Abstract
C12H15NO9Ni, triclinic,
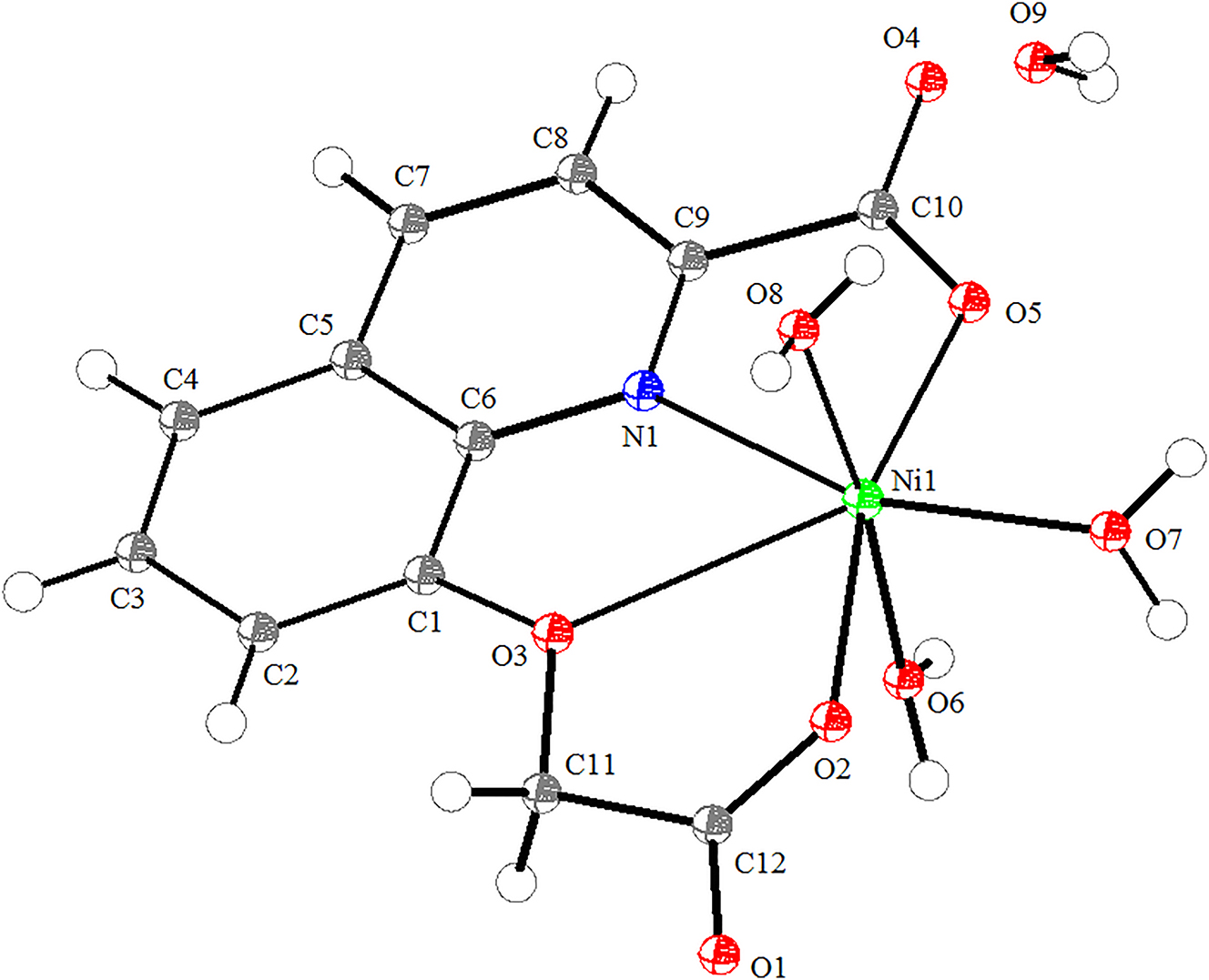
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.16 × 0.12 × 0.11 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 2.47 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB Synergy, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 73.2°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 9208, 2734, 0.033 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 2512 |
| N(param)refined: | 236 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], Olex2 [2], SHELX [3], Diamond [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni1 | 0.30428 (6) | 0.27455 (5) | 0.85138 (3) | 0.03752 (18) |
| O1 | −0.1866 (3) | 0.0015 (3) | 0.8495 (2) | 0.0572 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0345 (3) | 0.1546 (3) | 0.87885 (16) | 0.0473 (5) |
| O3 | 0.1822 (4) | 0.1770 (4) | 0.67425 (19) | 0.0739 (8) |
| O4 | 0.7922 (3) | 0.5095 (3) | 0.8032 (2) | 0.0592 (6) |
| O5 | 0.5346 (3) | 0.3887 (2) | 0.87758 (17) | 0.0464 (4) |
| O6 | 0.4319 (3) | 0.0421 (3) | 0.8699 (2) | 0.0540 (5) |
| H6A | 0.544 (3) | 0.020 (4) | 0.873 (4) | 0.081* |
| H6B | 0.384 (4) | −0.041 (3) | 0.898 (3) | 0.081* |
| O7 | 0.2121 (4) | 0.2864 (3) | 1.0243 (2) | 0.0654 (7) |
| H7A | 0.210 (7) | 0.199 (3) | 1.066 (2) | 0.098* |
| H7B | 0.263 (6) | 0.344 (5) | 1.062 (2) | 0.098* |
| O8 | 0.1662 (4) | 0.5009 (3) | 0.8190 (2) | 0.0472 (5) |
| H8A | 0.184 (6) | 0.562 (5) | 0.855 (4) | 0.067 (14)* |
| H8B | 0.080 (6) | 0.492 (5) | 0.815 (4) | 0.061 (14)* |
| N1 | 0.4867 (3) | 0.3076 (3) | 0.67813 (18) | 0.0366 (5) |
| C1 | 0.2942 (4) | 0.1880 (4) | 0.5731 (2) | 0.0447 (6) |
| C2 | 0.2578 (4) | 0.1391 (4) | 0.4742 (2) | 0.0492 (7) |
| H2 | 0.149356 | 0.088654 | 0.473069 | 0.059* |
| C3 | 0.3857 (5) | 0.1658 (4) | 0.3739 (2) | 0.0498 (7) |
