Abstract
C52H34N16, monoclinic, P21/n, a = 9.3698(9) Å, b = 10.4687(9) Å, c = 22.1994(16) Å, β = 99.317(9)°, V = 2148.8(3) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0851, wR ref (F 2 ) = 0.1540, T = 293(2) K.
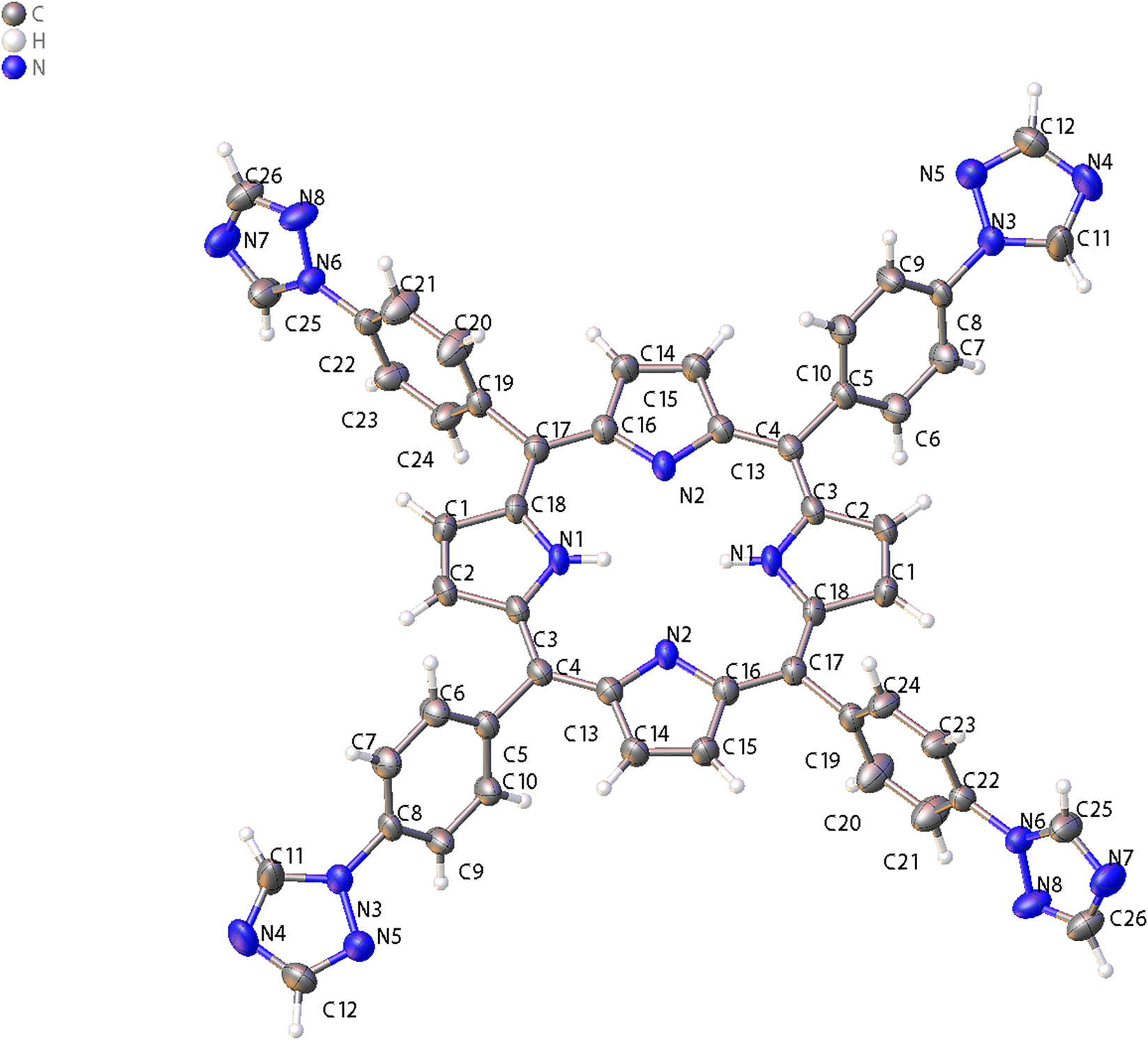
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains the crystallographic data and the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif-file attached to this article.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Purple block |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.16 × 0.12 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.09 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Rigaku XtaLAB Synergy, ω scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 29.3°, 100 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 18650, 5909, 0.077 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 2,847 |
| N(param)refined: | 371 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 Olex2, 2 SHELX 3 |
1 Source of materials
A solution of 4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzaldehyde (4.00 g, 46.2 mmol) in 90 mL propionic acid was charged into a 200 mL three-necked flask equipped with mechanical stirring and heated to reflux. Separately, freshly distilled pyrrole (3.05 g, 46.2 mmol) dissolved in 20 mL propionic acid was transferred to a constant-pressure dropping funnel. When the oil bath temperature stabilized at 130 °C, the pyrrole solution was added dropwise over 20 min, during which the reaction mixture gradually darkened to a brownish-black color. The stirring rate was subsequently increased to vigorous agitation, and the reaction was continued for an additional 40 min under these conditions. After cooling to 80 °C with maintained stirring, 100 mL of anhydrous ethanol was carefully introduced. The mixture was stored refrigerated overnight, followed by vacuum filtration to afford 0.92 g of a purplish-black solid. Dissolve the dried crude porphyrin product in chloroform, then transfer it to a silica gel-packed chromatography column. Elute using a mixture of chloroform and petroleum ether in a 15:1 volume ratio (v/v) as the eluent. Collect the first colored band to obtain the corresponding pure porphyrin compound. Crystals were grown by slow vapor diffusion of n-hexane into a toluene solution of the target porphyrin product at ambient temperature under sealed conditions. 1H-NMR (CDCl3, ppm): C2.78 (s, 2H), 8.09 C8.16 (d, 8H), 8.35 C8.40 (d, 8H), 8.87–8.98 (d, 16H).
2 Experimental details
