Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imdazole-κ2N:N′)-(1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imdazole-κ1N)-(methanol-κ1O)mercury(II)] dinitrate, C21H22N12O7Hg
Abstract
C21H22N12O7Hg, monoclinic, P2/n (no. 13), a = 13.655(3) Å, b = 8.7038(17) Å, c = 23.260(5) Å, β = 102.51(3)°, V = 2698.8(10) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0446, wRref(F2) = 0.0875, T = 293(2) K.
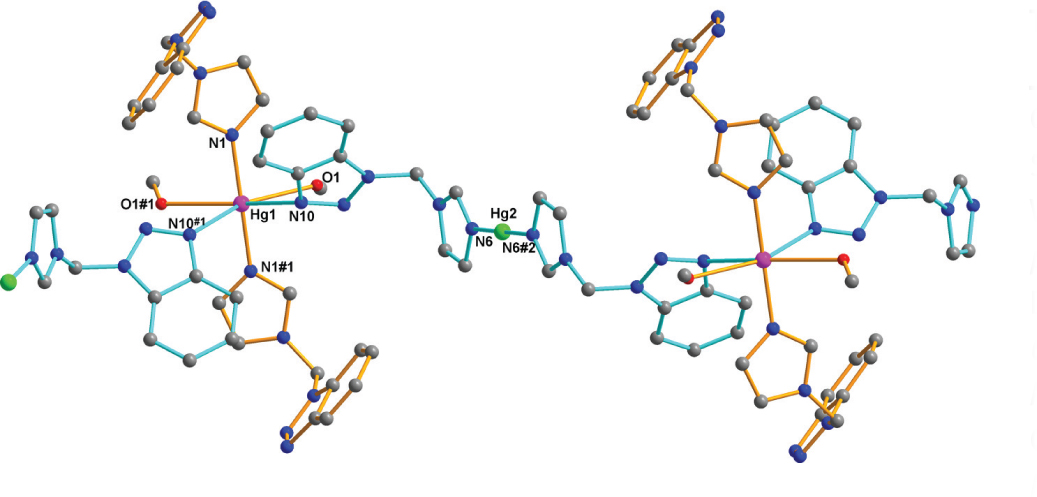
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless platelike |
| Size: | 0.12 × 0.10 × 0.06 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 5.77 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Rigaku Saturn, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.5°, 99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 12128, 5010, 0.041 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 4128 |
| N(param)refined: | 372 |
| Programs: | SHELX [1], [2], CrystalClear [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hg1 | 0.250000 | 0.14791(4) | 0.750000 | 0.04013(12) |
| Hg2 | 0.500000 | 1.000000 | 0.500000 | 0.04030(12) |
| N1 | 0.1078(3) | 0.1370(6) | 0.6947(2) | 0.0405(13) |
| N2 | −0.0538(3) | 0.1719(6) | 0.6643(2) | 0.0416(13) |
| N3 | −0.1740(4) | 0.3766(6) | 0.6462(2) | 0.0426(13) |
| N4 | −0.2078(4) | 0.4103(7) | 0.5879(2) | 0.0508(14) |
| N5 | −0.2137(4) | 0.5599(7) | 0.5820(2) | 0.0521(15) |
| N6 | 0.4880(3) | 0.7826(6) | 0.5346(2) | 0.0351(12) |
| N7 | 0.4333(3) | 0.5563(6) | 0.5515(2) | 0.0318(11) |
| N8 | 0.3115(4) | 0.4306(6) | 0.5964(2) | 0.0375(12) |
| N9 | 0.3464(4) | 0.3571(6) | 0.6480(2) | 0.0460(14) |
| N10 | 0.2862(4) | 0.3863(7) | 0.6836(3) | 0.0539(16) |
| N11 | 0.5874(4) | 1.1421(7) | 0.6476(3) | 0.0431(13) |
| N12 | 0.7412(5) | 0.9757(7) | 0.4929(3) | 0.0564(17) |
| O1 | 0.3260(4) | 0.0021(7) | 0.6701(2) | 0.0788(18) |
| H1 | 0.337950 | 0.039661 | 0.639985 | 0.095* |
| O2 | 0.5865(9) | 1.0094(9) | 0.6534(4) | 0.176(4) |
| O3 | 0.6175(5) | 1.2192(10) | 0.6902(3) | 0.132(3) |
| O4 | 0.5651(5) | 1.1938(8) | 0.5997(3) | 0.112(3) |
| O5 | 0.6732(4) | 0.9313(7) | 0.4511(2) | 0.0769(17) |
| O6 | 0.7156(4) | 1.0127(6) | 0.5389(2) | 0.0722(16) |
| O7 | 0.8281(5) | 0.9873(9) | 0.4891(3) | 0.123(3) |
| C1 | 0.0233(4) | 0.1754(7) | 0.7114(3) | 0.0375(15) |
| H1A | 0.018523 | 0.200658 | 0.749522 | 0.045* |
| C2 | 0.0813(5) | 0.1101(8) | 0.6349(3) | 0.0541(19) |
| H2A | 0.125545 | 0.081764 | 0.611491 | 0.065* |
| C3 | −0.0166(5) | 0.1305(9) | 0.6157(3) | 0.059(2) |
| H3A | −0.053003 | 0.119210 | 0.577276 | 0.071* |
| C4 | −0.1579(4) | 0.2177(7) | 0.6634(3) | 0.0460(17) |
