Abstract
C19H14Cl2N2O3, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 10.635(3) Å, b = 8.772(3) Å, c = 19.656(6) Å, β = 98.256(10)°, V = 1814.8(10) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.0602, wR ref (F2) = 0.1547, T = 205 K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.28 × 0.17 × 0.12 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.38 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.5°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 11,337, 3365, 0.092 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 1909 |
| N(param)refined: | 237 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2, 3], OLEX2 [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.2978 (4) | 0.4369 (5) | 0.2796 (2) | 0.0424 (10) |
| C2 | 0.3766 (3) | 0.3319 (4) | 0.32746 (19) | 0.0324 (9) |
| C3 | 0.3187 (3) | 0.2273 (4) | 0.3662 (2) | 0.0392 (10) |
| H3 | 0.2304 | 0.2121 | 0.3572 | 0.047* |
| C4 | 0.3906 (4) | 0.1463 (5) | 0.4175 (2) | 0.0462 (11) |
| H4 | 0.3516 | 0.0735 | 0.4427 | 0.055* |
| C5 | 0.5202 (4) | 0.1710 (5) | 0.4323 (2) | 0.0435 (10) |
| H5 | 0.5680 | 0.1171 | 0.4685 | 0.052* |
| C6 | 0.5796 (3) | 0.2732 (4) | 0.39478 (19) | 0.0372 (10) |
| H6 | 0.6676 | 0.2891 | 0.4051 | 0.045* |
| C7 | 0.5084 (3) | 0.3536 (4) | 0.34123 (18) | 0.0310 (9) |
| C8 | 0.4886 (3) | 0.4733 (5) | 0.23293 (19) | 0.0404 (10) |
| H8A | 0.4846 | 0.3767 | 0.2077 | 0.048* |
| H8B | 0.5298 | 0.5487 | 0.2067 | 0.048* |
| C9 | 0.6708 (3) | 0.5400 (4) | 0.32343 (19) | 0.0331 (9) |
| C10 | 0.7855 (3) | 0.5188 (4) | 0.29773 (19) | 0.0340 (9) |
| C11 | 0.8936 (3) | 0.6009 (4) | 0.3231 (2) | 0.0397 (10) |
| H11 | 0.9696 | 0.5854 | 0.3049 | 0.048* |
| C12 | 0.8894 (3) | 0.7060 (5) | 0.3756 (2) | 0.0386 (10) |
| C13 | 0.7759 (3) | 0.7303 (4) | 0.40163 (19) | 0.0378 (10) |
| H13 | 0.7725 | 0.8017 | 0.4370 | 0.045* |
| C14 | 0.6687 (3) | 0.6499 (4) | 0.3755 (2) | 0.0353 (9) |
| C15 | 1.0045 (4) | 0.7920 (5) | 0.40531 (19) | 0.0426 (10) |
| C16 | 1.1209 (4) | 0.7318 (6) | 0.4357 (2) | 0.0517 (12) |
| C17 | 1.1640 (5) | 0.5727 (6) | 0.4460 (3) | 0.0734 (15) |
| H17A | 1.2541 | 0.5712 | 0.4634 | 0.110* |
| H17B | 1.1490 | 0.5187 | 0.4025 | 0.110* |
| H17C | 1.1173 | 0.5235 | 0.4788 | 0.110* |
| C18 | 1.0166 (4) | 0.9477 (5) | 0.4114 (2) | 0.0515 (12) |
| C19 | 0.9335 (4) | 1.0780 (5) | 0.3873 (2) | 0.0612 (14) |
| H19A | 0.9383 | 1.1544 | 0.4233 | 0.092* |
