Abstract
C15H13ClN2O4, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 16.632(2) Å, b = 7.2033(9) Å, c = 12.9261(17) Å, β = 112.87°, V = 1427.0(3) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0409, wRref(F2) = 0.1260, T = 296(2) K.
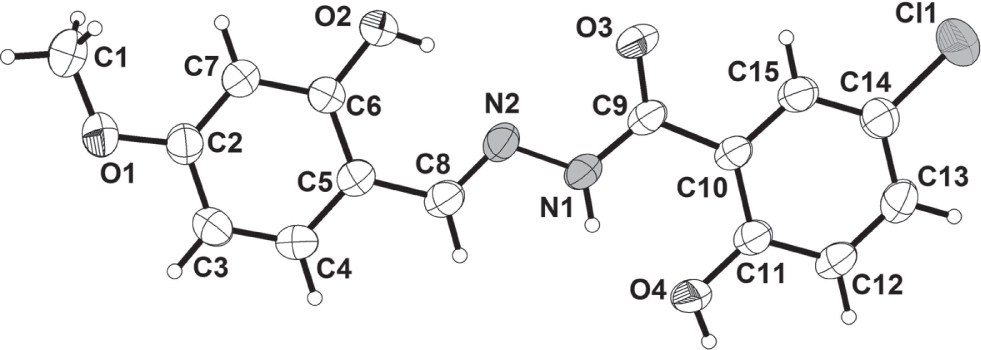
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.08 × 0.06 × 0.04 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.29 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω-scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.1°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 16118, 3329, 0.028 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2608 |
| N(param)refined: | 202 |
| Programs: | Bruker programs [1], SHELX [2], [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | 0.89078(7) | 0.0820(2) | 0.89053(10) | 0.0556(3) |
| O2 | 0.58815(7) | 0.2280(2) | 0.73958(10) | 0.0575(4) |
| H2 | 0.5472 | 0.2414 | 0.6790 | 0.086* |
| O3 | 0.35144(8) | 0.36938(19) | 0.49349(8) | 0.0506(3) |
| O4 | 0.37832(7) | 0.26592(19) | 0.19203(9) | 0.0493(3) |
| H4A | 0.3720 | 0.2315 | 0.1289 | 0.074* |
| N1 | 0.44313(8) | 0.28060(19) | 0.41359(10) | 0.0413(3) |
| H1 | 0.4514 | 0.2631 | 0.3527 | 0.050* |
| N2 | 0.51065(8) | 0.25111(19) | 0.51683(10) | 0.0402(3) |
| Cl1 | 0.04256(3) | 0.48559(9) | 0.19785(4) | 0.0736(2) |
| C1 | 0.89702(12) | 0.1094(3) | 1.00140(15) | 0.0619(5) |
| H1A | 0.8804 | 0.2344 | 1.0096 | 0.093* |
| H1B | 0.9560 | 0.0882 | 1.0528 | 0.093* |
| H1C | 0.8589 | 0.0243 | 1.0172 | 0.093* |
| C2 | 0.81249(10) | 0.1099(2) | 0.80400(13) | 0.0414(3) |
| C3 | 0.81304(11) | 0.0923(3) | 0.69732(14) | 0.0479(4) |
| H3 | 0.8643 | 0.0609 | 0.6885 | 0.057* |
| C4 | 0.73774(11) | 0.1216(2) | 0.60519(13) | 0.0449(4) |
| H4 | 0.7389 | 0.1099 | 0.5341 | 0.054* |
| C5 | 0.65970(10) | 0.1681(2) | 0.61405(12) | 0.0368(3) |
| C6 | 0.66038(9) | 0.1833(2) | 0.72224(12) | 0.0386(3) |
| C7 | 0.73652(10) | 0.1529(2) | 0.81666(13) | 0.0418(4) |
| H7 | 0.7358 | 0.1616 | 0.8881 | 0.050* |
| C8 | 0.58319(10) | 0.2030(2) | 0.51312(12) | 0.0406(3) |
| H8 | 0.5871 | 0.1900 | 0.4436 | 0.049* |
| C9 | 0.36536(10) | 0.3362(2) | 0.40889(11) | 0.0367(3) |
| C10 | 0.29387(9) | 0.3547(2) | 0.29488(11) | 0.0344(3) |
| C11 | 0.30008(9) | 0.3148(2) | 0.19265(12) | 0.0369(3) |
| C12 | 0.22591(11) | 0.3265(2) | 0.09316(12) | 0.0429(4) |
| H12 | 0.2304 | 0.2998 | 0.0252 | 0.052* |
| C13 | 0.14659(10) | 0.3766(2) | 0.09375(13) | 0.0460(4) |
| H13 | 0.0973 | 0.3820 | 0.0272 | 0.055* |
| C14 | 0.14129(10) | 0.4187(2) | 0.19461(13) | 0.0437(4) |
| C15 | 0.21367(10) | 0.4080(2) | 0.29366(12) | 0.0405(3) |
| H15 | 0.2085 | 0.4372 | 0.3609 | 0.049* |
Source of material
A mixture of 2-hydroxy-5-chlorobenzohydrazide (0.186 g, 1 mmol) and 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde (0.152 g, 1 mmol) in 50 mL methanol was stirred at room temperature for 1 h. The mixture was filtered to remove impurties, and then left at room temperature. After a few days, colourless blocks of the title compound formed. Yield (0.25 g, 80%).
