Abstract
C30H22F2N2O4Zn, monoclinic, P2/c (no. 13), a = 9.5936(8) Å, b = 11.2561(10) Å, c = 11.9682(10) Å, β = 104.598(3)°, V = 1250.68(19) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0661, wR ref (F2) = 0.1259, T = 173(2) K.
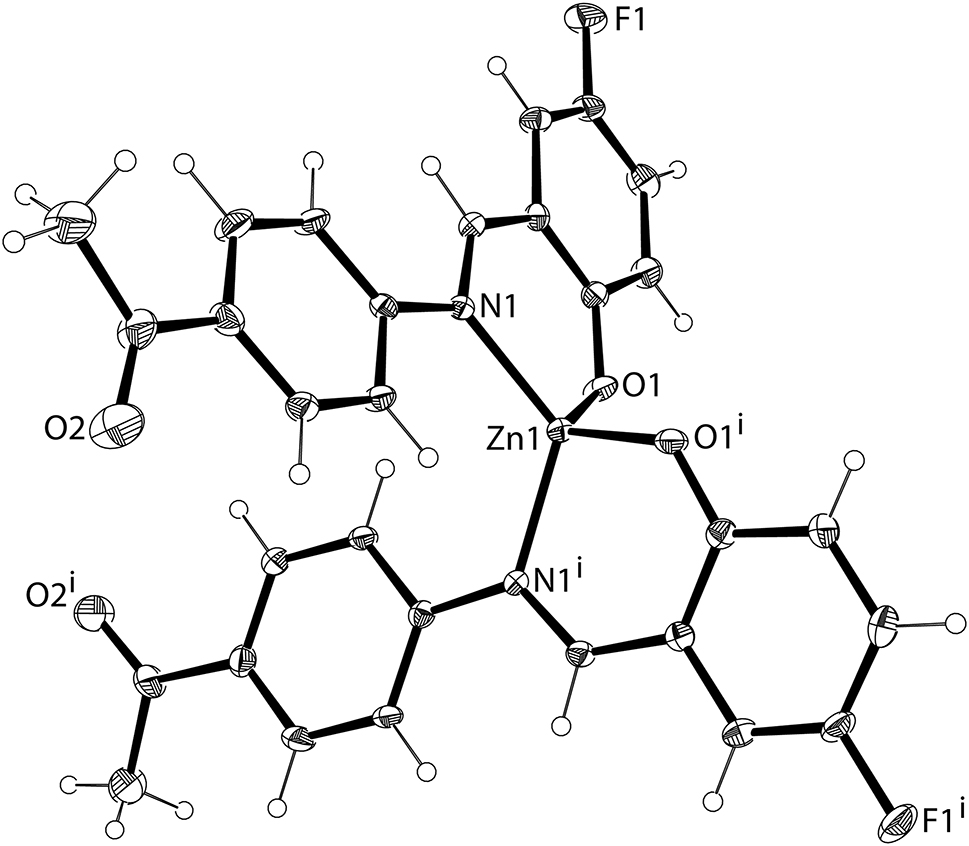
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.12 × 0.10 × 0.09 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.04 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8 Venture, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 26.8°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 11,343, 2650, 0.089 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 2039 |
| N(param)refined: | 178 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn1 | 0.500000 | 0.50312 (6) | 0.750000 | 0.02094 (19) |
| F1 | −0.0886 (3) | 0.3000 (3) | 0.3550 (2) | 0.0434 (7) |
| O1 | 0.3271 (3) | 0.4151 (3) | 0.7440 (2) | 0.0285 (7) |
| N1 | 0.4258 (3) | 0.5871 (3) | 0.5981 (3) | 0.0189 (7) |
| C1 | 0.2304 (4) | 0.3901 (4) | 0.6473 (4) | 0.0232 (9) |
| O2 | 0.8369 (4) | 1.0277 (4) | 0.5818 (3) | 0.0671 (13) |
| C2 | 0.2228 (4) | 0.4488 (4) | 0.5415 (3) | 0.0209 (8) |
| C3 | 0.1132 (4) | 0.4163 (4) | 0.4424 (4) | 0.0261 (9) |
| H3 | 0.107054 | 0.454527 | 0.370547 | 0.031* |
| C4 | 0.0172 (4) | 0.3301 (4) | 0.4510 (4) | 0.0297 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0218 (5) | 0.2712 (4) | 0.5522 (4) | 0.0339 (11) |
| H5 | −0.046314 | 0.210773 | 0.555341 | 0.041* |
| C6 | 0.1270 (5) | 0.3015 (4) | 0.6491 (4) | 0.0313 (10) |
| H6 | 0.130238 | 0.261505 | 0.719569 | 0.038* |
| C7 | 0.3143 (4) | 0.5436 (4) | 0.5238 (3) | 0.0221 (9) |
| H7 | 0.290980 | 0.578927 | 0.449336 | 0.027* |
| C9 | 0.4573 (5) | 0.7476 (4) | 0.4643 (4) | 0.0327 (11) |
| H9 | 0.372022 | 0.724272 | 0.409095 | 0.039* |
| C8 | 0.5011 (4) | 0.6866 (3) | 0.5678 (3) | 0.0204 (8) |
| C10 | 0.5377 (5) | 0.8426 (4) | 0.4411 (4) | 0.0389 (12) |
| H10 | 0.508269 | 0.882757 | 0.369127 | 0.047* |
| C11 | 0.6610 (5) | 0.8798 (4) | 0.5220 (4) | 0.0310 (10) |
| C12 | 0.7035 (4) | 0.8192 (4) | 0.6255 (4) | 0.0260 (9) |
| H12 | 0.787594 | 0.843274 | 0.681641 | 0.031* |
| C13 | 0.6242 (4) | 0.7242 (4) | 0.6475 (3) | 0.0245 (9) |
| H13 | 0.654574 | 0.683478 | 0.719078 | 0.029* |
| C14 | 0.7488 (5) | 0.9832 (4) | 0.5013 (4) | 0.0420 (12) |
| C15 | 0.7259 (7) | 1.0315 (5) | 0.3818 (5) | 0.0618 (18) |
| H15A | 0.739698 | 0.967965 | 0.329595 | 0.093* |
| H15B | 0.795229 | 1.095389 | 0.381584 | 0.093* |
| H15C | 0.627748 | 1.062833 | 0.355738 | 0.093* |
1 Source of material
Synthesis of the ligand: Synthesis of the title complex was prepared by a similar method reported earlier [3], [4], [5]. The batch size was: An ethanol solution (3 mL) of 5-fluoro-2-hydroxy-benzaldehyde (420 mg, 3 mmol) was added dropwise to an ethanol solution (3 mL) of 1-(4-amino-phenyl)ethanone (405 mg, 3 mmol). The mixture was stirred at 238 K for 6 h. We filtered and purified the mixture to obtain the title ligand.
Synthesis of the zinc(II) complex: A methanol solution (2 mL) of the zinc acetate dihydrate (43.9 mg, 0.2 mmol) was added dropwise to a dichloromethane solution (2 mL) of the aforementioned ligand (102.9 mg, 0.4 mmol). The mixture was filtered after being stirred for 1 h at room temperature, and the filtrate was allowed to stand for three weeks at a quiet environment. After partial evaporation of the solvent, several clear light yellow block crystals were obtained.
2 Experimental details
Hydrogen atoms were placed in their geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms.
3 Comment
Schiff bases have become very popular ligands due to their versatility and ease of preparation [6]. The fluoroaromatic Schiff base ligands and their metal complexes have demonstrated to be important in several applications [7]. They can form stable complexes with alkali metals [8] and transition metals [9, 10] and so on. So far, we have designed and synthesized a variety of bis–Schiff base N2O2 type ligands and complexes [11, 12]. More attention has been paid to exploring their mechanisms and applications.
In this article, we designed and synthesized a new zinc(II) complex. The single crystal structure of the title complex has been characterized by X-ray crystallography. Zn1 is tetracoordinated and forms a slightly distorted tetrahedral geometry configuration by two O atoms and two N atoms (cf. the Figure). The Zn1–N1 bond lengths are 2.013(3) and 2.014(3) Å respectively, while the Zn1–O1 bond lengths are both 1.918(3) Å. The angles of N1–Zn1–O1 and N1–Zn1–O1i are 95.93(12)° and 112.45(12)°, respectively. All geometric parameters are similar to those reported in the previous literature [13, 14].