A suitable crystal was selected and mounted on the diffractometer and the data was collected. The structure was solved with the ShelXT 4 structure solution program and refined with the XL 5 refinement package. A aromatic/amide H refined with riding coordinates: N1(H1).
3 Comment
As a quintessential macrocyclic system, porphyrin-based materials have evolved over decades into an interdisciplinary theoretical framework through systematic structure-property engineering. Their groundbreaking applications spanning biomedical fields, electronic materials engineering, catalytic science, and functional assembly systems have been propelling the innovation of molecular design strategies. Precise modulation of their physicochemical properties and bioactivities is achievable through three-dimensional structural editing: (1) peripheral substituent functionalization, (2) topological engineering of meso-substituents, and (3) metal-ligand coordination at the macrocyclic core. Particularly, meso-symmetrically substituted porphyrins exhibit unparalleled supramolecular assembly capabilities derived from their square-planar molecular symmetry (D4h point group) and self-complementary hydrogen bonding – interactions, establishing them as a paradigm in supramolecular material systems. 6 , 7 , 8
The molecular asymmetric unit contains one half of a porphyrin (see the figure). The aromatic pyrrole rings are interconnected via a meso-methylidyne bridge at their -positions, with para-substituted phenyl rings bearing 1,2,4-triazole groups attached to the meso-carbon bridge. The porphyrin core comprises 24 principal atoms. Where the N(1) and N(2) atoms collectively form an N4 coordination core. While the core adopts a nearly planar geometry, it exhibits slight distortion. The deviation from planarity likely arises from steric crowding caused by adjacent phenyl rings, hydrogen atoms on the pyrrole rings, and other spatially proximate interactions. The average C–N bond length in the molecule was determined to be 1.33 Å and 0.3 Å, while the C–C bond lengths measured 1.37 Å and 1.38 Å. These values exhibit close agreement with reported bond parameters for porphyrin-based systems, 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 indicating that the 1,2,4-triazole substitution induces negligible electronic perturbation to the porphyrin core. The phenyl and triazole rings are not in the same plane. The dihedral angle between benzene ring A (C(5), C(6), C(7), C(8), C(9), C(10)) and the triazole rings is 132.38°, while 16.74° between benzene ring B (C(19), C(20), C(21), C(22), C(23), C(24)) and the triazole rings.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge support from the project of Ji’an City Key Technology Plan Project (20233–117677).
