Abstract
C12H13FN4, triclinic,
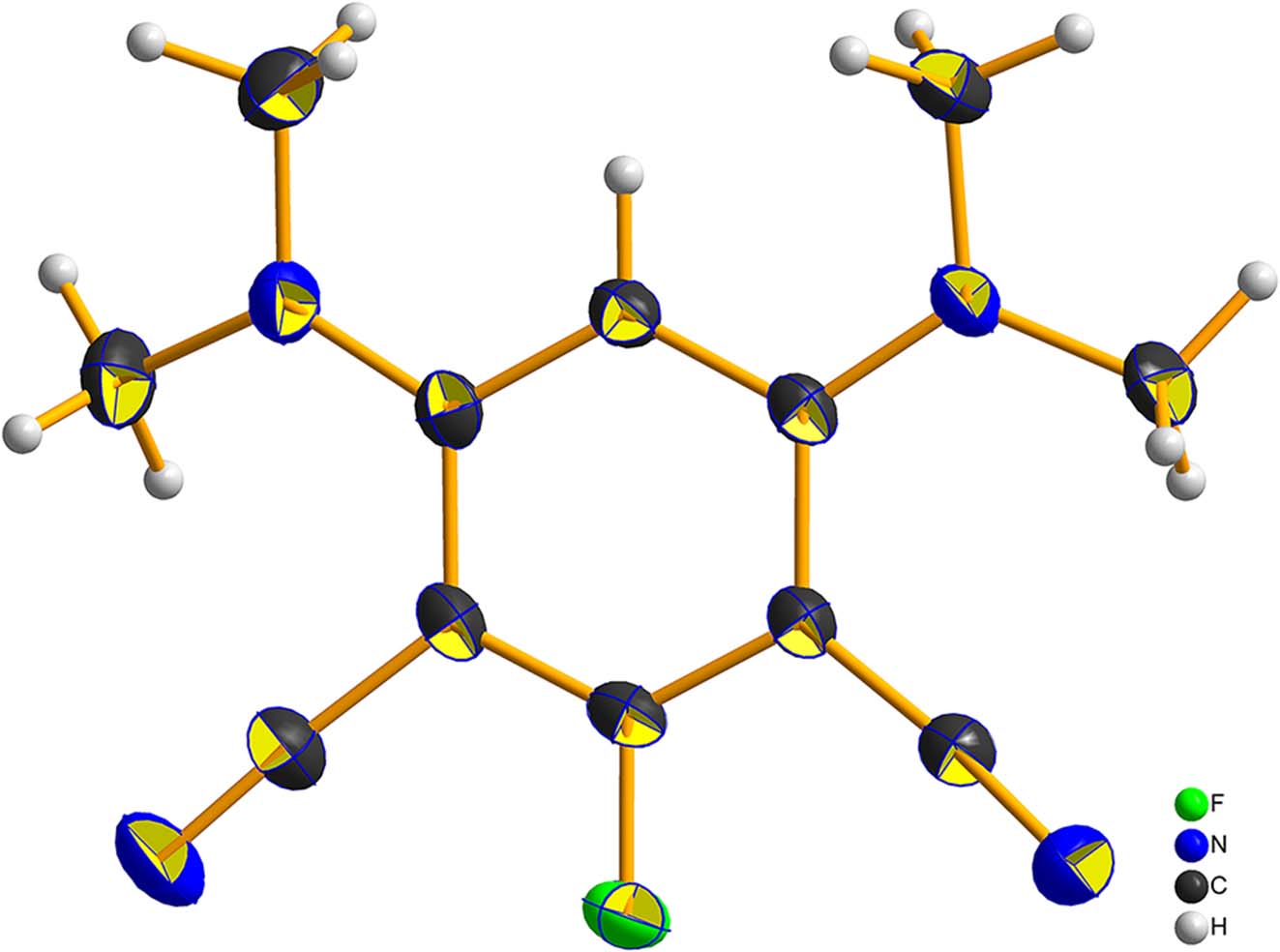
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains the crystallographic data and the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif-file attached to this article.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.22 mm |
| Wavelength: | CuKα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 0.80 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Rigaku XtaLAB Synergy, ω scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 65.0°, 97 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 4145, 1879, 0.035 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 1,647 |
| N(param)refined: | 159 |
| Programs: | Rigaku, 1 Olex2, 2 SHELX 3 |
1 Source of materials
The 1,3,5-trifluoro-2,4,6-triiodobenzene (1.02 g, 2 mmol) and copper(I) cyanide (1.08 g, 6 mmol) were placed in a 50 mL round bottomed flask with 20 mL of dry N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF). The mixture was refluxed for 24 h under N2 atmosphere. When the reaction was finished, 10 mL of concentrated ammonia water and 20 mL of dichloromethane were sequentially added to the reaction. After separation, the aqueous phase was extracted three times with dichloromethane, and the organic phases were combined. The organic phases were then washed three times with water, and finally dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate. Most of the dichloromethane was removed using a rotary evaporator, and after cooling and standing overnight, colorless block crystals were obtained. After filtration, about 186 mg were obtained with a yield of approximately 40 %.
