Abstract
C17H13F4NO4, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 5.470(4) Å, b = 26.141(17) Å, c = 11.689(8) Å, β = 90.01°, V = 1671.3(19) Å3, Z = 4,
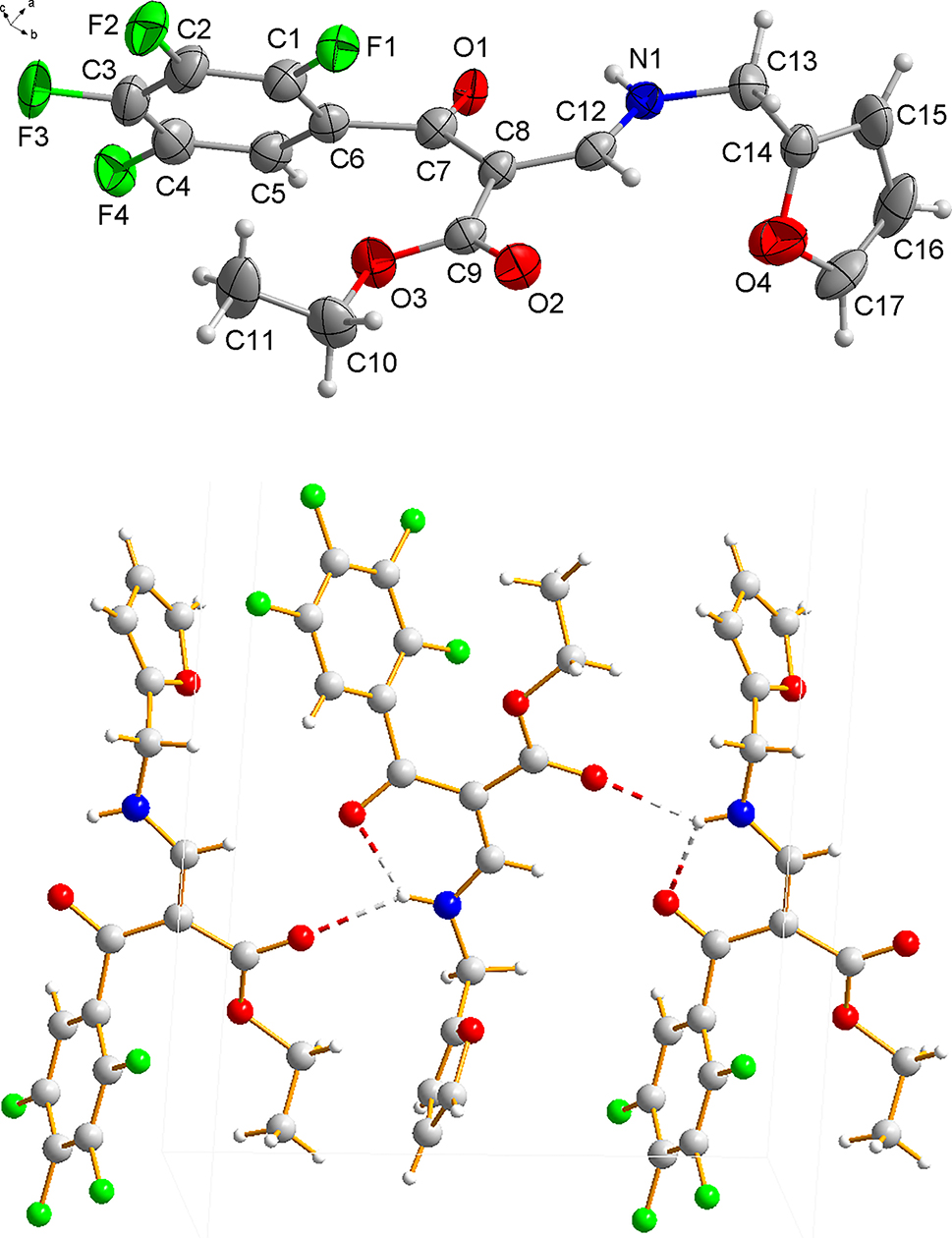
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.23 × 0.15 × 0.12 mm |
| Wavelength: μ: |
Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) 0.13 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: θmax, completeness: |
Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω 25.5°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 12318, 3110, 0.038 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2003 |
| N(param)refined: | 236 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2, 3], Diamond [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.4256 (7) | 0.10776 (13) | 0.1482 (3) | 0.0640 (9) |
| C2 | 0.2953 (8) | 0.06564 (14) | 0.1825 (4) | 0.0774 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0946 (8) | 0.07244 (17) | 0.2500 (4) | 0.0809 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0326 (7) | 0.12043 (17) | 0.2814 (3) | 0.0708 (10) |
| C5 | 0.1619 (6) | 0.16284 (14) | 0.2500 (3) | 0.0605 (9) |
| H5 | 0.1158 | 0.1951 | 0.2757 | 0.073* |
| C6 | 0.3622 (6) | 0.15700 (12) | 0.1794 (2) | 0.0525 (8) |
| C7 | 0.5149 (6) | 0.20285 (11) | 0.1511 (2) | 0.0526 (8) |
| C8 | 0.5884 (6) | 0.21432 (11) | 0.0353 (2) | 0.0488 (7) |
| C9 | 0.4732 (6) | 0.19397 (12) | −0.0691 (3) | 0.0539 (8) |
| C10 | 0.1507 (8) | 0.14148 (17) | −0.1463 (3) | 0.0848 (12) |
| H10A | 0.0057 | 0.1607 | −0.1673 | 0.102* |
| H10B | 0.2596 | 0.1408 | −0.2117 | 0.102* |
| C11 | 0.0838 (13) | 0.0905 (2) | −0.1161 (4) | 0.143 (2) |
| H11A | 0.2276 | 0.0695 | −0.1128 | 0.215* |
| H11B | −0.0264 | 0.0771 | −0.1725 | 0.215* |
| H11C | 0.0050 | 0.0907 | −0.0427 | 0.215* |
| C12 | 0.7787 (6) | 0.24847 (11) | 0.0165 (3) | 0.0527 (8) |
| H12 | 0.8230 | 0.2534 | −0.0595 | 0.063* |
| C13 | 1.0980 (6) | 0.31036 (13) | 0.0625 (3) | 0.0636 (9) |
| H13A | 1.1491 | 0.3042 | −0.0157 | 0.076* |
| H13B | 1.2378 | 0.3045 | 0.1119 | 0.076* |
| C14 | 1.0188 (6) | 0.36375 (13) | 0.0739 (3) | 0.0577 (8) |
| C15 | 1.1403 (9) | 0.40227 (17) | 0.1157 (4) | 0.1003 (15) |
| H15 | 1.2973 | 0.4017 | 0.1462 | 0.120* |
| C16 | 0.9833 (15) | 0.44570 (19) | 0.1051 (5) | 0.132 (2) |
| H16 | 1.0164 | 0.4784 | 0.1322 | 0.158* |
| C17 | 0.7904 (13) | 0.43205 (19) | 0.0524 (5) | 0.1170 (19) |