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction. CrysAlisPRO; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction: Yarnton, England, 2015.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Bourhis, L. J.; Dolomanov, O. V.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. The Anatomy of a Comprehensive Constrained, Restrained Refinement Program for the Modern Computing Environment – Olex2 Dissected. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 59–75. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314022207.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Ishihara, S.; Hill, J. P.; Shundo, A.; Richards, G. J.; Labuta, J.; Ohkubo, K.; Fukuzumi, S.; Sato, A.; Elsegood, M. R. J.; Teat, S. J.; Ariga, K. Reversible Photoredox Switching of Porphyrin-Bridged Bis-2,6-Di-Tert-Butylphenols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133 (40), 16119–16126. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja2056165.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Stefak, R.; Ratel-Ramond, N.; Rapenne, G. Synthesis and Electrochemical Characteristics of a Donor-Acceptor Porphyrinate Rotor Mounted on a Naphthalocyaninato Europium Complex. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 2012, 380, 181–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2011.10.051.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Bondon, A.; Leroy, J. β-Fluorinated Porphyrins and Related Compounds: An Overview. Eur. J. Org Chem. 2008, 3, 417–433. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.200700734.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Huang, N.; Yuan, S.; Drake, H.; Yang, X. Y.; Pang, J. D.; Qin, J. S.; Li, J. L.; Zhang, Y. M.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, D. L.; Zhou, H. C. Systematic Engineering of Single Substitution in Zirconium Metal-Organic Frameworks Toward High-Performance Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 18590–18597. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b09553.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Yang, L. X.; Li, H. L.; Liu, D.; Su, H. F.; Wang, K.; Liu, G. Y.; Luo, X. G.; Wu, F. S. Organic Small Molecular Nanoparticles Based on Self-Assembly of Amphiphilic Fluoroporphyrins for Photodynamic and Photothermal Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 182, 110345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110345.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Zhang, D. W.; Chen, W. T. Two Novel TCPP Porphyrinic Compounds: In Situ Synthese, Characterization and Reaction Mechanism. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2017, 62, 3381–3385. https://doi.org/10.4067/s0717-97072017000100015.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Dar, U. A.; Shah, S. A. Exploring Crystal Structure of 5,10,15,20-Tetrakis (4-Iodophenyl) Porphyrin; H2TIPP: Experimental and Theoretical Investigations. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1240, 130601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.130601.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (S)-N-(10-((2,2-dimethoxyethyl)amino)-1,2,3-trimethoxy-9-oxo-5,6,7,9-tetrahydrobenzo[a]heptalen-7-yl)acetamide, C25H32N2O7
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-difluoro-3,3′-dimethyl-5,5′-di(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)- [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarbonitrile, C40H24F2N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(di-ethylenediamine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II) tetradedocyloxidohexavanadate] (V4+/V5+ = 2/1), C4H16CdN4O14V6
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(dimethylformamide-κ1N)-(μ4-2′,3,3″,5′-tetrakis(trifluoromethyl)-[1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4″-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,O′: O″,O‴)dicadmium(II)], C27H15CdF12NO5
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenylcarboxylato-O,O′)-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-bis(μ2-salicyladoximato-κ2N,O,O′)-(μ2-isopropoxo)-tris(isopropoxy-κ1O trititanium(IV)), C48H55N2O13Fe2Ti3
- Crystal structure of 3-(diethylamino)-7,9,11-trimethyl-8-phenyl-6H,13H-12λ4,13λ4-chromeno[3′,4′:4,5]pyrrolo[1,2-c]pyrrolo[2,1-f][1,3,2]diazaborinin-6-one, C28H26BF2N3O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-μ2-2-nitro-benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-zinc(II)], C20H13N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-{μ3-1-(3-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′′}manganese(II)] hydrate
