Abstract
C58H56Au2Cl2FeN4O2P2S2, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 8.5422(3) Å, b = 13.2143(4) Å, c = 14.0226(4)) Å, α = 65.764(3)°, β = 78.311(2)°, γ = 80.090(3)°, V = 1406.39(8) Å3, Z = 1, Rgt(F) = 0.0213, wRref(F2) = 0.0477, T = 100 K.
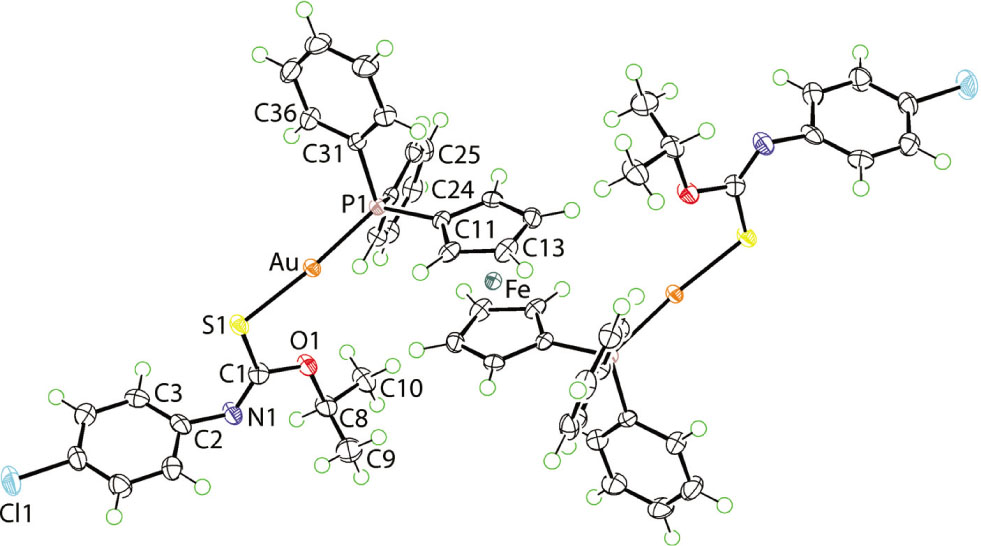
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow plate |
| Size: | 0.26 × 0.17 × 0.04 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 5.73 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 32730, 6449, 0.059 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 6051 |
| N(param)refined: | 334 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], [3], WinGX/ORTEP [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | 0.63437(2) | 0.01557(2) | 0.79829(2) | 0.01259(4) |
| Fe | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.01140(11) |
| Cl1 | 0.30531(9) | −0.41350(7) | 0.51971(6) | 0.03149(18) |
| S1 | 0.56705(7) | −0.09673(6) | 0.72579(5) | 0.01631(14) |
| P1 | 0.69419(7) | 0.14215(5) | 0.85151(5) | 0.01115(13) |
| O1 | 0.8815(2) | −0.09928(16) | 0.67806(14) | 0.0185(4) |
| N1 | 0.7767(3) | −0.2071(2) | 0.62072(18) | 0.0196(5) |
| C1 | 0.7534(3) | −0.1410(2) | 0.6678(2) | 0.0167(6) |
| C2 | 0.6508(3) | −0.2509(2) | 0.6030(2) | 0.0175(6) |
| C3 | 0.5600(3) | −0.1887(2) | 0.5226(2) | 0.0193(6) |
| H3 | 0.571185 | −0.111362 | 0.484707 | 0.023* |
| C4 | 0.4526(3) | −0.2381(2) | 0.4966(2) | 0.0193(6) |
| H4 | 0.390654 | −0.195181 | 0.441463 | 0.023* |
| C5 | 0.4377(3) | −0.3500(2) | 0.5520(2) | 0.0200(6) |
| C6 | 0.5270(3) | −0.4141(2) | 0.6328(2) | 0.0225(6) |
| H6 | 0.515209 | −0.491324 | 0.670599 | 0.027* |
| C7 | 0.6335(3) | −0.3638(2) | 0.6577(2) | 0.0203(6) |
| H7 | 0.695383 | −0.407050 | 0.712781 | 0.024* |
| C8 | 1.0411(3) | −0.1426(2) | 0.6401(2) | 0.0208(6) |
| H8 | 1.036905 | −0.151679 | 0.573342 | 0.025* |
| C9 | 1.0896(4) | −0.2542(3) | 0.7226(3) | 0.0301(7) |
| H9A | 1.010962 | −0.306160 | 0.736061 | 0.045* |
| H9B | 1.093678 | −0.245513 | 0.788192 | 0.045* |
| H9C | 1.195837 | −0.283438 | 0.697280 | 0.045* |
| C10 | 1.1511(3) | −0.0545(3) | 0.6167(2) | 0.0241(6) |
| H3A | 1.111529 | 0.015982 | 0.563525 | 0.036* |
| H3B | 1.259812 | −0.078303 | 0.589654 | 0.036* |
| H3C | 1.153145 | −0.043980 | 0.681625 | 0.036* |
| C11 | 0.7855(3) | 0.0922(2) | 0.96937(19) | 0.0123(5) |
