Abstract
C12H15N3S2, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 5.51310(10) Å, b = 15.4525(4) Å, c = 15.9261(4) Å, β = 99.844(2)°, V = 1336.79(5) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.0359, wR ref (F2) = 0.1009, T = 160 K.
1 Source of material
A mixture of thiophene-2-carbohydrazide (1.42 g, 0.01 mol) and cyclohexyl isothiocyanate (1.41 g, 0.01 mol), in ethanol (10 mL), was heated under reflux for 30 min, and the solvent was then distilled off under vacuum. Sodium hydroxide in a 10 % aqueous solution (8 mL) was then added to the residue, and the mixture was heated under reflux for 2 h, then filtered hot. On cooling, the mixture was acidified with hydrochloric acid (pH 1–2) and the precipitated crude product was filtered, washed with water, dried and crystallised from aqueous ethanol to yield 2.28 g (86 %) of the title compound as colourless prisms. Single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained by slow evaporation of a solution of the title compound in EtOH/CHCl3 (2:1, v/v) held at room temperature for 2 days. M. pt: 469–471 K (uncorrected). 1H NMR (CDCl3, 500.13 MHz): δ 13.6 (s, 1H, NH), 6.98 (t, 1H, Thiophene–H, J = 4.2 Hz), 7.10 (d, 1H, Thiophene–H, J = 4.2 Hz), 7.18 (d, 1H, Thiophene–H, J = 4.2 Hz), 2.54–2.68 (m, 1H, Cyclohexyl–H), 1.50–1.72 (m, 4H, Cyclohexyl–H), 1.12–1.44 (m, 6H, Cyclohexyl–H). 13C NMR (CDCl3, 125.76 MHz): δ 169.26 (C=S), 148.66 (Triazole–C5), 124.62, 126.04, 127.88, 128.0 (Thiophene–C), 24.44, 25.98, 30.88, 66.62 (Cyclohexyl–C).
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless prism |
| Size: | 0.22 × 0.11 × 0.05 mm |
| Wavelength: μ: |
CuKα radiation (1.54184 Å) 3.46 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: θmax, completeness: |
Rigaku Synergy, ω scan 74.5°, 100 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 14587, 2725, 0.051 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2,403 |
| N(param)refined: | 196 |
| Programs: | Rigaku, 1 SHELX, 2 , 3 WinGX 4 |
2 Experimental details
The C-bound H atoms were geometrically placed (C–H = 0.95–1.00 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). The N-bound H atom was refined freely. The S2-containing thiophen-2-yl ring was disordered over two co-planar orientations, each of which was refined independently. The major component of the disorder had a site occupancy factor = 0.544(2).
3 Discussion
The 1,2,4-triazole scaffold is recognised as an essential component of several biologically interesting drugs and exhibits a wide range of chemotherapeutic properties. 5 , 6 Marketed triazole-based drugs are extensively used as advantageous anti-fungal, 7 anti-cancer, 8 anti-bacterial 9 and anti-viral 10 agents. In addition, the thiophene heterocycle constitutes a main building block of many drugs. 11
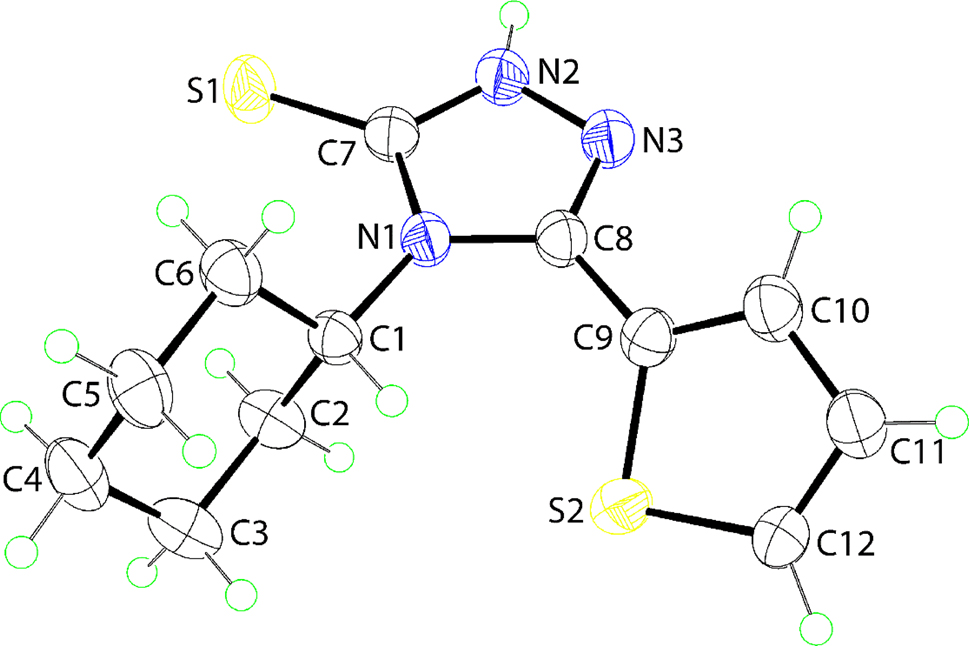
The molecular structure of the title triazole-thiophene hybrid molecule, (I), is shown in figure (50 % probability ellipsoids; only the major component of the disordered S2-containing thiophen-2-yl ring is shown for reasons of clarity). The molecule comprises a central 1,2,4-triazole-3-thione group connected at the 4-position to a cyclohexyl ring, and at the 5-position to a thiophen-2-yl ring; the dihedral angle between the two five-membered rings is 35.9(3)° consistent with a splayed orientation. Within the 1,2,4-triazole ring, the lengthening of the formally C8–N3 [1.3041(19) Å] double bond and the shortening, for example, of the formally N2–N3 [1.3640(18) Å] and C8–N1 [1.3854(18) Å] single bonds indicate significant delocalisation of π-electron density over the constituent atoms.
