Abstract
C51H70O9, triclinic, space group P1 (no. 1), a = 7.67650(10) Å, b = 11.9494(2) Å, c = 13.8656(2) Å, α = 114.055(1)∘, β = 103.568(1)∘, γ = 93.456(1)∘, V = 1111.46(3) Å3, Z = 1, T = 100(11) K.
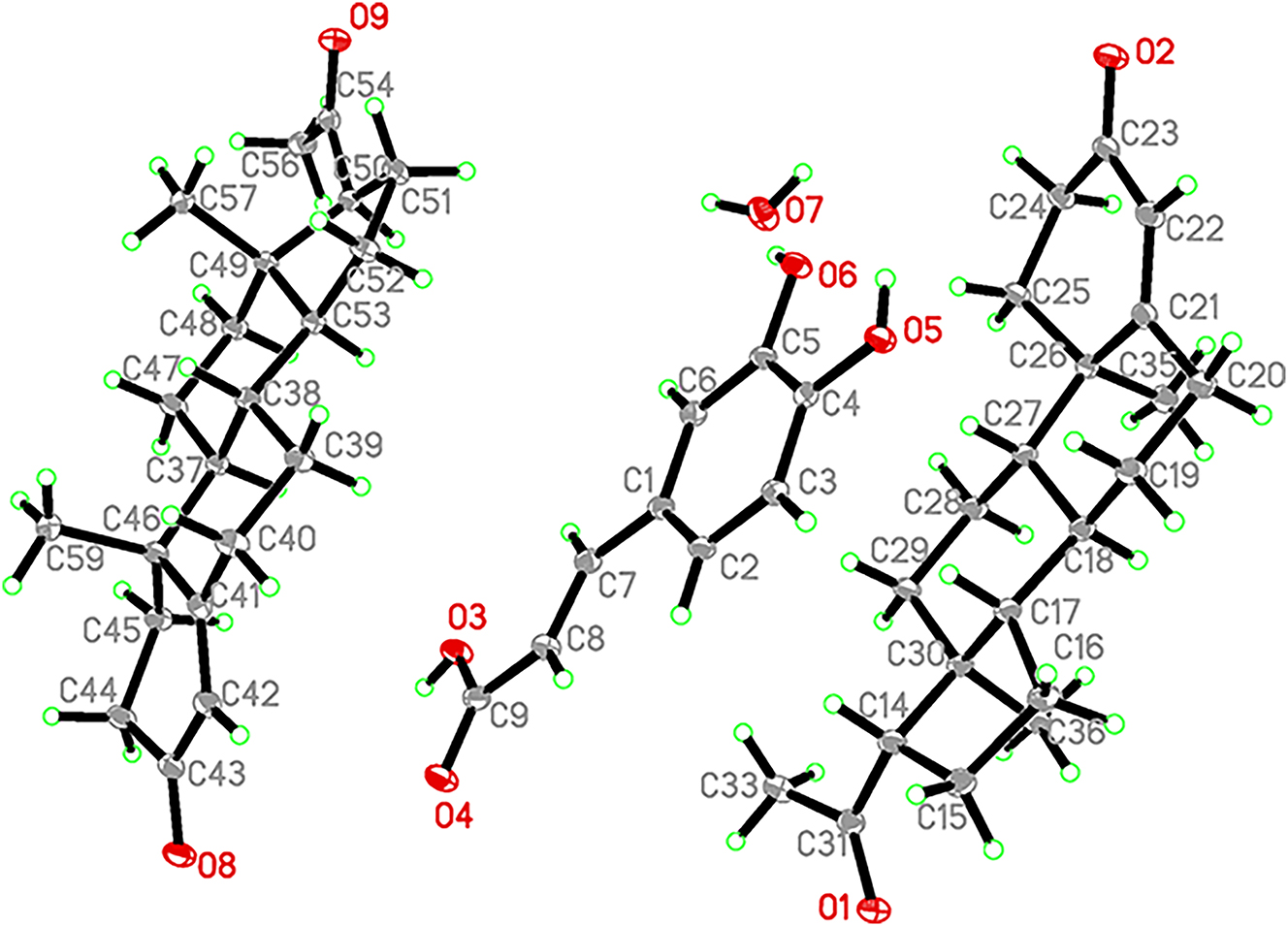
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains the crystallographic data and the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif-file attached to this article.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Clear light colourless block |
| Size: | 0.14 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 0.66 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Rigaku XtaLAB, ω scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 74.2°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 10,987, 5,428, 0.020 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 5,348 |
| N(param)refined: | 553 |
| Programs: | Rigaku, 1 Olex2, 2 SHELX 3 |
1 Source of materials
Equimolar quantities of progesterone (31.5 mg, 0.1 mmol) and caffeic acid (18.0 mg, 0.1 mmol) were dissolved in a 5 mL ethanol/water (v/v = 2:1) solution. The mixture was vigorously stirred for 20 min to ensure complete dissolution. Then the solution was subjected to slow solvent evaporation at room temperature. After 7 days, colorless block crystals were obtained.
2 Experimental details
Using Olex2, 2 the structure was refined with the SHELXL 3 refinement package using least squares minimisation. All H atoms bonded to C or O were idealized and refined using riding model.
3 Comment
Progesterone (PROG) is a key steroid hormone that plays a crucial role in reproductive health. 4 However, PROG has a water solubility of only 5.46 mg/L at room temperature, which suggests it has low oral bioavailability and poor absorption in the body. 5 In recent years, various methods have been developed to improve drug dissolution and bioavailability. 6 Co-crystallization involves the formation of a crystalline complex between progesterone and special cocrystal former, which could significantly improve its pharmacological properties and clinical efficacy. For example, the cocrystal of PROG and isophthalic acid (IPA), showed approximately 3–4 times improvements in AUC0–24h and AUC0–∞, compared with the free PROG. 7 Here, we have firstly prepared the cocrystal of PROG and caffeic acid (CA).
The asymmetric unit of the title compound contains two PROG molecules, one CA molecule, and one water molecule. Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the formation of the cocrystal. The –OH and –COOH groups of CA act as hydrogen bond acceptors, forming O–H⋯O hydrogen bonds with the –C=O groups of PROG molecules, connecting adjacent PROG molecules to create a two-dimensional layered hydrogen bond network. Furthermore, water molecules link the layers of CA through O–H⋯O bonds, resulting in a three-dimensional network structure. Geometric parameters are in general in the expected ranges. 8 , 9
Acknowledgments
This project was sponsored by the Scientific and Technological Brainstorm Project of Henan Province (242102310525).
References
1. Rigaku Oxford DiffractionCrysAlisPRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, England (2015).Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. Olex2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Bulletti, C.; Bulletti, F. M.; Sciorio, R.; Guido, M. Progesterone: The Key Factor of the Beginning of Life. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14138; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214138.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Hassan, A. S.; Soliman, G. M.; El-Mahdy, M. M.; El-Gindy, G. E. A. Solubilization and Enhancement of Ex Vivo Vaginal Delivery of Progesterone Using Solid Dispersions, Inclusion Complexes and Micellar Solubilization. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 110–121; https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201814666170320142136.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Patil, N.; Maheshwari, R.; Wairkar, S. Advances in Progesterone Delivery Systems: Still Work in Progress? Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 643, 123250; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123250.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Xiong, J.; Xu, D.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, S. Improving the Solubility and Bioavailability of Progesterone Cocrystals with Selected Carboxylic Acids. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 816; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060816.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. Garcia-Granda, S.; Beurskens, G.; Beurskens, P. T.; Krishna, T. S. R.; Desiraju, G. R. Structure of 3,4-Dihydroxy-Trans-Cinnamic Acid (Caffeic Acid) and Its Lack of Solid-State Topochemical Reactivity. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 1987, 43, 683; https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108270187094526.Search in Google Scholar
9. Wang, P.; Sun, R.; Yang, X. Cocrystal Structure of Progesterone-isophthalic Acid. Z. Kristallogr. - N. Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239, 919–921. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2024-0233.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (S)-N-(10-((2,2-dimethoxyethyl)amino)-1,2,3-trimethoxy-9-oxo-5,6,7,9-tetrahydrobenzo[a]heptalen-7-yl)acetamide, C25H32N2O7
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-difluoro-3,3′-dimethyl-5,5′-di(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)- [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarbonitrile, C40H24F2N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(di-ethylenediamine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II) tetradedocyloxidohexavanadate] (V4+/V5+ = 2/1), C4H16CdN4O14V6
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(dimethylformamide-κ1N)-(μ4-2′,3,3″,5′-tetrakis(trifluoromethyl)-[1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4″-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,O′: O″,O‴)dicadmium(II)], C27H15CdF12NO5
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenylcarboxylato-O,O′)-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-bis(μ2-salicyladoximato-κ2N,O,O′)-(μ2-isopropoxo)-tris(isopropoxy-κ1O trititanium(IV)), C48H55N2O13Fe2Ti3
- Crystal structure of 3-(diethylamino)-7,9,11-trimethyl-8-phenyl-6H,13H-12λ4,13λ4-chromeno[3′,4′:4,5]pyrrolo[1,2-c]pyrrolo[2,1-f][1,3,2]diazaborinin-6-one, C28H26BF2N3O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-μ2-2-nitro-benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-zinc(II)], C20H13N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-{μ3-1-(3-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′′}manganese(II)] hydrate
- Crystal structure of N′-((1-hydroxycyclohexyl)(phenyl)methyl)-2-methoxybenzohydrazide methanol solvate, C22H28N2O4
- The cocrystal of caffeic acid — progesterone — water (1/2/1), C51H70O9
- Crystal structure of (((oxido(quinolin-6-yl)methoxy)triphenyl-λ5-stibanyl)oxy)(quinolin-7-yl)methanolate
- Crystal structure of [(E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-(2-(((E)-pyren-1-ylmethylene)amino)ethyl)-4′-(2-((E)-1,3,3-trimethylindolin-2-ylidene)ethylidene)-1′,2′,3′,4′-tetrahydrospiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one]-methanol, solvate C57H56N4O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(acridin-9-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione, C17H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of N-(4-acetylphenyl)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanamide, C22H21NO3
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)porphyrin, C52H34N16
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-μ2-[phenylmethanedithiolato-κ4S:S,S′:S′]diiron (Fe–Fe) C13H6Fe2O6S2
- Crystal structure of diiodo-bis(1-((2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ1N)cadmium(II), C34H34CdI2N10
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(3-bromophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H15BrFeO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ3N,O:O′)(6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C12H6Cl2N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-μ 3-(5-(3,5-dicarboxy-2,4,6-trimethylbenzyl)-2,4,6-trimethylisophthalato)-κ 6O,O′:O″,O‴:O‴′,O‴″) terbium(III)-monohydrate], C23H28TbO12
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one – ethanol (1/2), C35H33ClN4O6
- The crystal structure of 3-(5-amino-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)-4-chloro-3-hydroxyindolin-2-one, C17H12ClN3O3
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium 4-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-4, 5-diphenyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl]benzenesulfonate, C29H26FN3O3S
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-ammonio-3-((5-carboxypentyl)thio)propanoate
- Crystal structure of 4-cyclohexyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C12H15N3S2
- The crystal structure of 4,6-bis(dimethylamino)-2-fluoroisophthalonitrile, C12H13FN4
- Hydrogen bonding in the crystal structure of nicotin-1,1′-dium tetrabromidomanganate(II)
- The crystal structure of bis(2-bromobenzyl)(2-((2-oxybenzylidene)amino)-4-methylpentanoato-κ3N, O,O′)tin(IV), C27H27Br2NO3Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(p-tolyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C20H18FeO
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H22FN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of poly(bis(μ2-1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-2,3,5,6-tetrafluoroterephthalato-κ2O:O′)-manganese(II), C38H24F4N12O4Mn
- Crystal structure of (3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C29H32BrO3P
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium hydrogencarbonate – (diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/1/3)
- Crystal structure of N, N-Dimethyl-N′-tosylformimidamide, C10H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H23N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-1,5-bis[(E)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene] thiocarbonohydrazide)-bis(dimethylformamide)-dizinc(II) dimethylformamide solvate, C40H46N10O6S2Zn2⋅C3H7NO
- Crystal structure of azido-κ1N{hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″}copper(II), C24H40BCuN9
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(azido-κ1N)rhenium(I), C15H8N5O3Re
- Crystal structure of 4-((triphenylphosphonio)methyl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II), C24H22Cl4NPZn
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (S)-N-(10-((2,2-dimethoxyethyl)amino)-1,2,3-trimethoxy-9-oxo-5,6,7,9-tetrahydrobenzo[a]heptalen-7-yl)acetamide, C25H32N2O7
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-difluoro-3,3′-dimethyl-5,5′-di(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)- [1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-dicarbonitrile, C40H24F2N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(di-ethylenediamine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II) tetradedocyloxidohexavanadate] (V4+/V5+ = 2/1), C4H16CdN4O14V6