| H17 | 0.6623 | 0.4536 | 0.0318 | 0.140* |
| F1 | 0.6232 (4) | 0.09953 (8) | 0.0822 (2) | 0.0898 (7) |
| F2 | 0.3637 (6) | 0.01847 (9) | 0.1490 (3) | 0.1212 (10) |
| F3 | −0.0329 (6) | 0.03107 (11) | 0.2835 (3) | 0.1268 (11) |
| F4 | −0.1667 (5) | 0.12543 (11) | 0.3494 (2) | 0.1085 (9) |
| N1 | 0.9043 (5) | 0.27469 (9) | 0.0925 (2) | 0.0562 (7) |
| H1 | 0.8700 | 0.2705 | 0.1637 | 0.067* |
| O1 | 0.5822 (5) | 0.22975 (9) | 0.23312 (18) | 0.0718 (7) |
| O2 | 0.5445 (5) | 0.20273 (10) | −0.16518 (19) | 0.0744 (7) |
| O3 | 0.2722 (5) | 0.16653 (10) | −0.05031 (19) | 0.0758 (7) |
| O4 | 0.8016 (6) | 0.37999 (12) | 0.0304 (3) | 0.1080 (11) |
1 Source of materials
To a stirred solution of 3-dimethylamino-2-(2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoyl)-acrylic acid ethyl ester (31.9 g, 0.1 mol) in CH2Cl2 (150 mL) was added α-furan-2-yl-methylamine (1.0 g, 0.1 mol), and then the reaction mixture was refluxed for about 0.5 h. After the reaction completed (monitored by TLC), the CH2Cl2 was distillated under reduced pressure to give crude product. The crude product was poured into water (40 mL) and extracted with EtOAc (50 mL × 3). The EtOAc solvent was evaporated to provide 3-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)-amino]-2-(2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoyl)-acrylic acid ethyl ester being suitable for X-ray analysis in 85.0 % yield. 1H (400 MHz) and 13C (100 MHz) NMR spectra of 3-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)-amino]-2-(2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoyl)-acrylic acid ethyl ester were recorded on a Bruker Avance 400 spectrometer in CDCl3 using tetramethylsilane (TMS) and CDCl3 (13C, δ 77.0 ppm) as internal standards. J-values were given in Hertz. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 1.09–1.13 (t, J = 8.0, 3H, OCH2CH3), 4.05–4.10 (q, J = 8.0, 12.0 Hz, 2H, OCH2CH3), 4.57–4.59 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, NHCH2), 6.34–6.39 (m, 2H, Furanyl-H), 6.95–7.01 (m, 1H, Ph–H), 7.45–7.47 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, OCH=C), 8.18–8.21 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H, C=CHNH), 10.98 (br, 1H, NH) ppm. 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 187.14, 166.25, 160.56, 160.11, 148.29, 143.69, 143.58, 143.50, 110.72, 109.98, 109.79, 109.29, 109.09, 101.62, 60.06, 46.50, 14.00 ppm.
