Abstract
C17H12O3, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 9.2911(15) Å, b = 17.525(3) Å, c = 8.5586(15) Å, β = 109.358(7)° V = 1314.8(4) Å3, Z = 4, R gt(F) = 0.0550, wR ref(F 2) = 0.1789, T = 296(2) K.
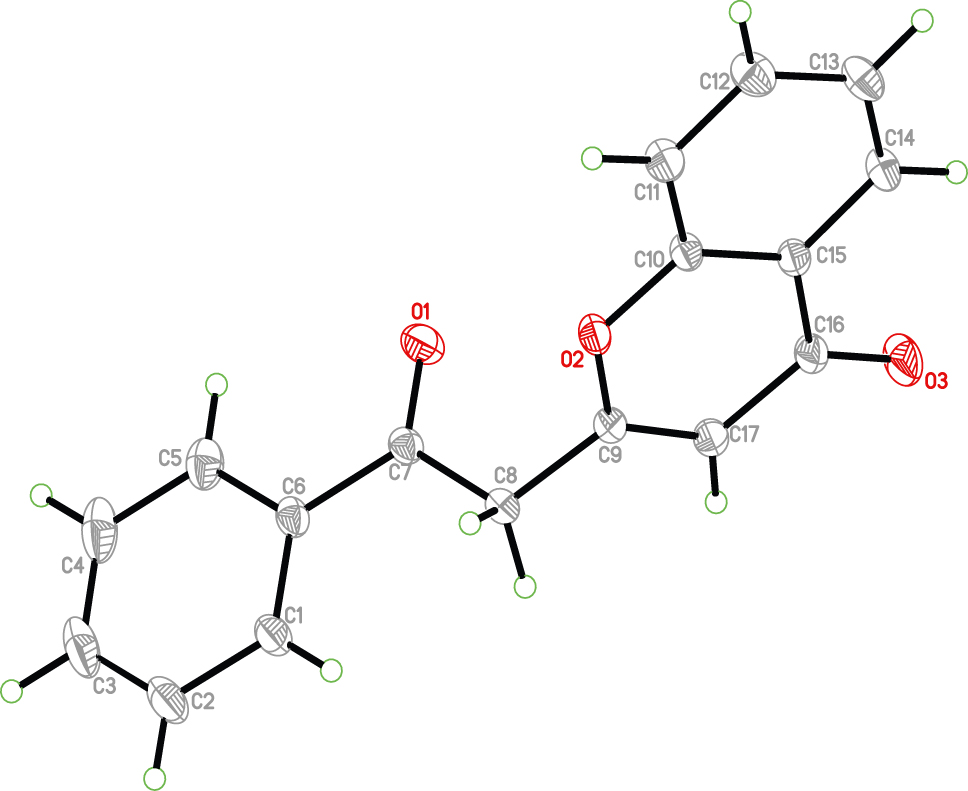
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size | 0.20 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.09 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II |
| θ max, completeness: | 35.3°, 98% |
| N(hkl) measured, N(hkl) unique, R int: | 20,222, 5866, 0.047 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl) gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 4208 |
| N(param) refined: | 181 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2, 3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | 0.48607 (9) | 0.32069 (5) | 0.65961 (10) | 0.03866 (19) |
| C1 | 0.56547 (14) | 0.43019 (6) | 0.33778 (16) | 0.0379 (2) |
| H1A | 0.4886 | 0.4119 | 0.2453 | 0.045* |
| O2 | 0.14057 (8) | 0.28875 (4) | 0.45857 (9) | 0.02961 (16) |
| C2 | 0.66908 (17) | 0.48384 (7) | 0.3190 (2) | 0.0488 (3) |
| H2A | 0.6614 | 0.5015 | 0.2140 | 0.059* |
| O3 | 0.18237 (12) | 0.05678 (4) | 0.45217 (15) | 0.0514 (3) |
| C3 | 0.78340 (16) | 0.51084 (7) | 0.4567 (2) | 0.0546 (4) |
| H3A | 0.8531 | 0.5463 | 0.4438 | 0.066* |
| C4 | 0.79493 (15) | 0.48560 (7) | 0.6131 (2) | 0.0539 (4) |
| H4A | 0.8719 | 0.5043 | 0.7051 | 0.065* |
| C5 | 0.69132 (13) | 0.43218 (7) | 0.63354 (17) | 0.0404 (2) |
| H5A | 0.6986 | 0.4155 | 0.7390 | 0.048* |
| C6 | 0.57688 (11) | 0.40388 (5) | 0.49533 (13) | 0.02925 (19) |
| C7 | 0.47216 (10) | 0.34448 (5) | 0.52173 (12) | 0.02690 (18) |
| C8 | 0.35020 (11) | 0.31260 (6) | 0.36904 (12) | 0.02945 (19) |
| H8A | 0.2872 | 0.3542 | 0.3087 | 0.035* |
| H8B | 0.3993 | 0.2893 | 0.2971 | 0.035* |
| C9 | 0.25091 (11) | 0.25487 (5) | 0.41135 (12) | 0.02708 (17) |
| C10 | 0.03868 (10) | 0.24332 (5) | 0.50129 (12) | 0.02673 (17) |
| C11 | −0.07174 (12) | 0.28160 (6) | 0.54927 (14) | 0.0339 (2) |
| H11A | −0.0752 | 0.3346 | 0.5501 | 0.041* |
| C12 | −0.17562 (13) | 0.23866 (7) | 0.59540 (16) | 0.0387 (2) |
| H12A | −0.2491 | 0.2631 | 0.6294 | 0.046* |
| C13 | −0.17188 (13) | 0.15882 (7) | 0.59168 (16) | 0.0389 (2) |
| H13A | −0.2434 | 0.1307 | 0.6219 | 0.047* |
| C14 | −0.06292 (12) | 0.12189 (6) | 0.54358 (14) | 0.0331 (2) |