| H4A | −0.203564 | 0.153275 | 0.635893 | 0.055* |
| H4B | −0.171778 | 0.203158 | 0.702205 | 0.055* |
| C5 | −0.1580(4) | 0.5092(7) | 0.6792(3) | 0.0377(15) |
| C6 | −0.1211(5) | 0.5375(8) | 0.7395(3) | 0.0518(18) |
| H6A | −0.101634 | 0.459759 | 0.767018 | 0.062* |
| C7 | −0.1164(5) | 0.6905(9) | 0.7539(3) | 0.060(2) |
| H7A | −0.093430 | 0.717027 | 0.793203 | 0.072* |
| C8 | −0.1442(5) | 0.8094(8) | 0.7130(3) | 0.0561(19) |
| H8A | −0.140314 | 0.910687 | 0.725951 | 0.067* |
| C9 | −0.1769(5) | 0.7788(8) | 0.6540(3) | 0.0532(18) |
| H9A | −0.193301 | 0.857239 | 0.626474 | 0.064* |
| C10 | −0.1844(4) | 0.6246(8) | 0.6375(3) | 0.0407(16) |
| C11 | 0.4129(4) | 0.6843(7) | 0.5196(2) | 0.0338(14) |
| H11A | 0.354665 | 0.701770 | 0.491186 | 0.041* |
| C12 | 0.5596(4) | 0.7129(7) | 0.5784(3) | 0.0391(15) |
| H12A | 0.620290 | 0.756122 | 0.597385 | 0.047* |
| C13 | 0.5260(4) | 0.5715(8) | 0.5886(3) | 0.0442(16) |
| H13A | 0.558927 | 0.499120 | 0.615368 | 0.053* |
| C14 | 0.3665(4) | 0.4223(7) | 0.5499(3) | 0.0363(14) |
| H14A | 0.319546 | 0.418655 | 0.512057 | 0.044* |
| H14B | 0.406039 | 0.328815 | 0.554161 | 0.044* |
| C15 | 0.2263(5) | 0.5134(7) | 0.5987(3) | 0.0417(16) |
| C16 | 0.1643(5) | 0.6106(9) | 0.5594(4) | 0.066(2) |
| H16A | 0.174773 | 0.628292 | 0.521710 | 0.079* |
| C17 | 0.0863(6) | 0.6798(10) | 0.5789(4) | 0.090(3) |
| H17A | 0.043226 | 0.746598 | 0.554358 | 0.108* |
| C18 | 0.0721(6) | 0.6488(11) | 0.6363(5) | 0.091(3) |
| H18A | 0.018504 | 0.695660 | 0.648129 | 0.110* |
| C19 | 0.1327(6) | 0.5539(10) | 0.6752(4) | 0.072(3) |
| H19A | 0.122048 | 0.536118 | 0.712770 | 0.086* |
| C20 | 0.2126(5) | 0.4843(7) | 0.6552(3) | 0.0472(18) |
| C21 | 0.3567(8) | −0.1480(11) | 0.6761(5) | 0.111(4) |
| H21A | 0.381793 | −0.178296 | 0.642327 | 0.166* |
| H21B | 0.408906 | −0.158580 | 0.710940 | 0.166* |
| H21C | 0.301042 | −0.212203 | 0.679380 | 0.166* |
Source of material
All chemicals were of reagent grade quality obtained from commercial sources and used without further purification. A methanol solution (3 mL) of bmi (0.1 mmol) is added dropwise into an aqueous solution (2 mL) of Hg(NO3)2 (0.1 mmol) to give a clear solution. The resultant solution was allowed to stand at room temperature. Good quality colourless crystals were obtained after 3 weeks (yield 39%, based on Hg).
Experimental details
Hydrogen atoms were positioned geometrically and refined as riding atoms, with C—H = 0.93 (aromatic) or 0.96 Å (CH3) or 0.97 Å (CH2) and O—H = 0.82 Å. Hydrogen atoms were refined with Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms and 1.2 Ueq(C, O) otherwise.