Experimental details
Atoms were geometrically placed (C—H = 0.95–0.98 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5 Ueq(parent atom) [1], [2], [3].
Discussion
Schiff bases show interesting properties due to o-hydroxy group forming intra-molecular hydrogen bonds. The hydrazones may act as an efficient chelating ligand, which coordinate with varous transition metals. Some complexes containing the hydrazones ligand have been repored [4], [5], [6]. Schiff base complexes are attracting considerable attention in several different fields ranging from bioinorganic chemistry to solid-state physics. Low-nuclearity species have been extensively studied as models for the water oxidizing complex in photosystem II, whereas nanometer-size clusters with high-spin ground states are currently being investigated as single-molecule magnets. However, to the best of our knowledge, the ligand has not been reported. The similar structure has been reported [7].
As shown in the figure, the title compound crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with one molecule in the asymmetric unit. The bond lengths of N2 = C8, N1—C9, C14—Cl1 and N2—N1 are 1.274, 1.333, 1.727 and 1.386 Å, respectively, which are similar with the directly related structures. The atoms O2, O3, N2, are the coordination atoms of the ligand, one ligand will coordinate with three metal atoms. The transition metal complexes have been reported, but the rare earth metal complexes have not been reported, our group will do this job in the future. This sentence was added after [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [15], [16].
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge scientific and technological project of Henan province (192102310232), the Anyang Key Laboratory for Chemical Biosensing (21302003), and Key discipline of environmental engineer of Anyang Institute of Technology the Natural Science Foundation of China (21471015, 21631003, 21561007, and 21701046), the Innovation Program for High-level Talents of Guizhou Province (No. 2016-5657), the Science and Technology Fund of Guizhou Province (No. 2016-1030), the Major Program for Creative Research Groups of Guizhou Provincial Education Department (2017-028), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (FRF-BD-17-016A).