| H3 | 0.360598 | 0.132296 | 0.306829 | 0.060* |
| C4 | 0.5447 (4) | 0.2395 (3) | 0.3733 (2) | 0.0459 (6) |
| H4 | 0.626630 | 0.256840 | 0.306118 | 0.055* |
| C5 | 0.5863 (4) | 0.2901 (3) | 0.4748 (2) | 0.0390 (6) |
| C6 | 0.4585 (4) | 0.2623 (3) | 0.5763 (2) | 0.0356 (5) |
| C7 | 0.7457 (4) | 0.3675 (4) | 0.4830 (3) | 0.0479 (7) |
| H7 | 0.833898 | 0.387850 | 0.419036 | 0.058* |
| C8 | 0.7717 (4) | 0.4132 (4) | 0.5849 (3) | 0.0488 (7) |
| H8 | 0.877276 | 0.464765 | 0.590861 | 0.059* |
| C9 | 0.6371 (4) | 0.3814 (3) | 0.6807 (2) | 0.0391 (6) |
| C10 | 0.6580 (4) | 0.4309 (4) | 0.7970 (3) | 0.0458 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0380 (4) | 0.0712 (4) | 0.6950 (2) | 0.0449 (6) |
| H11A | 0.086132 | −0.039633 | 0.677089 | 0.054* |
| H11B | −0.056235 | 0.107308 | 0.649378 | 0.054* |
| C12 | −0.0438 (4) | 0.0766 (3) | 0.8186 (2) | 0.0403 (6) |
| O9 | 0.2594 (4) | 0.7437 (3) | 0.94430 (19) | 0.0488 (5) |
| H9A | 0.323 (7) | 0.700 (5) | 0.977 (4) | 0.070 (15)* |
| H9B | 0.184 (7) | 0.786 (6) | 0.988 (4) | 0.082 (15)* |
-
*The Uiso*/Ueq values represents the ratio of isotropic U value to equivalent isotropic atomic displacement parameter.
1 Source of materials
An amount of 0.2672 g 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylic acid (1.0 mmol), 0.1341 g 1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin-3-amine (1.0 mmol),0.040 g NaOH (2.0 mmol) and 0.1244 g nickel(II) acetate tetrahydrate (0.5 mmol) solids were added to the 30 ml ethanol-water (v:v = 2:1) mixed solution with stirring. The solution turned immediately clarified. The mixture was stirred for 4.5 h at 68 °C. After the reaction was stopped and cooled to room temperature, the solution was filtered into a small beaker. The colourless block crystals of the title Ni(II) complex were received in four weeks.
