Abstract
C16H17NO2, orthorhombic, P212121 (no. 19), a = 6.3761(2) Å, b = 12.0521(4) Å, c = 17.3288(5) Å, V = 1331.64(7) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0462, wRref(F2) = 0.1243, T = 153(2) K.
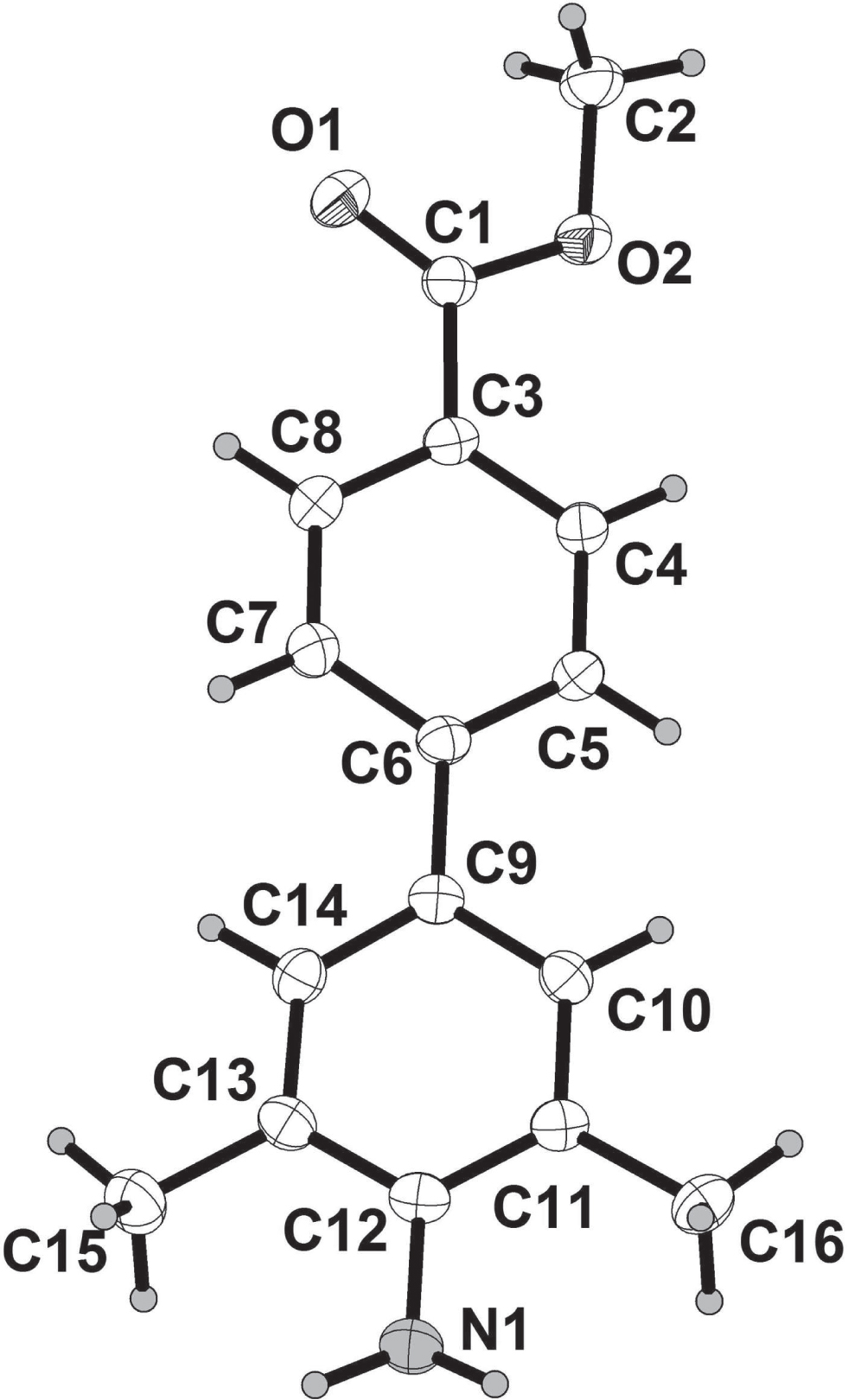
The asymmetric unit of the title crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Block, white |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54178 Å) |
| μ: | 0.67 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Agilent CCD, φ and ω-scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 73.6°, >97% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 2972, 2125, 0.026 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2010 |
| N(param)refined: | 184 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2, 3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | −0.3748(2) | −0.01044(15) | −0.03251(9) | 0.0348(4) |
| O2 | −0.0797(2) | −0.01015(13) | −0.10231(7) | 0.0266(4) |
| N1 | 0.6156(3) | 0.37525(17) | 0.38730(10) | 0.0318(4) |
| H1A | 0.545(5) | 0.389(3) | 0.4359(16) | 0.052(8)* |
| H1B | 0.717(5) | 0.426(2) | 0.3745(13) | 0.039(7)* |
| C1 | −0.1904(3) | 0.01148(17) | −0.03871(11) | 0.0232(4) |
| C2 | −0.1975(4) | −0.05720(19) | −0.16556(11) | 0.0306(5) |
| H2A | −0.3055 | −0.0063 | −0.1810 | 0.046* |
| H2B | −0.2601 | −0.1258 | −0.1494 | 0.046* |
| H2C | −0.1053 | −0.0707 | −0.2083 | 0.046* |
| C3 | −0.0620(3) | 0.06490(17) | 0.02223(10) | 0.0221(4) |
| C4 | 0.1455(3) | 0.09717(18) | 0.01065(10) | 0.0244(4) |
| H4 | 0.2096 | 0.0838 | −0.0367 | 0.029* |
| C5 | 0.2570(3) | 0.14897(18) | 0.06889(10) | 0.0240(4) |
| H5 | 0.3950 | 0.1704 | 0.0598 | 0.029* |
| C6 | 0.1671(3) | 0.16990(16) | 0.14115(10) | 0.0215(4) |
| C7 | −0.0423(3) | 0.13758(18) | 0.15166(11) | 0.0263(4) |
| H7 | −0.1073 | 0.1513 | 0.1987 | 0.032* |
| C8 | −0.1544(3) | 0.08566(18) | 0.09357(11) | 0.0270(4) |
| H8 | −0.2926 | 0.0645 | 0.1023 | 0.032* |
| C9 | 0.2866(3) | 0.22263(15) | 0.20517(10) | 0.0210(4) |
| C10 | 0.4705(3) | 0.28263(16) | 0.19202(10) | 0.0228(4) |
| H10 | 0.5217 | 0.2879 | 0.1419 | 0.027* |
| C11 | 0.5800(3) | 0.33479(15) | 0.25138(11) | 0.0226(4) |
| C12 | 0.5052(3) | 0.32717(16) | 0.32712(10) | 0.0231(4) |
| C13 | 0.3237(3) | 0.26408(17) | 0.34238(11) | 0.0256(4) |