References
1. Bruker: APEX3, SAINT-Plus, XPREP. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2016).Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXT – Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Thompsom, L. K.; Matthews, C. J.; Zhao, L.; Claire, W.; Leech, M. A.; Howard, J. A. K.; Katsuki, T.: Supramolecular metal helicate structures with incomplete metal ion coordination. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton. Trans. 15 (2001) 2258–2262.10.1039/b102344fSuche in Google Scholar
5. Niel, V.; Milway, V. A.; Dawe, L. N.; Grove, H.; Tandon, S. S.; Abedin, T. S. M.; Kelly, T. L.; Spencer, E. C.; Howard, J. A. K.; Collins, J. L.; Miller, D. O.: Coordination oligomers in self-assembly reactions of some tritopic picolinic dihydrazone ligandss mononuclear, dinuclear, hexanuclear, heptanuclear, and nonanuclear examples. Inorg. Chem. 47 (2008) 176–189.10.1021/ic7016787Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Zhao, L.; Xu, Z. Q.; Grove, H.; Milway, V. A.; Dawe, L. N.; Abedin, T. S. M.; Thompson, L. K.; Kelly, T. L.; Harvey, R. G.; Miller, D. O.; Weeks, L.; Shapter, J. G.; Pope, K. J.: Supramolecular Mn(II) and Mn(II)/Mn(III) grid complexes with [Mn9(μ2-O)12] core structures. Structural, magnetic, and redox properties and surface studies. Inorg. Chem. 43 (2004) 3812–3824.10.1021/ic030319vSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Han, Y. Y.; Zhao, Q. R.: N′-(2-Chlorobenzylidene)-2-hydroxy-3-methylbenzohydrazide. Acta. Crystallogr. E66 (2010) o1025.10.1107/S1600536810012110Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. Yuan, J.; Xing, A.-P.; Cheng, D.: Crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-N′-(pyrimidin-2-yl)benzohydrazide, C11H10N4O2. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 233 (2018) 817–818.10.1515/ncrs-2018-0029Suche in Google Scholar
9. Barbazán, P.; Carballo, R.; Vázquez-López, E. M.: Synthesis and structure of 2-acetylpyridine-salicyloylhydrazone and its copper(II) and zinc(II) complexes. The effect of the metal coordination on the weak intermolecular interactions. CrystEngComm 9 (2007) 668–675.10.1039/b703442cSuche in Google Scholar
10. Addison, A. W.; Rao, T. N.; Reedijk, J.; van Rijn, J.; Verschoor, G. C.: Synthesis, structure, and spectroscopic properties of copper(II) compounds containing nitrogen–sulphur donor ligands; the crystal and molecular structure of aqua [1,7-bis(N-methylbenzimidazol-2′-yl)-2,6-dithiaheptane] copper(II) perchlorate. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 7 (1984) 1349–1356.10.1039/DT9840001349Suche in Google Scholar
11. Karmakar, R.; Choudhury, C. R.; Batsanov, A. S.; Batten S. R.; Mitra, S.: Synthesis and structural characterisation of two copper(II) complexes of N-(1-acetyl-2-propylidene)(2-pyridylmethyl) amine. Struct. Chem. 16 (2005) 535–539.10.1007/s11224-005-6057-xSuche in Google Scholar
12. Waldmann, O.; Zhao, L.; Thompson, L. K.: Field-dependent anisotropy change in a supramolecular Mn(II)-[3 × 3] grid. Chem. Phys. Lett. 88 (2002) 066401.10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.066401Suche in Google Scholar
13. Zhao, L.; Xu, Z.; Thompson, L. K.; Miller, D. O.: Self assembled polynuclear [3×3] grids — structural and magnetic properties of Mn(II), Fe(III), Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) complexes with M9(μ2-O)12 cores. Polyhedron 20 (2001) 1359–1364.10.1016/S0277-5387(01)00619-2Suche in Google Scholar
14. Dawe, L. N.; Abedin, T. S. M.; Kelly, T. L.; Thompson, L. K.; Miller, D. O.; Zhao, L.; Wilson, C.; Leech, M. A.; Howard, J. A. K.: Self-assembled polymetallic square grids ([2 × 2] M4, [3 ×3 ] M9) and trigonal bipyramidal clusters (M5)–structural and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Chem. 16 (2006) 2645–2659.10.1039/B602595ASuche in Google Scholar
15. Thompson, L. K.; Zhao, L.; Xu, Z.; Miller, D. O.; Reiff, W. M.: Self-assembled supramolecular M9 (Mn(II), Fe(III), Zn(II)), M5 (Fe(III)), and [M3]2 (Pb(II)) complexes: structural, magnetic, and mössbauer properties. Inorg. Chem. 42 (2003) 128–139.10.1021/ic020468ySuche in Google Scholar PubMed
16. Milway, V. A.; Thompson, L. K.; Miller, D. O.: Self-assembly by ligand disassembly?–formation of an unusual dodecanuclear [Co(ii)6Co(iii)6] cluster. Chem. Commun. 16 (2004) 1790–1791.10.1039/B405131ASuche in Google Scholar
©2020 Wang Xin et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2N:O)silver(I)], C15H8AgNO4S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium) bis(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)succinato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) tetrahydrate, C48H70CuN8O12, [C10H14N2]2[Cu(C14H17N2O4)2] ⋅ 4 H2O
- Crystal structure of triaqua-bis(2-(6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-1-(2-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-3-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-κ2O,O′)calcium(II) – ethanol (1/2), C44H76CaO19S2
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5-(4-(diphenylamino)phenyl)thiophene-2-carboxylate, C25H21NO2S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(2-methyl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- The crystal structure of (E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N′-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H13ClN2O4
