Abstract
C8H10N2O2, orthorhombic, Pbca (no. 61), a = 11.0571(2) Å, b = 8.1172(2) Å, c = 17.6080(4) Å, V = 1580.37(6) Å3, Z = 8, R gt (F) = 0.0324, wR ref (F 2) = 0.0872, T = 100(2) K.
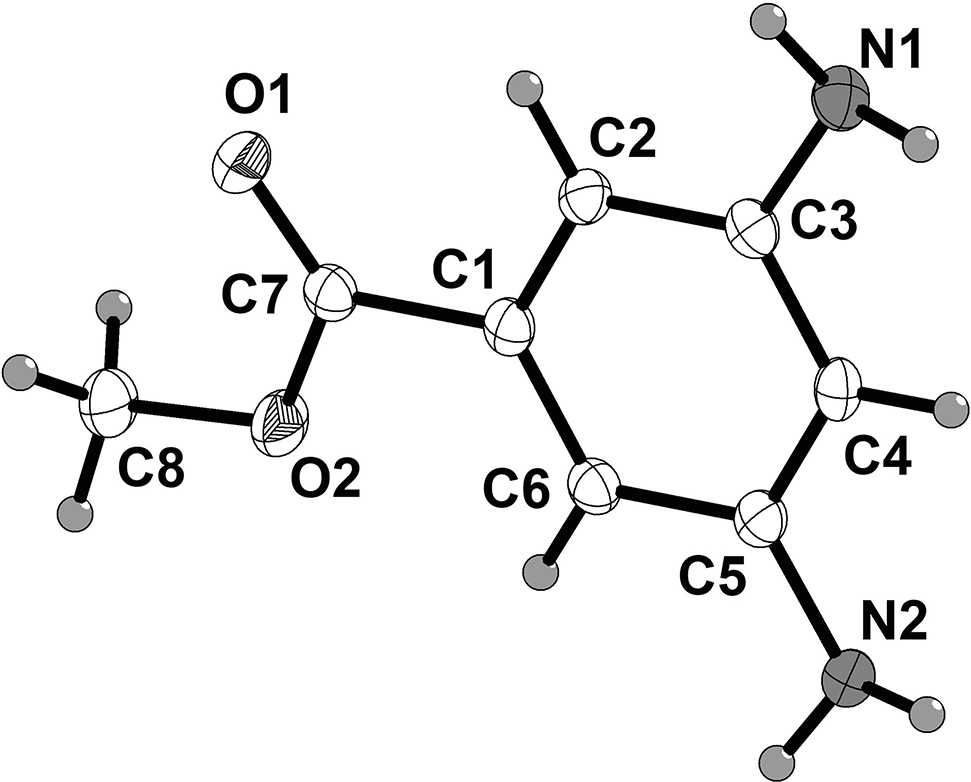
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Brown block |
| Size: | 0.22 × 0.12 × 0.04 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54178 Å) |
| μ: | 0.85 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 72.2°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 7172, 1552, 0.030 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 1383 |
| N(param)refined: | 126 |
| Programs: | SHELX [1], [2], [3], Bruker [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.10499 (10) | 0.86389 (13) | 0.54508 (6) | 0.0175 (3) |
| C2 | 0.19368 (10) | 0.96328 (14) | 0.57782 (6) | 0.0181 (2) |
| H2 | 0.2675 | 0.9842 | 0.5519 | 0.022* |
| C3 | 0.17198 (10) | 1.03160 (13) | 0.64950 (6) | 0.0176 (3) |
| C4 | 0.06231 (10) | 1.00068 (13) | 0.68634 (6) | 0.0184 (3) |
| H4 | 0.0479 | 1.0478 | 0.7349 | 0.022* |
| C5 | −0.02618 (10) | 0.90202 (14) | 0.65310 (6) | 0.0181 (3) |
| C6 | −0.00405 (10) | 0.83186 (14) | 0.58180 (6) | 0.0183 (3) |
| H6 | −0.0629 | 0.7630 | 0.5587 | 0.022* |
| C7 | 0.12825 (10) | 0.79163 (14) | 0.46850 (6) | 0.0186 (3) |
| C8 | 0.05297 (12) | 0.61452 (16) | 0.37332 (7) | 0.0275 (3) |
| H8A | 0.0734 | 0.6985 | 0.3355 | 0.041* |
| H8B | −0.0229 | 0.5605 | 0.3589 | 0.041* |
| H8C | 0.1179 | 0.5324 | 0.3757 | 0.041* |
| N1 | 0.26091 (10) | 1.12400 (12) | 0.68744 (6) | 0.0220 (2) |
| N2 | −0.13493 (9) | 0.86971 (13) | 0.69082 (6) | 0.0213 (2) |
| O1 | 0.21725 (7) | 0.81797 (11) | 0.43036 (5) | 0.0247 (2) |
| O2 | 0.03905 (8) | 0.69125 (11) | 0.44674 (5) | 0.0268 (2) |
| H2A | −0.1597 (14) | 0.952 (2) | 0.7245 (9) | 0.027 (4)* |
| H2B | −0.1931 (16) | 0.838 (2) | 0.6602 (10) | 0.035 (4)* |
| H1B | 0.2294 (14) | 1.194 (2) | 0.7217 (9) | 0.032 (4)* |
| H1A | 0.3134 (16) | 1.179 (2) | 0.6564 (10) | 0.035 (4)* |
Source of materials