Comment
It is known that inorganic or organic counter anions can influence the coordination mode of the organic ligands and thus, influence the architectures and physical properties of the final products [4], [5], [6], [7], [8]. For example, two complexes with different compositions and structures can be obtained by the reaction of 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid and 2-(1H-imidazol-1-methyl)-1H-benzimidazole with CdCl2 or CdBr2 [9]. Yao reported a series of Cd(II) complexes by effective control of the anions [4]. Self-assembly of 1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imdazole (bmi) with HgCl2 or HgBr2 or HgI2 results in the formation of [Hg(bmi)Cl2]2, [Hg(bmi)2Br2], and [Hg(bmi)2I2] [10], [11]. In order to further explore the influence of counter anions on the formation of complexes, we were motivated to synthesize a new Hg(II) complex [Hg(bmi)2(CH3OH)] ⋅ 2NO3}n by using bmi and Hg(NO3)2 as starting materials.
The asymmetric unit comprises two crystallographically independent halves of Hg(II) ions, two crystallographically independent bmi ligands, one coordinating methanol molecule and two uncoordinating nitrate anions. Each Hg1 ion is coordinated by four N atoms from four bmi ligands and by two O atoms from two methanol molecules resulting in a distorted octahedral geometry. Whereas each Hg2 ion is two-coordinated by two N atoms from two bmi ligands. The Hg-O bond length is 2.642(5) Å and Hg-N distances range from 2.076(5) to 2.695(6) Å, respectively; these values are comparable to distances reported in the literature for Hg(II) complexes [10], [12], [13], [14]. There are two kinds of crystallographically independent bmi ligands. One bmi ligand coordinates to Hg(II) in the monodentate mode through the nitrogen atom of the imidazole ring [15]. The other bmi ligand coordinates to two Hg(II) ions as bridging ligand through the nitrogen atoms of imidazole and benzotriazole rings. Hg1 and Hg2 ions are connected by bridging bmi ligands to form an one-dimensional chain with Hg1-Hg2 distance of 10.4438(16) Å. In addition, there is one O—H⋯O hydrogen bond, two C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds and eight C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. Adjacent chains are linked by the mentioned hydrogen bonds, leading to a three-dimensional supramolecular architecture in the solid state.
Acknowledgements
This paper was supported by construction plan of high-level specialty with Chinese characteristics teaching letter (No.14, 2019); 2019 National vocational education teachers teaching innovation team; 333 high-level talents Project of Jiangsu Province; Qinglan Project of Jiangsu Province (2020).
References
1. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Rigaku/MSC. CrystalClear. Rigaku/MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA (2004).Suche in Google Scholar
4. Zhang, R. B.; Li, Z. J.; Qin, Y. Y.; Cheng, J. K.; Zhang, J.; Yao, Y. G.: Synthesis, structure, and physical properties of a new anions-controlled Cd(II)-guanazole (3,5-diamino-1,2,4-triazole) hybrid family. Inorg. Chem. 47 (2008) 4861–4876.10.1021/ic8001042Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Huang, Q. Y.; Wang, X. X.; Li, T.; Meng, X. R.: Construction of zinc-organic frameworks by flexible aliphatic dicarboxylates plus 2-(1H-imidazolyl-1-methyl)-1H-benzimidazole ligand. J. Coord. Chem. 68 (2015) 88–105.10.1080/00958972.2014.984702Suche in Google Scholar
6. Duan, W. L.; Zhang, Y. H.; Wang, X. X.; Meng, X. R.: Construction of two Cd(II) complexes by flexible adipic acid plus 2-((benzoimidazol-yl)methyl)-1H-tetrazole ligand. J. Mol. Struct. 1098 (2015) 66–71.10.1016/j.molstruc.2015.06.010Suche in Google Scholar
7. Zhao, L.; Wang, Z. W.; Zhao, D.; Meng, X. R.: Syntheses and crystal structures of three Cu(II) complexes based on 2,2′-(ethane-1,2-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylic acid). Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Nano-Met. Chem. 44 (2014) 195–202.10.1080/15533174.2013.769586Suche in Google Scholar
8. Lee, E.; Ju, H.; Kim, S.; Park, K. M.; Lee, S. S.: Anion-directed coordination networks of a flexible S-pivot ligand and anion exchange in the solid state. Cryst. Growth Des. 15 (2015) 5427–5436.10.1021/acs.cgd.5b01050Suche in Google Scholar
9. Yang, Y. Q.; Su, C. F.; Zhang, J. D.; Yang, H. X.; Zhang, G. Y.; Meng, X. R.: Construction of Cd(II) complexes based on 2-(1H-imidazol-1-methyl)-1H-benzimidazole and 1,4-benzenedicarboxylate. J. Coord. Chem. 69 (2016) 3762–3775.10.1080/00958972.2016.1237634Suche in Google Scholar
10. Duan, L. K.; Liu, S. L.; Zhou, W.; Meng, X. R.: Syntheses, crystal structures, and fluorescent properties of three complexes based on 1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imidazole. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Nano-Met. Chem. 40 (2010) 319–327.10.1080/15533174.2010.486818Suche in Google Scholar