2 Experimental details
The hydrogen atoms were positioned geometrically (C–H = 0.93–0.97 Å, O–H = 0.65–0.85 Å). Their U iso values were set to 1.2U eq or 1.5U eq of the parent atoms.
3 Comment
The 8–carboxymethoxyquinoline-2-carboxylate ligand could form mononuclear compounds or coordination polymer with metal ions, since it has multiple coordination atoms (O,O,N,O). The crystal structures of Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II) complexes constructed by 8-carboxymethoxyquinoline-2-carboxylate have been reported, and they show the different coordination structures [5, 6]. Interestingly, despite the same starting material and synthesis conditions, it can form structurally different complexes with Ni(II) ions. Our research group has also been studying the synthesis and structure of related metal complexes [7], [8], [9], [10]. In this work, we synthesized and structurally resolved a Ni(II) complex different from that reported in ref. [6] with 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylic acid, 1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin-3-amine, NaOH and nickel(II) acetate tetrahydrate. The molecular structure of Ni(II) complex is shown in the Figure. The Ni(II) complex is a mononuclear compound and made up of one Ni(II) ion, one 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate ligand, three coordinated water molecules, and one uncoordinated water molecule. The central Ni(II) ion is six-coordinated in an octahedral environment with two carboxylic O atoms (O2 and O5) and one N atom (N1) from one 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate ligand, and three O atoms (O6, O7 and O8) from three coordinating water molecules. The bond angle of O6–Ni1–O8 is 174.27(10)°, indicating that O6 and O8 atoms occupy the axial positions, and O2, O5, O7, N1 atoms forms the equatorial plane. The bond lengths of Ni–O are 2.058(2)–2.245(2) Å, and that of Ni–N is 2.287(2) Å. Furthermore, Ni(II) complex forms 3D supramolecular structure through intermolecular hydrogen bonding and p–p stacking interactions. In ref. [6], the carboxylic O atoms and ether O atom of 8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate ligand are coordinated with Ni(II) ion, however, the ether O atom does not take part in coordination in this work. It is worth mentioning that, although 1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin-3-amine is not involved in forming the Ni(II) complex, it seems to have an effect on the coordination mode of the Ni(II) ion.
Funding source: National Natural Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 21171132
Funding source: Science Foundation of Weifang
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2020ZJ1054
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21171132, https://doi.org/10.13039/501100001809), and Science Foundation of Weifang (2020ZJ1054).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2000.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Brandenburg, K. DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Ver. 3.2; Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
5. Zhang, Y. P., Yang, J. J., Lu, J. Y., Gao, C. Y., Zhao, J. Z. Syntheses, structures, DNA/BSA binding and DNA cleavage of mononuclear manganese(II) and cobalt(II) complexes with N,O-chelating quinoline derivative ligand. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 32, 2172–2182.Search in Google Scholar
6. Lou, H. D., Yin, L., Zhang, B. Q., Ouyang, Z. W., Li, B., Wang, Z. X. Series of single-ion and 1D chain complexes based on quinolinic derivative: synthesis, crystal structures, HF–EPR, and magnetic properties. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 7757–7762; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b00812.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Wang, L. H., Liang, L., Li, X. T., Cao, S. H., Tai, X. S. The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C24H16N2O4Cu. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2021, 236, 1251–1253; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2021-0293.Search in Google Scholar
8. Tai, X. S., Xia, Y. P. The crystal structure of [(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)cobalt(II)]-monohydrate, C36H26N4O5Co. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 225–227; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2021-0473.Search in Google Scholar
9. Wang, L. H., Tai, X. S., Xia, Y. P. The crystal structure of catena-poly [(m2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)zinc(II)], C34H24N4O4Zn. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 305–307; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0003.Search in Google Scholar
10. Wang, L. H., Tai, H. W., Song, G. Q., Tai, X. S. The crystal structure of aqua-bis{2-bromo-6-((2-(2-phenylacetyl) hydrazineylidene)methyl)phenolato-κ3N,O,O′}-dimethylformamide-κ1O-erbium(III) chloride-dimethylformamide-water (1/2/1), C39H49N7O9Br2ClEr. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 437–439; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0014.Search in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-3,3′-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate-N:N′:O:O′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of (8R,8′S,13S,13′R)-8,8′-bis(hydroxymethyl)-9,9′,10,10′-tetramethoxy-5,5′,6,6′,8,8′,13,13′-octahydro-[13,13′-bi[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinoline]-7,7′-diium chloride-methanol (1/2), C46H58N2O14Cl2