2 Experimental details
All H atoms were included in calculated positions and refined as riding atoms, with C–H = 0.90–0.97 Å with Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms and 1.2 Ueq(C) for all other H atoms.
3 Comment
Quinolones have been popularized rapidly in clinic and become significant drug in the development, production and application all over the world due to wider antibacterial spectrum and stronger antibacterial activity than common antibiotics [5, 6]. After being used or even abused for a long time, quinolones have been seriously resisted by bacteria because of gene mutations and also have the inevitable side effects [7], [8], [9]. Nowadays, a new effective fluoroquinolones against bacteria drug-resistant and side effects have been researched and developed [10–13]. Recently, an impactful and high-yielding method for the synthesis of fluoroquinolones is developed in our group, and single crystals of several key intermediates are achieved.
In the molecule of the title compound bond lengths and angles within 3-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)-amino]-2-(2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoyl)-acrylic acid ethyl ester are very similar to those given in the literature [11, 12]. The dihedral angles between the C1–C6 benzene ring, O2–C9–O3 carboxyl group and the furan ring are
Acknowledgments
X-ray data were collected at Instrumental Analysis Center Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang, 330063, People’s Republic of China.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This study was supported by grants from Natural Science Foundation of Science and Technology Department of Jiangxi Province (No. 20151BBF60081; 20171BBE50027; 20171BBG70029; 20202BBEL53028), Science and Technology Research Project of Education Department of Jiangxi Province (No. GJJ170275, GJJ2210601), Natural Science Foundation of Nanchang City (No. 2014HZZC07; 2018CXTD014), Natural Science Foundation of Fuzhou City, Jiangxi Province (No.202205127297), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Agriculture University (No. 09004634; 09005194; 201610410007; 201610410079), and 2021 Innovation Team Project of Ji’an City, Jiangxi Province.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Brandenburg, K. DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Ver. 4.0; Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2015.Search in Google Scholar
5. Andersson, M. I., MacGowan, A. P. Development of the quinolones. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 1–11; https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkg212.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Andriole, V. T. The quinolones: past, present, and future. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, S113–S119; https://doi.org/10.1086/428051.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Stahlmann, R., Lode, H. Toxicity of quinolones. Drugs 1999, 58, 37–42; https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199958002-00007.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Rubinstein, E. History of quinolones and their side effects. Chemotherapy 2001, 47, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1159/000057838.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Naeem, A., Badshah, S. L., Muska, M., Abmad, N., Khan, K. The current case of quinolones: synthetic approaches and antibacterial activity. Molecules 2016, 21, 268; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040268.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
10. Zhanel, G. G., Ennis, K., Vercaigne, L., Walkty, A., Gin, A. S., Embil, J., Smith, H., Hoban, D. J. A critical review of the fluoroquinolones. Drugs 2002, 62, 13–59; https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200262010-00002.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Zhang, C. Y., Nie, X. L., Huang, G. P., Xiong, Y. Z., Huang, J. P. Crystal structure of 1-cyclopropyl-7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline -3-carboxylic acid, C15H13F2NO4. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2021, 236, 923–925; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2021–0151.10.1515/ncrs-2021-0151Search in Google Scholar
12. Fang, S. F., Peng, W. W., Xiong, Y. Z., Nie, X. L., Huang, J. P. Crystal structure of 3-(2-chloro-benzyl)-7-[4-(2-chloro-benzyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-5,6,8-trifluoro-3H-quinazolin-4-one, C26H21Cl2F3N4O. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2021, 236, 815–817; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020–0128.10.1515/ncrs-2021-0085Search in Google Scholar
13. Dankhoff, K., Weber, B. Novel Cu(II) complexes with NNO–Schiff base-like ligands-structures and magnetic properties. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2018, 20, 818–828; https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ce02007d.Search in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-3,3′-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate-N:N′:O:O′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of (8R,8′S,13S,13′R)-8,8′-bis(hydroxymethyl)-9,9′,10,10′-tetramethoxy-5,5′,6,6′,8,8′,13,13′-octahydro-[13,13′-bi[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinoline]-7,7′-diium chloride-methanol (1/2), C46H58N2O14Cl2
- The crystal structure of 8-methoxy-2,2-diphenyl-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C29H25BN2O3S