| H19B | 0.8465 | 1.0428 | 0.3762 | 0.092* |
| H19C | 0.9611 | 1.1220 | 0.3467 | 0.092* |
| Cl1 | 0.79365 (11) | 0.38389 (13) | 0.23440 (6) | 0.0543 (3) |
| Cl2 | 0.52880 (9) | 0.68222 (13) | 0.40873 (6) | 0.0512 (3) |
| N1 | 0.5624 (3) | 0.4532 (3) | 0.29869 (15) | 0.0359 (8) |
| N2 | 1.1994 (3) | 0.8430 (4) | 0.45971 (19) | 0.0555 (10) |
| O1 | 0.3611 (2) | 0.5235 (3) | 0.23862 (14) | 0.0482 (8) |
| O2 | 0.1850 (3) | 0.4520 (4) | 0.27784 (16) | 0.0647 (9) |
| O3 | 1.1340 (3) | 0.9826 (4) | 0.44338 (17) | 0.0679 (9) |
1 Source of materials
To a stirred mixture of 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)amino)benzoic acid (1.88 g, 5 mmol) and dibromomethane (2.60 g, 15 mmol) in dioxane (20 mL) was added potassium carbonate (2.76 g, 20 mmol) and the reaction mixture was refluxed for 6 h. The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC. After completion of reaction, the mixture was evaporated to give residue under reduced pressure. The title compound was separated by silica-gel column chromatography with ethyl acetate-petroleum ether (20 %) gradient solvent system. The target product was obtained as a white solid. Yield: 53.1 %.
2 Experimental details
Hydrogen atoms were positioned at idealized positions and refined as riding atoms, with their Uiso (isotropic displacement parameter) values set to 1.2 times the Ueq (equivalent isotropic displacement parameter) values of the respective parent atoms. The crystal structure was solved using ShelXT [2] and refined in the Olex2 software [4].
3 Comment
Aniline and its derivatives are widely recognized as one of the primary materials utilized in various industrial sectors [5]. Several crystal structures of compounds with comparable architectures have been documented [6], [7], [8], [9], [10].
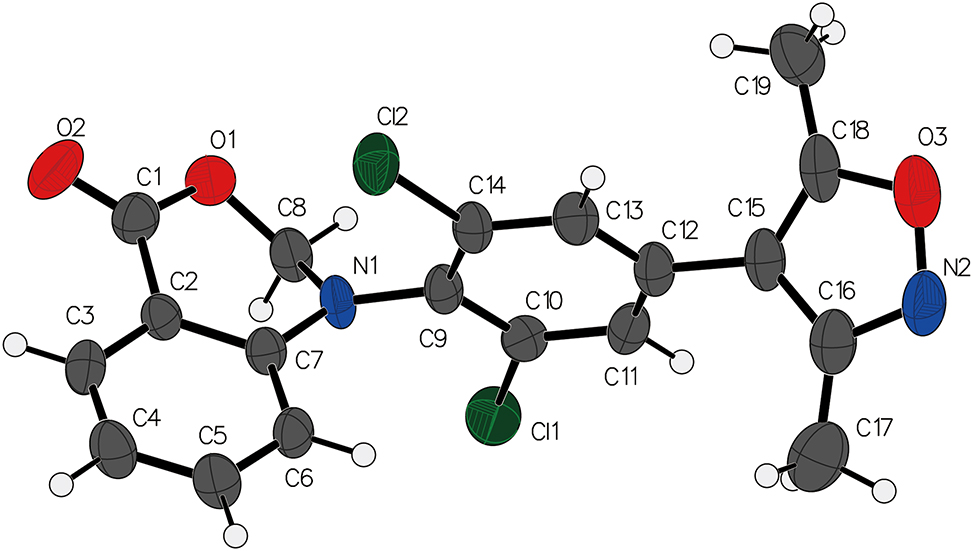
The crystal structure of the reported compound reveals that the two phenyl rings are not in the same plane to each other, exhibiting a dihedral angle of 60.2°. Additionally, the pyrazole heterocycle and the dichlorophenyl ring form a dihedral angle of 72°. It should be noted that the atoms in the [1,3]oxazine ring do not lie in the same plane, evidenced by a dihedral angle of 52.6(5)° for C1–O1–C8–N1. The bond lengths and bond angles of all substances evaluated fall within the normal range as per established standards in the field [11], [12], [13].