11. Wei, X.; Li, J. H.; Huang, Q. Y.; Meng, X. R.: Two new isostructural mercury(II) complexes involving the N-heterocyclic1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,3-imidazole ligand: syntheses, structures and properties. Acta Crystallogr. C73 (2017) 314–318.10.1107/S2053229617003199/wq3128sup4.pdfSuche in Google Scholar
12. Pettinari, C.; Marinelli, A.; Marchetti, F.; Ngoune, J.; Galindo, A.; Álvarez, E.; Gómez, M.: Synthesis and coordination chemistry of two N2-donor chelating di(indazolyl)methane ligands: structural characterization and comparison of their metal chelation aptitudes. Inorg. Chem. 49 (2010) 10543–10556.10.1021/ic101577kSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Ueyama, N.; Taniuchi, K.; Okamura, T.; Nakamura, A.; Maeda, H.; Emura, S.: Effect of the N—H⋯S hydrogen bond on the nature of Hg-S bonding in bis[2-(acylamino)benzenethiolato]mercury(II) and bis[2,6-bis(acylamino)benzenethiolato]mercury(II) complexes. Inorg. Chem. 35 (1996) 1945–1951.10.1021/ic950472sSuche in Google Scholar
14. Ding, Y. N.; Zhou, X. L.; Jin, G. H.; Zhao, D.; Meng, X. R.: Syntheses, crystal structures, and fluorescent properties of two binuclear Hg(II) complexes based on 2-((benzoimidazolyl)methyl)-1H-tetrazole. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Nano-Met. Chem. 42 (2012) 438–443.10.1080/15533174.2011.611848Suche in Google Scholar
15. Yang, H.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-M.; He, F.; Li, H.; Wang, H.-F.; Li, Y.-H.: Crystal structure of bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,3-(2-methyl-imdazol)-κN}-dithiocyano-κN-zinc(II) C24H22N12S2Zn. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 233 (2018) 839–841.10.1515/ncrs-2018-0047Suche in Google Scholar
©2020 Shu-Xiang Sun et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-5-(4-carboxy-benzylamino)-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-4,4′-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl-κ2N:N′)dicadmium(II)], C25H22N3O8Cd
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-(2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium-1-yl)phenoxy)acetate, C19H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-μ2-bis(2-(2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C38H28Cl4N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-benzyl-3-hydroxy-3,6-diphenylpiperazine-2,5-dione, C33H29N3O3
- The crystal structure 2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′-(2-(3-amino-4-chlorobenzoyl)benzoato-κ1O)-(2-(3-amino-4-chlorobenzoyl)benzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II) — ethanol (1/1), C40H32Cl2N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-2-carboxy-4-(3-carboxy-5-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-bis(μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-k1N)copper(II)], C60H40N4O9Cu
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium catena-[di(μ-aqua)-bis(μ9-benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylato)pentalithium], C20H16Li5NO13
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(3,5-di(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-ido-κ1N)nickel(II) dihydrate, C24H28O6N10Ni
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1-methylimidazole-κ1N)-oxido-(sulfato-κ1O)vanadium(IV), C16H24N8O5SV
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(6,11-dioxo-2,3,6,11-tetrahydro-1H-benzo[f]pyrrolo[2,1-a]isoindole-5-carbonyl)benzoate, C24H17NO5
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-hydroxy-4-(2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethoxy)benzylidene) nicotinohydrazide monohydrate, C20H24N4O3 ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-(1-(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-κ3N:N′:N′′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/4), C42H52N18O10Co
- The crystal structure bis{hexakis(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)cobalt(II)} tetrakis(μ3-oxido)-octakis(μ2-oxido)-tetradecaoxido-octamolybdate(VI), C24H36CoMo4N12O13
- Crystal structure of di-μ-nicotinato-κ2N:O; κ2O:N-bis-[aqua-bis(benzyl)(nicotinato-κ2O,O′)tin(IV)], C52H48N4O10Sn2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)phenoxy)benzoic acidmanganese(II) monohydrate, C40H30N8O7MnCl2
- The crystal structure of benzyl 3β-acetylglycyrrhetate, C39H54O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-benzyl-3-(4-methoxystyryl)quinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C24H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of trans-dichloridobis(4-chlorophenyl-κC1)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tin(IV) dimethylsulphoxide solvate, C26H22Cl4N2OSSn
- Crystal structure of phenyl(1,3,4a-triphenyl-4a,5,6,10b-tetrahydro-1H-[1,4]oxazino[2,3-c]quinolin-5-yl)methanone, C36H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4aS,5S,6aS,6a1S, 10aS)-4a,5,6a,6a1,9,10-hexahydro-7H-4,5-methanocyclobuta[4,5]naphtho[8a,1-b]pyran-6(2H)-one, C15H16O2
- Crystal structure of [(Z)-O-isopropyl N-(4-chlorophenyl)thiocarbamato-κS]-(triphenylphosphine-κP)-gold(I), C28H26AuClNOPS
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-P,P′)-bis[(Z)-O-isopropyl N-(4-chlorophenyl)thiocarbamato-S]-di-gold(I) acetonitrile di-solvate, C54H50Au2Cl2FeN2O2P2S2⋅2(C2H3N)