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(dimethylformamide-κ1N)-(μ4-2′,3,3″,5′-tetrakis(trifluoromethyl)-[1,1′:4′,1″-terphenyl]-4,4″-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,O′: O″,O‴)dicadmium(II)], C27H15CdF12NO5
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-ferrocenylcarboxylato-O,O′)-(μ3-oxido-κ3O:O:O)-bis(μ2-salicyladoximato-κ2N,O,O′)-(μ2-isopropoxo)-tris(isopropoxy-κ1O trititanium(IV)), C48H55N2O13Fe2Ti3
- Crystal structure of 3-(diethylamino)-7,9,11-trimethyl-8-phenyl-6H,13H-12λ4,13λ4-chromeno[3′,4′:4,5]pyrrolo[1,2-c]pyrrolo[2,1-f][1,3,2]diazaborinin-6-one, C28H26BF2N3O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-μ2-2-nitro-benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-zinc(II)], C20H13N3O7Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-{μ3-1-(3-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′′}manganese(II)] hydrate
- Crystal structure of N′-((1-hydroxycyclohexyl)(phenyl)methyl)-2-methoxybenzohydrazide methanol solvate, C22H28N2O4
- The cocrystal of caffeic acid — progesterone — water (1/2/1), C51H70O9
- Crystal structure of (((oxido(quinolin-6-yl)methoxy)triphenyl-λ5-stibanyl)oxy)(quinolin-7-yl)methanolate
- Crystal structure of [(E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-(2-(((E)-pyren-1-ylmethylene)amino)ethyl)-4′-(2-((E)-1,3,3-trimethylindolin-2-ylidene)ethylidene)-1′,2′,3′,4′-tetrahydrospiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one]-methanol, solvate C57H56N4O3
- The crystal structure of 1-(acridin-9-yl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione, C17H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of N-(4-acetylphenyl)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanamide, C22H21NO3
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl)porphyrin, C52H34N16
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-μ2-[phenylmethanedithiolato-κ4S:S,S′:S′]diiron (Fe–Fe) C13H6Fe2O6S2
- Crystal structure of diiodo-bis(1-((2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ1N)cadmium(II), C34H34CdI2N10
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(3-bromophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H15BrFeO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly(μ2-6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ3N,O:O′)(6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2O,N)copper(II), C12H6Cl2N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-μ 3-(5-(3,5-dicarboxy-2,4,6-trimethylbenzyl)-2,4,6-trimethylisophthalato)-κ 6O,O′:O″,O‴:O‴′,O‴″) terbium(III)-monohydrate], C23H28TbO12
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one – ethanol (1/2), C35H33ClN4O6
- The crystal structure of 3-(5-amino-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)-4-chloro-3-hydroxyindolin-2-one, C17H12ClN3O3
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium 4-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-4, 5-diphenyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl]benzenesulfonate, C29H26FN3O3S
- Crystal structure of (R)-2-ammonio-3-((5-carboxypentyl)thio)propanoate
- Crystal structure of 4-cyclohexyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C12H15N3S2
- The crystal structure of 4,6-bis(dimethylamino)-2-fluoroisophthalonitrile, C12H13FN4
- Hydrogen bonding in the crystal structure of nicotin-1,1′-dium tetrabromidomanganate(II)
- The crystal structure of bis(2-bromobenzyl)(2-((2-oxybenzylidene)amino)-4-methylpentanoato-κ3N, O,O′)tin(IV), C27H27Br2NO3Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(p-tolyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C20H18FeO
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C21H22FN3O
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of poly(bis(μ2-1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-2,3,5,6-tetrafluoroterephthalato-κ2O:O′)-manganese(II), C38H24F4N12O4Mn
- Crystal structure of (3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C29H32BrO3P
- Crystal structure of tetraethylammonium hydrogencarbonate – (diaminomethylene)thiourea – water (2/1/3)
- Crystal structure of N, N-Dimethyl-N′-tosylformimidamide, C10H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2-methyl-5-oxo-4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H23N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-1,5-bis[(E)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene] thiocarbonohydrazide)-bis(dimethylformamide)-dizinc(II) dimethylformamide solvate, C40H46N10O6S2Zn2⋅C3H7NO
- Crystal structure of azido-κ1N{hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl)borato-κ3N,N′,N″}copper(II), C24H40BCuN9
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(azido-κ1N)rhenium(I), C15H8N5O3Re
- Crystal structure of 4-((triphenylphosphonio)methyl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II), C24H22Cl4NPZn