- Crystal structure of aqua-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N‴)copper(II) 5-carboxyisophthalate tetrahydrate, C25H50N4CuO11
- The crystal structure of 1-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfonyl)-2,2-diphenyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ij]quinoline, C31H23BN2O2S
- Crystal structure of iodido-(η6-benzene) (1-(pyridin-2-yl)-N-(p-fluoro-methanamine)-κ2N,Nʹ)ruthenium(II) hexaflourophosphate, (C18H15F7IN2RuP)
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolyl) propylidene)-1,3-dihydro-2H-inden-2-one, C25H20O2
- Crystal structure of tricyclohexyl[4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-benzoato-κO]tin(IV), C27H39N3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-2,6-difluorophenyl)amino)benzoate, C20H18F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)propane-1,3-diol, C6H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitrophenyl) hydrazine, C12H8N6O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)-1,2-dihydro-4H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-4-one, C19H14Cl2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-5-oxo-4-(1-oxo-4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)isoindolin-2-yl)pentanoic acid, C17H19N3O5
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(2-(((Z)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino) phenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C33H23Br2N5O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-methoxy-6-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C11H11N3O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-((tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)methyl)-5,5-diphenyl-6-(p-tolyl) tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-one, C41H42O2Si
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-5-(4-cyanophenoxy)benzyl 1-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carboxylate, C21H19BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C10H14F6N2P
- The crystal structure of 2,2-di(thiophen-3-yl)-1-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C24H19BN2O2S3
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-1-(2-iodobenzoyl)-1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde, C16H9BrINO2
- The crystal structure of monocarbonyl-2-carboxypyridinato-κ2N,O-triphenylphosphine-rhodium(I) acetonitrile solvate, C26H20.50N1.50O3PRh
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-tetrakis(1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ1N)manganese(II), C60H68O4N12Cl10Mn
- Crystal structure of 3-(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)-1-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-2,2-diphenylpropan-1-ol, C37H36Cl2OSi
- Crystal structure of langite from Mine du Pradet (France)
- The crystal structure of 5′-(furan-2-yl)-3′-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]-4′-carboxylic acid, C30H27NO5S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(((4-acetophenone)imino)methyl)-4-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C30H22F2N2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of poly[(tripyridine-κ3N,N′,N″) μ3-(pyridine-3,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N:O:O′) manganese(II)], C22H22N4O8Mn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15ClN2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino) ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II), C40H46CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-[(1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)cobalt(II)], C6H12CoN2O8
- (6R,7S)-2,3,13-trimethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[3′,4′]cycloocta [1′,2′:4,5]benzo[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-1-ol, C22H26O6
- Crystal structure of 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)amino)benzoic acid, C18H14Cl2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (5aS,6aS,8aR,9R,11aS, 11bS,13R,13aS)-1,1,8a,11a-tetramethyl-9-((S)-1-((S)-5-methyl-6-oxo-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-3-oxo-1,7,8,8a,9,10,11,11a,11b,12,13,13a-dodecahydro-3H,6H-cyclopenta[5,6]cyclopropa[1,8a]naphtho[2,1-c]oxepin-13-yl acetate, C32H44O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-O,O′:O″)cobalt(II)], C12H12N2O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)-amino]-2-(2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoyl)-acrylic acid ethyl ester, C17H13F4NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3-methoxybenzoate, C13H16O6
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile, C13H7BrClF3N2
- The crystal structure of triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O,O)nickel(II) monohydrate, C12H15NO9Ni
- Crystal structure of dihydroxy(2,4,6-triisopro-pylphenyl)telluronium trifluoromethanesulfonate, C16H25F3O5STe
- The crystal structure of 1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tris(dibromomethyl)benzene, C9H6Br6
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-N-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-imine, C25H21N5OS
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(phenylimino)-2,3-dihydrothiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C24H16N2O3S
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-3,3′-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate-N:N′:O:O′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of (8R,8′S,13S,13′R)-8,8′-bis(hydroxymethyl)-9,9′,10,10′-tetramethoxy-5,5′,6,6′,8,8′,13,13′-octahydro-[13,13′-bi[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinoline]-7,7′-diium chloride-methanol (1/2), C46H58N2O14Cl2
