Abstract
C24H21F6NO3, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 16.0076(10) Å, b = 7.7424(4) Å, c = 17.3259(11) Å, β = 96.161(5)°, V = 2134.9(2) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.0563, wR ref(F 2) = 0.1517, T = 100.0(1) K.
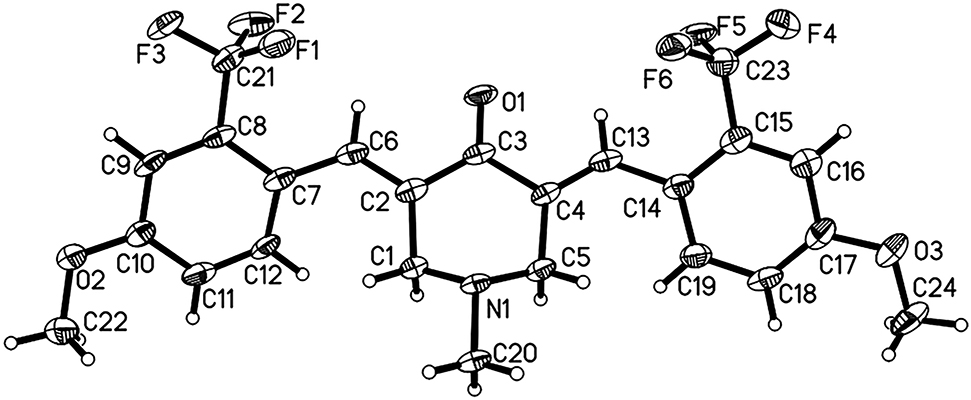
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.11 × 0.10 × 0.08 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.13 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 8653, 3958, 0.040 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 3232 |
| N(param)refined: | 310 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.58995 (13) | 0.3371 (3) | 0.09157 (12) | 0.0189 (5) |
| H1A | 0.605963 | 0.421036 | 0.132044 | 0.023* |
| H1B | 0.626498 | 0.237557 | 0.100498 | 0.023* |
| C2 | 0.49983 (13) | 0.2824 (3) | 0.09579 (12) | 0.0188 (5) |
| C3 | 0.45205 (13) | 0.2146 (3) | 0.02408 (12) | 0.0183 (5) |
| C4 | 0.49522 (13) | 0.2158 (3) | −0.04905 (12) | 0.0178 (5) |
| C5 | 0.58385 (13) | 0.2841 (3) | −0.04460 (12) | 0.0196 (5) |
| H5A | 0.622935 | 0.188860 | −0.035028 | 0.024* |
| H5B | 0.592958 | 0.335375 | −0.094098 | 0.024* |
| C6 | 0.46004 (14) | 0.2882 (3) | 0.16050 (12) | 0.0201 (5) |
| H6 | 0.403223 | 0.260128 | 0.154364 | 0.024* |
| C7 | 0.49564 (13) | 0.3334 (3) | 0.23924 (12) | 0.0198 (5) |
| C8 | 0.44807 (13) | 0.4112 (3) | 0.29482 (12) | 0.0200 (5) |
| C9 | 0.48440 (14) | 0.4547 (3) | 0.36771 (13) | 0.0239 (5) |
| H9 | 0.452093 | 0.506695 | 0.402739 | 0.029* |
| C10 | 0.56946 (14) | 0.4216 (3) | 0.38967 (12) | 0.0219 (5) |
| C11 | 0.61603 (14) | 0.3357 (3) | 0.33852 (12) | 0.0226 (5) |
| H11 | 0.671741 | 0.306240 | 0.353469 | 0.027* |
| C12 | 0.57907 (13) | 0.2947 (3) | 0.26552 (12) | 0.0209 (5) |
| H12 | 0.611366 | 0.238054 | 0.231831 | 0.025* |
| C13 | 0.45160 (13) | 0.1566 (3) | −0.11345 (12) | 0.0199 (5) |
| H13 | 0.397470 | 0.118478 | −0.107950 | 0.024* |
| C14 | 0.47775 (13) | 0.1436 (3) | −0.19215 (12) | 0.0187 (5) |
| C15 | 0.41857 (14) | 0.1618 (3) | −0.25854 (12) | 0.0211 (5) |
| C16 | 0.44102 (14) | 0.1459 (3) | −0.33253 (13) | 0.0242 (5) |
| H16 | 0.400995 | 0.160780 | −0.375031 | 0.029* |
| C17 | 0.52404 (14) | 0.1073 (3) | −0.34380 (12) | 0.0236 (5) |
| C18 | 0.58299 (14) | 0.0865 (3) | −0.28080 (13) | 0.0232 (5) |
| H18 | 0.638223 | 0.059735 | −0.288162 | 0.028* |
| C19 | 0.56019 (13) | 0.1053 (3) | −0.20603 (12) | 0.0212 (5) |
| H19 | 0.600988 | 0.092037 | −0.164012 | 0.025* |
| C20 | 0.68703 (13) | 0.4750 (3) | 0.01643 (13) | 0.0218 (5) |
| H20A | 0.725461 | 0.380431 | 0.026475 | 0.033* |
| H20B | 0.698107 | 0.560944 | 0.056145 | 0.033* |
| H20C | 0.694110 | 0.524731 | −0.033198 | 0.033* |
| C21 | 0.35576 (14) | 0.4435 (3) | 0.27449 (13) | 0.0245 (5) |
| C22 | 0.69049 (15) | 0.4672 (3) | 0.47956 (14) | 0.0319 (6) |
| H22A | 0.707049 | 0.348018 | 0.482764 | 0.048* |
| H22B | 0.706336 | 0.522605 | 0.528516 | 0.048* |
| H22C | 0.717879 | 0.523495 | 0.439804 | 0.048* |
| C23 | 0.32754 (14) | 0.1935 (3) | −0.24898 (13) | 0.0230 (5) |
| C24 | 0.62044 (16) | 0.0421 (4) | −0.43534 (15) | 0.0403 (7) |
| H24A | 0.661283 | 0.121630 | −0.411280 | 0.061* |
| H24B | 0.623326 | 0.041165 | −0.490398 | 0.061* |
| H24C | 0.631866 | −0.071604 | −0.414813 | 0.061* |
| F1 | 0.33702 (8) | 0.52726 (17) | 0.20745 (7) | 0.0280 (3) |
| F2 | 0.31109 (8) | 0.29569 (18) | 0.26835 (8) | 0.0346 (4) |
| F3 | 0.32217 (8) | 0.53810 (19) | 0.32878 (8) | 0.0350 (4) |
| F4 | 0.28055 (8) | 0.22091 (19) | −0.31646 (7) | 0.0352 (4) |
| F5 | 0.29317 (8) | 0.05606 (16) | −0.21648 (8) | 0.0294 (4) |
| F6 | 0.31521 (8) | 0.32848 (15) | −0.20345 (7) | 0.0249 (3) |
| N1 | 0.60094 (11) | 0.4123 (2) | 0.01625 (10) | 0.0187 (4) |
| O1 | 0.38112 (9) | 0.15587 (19) | 0.02407 (8) | 0.0219 (4) |
| O2 | 0.60103 (10) | 0.4784 (2) | 0.46102 (8) | 0.0292 (4) |
| O3 | 0.53849 (10) | 0.0945 (2) | −0.41980 (9) | 0.0342 (4) |
Source of material
N-methyl-4-piperidone (0.3 mL, 3.0 mmol) and 4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl) benzaldehyde (880.7 mg, 5.0 mmol) were dissolved in 12 mL acetic acid. Then dry hydrogen chloride gas was flowed continuously into the solution for 50 min. After gas insertion, the reaction system was stirred at room temperature for eight days. The response endpoint was detected by thin layer chromatography. When the reaction was finished, the precipitate was filtered from the reaction system, then it was dissolved in distilled water and set to a neutral pH with saturated aqueous Na2CO3 solution. The precipitate was filtered from the system and dissolved with dichloromethane. The organic phase was washed with deionized water and brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and condensed under vacuum. The crude product was purified by silica-gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 8:1, v/v). Crystals were obtained via solvent evaporation in the mixed solvents of dichloromethane and methanol (1:1, v/v) and drying under vacuum at 333 K for 4 h.
Experimental details
The H atoms were placed in idealized positions and treated as riding on their parent atoms, with d(C–H) = 0.96 Å (methyl), U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C), and d(C–H) = 0.97 Å (methylene), U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C), and d(C–H) = 0.93 Å (aromatic), U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C).
Comment
Curcumin has anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, anti-oxidation and other activities. But its clinical application is limited because of its low stability, poor bioavailability and false positive. So structural modification based on curcumin was carried out and large amounts of curcumin analogues have been reported. There in, (3E, 5E)-3,5-bis(arylene)-4-piperidones (BAPs) was a very distinguished class because they could inhibit tumor growth by anti-inflammatory and inhibiting NF-κB dependent signaling pathways [4]. Some symmetric and asymmetric BAPs had been designed as anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory agents [5], [6]. However, BAPs have rarely been developed as anti-neuroinflammatory drugs, so the synthesis of novel BAPs with anti-neuroinflammatory activities are of great significance.
Single-crystal structure analysis reveals that the title compound contains one molecule in the asymmetric unit (cf. the figure). Bond lengths and angles are all in the expected ranges. Arylidene moieties on both sides of piperidone adopt the E stereochemistry [7]. The dihedral angles between the benzylidene moieties and piperidone ring are 44.82° and 40.62°, respectively. In title compound, the peripheric heteroatoms (such as F, N, O, S) may act as hydrogen bonding acceptors for bioactive molecules with the aim of creating more anti-inflammatory activity [8].
Funding source: Science and Technology Innovation Development Plan of Yantai
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2020XDRH105
Funding source: National Natural Science Foundation of China 10.13039/501100001809
Award Identifier / Grant number: 81473104
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Science and Technology Innovation Development Plan of Yantai (No. 2020XDRH105) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81473104).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Rigaku, O. D. CrysAlisPRO; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd: Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England, 2017.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Su, C. M., Hou, G. G., Wang, C. H., Zhang, H. Q., Yang, C., Liu, M., Hou, Y. Potential multifunctional agents with anti-hepatoma and anti-inflammation properties by inhibiting NF-κB activation. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 1287–1297; https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2019.1635124.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Xiong, C. L., Lan, Y. D., Song, X. Y., Xiong, W. M., Nie, X. L. Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxy 3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C12H14O6. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2021, 236, 573–575; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020-0632.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Zhang, X. F., Meng, Q. G. Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-2-((2-methoxy-3-pyridyl) methylene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2021, 236, 507–509; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020-0603.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Sun, Y., Liu, Y. K., Li, J. D., Meng, Q. G., Hou, G. G. Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)piperidin-4-one, C24H18F2N2O3S. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 377–379; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2019-0683.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Zhou, Y. Q., Hou, G. G., Meng, Q. G., Hou, Y. Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)-5-(2-(trifluoromethyl) benzylidene)piperidin-4-one, C25H18ClF3N2O3S. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 411–413; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2019-0716.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2021 Xia Zhou et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of [aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3 O,N,O′)-(1,10-phenanothroline-κ2 N,N′)copper(II)] dihydrate, C19H16O7N3CuI
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazolium) octamolybdate, C24H44Mo8N8O26
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(µ2-3,5-bis(1-imidazolyl)pyridine-κ2 N:N′)-(µ2-3-nitrophthalato-k3 O,O′:O″)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C30H25N11O8Cd
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2-(3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)pyridine-κ2 N:N′)-bis(3,5-dicarboxybenzoato-κ1 O)cobalt(II), C38H30CoN12O14
- Crystal structure of the nickel(II) complex aqua-(2,6-di(pyrazin-2-yl)-4,4′-bipyridine-κ3 N,N′,N′′)-(phthalato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II) tetrahydrate, C26H26N6O9Ni
- The crystal structure of 1-[5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridine-3-sulfonyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]-N-methylmethanaminium 3-carboxyprop-2-enoate, C21H20FN3O6S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane - 4,4-dihydroxydiphenylmethane (1/1), C25H21N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-((E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium trifluoroacetate dihydrate, C34H36Cl4N10O12
- Crystal structure of 1-cyclopropyl-7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C15H13F2NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinin-2(3H)-yl)benzoate, C18H15BN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C14H11ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of Al-rich fluorophlogopite, K1.0(Mg2.8Al0.2)(Si2.8Al1.2)O10F2
- The crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium hexafluoridoantimonate(V), C20H22F6I2N3Sb
- Crystal structure of tris(3-iodopyridin-1-ium) catena-poly[(hexachlorido-κ1 Cl)-(μ2-trichlorido-κ2 Cl:Cl)diantimony(III)], C15H15Cl9I3N3Sb2
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1.3.2]diazaborinin-2(3H-yl)benzoate C18H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(4-methoxybenzoyl)naphthalene-2,7-diyl dibenzoate, C40H28O8
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3,6,8-tetramethylBOPHY (BOPHY = bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine), C14H15B2BrF4N4
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(2-fluorobenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C12H9ClFN3
- Crystal structure of bis(µ2- 4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O:N:O′)-bis(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O:N:O′)-bis(µ2-1-(4-pyridyl)piperazine-κ2N:N′)-hexa-aqua-tetra-copper(II), C46H46Cu4I4N10O22
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-2,5-dihydroxyterephthalato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-bis(4-pyridylformyl)piperazine-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C24H28CdN4O12
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-(μ3-2,3,5,6-tetrafluoroterephthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)cadmium(II)], C17H14N4O5F4Cd
- Crystal structure of 6-(quinolin-8-yl)benzo[a]phenanthridin-5(6H)-one, C26H16N2O
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis(6-chloropicolinato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C12H8Cl2N2O5Cu
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κ2N:N′) disilver(I)] 4-oxidopyridine-3-sulfonate trihydrate, C25H29Ag2N5O9S
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-bromophenyl)pyrimidin-2-amine, C10H8BrN3
- Crystal structure of 6-oxo-4-phenyl-1-propyl-1,6-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C15H14N2O
- Crystal structure of 4-(2,2-difluoroethyl)-2,4-dimethyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)isoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione, C14H12F5NO2
- Crystal structure of dibromido-(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)-(3-(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-1-yl)propanoato-κ1O)zinc(II), C11H16Br2N4O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(((2 (dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene)) bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)- titanium(IV) ─ dichloromethane (2/1), C33H29N3O6Ti
- The layered crystal structure of bis(theophyllinium) hexachloridostannate (IV), C14H18N8O8SnCl6
- The crystal structre of 3-(1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-3-yl)propane-1-sulfonate, C8H12N2O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of di-tert-butyl 1″-acetyl-2,2″,9′-trioxo-4a′,9a′-dihydro-1′H,3′H,9′H-dispiro[indoline-3,2′-xanthene-4′,3″-indoline]-1,3′-dicarboxylate, C39H38N2O9
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-(quinolin-8-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-fluoro-4-(p-tolylethynyl)benzene, C15H11F
- The crystal structure of bis[4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl) phenolato-κ2N,O] copper(II), C18H12Br2CuN4O2
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 3-imidazolato-κ 3 N:N:N′)(tetrahydrofuran- κ 1 O)lithium(I)], C7H11LiN2O
- Crystal structure of N′,N′′′-((1E,1′E)-(propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2diyl))bis(methaneylylidene))di(nicotinohydrazide) pentahydrate, C25H24N8O2·5H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-1-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophos-phate(V), C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C22H14N2O4S2Cu
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-3-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide hemihydrate, C6H8IN2O2.5
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-tetralone, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of [μ-hydroxido-bis[(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tricarbonylrhenium(I)] bromide hemihydrate, C30H26N4O9Re2Br
- The crystal structure of 2,5-bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)thiazolo[5,4-d]thiazole, C20H18N2S2
- The crystal structure of 5-benzoyl-1-[(E)-(4-fluorobenzylidene)amino]-4-phenylpyrimidin-2(1H)-one, C24H16FN3O2
- Crystal structure of monocarbonyl(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O′)(tricyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C25H39N2O3PRh
- Crystal structure of poly[bis[μ3-1,3,5-tris[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzene-κ3N:N′:N″]nickel(II)] hexafluorosilicate, C36H36N12NiSiF6
- The crystal structure of 13-(pyrazole-1-yl-4-carbonitrile)-matrine, C19H25N5O
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis((E)-4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-1-methylpiperidin-4-one, C24H21F6NO3