Remarkably, the crystal structure of the title compound does not exhibit evident hydrogen bonding or p⃛p interactions between molecules, suggesting that the crystal packing is primarily governed by van der Waals forces and stacking interactions.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Drug Synthesis of Xianyang city (2021QXNL-PT-0008) and Effective Substances of Traditional Chinese Medicine Innovative Team in Shaanxi Institute of International Trade & Commerce (SSY18TD01).
References
1. Bruker. SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
5. Mary, A., Kanagathara, N., Baby Suganthi, A. R. A brief review on aniline and its derivatives. Mater. Today: Proc. 2020, 33, 4751–4755; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.08.358.Search in Google Scholar
6. Liu, D., Zhang, Z., Zhang, H., Wang, Y. A novel approach towards white photoluminescence and electroluminescence by controlled protonation of a blue fluorophore. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 10001–10003; https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc45991h.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Chupakhin, O. N., Shchepochkin, A. V., Charushin, V. N., Maiorova, A. V., Kulikova, T. V., Shunyaev, K. Y., Enyashin, A. N., Slepukhin, P. A., Suvorova, A. I. Electrochemical oxidative aromatization of 9-substituted 9,10-dihydroacridines: cleavage of C–H vs C–X bond. Chem. Heterocycl. Comp. 2019, 55, 956–963; https://doi.org/10.1007/s10593-019-02562-x.Search in Google Scholar
8. Gong, Y., Tan, Y., Liu, J., Lu, P., Feng, C., Yuan, W. Z., Lu, Y., Sun, J. Z., He, G., Zhang, Y. Twisted D-π–a solid emitters: efficient emission and high contrast mechanochromism. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 4009–4011; https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc39243k.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Louillat, M.-L., Patureau, F. W. Toward polynuclear Ru–Cu catalytic dehydrogenative C–N bond formation, on the reactivity of carbazoles. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 164–167; https://doi.org/10.1021/ol303216u.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Aigret, B. M., Jacobs, J., Van Meervelt, L., De Borggraeve, W. M. Asymmetric synthesis of 1-aza-4-deoxypicropodophyllotoxin. Synlett 2013, 24, 1097–1100; https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1338414.Search in Google Scholar
11. Bhunia, A., Porwal, D., Gonnade, R. G., Biju, A. T. Multicomponent reactions involving arynes, quinolines, and aldehydes. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 4620–4623; https://doi.org/10.1021/ol4023134.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Shidlovskii, A. F., Golubev, A. S., Gusev, D. V., Suponitsky, K. Y., Peregudov, A. S., Chkanikov, N. D. A new synthesis of N-substituted o-trifluoroacetylanilines. J. Fluorine Chem. 2012, 143, 272–280; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluchem.2012.07.002.Search in Google Scholar
13. Thamotharan, S., Parthasarathi, V., Vijayalakshmi, L., Anuradha, B., Desai, B., Shah, A. 3-Benzylidene-1-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)indolin-2-one. Acta Crystallogr. 2002, E58, o885–o886; https://doi.org/10.1107/s160053680201111x.Search in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-3,3′-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate-N:N′:O:O′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of (8R,8′S,13S,13′R)-8,8′-bis(hydroxymethyl)-9,9′,10,10′-tetramethoxy-5,5′,6,6′,8,8′,13,13′-octahydro-[13,13′-bi[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinoline]-7,7′-diium chloride-methanol (1/2), C46H58N2O14Cl2
- The crystal structure of 8-methoxy-2,2-diphenyl-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C29H25BN2O3S
- Crystal structure of aqua-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N‴)copper(II) 5-carboxyisophthalate tetrahydrate, C25H50N4CuO11
- The crystal structure of 1-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfonyl)-2,2-diphenyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ij]quinoline, C31H23BN2O2S
- Crystal structure of iodido-(η6-benzene) (1-(pyridin-2-yl)-N-(p-fluoro-methanamine)-κ2N,Nʹ)ruthenium(II) hexaflourophosphate, (C18H15F7IN2RuP)
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolyl) propylidene)-1,3-dihydro-2H-inden-2-one, C25H20O2
- Crystal structure of tricyclohexyl[4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-benzoato-κO]tin(IV), C27H39N3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-2,6-difluorophenyl)amino)benzoate, C20H18F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)propane-1,3-diol, C6H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitrophenyl) hydrazine, C12H8N6O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)-1,2-dihydro-4H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-4-one, C19H14Cl2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-5-oxo-4-(1-oxo-4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)isoindolin-2-yl)pentanoic acid, C17H19N3O5
