Abstract
C11H11N3O2S, orthorhombic, Pna21 (no. 33), a = 22.6572(9) Å, b = 10.0205(4) Å, c = 4.9023(2) Å, V = 1113.01(8) Å3, Z = 5, Rgt(F) = 0.0341, wRref(F2) = 0.0857, T = 297 K.
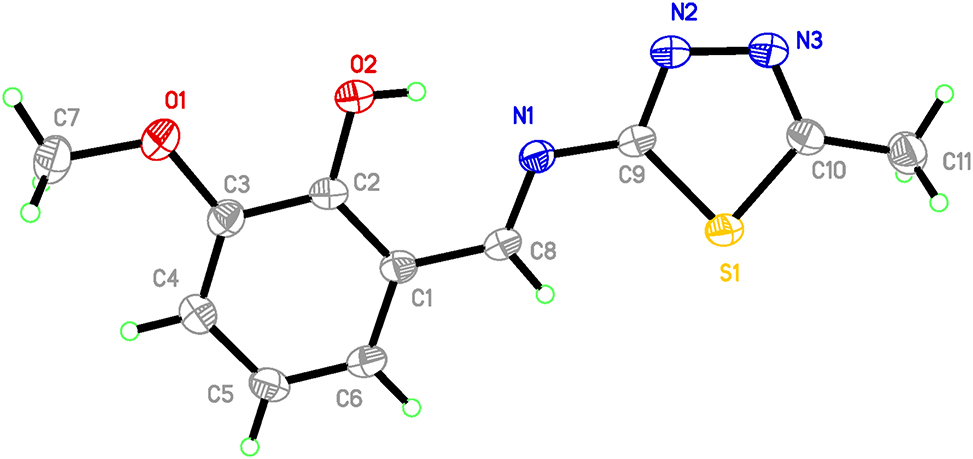
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless needle |
| Size: | 0.21 × 0.18 × 0.14 mm |
| Wavelength: | MoKα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.28 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | ROD, Synergy Custom DW system |
| θmax, completeness: | 26.3°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 5529, 1998, 0.026 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 1768 |
| N(param)refined: | 157 |
| Programs: | Olex2 [1], Shelx [2] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.12996 (13) | 0.6004 (3) | 0.7664 (7) | 0.0379 (7) |
| C2 | 0.09815 (13) | 0.7174 (3) | 0.7188 (6) | 0.0378 (7) |
| C3 | 0.05407 (13) | 0.7189 (3) | 0.5180 (7) | 0.0429 (8) |
| C4 | 0.04305 (13) | 0.6061 (3) | 0.3677 (7) | 0.0455 (8) |
| H4 | 0.0135 | 0.6068 | 0.2361 | 0.055* |
| C5 | 0.07605 (14) | 0.4900 (3) | 0.4114 (8) | 0.0469 (7) |
| H5 | 0.0689 | 0.4145 | 0.3064 | 0.056* |
| C6 | 0.11856 (14) | 0.4873 (3) | 0.6071 (8) | 0.0440 (8) |
| H6 | 0.1402 | 0.4098 | 0.6353 | 0.053* |
| C7 | −0.01873 (16) | 0.8466 (4) | 0.2824 (8) | 0.0627 (11) |
| H7A | −0.0006 | 0.8310 | 0.1084 | 0.094* |
| H7B | −0.0361 | 0.9340 | 0.2844 | 0.094* |
| H7C | −0.0488 | 0.7809 | 0.3134 | 0.094* |
| C8 | 0.17582 (13) | 0.5952 (3) | 0.9721 (7) | 0.0393 (7) |
| H8 | 0.1951 | 0.5147 | 1.0024 | 0.047* |
| C9 | 0.23554 (13) | 0.6852 (3) | 1.3064 (7) | 0.0402 (8) |
| C10 | 0.31278 (13) | 0.6336 (3) | 1.6205 (7) | 0.0435 (7) |
| C11 | 0.35918 (15) | 0.5776 (4) | 1.7974 (8) | 0.0584 (10) |
| H11A | 0.3925 | 0.5521 | 1.6881 | 0.088* |
| H11B | 0.3441 | 0.5006 | 1.8910 | 0.088* |
| H11C | 0.3712 | 0.6434 | 1.9283 | 0.088* |
| N1 | 0.19088 (11) | 0.6974 (2) | 1.1146 (6) | 0.0386 (6) |
| N2 | 0.25635 (13) | 0.7905 (2) | 1.4268 (7) | 0.0537 (7) |
| N3 | 0.30113 (14) | 0.7610 (3) | 1.6066 (7) | 0.0569 (8) |
| O1 | 0.02461 (11) | 0.8376 (2) | 0.4912 (5) | 0.0587 (7) |
| O2 | 0.10777 (10) | 0.8308 (2) | 0.8615 (5) | 0.0517 (7) |
| H2 | 0.1340 | 0.8180 | 0.9738 | 0.078* |
| S1 | 0.26903 (4) | 0.53806 (7) | 1.4100 (2) | 0.0481 (3) |
1 Experimental details
The structure was solved with Shelxt program and refined with the Shelxt refinement package under Olex2 suite [1, 2]. All hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions and refined as riding atoms, with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H and hydroxyl H atoms. Uiso(H) was set to 1.2Ueq(C) for all other H atoms.