2 Experimental details
The data were collected and processed using CrysAlisPRO. 1 The structures were solved using Olex2 software 2 and refined with the SHELXL. 3 The hydrogen atom positions were fixed geometrically at the calculated distances and allowed to ride on the parent atoms. The Uiso of the H-atoms were set to 1.2 and 1.5 times Ueq of the parent atoms with C–H = 0.96 Å (aliphatic) and C–H = 0.93 Å (aromatic).
3 Comment
The potential of organic cyanates in synthetic chemistry is extensive, with a wide range of applications in the production of carboxylic acid compounds, 3 amides, 4 aldehyde compounds, 5 ketone compounds, 6 and some heterocyclic compounds 7 under specific conditions. Furthermore, cyanoaromatic compounds, such as polycyanobenzenes, have been in the focus of extensive research due to their significant photophysical and electron transfer properties. 8 These compounds are frequently employed as photocatalysts in various applications. 9 , 10
In the asymmetric unit, there is one complete 4,6-bis(dimethylamino)-2-fluoroisophthalonitrile molecule. In this molcule the dimethylamine group is the decomposition product of DMF molecules under heat condition, which subsequently undergoes nucleophilic substitution to obtain the product. Cyan group is generated through the Rosenmund von Braun reaction between iodobenzene and cuprous cyanide. 11 The departure reaction of iodine atoms on the benzene ring occurred under copper catalysis during the reaction process. 12 After undergoing the above chemical reactions, the target product was finally obtained. The C–C bond distances on the aromatic ring range from 1.382(2) to 1.436(2) Å. C(sp2)–N bond distances are 1.359(2) and 1.361(2) Å. And C(sp3)–N bond distances range from 1.444(3) to 1.460(3) Å. C–N bond distances of cyano group are 1.153(2) and 1.148(2) Å. C(sp2)–F bond distance is 1.3526(19) Å. All bond distances are within the normal range. 13 , 14
References
1. Agilent Technologies. CrysAlisPRO Software System (Version 171.38.43f); Agilent Technologies UK Ltd: Oxford, UK, 2015.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Daw, P.; Sinha, A.; Rahaman, S. M. W.; Dinda, S.; Bera, J. K. Bifunctional Water Activation for Catalytic Hydration of Organonitriles. Organometallics 2012, 31 (9), 3790–3797. https://doi.org/10.1021/om300297y.Search in Google Scholar
5. Paul, B.; Maji, M.; Kundu, S. Atom-Economical and Tandem Conversion of Nitriles to N-Methylated Amides Using Methanol and Water. ACS Catal. 2019, 9 (11), 10469–10476. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b03916.Search in Google Scholar
6. Wang, K. Z.; Jiang, P. B.; Yang, M.; Ma, P.; Qin, J. H.; Huang, X. K.; Ma, L.; Li, R. Metal-Free Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanosheets: A Catalyst for the Direct Synthesis of Imines Under Mild Conditions. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 2448–2461. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9GC00908F.Search in Google Scholar
7. Hatano, M.; Kuwano, K.; Asukai, R.; Nagayoshi, A.; Hoshihara, H.; Hirata, T.; Umezawa, M.; Tsubaki, S.; Yoshikawa, T.; Sakata, K. Zinc Chloride-Catalyzed Grignard Addition Reaction of Aromatic Nitriles. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 8569–8577. https://doi.org/10.1039/D4SC01659A.Search in Google Scholar
8. Yan, L. W.; Gou, S. H.; Ye, Z. B.; Zhang, S. H.; Ma, L. H. Self-Healing and Moldable Material with the Deformation Recovery Ability from Self-Assembled Supramolecular Metallogels. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12847–12850. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CC06154C.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Li, Y.; Ren, T.; Dong, W.-J. Tuning Photophysical Properties of Triphenylamine and Aromatic Cyano Conjugate-Based Wavelength-Shifting Compounds by Manipulating Intramolecular Charge Transfer Strength. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 2013, 251, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2012.10.002.Search in Google Scholar