- The crystal structure of (2Z,2′Z)-N′,N′′′′-(pyridine-2,6-dicarbonyl)dipicolinohydrazonamide, C19H17N9O2
- Photochromic properties and crystal structure of 3,3′-(perfluorocyclopent-1-ene-1,2-diyl)bis(5-(4-(azidomethyl)phenyl)-2-methylthiophene), C29H20F6N6S2
- Crystal structure of aqua-dichlorido-(4-(((3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)hydrazono)(oxido)methyl)pyridin-1-ium-κ3N,O,O′)iron(III), C15H16Cl2N3O4Fe
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrabromo-6-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-nickel(II)], C26H14Br8NiN2O10
- Crystal structure of diethanol-κ1O-bis(μ2-N-((2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)pyrazine-2-carbohydrazonato-κ5N,O,O′:O′:N′)-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dieuropium(III), C36H32N10O12Eu2
- The crystal structure of 2-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-((3,4-difluorobenzyl)oxy)styryl)-4,6-dimethoxybenzaldehyde, C24H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoylpyrene, C23H14O
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6-p-cymene)-(N-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) – acetone (1/1), C22H23ClN2F7OPRu
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,3,5,7-tetraphenyl-8-(N-phenylformamido)-2-oxa-5-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct -3-en-7-yl benzoate, C44H34N2O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(3-acetyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-7-(diethylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C21H21N3O4S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-κ2O:O′)nickel(II)], C18H12F4NiN2O6
- Crystal structure of 4-hydroxynaphtho[2,3-b]benzofuran-6,11-dione, C16H8O4
- The crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]dodecane – acetone (1/1), C45H48N2O5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)iminio)methyl)-6-bromophenolate, C17H15N2BrO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-oxalyl dihydrazide-κ4N,O:N′,O′)-bis(μ2-pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)dicadmium(II)] hexahydrate, C16H28O18N6Cd2
- Crystal structure of poly[tetra-(μ4-naphthalene-1,8-dicarboxylato-κ4O:O,O′: O′′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ4-oxo-κ4O:O:O:O) penta-lead(II)], C48H24O17Pb5
- Crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[c,f][1,5]oxabismocin-12 (7H)-yl acetate, C16H15O3Bi
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-chloro-6-nitrophenyl)-1-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl)diazene 1-oxide, C12H6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of bis(3-methyl-N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)nickel(II), C28H26N8O2Ni
- Crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]-dodecane, C40H36Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis[(μ2-4⋯O,O′:O′)-(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)]-di-lead(II)μ-4-hydroxybenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′;κ3O,O′:O′-bis-[(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)di-lead(II)] monohydrate, C52H36N4O12Pb2 ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ3-3,4,5,6-tetrafluoro-phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethene-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C14H9CoF4NO6
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-4-phenyl-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H10O3
- Crystal structure of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(5-oxohexyl)-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C20H24N4O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O)-bis(nitrato-κ1O)zinc(II)], C17H16N6O7Zn
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(6-aminopicolinato-κ2N,O)magnesium(II), C12H14O6N4Mg
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxamide-κ2N,O)-[tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′]nickel(II) diperchlorate — methanol (1/3), C33H39Cl2N9NiO12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3-(4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-acrylato-κO1)-(μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N3:N3′)cobalt(II)], C32H26CoF6N4O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate monohydrate, C22H25NO5S⋅H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(N-oxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl) acetamide κ2O,O′)-diaqua-zinc(II), C6H12ZnN10O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-chlorophenylimino)methyl)pyridinium 3,5-dinitrobenzoate, C19H13ClN4O6
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis((E)-2-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)phenol)zinc(II), C24H20Cl2N4O2Zn
- Crystal structure of cyclo-[tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-p-xylylenediamine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(II)] dimethyl sulfoxide solvate, C20H36Cl4N4O2Pd2S2
- Crystal structure of 4-(3-fluorophenyl)-7-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H9FO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-(pyrimidin-2-yl)hydrazono)methyl)quinolin-1-ium perchlorate – methanol (1/1), C15H16N5O5Cl