- Crystal structure of N′-((1-hydroxycyclohexyl)(phenyl)methyl)-2-methoxybenzohydrazide methanol solvate, C22H28N2O4
- The cocrystal of caffeic acid — progesterone — water (1/2/1), C51H70O9
- Crystal structure of (((oxido(quinolin-6-yl)methoxy)triphenyl-λ5-stibanyl)oxy)(quinolin-7-yl)methanolate
- Crystal structure of [(E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-(2-(((E)-pyren-1-ylmethylene)amino)ethyl)-4′-(2-((E)-1,3,3-trimethylindolin-2-ylidene)ethylidene)-1′,2′,3′,4′-tetrahydrospiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one]-methanol, solvate C57H56N4O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(acridin-9-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione, C17H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of N-(4-acetylphenyl)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanamide, C22H21NO3
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)porphyrin, C52H34N16
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-μ2-[phenylmethanedithiolato-κ4S:S,S′:S′]diiron (Fe–Fe) C13H6Fe2O6S2
- Crystal structure of diiodo-bis(1-((2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ1N)cadmium(II), C34H34CdI2N10
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(3-bromophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H15BrFeO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ3N,O:O′)(6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C12H6Cl2N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-μ 3-(5-(3,5-dicarboxy-2,4,6-trimethylbenzyl)-2,4,6-trimethylisophthalato)-κ 6O,O′:O″,O‴:O‴′,O‴″) terbium(III)-monohydrate], C23H28TbO12
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one – ethanol (1/2), C35H33ClN4O6
- The crystal structure of 3-(5-amino-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)-4-chloro-3-hydroxyindolin-2-one, C17H12ClN3O3
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium 4-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-4, 5-diphenyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl]benzenesulfonate, C29H26FN3O3S
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-ammonio-3-((5-carboxypentyl)thio)propanoate
- Crystal structure of 4-cyclohexyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C12H15N3S2
- The crystal structure of 4,6-bis(dimethylamino)-2-fluoroisophthalonitrile, C12H13FN4
- Hydrogen bonding in the crystal structure of nicotin-1,1′-dium tetrabromidomanganate(II)
- The crystal structure of bis(2-bromobenzyl)(2-((2-oxybenzylidene)amino)-4-methylpentanoato-κ3N, O,O′)tin(IV), C27H27Br2NO3Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(p-tolyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C20H18FeO
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H22FN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of poly(bis(μ2-1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-2,3,5,6-tetrafluoroterephthalato-κ2O:O′)-manganese(II), C38H24F4N12O4Mn
- Crystal structure of (3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C29H32BrO3P
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium hydrogencarbonate – (diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/1/3)
- Crystal structure of N, N-Dimethyl-N′-tosylformimidamide, C10H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H23N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-1,5-bis[(E)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene] thiocarbonohydrazide)-bis(dimethylformamide)-dizinc(II) dimethylformamide solvate, C40H46N10O6S2Zn2⋅C3H7NO
- Crystal structure of azido-κ1N{hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″}copper(II), C24H40BCuN9
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(azido-κ1N)rhenium(I), C15H8N5O3Re
- Crystal structure of 4-((triphenylphosphonio)methyl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II), C24H22Cl4NPZn
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (S)-N-(10-((2,2-dimethoxyethyl)amino)-1,2,3-trimethoxy-9-oxo-5,6,7,9-tetrahydrobenzo[a]heptalen-7-yl)acetamide, C25H32N2O7
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-difluoro-3,3′-dimethyl-5,5′-di(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)- [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarbonitrile, C40H24F2N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(di-ethylenediamine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II) tetradedocyloxidohexavanadate] (V4+/V5+ = 2/1), C4H16CdN4O14V6
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(dimethylformamide-κ1N)-(μ4-2′,3,3″,5′-tetrakis(trifluoromethyl)-[1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4″-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,O′: O″,O‴)dicadmium(II)], C27H15CdF12NO5