In the crystallographic literature, there are two related N-alkyl structures available for comparison, namely alkyl = ethyl 12 and cyclohexyl, 13 hereafter (II) and (III), respectively. Each of (II) and (III) exhibit similar patterns in the bond lengths within the 1,2,4-triazole ring as for (I). The relative orientations of the five-membered rings differ, however. Thus, in (II) and (III), the dihedral angles are 13.53(12) and 6.19(7)°, respectively, indicating closer to co-planar orientations than for (I). This difference is likely to arise due to steric considerations in (I). The separation between the methine–C–H and the thiophen-2-yl–C–H atoms of the disordered component of the ring is 2.25 Å which would contract if a more co-planar orientation was adopted.
In the molecular packing, the most prominent intermolecular interactions correspond to amine–N–H⋯S(thione) hydrogen-bonding [N2–H2n⋯S1 i : H2n⋯S1 i = 2.38(2) Å, N2⋯S1 i = 3.2511(14) Å with angle at H2n = 169.1(19)° for symmetry operation (i) 2 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z]. The hydrogen bonds occur within a centrosymmetric aggregate through an eight-membered {⋯HNCS}2 synthon. Similar synthons are noted in the crystals of (II) and (III).
-
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
-
Research funding: This study was financially supported by the the Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project No. PNURSP2023R3, from the Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
References
1. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction. CrysalisPRO; Rigaku Corporation: Oxford, UK, 2024.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of Shelx. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108767307043930.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Farrugia, L. J. WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an Update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854; https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889812029111.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Aggarwal, R.; Sumran, G. An Insight on Medicinal Attributes of 1,2,4-triazoles. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 205, 112652; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112652.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
6. Tratrat, C. 1,2,4-Triazole: a Privileged Scaffold for the Development of Potent Antifungal Agents – a Brief Review. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 2235–2258; https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026620666200704140107.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Lass-Flrl, C. Triazole Antifungal Agents in Invasive Fungal Infections. Drugs 2011, 71, 2405–2419; https://doi.org/10.2165/11596540-000000000-00000.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Wen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, J.; Liu, X. Recent Development of 1,2,4-triazole-containing Compounds as Anticancer Agents. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1441–1460; https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026620666200128143230.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Tian, G.; Song, Q.; Liu, Z.; Guo, J.; Cao, S.; Long, S. Recent Advances in 1,2,3- and 1,2,4-triazole Hybrids as Antimicrobials and their SAR: a Critical Review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 259, 115603; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115603.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Paeshuyse, J.; Dallmeier, K.; Neyts, J. Ribavirin for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection: a Review of the Proposed Mechanisms of Action. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2011, 1, 590–598; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.030.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Bozorov, K.; Nie, L. F.; Zhao, J.; Aisa, H. A. 2-Aminothiophene Scaffolds: Diverse Biological and Pharmacological Attributes in Medicinal Chemistry. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 140, 465–493; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.09.039.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Wawrzycka-Gorczyca, I.; Siwek, A. Synthesis, X-ray Crystal Structure and Theoretical Study of 4-Ethyl-5-(2-thienyl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione; Structural Comparison with Its Aromatic Analogs. Z. Kristallogr. Cryst. Mater. 2011, 226, 861–868; https://doi.org/10.1524/zkri.2011.1444.Suche in Google Scholar
13. Al-Shehri, M. M.; El-Emam, A. A.; El-Brollosy, N. R.; Ng, S. W.; Tiekink, E. R. T. 4-Benzyl-3-(thiophen2yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5-thione. Acta Crystallogr., Sect. E:2013, 69, o697; https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600536813009501.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (S)-N-(10-((2,2-dimethoxyethyl)amino)-1,2,3-trimethoxy-9-oxo-5,6,7,9-tetrahydrobenzo[a]heptalen-7-yl)acetamide, C25H32N2O7
