Abstract
C2H6O⋅C6H6N2O⋅C7H6O4, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 7.4217(18) Å, b = 7.7021(18) Å, c = 15.362(4) Å, α = 79.223(2)°, β = 82.086(3)°, γ = 65.182(2)°, V = 781.2(3) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0444, wRref(F2) = 0.1341, T = 296(2) K.
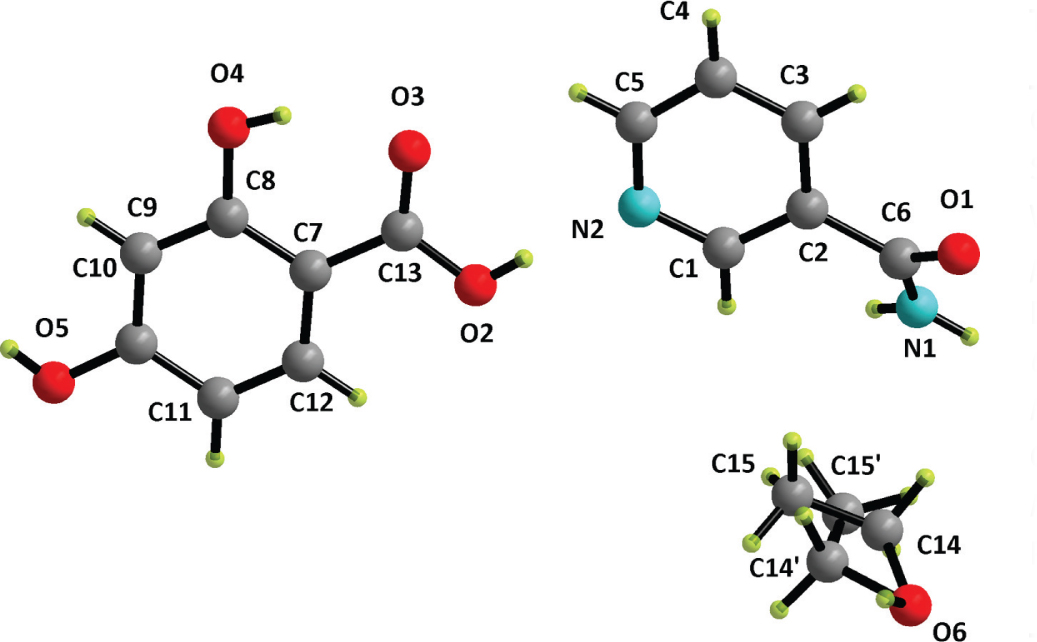
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.42 × 0.35 × 0.27 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.11 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.5°, 99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 5984, 2887, 0.014 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2225 |
| N(param)refined: | 232 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], [3], Olex2 [4], Diamond [5] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.8679(3) | 0.5277(3) | 0.71896(11) | 0.0427(4) |
| H1 | 0.9264 | 0.3957 | 0.7388 | 0.051* |
| C2 | 0.8508(3) | 0.6550(3) | 0.77568(11) | 0.0413(4) |
| C3 | 0.7657(3) | 0.8516(3) | 0.74504(12) | 0.0480(4) |
| H3 | 0.7501 | 0.9410 | 0.7817 | 0.058* |
| C4 | 0.7045(3) | 0.9128(3) | 0.65966(12) | 0.0501(5) |
| H4A | 0.6507 | 1.0437 | 0.6372 | 0.060* |
| C5 | 0.7248(3) | 0.7761(3) | 0.60848(11) | 0.0469(4) |
| H5A | 0.6812 | 0.8179 | 0.5513 | 0.056* |
| C6 | 0.9141(3) | 0.5864(3) | 0.86878(11) | 0.0475(4) |
| C7 | 0.7387(2) | 0.3156(2) | 0.39116(10) | 0.0373(4) |
| C8 | 0.6794(2) | 0.3947(2) | 0.30447(11) | 0.0386(4) |
| C9 | 0.6861(3) | 0.2763(2) | 0.24520(11) | 0.0424(4) |
| H9 | 0.6472 | 0.3294 | 0.1878 | 0.051* |
| C10 | 0.7509(3) | 0.0789(3) | 0.27166(12) | 0.0440(4) |
| C11 | 0.8093(3) | −0.0019(3) | 0.35758(12) | 0.0477(4) |
| H11 | 0.8524 | −0.1344 | 0.3754 | 0.057* |
| C12 | 0.8025(3) | 0.1164(3) | 0.41530(12) | 0.0441(4) |
| H12 | 0.8417 | 0.0621 | 0.4726 | 0.053* |
| C13 | 0.7363(2) | 0.4415(3) | 0.45270(11) | 0.0408(4) |
| C14a | 0.7028(9) | 0.1979(11) | 0.9960(3) | 0.141(2) |
| H14Aa | 0.7093 | 0.3129 | 1.0098 | 0.169* |
| H14Ba | 0.8375 | 0.0991 | 0.9954 | 0.169* |
| C14′b | 0.6282(19) | 0.148(2) | 0.9723(6) | 0.092(4) |
| H14Cb | 0.5281 | 0.2674 | 0.9451 | 0.110* |
| H14Db | 0.6130 | 0.0418 | 0.9534 | 0.110* |
| C15a | 0.6427(11) | 0.2394(9) | 0.9120(3) | 0.138(2) |
| H15Aa | 0.5635 | 0.1703 | 0.9075 | 0.207* |