| H14A | −0.0611 | 0.0689 | 0.5411 | 0.040* |
| C15 | 0.04583 (10) | 0.16409 (5) | 0.49806 (11) | 0.02678 (17) |
| C16 | 0.16658 (12) | 0.12662 (5) | 0.45059 (13) | 0.0313 (2) |
| C17 | 0.26758 (12) | 0.17865 (5) | 0.40546 (13) | 0.03060 (19) |
| H17A | 0.3455 | 0.1590 | 0.3717 | 0.037* |
Source of material
The round-bottomed flask is charged with 2-hydroxyacetophenone, -4H-chromen-4-one, carbon disulfide, potassium carbonate and bromoethane and heated to 35 °C with efficient stirring. The reaction was monitored by thin layer chromatography (TLC, 254 nm). After the reaction was completed, the resulting mixture was cooled to room temperature, then poured into ice water and extracted with ethyl acetate, the combined organic layers were washed with anhydrous Na2SO4, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by column chromatography (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate 5:1) to give the title compound as a light yellow solid.
Experimental details
Hydrogen atoms were placed in their geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with constrained isotropic displacement parameters.
Comment
Chromone derivatives, as a kind of natural products, exist widely in plants and have diverse structural skeletons and biological activities. Some chromones are also important resources for the preparation of fluorescent probes. When a specific metal ion is added, the ring-opening process of the fluorescein part can be observed when the probe recombines with the metal ion, which leads to the appearance of color and fluorescence [4]. It can be used for fluorescence detection of Zn2+ [5], Cu2+ [6, 7], Mg2+ [7], [8], [9], Al3+ [10], and the preparation of discoloration dyes [7, 11].
There is a molecule in the asymmetric unit (see the figure). This molecule consists of a phenyl ring, chromone skeleton and the acetyl group. The structural analysis of the crystal shows that the benzo moiety (C10/C11/C12/C13/C14/C15) and the oxygen containing heterocyclic moiety (C10/C15/C16/C17/C9/O2) are almost in the same plane; the dihedral angle between them is 0.8°. The dihedral angle between the phenyl ring (C1/C2/C3/C4/C5/C6) and the chromone skeleton is 83°. The bond length and bond angle of the compound are in the normal range [12], [13], [14]. No strong hydrogen bond was observed in the compound.