- Crystal structure of (6aR,6a1S,10aS)-2,4a,6a,6a1,9,10-hexahydro-7H-4,5-methanocyclobuta[4,5]naphtho[8a,1-b]pyran, C15H16O
- Crystal structure of 5,17-diformyl-25,26,27,28-tetrahydroxycalix[4]arene- dichloromethane, C31H26Cl2O6
- Crystal structure of 2-tert-butyl 1-methyl 5-{4-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl}-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1,2-dicarboxylate, C19H24N2O6
- Crystal structure of [2-carboxybenzene-1-thiolato-S]-(triethylphosphane-P)-gold(I), C13H20AuO2PS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(5-methyl-2-aldehyde-phenolato-κ2O1,O2)copper(II), C16H14CuO4
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(di(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-μ4-silanetetrayltetrakis(benzene-4,1-diyl)tetrakis (hydrogen phosphonato)-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′) dicadmium(II)], C44H42N4O15P4Cd2Si
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(N,N-diethylcarbamodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-P)-di-silver(I), C22H50Ag2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(pyrrolidine-1-carbodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-κP)disilver(I), C22H46Ag2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-methylcarbamodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-P)-di-silver(I), C20H46Ag2N2O2P2S4
- The crystal structure of (2E,2′E)-,2,2′-bis[1-(2-pyrazinyl)ethylidene]carbonimidic dihydrazide, C13H15N9
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(quinolin-2-ylmethyl)-2-((1-(quinolin-2-ylmethyl)pyridin-2(1H)-ylidene)amino)pyridin-1-ium, C30H25BrN5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imdazole-κ2N:N′)-(1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imdazole-κ1N)-(methanol-κ1O)mercury(II)] dinitrate, C21H22N12O7Hg
- Crystal structure of 1-(6-hydroxy-2-phenylbenzofuran-5-yl)ethan-1-one, C16H12O3
- The crystal structure of oxonium hexaquaaluminium disulfate hexahydrate
- Crystal structure of catena{(μ2-1,10-phenanthroline-κ4N,N,N′,N′)-(μ2-1,10-phenanthroline-κ3N,N,N′)potassium(I) {[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)iminiumyl](sulfanidyl)methyl}sulfanide hemi(1,10-phenanthroline)}, {C24H16KN4, 0.5(C12H8N2), C5H10NO2S2}
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[(N,N-di-isobutyl)dithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′]-di(4-methylbenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C25H36ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)-(4-chloro-4-pyridyl-2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine-κ2N,N′) rhodium(III) hexaflourophosphate, C31H29Cl2F6N3PRh
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis-(3,5-dinitro-1,2,4-triazolato-κ2N:O)-(μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C16H10CuN14O8
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-bis(μ3-3,3′-((5-carboxylato-1,3-phenylene)bis(oxy))dibenzoato)-tris(1,10-phenanthroline)cobalt(II)], C78H46N6O20Co3
- The crystal structure of 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid–nicotinamide–methanol (1/1/1), C15H18N2O6
- The crystal structure of aqua{N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis[(1H-benzimidazol-κN3) methyl]cyclohexane-1,2-diamine}lead(II) diacetate–methanol (1/2), C44H54N10O7Pb
- Crystal structure of (2-amino-5-bromo-3-iodophenyl)(3-(4-chlorophenyl)oxiran-2-yl)methanone, C15H10BrClINO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 3-octyl-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione, C23H28N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-azido-N-(4-nitrophenyl)acetamide, C8H7N5O3
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (1S,2R,5R)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-oxa-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-3-carboxylate, C17H23NO5
- Crystal structure of 4-[(4-methoxy-2-nitrophenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H14N2O6
- Crystal structure of 3-ethyl-1-[(E)-[(2E)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]amino]thiourea, C12H15N3S
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridin-1,1′-dium poly[bis(μ4-benzene-1,3,5-triyltris(hydrogen phosphonato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′))zinc(II)], C11H11NO9P3Zn
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)butane-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-κS]-di-gold(I), C44H42Au2F2N2O2P2S2
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)hexane-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-κS]digold(I), C46H46Au2F2N2O2P2S2
- Crystal structure of tetrakis (N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-isopropylcarbamodithioato-κS,S′)-(μ2(2-(pyridin-4-yl)vinyl)pyridine-κN,N′)dicadmium(II), C36H58Cd2N6O4S8
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-en-1-yl)-1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carbonitrile, C20H12F6N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(octahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrolium)pentachlorobismuthate(III), (C7NH14)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of diaqua-tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(p-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κN)samarium(III), C24H36N9O15Sm