| H15Ba | 0.7572 | 0.2015 | 0.8708 | 0.207* |
| H15Ca | 0.5651 | 0.3758 | 0.8985 | 0.207* |
| C15′b | 0.825(2) | 0.142(4) | 0.9401(13) | 0.181(9) |
| H15Db | 0.8747 | 0.1854 | 0.9826 | 0.271* |
| H15Eb | 0.8158 | 0.2252 | 0.8844 | 0.271* |
| H15Fb | 0.9142 | 0.0122 | 0.9323 | 0.271* |
| N1 | 1.0752(2) | 0.4266(2) | 0.88331(10) | 0.0580(5) |
| H1A | 1.1148 | 0.3834 | 0.9362 | 0.070* |
| H1B | 1.1408 | 0.3653 | 0.8399 | 0.070* |
| N2 | 0.8040(2) | 0.5862(2) | 0.63687(9) | 0.0435(4) |
| O1 | 0.8151(2) | 0.6792(2) | 0.92925(8) | 0.0694(5) |
| O2 | 0.8033(2) | 0.35151(19) | 0.53040(8) | 0.0560(4) |
| H2 | 0.7950 | 0.4307 | 0.5615 | 0.084* |
| O3 | 0.6785(2) | 0.61795(18) | 0.43230(8) | 0.0526(4) |
| O4 | 0.6182(2) | 0.58690(17) | 0.27520(8) | 0.0531(4) |
| H4 | 0.6095 | 0.6438 | 0.3167 | 0.080* |
| O5 | 0.7605(2) | −0.04366(19) | 0.21642(9) | 0.0605(4) |
| H5 | 0.7058 | 0.0189 | 0.1710 | 0.091* |
| O6 | 0.5927(3) | 0.1356(3) | 1.06639(11) | 0.0925(6) |
| H6 | 0.4744 | 0.1931 | 1.0571 | 0.139* |
aOccupancy: 0.746(8), bOccupancy: 0.254(8).
Source of material
2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid (1 mmol) and nicotinamide (1 mmol) were dissolved in the ethanol (4 mL)-water (2 mL), and this solution was slowly evaporated at room temperature, resulting in colorless block crystals after one week.
Experimental details
The Uiso values were set to 1.5Ueq(C) hydrogen atoms in hydroxyl and methyl groups, and 1.2Ueq(C or N) for the rest. The electron density indicated disorder in ethanol.
Comment
Numerous research regarding co-crystals of nicotinamide molecules have been carried out due to its importance as a pyridine derivative with biological activity and pharmacological property. The pyridine nitrogen atom and the carbonyl oxygen atom of nicotinamide are acceptors, but amide protons are donors, thus affording abundant hydrogen-bond motifs with organic carboxylic acids. For example, malonic acid [6], citric acid [7], pimelic acid [6], [7], succinic acid [8], cycle-carboxylic acids [9] and benzoic acids [6, 10; 11; 12] have been used to construct co-crystals with nicotinamide to investigate the stoichiometric variation, proton transfer, polymorphism and phase transition.
