Abstract
C30H20O4N2Cl2S2, Orthorhombic, Pca21, a = 16.9808(14) Å, b = 7.5227(6) Å, c = 20.8027(16) Å, V = 2657.4(4) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.0642, wRref(F2) = 0.1809, T = 293 K.
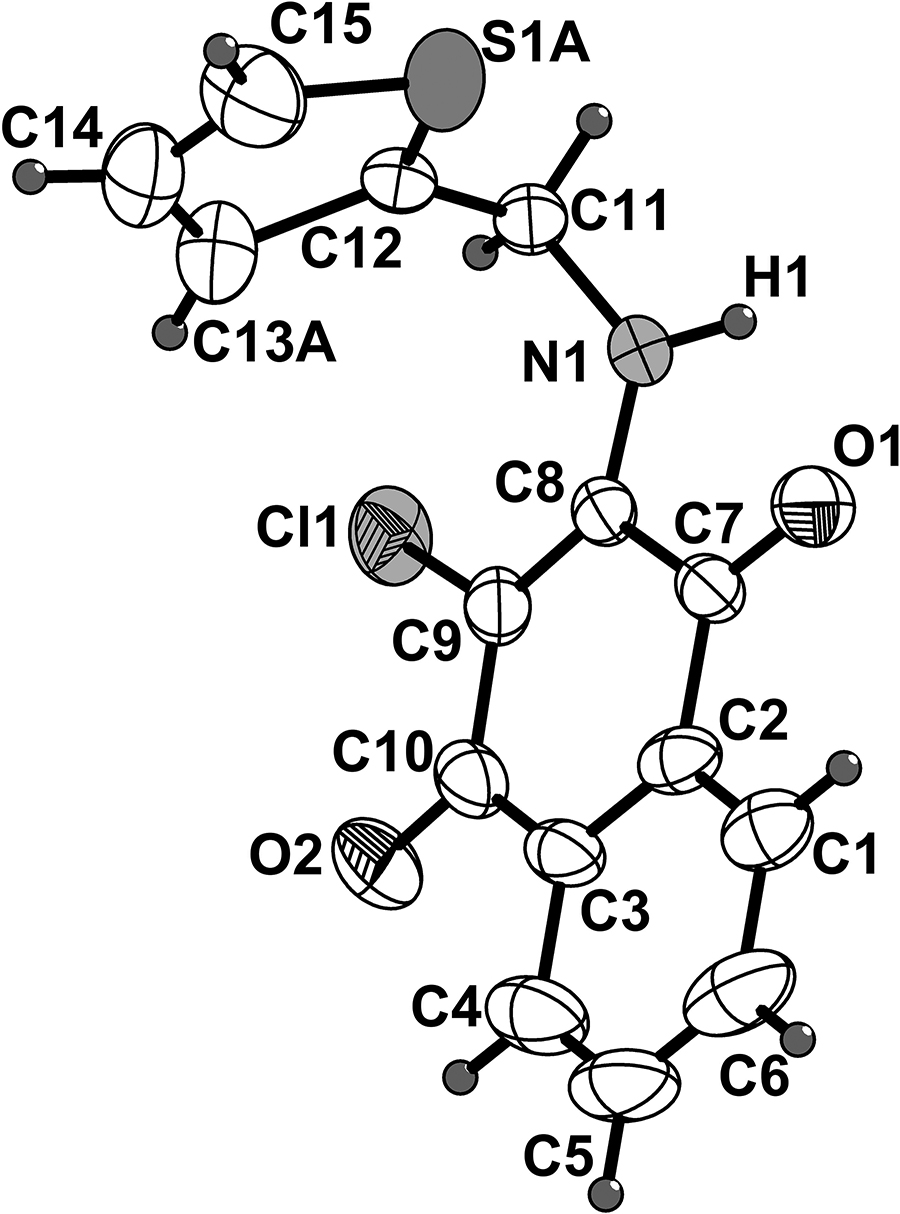
One of the two crystallographically independent molecules of the title crystal structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Red block |
| Size: | 0.35 × 0.29 × 0.21 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.44 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX3, φ and ω-scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 39,478, 6092, 0.060 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 4101 |
| N(param)refined: | 341 |
| Programs: | Bruker programs [1], OLEX2 [2, 3], SUPERFLIP [4], EDMA [5, 6], SHELX [7] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl1 | −0.19535 (13) | 0.0023 (2) | −0.08712 (12) | 0.0551 (6) |
| S1Aa | −0.4205 (4) | 0.4825 (8) | −0.1413 (3) | 0.0572 (9) |
| S1Bb | −0.3088 (4) | 0.3830 (7) | −0.0421 (2) | 0.0572 (9) |
| O1 | −0.2790 (3) | 0.2241 (7) | −0.3049 (2) | 0.0509 (12) |
| O2 | −0.0461 (3) | 0.0888 (9) | −0.1424 (3) | 0.0714 (17) |
| N1 | −0.3209 (3) | 0.1229 (7) | −0.1912 (3) | 0.0392 (12) |
| H1 | −0.348883 | 0.099891 | −0.224556 | 0.047* |
| C1 | −0.1265 (3) | 0.3137 (6) | −0.3464 (2) | 0.0484 (17) |
| H1A | −0.167155 | 0.337263 | −0.375116 | 0.058* |
| C2 | −0.14331 (19) | 0.2425 (6) | −0.2863 (2) | 0.0398 (17) |
| C3 | −0.0826 (2) | 0.2073 (6) | −0.2433 (2) | 0.0443 (17) |
| C4 | −0.0051 (2) | 0.2432 (6) | −0.2604 (3) | 0.064 (2) |
| H4 | 0.035524 | 0.219673 | −0.231691 | 0.076* |
| C5 | 0.0117 (2) | 0.3145 (7) | −0.3206 (3) | 0.075 (3) |