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenylcarboxylato-O,O′)-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-bis(μ2-salicyladoximato-κ2N,O,O′)-(μ2-isopropoxo)-tris(isopropoxy-κ1O trititanium(IV)), C48H55N2O13Fe2Ti3
- Crystal structure of 3-(diethylamino)-7,9,11-trimethyl-8-phenyl-6H,13H-12λ4,13λ4-chromeno[3′,4′:4,5]pyrrolo[1,2-c]pyrrolo[2,1-f][1,3,2]diazaborinin-6-one, C28H26BF2N3O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-μ2-2-nitro-benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-zinc(II)], C20H13N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-{μ3-1-(3-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′′}manganese(II)] hydrate
- Crystal structure of N′-((1-hydroxycyclohexyl)(phenyl)methyl)-2-methoxybenzohydrazide methanol solvate, C22H28N2O4
- The cocrystal of caffeic acid — progesterone — water (1/2/1), C51H70O9
- Crystal structure of (((oxido(quinolin-6-yl)methoxy)triphenyl-λ5-stibanyl)oxy)(quinolin-7-yl)methanolate
- Crystal structure of [(E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-(2-(((E)-pyren-1-ylmethylene)amino)ethyl)-4′-(2-((E)-1,3,3-trimethylindolin-2-ylidene)ethylidene)-1′,2′,3′,4′-tetrahydrospiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one]-methanol, solvate C57H56N4O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(acridin-9-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione, C17H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of N-(4-acetylphenyl)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanamide, C22H21NO3
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)porphyrin, C52H34N16
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-μ2-[phenylmethanedithiolato-κ4S:S,S′:S′]diiron (Fe–Fe) C13H6Fe2O6S2
- Crystal structure of diiodo-bis(1-((2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ1N)cadmium(II), C34H34CdI2N10
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(3-bromophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H15BrFeO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ3N,O:O′)(6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C12H6Cl2N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-μ 3-(5-(3,5-dicarboxy-2,4,6-trimethylbenzyl)-2,4,6-trimethylisophthalato)-κ 6O,O′:O″,O‴:O‴′,O‴″) terbium(III)-monohydrate], C23H28TbO12
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one – ethanol (1/2), C35H33ClN4O6
- The crystal structure of 3-(5-amino-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)-4-chloro-3-hydroxyindolin-2-one, C17H12ClN3O3
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium 4-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-4, 5-diphenyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl]benzenesulfonate, C29H26FN3O3S
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-ammonio-3-((5-carboxypentyl)thio)propanoate
- Crystal structure of 4-cyclohexyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C12H15N3S2
- The crystal structure of 4,6-bis(dimethylamino)-2-fluoroisophthalonitrile, C12H13FN4
- Hydrogen bonding in the crystal structure of nicotin-1,1′-dium tetrabromidomanganate(II)
- The crystal structure of bis(2-bromobenzyl)(2-((2-oxybenzylidene)amino)-4-methylpentanoato-κ3N, O,O′)tin(IV), C27H27Br2NO3Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(p-tolyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C20H18FeO
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H22FN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of poly(bis(μ2-1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-2,3,5,6-tetrafluoroterephthalato-κ2O:O′)-manganese(II), C38H24F4N12O4Mn
- Crystal structure of (3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C29H32BrO3P
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium hydrogencarbonate – (diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/1/3)
- Crystal structure of N, N-Dimethyl-N′-tosylformimidamide, C10H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H23N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-1,5-bis[(E)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene] thiocarbonohydrazide)-bis(dimethylformamide)-dizinc(II) dimethylformamide solvate, C40H46N10O6S2Zn2⋅C3H7NO
- Crystal structure of azido-κ1N{hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″}copper(II), C24H40BCuN9
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(azido-κ1N)rhenium(I), C15H8N5O3Re
- Crystal structure of 4-((triphenylphosphonio)methyl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II), C24H22Cl4NPZn