The asymmetric unit of the title structure comprises one nicotinamide, one 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid molecule and one disordered ethanol molecule (see the Figure). This co-crystal is isostructural to the 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid–nicotinamide-methanol co-crystal molecule [6], however, the large difference in structural parameters is still found. For example, the angle of C1—C2—C6—N1 twists more strongly [37.9(3)°]. The lengths of C—O and C—N bonds in the amide group are larger about 0.33 and 0.44 Å compared with its isostructural compound [6], respectively. The C—O bond lengths of 1.310(2) and 1.232(2) Å for the carboxylic acid group are more typical characteristics of an organic acid, revealing no proton transfer between nicotinamide and 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid.
Complex hydrogen bonds are found in this co-crystal. Two nicotinamide molecules construct a dimer by amide–amide hydrogen bonds. This dimer connects two 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid with an intra molecular hydrogen bond, through the heteromeric O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds between the COOH group of acid and the pyridine N of the nicotinamide, to generate a tetramer. Furthermore each 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid in this tetramer is connected to one ethanol molecule by its phenol oxygen in the para-position, forming a phenol–alcohol hydrogen bond. More importantly, the two carbonyl oxygen atoms of the amide group form a hydrogen bond with two adjacent ethanol molecules. These intermolecular hydrogen bonds result in a 3-D hydrogen bonded network. In addition, the pyridine and benzene ring further stabilize this crystal by the π-π packing interactions with the Cg-Cg distance of 3.76 Å.
Acknowledgements
The Special Scientific Research Projects of the Henan Academy of Sciences (200403007, 200603026) is gratefully acknowledged.
References
1. Bruker. SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2009).Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXT – Integrated space-group and crystal structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H.: OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 42 (2009) 339–341.10.1107/S0021889808042726Suche in Google Scholar
5. Brandenburg, K.: DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Version 3.2i. Crystal Impact, Bonn, Germany (2012).Suche in Google Scholar
6. Lemmerer, A.; Bernstein, J.: The co-crystal of two GRAS substances: (citric acid).(nicotinamide). formation of four hydrogen bonding heterosynthons in one co-crystal. CrystEngComm 12 (2010) 2029–2033.10.1039/b927422gSuche in Google Scholar
7. Thompson, L. J.; Voguri, R. S.; Cowell, A.; Male, L.; Tremayne, M.: The cocrystal nicotinamide-succinic acid (2/1). Acta Crystallogr. C66 (2010) o421–o424.10.1107/S0108270110027319Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Lemmerer, A.; Fernandes, M. A.: Adventures in co-crystal land: high Z′, stoichiometric variations, polymorphism and phase transitions in the co-crystals of four liquid and solid cyclic carboxylic acids with the supramolecular reagent isonicotinamide. New J. Chem. 36 (2012) 2242–2252.10.1039/c2nj40186jSuche in Google Scholar
9. Aakeröy, C. B.; Beatty, A. M.; Helfrich, B. A.; Nieuwenhuyzen, M.: Do polymorphic compounds make good cocrystallizing agents? a structural case study that demonstrates the importance of synthon flexibility. Cryst. Growth Des. 3 (2003) 159–165.10.1021/cg025593zSuche in Google Scholar
10. Zhang, S.-W.; Harasimowicz, M. T.; de Villiers, M. M.; Yu, L.: Cocrystals of nicotinamide and (R)-mandelic acid in many ratios with anomalous formation properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 (2013) 18981–18989.10.1021/ja4103887Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Ngoma Tchibouanga, R. R.; Jacobs, A.: 3-Chloro-4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid co-crystals with nicotinamide, isonicotinamide, phenazine and 4,4′-bipyridine: an investigation of synthon motifs. J. Mol. Struct. 1204 (2020) 127195.10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.127195Suche in Google Scholar
12. Wicker, J. G. P.; Crowley, L. M.; Robshaw, O.; Little, E. J.; Stokes, S. P.; Cooper, R. I.; Lawrence, S. E.: Will they co-crystallize? CrystEngComm 19 (2017) 5336–5340.10.1039/C7CE00587CSuche in Google Scholar
©2020 Bencai Dai et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-5-(4-carboxy-benzylamino)-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-4,4′-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl-κ2N:N′)dicadmium(II)], C25H22N3O8Cd