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(2-(((Z)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino) phenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C33H23Br2N5O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-methoxy-6-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C11H11N3O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-((tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)methyl)-5,5-diphenyl-6-(p-tolyl) tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-one, C41H42O2Si
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-5-(4-cyanophenoxy)benzyl 1-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carboxylate, C21H19BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C10H14F6N2P
- The crystal structure of 2,2-di(thiophen-3-yl)-1-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C24H19BN2O2S3
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-1-(2-iodobenzoyl)-1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde, C16H9BrINO2
- The crystal structure of monocarbonyl-2-carboxypyridinato-κ2N,O-triphenylphosphine-rhodium(I) acetonitrile solvate, C26H20.50N1.50O3PRh
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-tetrakis(1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ1N)manganese(II), C60H68O4N12Cl10Mn
- Crystal structure of 3-(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)-1-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-2,2-diphenylpropan-1-ol, C37H36Cl2OSi
- Crystal structure of langite from Mine du Pradet (France)
- The crystal structure of 5′-(furan-2-yl)-3′-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]-4′-carboxylic acid, C30H27NO5S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(((4-acetophenone)imino)methyl)-4-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C30H22F2N2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of poly[(tripyridine-κ3N,N′,N″) μ3-(pyridine-3,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N:O:O′) manganese(II)], C22H22N4O8Mn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15ClN2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino) ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II), C40H46CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-[(1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)cobalt(II)], C6H12CoN2O8
- (6R,7S)-2,3,13-trimethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[3′,4′]cycloocta [1′,2′:4,5]benzo[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-1-ol, C22H26O6
- Crystal structure of 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)amino)benzoic acid, C18H14Cl2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (5aS,6aS,8aR,9R,11aS, 11bS,13R,13aS)-1,1,8a,11a-tetramethyl-9-((S)-1-((S)-5-methyl-6-oxo-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-3-oxo-1,7,8,8a,9,10,11,11a,11b,12,13,13a-dodecahydro-3H,6H-cyclopenta[5,6]cyclopropa[1,8a]naphtho[2,1-c]oxepin-13-yl acetate, C32H44O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-O,O′:O″)cobalt(II)], C12H12N2O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)-amino]-2-(2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoyl)-acrylic acid ethyl ester, C17H13F4NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3-methoxybenzoate, C13H16O6
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile, C13H7BrClF3N2
- The crystal structure of triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O,O)nickel(II) monohydrate, C12H15NO9Ni
- Crystal structure of dihydroxy(2,4,6-triisopro-pylphenyl)telluronium trifluoromethanesulfonate, C16H25F3O5STe
- The crystal structure of 1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tris(dibromomethyl)benzene, C9H6Br6
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-N-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-imine, C25H21N5OS
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(phenylimino)-2,3-dihydrothiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C24H16N2O3S
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-3,3′-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate-N:N′:O:O′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of (8R,8′S,13S,13′R)-8,8′-bis(hydroxymethyl)-9,9′,10,10′-tetramethoxy-5,5′,6,6′,8,8′,13,13′-octahydro-[13,13′-bi[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinoline]-7,7′-diium chloride-methanol (1/2), C46H58N2O14Cl2
- The crystal structure of 8-methoxy-2,2-diphenyl-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C29H25BN2O3S
- Crystal structure of aqua-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N‴)copper(II) 5-carboxyisophthalate tetrahydrate, C25H50N4CuO11
- The crystal structure of 1-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfonyl)-2,2-diphenyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ij]quinoline, C31H23BN2O2S