Funding source: Nanjing Senega Medical Technology Co. Ltd.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by Nanjing Senega Medical Technology Co. Ltd. Also, we appreciate Wang huaqin in Nanjing University and Wu wenyuan in Nanjing Tech University for some data analysis.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar
4. Huo, F.-J., Zhang, J.-J., Yang, Y.-T., Chao, J.-B., Yin, C.-X., Zhang, Y.-B., Chen, T.-G. A fluorescein-based highly specific colorimetric and fluorescent probe for hypochlorites in aqueous solution and its application in tap water. Sens. Actuators, B 2012, 166–167, 44–49.10.1016/j.snb.2011.11.081Search in Google Scholar
5. Liu, L.-M., Yang, Z.-Y. A rhodamine and chromone based “turn-on” fluorescent probe (RC1) for Zn(II) in aqueous solutions and its application. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 2018, 364, 558–563.10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.06.037Search in Google Scholar
6. Lee, H., Kim, C. A chromone-based fluorescent chemosensor for detecting Cu2+. Bull. Kor. Chem. Soc. 2019, 41, 201–204.10.1002/bkcs.11927Search in Google Scholar
7. Pivovarenko, V. G., Bugera, O., Humbert, N., Klymchenko, A. S., Mély, Y. A toolbox of chromones and quinolones for measuring a wide range of ATP concentrations. Chem. Eur J. 2017, 23, 11927–11934.10.1002/chem.201702484Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Yadav, N., Kumar, R., Singh, A. K., Mohiyuddin, S., Gopinath, P. Systematic approach of chromone skeleton for detecting Mg2+, ion: applications for sustainable cytotoxicity and cell imaging possibilities. Spectrochim. Acta A 2020, 235, 118290.10.1016/j.saa.2020.118290Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Li, C.-R., Li, S.-L., Wang, G.-Q., Yang, Z.-Y. Spectroscopic properties of a chromone-fluorescein conjugate as Mg2+ “turn on” fluorescent probe. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 2018, 356, 700–707.10.1016/j.jphotochem.2016.03.001Search in Google Scholar
10. Kim, H., Manivannan, R., Son, Y.-A. A chromone based fluorescent probe for the effective detection of aluminium ion. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 2840–2846.10.1166/jnn.2020.17463Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Kyriukha, Y. A., Kucherak, O. A., Yushchenko, T. I., Shvadchak, V. V., Yushchenko, D. A. 3-hydroxybenzo[g]chromones: fluorophores with red-shifted absorbance and highly sensitive to polarity emission. Sens. Actuators, B 2018, 265, 691–698.10.1016/j.snb.2018.03.058Search in Google Scholar
12. Dziewulska-Kułaczkowska, A., Mazur, L. Structural studies and characterization of 3-formylchromone and products of its reactions with chosen primary aromatic amines. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 985, 233–242.10.1016/j.molstruc.2010.10.049Search in Google Scholar
13. Binbuga, N., Schultz, T. P., Henry, W. P. Intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonding in 3-hydroxy- and 5-hydroxychromone. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 5762–5765.10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.07.100Search in Google Scholar
14. Yagishita, F., Baba, N., Ueda, Y., Katabira, S., Kasashima, Y., Mino, T., Sakamoto, M. Diastereoselective photodimerization reactions of chromone-2-carboxamides to construct a C2-chiral scaffold. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 9644–9649.10.1039/C4OB01827CSearch in Google Scholar
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of undecacalcium decaarsenide, Ca11As10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4- ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H -pyrazol-3-one-κ2 N: O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)porphyrin-21,23-diido-κ4 N 4-naphthalocyanido-κ4 N 4-neodymium(IV) - chloroform (1/6) C114H90N12Cl18Nd
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(2-chlorobenzyl)urea, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis[benzyl(methyl)carbamodithioato-κ 2 S,S′]-di-n-butyltin(IV), C26H38N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate – methanol (1/2), C25H32N2O4S⋅2CH3OH
- Synthesis and crystal structure of {(N′,N″-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))-bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato)-κ6 N 2 O 4}copper(II), C30H24CuN4O6
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((5-(nitro)-2-oxidophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Br2MnN5O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta-[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C13H10N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ3-2-aminonicotinato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O′″)-(μ4-oxalato-κ6 N:N′:O,O′:O″,O′″)dicopper(I)-disamarium(III)], [SmCu(C6N2H5O2)2(C2O4)] n