| C14 | 0.2205(3) | 0.21392(16) | 0.28138(11) | 0.0241(4) |
| H14 | 0.1010 | 0.1723 | 0.2919 | 0.029* |
| C15 | 0.2467(4) | 0.2485(2) | 0.42396(12) | 0.0374(6) |
| H15A | 0.1360 | 0.1945 | 0.4245 | 0.056* |
| H15B | 0.1949 | 0.3178 | 0.4435 | 0.056* |
| H15C | 0.3602 | 0.2231 | 0.4558 | 0.056* |
| C16 | 0.7758(3) | 0.40006(18) | 0.23400(12) | 0.0299(5) |
| H16A | 0.8878 | 0.3748 | 0.2666 | 0.045* |
| H16B | 0.7504 | 0.4774 | 0.2434 | 0.045* |
| H16C | 0.8140 | 0.3896 | 0.1809 | 0.045* |
Source of material
Synthesis of 4-iodo-2,6-dimethylaniline [4, 5] . In a round bottom flask 2,6-dimethylaniline (18.12 g, 150 mmol, 1.0 equiv) and NaHCO3 (37.8 g, 450 mmol, 3.0 equiv) were introduced in MeOH (400 mL). Iodine (40 g, 157.5 mmol, 1.05 equiv) in CH2Cl2 (200 mL) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12 hours. Then, the solids were filtered off the mixture and rinsed with CH2Cl2. The filtrate was concentrated under vacuum leading to a dark orange oil. A saturated solution of sodium thiosulfate was added and the reaction mixture was stirred for 2 hours. After extraction with CH2Cl2, the combined organic layers were dried over MgSO4 and concentrated under vacuum. The product was obtained as brown oil (25.6 g, 69% yield). Synthesis of the title compound [6]. A mixture of (4-(methoxycarbonyl)phenyl)boronic acid (9.37 g, 52.09 mmol, 1.1 equiv), 4-iodo-2,6-dimethylaniline (11.7 g, 47.35 mmol, 1.0 equiv), palladium tetrakis(triphenylphosphine) (1.64 g, 1.42 mmol, 3 mol%), and K2CO3 (21.6 g, 156 mmol, 3.3 equiv) in 330 mL of dioxane/H2O (3/1) was stirred under nitrogen for 72 h at 90 °C. After the mixture was cooled to room temperature, it was extracted with CH2Cl2 and washed with H2O several times. The organic layer was dried with MgSO4, and the solvent was removed with a rotary evaporator. The crude product was purified by column chromatography using silica gel and petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (20/1) as the eluent. The product was obtained after removal of the solvents (7.2 g, 60% yield). The crystal suitable for X-ray analysis was obtained by slow evaporation of methanol at room temperature over a period of seven days, yield: 0.62 g (88.5%). Melting point: 113–114 °C. Elemental analysis–found: C, 75.22%; H, 6.73%; N, 5.52%; calculated for C16H17NO2: C, 75.27%; H, 6.71%; N, 5.49%.
Experimental details
All hydrogen atoms were identified in difference Fourier syntheses. The structure was solved by direct methods [2] and refined on F2 by full-matrix least-squares technique using the SHELX program [3]. Except the solvent molecules, hydrogen atoms attached to carbon were placed in geometrically idealized positions and refined using a riding model.
Discussion
In recent years, biphenyl moieties have emerged as versatile and useful building units in a variety of synthetic transformations, which can build all kinds of biologically active molecules [7], [8], [9]. For example, biphenyl mannoside FimH inhibitors were designed. Diverse modifications to the biphenyl ring to improve drug like physical and pharmacokinetic properties of mannosides were assessed for FimH binding affinity based on their effects on hemagglutination and biofilm formation along with direct FimH binding assays [10].
The title compound is composed of two substituted phenyl moieties. The dihedral angle between the planes of two aromatic rings is 18.5°. The bond lengths of C12—N1 and C1—O1 are 1.385(3) Å and 1.210(2) Å, respectively. And the bond lengths of C1—O2 and C2—O2 are 1.334(2) Å and 1.445(2) Å, respectively. As a result of the conjugation of these aromatic rings, the bond length of C6—C9 is 1.488(3) Å, which is shorter than that of typical C—C (1.53 Å). The bond angle (C1—O2—C2) and (O1—C1—O2) are 115.37(16)° and 122.99(19)°, respectively. There is an intermolecular hydrogen bond (d D⋯A 3.254 Å; H⋯A 2.335 Å) between H1A and O1 atom (symmetry code: −x, y + 1/2, −z + 1/2), which produce one dimensional chains to stabilize the crystal structure. In the crystal packing, dipole-dipole and van der Waals interactions are effective besides an intermolecular hydrogen bond in the molecular packing. Bond lengths and angles of the title molecule are in the typical ranges [11, 12] .
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for financial support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 21362047) and Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Province (grant no. QKHSYZ-2013-3061 and QKHJZ-2014-2175).
References
Agilent Technologies: CrysAlisPRO Software system, version 1.171.38.43, Agilent Technologies UK Ltd, Oxford, UK (2015).Search in Google Scholar
Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXS-97. Program for the Solution of Crystal Structures. University of Göttingen, Germany (1997).Search in Google Scholar
Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar
D’Souza, B. R.; Lane, T. K.; Louie, J.: Iron-catalyzed cycloaddition of alkynenitriles and alkynes. Org. Lett. 13 (2011) 2936–2939.10.1021/ol2009939Search in Google Scholar
Brody, M. S.; Finn, M. G.: Palladium-catalyzed coupling of functionalized bromoarenes to a polystyrene-bound aryl tributylstannane. Tetrahedron Lett. 40 (1999) 415–418.10.1016/S0040-4039(98)02384-3Search in Google Scholar
Shi, D.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, H.; Cai, B.; Lu, J.: Synthesis, structures, and properties of two three-dimensional metal-organic frameworks, based on concurrent ligand extension. Inorg. Chem. 51 (2012) 6498–6506.10.1021/ic202624eSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
Ghisaidoobe, A. T.; van den Berg, R. J. B. H. N.; Butt, S. S.; Strijland, A.; Donker–Koopman, W. E.; Scheij, S.; van den Nieuwendijk, A. M. C. H.; Koomen, G. J.; van Loevezijn, A.; Leemhuis, M.; Wennekes, T.; van der Stelt, M.; van der Marel, G. A.; van Boeckel, C. A. A.; Aerts, J. M. F. G.; Overkleeft, H. S.: Identification and development of biphenyl substituted iminosugars as improved dual glucosylceramide synthase/neutral glucosylceramidase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 57 (2014) 9096–9104.10.1021/jm501181zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
Uehling, D. E.; Shearer, B. G.; Donaldson, K. H.; Chao, E. Y.; Deaton, D. N.; Adkison, K. K.; Brown, K. K.; Cariello, N. F.; Faison, W. L.; Lancaster, M. E.; Lin, J.; Hart, R.; Milliken, T. O.; Paulik, M. A.; Sherman, B. W.; Sugg, E. E.; Cowan, C.: Biarylaniline phenethanolamines as potent and selective β3 adrenergic receptor agonists. J. Med. Chem. 49 (2006) 2758–2771.10.1021/jm0509445Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Woo, L. W. L.; Jackson, T.; Putey, A.; Cozier, G.; Leonard, P.; Acharya, K. R.; Chander, S. K.; Purohit, A.; Reed, M. J.; Potter, B. V. L.: Highly potent first examples of dual aromatase–steroid sulfatase inhibitors based on a biphenyl template. J. Med. Chem. 53 (2010) 2155–2170.10.1021/jm901705hSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
Han, Z.; Pinkner, J. S.; Ford, B.; Chorell, E.; Crowley, J. M.; Cusumano, C. K.; Campbell, S.; Henderson, J. P.; Hultgren, S. J.; Janetka, J. W.: Lead optimization studies on FimH antagonists: discovery of potent and orally bioavailable ortho–substituted biphenyl mannosides. J. Med. Chem. 51 (2008) 4002–4020.10.1021/jm300165mSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Hartmann, M.; Daniliuc, C. G.; Studer, A.: Preparation of phenanthrenes from ortho–amino–biphenyls and alkynes via base–promoted homolytic aromatic substitution. Chem. Commun. 51 (2015) 3121–3123.10.1039/C4CC10063HSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
Dikhtiarenko, A.; Olivos Suarez, A. I.; Pustovarenko, A.; García-Granda, S.; Gascon J.: Crystal structure of 2,2′-diamino-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid dihydrate, C14H16N2O6. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 231 (2016) 65–67.10.1515/ncrs-2014-9143Search in Google Scholar
©2018 Mao-Yuan Zhang et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Bis(tetraethylammonium) carbonate – boric acid – water (1/2/5), C17H56B2N2O14
- Crystal structure of 4-methoxy-6-phenyl-2H-pyran-2-one, C12H10O3
- Crystal structure of tris{(3-((E)-(((E)-2-oxidobenzylidene)hydrazono)methyl)-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-olato-κ3O,N:N′)}dicobalt(III)tris(dimethylformamide), C60H50Co2N9O15
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(1-methyl-[4,4′-bipyridin]-1-ium-κN)-tetrakis(μ3-sulfato-κ3O:O′:O′′)trizinc(II)], C22H22Zn3N4O16S4
- Crystal structure of (5Z,10Z)-3,13-dichloro-17,18-dioxo-5,11-diphenyl-8,9,17,18-tetrahydro-7H-dibenzo[e,n][1,4,8,12]tetraazacyclopentadecine-16,19-diido-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)copper(II), C31H22N4O2Cl2Cu
- Crystal structure of bis{5-methoxy-2-(((2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C34H24N2O8Zn
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-((((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))diphenolato-κ2N;κ4O)nickel(II), C28H22N2O4Ni