To a solution of methyl 3,5-dinitrobenzoate (3.0 g, 13.3 mmol) [5, 6] in a 1:1 mixture of dry THF (100 mL) and dry ethanol (100 mL) was added 10% Pd–C (1.2 g, 11.3 mmol). The flask was degassed and purged with pure hydrogen for 45 min. The reaction was left stirring for 48 h. The reaction was filtered using Celite-545, and the solution was concentrated by evaporating most of the reaction solvent using a rotary evaporator. The residue was poured into n-hexane (150 mL). The product was filtered and the solvent was removed in vacuo to afford the title compound as brown powder (2.0 g, 91%). A sample of the title compound was dissolved in a mixture of DMSO/EtOH 10:1 v/v and left undisturbed. Unexpectedly the starting material was grown by slow evaporation of the solution over a period of seven days.
Experimental details
The structure was solved by Direct Methods. H atoms were included in calculated positions with C–H lengths of 0.95(CH), 0.99(CH2) & 0.98(CH3) Å; U iso(H) values were fixed at 1.2U eq(C) except for CH3 where it was 1.5U eq(C).
Comment
The title compound molecular structure is shown in the figure. It is a highly planar structure, in which the ester and aromatic ring both occupy the same plane, indicating conjugation of both the CH3O lone pair and the aromatic system with the carbonyl. The X-ray structure revealed close contacts between both of the aromatic amino groups and nearby molecules in the crystal. One aromatic amine has intermolecular NH π-aromatic interactions with a neighboring aromatic system. This is evident from the close contacts between the aromatic NH and aromatic carbons ipso (2.628 Å) and ortho (2.692 and 2.776 Å) to the methyl ester. The other aromatic NH is involved in intermolecular hydrogen bonding with the methyl ester carbonyl oxygen at a distance of 2.265 Å. All bond lengths are in the expected ranges [7].
Funding source: TWAS
Award Identifier / Grant number: 16-490 RG/CHE/AF/AC_G – FR3240293296
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the world academy of sciences for the advancement of science in developing countries TWAS for their financial support. Funding for this research was provided by: the world academy of sciences for the advancement of science in developing countries TWAS (grant no. 16-490 RG/CHE/AF/AC_G – FR3240293296 to Adel M. Awadallah, Rami Y. Morjan); the world academy of sciences for the advancement of science in developing countries TWAS (scholarship no. 16-490 RG/CHE/AF/AC_G – FR3240293296 to Jannat N. Azzara).