- The crystal structure of bis(N-(amino(pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)zinc(II) – methanol (2/5), C57H60Cl2N16O13Zn2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4,4′-di(4-pyridyl)-6,6′-di(tert-butyl)-2,2′-[propylenedioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenol, C35H40N4O4
- Crystal structure of (3E,3′E)-3,3′-((1,3,4-thiadiazole-2,5-diyl)bis(sulfanediyl))bis(4-hydroxy-4-phenylbut-3-en-2-one), C22H18N2O4S3
- Crystal structure of (N-benzyl-N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)di(4-chlorobenzyl)chloridotin(IV), C23H22Cl3NS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) sodium bromide hydrate, [Na(18-crown-6)]Br ⋅ H2O, C12H26BrNaO7
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H13F2N1O4
- Crystal structure of chlorido (2-(4-ethylphenyl)pyrimidine-k2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-kP) palladium(II), C30H26ClN2PPd
- Crystal structure of 18-crown-6 – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene – acetonitrile (1/1/2), C22H30F4I2N2O6
- Crystal structure of diisobutyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C16H24O6
- Crystal structure of poly[[tris(μ2-cis-1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylato)-κ2O, O′]-bis[μ3-1,3,5-tris[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzene-κ3N, N′,N′′]-trizinc(II)] – water (1/20), C60H106N12O32Zn3
- The synthesis and crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide–tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C16H14N4Cl2F6O3S
- Crystal structure of dimethylbis(diisopropyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C16H34N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of diisopropyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C14H20O6
- The synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl (E)-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-5-((2-methoxybenzylidene)amino)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C22H15N3Cl2F6O4S
- The crystal structure of a matrine derivative, 13-(methylamine-1-yl) carbodithioate matrine, C17H27N3OS2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxy-6-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C26H20CuN2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-p-fluorophenyl-5-dihydroxymethyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C9H7FN2O3
- Crystal structure of dichloridobis(4-chlorophenyl-κC1)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tin(IV), C24H16Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of bis{bromido-triphenyltin(IV)}(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′), C46H38Br2N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-chloro-quinolin-8-yloxy)-N-quinolin-8-yl-acetamide, C20H14N3O2Cl
- Crystal structure of bis(N-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(II) — dimethylformamide (1/1), C41H41N9O5Co
- Crystal structure of bis[2-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-1-tosylhydrazin-1-ido-κ3-N,N′,O]copper(II), C30H34N8O4S2Cu
- Crystal structure of (2-p-tolylpyrimidine-κ2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-κP) palladium(II), C29H24ClN2PPd
- Halogen bonding in crystal structure of bis(1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium triiodide, C16H32CsI3O8
- The synthesis and crystal structure of N-(3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfinyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-2-phenylacetamide, C20H10N4Cl2F6O2S
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)nicotinic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-methylbenzyl)thiazolidin-2-one, C11H13ONS
- The crystal structure of 2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(isoquinolin-1-yl)ethane-1,1-diol, C11H8F3NO2
- The crystal structure of 3-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- The crystal structure of 5-nitropicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 3-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-1,5-dioxaspiro[5.5]undecane-2,4-dione, C16H18O5
- Crystal structure of [[Mo3Se7(S2CNEt2)3]2(μ-Se)] ⋅ 2(C6H4Cl2), C42H68Cl4Mo6N6S12Se15
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-hydroxy-3-((5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)thio)pent-3-en-2-one, C13H12N2O3S
- The crystal structure of (2,3-dioxo-5,6:13,14-dibenzo-9,10-benzo-1,4,8,11-7, 11-diene-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-nickel(II), Ni(C22H14N4O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-(1-benzyl-2-ethyl-4-nitro-1H-imidazol-5-ylthio)-propanoic acid, C15H17N3O4S
- The crystal structure of dichlorobis(2-(dicyclohexylphosphino)-2′,4′,6′-tri-i-propyl-1,1′-biphenyl) palladium(II)-dichloroform, C68H100Cl8P2Pd
- Crystal structure and antimicrobial properties of (1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium(I) pentaiodide, C16H32CsI5O8
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2N:O)silver(I)], C15H8AgNO4S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium) bis(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)succinato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) tetrahydrate, C48H70CuN8O12, [C10H14N2]2[Cu(C14H17N2O4)2] ⋅ 4 H2O