- The crystal structure of 8-methoxy-2,2-diphenyl-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C29H25BN2O3S
- Crystal structure of aqua-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N‴)copper(II) 5-carboxyisophthalate tetrahydrate, C25H50N4CuO11
- The crystal structure of 1-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfonyl)-2,2-diphenyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ij]quinoline, C31H23BN2O2S
- Crystal structure of iodido-(η6-benzene) (1-(pyridin-2-yl)-N-(p-fluoro-methanamine)-κ2N,Nʹ)ruthenium(II) hexaflourophosphate, (C18H15F7IN2RuP)
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolyl) propylidene)-1,3-dihydro-2H-inden-2-one, C25H20O2
- Crystal structure of tricyclohexyl[4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-benzoato-κO]tin(IV), C27H39N3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-2,6-difluorophenyl)amino)benzoate, C20H18F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)propane-1,3-diol, C6H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitrophenyl) hydrazine, C12H8N6O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)-1,2-dihydro-4H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-4-one, C19H14Cl2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-5-oxo-4-(1-oxo-4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)isoindolin-2-yl)pentanoic acid, C17H19N3O5
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(2-(((Z)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino) phenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C33H23Br2N5O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-methoxy-6-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C11H11N3O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-((tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)methyl)-5,5-diphenyl-6-(p-tolyl) tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-one, C41H42O2Si
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-5-(4-cyanophenoxy)benzyl 1-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carboxylate, C21H19BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C10H14F6N2P
- The crystal structure of 2,2-di(thiophen-3-yl)-1-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C24H19BN2O2S3
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-1-(2-iodobenzoyl)-1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde, C16H9BrINO2
- The crystal structure of monocarbonyl-2-carboxypyridinato-κ2N,O-triphenylphosphine-rhodium(I) acetonitrile solvate, C26H20.50N1.50O3PRh
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-tetrakis(1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ1N)manganese(II), C60H68O4N12Cl10Mn
- Crystal structure of 3-(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)-1-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-2,2-diphenylpropan-1-ol, C37H36Cl2OSi
- Crystal structure of langite from Mine du Pradet (France)
- The crystal structure of 5′-(furan-2-yl)-3′-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]-4′-carboxylic acid, C30H27NO5S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(((4-acetophenone)imino)methyl)-4-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C30H22F2N2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of poly[(tripyridine-κ3N,N′,N″) μ3-(pyridine-3,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N:O:O′) manganese(II)], C22H22N4O8Mn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15ClN2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino) ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II), C40H46CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-[(1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)cobalt(II)], C6H12CoN2O8
- (6R,7S)-2,3,13-trimethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[3′,4′]cycloocta [1′,2′:4,5]benzo[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-1-ol, C22H26O6
- Crystal structure of 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)amino)benzoic acid, C18H14Cl2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (5aS,6aS,8aR,9R,11aS, 11bS,13R,13aS)-1,1,8a,11a-tetramethyl-9-((S)-1-((S)-5-methyl-6-oxo-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-3-oxo-1,7,8,8a,9,10,11,11a,11b,12,13,13a-dodecahydro-3H,6H-cyclopenta[5,6]cyclopropa[1,8a]naphtho[2,1-c]oxepin-13-yl acetate, C32H44O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-O,O′:O″)cobalt(II)], C12H12N2O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)-amino]-2-(2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoyl)-acrylic acid ethyl ester, C17H13F4NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3-methoxybenzoate, C13H16O6
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile, C13H7BrClF3N2
- The crystal structure of triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O,O)nickel(II) monohydrate, C12H15NO9Ni
- Crystal structure of dihydroxy(2,4,6-triisopro-pylphenyl)telluronium trifluoromethanesulfonate, C16H25F3O5STe
- The crystal structure of 1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tris(dibromomethyl)benzene, C9H6Br6
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-N-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-imine, C25H21N5OS
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(phenylimino)-2,3-dihydrothiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C24H16N2O3S
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-3,3′-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate-N:N′:O:O′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of (8R,8′S,13S,13′R)-8,8′-bis(hydroxymethyl)-9,9′,10,10′-tetramethoxy-5,5′,6,6′,8,8′,13,13′-octahydro-[13,13′-bi[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinoline]-7,7′-diium chloride-methanol (1/2), C46H58N2O14Cl2