| C12 | 0.7605(3) | −0.0127(2) | 1.0558(2) | 0.0156(5) |
| H12 | 0.696711 | −0.070811 | 1.058430 | 0.019* |
| C13 | 0.8422(3) | −0.0193(2) | 1.1371(2) | 0.0189(6) |
| H13 | 0.847480 | −0.083630 | 1.206642 | 0.023* |
| C14 | 0.9189(3) | 0.0796(2) | 1.1017(2) | 0.0185(6) |
| H14 | 0.986627 | 0.097186 | 1.142312 | 0.022* |
| C15 | 0.8839(3) | 0.1491(2) | 0.9984(2) | 0.0165(5) |
| H15 | 0.921614 | 0.224289 | 0.953905 | 0.020* |
| C21 | 0.8292(3) | 0.2338(2) | 0.74741(19) | 0.0127(5) |
| C22 | 0.9218(3) | 0.1946(2) | 0.6736(2) | 0.0160(5) |
| H22 | 0.907810 | 0.123750 | 0.676131 | 0.019* |
| C23 | 1.0347(3) | 0.2587(2) | 0.5961(2) | 0.0194(6) |
| H23 | 1.098916 | 0.231416 | 0.546289 | 0.023* |
| C24 | 1.0531(3) | 0.3626(2) | 0.5918(2) | 0.0211(6) |
| H24 | 1.131216 | 0.406174 | 0.539390 | 0.025* |
| C25 | 0.9581(3) | 0.4036(2) | 0.6634(2) | 0.0195(6) |
| H25 | 0.970266 | 0.475519 | 0.659216 | 0.023* |
| C26 | 0.8451(3) | 0.3396(2) | 0.7415(2) | 0.0156(5) |
| H26 | 0.779454 | 0.367751 | 0.790232 | 0.019* |
| C31 | 0.5156(3) | 0.2303(2) | 0.8757(2) | 0.0127(5) |
| C32 | 0.4632(3) | 0.2343(2) | 0.9748(2) | 0.0181(6) |
| H32 | 0.526413 | 0.195654 | 1.030079 | 0.022* |
| C33 | 0.3183(3) | 0.2950(2) | 0.9932(2) | 0.0227(6) |
| H33 | 0.282174 | 0.296676 | 1.061239 | 0.027* |
| C34 | 0.2270(3) | 0.3527(2) | 0.9127(2) | 0.0252(7) |
| H34 | 0.128475 | 0.394374 | 0.925154 | 0.030* |
| C35 | 0.2801(3) | 0.3494(3) | 0.8139(2) | 0.0262(7) |
| H35 | 0.217724 | 0.389728 | 0.758392 | 0.031* |
| C36 | 0.4225(3) | 0.2882(2) | 0.7947(2) | 0.0196(6) |
| H36 | 0.456788 | 0.285674 | 0.726794 | 0.024* |
| N41 | 0.8023(4) | 0.4581(3) | −0.0728(3) | 0.0438(8) |
| C41 | 0.7217(4) | 0.4258(3) | 0.0054(3) | 0.0322(7) |
| C42 | 0.6152(4) | 0.3863(3) | 0.1074(3) | 0.0447(9) |
| H42A | 0.626695 | 0.304563 | 0.138649 | 0.067* |
| H42B | 0.503501 | 0.413410 | 0.096107 | 0.067* |
| H42C | 0.644434 | 0.414601 | 0.155314 | 0.067* |
Source of material
NaOH (Merck; 0.020 g, 0.50 mmol) in water (5 mL) was added to a suspension of (dppf)(AuCl)2 (0.255 g, 0.25 mmol) in acetonitrile (20 mL), followed by addition of iPrOC(=S)N(H)C6H4Cl-4 (0.115 g, 0.50 mmol) in dichloromethane (20 mL). After stirring for 3 h, the solution was left for slow evaporation at room temperature, yielding yellow crystals after 3 weeks. Yield: 0.278 g (79%). M. pt: (Biobase automatic melting point apparatus MP450): 473–474 K.