| H5 | 0.063524 | 0.338538 | −0.332028 | 0.090* |
| C6 | −0.0490 (3) | 0.3497 (7) | −0.3635 (2) | 0.068 (2) |
| H6 | −0.037815 | 0.397334 | −0.403741 | 0.081* |
| C7 | −0.2253 (3) | 0.2047 (7) | −0.2686 (3) | 0.0354 (14) |
| C8 | −0.2425 (3) | 0.1411 (7) | −0.2011 (3) | 0.0307 (12) |
| C9 | −0.1820 (4) | 0.1018 (8) | −0.1612 (3) | 0.0381 (14) |
| C10 | −0.0999 (4) | 0.1308 (8) | −0.1789 (4) | 0.0454 (16) |
| C11 | −0.3637 (4) | 0.1380 (9) | −0.1299 (3) | 0.0391 (14) |
| H11A | −0.339189 | 0.060979 | −0.098350 | 0.047* |
| H11B | −0.417472 | 0.097800 | −0.136060 | 0.047* |
| C12 | −0.3646 (3) | 0.3238 (9) | −0.1049 (3) | 0.0389 (16) |
| C13Aa | −0.3055 (17) | 0.421 (3) | −0.0564 (12) | 0.0572 (9) |
| H13Aa | −0.260820 | 0.371588 | −0.037770 | 0.069* |
| C13Bb | −0.4039 (16) | 0.465 (3) | −0.1255 (11) | 0.0572 (9) |
| H13Bb | −0.440066 | 0.458116 | −0.158958 | 0.069* |
| C14 | −0.3325 (5) | 0.5899 (12) | −0.0472 (5) | 0.069 (2) |
| H14a | −0.315837 | 0.664645 | −0.014319 | 0.082* |
| H14Ab | −0.309934 | 0.674803 | −0.020466 | 0.082* |
| C15 | −0.3865 (5) | 0.6346 (13) | −0.0919 (5) | 0.072 (3) |
| H15a | −0.404455 | 0.751174 | −0.094774 | 0.086* |
| H15Ab | −0.407988 | 0.746210 | −0.099887 | 0.086* |
| Cl2 | −0.05384 (12) | 0.9930 (2) | −0.47863 (11) | 0.0534 (6) |
| S2Ac | 0.0555 (5) | 0.5925 (11) | −0.5214 (5) | 0.0483 (7) |
| S2Bd | 0.17186 (17) | 0.5038 (3) | −0.42562 (17) | 0.0483 (7) |
| O3 | 0.0315 (3) | 0.7682 (7) | −0.2609 (2) | 0.0526 (13) |
| O4 | −0.2030 (3) | 0.9040 (8) | −0.4229 (3) | 0.0653 (15) |
| N2 | 0.0727 (3) | 0.8673 (7) | −0.3768 (3) | 0.0413 (12) |
| H2 | 0.101284 | 0.890664 | −0.343725 | 0.050* |
| C16 | −0.1210 (2) | 0.6810 (6) | −0.21950 (19) | 0.0477 (17) |