Funding source: Open Project Program of Shihezi University
Award Identifier / Grant number: ZZZC2021117
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This project was supported by the Open Project Program of Shihezi University (ZZZC2021117).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX3, SAINT; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2016.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
3. Jin, Y., Fu, T., Ma, B. Y., Wei, P., Zhao, J. X., Zhao, L. Crystal structure of 1-{4-[(4-fluoro-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)amino]phenyl}ethanone, C15H12FNO2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 1099–1100; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020-0186.Search in Google Scholar
4. Fu, T., Ma, J. X., Li, Q. L., Wei, P., Zhao, J. X., Zhao, L. Crystal structure of (E)-1-{4-[(4-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino]phenyl} ethanone O-methyl oxime, C16H15FN2O2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 293–295; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2019-0614.Search in Google Scholar
5. Zhao, J. X. Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(2-(((4-(1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl) phenyl)imino)methyl)-5-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O)zinc(II)-methanol(1/1), C33H32F2N4O4Zn. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 69–71; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2019-0491.Search in Google Scholar
6. Chang, J., Zhang, H. J., Jia, H. R., Sun, Y. X. Binuclear nickel(II) and zinc(II) complexes based on 2-amino-3-hydroxy-pyridine Schiff base: syntheses, supramolecular structures and spectral properties. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 34, 2097–2107.Search in Google Scholar
7. Luo, Y. Y., Wang, J. Q., Ding, X., Ni, R., Li, M. H., Yang, T., Wang, J., Jing, C. L., You, Z. L. Syntheses, crystal structures and antimicrobial activities of polynuclear CoII, NiII and ZnII complexes derived from the N,N′-bis (4-fluorosalicylidene)-1,3-propanediamine Schiff base. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2021, 516, 120146; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2020.120146.Search in Google Scholar
8. Garcia-Valle, F. M., Tabernero, V., Cuenca, T., Mosquera, M. E., Cano, J. Intramolecular C–F activation in Schiff-base alkali metal complexes. Organometallics 2019, 38, 894–904; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.organomet.8b00868.Search in Google Scholar
9. Kumar, N., Asatkar, A. K., Panda, S., Zade, S. S. Synthesis, characterization and supramolecular building motifs of substituted salphen- and thiasalphen-metal complexes. Polyhedron 2016, 117, 718–728; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2016.06.050.Search in Google Scholar
10. Fu, T., Ma, J. X., Wei, P., Li, Q. L., Zhao, J. X., Zhao, L. Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-(((4-(1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino) methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II)-dichloromethane(1/1), C34H32Br2Cl4CoN4O4. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 59–60; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2019-0474.Search in Google Scholar
11. Zhao, J. X., Wang, X. J. Crystal structure of N,N′-bis(4-fluorosalicylaldehyde)-3,6-dioxa-1,8-diaminooctane, C20H22F2N2O4. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 937–938; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0317.Search in Google Scholar
12. Zhao, J. X., Wang, X. J. Crystal structure of {N,N′-bis(4-fluorosalicylaldehyde)-3,6-dioxa-1,8-diaminooctane-κ4O,N,N′,O′}zinc(II), C20H20F2N2O4Zn. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 985–986; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0323.Search in Google Scholar
13. Li, Q. L., Li, P. P., Ma, J. X., Zhao, J. X., Zhao, L. Crystal structure of bis{2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl) imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C32H30N4O4Zn. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2018, 233, 637–639; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2017-0404.Search in Google Scholar
14. Hulushe, S. T., Malan, F. P., Hosten, E. C., Akerman, M. P., Lemmerer, A., Khanye, S. D., Watkins, G. M. Cation-/ligand-induced solvent-assisted transformations of Zn(II) and Cu(II) complexes featuring single-pocket multidentate chelating members. Cryst. Growth Des. 2023, 23, 4836–4854; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.3c00055.Search in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-3,3′-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate-N:N′:O:O′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of (8R,8′S,13S,13′R)-8,8′-bis(hydroxymethyl)-9,9′,10,10′-tetramethoxy-5,5′,6,6′,8,8′,13,13′-octahydro-[13,13′-bi[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinoline]-7,7′-diium chloride-methanol (1/2), C46H58N2O14Cl2
- The crystal structure of 8-methoxy-2,2-diphenyl-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C29H25BN2O3S
- Crystal structure of aqua-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N‴)copper(II) 5-carboxyisophthalate tetrahydrate, C25H50N4CuO11
- The crystal structure of 1-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfonyl)-2,2-diphenyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ij]quinoline, C31H23BN2O2S