- The crystal structure of 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoic- acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide—water (1/1/1), C12H13N3O7
- Crystal structure of N-ethyl-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-phenyl]piperazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H18F3N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-anilino-1,4-diphenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ium iodide, C20H17N4I
- The crystal structure of (tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine)-benzoato-copper(II) perchlorate monohydrate, CuC31H28N7O7Cl
- Crystal structure of [2-hydroxy-3-methyl-benzoato-k1 O-triphenyltin(IV)], C26H22O3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)-benzoato-k1 O)zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- The crystal structure of dicarbonyl-(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O)-rhodium(I), C8H5N2O4Rh
- The crystal structure of oxalic acid – 2-ethoxybenzamide (2/1), C20H24N2O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 7-ethyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C10H15N5O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(N,N-dimethylacetamide-κO) (μ4-2-nitroisophthalato-κ 4 O:O′:O″:O′″)manganese(II)], C11H10N2O7Mn
- Crystal structure of 14-O-acetyldelcosine, C26H41NO8
- The crystal structure of poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-(μ 4-2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5 O:O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H13CdClN2O5
- Crystal structure of propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphine sulfide) ethanol solvate, C27H26P2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{[(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)-hydrazinocarbonylmethyl]-trimethylammonium} tetrabromozincate, C32H54N8O4ZnBr4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2′-(2,5-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-3,4-diyl)dibenzoate, C34H30O7
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H12O3
- The crystal structure of tetra(imidazole-κ1 N)zinc(II) μ2-oxido-hexaoxido-divanadium(VI) C12H16N8O6V2Zn
- Crystal structure of S-2-(1-(5-methylpyridin-2-ylamino)octyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione, C24H28N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxido-2-oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-oktakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) – methanol – pyridine (1/1/1) C76H65N13Cl2Ni3O9
- The crystal structure of methyl 3,5-diaminobenzoate, C8H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 10-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-5H-dibenzo[a,d][7]annelen-5-one, C27H17NO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C16H20N2O5
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19BrN2O
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl)-3,6-bis ((4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)methylene)-1,4-dialuminacyclohexane – benzene (1/2), C50H72Al2B2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ 3-diphenylphosphinato)-tetrakis(μ 2-diphenylphosphinato)-bis(diphenylphosphinato)-bis(μ 2-hydroxo)dicopper(II)-ditin(IV), C104H100O18P8Cu2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 3-((3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)methoxy)benzo[d] isothiazole 1,1-dioxide, C11H6Cl2N2O3S2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H11FO3
- The crystal structure of tris(carbonyl)-bis(carbonyl)-[μ-propane-1,2- dithiolato]-(benzyldiphenylphosphine)diiron (Fe—Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenethyl)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium nitrate, C16H23N4O4Cl
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-disulfanediyldi(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine) monohydrate, C4H8N8OS2
- The crystal structure of trans-[bis(4-methylpyridine-κN)bis(quinoline-2-carboxylato- κ 2 N,O)cadmium(II)], C32H26CdN4O4
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2′-hydroxy-4′,6′-dimethoxy-3-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C28H28O7
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of undecacalcium decaarsenide, Ca11As10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4- ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H -pyrazol-3-one-κ2 N: O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)porphyrin-21,23-diido-κ4 N 4-naphthalocyanido-κ4 N 4-neodymium(IV) - chloroform (1/6) C114H90N12Cl18Nd
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(2-chlorobenzyl)urea, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis[benzyl(methyl)carbamodithioato-κ 2 S,S′]-di-n-butyltin(IV), C26H38N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate – methanol (1/2), C25H32N2O4S⋅2CH3OH