| H16 | −0.080097 | 0.655324 | −0.191214 | 0.057* |
| C17 | −0.10454 (18) | 0.7534 (5) | −0.2795 (2) | 0.0365 (15) |
| C18 | −0.1656 (2) | 0.7918 (5) | −0.32177 (18) | 0.0411 (16) |
| C19 | −0.2431 (2) | 0.7578 (6) | −0.3041 (2) | 0.053 (2) |
| H19 | −0.283933 | 0.783530 | −0.332339 | 0.064* |
| C20 | −0.2595 (2) | 0.6854 (6) | −0.2441 (3) | 0.062 (2) |
| H20 | −0.311327 | 0.662666 | −0.232203 | 0.074* |
| C21 | −0.1984 (3) | 0.6470 (6) | −0.2018 (2) | 0.059 (2) |
| H21 | −0.209410 | 0.598562 | −0.161640 | 0.071* |
| C22 | −0.0223 (4) | 0.7878 (8) | −0.2975 (3) | 0.0352 (14) |
| C23 | −0.0053 (3) | 0.8517 (7) | −0.3653 (3) | 0.0334 (13) |
| C24 | −0.0672 (4) | 0.8932 (8) | −0.4045 (3) | 0.0382 (14) |
| C25 | −0.1492 (3) | 0.8664 (8) | −0.3866 (3) | 0.0407 (15) |
| C26 | 0.1156 (4) | 0.8500 (9) | −0.4376 (3) | 0.0418 (15) |
| H26A | 0.169278 | 0.890456 | −0.431589 | 0.050* |
| H26B | 0.091109 | 0.925967 | −0.469581 | 0.050* |
| C27 | 0.1167 (3) | 0.6627 (10) | −0.4622 (2) | 0.0401 (16) |
| C28Ac | 0.142 (2) | 0.510 (2) | −0.4309 (10) | 0.0483 (7) |
| H28Ac | 0.157516 | 0.508141 | −0.388066 | 0.058* |
| C29 | 0.1409 (5) | 0.3505 (10) | −0.4730 (4) | 0.059 (2) |
| H29d | 0.157910 | 0.233581 | −0.468600 | 0.071* |
| H29Ac | 0.168864 | 0.244904 | −0.468470 | 0.071* |
| C28Bd | 0.0812 (7) | 0.5920 (13) | −0.5164 (6) | 0.0483 (7) |
| H28Bd | 0.054888 | 0.658046 | −0.547458 | 0.058* |
| C30 | 0.0911 (5) | 0.3955 (9) | −0.5179 (4) | 0.064 (2) |
| H30d | 0.065959 | 0.317940 | −0.546068 | 0.077* |
| H30Ac | 0.075901 | 0.311728 | −0.548380 | 0.077* |
-
aOccupancy: 0.501(6), bOccupancy: 0.499(6), cOccupancy: 0.209(6), dOccupancy: 0.791(6).