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: The world academy of sciences for the advancement of science in developing countries TWAS (grant no. 16-490 RG/CHE/AF/AC_G – FR3240293296 to Adel M. Awadallah, Rami Y. Morjan); the world academy of sciences for the advancement of science in developing countries TWAS (scholarship no. 16-490 RG/CHE/AF/AC_G – FR3240293296 to Jannat N. Azarah).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
4. Bruker. APEX2, SMART (Version 5.630) and SAINT-Plus (Version 6.45A); Madison: WI, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
5. Gennas, G., Talman, V., Aitio, O., Ekokoski, E., Finel, M., Tuominen, R., Yli-Kauhaluoma, J. Design, synthesis, and biological activity of isophthalic acid derivatives targeted to the C1 domain of protein kinase C. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 3969–3981; https://doi.org/10.1021/jm900229p.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Rzaczynska, Z., Mrozek, R., Lenik, J., Sikorska, M., Glowiak, T. The crystal structures and vibrational spectra of 3,4-diaminobenzoic and 3,5-diaminobenzoic acids. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2000, 30, 519–524; https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1011333621635.10.1023/A:1011333621635Search in Google Scholar
7. Rzaczyńska, Z., Mrozek, R., Lenik, J., Sikorska, M., Głowiak, T. The crystal structures and vibrational spectra of 3,4-diaminobenzoic and 3,5-diaminobenzoic acids. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2000, 30, 519–524; https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1011333621635.10.1023/A:1011333621635Search in Google Scholar
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of undecacalcium decaarsenide, Ca11As10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4- ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H -pyrazol-3-one-κ2 N: O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)porphyrin-21,23-diido-κ4 N 4-naphthalocyanido-κ4 N 4-neodymium(IV) - chloroform (1/6) C114H90N12Cl18Nd
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(2-chlorobenzyl)urea, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis[benzyl(methyl)carbamodithioato-κ 2 S,S′]-di-n-butyltin(IV), C26H38N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate – methanol (1/2), C25H32N2O4S⋅2CH3OH
- Synthesis and crystal structure of {(N′,N″-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))-bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato)-κ6 N 2 O 4}copper(II), C30H24CuN4O6
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((5-(nitro)-2-oxidophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Br2MnN5O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta-[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C13H10N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ3-2-aminonicotinato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O′″)-(μ4-oxalato-κ6 N:N′:O,O′:O″,O′″)dicopper(I)-disamarium(III)], [SmCu(C6N2H5O2)2(C2O4)] n
- The crystal structure of 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoic- acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide—water (1/1/1), C12H13N3O7
- Crystal structure of N-ethyl-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-phenyl]piperazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H18F3N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-anilino-1,4-diphenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ium iodide, C20H17N4I
- The crystal structure of (tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine)-benzoato-copper(II) perchlorate monohydrate, CuC31H28N7O7Cl
- Crystal structure of [2-hydroxy-3-methyl-benzoato-k1 O-triphenyltin(IV)], C26H22O3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)-benzoato-k1 O)zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- The crystal structure of dicarbonyl-(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O)-rhodium(I), C8H5N2O4Rh
- The crystal structure of oxalic acid – 2-ethoxybenzamide (2/1), C20H24N2O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 7-ethyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C10H15N5O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(N,N-dimethylacetamide-κO) (μ4-2-nitroisophthalato-κ 4 O:O′:O″:O′″)manganese(II)], C11H10N2O7Mn
- Crystal structure of 14-O-acetyldelcosine, C26H41NO8
- The crystal structure of poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-(μ 4-2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5 O:O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H13CdClN2O5
- Crystal structure of propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphine sulfide) ethanol solvate, C27H26P2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{[(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)-hydrazinocarbonylmethyl]-trimethylammonium} tetrabromozincate, C32H54N8O4ZnBr4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2′-(2,5-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-3,4-diyl)dibenzoate, C34H30O7
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H12O3
- The crystal structure of tetra(imidazole-κ1 N)zinc(II) μ2-oxido-hexaoxido-divanadium(VI) C12H16N8O6V2Zn
- Crystal structure of S-2-(1-(5-methylpyridin-2-ylamino)octyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione, C24H28N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxido-2-oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-oktakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) – methanol – pyridine (1/1/1) C76H65N13Cl2Ni3O9
- The crystal structure of methyl 3,5-diaminobenzoate, C8H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 10-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-5H-dibenzo[a,d][7]annelen-5-one, C27H17NO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C16H20N2O5
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19BrN2O
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl)-3,6-bis ((4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)methylene)-1,4-dialuminacyclohexane – benzene (1/2), C50H72Al2B2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ 3-diphenylphosphinato)-tetrakis(μ 2-diphenylphosphinato)-bis(diphenylphosphinato)-bis(μ 2-hydroxo)dicopper(II)-ditin(IV), C104H100O18P8Cu2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 3-((3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)methoxy)benzo[d] isothiazole 1,1-dioxide, C11H6Cl2N2O3S2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H11FO3