- Crystal structure of iodido-(η6-benzene) (1-(pyridin-2-yl)-N-(p-fluoro-methanamine)-κ2N,Nʹ)ruthenium(II) hexaflourophosphate, (C18H15F7IN2RuP)
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolyl) propylidene)-1,3-dihydro-2H-inden-2-one, C25H20O2
- Crystal structure of tricyclohexyl[4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-benzoato-κO]tin(IV), C27H39N3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-2,6-difluorophenyl)amino)benzoate, C20H18F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)propane-1,3-diol, C6H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitrophenyl) hydrazine, C12H8N6O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)-1,2-dihydro-4H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-4-one, C19H14Cl2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-5-oxo-4-(1-oxo-4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)isoindolin-2-yl)pentanoic acid, C17H19N3O5
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(2-(((Z)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino) phenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C33H23Br2N5O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-methoxy-6-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C11H11N3O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-((tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)methyl)-5,5-diphenyl-6-(p-tolyl) tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-one, C41H42O2Si
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-5-(4-cyanophenoxy)benzyl 1-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carboxylate, C21H19BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C10H14F6N2P
- The crystal structure of 2,2-di(thiophen-3-yl)-1-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C24H19BN2O2S3
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-1-(2-iodobenzoyl)-1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde, C16H9BrINO2
- The crystal structure of monocarbonyl-2-carboxypyridinato-κ2N,O-triphenylphosphine-rhodium(I) acetonitrile solvate, C26H20.50N1.50O3PRh
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-tetrakis(1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ1N)manganese(II), C60H68O4N12Cl10Mn
- Crystal structure of 3-(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)-1-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-2,2-diphenylpropan-1-ol, C37H36Cl2OSi
- Crystal structure of langite from Mine du Pradet (France)
- The crystal structure of 5′-(furan-2-yl)-3′-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]-4′-carboxylic acid, C30H27NO5S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(((4-acetophenone)imino)methyl)-4-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C30H22F2N2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of poly[(tripyridine-κ3N,N′,N″) μ3-(pyridine-3,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N:O:O′) manganese(II)], C22H22N4O8Mn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15ClN2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino) ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II), C40H46CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-[(1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)cobalt(II)], C6H12CoN2O8
- (6R,7S)-2,3,13-trimethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[3′,4′]cycloocta [1′,2′:4,5]benzo[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-1-ol, C22H26O6
- Crystal structure of 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)amino)benzoic acid, C18H14Cl2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (5aS,6aS,8aR,9R,11aS, 11bS,13R,13aS)-1,1,8a,11a-tetramethyl-9-((S)-1-((S)-5-methyl-6-oxo-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-3-oxo-1,7,8,8a,9,10,11,11a,11b,12,13,13a-dodecahydro-3H,6H-cyclopenta[5,6]cyclopropa[1,8a]naphtho[2,1-c]oxepin-13-yl acetate, C32H44O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-O,O′:O″)cobalt(II)], C12H12N2O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)-amino]-2-(2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoyl)-acrylic acid ethyl ester, C17H13F4NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3-methoxybenzoate, C13H16O6
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile, C13H7BrClF3N2
- The crystal structure of triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O,O)nickel(II) monohydrate, C12H15NO9Ni
- Crystal structure of dihydroxy(2,4,6-triisopro-pylphenyl)telluronium trifluoromethanesulfonate, C16H25F3O5STe
- The crystal structure of 1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tris(dibromomethyl)benzene, C9H6Br6
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-N-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-imine, C25H21N5OS
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(phenylimino)-2,3-dihydrothiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C24H16N2O3S