Source of materials
2,3-Dichloro-1,4-naphthoquinone (0.22 mmol) and NaHCO3 (0.44 mmol) were mixed uniformly and moved to a 100 mL double mouth flask. Thiophen-2-ylmethan-amine (0.22 mmol, dissolved with 40 mL of anhydrous methanol) was added to the above mixed solid to start reaction with magnetic stirring at 0 °C in anhydrous environment. The reaction process was monitored by TLC using petroleum ether (60–90 °C boiling range)/acetic ether (6:1 v/v) as developing phase. After 24 h, the reacting mixture was concentrated by a rotary evaporator (60 °C) to achieve a crude solid. This solid was subsequently dissolved in a mixed solvent of methanol-tetrahydrofuran to give a clear red solution after filtration, from which red flat crystals were obtained during the course of volatilization at room temperature. The melting point was determined as 411–412 K using a XT-4 melting point instrument (Beijing Taike Instrument Co., Ltd, China). NMR spectra were performed on a DRX-400 Bruker NMR spectrometer (Bruker, Germany). HRAPCI-MS: [M+H]− found 304.01892; C15H11O2NClS [M+H]+ requires 304.01935. 1 H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: [ppm] 8.15 (dd, J = 7.6, 1.3 Hz, 1H, H-4), 8.04 (dd, J = 7.6, 1.4 Hz, 1H, H-1), 7.73 (td, J = 7.6, 1.4 Hz, 1H, H-5), 7.64 (td, J = 7.6, 1.3 Hz, 1H, H-6), 7.29 (dd, J = 5.1, 1.2 Hz, 1H, H-15), 7.07 (dd, J = 3.5, 1.2 Hz, 1H, H-13), 7.00 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.5 Hz, 1H, H-14), 6.19 (s, 1H, N–H), 5.23 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, 2H, H-11). 13 C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ: [ppm] 180.3 (C-10), 176.9 (C-7), 143.6 (C-8), 140.2 (C-12), 134.9 (C-6), 132.6 (C-5), 132.5 (C-3), 129.8 (C-2), 127.2 (C-15), 126.9 (C-1), 126.5 (C-4, 13), 125.9 (C-14), C-9 (signal absence), 43.7 (C-11).
Experimental details
Using Olex2 [2], the structure was solved with the olex2.solve [3] structure solution program using Charge Flipping and refined with the SHELXL [7] refinement package using Least Squares minimization. The H atoms were placed in idealized positions and treated as riding on their parent atoms, with d(C–H) = (0.97) Å (methylene), Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C), d(C–H) = (0.93) Å (aromatic), Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C), and d(N–H) = (0.86) Å, Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(N).
Comment
Derivatives with similar structure to that of the title compound have been reported to possess various bioactivities: 2-chloro-3-((furan-2-ylmethyl)amino)-1,4-naphthoquinone showed high antifungal activity against Candida albicans and Aspergillus niger, while 2-chloro-3-((pyridin-2-ylmethyl) or (pyridin-3-ylmethyl) amino)-1,4-naphthoquinone manifested excellent activity against gram positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis) [8]. The compound 2-chloro-3-(benzylamino)-naphthalene-1,4-dione is one of the best performing multitarget-directed molecules in the anti-Alzheimer’s Disease agents screening, which experienced a high potency profile in inhibiting β-amyloid (Aβ40) aggregation, PHF6 tau fragment, AChE enzyme jointly with a remarkable inhibitory activity against MAO B [9]. It also had some effect on neutrophil degranulation in anti-inflammatory investigation and significant inhibitory effect on mast cell degranulation in antiallergic assay [10]. In our group, the title compound was synthesized for anticancer assay and further to investigate its interactions with Caspase-3 and Topoisomerase-II α/β, so it is necessary to study the single crystal structure.
The asymmetric unit of the title structure contains two molecules 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, in which the thiophene moieties are disordered, but all other values of the geometric parameters are normal. The crystal packing is stabilized by intermolecular hydrogen bonds: N1–H1…O3 (d(N1–H1…O3) = 3.010 Å; ∠ N1–H1…O3 = 130°), N2–H2A…O1 (d(N2–H2A…O1) = 3.008 Å; ∠ N2–H2A…O1 = 133°).
