) complexes with a tridentate amine and its Schiff bases. Polyhedron 2012, 31, 82–88; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2011.08.040.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Wu, Q., Huang, M., Li, T., Jiao, L., Tu, Y., Xu, X., Ma, X., Tian, H., Qiao, Y. Crystal and electronic structure of poly-halogenated lanthanide Schiff base complex: insights into halogen bond from structural and theoretical analysis. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1225, 129054; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129054.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Pogány, L., Brachňaková, B., Masárová, P., Moncol, J., Pavlik, J., Gál, M., Mazúr, M., Herchel, R., Nemec, I., Šalitroš, I. Impact of the Schiff base ligand substituents on the solid state and solution properties of eleven iron(iii) complexes. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 13916–13928; https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nj03087e.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Natke, D., Preiss, A., Klimke, S., Shiga, T., Boca, R., Ohba, M., Oshio, H., Renz, F. Structural, magnetic, and electrochemical characterization of iron(III) and cobalt complexes with penta-N3O2-dentate ligands. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 2021, 1498–1504; https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.202100081.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2021 Rui Duan et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO