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-((1E,1′E)-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(naphthalen-2-olato)cobalt(II), C36H26N2O4Co
- Crystal structure of camptothecin, C20H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of (2-(chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato–κ2O,O′)(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, Ni(C16H36N4)(C12H12O4Cl)ClO4⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-chloro-6-methoxyquinolin-3-yl)-5-phenylisoxazole (C19H13ClN2O2)
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-bis{[(E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)aniline]copper (II)}, C44H56Cu2N4O8
- Crystal structure of diethyl 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dioxane-5,5-dicarboxylate, C16H19Cl1O6
- Crystal structure of (μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-3,3′-dicarboxylato)-bis(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)-di-nickel(II) perchlorate N,N′-dimethylformamide solvate, C50H92Cl2N12Ni2O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′)-(1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κN)nickel(II)] 2-aminonicotinate nitrate – 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane – water (2/1/8), C36H44N8NiO12
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenoxy)phthalato-κ3O,O′:O′′)-(μ2-1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C22H14CuNO9
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(methanol-κO)-bis(μ2-4-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoato-κ2N:O)-bis(triphenylphospine-κP)disilver(I)], C61H52Ag2N2O6P2
- The crystal structure of 6-(4-bromobenzyl)-1,3,5-trimethyl-7-phenyl-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine-2,4(3H)-dione, C22H20BrN3O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(2-(2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetato-κO;κ2O′,O′′)-(μ2-1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C44H32N4ZnCl4O4
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[N-phenyl-2-(quinolin-8-yloxy)acetamide-κ3-N,O,O′]-nitrato(κ2O,O′)-cerium(III) dinitrate - acetone (1/2), C40H44N7O17Ce
- Crystal structure of the 2D coordination polymer poly[aqua(μ2-2,2′-(1,2-phenylene)diacetato-κ3O,O′:O′)-(μ2-4,4′-bis((1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1,1′-biphenyl-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C28H26CoN6O5
- Crystal structure of (dimethylformamide-κO)(perchlorato-κ2O,O′){μ2-6,6′-((1,2-phenylenebis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-bromo-2-methoxyphenolate)-κ8N,N′,O:O,O′:O′,O′′,O′′′}sodium(I)nickel(II), C25H23Br2ClN3NaNiO9
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)(pyrimidin-2-yl)amido-κ2N,N′)-bis(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-N,N′-κ2N:N′)zinc(II) – methanol (1/2), C32H34N10O6S2Zn
- Synthesis and crystal structure poly[aqua(μ3-2-(((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)ammonio)acetate-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′) sodium] monohydrate, C18H18NNaO11S
- Crystal structure of methyl 4′-amino-3′,5′-diisopropyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C20H25NO2
- Crystal structure of (η6-1-isopropyl-4-methyl benzene)-(N-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) perchlorate, C22H22Cl4N2O4Ru
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-(1-Chlorocyclopropyl)-3-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-hydroxypropyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3(2H)-thione, C14H15Cl2N3OS
- Crystal structure of methyl 4′-amino-3′,5′-dimethyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C16H17NO2
- The crystal structure of 1-(5-ferrocenyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pentan-1-on, C19H19F3FeN2O
- The crystal structure of (3S,12R,20R,24S)-3,12-diacetyl-20,24-epoxy-dammarane-3,12,25-triol acetone solvate, C34H56O6
- Crystal structure of methyl 10-(pyridin-4-yl)-anthracene-9-carboxylate, C21H15NO2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(di(N2,N6-dihydroxypyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide))potassium(I)]tetrahydrate, C14H25N6O14K
- Crystal structure of poly{[μ2-(E)-1,4-bis(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)but-2-ene-κ2N:N′][μ3–cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′]cadmium(II)}, C26H26CdN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ3-[2,2′-bipyridine]-3,3′-dicarboxylato-κ4N,N′:O:O′)zinc(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C15H15N3O6Zn