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-(2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)phenyl)-2-(4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)acetate, C23H23NO6
- Crystal structure of O-hexyl benzoylcarbamothioate, C14H19NO2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(O-methyl phenylcarbamothioamide-κS)-bis(triphenylphosphane-κP)silver(I), C44H39AgClNOP2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(O-ethyl phenylcarbamothioamide-κS)-bis(triphenylphosphane-κP)-silver(I), C45H41AgClNOP2S
- Crystal structure of 4-[(2-methoxyphenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H15NO4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazinane-3-carboxylate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua(μ2-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato)cadmium(II)], C6H8CdN2O7
- Crystal structure of (1S)-N-(chloromethyl)-1-((4S,6aR,8aS, 8bR,9aR)-4-methoxy-6a,8a-dimethyl-1,3,4, 5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9a,10,10a,10b-tetradecahydro-8bH-naphtho[2′,1′:4,5] indeno[1,2-b]oxiren-8b-yl)-N-methylethan-1-amine, C24H46ClNO5
- Crystal structure of 4-[(3,5-dichlorophenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C11H11Cl2NO3
- Crystal structure of (2Z)-2-amino-3-[(E)-[(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)methylidene]-amino]but-2-enedinitrile, C11H8N4O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-1-[(E)-(4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)amino]thiourea, C12H17N3S
- Crystal structure of carbonyl{hydridotris[3-phenyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl]borato-κ3N,N′N′′}copper(I), C31H28BCuN6O
- Crystal structure of ethane-1,2-diylbis(diphenylphosphine oxide) – dihydrogenperoxide (1/2), C26H28O6P2
- Crystal structure of 2-(pyridin-2-ylamino)pyridinium chloride dibenzyldichlorostannane, [C10H10N3]Cl, C14H14Cl2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-[(3-methoxyphenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H15NO4
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(tri-4-tolylphosphane oxide-κO)-di(4-chlorophenyl-κC)tin(IV), C54H50Cl4O2P2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichloridodimethylbis(tri-4-tolylphosphane oxide-κO)-tin(IV), C44H48Cl2O2P2Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)-bis(4-tolyl-κC)tin(IV), C24H22ClNOSn
- Crystal structure of (E)-dichloro(1-chloro-3-methoxyprop-1-en-2-yl)(4-methoxyphenyl)-λ4-tellane, C11H13Cl3O2Te
- Crystal structure of bis{N-methyl-N′-[3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylpropane-1-ylidene]carbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C26H36N6O2S2Zn
- Crystal structure of (2-carboxy-4-(3-carboxy-5-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II), C40H24N4O9Co
- The crystal structure of (3S,8R,10R,14R)-17-((2S,5S)-5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-12-oxohexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl acetate, C32H52O5
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-S]digold(I) chloroform solvate, C50H42Au2F2FeN2O2P2S2, CHCl3
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C24H20N8O4MoCo
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-5-(4-carboxy-benzylamino)-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-4,4′-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl-κ2N:N′)dicadmium(II)], C25H22N3O8Cd
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-(2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium-1-yl)phenoxy)acetate, C19H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-μ2-bis(2-(2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C38H28Cl4N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-benzyl-3-hydroxy-3,6-diphenylpiperazine-2,5-dione, C33H29N3O3
- The crystal structure 2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′-(2-(3-amino-4-chlorobenzoyl)benzoato-κ1O)-(2-(3-amino-4-chlorobenzoyl)benzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II) — ethanol (1/1), C40H32Cl2N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-2-carboxy-4-(3-carboxy-5-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-bis(μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-k1N)copper(II)], C60H40N4O9Cu
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium catena-[di(μ-aqua)-bis(μ9-benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylato)pentalithium], C20H16Li5NO13
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(3,5-di(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-ido-κ1N)nickel(II) dihydrate, C24H28O6N10Ni
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1-methylimidazole-κ1N)-oxido-(sulfato-κ1O)vanadium(IV), C16H24N8O5SV
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(6,11-dioxo-2,3,6,11-tetrahydro-1H-benzo[f]pyrrolo[2,1-a]isoindole-5-carbonyl)benzoate, C24H17NO5