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-difluoro-3,3′-dimethyl-5,5′-di(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)- [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarbonitrile, C40H24F2N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(di-ethylenediamine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II) tetradedocyloxidohexavanadate] (V4+/V5+ = 2/1), C4H16CdN4O14V6
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(dimethylformamide-κ1N)-(μ4-2′,3,3″,5′-tetrakis(trifluoromethyl)-[1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4″-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,O′: O″,O‴)dicadmium(II)], C27H15CdF12NO5
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenylcarboxylato-O,O′)-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-bis(μ2-salicyladoximato-κ2N,O,O′)-(μ2-isopropoxo)-tris(isopropoxy-κ1O trititanium(IV)), C48H55N2O13Fe2Ti3
- Crystal structure of 3-(diethylamino)-7,9,11-trimethyl-8-phenyl-6H,13H-12λ4,13λ4-chromeno[3′,4′:4,5]pyrrolo[1,2-c]pyrrolo[2,1-f][1,3,2]diazaborinin-6-one, C28H26BF2N3O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-μ2-2-nitro-benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-zinc(II)], C20H13N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-{μ3-1-(3-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′′}manganese(II)] hydrate
- Crystal structure of N′-((1-hydroxycyclohexyl)(phenyl)methyl)-2-methoxybenzohydrazide methanol solvate, C22H28N2O4
- The cocrystal of caffeic acid — progesterone — water (1/2/1), C51H70O9
- Crystal structure of (((oxido(quinolin-6-yl)methoxy)triphenyl-λ5-stibanyl)oxy)(quinolin-7-yl)methanolate
- Crystal structure of [(E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-(2-(((E)-pyren-1-ylmethylene)amino)ethyl)-4′-(2-((E)-1,3,3-trimethylindolin-2-ylidene)ethylidene)-1′,2′,3′,4′-tetrahydrospiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one]-methanol, solvate C57H56N4O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(acridin-9-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione, C17H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of N-(4-acetylphenyl)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanamide, C22H21NO3
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)porphyrin, C52H34N16
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-μ2-[phenylmethanedithiolato-κ4S:S,S′:S′]diiron (Fe–Fe) C13H6Fe2O6S2
- Crystal structure of diiodo-bis(1-((2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ1N)cadmium(II), C34H34CdI2N10
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(3-bromophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H15BrFeO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ3N,O:O′)(6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C12H6Cl2N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-μ 3-(5-(3,5-dicarboxy-2,4,6-trimethylbenzyl)-2,4,6-trimethylisophthalato)-κ 6O,O′:O″,O‴:O‴′,O‴″) terbium(III)-monohydrate], C23H28TbO12
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one – ethanol (1/2), C35H33ClN4O6
- The crystal structure of 3-(5-amino-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)-4-chloro-3-hydroxyindolin-2-one, C17H12ClN3O3
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium 4-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-4, 5-diphenyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl]benzenesulfonate, C29H26FN3O3S
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-ammonio-3-((5-carboxypentyl)thio)propanoate
- Crystal structure of 4-cyclohexyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C12H15N3S2
- The crystal structure of 4,6-bis(dimethylamino)-2-fluoroisophthalonitrile, C12H13FN4
- Hydrogen bonding in the crystal structure of nicotin-1,1′-dium tetrabromidomanganate(II)
- The crystal structure of bis(2-bromobenzyl)(2-((2-oxybenzylidene)amino)-4-methylpentanoato-κ3N, O,O′)tin(IV), C27H27Br2NO3Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(p-tolyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C20H18FeO
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H22FN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of poly(bis(μ2-1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-2,3,5,6-tetrafluoroterephthalato-κ2O:O′)-manganese(II), C38H24F4N12O4Mn
- Crystal structure of (3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C29H32BrO3P
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium hydrogencarbonate – (diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/1/3)
- Crystal structure of N, N-Dimethyl-N′-tosylformimidamide, C10H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H23N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-1,5-bis[(E)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene] thiocarbonohydrazide)-bis(dimethylformamide)-dizinc(II) dimethylformamide solvate, C40H46N10O6S2Zn2⋅C3H7NO
- Crystal structure of azido-κ1N{hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″}copper(II), C24H40BCuN9
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(azido-κ1N)rhenium(I), C15H8N5O3Re
- Crystal structure of 4-((triphenylphosphonio)methyl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II), C24H22Cl4NPZn
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (S)-N-(10-((2,2-dimethoxyethyl)amino)-1,2,3-trimethoxy-9-oxo-5,6,7,9-tetrahydrobenzo[a]heptalen-7-yl)acetamide, C25H32N2O7