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-(2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium-1-yl)phenoxy)acetate, C19H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-μ2-bis(2-(2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C38H28Cl4N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-benzyl-3-hydroxy-3,6-diphenylpiperazine-2,5-dione, C33H29N3O3
- The crystal structure 2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′-(2-(3-amino-4-chlorobenzoyl)benzoato-κ1O)-(2-(3-amino-4-chlorobenzoyl)benzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II) — ethanol (1/1), C40H32Cl2N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-2-carboxy-4-(3-carboxy-5-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-bis(μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-k1N)copper(II)], C60H40N4O9Cu
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium catena-[di(μ-aqua)-bis(μ9-benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylato)pentalithium], C20H16Li5NO13
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(3,5-di(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-ido-κ1N)nickel(II) dihydrate, C24H28O6N10Ni
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1-methylimidazole-κ1N)-oxido-(sulfato-κ1O)vanadium(IV), C16H24N8O5SV
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(6,11-dioxo-2,3,6,11-tetrahydro-1H-benzo[f]pyrrolo[2,1-a]isoindole-5-carbonyl)benzoate, C24H17NO5
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-hydroxy-4-(2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethoxy)benzylidene) nicotinohydrazide monohydrate, C20H24N4O3 ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-(1-(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-κ3N:N′:N′′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/4), C42H52N18O10Co
- The crystal structure bis{hexakis(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)cobalt(II)} tetrakis(μ3-oxido)-octakis(μ2-oxido)-tetradecaoxido-octamolybdate(VI), C24H36CoMo4N12O13
- Crystal structure of di-μ-nicotinato-κ2N:O; κ2O:N-bis-[aqua-bis(benzyl)(nicotinato-κ2O,O′)tin(IV)], C52H48N4O10Sn2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)phenoxy)benzoic acidmanganese(II) monohydrate, C40H30N8O7MnCl2
- The crystal structure of benzyl 3β-acetylglycyrrhetate, C39H54O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-benzyl-3-(4-methoxystyryl)quinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C24H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of trans-dichloridobis(4-chlorophenyl-κC1)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tin(IV) dimethylsulphoxide solvate, C26H22Cl4N2OSSn
- Crystal structure of phenyl(1,3,4a-triphenyl-4a,5,6,10b-tetrahydro-1H-[1,4]oxazino[2,3-c]quinolin-5-yl)methanone, C36H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4aS,5S,6aS,6a1S, 10aS)-4a,5,6a,6a1,9,10-hexahydro-7H-4,5-methanocyclobuta[4,5]naphtho[8a,1-b]pyran-6(2H)-one, C15H16O2
- Crystal structure of [(Z)-O-isopropyl N-(4-chlorophenyl)thiocarbamato-κS]-(triphenylphosphine-κP)-gold(I), C28H26AuClNOPS
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-P,P′)-bis[(Z)-O-isopropyl N-(4-chlorophenyl)thiocarbamato-S]-di-gold(I) acetonitrile di-solvate, C54H50Au2Cl2FeN2O2P2S2⋅2(C2H3N)
- Crystal structure of (6aR,6a1S,10aS)-2,4a,6a,6a1,9,10-hexahydro-7H-4,5-methanocyclobuta[4,5]naphtho[8a,1-b]pyran, C15H16O
- Crystal structure of 5,17-diformyl-25,26,27,28-tetrahydroxycalix[4]arene- dichloromethane, C31H26Cl2O6
- Crystal structure of 2-tert-butyl 1-methyl 5-{4-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl}-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1,2-dicarboxylate, C19H24N2O6
- Crystal structure of [2-carboxybenzene-1-thiolato-S]-(triethylphosphane-P)-gold(I), C13H20AuO2PS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(5-methyl-2-aldehyde-phenolato-κ2O1,O2)copper(II), C16H14CuO4
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(di(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-μ4-silanetetrayltetrakis(benzene-4,1-diyl)tetrakis (hydrogen phosphonato)-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′) dicadmium(II)], C44H42N4O15P4Cd2Si
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(N,N-diethylcarbamodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-P)-di-silver(I), C22H50Ag2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(pyrrolidine-1-carbodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-κP)disilver(I), C22H46Ag2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-methylcarbamodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-P)-di-silver(I), C20H46Ag2N2O2P2S4
- The crystal structure of (2E,2′E)-,2,2′-bis[1-(2-pyrazinyl)ethylidene]carbonimidic dihydrazide, C13H15N9