Elemental Analysis for C54H50Au2Cl2FeN2O2P2S2 (Leco TruSpec Micro CHN Elemental Analyser): C, 46.14; H, 3.58; N, 1.99%. Found: C, 46.03; H, 3.28; N, 1.86%. IR (Bruker Vertex 70v FTIR Spectrophotometer; cm−1): 1435 (s) ν(C=N), 1140 (s) ν(C—O), 1091 (s) ν(C—S). 1H NMR (Bruker Ascend 400 MHz NMR spectrometer with chemical shifts relative to tetramethylsilane in CDCl3 solution at 298 K, ppm): δ 7.50–7.40 (m, br, 20H, Ph2P), 7.07 (d, 4H, m-aryl-H, JHH = 8.52 Hz), 6.79 (d, 4H, o-aryl-H, JHH = 8.48 Hz), 5.29 (sept, 2H, OCH, JHH = 6.17 Hz), 4.64 (s, br, 4H, β-PC5H4), 4.21 (s, br, 4H, γ-PC5H4), 1.33 (d, 12H, CH3, JHH = 6.20 Hz). 13C{1H} NMR (as for 1H NMR): δ 163.6 (Cq), 149.8 (aryl, Cipso), 133.6 (d, m-PC6H5, 3JCP = 14.02 Hz), 131.7 (d, p-PC6H5, 4JCP = 2.25 Hz), 130.8 (d, i-PC6H5, 1JCP = 58.57 Hz), 129.0 (d, o-PC6H5, 2JCP = 11.52 Hz), 128.7 (aryl, Cmeta), 127.4 (aryl, Cpara), 123.3 (aryl, Cortho), 75.0 (d, β-PC5H4, 2JCP = 8.46 Hz), 74.8 (d, γ-PC5H4, 3JCP = 13.15 Hz), 71.8 (d, α-PC5H4, 1JCP = 65.48 Hz), 70.6 (OCH), 22.2 (CH3). 31P{1H} NMR (as for 1H NMR but with chemical shift referenced to 85% aqueous H3PO4 as the external reference): δ 32.6.
Crystals of (I) for the X-ray structure determination were grown from the slow evaporation of an acetonitrile solution of (I) and analysed directly.
Experimental details
The C-bound H atoms were geometrically placed (C—H = 0.95–1.00 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5Ueq(C). The maximum and minimum residual electron density peaks of 1.15 and 1.02 eÅ−3, respectively, were located 0.99 Å and 0.66 Å, respectively, from the Au atom.
Comment
The original interest in binuclear phosphane gold(I) thioamide molecules of the formula dppf{Au[SC(OR)=NC6H4Y-4]}2 related to an investigation of the solid-state photoluminescent properties of the R = Me and Y = NO2 derivative, isolated as a di-chloroform solvate [5]; dppf is 1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene. Subsequently, crystal structure determinations for the R = Et and Y = H, as a dichloromethane solvate [6], and R = iPr with Y = Me [7] and Y = NO2, isolated as a di-chloroform solvate [8], species have been described. In this contribution, the crystal and molecular structures of the R = iPr and Y = Cl compound isolated as an acetonitrile di-solvate, (I), is described.
The molecular structure of the binuclear species in (I) is shown in the figure (70% displacement ellipsoids; unlabelled atoms are related by the symmetry operation (i) 2 − x, −y, 2 − z). The crystallographic asymmetric unit comprises half a binuclear molecule, as the Fe atom is situated on a centre of inversion, and a solvent acetonitrile molecule. The independent gold(I) atom adopts the expected linear geometry [P1—Au—S1 = 173.31(2)°], being coordinated by phosphane-P [Au—P1 = 2.2560(7) Å] and thiolate-S [Au—S1 = 2.3099(7) Å] atoms. The crystal structure of the uncoordinated ligand in its protonated form, i.e. iPrOC(=S)N(H)C6H4Cl-4, is available in the literature [9]. The C1—S1 [1.755(3) Å] and C1—N1 [1.265(3) Å] bond lengths in (I) are significantly elongated and contracted compared with the equivalent bonds, i.e. 1.6708(15) and 1.3388(18) Å, respectively, in the acid. As is uniformly found in dppf{Au[SC(OR)=NC6H4Y-4]}2 structures, an intramolecular Au⋯O interaction is observed. In (I), the Au⋯O separation is 3.026(2) Å.
The molecular packing for (I) features P-phenyl-C—H⋯N(imino) [C23—H23⋯N1ii: H23⋯N1ii = 2.49 Å, C23⋯N1ii = 3.412(4) Å with angle at H23 = 163° for (ii) 2 − x, − y, 1 − z] interactions that lead to the formation of supramolecular chains with a linear topology along the c-axis. The other directional interactions are of the type cyclopentadienyl-C—H⋯π(P-phenyl) [C12—H12⋯Cg(C31–C36)iii: H12⋯Cg(C31–C36)iii = 2.85 Å with angle at H12 = 156° for (iii) 1 − x, −y, 2 − z] and chlorophenyl-C—Cl⋯π(P-phenyl) interactions are noted [C5—Cl1⋯Cg(C21–C26)iv: Cl1⋯Cg(C21–C26)iv = 3.4004(13) Å with angle at Cl1 = 129.10(10)° for (iv) 1 − x, − y, 1 − z] which link chains into a supramolecular layer in the ac-plane. The layers stack along the b-axis without directional interactions between them. The closest contact between the binuclear and solvent acetonitrile molecules is a weak P-phenyl-C—H⋯N(acetonitrile) interaction [C26—H26⋯N41v: H26⋯N41v = 2.70 Å, C26⋯N41v = 3.483(6) Å with angle at H26 = 141° for (v) x, y, 1 + z].