- Crystal structure of triaqua-bis(2-(6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-1-(2-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-3-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-κ2O,O′)calcium(II) – ethanol (1/2), C44H76CaO19S2
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5-(4-(diphenylamino)phenyl)thiophene-2-carboxylate, C25H21NO2S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(2-methyl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- The crystal structure of (E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N′-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H13ClN2O4
- The crystal structure of (2Z,2′Z)-N′,N′′′′-(pyridine-2,6-dicarbonyl)dipicolinohydrazonamide, C19H17N9O2
- Photochromic properties and crystal structure of 3,3′-(perfluorocyclopent-1-ene-1,2-diyl)bis(5-(4-(azidomethyl)phenyl)-2-methylthiophene), C29H20F6N6S2
- Crystal structure of aqua-dichlorido-(4-(((3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)hydrazono)(oxido)methyl)pyridin-1-ium-κ3N,O,O′)iron(III), C15H16Cl2N3O4Fe
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrabromo-6-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-nickel(II)], C26H14Br8NiN2O10
- Crystal structure of diethanol-κ1O-bis(μ2-N-((2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)pyrazine-2-carbohydrazonato-κ5N,O,O′:O′:N′)-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dieuropium(III), C36H32N10O12Eu2
- The crystal structure of 2-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-((3,4-difluorobenzyl)oxy)styryl)-4,6-dimethoxybenzaldehyde, C24H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoylpyrene, C23H14O
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6-p-cymene)-(N-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) – acetone (1/1), C22H23ClN2F7OPRu
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,3,5,7-tetraphenyl-8-(N-phenylformamido)-2-oxa-5-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct -3-en-7-yl benzoate, C44H34N2O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(3-acetyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-7-(diethylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C21H21N3O4S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-κ2O:O′)nickel(II)], C18H12F4NiN2O6
- Crystal structure of 4-hydroxynaphtho[2,3-b]benzofuran-6,11-dione, C16H8O4
- The crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]dodecane – acetone (1/1), C45H48N2O5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)iminio)methyl)-6-bromophenolate, C17H15N2BrO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-oxalyl dihydrazide-κ4N,O:N′,O′)-bis(μ2-pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)dicadmium(II)] hexahydrate, C16H28O18N6Cd2
- Crystal structure of poly[tetra-(μ4-naphthalene-1,8-dicarboxylato-κ4O:O,O′: O′′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ4-oxo-κ4O:O:O:O) penta-lead(II)], C48H24O17Pb5
- Crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[c,f][1,5]oxabismocin-12 (7H)-yl acetate, C16H15O3Bi
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-chloro-6-nitrophenyl)-1-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl)diazene 1-oxide, C12H6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of bis(3-methyl-N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)nickel(II), C28H26N8O2Ni
- Crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]-dodecane, C40H36Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis[(μ2-4⋯O,O′:O′)-(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)]-di-lead(II)μ-4-hydroxybenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′;κ3O,O′:O′-bis-[(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)di-lead(II)] monohydrate, C52H36N4O12Pb2 ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ3-3,4,5,6-tetrafluoro-phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethene-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C14H9CoF4NO6
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-4-phenyl-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H10O3
- Crystal structure of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(5-oxohexyl)-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C20H24N4O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O)-bis(nitrato-κ1O)zinc(II)], C17H16N6O7Zn
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(6-aminopicolinato-κ2N,O)magnesium(II), C12H14O6N4Mg
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxamide-κ2N,O)-[tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′]nickel(II) diperchlorate — methanol (1/3), C33H39Cl2N9NiO12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3-(4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-acrylato-κO1)-(μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N3:N3′)cobalt(II)], C32H26CoF6N4O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate monohydrate, C22H25NO5S⋅H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(N-oxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl) acetamide κ2O,O′)-diaqua-zinc(II), C6H12ZnN10O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-chlorophenylimino)methyl)pyridinium 3,5-dinitrobenzoate, C19H13ClN4O6
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis((E)-2-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)phenol)zinc(II), C24H20Cl2N4O2Zn