- Crystal structure of iodido-(η6-benzene) (1-(pyridin-2-yl)-N-(p-fluoro-methanamine)-κ2N,Nʹ)ruthenium(II) hexaflourophosphate, (C18H15F7IN2RuP)
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolyl) propylidene)-1,3-dihydro-2H-inden-2-one, C25H20O2
- Crystal structure of tricyclohexyl[4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-benzoato-κO]tin(IV), C27H39N3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-2,6-difluorophenyl)amino)benzoate, C20H18F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)propane-1,3-diol, C6H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitrophenyl) hydrazine, C12H8N6O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)-1,2-dihydro-4H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-4-one, C19H14Cl2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-5-oxo-4-(1-oxo-4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)isoindolin-2-yl)pentanoic acid, C17H19N3O5
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(2-(((Z)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino) phenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C33H23Br2N5O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-methoxy-6-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C11H11N3O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-((tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)methyl)-5,5-diphenyl-6-(p-tolyl) tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-one, C41H42O2Si
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-5-(4-cyanophenoxy)benzyl 1-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carboxylate, C21H19BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C10H14F6N2P
- The crystal structure of 2,2-di(thiophen-3-yl)-1-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C24H19BN2O2S3
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-1-(2-iodobenzoyl)-1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde, C16H9BrINO2
- The crystal structure of monocarbonyl-2-carboxypyridinato-κ2N,O-triphenylphosphine-rhodium(I) acetonitrile solvate, C26H20.50N1.50O3PRh
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-tetrakis(1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ1N)manganese(II), C60H68O4N12Cl10Mn
- Crystal structure of 3-(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)-1-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-2,2-diphenylpropan-1-ol, C37H36Cl2OSi
- Crystal structure of langite from Mine du Pradet (France)
- The crystal structure of 5′-(furan-2-yl)-3′-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]-4′-carboxylic acid, C30H27NO5S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(((4-acetophenone)imino)methyl)-4-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C30H22F2N2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of poly[(tripyridine-κ3N,N′,N″) μ3-(pyridine-3,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N:O:O′) manganese(II)], C22H22N4O8Mn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15ClN2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino) ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II), C40H46CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-[(1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)cobalt(II)], C6H12CoN2O8
- (6R,7S)-2,3,13-trimethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[3′,4′]cycloocta [1′,2′:4,5]benzo[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-1-ol, C22H26O6
- Crystal structure of 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)amino)benzoic acid, C18H14Cl2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (5aS,6aS,8aR,9R,11aS, 11bS,13R,13aS)-1,1,8a,11a-tetramethyl-9-((S)-1-((S)-5-methyl-6-oxo-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-3-oxo-1,7,8,8a,9,10,11,11a,11b,12,13,13a-dodecahydro-3H,6H-cyclopenta[5,6]cyclopropa[1,8a]naphtho[2,1-c]oxepin-13-yl acetate, C32H44O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-O,O′:O″)cobalt(II)], C12H12N2O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)-amino]-2-(2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoyl)-acrylic acid ethyl ester, C17H13F4NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3-methoxybenzoate, C13H16O6
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile, C13H7BrClF3N2
- The crystal structure of triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O,O)nickel(II) monohydrate, C12H15NO9Ni
- Crystal structure of dihydroxy(2,4,6-triisopro-pylphenyl)telluronium trifluoromethanesulfonate, C16H25F3O5STe
- The crystal structure of 1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tris(dibromomethyl)benzene, C9H6Br6
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-N-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-imine, C25H21N5OS
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(phenylimino)-2,3-dihydrothiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C24H16N2O3S
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-3,3′-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate-N:N′:O:O′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of (8R,8′S,13S,13′R)-8,8′-bis(hydroxymethyl)-9,9′,10,10′-tetramethoxy-5,5′,6,6′,8,8′,13,13′-octahydro-[13,13′-bi[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinoline]-7,7′-diium chloride-methanol (1/2), C46H58N2O14Cl2