In order to assess the molecular packing further, the Hirshfeld surfaces were calculated along with the full and delineated two-dimensional fingerprint plots employing Crystal Explorer 17 [10] and literature procedures [11]. The most dominant contribution to the calculated surface is from H⋯H contacts at 45.9% with the next most significant contribution coming from H⋯C/C⋯.H contacts, at 23.1%. The percentage contribution from H⋯N/N⋯H contacts is 6.3% with characteristic spikes due to the C—H⋯N interactions being apparent. Other significant contributions are made by H⋯S/S⋯H contacts [7.4%], at distances greater that van der Waals separation as well as contacts involving the chloride atom, i.e. H⋯Cl/Cl⋯H [7.6%] and C⋯Cl/C⋯Cl [3.1%]. The structure of the R = iPr with Y = Me derivative [7], (II), also features P-phenyl-C—H⋯N(imino) interactions leading to supramolecular chains as described for (I). Reflecting the absence of the chloride substituent present in (I), the H⋯H surface contacts in (II) increases to 60.0% followed by H⋯C/C⋯H contacts at 25.0%.
Finally, it is noted that there are no Au⋯Au (aurophilic) interactions in (I), nor are they observed in (II) [7] and in the R = Et and Y = H compound [6]. These three structures have the common feature of having the iron atom located on a centre of inversion. By contrast, the two structures with R = Me and Y = NO2 [5] and R = iPr and Y = NO2 [8] are 2-fold symmetric and feature intramolecular Au⋯Au interactions.
Acknowledgements
Sunway University Sdn Bhd is thanked for financial support of this work through Grant No. STR-RCTR-RCCM-001–2019.
References
1. Agilent Technologies (2014). CrysAlisPRO. Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, U.S.A.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Cryst. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Search in Google Scholar
5. Ho, S. Y.; Cheng, E. C.-C.; Tiekink, E. R. T.; Yam, V. W.-W.: Luminescent phosphine gold(I) thiolates: Correlation between crystal structure and photoluminescent properties in [R3PAu{SC(OMe)=NC6H4NO2-4}] (R = Et, Cy, Ph) and [(Ph2P-R-PPh2){AuSC(OMe)=NC6H4NO2-4}2] (R = CH2, (CH2)2, (CH2)3, (CH2)4, Fc). Inorg. Chem. 45 (2006) 8165–8174.10.1021/ic0608243Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Ho, S. Y.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: [1,1-μ-Bis(diphenylphosphino)-ferrocene]bis{[(Z)-O-ethyl N-phenylthiocarbamato-]κS]gold(I)} dichloromethane solvate. Acta Crystallogr. E66 (2010) m608–m609.10.1107/S160053681001562XSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
7. Tadbuppa, P. P.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: [μ-1,1′-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P:P′]bis{[(Z)-O-isopropyl-N-(4-methylphenyl)thiocarbamato-κS]gold(I)}. Acta Crystallogr. E65 (2009) m1597.10.1107/S1600536809047898Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. Ho, S. Y.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: [μ-1,1′-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κP:P′-bis{[(Z)-O-isopropyl N-(4-nitrophenyl)thiocarbamato-κS]gold(I)} chloroform disolvate. Acta Crystallogr. E65 (2009) m1466–m1467.10.1107/S1600536809043864Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Kuan, F. S.; Mohr, F.; Tadbuppa, P. P.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Principles of crystal packing in O-isopropyl-N-aryl-thiocarbamides: iPrOC(=S)N(H)C6H4-4-Y: Y = H, Cl, and Me. CrystEngComm 9 (2007) 574–581.10.1039/B701489ASearch in Google Scholar
10. Turner, M. J.; McKinnon, J. J.; Wolff, S. K.; Grimwood, D. J.; Spackman, P. R.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spackman, M. A.: Crystal Explorer v17. The University of Western Australia, Australia (2017).Search in Google Scholar
11. Tan, S. L.; Jotani, M. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Utilizing Hirshfeld surface calculations, non-covalent interaction (NCI) plots and the calculation of interaction energies in the analysis of molecular packing. Acta Crystallogr. E75 (2019) 308–318.10.1107/S2056989019001129Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
©2020 Chien Ing Yeo et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-5-(4-carboxy-benzylamino)-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-4,4′-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl-κ2N:N′)dicadmium(II)], C25H22N3O8Cd
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-(2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium-1-yl)phenoxy)acetate, C19H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-μ2-bis(2-(2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C38H28Cl4N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-benzyl-3-hydroxy-3,6-diphenylpiperazine-2,5-dione, C33H29N3O3
- The crystal structure 2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′-(2-(3-amino-4-chlorobenzoyl)benzoato-κ1O)-(2-(3-amino-4-chlorobenzoyl)benzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II) — ethanol (1/1), C40H32Cl2N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-2-carboxy-4-(3-carboxy-5-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-bis(μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-k1N)copper(II)], C60H40N4O9Cu
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium catena-[di(μ-aqua)-bis(μ9-benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylato)pentalithium], C20H16Li5NO13
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(3,5-di(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-ido-κ1N)nickel(II) dihydrate, C24H28O6N10Ni