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(quinolin-2-ylmethyl)-2-((1-(quinolin-2-ylmethyl)pyridin-2(1H)-ylidene)amino)pyridin-1-ium, C30H25BrN5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imdazole-κ2N:N′)-(1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imdazole-κ1N)-(methanol-κ1O)mercury(II)] dinitrate, C21H22N12O7Hg
- Crystal structure of 1-(6-hydroxy-2-phenylbenzofuran-5-yl)ethan-1-one, C16H12O3
- The crystal structure of oxonium hexaquaaluminium disulfate hexahydrate
- Crystal structure of catena{(μ2-1,10-phenanthroline-κ4N,N,N′,N′)-(μ2-1,10-phenanthroline-κ3N,N,N′)potassium(I) {[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)iminiumyl](sulfanidyl)methyl}sulfanide hemi(1,10-phenanthroline)}, {C24H16KN4, 0.5(C12H8N2), C5H10NO2S2}
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[(N,N-di-isobutyl)dithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′]-di(4-methylbenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C25H36ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)-(4-chloro-4-pyridyl-2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine-κ2N,N′) rhodium(III) hexaflourophosphate, C31H29Cl2F6N3PRh
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis-(3,5-dinitro-1,2,4-triazolato-κ2N:O)-(μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C16H10CuN14O8
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-bis(μ3-3,3′-((5-carboxylato-1,3-phenylene)bis(oxy))dibenzoato)-tris(1,10-phenanthroline)cobalt(II)], C78H46N6O20Co3
- The crystal structure of 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid–nicotinamide–methanol (1/1/1), C15H18N2O6
- The crystal structure of aqua{N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis[(1H-benzimidazol-κN3) methyl]cyclohexane-1,2-diamine}lead(II) diacetate–methanol (1/2), C44H54N10O7Pb
- Crystal structure of (2-amino-5-bromo-3-iodophenyl)(3-(4-chlorophenyl)oxiran-2-yl)methanone, C15H10BrClINO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 3-octyl-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione, C23H28N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-azido-N-(4-nitrophenyl)acetamide, C8H7N5O3
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (1S,2R,5R)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-oxa-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-3-carboxylate, C17H23NO5
- Crystal structure of 4-[(4-methoxy-2-nitrophenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H14N2O6
- Crystal structure of 3-ethyl-1-[(E)-[(2E)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]amino]thiourea, C12H15N3S
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridin-1,1′-dium poly[bis(μ4-benzene-1,3,5-triyltris(hydrogen phosphonato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′))zinc(II)], C11H11NO9P3Zn
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)butane-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-κS]-di-gold(I), C44H42Au2F2N2O2P2S2
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)hexane-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-κS]digold(I), C46H46Au2F2N2O2P2S2
- Crystal structure of tetrakis (N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-isopropylcarbamodithioato-κS,S′)-(μ2(2-(pyridin-4-yl)vinyl)pyridine-κN,N′)dicadmium(II), C36H58Cd2N6O4S8
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-en-1-yl)-1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carbonitrile, C20H12F6N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(octahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrolium)pentachlorobismuthate(III), (C7NH14)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of diaqua-tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(p-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κN)samarium(III), C24H36N9O15Sm
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-(2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)phenyl)-2-(4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)acetate, C23H23NO6
- Crystal structure of O-hexyl benzoylcarbamothioate, C14H19NO2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(O-methyl phenylcarbamothioamide-κS)-bis(triphenylphosphane-κP)silver(I), C44H39AgClNOP2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(O-ethyl phenylcarbamothioamide-κS)-bis(triphenylphosphane-κP)-silver(I), C45H41AgClNOP2S
- Crystal structure of 4-[(2-methoxyphenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H15NO4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazinane-3-carboxylate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua(μ2-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato)cadmium(II)], C6H8CdN2O7
- Crystal structure of (1S)-N-(chloromethyl)-1-((4S,6aR,8aS, 8bR,9aR)-4-methoxy-6a,8a-dimethyl-1,3,4, 5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9a,10,10a,10b-tetradecahydro-8bH-naphtho[2′,1′:4,5] indeno[1,2-b]oxiren-8b-yl)-N-methylethan-1-amine, C24H46ClNO5