- The crystal structure of N,N′-(Disulfanediyldi-2,1-phenylene)di(6′-methylpyridine)-2-carboxamide, C26H22N4O2S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C19H16FNO2
- The crystal structure of cis-diaqua-bis (N-butyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)pyridin-2-amine-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride trihydrate, C28H44Cl2N6O5Co
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- The crystal structure of 6-bromohexanoic acid, C6H11BrO2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-thiophenol, C6H5ClS
- The crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl chloride, C7H6BrCl
- The crystal structure of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate, C10H18O5
- The crystal structure of (2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol, C12H15ClO3
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal: 2-hydroxybenzoic acid – N′-(butan-2-ylidene)pyridine-4-carbohydrazide, C10H13N3O·C7H6O3
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((5-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(butane-1,4-diyl)bis(3-propyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C32H56F24N8P4
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2)-cadmium(II), C14H20CdCl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-cyanobenzyl)-3-cyano-4-phenyl-4-(2-cyanobenzyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine monohydrate, C56H42N8O
- The crystal structure of 3-(carboxymethyl)-1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride, C7H9N2O2Cl
- The crystal structure of adamantylmethoxydiphenylsilane, C23H28OSi
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of (2E,4Z,13E,15Z)-3,5,14,16-tetramethyl-2,6,13,17-tetraazatricyclo[16.4.0.07,12]docosa-1(22),2,4,7,9,11,13,15,18,20-decaene, C22H24N4
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2 N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C18H28N10O8Co
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of [aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3 O,N,O′)-(1,10-phenanothroline-κ2 N,N′)copper(II)] dihydrate, C19H16O7N3CuI
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazolium) octamolybdate, C24H44Mo8N8O26
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(µ2-3,5-bis(1-imidazolyl)pyridine-κ2 N:N′)-(µ2-3-nitrophthalato-k3 O,O′:O″)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C30H25N11O8Cd
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2-(3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)pyridine-κ2 N:N′)-bis(3,5-dicarboxybenzoato-κ1 O)cobalt(II), C38H30CoN12O14
- Crystal structure of the nickel(II) complex aqua-(2,6-di(pyrazin-2-yl)-4,4′-bipyridine-κ3 N,N′,N′′)-(phthalato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II) tetrahydrate, C26H26N6O9Ni
- The crystal structure of 1-[5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridine-3-sulfonyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]-N-methylmethanaminium 3-carboxyprop-2-enoate, C21H20FN3O6S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane - 4,4-dihydroxydiphenylmethane (1/1), C25H21N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-((E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium trifluoroacetate dihydrate, C34H36Cl4N10O12
- Crystal structure of 1-cyclopropyl-7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C15H13F2NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinin-2(3H)-yl)benzoate, C18H15BN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C14H11ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of Al-rich fluorophlogopite, K1.0(Mg2.8Al0.2)(Si2.8Al1.2)O10F2
- The crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium hexafluoridoantimonate(V), C20H22F6I2N3Sb
- Crystal structure of tris(3-iodopyridin-1-ium) catena-poly[(hexachlorido-κ1 Cl)-(μ2-trichlorido-κ2 Cl:Cl)diantimony(III)], C15H15Cl9I3N3Sb2
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1.3.2]diazaborinin-2(3H-yl)benzoate C18H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(4-methoxybenzoyl)naphthalene-2,7-diyl dibenzoate, C40H28O8
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3,6,8-tetramethylBOPHY (BOPHY = bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine), C14H15B2BrF4N4
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(2-fluorobenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C12H9ClFN3
- Crystal structure of bis(µ2- 4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O:N:O′)-bis(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O:N:O′)-bis(µ2-1-(4-pyridyl)piperazine-κ2N:N′)-hexa-aqua-tetra-copper(II), C46H46Cu4I4N10O22
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-2,5-dihydroxyterephthalato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-bis(4-pyridylformyl)piperazine-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C24H28CdN4O12
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-(μ3-2,3,5,6-tetrafluoroterephthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)cadmium(II)], C17H14N4O5F4Cd
- Crystal structure of 6-(quinolin-8-yl)benzo[a]phenanthridin-5(6H)-one, C26H16N2O
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis(6-chloropicolinato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C12H8Cl2N2O5Cu