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1-methylimidazole-κ1N)-oxido-(sulfato-κ1O)vanadium(IV), C16H24N8O5SV
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(6,11-dioxo-2,3,6,11-tetrahydro-1H-benzo[f]pyrrolo[2,1-a]isoindole-5-carbonyl)benzoate, C24H17NO5
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-hydroxy-4-(2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethoxy)benzylidene) nicotinohydrazide monohydrate, C20H24N4O3 ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-(1-(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-κ3N:N′:N′′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/4), C42H52N18O10Co
- The crystal structure bis{hexakis(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)cobalt(II)} tetrakis(μ3-oxido)-octakis(μ2-oxido)-tetradecaoxido-octamolybdate(VI), C24H36CoMo4N12O13
- Crystal structure of di-μ-nicotinato-κ2N:O; κ2O:N-bis-[aqua-bis(benzyl)(nicotinato-κ2O,O′)tin(IV)], C52H48N4O10Sn2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)phenoxy)benzoic acidmanganese(II) monohydrate, C40H30N8O7MnCl2
- The crystal structure of benzyl 3β-acetylglycyrrhetate, C39H54O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-benzyl-3-(4-methoxystyryl)quinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C24H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of trans-dichloridobis(4-chlorophenyl-κC1)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tin(IV) dimethylsulphoxide solvate, C26H22Cl4N2OSSn
- Crystal structure of phenyl(1,3,4a-triphenyl-4a,5,6,10b-tetrahydro-1H-[1,4]oxazino[2,3-c]quinolin-5-yl)methanone, C36H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4aS,5S,6aS,6a1S, 10aS)-4a,5,6a,6a1,9,10-hexahydro-7H-4,5-methanocyclobuta[4,5]naphtho[8a,1-b]pyran-6(2H)-one, C15H16O2
- Crystal structure of [(Z)-O-isopropyl N-(4-chlorophenyl)thiocarbamato-κS]-(triphenylphosphine-κP)-gold(I), C28H26AuClNOPS
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-P,P′)-bis[(Z)-O-isopropyl N-(4-chlorophenyl)thiocarbamato-S]-di-gold(I) acetonitrile di-solvate, C54H50Au2Cl2FeN2O2P2S2⋅2(C2H3N)
- Crystal structure of (6aR,6a1S,10aS)-2,4a,6a,6a1,9,10-hexahydro-7H-4,5-methanocyclobuta[4,5]naphtho[8a,1-b]pyran, C15H16O
- Crystal structure of 5,17-diformyl-25,26,27,28-tetrahydroxycalix[4]arene- dichloromethane, C31H26Cl2O6
- Crystal structure of 2-tert-butyl 1-methyl 5-{4-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl}-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1,2-dicarboxylate, C19H24N2O6
- Crystal structure of [2-carboxybenzene-1-thiolato-S]-(triethylphosphane-P)-gold(I), C13H20AuO2PS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(5-methyl-2-aldehyde-phenolato-κ2O1,O2)copper(II), C16H14CuO4
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(di(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-μ4-silanetetrayltetrakis(benzene-4,1-diyl)tetrakis (hydrogen phosphonato)-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′) dicadmium(II)], C44H42N4O15P4Cd2Si
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(N,N-diethylcarbamodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-P)-di-silver(I), C22H50Ag2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(pyrrolidine-1-carbodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-κP)disilver(I), C22H46Ag2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-methylcarbamodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-P)-di-silver(I), C20H46Ag2N2O2P2S4
- The crystal structure of (2E,2′E)-,2,2′-bis[1-(2-pyrazinyl)ethylidene]carbonimidic dihydrazide, C13H15N9
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(quinolin-2-ylmethyl)-2-((1-(quinolin-2-ylmethyl)pyridin-2(1H)-ylidene)amino)pyridin-1-ium, C30H25BrN5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imdazole-κ2N:N′)-(1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imdazole-κ1N)-(methanol-κ1O)mercury(II)] dinitrate, C21H22N12O7Hg
- Crystal structure of 1-(6-hydroxy-2-phenylbenzofuran-5-yl)ethan-1-one, C16H12O3
- The crystal structure of oxonium hexaquaaluminium disulfate hexahydrate
- Crystal structure of catena{(μ2-1,10-phenanthroline-κ4N,N,N′,N′)-(μ2-1,10-phenanthroline-κ3N,N,N′)potassium(I) {[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)iminiumyl](sulfanidyl)methyl}sulfanide hemi(1,10-phenanthroline)}, {C24H16KN4, 0.5(C12H8N2), C5H10NO2S2}
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[(N,N-di-isobutyl)dithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′]-di(4-methylbenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C25H36ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)-(4-chloro-4-pyridyl-2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine-κ2N,N′) rhodium(III) hexaflourophosphate, C31H29Cl2F6N3PRh
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis-(3,5-dinitro-1,2,4-triazolato-κ2N:O)-(μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C16H10CuN14O8
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-bis(μ3-3,3′-((5-carboxylato-1,3-phenylene)bis(oxy))dibenzoato)-tris(1,10-phenanthroline)cobalt(II)], C78H46N6O20Co3
- The crystal structure of 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid–nicotinamide–methanol (1/1/1), C15H18N2O6
- The crystal structure of aqua{N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis[(1H-benzimidazol-κN3) methyl]cyclohexane-1,2-diamine}lead(II) diacetate–methanol (1/2), C44H54N10O7Pb
- Crystal structure of (2-amino-5-bromo-3-iodophenyl)(3-(4-chlorophenyl)oxiran-2-yl)methanone, C15H10BrClINO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 3-octyl-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione, C23H28N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-azido-N-(4-nitrophenyl)acetamide, C8H7N5O3