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-hydroxy-4-(2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethoxy)benzylidene) nicotinohydrazide monohydrate, C20H24N4O3 ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-(1-(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-κ3N:N′:N′′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/4), C42H52N18O10Co
- The crystal structure bis{hexakis(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)cobalt(II)} tetrakis(μ3-oxido)-octakis(μ2-oxido)-tetradecaoxido-octamolybdate(VI), C24H36CoMo4N12O13
- Crystal structure of di-μ-nicotinato-κ2N:O; κ2O:N-bis-[aqua-bis(benzyl)(nicotinato-κ2O,O′)tin(IV)], C52H48N4O10Sn2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)phenoxy)benzoic acidmanganese(II) monohydrate, C40H30N8O7MnCl2
- The crystal structure of benzyl 3β-acetylglycyrrhetate, C39H54O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-benzyl-3-(4-methoxystyryl)quinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C24H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of trans-dichloridobis(4-chlorophenyl-κC1)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tin(IV) dimethylsulphoxide solvate, C26H22Cl4N2OSSn
- Crystal structure of phenyl(1,3,4a-triphenyl-4a,5,6,10b-tetrahydro-1H-[1,4]oxazino[2,3-c]quinolin-5-yl)methanone, C36H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4aS,5S,6aS,6a1S, 10aS)-4a,5,6a,6a1,9,10-hexahydro-7H-4,5-methanocyclobuta[4,5]naphtho[8a,1-b]pyran-6(2H)-one, C15H16O2
- Crystal structure of [(Z)-O-isopropyl N-(4-chlorophenyl)thiocarbamato-κS]-(triphenylphosphine-κP)-gold(I), C28H26AuClNOPS
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-P,P′)-bis[(Z)-O-isopropyl N-(4-chlorophenyl)thiocarbamato-S]-di-gold(I) acetonitrile di-solvate, C54H50Au2Cl2FeN2O2P2S2⋅2(C2H3N)
- Crystal structure of (6aR,6a1S,10aS)-2,4a,6a,6a1,9,10-hexahydro-7H-4,5-methanocyclobuta[4,5]naphtho[8a,1-b]pyran, C15H16O
- Crystal structure of 5,17-diformyl-25,26,27,28-tetrahydroxycalix[4]arene- dichloromethane, C31H26Cl2O6
- Crystal structure of 2-tert-butyl 1-methyl 5-{4-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl}-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1,2-dicarboxylate, C19H24N2O6
- Crystal structure of [2-carboxybenzene-1-thiolato-S]-(triethylphosphane-P)-gold(I), C13H20AuO2PS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(5-methyl-2-aldehyde-phenolato-κ2O1,O2)copper(II), C16H14CuO4
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(di(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-μ4-silanetetrayltetrakis(benzene-4,1-diyl)tetrakis (hydrogen phosphonato)-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′) dicadmium(II)], C44H42N4O15P4Cd2Si
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(N,N-diethylcarbamodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-P)-di-silver(I), C22H50Ag2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(pyrrolidine-1-carbodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-κP)disilver(I), C22H46Ag2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-methylcarbamodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-P)-di-silver(I), C20H46Ag2N2O2P2S4
- The crystal structure of (2E,2′E)-,2,2′-bis[1-(2-pyrazinyl)ethylidene]carbonimidic dihydrazide, C13H15N9
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(quinolin-2-ylmethyl)-2-((1-(quinolin-2-ylmethyl)pyridin-2(1H)-ylidene)amino)pyridin-1-ium, C30H25BrN5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imdazole-κ2N:N′)-(1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imdazole-κ1N)-(methanol-κ1O)mercury(II)] dinitrate, C21H22N12O7Hg
- Crystal structure of 1-(6-hydroxy-2-phenylbenzofuran-5-yl)ethan-1-one, C16H12O3
- The crystal structure of oxonium hexaquaaluminium disulfate hexahydrate
- Crystal structure of catena{(μ2-1,10-phenanthroline-κ4N,N,N′,N′)-(μ2-1,10-phenanthroline-κ3N,N,N′)potassium(I) {[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)iminiumyl](sulfanidyl)methyl}sulfanide hemi(1,10-phenanthroline)}, {C24H16KN4, 0.5(C12H8N2), C5H10NO2S2}
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[(N,N-di-isobutyl)dithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′]-di(4-methylbenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C25H36ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)-(4-chloro-4-pyridyl-2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine-κ2N,N′) rhodium(III) hexaflourophosphate, C31H29Cl2F6N3PRh
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis-(3,5-dinitro-1,2,4-triazolato-κ2N:O)-(μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C16H10CuN14O8
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-bis(μ3-3,3′-((5-carboxylato-1,3-phenylene)bis(oxy))dibenzoato)-tris(1,10-phenanthroline)cobalt(II)], C78H46N6O20Co3
- The crystal structure of 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid–nicotinamide–methanol (1/1/1), C15H18N2O6
- The crystal structure of aqua{N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis[(1H-benzimidazol-κN3) methyl]cyclohexane-1,2-diamine}lead(II) diacetate–methanol (1/2), C44H54N10O7Pb