- Crystal structure of cyclo-[tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-p-xylylenediamine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(II)] dimethyl sulfoxide solvate, C20H36Cl4N4O2Pd2S2
- Crystal structure of 4-(3-fluorophenyl)-7-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H9FO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-(pyrimidin-2-yl)hydrazono)methyl)quinolin-1-ium perchlorate – methanol (1/1), C15H16N5O5Cl
- The crystal structure of bis(N-(amino(pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)zinc(II) – methanol (2/5), C57H60Cl2N16O13Zn2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4,4′-di(4-pyridyl)-6,6′-di(tert-butyl)-2,2′-[propylenedioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenol, C35H40N4O4
- Crystal structure of (3E,3′E)-3,3′-((1,3,4-thiadiazole-2,5-diyl)bis(sulfanediyl))bis(4-hydroxy-4-phenylbut-3-en-2-one), C22H18N2O4S3
- Crystal structure of (N-benzyl-N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)di(4-chlorobenzyl)chloridotin(IV), C23H22Cl3NS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) sodium bromide hydrate, [Na(18-crown-6)]Br ⋅ H2O, C12H26BrNaO7
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H13F2N1O4
- Crystal structure of chlorido (2-(4-ethylphenyl)pyrimidine-k2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-kP) palladium(II), C30H26ClN2PPd
- Crystal structure of 18-crown-6 – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene – acetonitrile (1/1/2), C22H30F4I2N2O6
- Crystal structure of diisobutyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C16H24O6
- Crystal structure of poly[[tris(μ2-cis-1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylato)-κ2O, O′]-bis[μ3-1,3,5-tris[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzene-κ3N, N′,N′′]-trizinc(II)] – water (1/20), C60H106N12O32Zn3
- The synthesis and crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide–tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C16H14N4Cl2F6O3S
- Crystal structure of dimethylbis(diisopropyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C16H34N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of diisopropyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C14H20O6
- The synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl (E)-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-5-((2-methoxybenzylidene)amino)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C22H15N3Cl2F6O4S
- The crystal structure of a matrine derivative, 13-(methylamine-1-yl) carbodithioate matrine, C17H27N3OS2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxy-6-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C26H20CuN2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-p-fluorophenyl-5-dihydroxymethyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C9H7FN2O3
- Crystal structure of dichloridobis(4-chlorophenyl-κC1)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tin(IV), C24H16Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of bis{bromido-triphenyltin(IV)}(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′), C46H38Br2N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-chloro-quinolin-8-yloxy)-N-quinolin-8-yl-acetamide, C20H14N3O2Cl
- Crystal structure of bis(N-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(II) — dimethylformamide (1/1), C41H41N9O5Co
- Crystal structure of bis[2-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-1-tosylhydrazin-1-ido-κ3-N,N′,O]copper(II), C30H34N8O4S2Cu
- Crystal structure of (2-p-tolylpyrimidine-κ2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-κP) palladium(II), C29H24ClN2PPd
- Halogen bonding in crystal structure of bis(1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium triiodide, C16H32CsI3O8
- The synthesis and crystal structure of N-(3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfinyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-2-phenylacetamide, C20H10N4Cl2F6O2S
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)nicotinic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-methylbenzyl)thiazolidin-2-one, C11H13ONS
- The crystal structure of 2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(isoquinolin-1-yl)ethane-1,1-diol, C11H8F3NO2
- The crystal structure of 3-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- The crystal structure of 5-nitropicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 3-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-1,5-dioxaspiro[5.5]undecane-2,4-dione, C16H18O5
- Crystal structure of [[Mo3Se7(S2CNEt2)3]2(μ-Se)] ⋅ 2(C6H4Cl2), C42H68Cl4Mo6N6S12Se15
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-hydroxy-3-((5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)thio)pent-3-en-2-one, C13H12N2O3S
- The crystal structure of (2,3-dioxo-5,6:13,14-dibenzo-9,10-benzo-1,4,8,11-7, 11-diene-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-nickel(II), Ni(C22H14N4O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-(1-benzyl-2-ethyl-4-nitro-1H-imidazol-5-ylthio)-propanoic acid, C15H17N3O4S
- The crystal structure of dichlorobis(2-(dicyclohexylphosphino)-2′,4′,6′-tri-i-propyl-1,1′-biphenyl) palladium(II)-dichloroform, C68H100Cl8P2Pd
- Crystal structure and antimicrobial properties of (1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium(I) pentaiodide, C16H32CsI5O8