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (1S,2R,5R)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-oxa-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-3-carboxylate, C17H23NO5
- Crystal structure of 4-[(4-methoxy-2-nitrophenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H14N2O6
- Crystal structure of 3-ethyl-1-[(E)-[(2E)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]amino]thiourea, C12H15N3S
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridin-1,1′-dium poly[bis(μ4-benzene-1,3,5-triyltris(hydrogen phosphonato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′))zinc(II)], C11H11NO9P3Zn
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)butane-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-κS]-di-gold(I), C44H42Au2F2N2O2P2S2
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)hexane-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-κS]digold(I), C46H46Au2F2N2O2P2S2
- Crystal structure of tetrakis (N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-isopropylcarbamodithioato-κS,S′)-(μ2(2-(pyridin-4-yl)vinyl)pyridine-κN,N′)dicadmium(II), C36H58Cd2N6O4S8
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-en-1-yl)-1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carbonitrile, C20H12F6N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(octahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrolium)pentachlorobismuthate(III), (C7NH14)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of diaqua-tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(p-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κN)samarium(III), C24H36N9O15Sm
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-(2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)phenyl)-2-(4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)acetate, C23H23NO6
- Crystal structure of O-hexyl benzoylcarbamothioate, C14H19NO2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(O-methyl phenylcarbamothioamide-κS)-bis(triphenylphosphane-κP)silver(I), C44H39AgClNOP2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(O-ethyl phenylcarbamothioamide-κS)-bis(triphenylphosphane-κP)-silver(I), C45H41AgClNOP2S
- Crystal structure of 4-[(2-methoxyphenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H15NO4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazinane-3-carboxylate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua(μ2-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato)cadmium(II)], C6H8CdN2O7
- Crystal structure of (1S)-N-(chloromethyl)-1-((4S,6aR,8aS, 8bR,9aR)-4-methoxy-6a,8a-dimethyl-1,3,4, 5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9a,10,10a,10b-tetradecahydro-8bH-naphtho[2′,1′:4,5] indeno[1,2-b]oxiren-8b-yl)-N-methylethan-1-amine, C24H46ClNO5
- Crystal structure of 4-[(3,5-dichlorophenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C11H11Cl2NO3
- Crystal structure of (2Z)-2-amino-3-[(E)-[(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)methylidene]-amino]but-2-enedinitrile, C11H8N4O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-1-[(E)-(4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)amino]thiourea, C12H17N3S
- Crystal structure of carbonyl{hydridotris[3-phenyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl]borato-κ3N,N′N′′}copper(I), C31H28BCuN6O
- Crystal structure of ethane-1,2-diylbis(diphenylphosphine oxide) – dihydrogenperoxide (1/2), C26H28O6P2
- Crystal structure of 2-(pyridin-2-ylamino)pyridinium chloride dibenzyldichlorostannane, [C10H10N3]Cl, C14H14Cl2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-[(3-methoxyphenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H15NO4
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(tri-4-tolylphosphane oxide-κO)-di(4-chlorophenyl-κC)tin(IV), C54H50Cl4O2P2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichloridodimethylbis(tri-4-tolylphosphane oxide-κO)-tin(IV), C44H48Cl2O2P2Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)-bis(4-tolyl-κC)tin(IV), C24H22ClNOSn
- Crystal structure of (E)-dichloro(1-chloro-3-methoxyprop-1-en-2-yl)(4-methoxyphenyl)-λ4-tellane, C11H13Cl3O2Te
- Crystal structure of bis{N-methyl-N′-[3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylpropane-1-ylidene]carbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C26H36N6O2S2Zn
- Crystal structure of (2-carboxy-4-(3-carboxy-5-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II), C40H24N4O9Co
- The crystal structure of (3S,8R,10R,14R)-17-((2S,5S)-5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-12-oxohexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl acetate, C32H52O5
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-S]digold(I) chloroform solvate, C50H42Au2F2FeN2O2P2S2, CHCl3
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C24H20N8O4MoCo
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-5-(4-carboxy-benzylamino)-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-4,4′-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl-κ2N:N′)dicadmium(II)], C25H22N3O8Cd
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-(2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium-1-yl)phenoxy)acetate, C19H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-μ2-bis(2-(2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C38H28Cl4N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-benzyl-3-hydroxy-3,6-diphenylpiperazine-2,5-dione, C33H29N3O3
- The crystal structure 2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′-(2-(3-amino-4-chlorobenzoyl)benzoato-κ1O)-(2-(3-amino-4-chlorobenzoyl)benzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II) — ethanol (1/1), C40H32Cl2N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-2-carboxy-4-(3-carboxy-5-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-bis(μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-k1N)copper(II)], C60H40N4O9Cu
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium catena-[di(μ-aqua)-bis(μ9-benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylato)pentalithium], C20H16Li5NO13
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(3,5-di(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-ido-κ1N)nickel(II) dihydrate, C24H28O6N10Ni
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1-methylimidazole-κ1N)-oxido-(sulfato-κ1O)vanadium(IV), C16H24N8O5SV
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(6,11-dioxo-2,3,6,11-tetrahydro-1H-benzo[f]pyrrolo[2,1-a]isoindole-5-carbonyl)benzoate, C24H17NO5
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-hydroxy-4-(2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethoxy)benzylidene) nicotinohydrazide monohydrate, C20H24N4O3 ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-(1-(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-κ3N:N′:N′′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/4), C42H52N18O10Co
- The crystal structure bis{hexakis(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)cobalt(II)} tetrakis(μ3-oxido)-octakis(μ2-oxido)-tetradecaoxido-octamolybdate(VI), C24H36CoMo4N12O13
- Crystal structure of di-μ-nicotinato-κ2N:O; κ2O:N-bis-[aqua-bis(benzyl)(nicotinato-κ2O,O′)tin(IV)], C52H48N4O10Sn2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)phenoxy)benzoic acidmanganese(II) monohydrate, C40H30N8O7MnCl2
- The crystal structure of benzyl 3β-acetylglycyrrhetate, C39H54O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-benzyl-3-(4-methoxystyryl)quinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C24H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of trans-dichloridobis(4-chlorophenyl-κC1)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tin(IV) dimethylsulphoxide solvate, C26H22Cl4N2OSSn
- Crystal structure of phenyl(1,3,4a-triphenyl-4a,5,6,10b-tetrahydro-1H-[1,4]oxazino[2,3-c]quinolin-5-yl)methanone, C36H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4aS,5S,6aS,6a1S, 10aS)-4a,5,6a,6a1,9,10-hexahydro-7H-4,5-methanocyclobuta[4,5]naphtho[8a,1-b]pyran-6(2H)-one, C15H16O2
- Crystal structure of [(Z)-O-isopropyl N-(4-chlorophenyl)thiocarbamato-κS]-(triphenylphosphine-κP)-gold(I), C28H26AuClNOPS
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-P,P′)-bis[(Z)-O-isopropyl N-(4-chlorophenyl)thiocarbamato-S]-di-gold(I) acetonitrile di-solvate, C54H50Au2Cl2FeN2O2P2S2⋅2(C2H3N)
- Crystal structure of (6aR,6a1S,10aS)-2,4a,6a,6a1,9,10-hexahydro-7H-4,5-methanocyclobuta[4,5]naphtho[8a,1-b]pyran, C15H16O
- Crystal structure of 5,17-diformyl-25,26,27,28-tetrahydroxycalix[4]arene- dichloromethane, C31H26Cl2O6
- Crystal structure of 2-tert-butyl 1-methyl 5-{4-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl}-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1,2-dicarboxylate, C19H24N2O6
- Crystal structure of [2-carboxybenzene-1-thiolato-S]-(triethylphosphane-P)-gold(I), C13H20AuO2PS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(5-methyl-2-aldehyde-phenolato-κ2O1,O2)copper(II), C16H14CuO4
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(di(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-μ4-silanetetrayltetrakis(benzene-4,1-diyl)tetrakis (hydrogen phosphonato)-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′) dicadmium(II)], C44H42N4O15P4Cd2Si
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(N,N-diethylcarbamodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-P)-di-silver(I), C22H50Ag2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(pyrrolidine-1-carbodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-κP)disilver(I), C22H46Ag2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-methylcarbamodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-P)-di-silver(I), C20H46Ag2N2O2P2S4
- The crystal structure of (2E,2′E)-,2,2′-bis[1-(2-pyrazinyl)ethylidene]carbonimidic dihydrazide, C13H15N9
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(quinolin-2-ylmethyl)-2-((1-(quinolin-2-ylmethyl)pyridin-2(1H)-ylidene)amino)pyridin-1-ium, C30H25BrN5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imdazole-κ2N:N′)-(1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imdazole-κ1N)-(methanol-κ1O)mercury(II)] dinitrate, C21H22N12O7Hg
- Crystal structure of 1-(6-hydroxy-2-phenylbenzofuran-5-yl)ethan-1-one, C16H12O3
- The crystal structure of oxonium hexaquaaluminium disulfate hexahydrate
- Crystal structure of catena{(μ2-1,10-phenanthroline-κ4N,N,N′,N′)-(μ2-1,10-phenanthroline-κ3N,N,N′)potassium(I) {[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)iminiumyl](sulfanidyl)methyl}sulfanide hemi(1,10-phenanthroline)}, {C24H16KN4, 0.5(C12H8N2), C5H10NO2S2}
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[(N,N-di-isobutyl)dithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′]-di(4-methylbenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C25H36ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)-(4-chloro-4-pyridyl-2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine-κ2N,N′) rhodium(III) hexaflourophosphate, C31H29Cl2F6N3PRh
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis-(3,5-dinitro-1,2,4-triazolato-κ2N:O)-(μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C16H10CuN14O8