By a search for a similar molecular scaffold three similar compounds, 2-chloro-3-((2-thienylethyl) amino)-1,4-naphtho-quinone [11], 2-bromo-3-((2-thienylmethyl)amino)-1,4-na-phthoquinone [12] and 2-chloro-3-((2-furylmethyl) amino)-1,4-naphthoquinone [8] were found, in which, the first one owned one more methylene than the title compound at the fatty-thienyl moiety [11], the second one was not 2-chloro but 2-bromo substituent [12], while the third one had a furan ring instead of the thienyl group in the title compound [8]. Furthermore, amazing difference among them was the number of molecules in the asymmetric unit of crystal structure, the three reported crystals had only one molecules in their asymmetric units [8, 11, 12].
Funding source: Education Department of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2019KY0329
Funding source: Guangxi Key Laboratory of Zhuang and Yao Ethnic Medicine
Award Identifier / Grant number: GXZYZZ2019-7
Funding source: Education Department of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region
Award Identifier / Grant number: J16067-11
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by grants from Promotion of Young and Middle-aged Teachers’ Basic Scientific Research Ability in Guangxi Universities, Education Department of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (grant no. 2019KY0329), Key laboratory opening topic fund, Guangxi Key Laboratory of Zhuang and Yao Ethnic Medicine (grant no. GXZYZZ2019-7), Opening topic fund of Key Laboratory of TCM Extraction and Purification and Quality Analysis (Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine), Education Department of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (grant no. J16067-11).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX3, SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2016.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Bourhis, L. J., Dolomanov, O. V., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. The anatomy of a comprehensive constrained, restrained refinement program for the modern computing environment – Olex2 dissected. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 59–75; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314022207.Search in Google Scholar
4. Palatinus, L., Chapuis, G. SUPERFLIP-a computer program for the solution of crystal structures by charge flipping in arbitrary dimensions. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 786–790; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889807029238.Search in Google Scholar
5. Palatinus, L., van der Lee, A. Symmetry determination following structure solution in P1. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2008, 41, 975–984; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808028185.Search in Google Scholar
6. Palatinus, L., Prathapa, S. J., van Smaalen, S. EDMA: a computer program for topological analysis of discrete electron densities. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 575–580; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889812016068.Search in Google Scholar
7. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and CrystalStructure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar
8. Singh, V. K., Verma, S. K., Kadu, R., Mobin, S. M. Identification of unusual C–Cl⃛π contacts in 2-(alkylamino)-3-chloro-1,4-naphthoquinones: effect of N-substituents on crystal packing, fluorescence, redox and anti-microbial properties. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 43669–43686; https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra02295a.Search in Google Scholar
9. Campora, M., Canale, C., Gatta, E., Tasso, B., Laurini, E., Relini, A., Pricl, S., Catto, M., Tonelli, M. Multitarget biological profiling of new naphthoquinone and anthraquinone-based derivatives for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 447–461; https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00624.Search in Google Scholar
10. Lien, J. C., Huang, L. J., Wang, J. P., Teng, C. M., Lee, K. H., Kou, S. C. Synthesis and antiplatelet, antiinflammatory, and antiallergic activities of 2-substituted 3-chloro-1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1997, 12, 2111–2120; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0968-0896(97)00133-8.Search in Google Scholar
11. Parthiban, C., Ciattini, S., Laura, C., Elango, K. P. Selective colorimetric sensing of fluoride in an aqueous solution by amino-naphthoquinone and its Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(ii) and Zn(II) complexes-effect of complex formation on sensing behavior. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 91265–91274; https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra19309a.Search in Google Scholar
12. Agarwal, G., Lande, D. N., Chakrovarty, D., Gejji, S. P., Gosavi-Mirkute, P., Patil, A., Salunke-Gawali, S. Bromine substituted aminonaphthoquinones: synthesis, characterization, DFT and metal ion binding studies. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 88010–88029; https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra20970j.Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Li-Mei Jia et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO

