Abstract
C7H6BrN5, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 8.3319(4) Å, b = 10.0666(5) Å, c = 11.4042(6) Å, α = 107.213(5)°, β = 99.394(4)°, γ = 95.540(4)°, V = 890.71(8) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0452, wRref(F2) = 0.0972, T = 293(2) K.
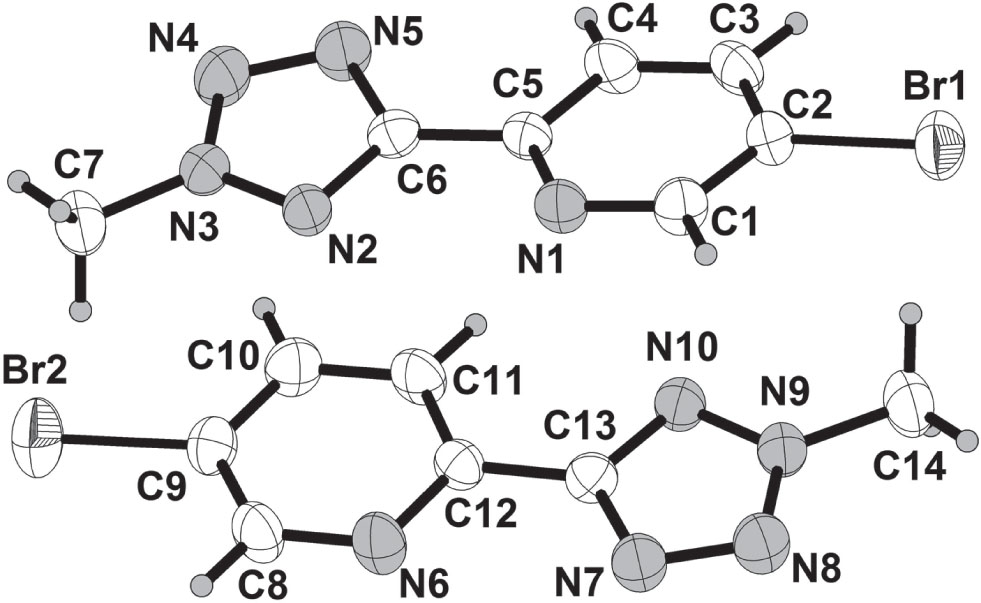
The asymmetric unit of the title structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.24 × 0.21 × 0.17 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 4.57 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Xcalibur, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 29.6°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 7994, 4190, 0.028 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2696 |
| N(param)refined: | 237 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], SUPERFLIP [3], Olex2 [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Br1 | 0.44510(5) | 0.72468(3) | 0.04301(4) | 0.05319(15) |
| Br2 | −0.28943(5) | −0.00876(4) | 0.28107(4) | 0.06311(17) |
| C1 | 0.2354(4) | 0.4913(3) | 0.0550(3) | 0.0401(8) |
| H1 | 0.2733 | 0.5332 | 0.1409 | 0.048* |
| C2 | 0.2927(4) | 0.5550(3) | −0.0250(3) | 0.0359(8) |
| C3 | 0.2416(4) | 0.4947(3) | −0.1518(3) | 0.0410(8) |
| H3 | 0.2811 | 0.5351 | −0.2072 | 0.049* |
| C4 | 0.1303(4) | 0.3729(3) | −0.1947(3) | 0.0409(8) |
| H4 | 0.0914 | 0.3296 | −0.2803 | 0.049* |
| C5 | 0.0764(4) | 0.3150(3) | −0.1091(3) | 0.0336(8) |
| C6 | −0.0449(4) | 0.1867(3) | −0.1516(3) | 0.0344(8) |
| C7 | −0.2890(5) | −0.0990(3) | −0.1233(4) | 0.0530(10) |
| H7A | −0.2119 | −0.1495 | −0.0892 | 0.079* |
| H7B | −0.3637 | −0.1630 | −0.1955 | 0.079* |
| H7C | −0.3499 | −0.0561 | −0.0613 | 0.079* |
| C8 | −0.0390(5) | 0.2006(3) | 0.4522(3) | 0.0465(9) |
| H8 | −0.0665 | 0.1557 | 0.5083 | 0.056* |
| C9 | −0.1221(4) | 0.1491(3) | 0.3300(3) | 0.0385(8) |
| C10 | −0.0824(4) | 0.2125(3) | 0.2452(3) | 0.0450(9) |
| H10 | −0.1361 | 0.1784 | 0.1616 | 0.054* |
| C11 | 0.0385(5) | 0.3275(3) | 0.2870(3) | 0.0429(9) |
| H11 | 0.0682 | 0.3726 | 0.2317 | 0.051* |
| C12 | 0.1164(4) | 0.3763(3) | 0.4122(3) | 0.0337(7) |
| C13 | 0.2456(4) | 0.4988(3) | 0.4608(3) | 0.0345(8) |
| C14 | 0.5067(5) | 0.7776(4) | 0.4374(4) | 0.0600(11) |
| H14A | 0.5730 | 0.8449 | 0.5121 | 0.090* |
| H14B | 0.4344 | 0.8247 | 0.3947 | 0.090* |
| H14C | 0.5767 | 0.7334 | 0.3835 | 0.090* |
| N1 | 0.1292(3) | 0.3736(3) | 0.0155(2) | 0.0387(7) |
| N2 | −0.0878(3) | 0.1123(3) | −0.0788(2) | 0.0367(7) |
| N3 | −0.1997(3) | 0.0108(3) | −0.1599(3) | 0.0385(7) |
| N4 | −0.2280(4) | 0.0181(3) | −0.2734(3) | 0.0506(8) |
| N5 | −0.1306(4) | 0.1302(3) | −0.2713(3) | 0.0497(8) |
| N6 | 0.0791(4) | 0.3119(3) | 0.4943(3) | 0.0456(8) |
| N7 | 0.3303(4) | 0.5504(3) | 0.5798(3) | 0.0437(7) |
| N8 | 0.4346(4) | 0.6601(3) | 0.5844(3) | 0.0460(8) |
| N9 | 0.4088(3) | 0.6704(3) | 0.4711(3) | 0.0408(7) |
| N10 | 0.2922(3) | 0.5733(3) | 0.3897(3) | 0.0402(7) |
Source of material
The title compound was synthesized according to a reported procedure [5]. Crystals were obtained by slow evaporation of mixed solution of petroleum ether and ethyl acetate (5:1, v/v) at room temperature after a week.
Experimental details
All H atoms were included in calculated positions and refined as riding atoms, with N—H = 0.86 Å, C—H = 0.93–0.98 Å, with Uiso (H) = 1.5Ueq(methyl C) or 1.2Ueq(C, N) for other H atoms.
Comment
The title compound is an important intermediate in the synthesis of Tedizolid. It has been reported that Tedizolid shows antibacterial activity and antioxidant activity [6], [7]. Tedizolid has an effective antibacterial effect on most clinically relevant gram-positive pathogens [8]. It has good therapeutic effect on pulmonary tuberculosis [9]. The title compound consist one tetrazole ring and pyridine ring, one methyl group bound to the tetrazole ring and one bromine atom bound to the pyridine ring. The structure of this compound is similar to the compounds which contain tetrazole rings [10], [11]. This contribution is part of our continuing interest in the synthesis organic pharmaceutics.
Single-crystal structure analysis reveals that there are two molecules in the asymmetric unit of the title crystal structure. Bond lengths and angles are all in the expected ranges. For example, the N—C bond distance (N1—C1) is 1.319(4) Å, and distance (N2—C6) is 1.339(4) Å. In title compound, there are 1,2,3,4-tetrazole rings. In one molecule, the N—N bond distance (N2—N3, N3—N4 and N5—N4) is 1.321(3) Å, 1.303(4) Å, and 1.316(4) Å, respectively. In another molecule, the N—N bond distance (N8—N7, N9—N8 and N9—N10) is 1.320(4) Å, 1.311(4) Å, and 1.322(4) Å, respectively. Interestingly, the two crystallographically independent molecules are conformers (180° rotation about the central C–C bond (see the figure). Each molecule is almost coplanar. In addition, the dihedral angles between 2-pyridine substituents and 1,2,3,4-tetrazole ring are 11.29(3) Å, and 1.62(3) Å.
Acknowledgements
X-ray data were collected at Institute of Medical Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050, Peoples Republic of China. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81473104).
References
1. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction: CrysAlisPRO Software system, version 1.171.39.32a. Rigaku Corporation, Oxford, UK (2017).Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Palatinus, L.; Chapuis, G.: SUPERFLIP: a computer program for the solution of crystal structures by charge flipping in arbitrary dimensions. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 40 (2007) 786–790.10.1107/S0021889807029238Suche in Google Scholar
4. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H.: OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 42 (2009) 339–341.10.1107/S0021889808042726Suche in Google Scholar
5. Méndez, Y.; De Armas, G.; Pérez, I.; Rojas, T.; Valdés-Tresanco, M. E.; Izquierdo, M.; Alonso Del Rivero, M.; Álvarez-Ginarte, Y. M.; Valiente, P. A.; Soto, C.; de León, L.; Vasco, A. V.; Scott, W. L.; Westermann, B.; González-Bacerio, J.; Rivera, D. G.: Discovery of potent and selective inhibitors of the Escherichia coli M1-aminopeptidase via multicomponent solid-phase synthesis of tetrazole-peptidomimetics. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 163 (2019) 481–499.10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.11.074Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Leal, J. G.; Sauer, A. C.; Mayer, J. C. P.; Stefanello, S. T.; Gonçalves, D. F.; Soares, F. A. A.; Dornelles, L.: Synthesis and electrochemical and antioxidant properties of chalcogenocyanate oxadiazole and 5-heteroarylchalcogenomethyl-1H-tetrazole derivatives. New J. Chem. 41 (2017) 5875–5883.10.1039/C7NJ00920HSuche in Google Scholar
7. Deshpande, D.; Srivastava, S.; Pasipanodya, J. G.; Lee, P. S.; Gumbo, T.: Tedizolid is highly bactericidal in the treatment of pulmonary Mycobacterium avium complex disease. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 72 (2017) ii30–ii35.10.1093/jac/dkx305Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Zurenko, G.; Bien, P.; Bensaci, M.; Patel, H. N.; Thorne, G.: Use of linezolid susceptibility test results as a surrogate for the susceptibility of Gram-positive pathogens to tedizolid, a novel oxazolidinone. Ann. Clin. Microb. Anti. 13 (2014) 46.10.1186/s12941-014-0046-0Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Deshpande, D.; Srivastava, S.; Nuermberger, E.; Koeuth, T.; Martin, K. R.; Cirrincione, K. N.; Gumbo, T.: Multiparameter Responses to Tedizolid Monotherapy and Moxifloxacin Combination Therapy Models of Children With Intracellular Tuberculosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 67 (2018) S342–S348.10.1093/cid/ciy612Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
10. Wu, G.; Kaneko, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shinozaki, Y.; Sugawa, K.; Islam, A.; Han, L.; Bedja, I.; Gupta, R. K.; Shen, Q.; Otsuki, J.: Neutral and anionic tetrazole-based ligands in designing novel ruthenium dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Power Sources 307 (2016) 416–425.10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.12.135Suche in Google Scholar
11. Caporale, C.; Bader, C. A.; Sorvina, A.; MaGee, K. D. M.; Skelton, B. W.; Gillam, T. A.; Wright, P. J.; Raiteri, P.; Stagni, S.; Morrison, J. L.; Plush, S. E.; Brooks, D. A.; Massi, M.: Investigating intracellular localisation and cytotoxicity trends for neutral and cationic iridium tetrazolato complexes in live cells. Chem. Eur. J. 23 (2017) 15666–15679.10.1002/chem.201701352Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
©2020 Xiao-Dong Mou et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2N:O)silver(I)], C15H8AgNO4S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium) bis(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)succinato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) tetrahydrate, C48H70CuN8O12, [C10H14N2]2[Cu(C14H17N2O4)2] ⋅ 4 H2O
- Crystal structure of triaqua-bis(2-(6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-1-(2-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-3-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-κ2O,O′)calcium(II) – ethanol (1/2), C44H76CaO19S2
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5-(4-(diphenylamino)phenyl)thiophene-2-carboxylate, C25H21NO2S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(2-methyl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- The crystal structure of (E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N′-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H13ClN2O4
- The crystal structure of (2Z,2′Z)-N′,N′′′′-(pyridine-2,6-dicarbonyl)dipicolinohydrazonamide, C19H17N9O2
- Photochromic properties and crystal structure of 3,3′-(perfluorocyclopent-1-ene-1,2-diyl)bis(5-(4-(azidomethyl)phenyl)-2-methylthiophene), C29H20F6N6S2
- Crystal structure of aqua-dichlorido-(4-(((3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)hydrazono)(oxido)methyl)pyridin-1-ium-κ3N,O,O′)iron(III), C15H16Cl2N3O4Fe
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrabromo-6-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-nickel(II)], C26H14Br8NiN2O10
- Crystal structure of diethanol-κ1O-bis(μ2-N-((2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)pyrazine-2-carbohydrazonato-κ5N,O,O′:O′:N′)-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dieuropium(III), C36H32N10O12Eu2
- The crystal structure of 2-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-((3,4-difluorobenzyl)oxy)styryl)-4,6-dimethoxybenzaldehyde, C24H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoylpyrene, C23H14O
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6-p-cymene)-(N-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) – acetone (1/1), C22H23ClN2F7OPRu
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,3,5,7-tetraphenyl-8-(N-phenylformamido)-2-oxa-5-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct -3-en-7-yl benzoate, C44H34N2O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(3-acetyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-7-(diethylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C21H21N3O4S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-κ2O:O′)nickel(II)], C18H12F4NiN2O6
- Crystal structure of 4-hydroxynaphtho[2,3-b]benzofuran-6,11-dione, C16H8O4
- The crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]dodecane – acetone (1/1), C45H48N2O5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)iminio)methyl)-6-bromophenolate, C17H15N2BrO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-oxalyl dihydrazide-κ4N,O:N′,O′)-bis(μ2-pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)dicadmium(II)] hexahydrate, C16H28O18N6Cd2
- Crystal structure of poly[tetra-(μ4-naphthalene-1,8-dicarboxylato-κ4O:O,O′: O′′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ4-oxo-κ4O:O:O:O) penta-lead(II)], C48H24O17Pb5
- Crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[c,f][1,5]oxabismocin-12 (7H)-yl acetate, C16H15O3Bi
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-chloro-6-nitrophenyl)-1-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl)diazene 1-oxide, C12H6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of bis(3-methyl-N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)nickel(II), C28H26N8O2Ni
- Crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]-dodecane, C40H36Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis[(μ2-4⋯O,O′:O′)-(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)]-di-lead(II)μ-4-hydroxybenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′;κ3O,O′:O′-bis-[(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)di-lead(II)] monohydrate, C52H36N4O12Pb2 ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ3-3,4,5,6-tetrafluoro-phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethene-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C14H9CoF4NO6
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-4-phenyl-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H10O3
- Crystal structure of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(5-oxohexyl)-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C20H24N4O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O)-bis(nitrato-κ1O)zinc(II)], C17H16N6O7Zn
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(6-aminopicolinato-κ2N,O)magnesium(II), C12H14O6N4Mg
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxamide-κ2N,O)-[tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′]nickel(II) diperchlorate — methanol (1/3), C33H39Cl2N9NiO12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3-(4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-acrylato-κO1)-(μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N3:N3′)cobalt(II)], C32H26CoF6N4O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate monohydrate, C22H25NO5S⋅H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(N-oxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl) acetamide κ2O,O′)-diaqua-zinc(II), C6H12ZnN10O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-chlorophenylimino)methyl)pyridinium 3,5-dinitrobenzoate, C19H13ClN4O6
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis((E)-2-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)phenol)zinc(II), C24H20Cl2N4O2Zn
- Crystal structure of cyclo-[tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-p-xylylenediamine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(II)] dimethyl sulfoxide solvate, C20H36Cl4N4O2Pd2S2
- Crystal structure of 4-(3-fluorophenyl)-7-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H9FO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-(pyrimidin-2-yl)hydrazono)methyl)quinolin-1-ium perchlorate – methanol (1/1), C15H16N5O5Cl
- The crystal structure of bis(N-(amino(pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)zinc(II) – methanol (2/5), C57H60Cl2N16O13Zn2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4,4′-di(4-pyridyl)-6,6′-di(tert-butyl)-2,2′-[propylenedioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenol, C35H40N4O4
- Crystal structure of (3E,3′E)-3,3′-((1,3,4-thiadiazole-2,5-diyl)bis(sulfanediyl))bis(4-hydroxy-4-phenylbut-3-en-2-one), C22H18N2O4S3
- Crystal structure of (N-benzyl-N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)di(4-chlorobenzyl)chloridotin(IV), C23H22Cl3NS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) sodium bromide hydrate, [Na(18-crown-6)]Br ⋅ H2O, C12H26BrNaO7
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H13F2N1O4
- Crystal structure of chlorido (2-(4-ethylphenyl)pyrimidine-k2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-kP) palladium(II), C30H26ClN2PPd
- Crystal structure of 18-crown-6 – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene – acetonitrile (1/1/2), C22H30F4I2N2O6
- Crystal structure of diisobutyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C16H24O6
- Crystal structure of poly[[tris(μ2-cis-1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylato)-κ2O, O′]-bis[μ3-1,3,5-tris[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzene-κ3N, N′,N′′]-trizinc(II)] – water (1/20), C60H106N12O32Zn3
- The synthesis and crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide–tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C16H14N4Cl2F6O3S
- Crystal structure of dimethylbis(diisopropyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C16H34N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of diisopropyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C14H20O6
- The synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl (E)-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-5-((2-methoxybenzylidene)amino)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C22H15N3Cl2F6O4S
- The crystal structure of a matrine derivative, 13-(methylamine-1-yl) carbodithioate matrine, C17H27N3OS2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxy-6-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C26H20CuN2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-p-fluorophenyl-5-dihydroxymethyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C9H7FN2O3
- Crystal structure of dichloridobis(4-chlorophenyl-κC1)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tin(IV), C24H16Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of bis{bromido-triphenyltin(IV)}(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′), C46H38Br2N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-chloro-quinolin-8-yloxy)-N-quinolin-8-yl-acetamide, C20H14N3O2Cl
- Crystal structure of bis(N-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(II) — dimethylformamide (1/1), C41H41N9O5Co
- Crystal structure of bis[2-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-1-tosylhydrazin-1-ido-κ3-N,N′,O]copper(II), C30H34N8O4S2Cu
- Crystal structure of (2-p-tolylpyrimidine-κ2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-κP) palladium(II), C29H24ClN2PPd
- Halogen bonding in crystal structure of bis(1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium triiodide, C16H32CsI3O8
- The synthesis and crystal structure of N-(3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfinyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-2-phenylacetamide, C20H10N4Cl2F6O2S
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)nicotinic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-methylbenzyl)thiazolidin-2-one, C11H13ONS
- The crystal structure of 2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(isoquinolin-1-yl)ethane-1,1-diol, C11H8F3NO2
- The crystal structure of 3-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- The crystal structure of 5-nitropicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 3-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-1,5-dioxaspiro[5.5]undecane-2,4-dione, C16H18O5
- Crystal structure of [[Mo3Se7(S2CNEt2)3]2(μ-Se)] ⋅ 2(C6H4Cl2), C42H68Cl4Mo6N6S12Se15
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-hydroxy-3-((5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)thio)pent-3-en-2-one, C13H12N2O3S
- The crystal structure of (2,3-dioxo-5,6:13,14-dibenzo-9,10-benzo-1,4,8,11-7, 11-diene-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-nickel(II), Ni(C22H14N4O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-(1-benzyl-2-ethyl-4-nitro-1H-imidazol-5-ylthio)-propanoic acid, C15H17N3O4S
- The crystal structure of dichlorobis(2-(dicyclohexylphosphino)-2′,4′,6′-tri-i-propyl-1,1′-biphenyl) palladium(II)-dichloroform, C68H100Cl8P2Pd
- Crystal structure and antimicrobial properties of (1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium(I) pentaiodide, C16H32CsI5O8
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2N:O)silver(I)], C15H8AgNO4S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium) bis(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)succinato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) tetrahydrate, C48H70CuN8O12, [C10H14N2]2[Cu(C14H17N2O4)2] ⋅ 4 H2O
- Crystal structure of triaqua-bis(2-(6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-1-(2-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-3-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-κ2O,O′)calcium(II) – ethanol (1/2), C44H76CaO19S2
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5-(4-(diphenylamino)phenyl)thiophene-2-carboxylate, C25H21NO2S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(2-methyl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- The crystal structure of (E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N′-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H13ClN2O4
- The crystal structure of (2Z,2′Z)-N′,N′′′′-(pyridine-2,6-dicarbonyl)dipicolinohydrazonamide, C19H17N9O2
- Photochromic properties and crystal structure of 3,3′-(perfluorocyclopent-1-ene-1,2-diyl)bis(5-(4-(azidomethyl)phenyl)-2-methylthiophene), C29H20F6N6S2
- Crystal structure of aqua-dichlorido-(4-(((3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)hydrazono)(oxido)methyl)pyridin-1-ium-κ3N,O,O′)iron(III), C15H16Cl2N3O4Fe
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrabromo-6-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-nickel(II)], C26H14Br8NiN2O10
- Crystal structure of diethanol-κ1O-bis(μ2-N-((2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)pyrazine-2-carbohydrazonato-κ5N,O,O′:O′:N′)-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dieuropium(III), C36H32N10O12Eu2
- The crystal structure of 2-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-((3,4-difluorobenzyl)oxy)styryl)-4,6-dimethoxybenzaldehyde, C24H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoylpyrene, C23H14O
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6-p-cymene)-(N-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) – acetone (1/1), C22H23ClN2F7OPRu
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,3,5,7-tetraphenyl-8-(N-phenylformamido)-2-oxa-5-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct -3-en-7-yl benzoate, C44H34N2O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(3-acetyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-7-(diethylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C21H21N3O4S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-κ2O:O′)nickel(II)], C18H12F4NiN2O6
- Crystal structure of 4-hydroxynaphtho[2,3-b]benzofuran-6,11-dione, C16H8O4
- The crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]dodecane – acetone (1/1), C45H48N2O5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)iminio)methyl)-6-bromophenolate, C17H15N2BrO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-oxalyl dihydrazide-κ4N,O:N′,O′)-bis(μ2-pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)dicadmium(II)] hexahydrate, C16H28O18N6Cd2
- Crystal structure of poly[tetra-(μ4-naphthalene-1,8-dicarboxylato-κ4O:O,O′: O′′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ4-oxo-κ4O:O:O:O) penta-lead(II)], C48H24O17Pb5
- Crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[c,f][1,5]oxabismocin-12 (7H)-yl acetate, C16H15O3Bi
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-chloro-6-nitrophenyl)-1-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl)diazene 1-oxide, C12H6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of bis(3-methyl-N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)nickel(II), C28H26N8O2Ni
- Crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]-dodecane, C40H36Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis[(μ2-4⋯O,O′:O′)-(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)]-di-lead(II)μ-4-hydroxybenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′;κ3O,O′:O′-bis-[(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)di-lead(II)] monohydrate, C52H36N4O12Pb2 ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ3-3,4,5,6-tetrafluoro-phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethene-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C14H9CoF4NO6
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-4-phenyl-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H10O3
- Crystal structure of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(5-oxohexyl)-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C20H24N4O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O)-bis(nitrato-κ1O)zinc(II)], C17H16N6O7Zn
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(6-aminopicolinato-κ2N,O)magnesium(II), C12H14O6N4Mg
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxamide-κ2N,O)-[tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′]nickel(II) diperchlorate — methanol (1/3), C33H39Cl2N9NiO12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3-(4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-acrylato-κO1)-(μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N3:N3′)cobalt(II)], C32H26CoF6N4O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate monohydrate, C22H25NO5S⋅H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(N-oxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl) acetamide κ2O,O′)-diaqua-zinc(II), C6H12ZnN10O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-chlorophenylimino)methyl)pyridinium 3,5-dinitrobenzoate, C19H13ClN4O6
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis((E)-2-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)phenol)zinc(II), C24H20Cl2N4O2Zn
- Crystal structure of cyclo-[tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-p-xylylenediamine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(II)] dimethyl sulfoxide solvate, C20H36Cl4N4O2Pd2S2
- Crystal structure of 4-(3-fluorophenyl)-7-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H9FO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-(pyrimidin-2-yl)hydrazono)methyl)quinolin-1-ium perchlorate – methanol (1/1), C15H16N5O5Cl
- The crystal structure of bis(N-(amino(pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)zinc(II) – methanol (2/5), C57H60Cl2N16O13Zn2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4,4′-di(4-pyridyl)-6,6′-di(tert-butyl)-2,2′-[propylenedioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenol, C35H40N4O4
- Crystal structure of (3E,3′E)-3,3′-((1,3,4-thiadiazole-2,5-diyl)bis(sulfanediyl))bis(4-hydroxy-4-phenylbut-3-en-2-one), C22H18N2O4S3
- Crystal structure of (N-benzyl-N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)di(4-chlorobenzyl)chloridotin(IV), C23H22Cl3NS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) sodium bromide hydrate, [Na(18-crown-6)]Br ⋅ H2O, C12H26BrNaO7
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H13F2N1O4
- Crystal structure of chlorido (2-(4-ethylphenyl)pyrimidine-k2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-kP) palladium(II), C30H26ClN2PPd
- Crystal structure of 18-crown-6 – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene – acetonitrile (1/1/2), C22H30F4I2N2O6
- Crystal structure of diisobutyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C16H24O6
- Crystal structure of poly[[tris(μ2-cis-1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylato)-κ2O, O′]-bis[μ3-1,3,5-tris[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzene-κ3N, N′,N′′]-trizinc(II)] – water (1/20), C60H106N12O32Zn3
- The synthesis and crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide–tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C16H14N4Cl2F6O3S
- Crystal structure of dimethylbis(diisopropyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C16H34N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of diisopropyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C14H20O6
- The synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl (E)-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-5-((2-methoxybenzylidene)amino)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C22H15N3Cl2F6O4S
- The crystal structure of a matrine derivative, 13-(methylamine-1-yl) carbodithioate matrine, C17H27N3OS2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxy-6-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C26H20CuN2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-p-fluorophenyl-5-dihydroxymethyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C9H7FN2O3
- Crystal structure of dichloridobis(4-chlorophenyl-κC1)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tin(IV), C24H16Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of bis{bromido-triphenyltin(IV)}(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′), C46H38Br2N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-chloro-quinolin-8-yloxy)-N-quinolin-8-yl-acetamide, C20H14N3O2Cl
- Crystal structure of bis(N-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(II) — dimethylformamide (1/1), C41H41N9O5Co
- Crystal structure of bis[2-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-1-tosylhydrazin-1-ido-κ3-N,N′,O]copper(II), C30H34N8O4S2Cu
- Crystal structure of (2-p-tolylpyrimidine-κ2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-κP) palladium(II), C29H24ClN2PPd
- Halogen bonding in crystal structure of bis(1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium triiodide, C16H32CsI3O8
- The synthesis and crystal structure of N-(3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfinyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-2-phenylacetamide, C20H10N4Cl2F6O2S
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)nicotinic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-methylbenzyl)thiazolidin-2-one, C11H13ONS
- The crystal structure of 2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(isoquinolin-1-yl)ethane-1,1-diol, C11H8F3NO2
- The crystal structure of 3-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- The crystal structure of 5-nitropicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 3-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-1,5-dioxaspiro[5.5]undecane-2,4-dione, C16H18O5
- Crystal structure of [[Mo3Se7(S2CNEt2)3]2(μ-Se)] ⋅ 2(C6H4Cl2), C42H68Cl4Mo6N6S12Se15
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-hydroxy-3-((5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)thio)pent-3-en-2-one, C13H12N2O3S
- The crystal structure of (2,3-dioxo-5,6:13,14-dibenzo-9,10-benzo-1,4,8,11-7, 11-diene-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-nickel(II), Ni(C22H14N4O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-(1-benzyl-2-ethyl-4-nitro-1H-imidazol-5-ylthio)-propanoic acid, C15H17N3O4S
- The crystal structure of dichlorobis(2-(dicyclohexylphosphino)-2′,4′,6′-tri-i-propyl-1,1′-biphenyl) palladium(II)-dichloroform, C68H100Cl8P2Pd
- Crystal structure and antimicrobial properties of (1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium(I) pentaiodide, C16H32CsI5O8