- Crystal structure of 4-[(3,5-dichlorophenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C11H11Cl2NO3
- Crystal structure of (2Z)-2-amino-3-[(E)-[(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)methylidene]-amino]but-2-enedinitrile, C11H8N4O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-1-[(E)-(4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)amino]thiourea, C12H17N3S
- Crystal structure of carbonyl{hydridotris[3-phenyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl]borato-κ3N,N′N′′}copper(I), C31H28BCuN6O
- Crystal structure of ethane-1,2-diylbis(diphenylphosphine oxide) – dihydrogenperoxide (1/2), C26H28O6P2
- Crystal structure of 2-(pyridin-2-ylamino)pyridinium chloride dibenzyldichlorostannane, [C10H10N3]Cl, C14H14Cl2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-[(3-methoxyphenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H15NO4
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(tri-4-tolylphosphane oxide-κO)-di(4-chlorophenyl-κC)tin(IV), C54H50Cl4O2P2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichloridodimethylbis(tri-4-tolylphosphane oxide-κO)-tin(IV), C44H48Cl2O2P2Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)-bis(4-tolyl-κC)tin(IV), C24H22ClNOSn
- Crystal structure of (E)-dichloro(1-chloro-3-methoxyprop-1-en-2-yl)(4-methoxyphenyl)-λ4-tellane, C11H13Cl3O2Te
- Crystal structure of bis{N-methyl-N′-[3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylpropane-1-ylidene]carbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C26H36N6O2S2Zn
- Crystal structure of (2-carboxy-4-(3-carboxy-5-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II), C40H24N4O9Co
- The crystal structure of (3S,8R,10R,14R)-17-((2S,5S)-5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-12-oxohexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl acetate, C32H52O5
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-S]digold(I) chloroform solvate, C50H42Au2F2FeN2O2P2S2, CHCl3
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C24H20N8O4MoCo
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ4-5-(4-carboxy-benzylamino)-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-4,4′-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl-κ2N:N′)dicadmium(II)], C25H22N3O8Cd
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-(2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium-1-yl)phenoxy)acetate, C19H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-μ2-bis(2-(2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)], C38H28Cl4N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-4-benzyl-3-hydroxy-3,6-diphenylpiperazine-2,5-dione, C33H29N3O3
- The crystal structure 2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′-(2-(3-amino-4-chlorobenzoyl)benzoato-κ1O)-(2-(3-amino-4-chlorobenzoyl)benzoato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II) — ethanol (1/1), C40H32Cl2N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-2-carboxy-4-(3-carboxy-5-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-bis(μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-k1N)copper(II)], C60H40N4O9Cu
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium catena-[di(μ-aqua)-bis(μ9-benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylato)pentalithium], C20H16Li5NO13
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(3,5-di(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-ido-κ1N)nickel(II) dihydrate, C24H28O6N10Ni
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1-methylimidazole-κ1N)-oxido-(sulfato-κ1O)vanadium(IV), C16H24N8O5SV
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(6,11-dioxo-2,3,6,11-tetrahydro-1H-benzo[f]pyrrolo[2,1-a]isoindole-5-carbonyl)benzoate, C24H17NO5
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-hydroxy-4-(2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethoxy)benzylidene) nicotinohydrazide monohydrate, C20H24N4O3 ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ3-(1-(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-κ3N:N′:N′′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/4), C42H52N18O10Co
- The crystal structure bis{hexakis(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)cobalt(II)} tetrakis(μ3-oxido)-octakis(μ2-oxido)-tetradecaoxido-octamolybdate(VI), C24H36CoMo4N12O13
- Crystal structure of di-μ-nicotinato-κ2N:O; κ2O:N-bis-[aqua-bis(benzyl)(nicotinato-κ2O,O′)tin(IV)], C52H48N4O10Sn2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2-(3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)phenoxy)benzoic acidmanganese(II) monohydrate, C40H30N8O7MnCl2