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-difluoro-3,3′-dimethyl-5,5′-di(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)- [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarbonitrile, C40H24F2N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(di-ethylenediamine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II) tetradedocyloxidohexavanadate] (V4+/V5+ = 2/1), C4H16CdN4O14V6
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(dimethylformamide-κ1N)-(μ4-2′,3,3″,5′-tetrakis(trifluoromethyl)-[1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4″-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,O′: O″,O‴)dicadmium(II)], C27H15CdF12NO5
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenylcarboxylato-O,O′)-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-bis(μ2-salicyladoximato-κ2N,O,O′)-(μ2-isopropoxo)-tris(isopropoxy-κ1O trititanium(IV)), C48H55N2O13Fe2Ti3
- Crystal structure of 3-(diethylamino)-7,9,11-trimethyl-8-phenyl-6H,13H-12λ4,13λ4-chromeno[3′,4′:4,5]pyrrolo[1,2-c]pyrrolo[2,1-f][1,3,2]diazaborinin-6-one, C28H26BF2N3O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-μ2-2-nitro-benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-zinc(II)], C20H13N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-{μ3-1-(3-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′′}manganese(II)] hydrate
- Crystal structure of N′-((1-hydroxycyclohexyl)(phenyl)methyl)-2-methoxybenzohydrazide methanol solvate, C22H28N2O4
- The cocrystal of caffeic acid — progesterone — water (1/2/1), C51H70O9
- Crystal structure of (((oxido(quinolin-6-yl)methoxy)triphenyl-λ5-stibanyl)oxy)(quinolin-7-yl)methanolate
- Crystal structure of [(E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-(2-(((E)-pyren-1-ylmethylene)amino)ethyl)-4′-(2-((E)-1,3,3-trimethylindolin-2-ylidene)ethylidene)-1′,2′,3′,4′-tetrahydrospiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one]-methanol, solvate C57H56N4O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(acridin-9-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione, C17H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of N-(4-acetylphenyl)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanamide, C22H21NO3
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)porphyrin, C52H34N16
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-μ2-[phenylmethanedithiolato-κ4S:S,S′:S′]diiron (Fe–Fe) C13H6Fe2O6S2
- Crystal structure of diiodo-bis(1-((2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ1N)cadmium(II), C34H34CdI2N10
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(3-bromophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H15BrFeO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ3N,O:O′)(6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C12H6Cl2N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-μ 3-(5-(3,5-dicarboxy-2,4,6-trimethylbenzyl)-2,4,6-trimethylisophthalato)-κ 6O,O′:O″,O‴:O‴′,O‴″) terbium(III)-monohydrate], C23H28TbO12
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one – ethanol (1/2), C35H33ClN4O6
- The crystal structure of 3-(5-amino-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)-4-chloro-3-hydroxyindolin-2-one, C17H12ClN3O3
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium 4-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-4, 5-diphenyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl]benzenesulfonate, C29H26FN3O3S
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-ammonio-3-((5-carboxypentyl)thio)propanoate
- Crystal structure of 4-cyclohexyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C12H15N3S2
- The crystal structure of 4,6-bis(dimethylamino)-2-fluoroisophthalonitrile, C12H13FN4
- Hydrogen bonding in the crystal structure of nicotin-1,1′-dium tetrabromidomanganate(II)
- The crystal structure of bis(2-bromobenzyl)(2-((2-oxybenzylidene)amino)-4-methylpentanoato-κ3N, O,O′)tin(IV), C27H27Br2NO3Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(p-tolyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C20H18FeO
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H22FN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of poly(bis(μ2-1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-2,3,5,6-tetrafluoroterephthalato-κ2O:O′)-manganese(II), C38H24F4N12O4Mn
- Crystal structure of (3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C29H32BrO3P
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium hydrogencarbonate – (diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/1/3)
- Crystal structure of N, N-Dimethyl-N′-tosylformimidamide, C10H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H23N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-1,5-bis[(E)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene] thiocarbonohydrazide)-bis(dimethylformamide)-dizinc(II) dimethylformamide solvate, C40H46N10O6S2Zn2⋅C3H7NO
- Crystal structure of azido-κ1N{hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″}copper(II), C24H40BCuN9
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(azido-κ1N)rhenium(I), C15H8N5O3Re
- Crystal structure of 4-((triphenylphosphonio)methyl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II), C24H22Cl4NPZn