- The crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-tris(μ2-2,6-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)naphthalene-κ2N:N′)-bis(thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylato-κ1O)]dicobalt(II), C30H24CoN6O6S
- Crystal structure of (S)-1-(5-(anthracen-9-yl)-3-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propan-1-one, C26H22N2O
- Crystal structure of 5-methyl-3,3-diphenyl-1-tosyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine, C25H25NO2S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of μ-[1,1′-di(mesitylphosphanido)ferrocene]bis[η5-cyclopentadienylnickel(II)] tetrahydrofurane solvate, C42H48FeNi2OP2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15ClN2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(1-(phenylsulfonyl)-2-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O)nickel(II), C24H22N8O4S2Ni
- Crystal Structure of bis(1-(phenylsulfonyl)-2-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O)copper(II), C24H22N8O4S2Cu
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[aqua{μ3-(1S,2S)-1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-1-ium-2-carboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′}sodium(I)] monohydrate, C21H22NNaO11S
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene–1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)propane (1/1), C19H14F4I2N2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ-N-i-propyl-N-n-propyldithiocarbamato-κ2S:S′) bis(N-i-propyl-N-n-propyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)dizinc(II), C28H56N4S8Zn2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ-N-i-propyl-N-n-propyldithiocarbamato-κ3S,S′:S)bis(N-i-propyl-N-n-propyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)dicadmium(II), C28H56Cd2N4S8
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-di-n-butyldithiocarbamato-κ3S,S′:S;κ3S:S:S′)-hexacarbonyl-di-rhenium(I), C24H36N2O6Re2
- Crystal structure of 7-(4-methylphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a][1,3,5]triazin-4-amine, C12H11N5
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal O-isopropyl phenylcarbamothioate – 4,4′-bipyridine (2/1), C15H17N2OS
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[chlorido-{μ2-2-(((3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methyl)amino)-3-hydroxybutanoato-κ4N,N,O:O′}copper(II)], C11H16ClCuN2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-di(ethanol)-bis{μ2-5-(N,N′-diethylamine)-5′-methoxyl-2,2′-[ethylenediyldioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenolato-κ6O:O,N,N,O′:O′}trinickel(II) – ethanol – acetonitrile (1/2/2), C58H86Ni3N8O18
- Crystal structure of the bis((E)-O-ethyl-N-phenylthiocarbamate) – 4,4′-bipyridine co-crystal (2/1), C28H30N4O2S2
- Crystal structure of the (E)-O-methyl-N-phenyl-thiocarbamate – 4,4′-bipyridine (1/1), C18H17N3OS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-diethyldithiocarbamato-κ3S,S′:S′)-bis(tricyclohexylphosphane-κP)dicopper(I), C46H86Cu2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of N-(3-chlorophenyl)ethoxycarbothioamide, C9H10ClNOS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-pyrrolidine-1-carbodithioato-κ3S,S′:S;κ3S:S:S′)-bis(tricyclohexylphosphane-P)-di-copper(I), C46H82Cu2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of N-(2-chlorophenyl)methoxycarbothioamide, C8H8ClNOS
- Crystal structure of chlorido-methanol-(N-(2-(oxy)-3-methoxybenzylidene)pyridine-4-carbohydrazonato-κ3O,N,O′)-(4-methylphenyl)methyl-tin(IV), C23H24ClN3O4Sn
- Crystal structure of N-(3-chlorophenyl)(propan-2-yloxy)carbothioamide, C10H12ClNOS
- Crystal structure of 1-[(Z)-[4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butan-2-ylidene]amino]-3-phenylurea, C18H21N3O2
- A triclinic polymorph of bis(μ-N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)dithiocarbamato-κ3S,S′:S′) bis(N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)dithiocarbamato-κ2S:S′)zinc(II), C20H40N4O8S8Zn2
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Bis(tetraethylammonium) carbonate – boric acid – water (1/2/5), C17H56B2N2O14
- Crystal structure of 4-methoxy-6-phenyl-2H-pyran-2-one, C12H10O3
- Crystal structure of tris{(3-((E)-(((E)-2-oxidobenzylidene)hydrazono)methyl)-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-olato-κ3O,N:N′)}dicobalt(III)tris(dimethylformamide), C60H50Co2N9O15
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(1-methyl-[4,4′-bipyridin]-1-ium-κN)-tetrakis(μ3-sulfato-κ3O:O′:O′′)trizinc(II)], C22H22Zn3N4O16S4