- The crystal structure of 8-methoxy-2,2-diphenyl-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C29H25BN2O3S
- Crystal structure of aqua-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N‴)copper(II) 5-carboxyisophthalate tetrahydrate, C25H50N4CuO11
- The crystal structure of 1-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfonyl)-2,2-diphenyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ij]quinoline, C31H23BN2O2S
- Crystal structure of iodido-(η6-benzene) (1-(pyridin-2-yl)-N-(p-fluoro-methanamine)-κ2N,Nʹ)ruthenium(II) hexaflourophosphate, (C18H15F7IN2RuP)
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolyl) propylidene)-1,3-dihydro-2H-inden-2-one, C25H20O2
- Crystal structure of tricyclohexyl[4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-benzoato-κO]tin(IV), C27H39N3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-2,6-difluorophenyl)amino)benzoate, C20H18F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)propane-1,3-diol, C6H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitrophenyl) hydrazine, C12H8N6O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)-1,2-dihydro-4H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-4-one, C19H14Cl2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-5-oxo-4-(1-oxo-4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)isoindolin-2-yl)pentanoic acid, C17H19N3O5
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(2-(((Z)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino) phenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C33H23Br2N5O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-methoxy-6-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C11H11N3O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-((tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)methyl)-5,5-diphenyl-6-(p-tolyl) tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-one, C41H42O2Si
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-5-(4-cyanophenoxy)benzyl 1-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carboxylate, C21H19BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C10H14F6N2P
- The crystal structure of 2,2-di(thiophen-3-yl)-1-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C24H19BN2O2S3
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-1-(2-iodobenzoyl)-1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde, C16H9BrINO2
- The crystal structure of monocarbonyl-2-carboxypyridinato-κ2N,O-triphenylphosphine-rhodium(I) acetonitrile solvate, C26H20.50N1.50O3PRh
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-tetrakis(1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ1N)manganese(II), C60H68O4N12Cl10Mn
- Crystal structure of 3-(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)-1-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-2,2-diphenylpropan-1-ol, C37H36Cl2OSi
- Crystal structure of langite from Mine du Pradet (France)
- The crystal structure of 5′-(furan-2-yl)-3′-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]-4′-carboxylic acid, C30H27NO5S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(((4-acetophenone)imino)methyl)-4-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C30H22F2N2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of poly[(tripyridine-κ3N,N′,N″) μ3-(pyridine-3,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N:O:O′) manganese(II)], C22H22N4O8Mn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15ClN2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino) ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II), C40H46CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-[(1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)cobalt(II)], C6H12CoN2O8
- (6R,7S)-2,3,13-trimethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[3′,4′]cycloocta [1′,2′:4,5]benzo[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-1-ol, C22H26O6
- Crystal structure of 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)amino)benzoic acid, C18H14Cl2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (5aS,6aS,8aR,9R,11aS, 11bS,13R,13aS)-1,1,8a,11a-tetramethyl-9-((S)-1-((S)-5-methyl-6-oxo-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-3-oxo-1,7,8,8a,9,10,11,11a,11b,12,13,13a-dodecahydro-3H,6H-cyclopenta[5,6]cyclopropa[1,8a]naphtho[2,1-c]oxepin-13-yl acetate, C32H44O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-O,O′:O″)cobalt(II)], C12H12N2O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)-amino]-2-(2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoyl)-acrylic acid ethyl ester, C17H13F4NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3-methoxybenzoate, C13H16O6
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile, C13H7BrClF3N2
- The crystal structure of triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O,O)nickel(II) monohydrate, C12H15NO9Ni
- Crystal structure of dihydroxy(2,4,6-triisopro-pylphenyl)telluronium trifluoromethanesulfonate, C16H25F3O5STe
- The crystal structure of 1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tris(dibromomethyl)benzene, C9H6Br6
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-N-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-imine, C25H21N5OS
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(phenylimino)-2,3-dihydrothiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C24H16N2O3S