- Synthesis and crystal structure of {(N′,N″-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))-bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato)-κ6 N 2 O 4}copper(II), C30H24CuN4O6
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((5-(nitro)-2-oxidophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Br2MnN5O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta-[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C13H10N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ3-2-aminonicotinato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O′″)-(μ4-oxalato-κ6 N:N′:O,O′:O″,O′″)dicopper(I)-disamarium(III)], [SmCu(C6N2H5O2)2(C2O4)] n
- The crystal structure of 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoic- acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide—water (1/1/1), C12H13N3O7
- Crystal structure of N-ethyl-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-phenyl]piperazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H18F3N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-anilino-1,4-diphenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ium iodide, C20H17N4I
- The crystal structure of (tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine)-benzoato-copper(II) perchlorate monohydrate, CuC31H28N7O7Cl
- Crystal structure of [2-hydroxy-3-methyl-benzoato-k1 O-triphenyltin(IV)], C26H22O3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)-benzoato-k1 O)zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- The crystal structure of dicarbonyl-(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O)-rhodium(I), C8H5N2O4Rh
- The crystal structure of oxalic acid – 2-ethoxybenzamide (2/1), C20H24N2O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 7-ethyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C10H15N5O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(N,N-dimethylacetamide-κO) (μ4-2-nitroisophthalato-κ 4 O:O′:O″:O′″)manganese(II)], C11H10N2O7Mn
- Crystal structure of 14-O-acetyldelcosine, C26H41NO8
- The crystal structure of poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-(μ 4-2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5 O:O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H13CdClN2O5
- Crystal structure of propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphine sulfide) ethanol solvate, C27H26P2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{[(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)-hydrazinocarbonylmethyl]-trimethylammonium} tetrabromozincate, C32H54N8O4ZnBr4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2′-(2,5-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-3,4-diyl)dibenzoate, C34H30O7
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H12O3
- The crystal structure of tetra(imidazole-κ1 N)zinc(II) μ2-oxido-hexaoxido-divanadium(VI) C12H16N8O6V2Zn
- Crystal structure of S-2-(1-(5-methylpyridin-2-ylamino)octyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione, C24H28N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxido-2-oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-oktakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) – methanol – pyridine (1/1/1) C76H65N13Cl2Ni3O9
- The crystal structure of methyl 3,5-diaminobenzoate, C8H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 10-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-5H-dibenzo[a,d][7]annelen-5-one, C27H17NO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C16H20N2O5
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19BrN2O
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl)-3,6-bis ((4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)methylene)-1,4-dialuminacyclohexane – benzene (1/2), C50H72Al2B2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ 3-diphenylphosphinato)-tetrakis(μ 2-diphenylphosphinato)-bis(diphenylphosphinato)-bis(μ 2-hydroxo)dicopper(II)-ditin(IV), C104H100O18P8Cu2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 3-((3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)methoxy)benzo[d] isothiazole 1,1-dioxide, C11H6Cl2N2O3S2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H11FO3
- The crystal structure of tris(carbonyl)-bis(carbonyl)-[μ-propane-1,2- dithiolato]-(benzyldiphenylphosphine)diiron (Fe—Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenethyl)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium nitrate, C16H23N4O4Cl
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-disulfanediyldi(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine) monohydrate, C4H8N8OS2
- The crystal structure of trans-[bis(4-methylpyridine-κN)bis(quinoline-2-carboxylato- κ 2 N,O)cadmium(II)], C32H26CdN4O4
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2′-hydroxy-4′,6′-dimethoxy-3-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C28H28O7