10. Bryden, M. A.; Millward, F.; Matulaitis, T.; Chen, D.; Villa, M.; Cetin, S.; Ceroni, P. ; Zysman-Colman, E. Moving Beyond Cyanoarene Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Compounds as Photocatalysts: An Assessment of the Performance of a Pyrimidyl Sulfone Photocatalyst in Comparison to 4CzIPN. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88 (10), 6364–6373. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.2c01137.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
11. Chen, S. P.; Pan, T.; Jiang, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, J. M.; Sheng, W. B. Regioselectivity for Nucleophilic Substitutions of Aryl Halides with DMF in Deep Eutectic Solvent. Tetrahedron 2025, 176, 134543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2025.134543.Search in Google Scholar
12. Leadbeater, N. E.; Torenius, H. M.; Tye, H. Ionic Liquids as Reagents and Solvents in Conjunction with Microwave Heating: Rapid Synthesis of Alkyl Halides from Alcohols and Nitriles from Aryl Halides. Tetrahedron 2003, 59 (13), 2253–2258. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(03)00214-X.Search in Google Scholar
13. Nguyen, T. T.; Phan, N. T. S. A Metal-Organic Framework Cu2(BDC)2(DABCO) as an Efficient and Reusable Catalyst for Ullmann-Type N-Arylation of Imidazoles. Catal. Lett. 2014, 144 (11), 1877–1883. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10562-014-1355-9.Search in Google Scholar
14. Matthew, R.; Cargill, A.; Katharine, E.; Linton, A.; Graham, S. A.; Dmitrii, S.; Yufit, B.; Judith, A. K.; Howard, B. Annelation Reactions of Pentafluorobenzonitrile. Tetrahedron 2010, 66 (13), 2356–2362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2010.01.104.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (S)-N-(10-((2,2-dimethoxyethyl)amino)-1,2,3-trimethoxy-9-oxo-5,6,7,9-tetrahydrobenzo[a]heptalen-7-yl)acetamide, C25H32N2O7
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-difluoro-3,3′-dimethyl-5,5′-di(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)- [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarbonitrile, C40H24F2N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(di-ethylenediamine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II) tetradedocyloxidohexavanadate] (V4+/V5+ = 2/1), C4H16CdN4O14V6
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(dimethylformamide-κ1N)-(μ4-2′,3,3″,5′-tetrakis(trifluoromethyl)-[1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4″-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,O′: O″,O‴)dicadmium(II)], C27H15CdF12NO5
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenylcarboxylato-O,O′)-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-bis(μ2-salicyladoximato-κ2N,O,O′)-(μ2-isopropoxo)-tris(isopropoxy-κ1O trititanium(IV)), C48H55N2O13Fe2Ti3
- Crystal structure of 3-(diethylamino)-7,9,11-trimethyl-8-phenyl-6H,13H-12λ4,13λ4-chromeno[3′,4′:4,5]pyrrolo[1,2-c]pyrrolo[2,1-f][1,3,2]diazaborinin-6-one, C28H26BF2N3O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-μ2-2-nitro-benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-zinc(II)], C20H13N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-{μ3-1-(3-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′′}manganese(II)] hydrate
- Crystal structure of N′-((1-hydroxycyclohexyl)(phenyl)methyl)-2-methoxybenzohydrazide methanol solvate, C22H28N2O4
- The cocrystal of caffeic acid — progesterone — water (1/2/1), C51H70O9
- Crystal structure of (((oxido(quinolin-6-yl)methoxy)triphenyl-λ5-stibanyl)oxy)(quinolin-7-yl)methanolate
- Crystal structure of [(E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-(2-(((E)-pyren-1-ylmethylene)amino)ethyl)-4′-(2-((E)-1,3,3-trimethylindolin-2-ylidene)ethylidene)-1′,2′,3′,4′-tetrahydrospiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one]-methanol, solvate C57H56N4O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(acridin-9-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione, C17H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of N-(4-acetylphenyl)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanamide, C22H21NO3
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)porphyrin, C52H34N16