- The crystal structure of benzyl 3β-acetylglycyrrhetate, C39H54O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-benzyl-3-(4-methoxystyryl)quinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C24H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of trans-dichloridobis(4-chlorophenyl-κC1)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tin(IV) dimethylsulphoxide solvate, C26H22Cl4N2OSSn
- Crystal structure of phenyl(1,3,4a-triphenyl-4a,5,6,10b-tetrahydro-1H-[1,4]oxazino[2,3-c]quinolin-5-yl)methanone, C36H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of (4aS,5S,6aS,6a1S, 10aS)-4a,5,6a,6a1,9,10-hexahydro-7H-4,5-methanocyclobuta[4,5]naphtho[8a,1-b]pyran-6(2H)-one, C15H16O2
- Crystal structure of [(Z)-O-isopropyl N-(4-chlorophenyl)thiocarbamato-κS]-(triphenylphosphine-κP)-gold(I), C28H26AuClNOPS
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-P,P′)-bis[(Z)-O-isopropyl N-(4-chlorophenyl)thiocarbamato-S]-di-gold(I) acetonitrile di-solvate, C54H50Au2Cl2FeN2O2P2S2⋅2(C2H3N)
- Crystal structure of (6aR,6a1S,10aS)-2,4a,6a,6a1,9,10-hexahydro-7H-4,5-methanocyclobuta[4,5]naphtho[8a,1-b]pyran, C15H16O
- Crystal structure of 5,17-diformyl-25,26,27,28-tetrahydroxycalix[4]arene- dichloromethane, C31H26Cl2O6
- Crystal structure of 2-tert-butyl 1-methyl 5-{4-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl}-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1,2-dicarboxylate, C19H24N2O6
- Crystal structure of [2-carboxybenzene-1-thiolato-S]-(triethylphosphane-P)-gold(I), C13H20AuO2PS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(5-methyl-2-aldehyde-phenolato-κ2O1,O2)copper(II), C16H14CuO4
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-(di(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-μ4-silanetetrayltetrakis(benzene-4,1-diyl)tetrakis (hydrogen phosphonato)-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′) dicadmium(II)], C44H42N4O15P4Cd2Si
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(N,N-diethylcarbamodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-P)-di-silver(I), C22H50Ag2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(pyrrolidine-1-carbodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-κP)disilver(I), C22H46Ag2N2P2S4
- Crystal structure of bis[μ2-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-methylcarbamodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)]-bis(triethylphosphine-P)-di-silver(I), C20H46Ag2N2O2P2S4
- The crystal structure of (2E,2′E)-,2,2′-bis[1-(2-pyrazinyl)ethylidene]carbonimidic dihydrazide, C13H15N9
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(quinolin-2-ylmethyl)-2-((1-(quinolin-2-ylmethyl)pyridin-2(1H)-ylidene)amino)pyridin-1-ium, C30H25BrN5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imdazole-κ2N:N′)-(1-((benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,3-imdazole-κ1N)-(methanol-κ1O)mercury(II)] dinitrate, C21H22N12O7Hg
- Crystal structure of 1-(6-hydroxy-2-phenylbenzofuran-5-yl)ethan-1-one, C16H12O3
- The crystal structure of oxonium hexaquaaluminium disulfate hexahydrate
- Crystal structure of catena{(μ2-1,10-phenanthroline-κ4N,N,N′,N′)-(μ2-1,10-phenanthroline-κ3N,N,N′)potassium(I) {[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)iminiumyl](sulfanidyl)methyl}sulfanide hemi(1,10-phenanthroline)}, {C24H16KN4, 0.5(C12H8N2), C5H10NO2S2}
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[(N,N-di-isobutyl)dithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′]-di(4-methylbenzyl-κC)tin(IV), C25H36ClNS2Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)-(4-chloro-4-pyridyl-2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine-κ2N,N′) rhodium(III) hexaflourophosphate, C31H29Cl2F6N3PRh
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis-(3,5-dinitro-1,2,4-triazolato-κ2N:O)-(μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C16H10CuN14O8
- Crystal structure of poly[triaqua-bis(μ3-3,3′-((5-carboxylato-1,3-phenylene)bis(oxy))dibenzoato)-tris(1,10-phenanthroline)cobalt(II)], C78H46N6O20Co3
- The crystal structure of 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid–nicotinamide–methanol (1/1/1), C15H18N2O6
- The crystal structure of aqua{N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis[(1H-benzimidazol-κN3) methyl]cyclohexane-1,2-diamine}lead(II) diacetate–methanol (1/2), C44H54N10O7Pb
- Crystal structure of (2-amino-5-bromo-3-iodophenyl)(3-(4-chlorophenyl)oxiran-2-yl)methanone, C15H10BrClINO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 3-octyl-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione, C23H28N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-azido-N-(4-nitrophenyl)acetamide, C8H7N5O3
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (1S,2R,5R)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-oxa-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-3-carboxylate, C17H23NO5
