Abstract
K1.0(Mg2.8Al0.2)(Si2.8Al1.2)O10F2, monoclinic, C2/m (no. 12), a = 5.3040(11) Å, b = 9.2288(18) Å, c = 10.1286(20) Å, β = 100.173(3)°, V = 488.00(17) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0387, wR ref (F2) = 0.1086, T = 298 K.
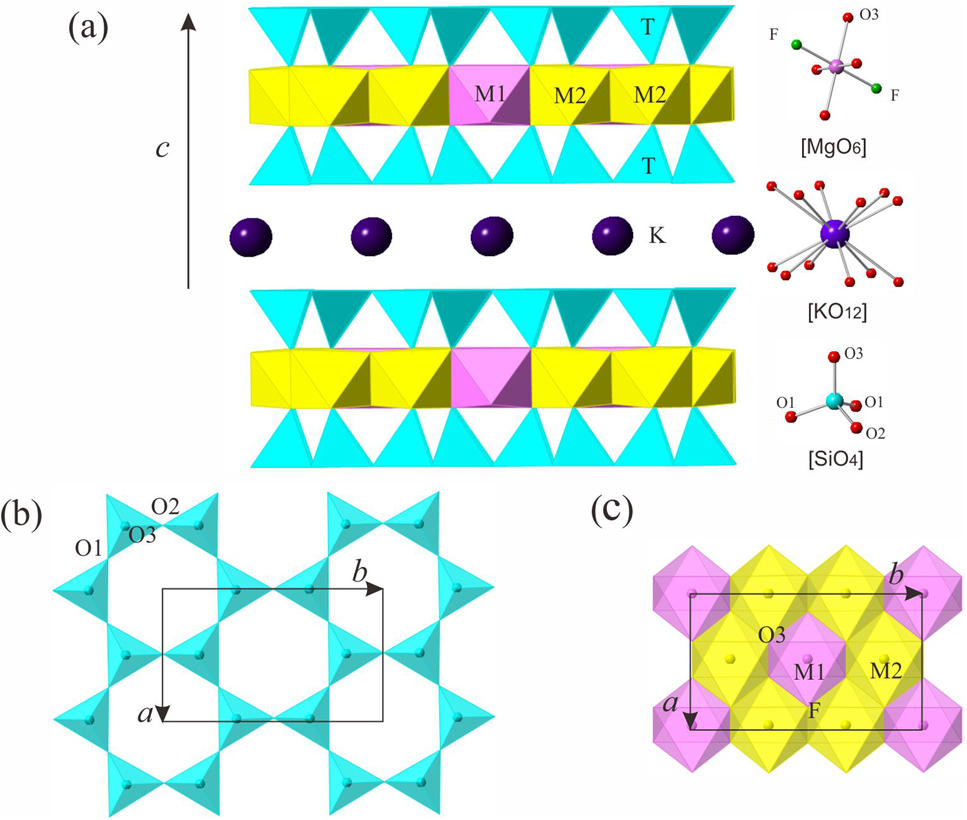
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless flake |
| Size: | 0.10 × 0.10 × 0.05 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.28 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 33.7°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 2246, 940, 0.017 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 874 |
| N(param)refined: | 53 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], [3], Olex2 [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.0287 (3) |
| F1 | 0.3672 (3) | 0.500000 | 0.59653 (16) | 0.0122 (3) |
| O1 | 0.5119 (4) | 0.000000 | 0.1673 (2) | 0.0163 (4) |
| O2 | 0.8282 (3) | 0.22812 (18) | 0.16727 (14) | 0.0164 (3) |
| O3 | 0.6313 (3) | 0.16655 (14) | 0.39191 (14) | 0.0098 (3) |
| Si1a | 0.57553 (9) | 0.16665 (5) | 0.22461 (5) | 0.00728 (15) |
| Al1b | 0.57553 (9) | 0.16665 (5) | 0.22461 (5) | 0.00728 (15) |
| Mg2c | 0.500000 | 0.33029 (9) | 0.500000 | 0.0084 (2) |
| Al3d | 0.500000 | 0.33029 (9) | 0.500000 | 0.0084 (2) |
| Mg1c | 0.000000 | 0.500000 | 0.500000 | 0.0089 (3) |
| Al2d | 0.000000 | 0.500000 | 0.500000 | 0.0089 (3) |
-
aOccupancy: 0.7, bOccupancy: 0.3, cOccupancy: 0.934, dOccupancy: 0.066.
Source of material
Pure raw materials of 11.6 wt% SiO2, 32.6 wt% Al2O3, 30.7 wt% MgO, and 25.1 wt% K2SiF2 were ground in an agate mortar and loaded into a corundum crucible. The muffle furnace was heated to 1450 °C in 4 h to completely melt the reactants. Then, the muffle furnace was cooled to 1000 °C at a rate of 10 °C/h to make the fluorophlogopite crystallize during this period. At last, the furnace was freely cooled to room temperature. The specimen thus obtained was an intimate aggregate of flakes of colorless and transparent crystals.
Experimental details
Crystals were selected from the aggregate and cut to a suitable size for the single crystal measurement. The chemical compositions of the measured single crystal were determined by electron microprobe analysis (EPMA, JEOL–JXA8230). Atomic occupancy of Si/Al ratio in the tetrahedral sites and Mg/Al ratio in the octahedral sheets were constrained according to the EPMA results. Moreover, atoms sharing the same sites were constrained to have identical thermal displacements.
Comment
Synthetic fluorophlogopite attracts considerable interest because of its wide applications to material science [5], [6], [7]. Fluorophlogopite belongs to tetrahedron-octahedron-tetrahedron (TOT) type in which one octahedral sheet is sandwiched between two tetrahedral sheets (Figure 1a). Cation substitutions of Al3+ for Si4+ in the tetrahedral sheet lend to a positive charge deficiency in the TOT layer. The negative charge of the TOT unit is balanced and bonded together by the K+ in the interlayer (Figure 1a) [8]. To date, fluorophlogopite with different Al content, K1.0Mg2.5Si4O10F2, K1.0Mg2.75(Si3.5Al0.5)O10F2, and K1.0Mg3(Si3Al1)O10F2 have been synthesized [9], [10], [11]. Previous research shows that K1.0Mg2.5Si4O10F2 is considerably brittle, while K1.0Mg3(Si3Al1)O10F2 is much more flexible. This suggests that the Al content has an important influence on the amount of negative charge which could affect the physical and chemical properties of the compound. However, Al-rich fluorophlogopite is poorly known.
EPMA shows that the chemical compositions of the synthetic Al-rich fluorophlogopite are: SiO2 40.03 wt%, Al2O3 17.06 wt%, FeO 0.02 wt%, MgO 26.87 wt%, Na2O 0.01 wt%, K2O 11.09 wt%, and F 9.05 wt%. The crystal formula based on EMPA is K1.0(Mg2.8Al0.2)(Si2.8Al1.2)O10F2, which is consistent with the result of structural refinement. This Al-rich fluorophlogopite belongs to the 1 M polytype (space group C2/m) with cell dimensions of a = 5.3040(11) Å, b = 9.2288(18) Å, c = 10.1286(20) Å, and β = 100.173(3)°. In the tetrahedral sheet, an individual TO4 tetrahedron is linked with neighboring TO4 by sharing the three basal oxygen atoms (i.e., O1 and O2) to form an infinite two-dimensional hexagonal mesh pattern (Figure 1b). Si and Al occupy the tetrahedral sites in a ratio Si:Al = 2.8:1.2. The average bond distance (<T–O> = 1.658 Å) of the Al-rich fluorophlogopite is obviously longer than in K1.0Mg2.5Si4O10F2 (<T–O> = 1.625 Å), K1.0Mg2.75(Si3.5Al0.5)O10F2 (<T–O> = 1.638 Å), and K1.0Mg3 (Si3Al1)O10F2 (<T–O> = 1.642 Å) [9], [10], [11]. Substitutions of Al3+ for Si4+ in the tetrahedral sheet decrease the bond lengths because the ionic radius of Al3+ (0.53 Å) is larger than that of Si4+ (0.40 Å). The tetrahedral rotation angle α is 8.66°. In the octahedral sheet, each octahedral coordination unit is comprised of four apical oxygen atoms (i.e., O3) and two F anions (Figure 1a). An individual octahedron is linked laterally by sharing edges to form octahedral sheets (Figure 1c). The octahedral sites are mainly occupied by Mg (2.8 atoms per formula unit) and minor amounts of Al (0.2 atoms per formula unit). The average bond distance of <M1–O> and <M2–O> are 2.058 and 2.054 Å, respectively. Similar bond distances between M1 and M2 sites confirm that Al is disordered in the octahedral sites [12]. The interlayer K+ is coordinated with 12 oxygen atoms (six from the upper and six from the lower tetrahedral sheets) (Figure 1a). The mean bond length of <K–O> is 3.138 Å.
Funding source: National Natural Science Foundation of China 10.13039/501100001809
Award Identifier / Grant number: 41772039
Funding source: Talent program of China Three Gorges University
Award Identifier / Grant number: 19103
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This study was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41772039) and Talent program of China Three Gorges University (No. 19103).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Agilent Technologies. CrysAlisPRO; Agilent Technologies: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2017.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
5. Shell, H. R., Ivey, K. H. Fluorine Micas; U. S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines: Washington, 1969.Search in Google Scholar
6. Hammouda, T., Pichavant, M., Barbey, P., Brearley, A. J. Synthesis of fluorphlogopite single crystals. applications to experimental studies. Eur. J. Mineral 1995, 7, 1381–1387; https://doi.org/10.1127/ejm/7/6/1381.Search in Google Scholar
7. Dong, G., Zhang, L. Investigation on grinding force and machining quality during rotary ultrasonic grinding deep-small hole of fluorophlogopite ceramics. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 104, 2815–2825; https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04138-7.Search in Google Scholar
8. Meunier, A. Clays; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005.Search in Google Scholar
9. Mccauley, J. W., Newnham, R. E., Gibbs, G. V. Crystal structure analysis of synthetic fluorophlogopite. Am. Mineral. 1973, 58, 249–254.Search in Google Scholar
10. Toraya, H., Iwai, S., Makimo, F., Kondo, R., Daimon, M. The crystal structure of tetrasilicic potassium fluor mica, KMg2,5Si4O10F2. Z. für Kristallogr. - Cryst. Mater. 1976, 144, 42–52; https://doi.org/10.1524/zkri.1976.144.1-6.42.Search in Google Scholar
11. Toraya, H., Iwai, S., Marumo, F., Nishikawa, T. The crystal structure of synthetic mica, KMg2.75Si3.5Al0.5O10F2. Mineral. J. 1978, 9, 210–220; https://doi.org/10.2465/minerj.9.210.Search in Google Scholar
12. Gianfagna, A., Scordari, F., Mazziotti-Tagliani, S., Ventruti, G., Ottolini, L. Fluorophlogopite from Biancavilla (Mt. Etna, Sicily, Italy): crystal structure and crystal chemistry of a new F-dominant analog of phlogopite. Am. Mineral. 2007, 92, 1601–1609; https://doi.org/10.2138/am.2007.2502.Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Chen Aiqing and Zhang Lixue, published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of [aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3 O,N,O′)-(1,10-phenanothroline-κ2 N,N′)copper(II)] dihydrate, C19H16O7N3CuI
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazolium) octamolybdate, C24H44Mo8N8O26
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(µ2-3,5-bis(1-imidazolyl)pyridine-κ2 N:N′)-(µ2-3-nitrophthalato-k3 O,O′:O″)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C30H25N11O8Cd
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2-(3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)pyridine-κ2 N:N′)-bis(3,5-dicarboxybenzoato-κ1 O)cobalt(II), C38H30CoN12O14
- Crystal structure of the nickel(II) complex aqua-(2,6-di(pyrazin-2-yl)-4,4′-bipyridine-κ3 N,N′,N′′)-(phthalato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II) tetrahydrate, C26H26N6O9Ni
- The crystal structure of 1-[5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridine-3-sulfonyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]-N-methylmethanaminium 3-carboxyprop-2-enoate, C21H20FN3O6S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane - 4,4-dihydroxydiphenylmethane (1/1), C25H21N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-((E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium trifluoroacetate dihydrate, C34H36Cl4N10O12
- Crystal structure of 1-cyclopropyl-7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C15H13F2NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinin-2(3H)-yl)benzoate, C18H15BN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C14H11ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of Al-rich fluorophlogopite, K1.0(Mg2.8Al0.2)(Si2.8Al1.2)O10F2
- The crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium hexafluoridoantimonate(V), C20H22F6I2N3Sb
- Crystal structure of tris(3-iodopyridin-1-ium) catena-poly[(hexachlorido-κ1 Cl)-(μ2-trichlorido-κ2 Cl:Cl)diantimony(III)], C15H15Cl9I3N3Sb2
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1.3.2]diazaborinin-2(3H-yl)benzoate C18H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(4-methoxybenzoyl)naphthalene-2,7-diyl dibenzoate, C40H28O8
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3,6,8-tetramethylBOPHY (BOPHY = bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine), C14H15B2BrF4N4
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(2-fluorobenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C12H9ClFN3
- Crystal structure of bis(µ2- 4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O:N:O′)-bis(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O:N:O′)-bis(µ2-1-(4-pyridyl)piperazine-κ2N:N′)-hexa-aqua-tetra-copper(II), C46H46Cu4I4N10O22
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-2,5-dihydroxyterephthalato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-bis(4-pyridylformyl)piperazine-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C24H28CdN4O12
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-(μ3-2,3,5,6-tetrafluoroterephthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)cadmium(II)], C17H14N4O5F4Cd
- Crystal structure of 6-(quinolin-8-yl)benzo[a]phenanthridin-5(6H)-one, C26H16N2O
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis(6-chloropicolinato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C12H8Cl2N2O5Cu
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κ2N:N′) disilver(I)] 4-oxidopyridine-3-sulfonate trihydrate, C25H29Ag2N5O9S
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-bromophenyl)pyrimidin-2-amine, C10H8BrN3
- Crystal structure of 6-oxo-4-phenyl-1-propyl-1,6-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C15H14N2O
- Crystal structure of 4-(2,2-difluoroethyl)-2,4-dimethyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)isoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione, C14H12F5NO2
- Crystal structure of dibromido-(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)-(3-(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-1-yl)propanoato-κ1O)zinc(II), C11H16Br2N4O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(((2 (dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene)) bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)- titanium(IV) ─ dichloromethane (2/1), C33H29N3O6Ti
- The layered crystal structure of bis(theophyllinium) hexachloridostannate (IV), C14H18N8O8SnCl6
- The crystal structre of 3-(1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-3-yl)propane-1-sulfonate, C8H12N2O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of di-tert-butyl 1″-acetyl-2,2″,9′-trioxo-4a′,9a′-dihydro-1′H,3′H,9′H-dispiro[indoline-3,2′-xanthene-4′,3″-indoline]-1,3′-dicarboxylate, C39H38N2O9
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-(quinolin-8-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-fluoro-4-(p-tolylethynyl)benzene, C15H11F
- The crystal structure of bis[4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl) phenolato-κ2N,O] copper(II), C18H12Br2CuN4O2
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 3-imidazolato-κ 3 N:N:N′)(tetrahydrofuran- κ 1 O)lithium(I)], C7H11LiN2O
- Crystal structure of N′,N′′′-((1E,1′E)-(propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2diyl))bis(methaneylylidene))di(nicotinohydrazide) pentahydrate, C25H24N8O2·5H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-1-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophos-phate(V), C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C22H14N2O4S2Cu
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-3-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide hemihydrate, C6H8IN2O2.5
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-tetralone, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of [μ-hydroxido-bis[(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tricarbonylrhenium(I)] bromide hemihydrate, C30H26N4O9Re2Br
- The crystal structure of 2,5-bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)thiazolo[5,4-d]thiazole, C20H18N2S2
- The crystal structure of 5-benzoyl-1-[(E)-(4-fluorobenzylidene)amino]-4-phenylpyrimidin-2(1H)-one, C24H16FN3O2
- Crystal structure of monocarbonyl(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O′)(tricyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C25H39N2O3PRh
- Crystal structure of poly[bis[μ3-1,3,5-tris[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzene-κ3N:N′:N″]nickel(II)] hexafluorosilicate, C36H36N12NiSiF6
- The crystal structure of 13-(pyrazole-1-yl-4-carbonitrile)-matrine, C19H25N5O
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis((E)-4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-1-methylpiperidin-4-one, C24H21F6NO3
- The crystal structure of N,N′-(Disulfanediyldi-2,1-phenylene)di(6′-methylpyridine)-2-carboxamide, C26H22N4O2S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C19H16FNO2
- The crystal structure of cis-diaqua-bis (N-butyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)pyridin-2-amine-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride trihydrate, C28H44Cl2N6O5Co
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- The crystal structure of 6-bromohexanoic acid, C6H11BrO2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-thiophenol, C6H5ClS
- The crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl chloride, C7H6BrCl
- The crystal structure of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate, C10H18O5
- The crystal structure of (2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol, C12H15ClO3
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal: 2-hydroxybenzoic acid – N′-(butan-2-ylidene)pyridine-4-carbohydrazide, C10H13N3O·C7H6O3
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((5-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(butane-1,4-diyl)bis(3-propyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C32H56F24N8P4
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2)-cadmium(II), C14H20CdCl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-cyanobenzyl)-3-cyano-4-phenyl-4-(2-cyanobenzyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine monohydrate, C56H42N8O
- The crystal structure of 3-(carboxymethyl)-1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride, C7H9N2O2Cl
- The crystal structure of adamantylmethoxydiphenylsilane, C23H28OSi
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of (2E,4Z,13E,15Z)-3,5,14,16-tetramethyl-2,6,13,17-tetraazatricyclo[16.4.0.07,12]docosa-1(22),2,4,7,9,11,13,15,18,20-decaene, C22H24N4
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2 N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C18H28N10O8Co
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of [aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3 O,N,O′)-(1,10-phenanothroline-κ2 N,N′)copper(II)] dihydrate, C19H16O7N3CuI
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazolium) octamolybdate, C24H44Mo8N8O26
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(µ2-3,5-bis(1-imidazolyl)pyridine-κ2 N:N′)-(µ2-3-nitrophthalato-k3 O,O′:O″)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C30H25N11O8Cd
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2-(3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)pyridine-κ2 N:N′)-bis(3,5-dicarboxybenzoato-κ1 O)cobalt(II), C38H30CoN12O14
- Crystal structure of the nickel(II) complex aqua-(2,6-di(pyrazin-2-yl)-4,4′-bipyridine-κ3 N,N′,N′′)-(phthalato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II) tetrahydrate, C26H26N6O9Ni
- The crystal structure of 1-[5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridine-3-sulfonyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]-N-methylmethanaminium 3-carboxyprop-2-enoate, C21H20FN3O6S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane - 4,4-dihydroxydiphenylmethane (1/1), C25H21N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-((E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium trifluoroacetate dihydrate, C34H36Cl4N10O12
- Crystal structure of 1-cyclopropyl-7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C15H13F2NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinin-2(3H)-yl)benzoate, C18H15BN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C14H11ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of Al-rich fluorophlogopite, K1.0(Mg2.8Al0.2)(Si2.8Al1.2)O10F2
- The crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium hexafluoridoantimonate(V), C20H22F6I2N3Sb
- Crystal structure of tris(3-iodopyridin-1-ium) catena-poly[(hexachlorido-κ1 Cl)-(μ2-trichlorido-κ2 Cl:Cl)diantimony(III)], C15H15Cl9I3N3Sb2
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1.3.2]diazaborinin-2(3H-yl)benzoate C18H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(4-methoxybenzoyl)naphthalene-2,7-diyl dibenzoate, C40H28O8
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3,6,8-tetramethylBOPHY (BOPHY = bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine), C14H15B2BrF4N4
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(2-fluorobenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C12H9ClFN3
- Crystal structure of bis(µ2- 4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O:N:O′)-bis(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O:N:O′)-bis(µ2-1-(4-pyridyl)piperazine-κ2N:N′)-hexa-aqua-tetra-copper(II), C46H46Cu4I4N10O22
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-2,5-dihydroxyterephthalato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-bis(4-pyridylformyl)piperazine-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C24H28CdN4O12
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-(μ3-2,3,5,6-tetrafluoroterephthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)cadmium(II)], C17H14N4O5F4Cd
- Crystal structure of 6-(quinolin-8-yl)benzo[a]phenanthridin-5(6H)-one, C26H16N2O
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis(6-chloropicolinato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C12H8Cl2N2O5Cu
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κ2N:N′) disilver(I)] 4-oxidopyridine-3-sulfonate trihydrate, C25H29Ag2N5O9S
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-bromophenyl)pyrimidin-2-amine, C10H8BrN3
- Crystal structure of 6-oxo-4-phenyl-1-propyl-1,6-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C15H14N2O
- Crystal structure of 4-(2,2-difluoroethyl)-2,4-dimethyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)isoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione, C14H12F5NO2
- Crystal structure of dibromido-(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)-(3-(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-1-yl)propanoato-κ1O)zinc(II), C11H16Br2N4O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(((2 (dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene)) bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)- titanium(IV) ─ dichloromethane (2/1), C33H29N3O6Ti
- The layered crystal structure of bis(theophyllinium) hexachloridostannate (IV), C14H18N8O8SnCl6
- The crystal structre of 3-(1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-3-yl)propane-1-sulfonate, C8H12N2O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of di-tert-butyl 1″-acetyl-2,2″,9′-trioxo-4a′,9a′-dihydro-1′H,3′H,9′H-dispiro[indoline-3,2′-xanthene-4′,3″-indoline]-1,3′-dicarboxylate, C39H38N2O9
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-(quinolin-8-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-fluoro-4-(p-tolylethynyl)benzene, C15H11F
- The crystal structure of bis[4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl) phenolato-κ2N,O] copper(II), C18H12Br2CuN4O2
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 3-imidazolato-κ 3 N:N:N′)(tetrahydrofuran- κ 1 O)lithium(I)], C7H11LiN2O
- Crystal structure of N′,N′′′-((1E,1′E)-(propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2diyl))bis(methaneylylidene))di(nicotinohydrazide) pentahydrate, C25H24N8O2·5H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-1-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophos-phate(V), C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C22H14N2O4S2Cu
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-3-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide hemihydrate, C6H8IN2O2.5
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-tetralone, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of [μ-hydroxido-bis[(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tricarbonylrhenium(I)] bromide hemihydrate, C30H26N4O9Re2Br
- The crystal structure of 2,5-bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)thiazolo[5,4-d]thiazole, C20H18N2S2
- The crystal structure of 5-benzoyl-1-[(E)-(4-fluorobenzylidene)amino]-4-phenylpyrimidin-2(1H)-one, C24H16FN3O2
- Crystal structure of monocarbonyl(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O′)(tricyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C25H39N2O3PRh
- Crystal structure of poly[bis[μ3-1,3,5-tris[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzene-κ3N:N′:N″]nickel(II)] hexafluorosilicate, C36H36N12NiSiF6
- The crystal structure of 13-(pyrazole-1-yl-4-carbonitrile)-matrine, C19H25N5O
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis((E)-4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-1-methylpiperidin-4-one, C24H21F6NO3
- The crystal structure of N,N′-(Disulfanediyldi-2,1-phenylene)di(6′-methylpyridine)-2-carboxamide, C26H22N4O2S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C19H16FNO2
- The crystal structure of cis-diaqua-bis (N-butyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)pyridin-2-amine-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride trihydrate, C28H44Cl2N6O5Co
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- The crystal structure of 6-bromohexanoic acid, C6H11BrO2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-thiophenol, C6H5ClS
- The crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl chloride, C7H6BrCl
- The crystal structure of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate, C10H18O5
- The crystal structure of (2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol, C12H15ClO3
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal: 2-hydroxybenzoic acid – N′-(butan-2-ylidene)pyridine-4-carbohydrazide, C10H13N3O·C7H6O3
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((5-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(butane-1,4-diyl)bis(3-propyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C32H56F24N8P4
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2)-cadmium(II), C14H20CdCl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-cyanobenzyl)-3-cyano-4-phenyl-4-(2-cyanobenzyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine monohydrate, C56H42N8O
- The crystal structure of 3-(carboxymethyl)-1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride, C7H9N2O2Cl
- The crystal structure of adamantylmethoxydiphenylsilane, C23H28OSi
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of (2E,4Z,13E,15Z)-3,5,14,16-tetramethyl-2,6,13,17-tetraazatricyclo[16.4.0.07,12]docosa-1(22),2,4,7,9,11,13,15,18,20-decaene, C22H24N4
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2 N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C18H28N10O8Co