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κ2N:N′) disilver(I)] 4-oxidopyridine-3-sulfonate trihydrate, C25H29Ag2N5O9S
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-bromophenyl)pyrimidin-2-amine, C10H8BrN3
- Crystal structure of 6-oxo-4-phenyl-1-propyl-1,6-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C15H14N2O
- Crystal structure of 4-(2,2-difluoroethyl)-2,4-dimethyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)isoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione, C14H12F5NO2
- Crystal structure of dibromido-(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)-(3-(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-1-yl)propanoato-κ1O)zinc(II), C11H16Br2N4O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(((2 (dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene)) bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)- titanium(IV) ─ dichloromethane (2/1), C33H29N3O6Ti
- The layered crystal structure of bis(theophyllinium) hexachloridostannate (IV), C14H18N8O8SnCl6
- The crystal structre of 3-(1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-3-yl)propane-1-sulfonate, C8H12N2O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of di-tert-butyl 1″-acetyl-2,2″,9′-trioxo-4a′,9a′-dihydro-1′H,3′H,9′H-dispiro[indoline-3,2′-xanthene-4′,3″-indoline]-1,3′-dicarboxylate, C39H38N2O9
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-(quinolin-8-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-fluoro-4-(p-tolylethynyl)benzene, C15H11F
- The crystal structure of bis[4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl) phenolato-κ2N,O] copper(II), C18H12Br2CuN4O2
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 3-imidazolato-κ 3 N:N:N′)(tetrahydrofuran- κ 1 O)lithium(I)], C7H11LiN2O
- Crystal structure of N′,N′′′-((1E,1′E)-(propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2diyl))bis(methaneylylidene))di(nicotinohydrazide) pentahydrate, C25H24N8O2·5H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-1-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophos-phate(V), C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C22H14N2O4S2Cu
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-3-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide hemihydrate, C6H8IN2O2.5
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-tetralone, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of [μ-hydroxido-bis[(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tricarbonylrhenium(I)] bromide hemihydrate, C30H26N4O9Re2Br
- The crystal structure of 2,5-bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)thiazolo[5,4-d]thiazole, C20H18N2S2
- The crystal structure of 5-benzoyl-1-[(E)-(4-fluorobenzylidene)amino]-4-phenylpyrimidin-2(1H)-one, C24H16FN3O2
- Crystal structure of monocarbonyl(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O′)(tricyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C25H39N2O3PRh
- Crystal structure of poly[bis[μ3-1,3,5-tris[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzene-κ3N:N′:N″]nickel(II)] hexafluorosilicate, C36H36N12NiSiF6
- The crystal structure of 13-(pyrazole-1-yl-4-carbonitrile)-matrine, C19H25N5O
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis((E)-4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-1-methylpiperidin-4-one, C24H21F6NO3
- The crystal structure of N,N′-(Disulfanediyldi-2,1-phenylene)di(6′-methylpyridine)-2-carboxamide, C26H22N4O2S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C19H16FNO2
- The crystal structure of cis-diaqua-bis (N-butyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)pyridin-2-amine-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride trihydrate, C28H44Cl2N6O5Co
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- The crystal structure of 6-bromohexanoic acid, C6H11BrO2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-thiophenol, C6H5ClS
- The crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl chloride, C7H6BrCl
- The crystal structure of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate, C10H18O5
- The crystal structure of (2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol, C12H15ClO3
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal: 2-hydroxybenzoic acid – N′-(butan-2-ylidene)pyridine-4-carbohydrazide, C10H13N3O·C7H6O3
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((5-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(butane-1,4-diyl)bis(3-propyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C32H56F24N8P4
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2)-cadmium(II), C14H20CdCl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-cyanobenzyl)-3-cyano-4-phenyl-4-(2-cyanobenzyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine monohydrate, C56H42N8O
- The crystal structure of 3-(carboxymethyl)-1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride, C7H9N2O2Cl
- The crystal structure of adamantylmethoxydiphenylsilane, C23H28OSi
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of (2E,4Z,13E,15Z)-3,5,14,16-tetramethyl-2,6,13,17-tetraazatricyclo[16.4.0.07,12]docosa-1(22),2,4,7,9,11,13,15,18,20-decaene, C22H24N4
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2 N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C18H28N10O8Co