- The crystal structure of 8-methoxy-2,2-diphenyl-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C29H25BN2O3S
- Crystal structure of aqua-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N‴)copper(II) 5-carboxyisophthalate tetrahydrate, C25H50N4CuO11
- The crystal structure of 1-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfonyl)-2,2-diphenyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ij]quinoline, C31H23BN2O2S
- Crystal structure of iodido-(η6-benzene) (1-(pyridin-2-yl)-N-(p-fluoro-methanamine)-κ2N,Nʹ)ruthenium(II) hexaflourophosphate, (C18H15F7IN2RuP)
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolyl) propylidene)-1,3-dihydro-2H-inden-2-one, C25H20O2
- Crystal structure of tricyclohexyl[4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-benzoato-κO]tin(IV), C27H39N3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-2,6-difluorophenyl)amino)benzoate, C20H18F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)propane-1,3-diol, C6H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitrophenyl) hydrazine, C12H8N6O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)-1,2-dihydro-4H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-4-one, C19H14Cl2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-5-oxo-4-(1-oxo-4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)isoindolin-2-yl)pentanoic acid, C17H19N3O5
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(2-(((Z)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino) phenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C33H23Br2N5O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-methoxy-6-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C11H11N3O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-((tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)methyl)-5,5-diphenyl-6-(p-tolyl) tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-one, C41H42O2Si
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-5-(4-cyanophenoxy)benzyl 1-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carboxylate, C21H19BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C10H14F6N2P
- The crystal structure of 2,2-di(thiophen-3-yl)-1-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C24H19BN2O2S3
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-1-(2-iodobenzoyl)-1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde, C16H9BrINO2
- The crystal structure of monocarbonyl-2-carboxypyridinato-κ2N,O-triphenylphosphine-rhodium(I) acetonitrile solvate, C26H20.50N1.50O3PRh
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-tetrakis(1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ1N)manganese(II), C60H68O4N12Cl10Mn
- Crystal structure of 3-(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)-1-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-2,2-diphenylpropan-1-ol, C37H36Cl2OSi
- Crystal structure of langite from Mine du Pradet (France)
- The crystal structure of 5′-(furan-2-yl)-3′-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]-4′-carboxylic acid, C30H27NO5S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(((4-acetophenone)imino)methyl)-4-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C30H22F2N2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of poly[(tripyridine-κ3N,N′,N″) μ3-(pyridine-3,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N:O:O′) manganese(II)], C22H22N4O8Mn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15ClN2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino) ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II), C40H46CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-[(1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)cobalt(II)], C6H12CoN2O8
- (6R,7S)-2,3,13-trimethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[3′,4′]cycloocta [1′,2′:4,5]benzo[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-1-ol, C22H26O6
- Crystal structure of 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)amino)benzoic acid, C18H14Cl2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (5aS,6aS,8aR,9R,11aS, 11bS,13R,13aS)-1,1,8a,11a-tetramethyl-9-((S)-1-((S)-5-methyl-6-oxo-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-3-oxo-1,7,8,8a,9,10,11,11a,11b,12,13,13a-dodecahydro-3H,6H-cyclopenta[5,6]cyclopropa[1,8a]naphtho[2,1-c]oxepin-13-yl acetate, C32H44O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-O,O′:O″)cobalt(II)], C12H12N2O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)-amino]-2-(2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoyl)-acrylic acid ethyl ester, C17H13F4NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3-methoxybenzoate, C13H16O6
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile, C13H7BrClF3N2
- The crystal structure of triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O,O)nickel(II) monohydrate, C12H15NO9Ni
- Crystal structure of dihydroxy(2,4,6-triisopro-pylphenyl)telluronium trifluoromethanesulfonate, C16H25F3O5STe
- The crystal structure of 1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tris(dibromomethyl)benzene, C9H6Br6
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-N-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-imine, C25H21N5OS
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(phenylimino)-2,3-dihydrothiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C24H16N2O3S