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-bis(μ3-3,3′-((5-carboxylato-1,3-phenylene)bis(oxy))dibenzoato)-tris(1,10-phenanthroline)cobalt(II)], C78H46N6O20Co3
- The crystal structure of 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid–nicotinamide–methanol (1/1/1), C15H18N2O6
- The crystal structure of aqua{N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis[(1H-benzimidazol-κN3) methyl]cyclohexane-1,2-diamine}lead(II) diacetate–methanol (1/2), C44H54N10O7Pb
- Crystal structure of (2-amino-5-bromo-3-iodophenyl)(3-(4-chlorophenyl)oxiran-2-yl)methanone, C15H10BrClINO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 3-octyl-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione, C23H28N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-azido-N-(4-nitrophenyl)acetamide, C8H7N5O3
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (1S,2R,5R)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-oxa-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-3-carboxylate, C17H23NO5
- Crystal structure of 4-[(4-methoxy-2-nitrophenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H14N2O6
- Crystal structure of 3-ethyl-1-[(E)-[(2E)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]amino]thiourea, C12H15N3S
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridin-1,1′-dium poly[bis(μ4-benzene-1,3,5-triyltris(hydrogen phosphonato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′))zinc(II)], C11H11NO9P3Zn
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)butane-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-κS]-di-gold(I), C44H42Au2F2N2O2P2S2
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)hexane-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-κS]digold(I), C46H46Au2F2N2O2P2S2
- Crystal structure of tetrakis (N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-isopropylcarbamodithioato-κS,S′)-(μ2(2-(pyridin-4-yl)vinyl)pyridine-κN,N′)dicadmium(II), C36H58Cd2N6O4S8
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-en-1-yl)-1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carbonitrile, C20H12F6N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(octahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrolium)pentachlorobismuthate(III), (C7NH14)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of diaqua-tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(p-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κN)samarium(III), C24H36N9O15Sm
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-(2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)phenyl)-2-(4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)acetate, C23H23NO6
- Crystal structure of O-hexyl benzoylcarbamothioate, C14H19NO2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(O-methyl phenylcarbamothioamide-κS)-bis(triphenylphosphane-κP)silver(I), C44H39AgClNOP2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(O-ethyl phenylcarbamothioamide-κS)-bis(triphenylphosphane-κP)-silver(I), C45H41AgClNOP2S
- Crystal structure of 4-[(2-methoxyphenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H15NO4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazinane-3-carboxylate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua(μ2-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato)cadmium(II)], C6H8CdN2O7
- Crystal structure of (1S)-N-(chloromethyl)-1-((4S,6aR,8aS, 8bR,9aR)-4-methoxy-6a,8a-dimethyl-1,3,4, 5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9a,10,10a,10b-tetradecahydro-8bH-naphtho[2′,1′:4,5] indeno[1,2-b]oxiren-8b-yl)-N-methylethan-1-amine, C24H46ClNO5
- Crystal structure of 4-[(3,5-dichlorophenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C11H11Cl2NO3
- Crystal structure of (2Z)-2-amino-3-[(E)-[(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)methylidene]-amino]but-2-enedinitrile, C11H8N4O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-1-[(E)-(4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)amino]thiourea, C12H17N3S
- Crystal structure of carbonyl{hydridotris[3-phenyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl]borato-κ3N,N′N′′}copper(I), C31H28BCuN6O
- Crystal structure of ethane-1,2-diylbis(diphenylphosphine oxide) – dihydrogenperoxide (1/2), C26H28O6P2
- Crystal structure of 2-(pyridin-2-ylamino)pyridinium chloride dibenzyldichlorostannane, [C10H10N3]Cl, C14H14Cl2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-[(3-methoxyphenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H15NO4
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(tri-4-tolylphosphane oxide-κO)-di(4-chlorophenyl-κC)tin(IV), C54H50Cl4O2P2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichloridodimethylbis(tri-4-tolylphosphane oxide-κO)-tin(IV), C44H48Cl2O2P2Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)-bis(4-tolyl-κC)tin(IV), C24H22ClNOSn
- Crystal structure of (E)-dichloro(1-chloro-3-methoxyprop-1-en-2-yl)(4-methoxyphenyl)-λ4-tellane, C11H13Cl3O2Te
- Crystal structure of bis{N-methyl-N′-[3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylpropane-1-ylidene]carbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C26H36N6O2S2Zn
- Crystal structure of (2-carboxy-4-(3-carboxy-5-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II), C40H24N4O9Co
- The crystal structure of (3S,8R,10R,14R)-17-((2S,5S)-5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-12-oxohexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl acetate, C32H52O5
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-S]digold(I) chloroform solvate, C50H42Au2F2FeN2O2P2S2, CHCl3
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C24H20N8O4MoCo