- Crystal structure of (5Z,10Z)-3,13-dichloro-17,18-dioxo-5,11-diphenyl-8,9,17,18-tetrahydro-7H-dibenzo[e,n][1,4,8,12]tetraazacyclopentadecine-16,19-diido-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)copper(II), C31H22N4O2Cl2Cu
- Crystal structure of bis{5-methoxy-2-(((2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C34H24N2O8Zn
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-((((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))diphenolato-κ2N;κ4O)nickel(II), C28H22N2O4Ni
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-((1E,1′E)-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(naphthalen-2-olato)cobalt(II), C36H26N2O4Co
- Crystal structure of camptothecin, C20H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of (2-(chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato–κ2O,O′)(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, Ni(C16H36N4)(C12H12O4Cl)ClO4⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-chloro-6-methoxyquinolin-3-yl)-5-phenylisoxazole (C19H13ClN2O2)
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-bis{[(E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)aniline]copper (II)}, C44H56Cu2N4O8
- Crystal structure of diethyl 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dioxane-5,5-dicarboxylate, C16H19Cl1O6
- Crystal structure of (μ2-2,2′-bipyridine-3,3′-dicarboxylato)-bis(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)-di-nickel(II) perchlorate N,N′-dimethylformamide solvate, C50H92Cl2N12Ni2O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′)-(1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κN)nickel(II)] 2-aminonicotinate nitrate – 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane – water (2/1/8), C36H44N8NiO12
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-3-(3,5-dicarboxyphenoxy)phthalato-κ3O,O′:O′′)-(μ2-1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)ethane-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C22H14CuNO9
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(methanol-κO)-bis(μ2-4-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoato-κ2N:O)-bis(triphenylphospine-κP)disilver(I)], C61H52Ag2N2O6P2
- The crystal structure of 6-(4-bromobenzyl)-1,3,5-trimethyl-7-phenyl-1,5-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine-2,4(3H)-dione, C22H20BrN3O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(2-(2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetato-κO;κ2O′,O′′)-(μ2-1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C44H32N4ZnCl4O4
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[N-phenyl-2-(quinolin-8-yloxy)acetamide-κ3-N,O,O′]-nitrato(κ2O,O′)-cerium(III) dinitrate - acetone (1/2), C40H44N7O17Ce
- Crystal structure of the 2D coordination polymer poly[aqua(μ2-2,2′-(1,2-phenylene)diacetato-κ3O,O′:O′)-(μ2-4,4′-bis((1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1,1′-biphenyl-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C28H26CoN6O5
- Crystal structure of (dimethylformamide-κO)(perchlorato-κ2O,O′){μ2-6,6′-((1,2-phenylenebis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-bromo-2-methoxyphenolate)-κ8N,N′,O:O,O′:O′,O′′,O′′′}sodium(I)nickel(II), C25H23Br2ClN3NaNiO9
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)(pyrimidin-2-yl)amido-κ2N,N′)-bis(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-N,N′-κ2N:N′)zinc(II) – methanol (1/2), C32H34N10O6S2Zn
- Synthesis and crystal structure poly[aqua(μ3-2-(((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)ammonio)acetate-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′) sodium] monohydrate, C18H18NNaO11S
- Crystal structure of methyl 4′-amino-3′,5′-diisopropyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C20H25NO2
- Crystal structure of (η6-1-isopropyl-4-methyl benzene)-(N-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) perchlorate, C22H22Cl4N2O4Ru
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-(1-Chlorocyclopropyl)-3-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-hydroxypropyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3(2H)-thione, C14H15Cl2N3OS
- Crystal structure of methyl 4′-amino-3′,5′-dimethyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C16H17NO2
- The crystal structure of 1-(5-ferrocenyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pentan-1-on, C19H19F3FeN2O
- The crystal structure of (3S,12R,20R,24S)-3,12-diacetyl-20,24-epoxy-dammarane-3,12,25-triol acetone solvate, C34H56O6