- The crystal structure of 8-methoxy-2,2-diphenyl-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C29H25BN2O3S
- Crystal structure of aqua-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N‴)copper(II) 5-carboxyisophthalate tetrahydrate, C25H50N4CuO11
- The crystal structure of 1-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfonyl)-2,2-diphenyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ij]quinoline, C31H23BN2O2S
- Crystal structure of iodido-(η6-benzene) (1-(pyridin-2-yl)-N-(p-fluoro-methanamine)-κ2N,Nʹ)ruthenium(II) hexaflourophosphate, (C18H15F7IN2RuP)
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolyl) propylidene)-1,3-dihydro-2H-inden-2-one, C25H20O2
- Crystal structure of tricyclohexyl[4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-benzoato-κO]tin(IV), C27H39N3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-2,6-difluorophenyl)amino)benzoate, C20H18F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)propane-1,3-diol, C6H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitrophenyl) hydrazine, C12H8N6O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)-1,2-dihydro-4H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-4-one, C19H14Cl2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-5-oxo-4-(1-oxo-4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)isoindolin-2-yl)pentanoic acid, C17H19N3O5
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(2-(((Z)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino) phenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C33H23Br2N5O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-methoxy-6-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C11H11N3O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-((tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)methyl)-5,5-diphenyl-6-(p-tolyl) tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-one, C41H42O2Si
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-5-(4-cyanophenoxy)benzyl 1-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carboxylate, C21H19BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C10H14F6N2P
- The crystal structure of 2,2-di(thiophen-3-yl)-1-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C24H19BN2O2S3
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-1-(2-iodobenzoyl)-1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde, C16H9BrINO2
- The crystal structure of monocarbonyl-2-carboxypyridinato-κ2N,O-triphenylphosphine-rhodium(I) acetonitrile solvate, C26H20.50N1.50O3PRh
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-tetrakis(1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ1N)manganese(II), C60H68O4N12Cl10Mn
- Crystal structure of 3-(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)-1-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-2,2-diphenylpropan-1-ol, C37H36Cl2OSi
- Crystal structure of langite from Mine du Pradet (France)
- The crystal structure of 5′-(furan-2-yl)-3′-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]-4′-carboxylic acid, C30H27NO5S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(((4-acetophenone)imino)methyl)-4-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C30H22F2N2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of poly[(tripyridine-κ3N,N′,N″) μ3-(pyridine-3,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N:O:O′) manganese(II)], C22H22N4O8Mn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15ClN2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino) ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II), C40H46CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-[(1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)cobalt(II)], C6H12CoN2O8
- (6R,7S)-2,3,13-trimethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[3′,4′]cycloocta [1′,2′:4,5]benzo[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-1-ol, C22H26O6
- Crystal structure of 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)amino)benzoic acid, C18H14Cl2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (5aS,6aS,8aR,9R,11aS, 11bS,13R,13aS)-1,1,8a,11a-tetramethyl-9-((S)-1-((S)-5-methyl-6-oxo-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-3-oxo-1,7,8,8a,9,10,11,11a,11b,12,13,13a-dodecahydro-3H,6H-cyclopenta[5,6]cyclopropa[1,8a]naphtho[2,1-c]oxepin-13-yl acetate, C32H44O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-O,O′:O″)cobalt(II)], C12H12N2O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)-amino]-2-(2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoyl)-acrylic acid ethyl ester, C17H13F4NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3-methoxybenzoate, C13H16O6
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile, C13H7BrClF3N2
- The crystal structure of triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O,O)nickel(II) monohydrate, C12H15NO9Ni
- Crystal structure of dihydroxy(2,4,6-triisopro-pylphenyl)telluronium trifluoromethanesulfonate, C16H25F3O5STe
- The crystal structure of 1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tris(dibromomethyl)benzene, C9H6Br6
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-N-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-imine, C25H21N5OS
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(phenylimino)-2,3-dihydrothiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C24H16N2O3S