- The crystal structure of tris(carbonyl)-bis(carbonyl)-[μ-propane-1,2- dithiolato]-(benzyldiphenylphosphine)diiron (Fe—Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenethyl)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium nitrate, C16H23N4O4Cl
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-disulfanediyldi(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine) monohydrate, C4H8N8OS2
- The crystal structure of trans-[bis(4-methylpyridine-κN)bis(quinoline-2-carboxylato- κ 2 N,O)cadmium(II)], C32H26CdN4O4
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2′-hydroxy-4′,6′-dimethoxy-3-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C28H28O7
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of undecacalcium decaarsenide, Ca11As10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4- ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H -pyrazol-3-one-κ2 N: O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)porphyrin-21,23-diido-κ4 N 4-naphthalocyanido-κ4 N 4-neodymium(IV) - chloroform (1/6) C114H90N12Cl18Nd
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(2-chlorobenzyl)urea, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis[benzyl(methyl)carbamodithioato-κ 2 S,S′]-di-n-butyltin(IV), C26H38N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate – methanol (1/2), C25H32N2O4S⋅2CH3OH
- Synthesis and crystal structure of {(N′,N″-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))-bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato)-κ6 N 2 O 4}copper(II), C30H24CuN4O6
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((5-(nitro)-2-oxidophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Br2MnN5O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta-[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C13H10N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ3-2-aminonicotinato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O′″)-(μ4-oxalato-κ6 N:N′:O,O′:O″,O′″)dicopper(I)-disamarium(III)], [SmCu(C6N2H5O2)2(C2O4)] n
- The crystal structure of 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoic- acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide—water (1/1/1), C12H13N3O7
- Crystal structure of N-ethyl-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-phenyl]piperazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H18F3N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-anilino-1,4-diphenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ium iodide, C20H17N4I
- The crystal structure of (tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine)-benzoato-copper(II) perchlorate monohydrate, CuC31H28N7O7Cl
- Crystal structure of [2-hydroxy-3-methyl-benzoato-k1 O-triphenyltin(IV)], C26H22O3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)-benzoato-k1 O)zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- The crystal structure of dicarbonyl-(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O)-rhodium(I), C8H5N2O4Rh
- The crystal structure of oxalic acid – 2-ethoxybenzamide (2/1), C20H24N2O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 7-ethyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C10H15N5O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(N,N-dimethylacetamide-κO) (μ4-2-nitroisophthalato-κ 4 O:O′:O″:O′″)manganese(II)], C11H10N2O7Mn
- Crystal structure of 14-O-acetyldelcosine, C26H41NO8
- The crystal structure of poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-(μ 4-2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5 O:O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H13CdClN2O5
- Crystal structure of propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphine sulfide) ethanol solvate, C27H26P2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{[(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)-hydrazinocarbonylmethyl]-trimethylammonium} tetrabromozincate, C32H54N8O4ZnBr4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2′-(2,5-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-3,4-diyl)dibenzoate, C34H30O7
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H12O3
- The crystal structure of tetra(imidazole-κ1 N)zinc(II) μ2-oxido-hexaoxido-divanadium(VI) C12H16N8O6V2Zn
- Crystal structure of S-2-(1-(5-methylpyridin-2-ylamino)octyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione, C24H28N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxido-2-oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-oktakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) – methanol – pyridine (1/1/1) C76H65N13Cl2Ni3O9
- The crystal structure of methyl 3,5-diaminobenzoate, C8H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 10-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-5H-dibenzo[a,d][7]annelen-5-one, C27H17NO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C16H20N2O5
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19BrN2O
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl)-3,6-bis ((4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)methylene)-1,4-dialuminacyclohexane – benzene (1/2), C50H72Al2B2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ 3-diphenylphosphinato)-tetrakis(μ 2-diphenylphosphinato)-bis(diphenylphosphinato)-bis(μ 2-hydroxo)dicopper(II)-ditin(IV), C104H100O18P8Cu2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 3-((3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)methoxy)benzo[d] isothiazole 1,1-dioxide, C11H6Cl2N2O3S2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H11FO3
- The crystal structure of tris(carbonyl)-bis(carbonyl)-[μ-propane-1,2- dithiolato]-(benzyldiphenylphosphine)diiron (Fe—Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenethyl)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium nitrate, C16H23N4O4Cl
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-disulfanediyldi(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine) monohydrate, C4H8N8OS2
- The crystal structure of trans-[bis(4-methylpyridine-κN)bis(quinoline-2-carboxylato- κ 2 N,O)cadmium(II)], C32H26CdN4O4
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2′-hydroxy-4′,6′-dimethoxy-3-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C28H28O7