- Crystal structure of 4-[(4-methoxy-2-nitrophenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H14N2O6
- Crystal structure of 3-ethyl-1-[(E)-[(2E)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]amino]thiourea, C12H15N3S
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridin-1,1′-dium poly[bis(μ4-benzene-1,3,5-triyltris(hydrogen phosphonato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′))zinc(II)], C11H11NO9P3Zn
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)butane-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-κS]-di-gold(I), C44H42Au2F2N2O2P2S2
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)hexane-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-κS]digold(I), C46H46Au2F2N2O2P2S2
- Crystal structure of tetrakis (N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-isopropylcarbamodithioato-κS,S′)-(μ2(2-(pyridin-4-yl)vinyl)pyridine-κN,N′)dicadmium(II), C36H58Cd2N6O4S8
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-en-1-yl)-1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carbonitrile, C20H12F6N2S
- Crystal structure of bis(octahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrolium)pentachlorobismuthate(III), (C7NH14)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of diaqua-tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(p-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κN)samarium(III), C24H36N9O15Sm
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-(2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)phenyl)-2-(4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)acetate, C23H23NO6
- Crystal structure of O-hexyl benzoylcarbamothioate, C14H19NO2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(O-methyl phenylcarbamothioamide-κS)-bis(triphenylphosphane-κP)silver(I), C44H39AgClNOP2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(O-ethyl phenylcarbamothioamide-κS)-bis(triphenylphosphane-κP)-silver(I), C45H41AgClNOP2S
- Crystal structure of 4-[(2-methoxyphenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H15NO4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazinane-3-carboxylate, C13H16N2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua(μ2-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato)cadmium(II)], C6H8CdN2O7
- Crystal structure of (1S)-N-(chloromethyl)-1-((4S,6aR,8aS, 8bR,9aR)-4-methoxy-6a,8a-dimethyl-1,3,4, 5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9a,10,10a,10b-tetradecahydro-8bH-naphtho[2′,1′:4,5] indeno[1,2-b]oxiren-8b-yl)-N-methylethan-1-amine, C24H46ClNO5
- Crystal structure of 4-[(3,5-dichlorophenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C11H11Cl2NO3
- Crystal structure of (2Z)-2-amino-3-[(E)-[(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)methylidene]-amino]but-2-enedinitrile, C11H8N4O2
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-1-[(E)-(4-phenylbutan-2-ylidene)amino]thiourea, C12H17N3S
- Crystal structure of carbonyl{hydridotris[3-phenyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl]borato-κ3N,N′N′′}copper(I), C31H28BCuN6O
- Crystal structure of ethane-1,2-diylbis(diphenylphosphine oxide) – dihydrogenperoxide (1/2), C26H28O6P2
- Crystal structure of 2-(pyridin-2-ylamino)pyridinium chloride dibenzyldichlorostannane, [C10H10N3]Cl, C14H14Cl2Sn
- Crystal structure of 4-[(3-methoxyphenyl)carbamoyl]butanoic acid, C12H15NO4
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(tri-4-tolylphosphane oxide-κO)-di(4-chlorophenyl-κC)tin(IV), C54H50Cl4O2P2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichloridodimethylbis(tri-4-tolylphosphane oxide-κO)-tin(IV), C44H48Cl2O2P2Sn
- Crystal structure of chlorido(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)-bis(4-tolyl-κC)tin(IV), C24H22ClNOSn
- Crystal structure of (E)-dichloro(1-chloro-3-methoxyprop-1-en-2-yl)(4-methoxyphenyl)-λ4-tellane, C11H13Cl3O2Te
- Crystal structure of bis{N-methyl-N′-[3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylpropane-1-ylidene]carbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C26H36N6O2S2Zn
- Crystal structure of (2-carboxy-4-(3-carboxy-5-carboxylatophenoxy)benzoato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II), C40H24N4O9Co
- The crystal structure of (3S,8R,10R,14R)-17-((2S,5S)-5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-12-oxohexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl acetate, C32H52O5
- Crystal structure of (μ2-1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-bis[(Z)N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-S]digold(I) chloroform solvate, C50H42Au2F2FeN2O2P2S2, CHCl3
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C24H20N8O4MoCo