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-μ2-[phenylmethanedithiolato-κ4S:S,S′:S′]diiron (Fe–Fe) C13H6Fe2O6S2
- Crystal structure of diiodo-bis(1-((2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ1N)cadmium(II), C34H34CdI2N10
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(3-bromophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H15BrFeO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ3N,O:O′)(6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C12H6Cl2N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-μ 3-(5-(3,5-dicarboxy-2,4,6-trimethylbenzyl)-2,4,6-trimethylisophthalato)-κ 6O,O′:O″,O‴:O‴′,O‴″) terbium(III)-monohydrate], C23H28TbO12
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one – ethanol (1/2), C35H33ClN4O6
- The crystal structure of 3-(5-amino-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)-4-chloro-3-hydroxyindolin-2-one, C17H12ClN3O3
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium 4-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-4, 5-diphenyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl]benzenesulfonate, C29H26FN3O3S
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-ammonio-3-((5-carboxypentyl)thio)propanoate
- Crystal structure of 4-cyclohexyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C12H15N3S2
- The crystal structure of 4,6-bis(dimethylamino)-2-fluoroisophthalonitrile, C12H13FN4
- Hydrogen bonding in the crystal structure of nicotin-1,1′-dium tetrabromidomanganate(II)
- The crystal structure of bis(2-bromobenzyl)(2-((2-oxybenzylidene)amino)-4-methylpentanoato-κ3N, O,O′)tin(IV), C27H27Br2NO3Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(p-tolyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C20H18FeO
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H22FN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of poly(bis(μ2-1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-2,3,5,6-tetrafluoroterephthalato-κ2O:O′)-manganese(II), C38H24F4N12O4Mn
- Crystal structure of (3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C29H32BrO3P
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium hydrogencarbonate – (diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/1/3)
- Crystal structure of N, N-Dimethyl-N′-tosylformimidamide, C10H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H23N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-1,5-bis[(E)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene] thiocarbonohydrazide)-bis(dimethylformamide)-dizinc(II) dimethylformamide solvate, C40H46N10O6S2Zn2⋅C3H7NO
- Crystal structure of azido-κ1N{hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″}copper(II), C24H40BCuN9
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(azido-κ1N)rhenium(I), C15H8N5O3Re
- Crystal structure of 4-((triphenylphosphonio)methyl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II), C24H22Cl4NPZn
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (S)-N-(10-((2,2-dimethoxyethyl)amino)-1,2,3-trimethoxy-9-oxo-5,6,7,9-tetrahydrobenzo[a]heptalen-7-yl)acetamide, C25H32N2O7
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-difluoro-3,3′-dimethyl-5,5′-di(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)- [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarbonitrile, C40H24F2N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(di-ethylenediamine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II) tetradedocyloxidohexavanadate] (V4+/V5+ = 2/1), C4H16CdN4O14V6
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(dimethylformamide-κ1N)-(μ4-2′,3,3″,5′-tetrakis(trifluoromethyl)-[1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4″-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,O′: O″,O‴)dicadmium(II)], C27H15CdF12NO5
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenylcarboxylato-O,O′)-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-bis(μ2-salicyladoximato-κ2N,O,O′)-(μ2-isopropoxo)-tris(isopropoxy-κ1O trititanium(IV)), C48H55N2O13Fe2Ti3