- Crystal structure of (2-amino-5-bromo-3-iodophenyl)(3-(4-chlorophenyl)oxiran-2-yl)methanone, C15H10BrClINO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 3-octyl-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione, C23H28N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-azido-N-(4-nitrophenyl)acetamide, C8H7N5O3
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (1S,2R,5R)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-oxa-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-3-carboxylate, C17H23NO5
- Crystal structure of 4-[(4-methoxy-2-nitrophenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H14N2O6
- Crystal structure of 3-ethyl-1-[(E)-[(2E)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]amino]thiourea, C12H15N3S
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridin-1,1′-dium poly[bis(μ4-benzene-1,3,5-triyltris(hydrogen phosphonato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′))zinc(II)], C11H11NO9P3Zn
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)butane-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-κS]-di-gold(I), C44H42Au2F2N2O2P2S2
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)hexane-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-κS]digold(I), C46H46Au2F2N2O2P2S2
- Crystal structure of tetrakis (N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-isopropylcarbamodithioato-κS,S′)-(μ2(2-(pyridin-4-yl)vinyl)pyridine-κN,N′)dicadmium(II), C36H58Cd2N6O4S8
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-en-1-yl)-1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carbonitrile, C20H12F6N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(octahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrolium)pentachlorobismuthate(III), (C7NH14)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of diaqua-tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(p-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κN)samarium(III), C24H36N9O15Sm
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-(2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)phenyl)-2-(4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)acetate, C23H23NO6
- Crystal structure of O-hexyl benzoylcarbamothioate, C14H19NO2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(O-methyl phenylcarbamothioamide-κS)-bis(triphenylphosphane-κP)silver(I), C44H39AgClNOP2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(O-ethyl phenylcarbamothioamide-κS)-bis(triphenylphosphane-κP)-silver(I), C45H41AgClNOP2S
- Crystal structure of 4-[(2-methoxyphenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H15NO4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazinane-3-carboxylate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua(μ2-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato)cadmium(II)], C6H8CdN2O7
- Crystal structure of (1S)-N-(chloromethyl)-1-((4S,6aR,8aS, 8bR,9aR)-4-methoxy-6a,8a-dimethyl-1,3,4, 5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9a,10,10a,10b-tetradecahydro-8bH-naphtho[2′,1′:4,5] indeno[1,2-b]oxiren-8b-yl)-N-methylethan-1-amine, C24H46ClNO5
- Crystal structure of 4-[(3,5-dichlorophenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C11H11Cl2NO3
- Crystal structure of (2Z)-2-amino-3-[(E)-[(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)methylidene]-amino]but-2-enedinitrile, C11H8N4O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-1-[(E)-(4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)amino]thiourea, C12H17N3S
- Crystal structure of carbonyl{hydridotris[3-phenyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl]borato-κ3N,N′N′′}copper(I), C31H28BCuN6O
- Crystal structure of ethane-1,2-diylbis(diphenylphosphine oxide) – dihydrogenperoxide (1/2), C26H28O6P2
- Crystal structure of 2-(pyridin-2-ylamino)pyridinium chloride dibenzyldichlorostannane, [C10H10N3]Cl, C14H14Cl2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-[(3-methoxyphenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H15NO4
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(tri-4-tolylphosphane oxide-κO)-di(4-chlorophenyl-κC)tin(IV), C54H50Cl4O2P2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichloridodimethylbis(tri-4-tolylphosphane oxide-κO)-tin(IV), C44H48Cl2O2P2Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)-bis(4-tolyl-κC)tin(IV), C24H22ClNOSn
- Crystal structure of (E)-dichloro(1-chloro-3-methoxyprop-1-en-2-yl)(4-methoxyphenyl)-λ4-tellane, C11H13Cl3O2Te
- Crystal structure of bis{N-methyl-N′-[3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylpropane-1-ylidene]carbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C26H36N6O2S2Zn
- Crystal structure of (2-carboxy-4-(3-carboxy-5-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II), C40H24N4O9Co
- The crystal structure of (3S,8R,10R,14R)-17-((2S,5S)-5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-12-oxohexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl acetate, C32H52O5
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-S]digold(I) chloroform solvate, C50H42Au2F2FeN2O2P2S2, CHCl3
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C24H20N8O4MoCo