- Crystal structure of methyl 10-(pyridin-4-yl)-anthracene-9-carboxylate, C21H15NO2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(di(N2,N6-dihydroxypyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide))potassium(I)]tetrahydrate, C14H25N6O14K
- Crystal structure of poly{[μ2-(E)-1,4-bis(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)but-2-ene-κ2N:N′][μ3–cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′]cadmium(II)}, C26H26CdN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ3-[2,2′-bipyridine]-3,3′-dicarboxylato-κ4N,N′:O:O′)zinc(II)] – dimethylformamide (1/1), C15H15N3O6Zn
- The crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-tris(μ2-2,6-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)naphthalene-κ2N:N′)-bis(thiophene-2,5-dicarboxylato-κ1O)]dicobalt(II), C30H24CoN6O6S
- Crystal structure of (S)-1-(5-(anthracen-9-yl)-3-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)propan-1-one, C26H22N2O
- Crystal structure of 5-methyl-3,3-diphenyl-1-tosyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine, C25H25NO2S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of μ-[1,1′-di(mesitylphosphanido)ferrocene]bis[η5-cyclopentadienylnickel(II)] tetrahydrofurane solvate, C42H48FeNi2OP2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H15ClN2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(1-(phenylsulfonyl)-2-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O)nickel(II), C24H22N8O4S2Ni
- Crystal Structure of bis(1-(phenylsulfonyl)-2-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O)copper(II), C24H22N8O4S2Cu
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[aqua{μ3-(1S,2S)-1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-1-ium-2-carboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′}sodium(I)] monohydrate, C21H22NNaO11S
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene–1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)propane (1/1), C19H14F4I2N2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ-N-i-propyl-N-n-propyldithiocarbamato-κ2S:S′) bis(N-i-propyl-N-n-propyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)dizinc(II), C28H56N4S8Zn2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ-N-i-propyl-N-n-propyldithiocarbamato-κ3S,S′:S)bis(N-i-propyl-N-n-propyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)dicadmium(II), C28H56Cd2N4S8
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-di-n-butyldithiocarbamato-κ3S,S′:S;κ3S:S:S′)-hexacarbonyl-di-rhenium(I), C24H36N2O6Re2
- Crystal structure of 7-(4-methylphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a][1,3,5]triazin-4-amine, C12H11N5
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal O-isopropyl phenylcarbamothioate – 4,4′-bipyridine (2/1), C15H17N2OS
- Crystal structure of the coordination polymer catena-poly[chlorido-{μ2-2-(((3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methyl)amino)-3-hydroxybutanoato-κ4N,N,O:O′}copper(II)], C11H16ClCuN2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-di(ethanol)-bis{μ2-5-(N,N′-diethylamine)-5′-methoxyl-2,2′-[ethylenediyldioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenolato-κ6O:O,N,N,O′:O′}trinickel(II) – ethanol – acetonitrile (1/2/2), C58H86Ni3N8O18
- Crystal structure of the bis((E)-O-ethyl-N-phenylthiocarbamate) – 4,4′-bipyridine co-crystal (2/1), C28H30N4O2S2
- Crystal structure of the (E)-O-methyl-N-phenyl-thiocarbamate – 4,4′-bipyridine (1/1), C18H17N3OS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-diethyldithiocarbamato-κ3S,S′:S′)-bis(tricyclohexylphosphane-κP)dicopper(I), C46H86Cu2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of N-(3-chlorophenyl)ethoxycarbothioamide, C9H10ClNOS
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-pyrrolidine-1-carbodithioato-κ3S,S′:S;κ3S:S:S′)-bis(tricyclohexylphosphane-P)-di-copper(I), C46H82Cu2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of N-(2-chlorophenyl)methoxycarbothioamide, C8H8ClNOS
- Crystal structure of chlorido-methanol-(N-(2-(oxy)-3-methoxybenzylidene)pyridine-4-carbohydrazonato-κ3O,N,O′)-(4-methylphenyl)methyl-tin(IV), C23H24ClN3O4Sn
- Crystal structure of N-(3-chlorophenyl)(propan-2-yloxy)carbothioamide, C10H12ClNOS
- Crystal structure of 1-[(Z)-[4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butan-2-ylidene]amino]-3-phenylurea, C18H21N3O2
- A triclinic polymorph of bis(μ-N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)dithiocarbamato-κ3S,S′:S′) bis(N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)dithiocarbamato-κ2S:S′)zinc(II), C20H40N4O8S8Zn2