- Crystal structure of 3-(diethylamino)-7,9,11-trimethyl-8-phenyl-6H,13H-12λ4,13λ4-chromeno[3′,4′:4,5]pyrrolo[1,2-c]pyrrolo[2,1-f][1,3,2]diazaborinin-6-one, C28H26BF2N3O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-μ2-2-nitro-benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-zinc(II)], C20H13N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-{μ3-1-(3-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′′}manganese(II)] hydrate
- Crystal structure of N′-((1-hydroxycyclohexyl)(phenyl)methyl)-2-methoxybenzohydrazide methanol solvate, C22H28N2O4
- The cocrystal of caffeic acid — progesterone — water (1/2/1), C51H70O9
- Crystal structure of (((oxido(quinolin-6-yl)methoxy)triphenyl-λ5-stibanyl)oxy)(quinolin-7-yl)methanolate
- Crystal structure of [(E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-(2-(((E)-pyren-1-ylmethylene)amino)ethyl)-4′-(2-((E)-1,3,3-trimethylindolin-2-ylidene)ethylidene)-1′,2′,3′,4′-tetrahydrospiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one]-methanol, solvate C57H56N4O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(acridin-9-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione, C17H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of N-(4-acetylphenyl)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanamide, C22H21NO3
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)porphyrin, C52H34N16
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-μ2-[phenylmethanedithiolato-κ4S:S,S′:S′]diiron (Fe–Fe) C13H6Fe2O6S2
- Crystal structure of diiodo-bis(1-((2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ1N)cadmium(II), C34H34CdI2N10
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(3-bromophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H15BrFeO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ3N,O:O′)(6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C12H6Cl2N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-μ 3-(5-(3,5-dicarboxy-2,4,6-trimethylbenzyl)-2,4,6-trimethylisophthalato)-κ 6O,O′:O″,O‴:O‴′,O‴″) terbium(III)-monohydrate], C23H28TbO12
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one – ethanol (1/2), C35H33ClN4O6
- The crystal structure of 3-(5-amino-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)-4-chloro-3-hydroxyindolin-2-one, C17H12ClN3O3
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium 4-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-4, 5-diphenyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl]benzenesulfonate, C29H26FN3O3S
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-ammonio-3-((5-carboxypentyl)thio)propanoate
- Crystal structure of 4-cyclohexyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C12H15N3S2
- The crystal structure of 4,6-bis(dimethylamino)-2-fluoroisophthalonitrile, C12H13FN4
- Hydrogen bonding in the crystal structure of nicotin-1,1′-dium tetrabromidomanganate(II)
- The crystal structure of bis(2-bromobenzyl)(2-((2-oxybenzylidene)amino)-4-methylpentanoato-κ3N, O,O′)tin(IV), C27H27Br2NO3Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(p-tolyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C20H18FeO
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H22FN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of poly(bis(μ2-1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-2,3,5,6-tetrafluoroterephthalato-κ2O:O′)-manganese(II), C38H24F4N12O4Mn
- Crystal structure of (3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C29H32BrO3P
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium hydrogencarbonate – (diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/1/3)
- Crystal structure of N, N-Dimethyl-N′-tosylformimidamide, C10H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H23N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-1,5-bis[(E)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene] thiocarbonohydrazide)-bis(dimethylformamide)-dizinc(II) dimethylformamide solvate, C40H46N10O6S2Zn2⋅C3H7NO
- Crystal structure of azido-κ1N{hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″}copper(II), C24H40BCuN9
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(azido-κ1N)rhenium(I), C15H8N5O3Re
- Crystal structure of 4-((triphenylphosphonio)methyl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II), C24H22Cl4NPZn