2 Source of material
All chemicals were commercially sourced and were not further purified. Weigh 0.1152 g (1.0 mmol) of 2-amino-5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole and 0.1522 g (1.0 mmol) of orthovanillin into a three necked flask containing 8.0 mL of anhydrous ethanol stirring at room temperature. In addition, add 1 mL of acetic acid as the catalyst and reflux at 80 °C for 2 h, and the solution turns yellow. The solution was filtered and then put into a Teflon-lined autoclave, and heated for three days at 80 °C, cooled to room temperature slowly and colorless needle crystals formed.
3 Comment
Schiff bases are a class of compounds formed by double bonding carbon atoms with nitrogen atoms [3], and their excellent coordination structure is due to the presence of C=N in the structure. The different structures and functional groups of reactants give Schiff bases different properties. Therefore, Schiff base compounds have important applications in multiple fields [4]. Schiff bases can be divided into salicylaldehydes, amino acids, acetamides, etc. according to the types of reactants [5]. Among them, salicylaldehydes Schiff bases are the most and earliest studied. They are a type of Schiff base obtained by condensation reaction between salicylaldehydes and amines, which is easy to prepare and has good biological activity, and is an oxygen-containing ligand. It have various coordination modes with different metal ions, providing conditions for the formation of highly biologically active Schiff base compounds [6].
From the data of bond length and bond angle of the title Schiff base compound, it can be seen that the C=N double bond length N1–C8 in Schiff base is 1.286(4) Å, which is longer than the average bond length of the usual C=N double bond [7, 8]. The bond length between the phenolic hydroxyl oxygen O1 in Schiff base and the carbon atom C3 on the benzene ring is 1.370(4) Å, which is between the C–O single bond and the C=O double bond [9–11]. And the bond length of C1–C8 is equal to 1.449(4) Å, which is 0.091 Å shorter than the typical C–C single bond (1.54 Å). Schiff base has intramolecular hydrogen bonds, where the phenolic hydroxyl O atom on orthovanillin forms an O2–H1⋯N1 hydrogen bond with the N atom in the Schiff base C=N double bond, forming a stable six-membered ring with C2, C1, and C8.
Funding source: The Guangxi Universities Research Foundation of Young and Middle-Aged Teachers Foundation
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2022KY0769
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2023KY0769
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2021KY0773
Funding source: Guangxi Minzu Normal University Foundation
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2023SBNGCC001
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2021YB038
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Guangxi Universities Research Foundation of Young and Middle-Aged Teachers Foundation (2022KY0769, 2023KY0769 and 2021KY0773) and the Guangxi Minzu Normal University Foundation (2023SBNGCC001, 2021YB038).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Xavier, A., Srividhya, N. Synthesis and study of Schiff base ligands. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2014, 7, 06–15; https://doi.org/10.9790/5736-071110615.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sinn, E., Harris, C. M. Schiff base metal complexes as ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1969, 4, 391–422; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0010-8545(00)80080-6.Search in Google Scholar
5. Da Silva, C. M., da Silva, D. L., Modolo, L. V., Alves, R. B., de Resende, M. A., Martins, C. V. B., de Fátima, Â. Schiff bases: a short review of their antimicrobial activities. J. Adv. Res. 2011, 2, 1–8; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2010.05.004.Search in Google Scholar
6. Mohamed, G. G., Omar, M. M., Hindy, A. M. Metal complexes of Schiff bases: preparation, characterization, and biological activity. Turk. J. Chem. 2006, 30, 361–382.Search in Google Scholar
7. Zhang, S. H., Wang, Y. G., Feng, C., Li, G. Z. Dinuclear copper (II) complex and 1–D copper (II) complex with taurine Schiff base: synthesis, crystal structure, and properties. J. Coord. Chem. 2010, 63, 3697–3705; https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2010.518760.Search in Google Scholar
8. Zhang, S. H., Tang, M. F., Ge, C. M. Microwave synthesis, crystal structure and magnetic behavior of a Schiff base trinuclear nickel cluster. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2009, 635, 1442–1446; https://doi.org/10.1002/zaac.200801402.Search in Google Scholar
9. Glockler, G. Carbon–oxygen bond energies and bond distances. J. Phys. Chem. 1958, 62, 1049–1054; https://doi.org/10.1021/j150567a006.Search in Google Scholar
10. Smith, B. The C=O bond, Part VIII. Spectroscopy 2018, 33, 24–29; https://doi.org/10.1186/s40814-017-0167-2.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
11. Wan, R., Ni, J. P., Han, F., Zhang, J. J., Wang, J. T. N-Benzylidene-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-amine. Acta Crystallogr. 2007, E63, o2363–o2364; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536807015668.Search in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-3,3′-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate-N:N′:O:O′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of (8R,8′S,13S,13′R)-8,8′-bis(hydroxymethyl)-9,9′,10,10′-tetramethoxy-5,5′,6,6′,8,8′,13,13′-octahydro-[13,13′-bi[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinoline]-7,7′-diium chloride-methanol (1/2), C46H58N2O14Cl2
- The crystal structure of 8-methoxy-2,2-diphenyl-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C29H25BN2O3S
- Crystal structure of aqua-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N‴)copper(II) 5-carboxyisophthalate tetrahydrate, C25H50N4CuO11
- The crystal structure of 1-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfonyl)-2,2-diphenyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ij]quinoline, C31H23BN2O2S
- Crystal structure of iodido-(η6-benzene) (1-(pyridin-2-yl)-N-(p-fluoro-methanamine)-κ2N,Nʹ)ruthenium(II) hexaflourophosphate, (C18H15F7IN2RuP)
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolyl) propylidene)-1,3-dihydro-2H-inden-2-one, C25H20O2
- Crystal structure of tricyclohexyl[4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-benzoato-κO]tin(IV), C27H39N3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-2,6-difluorophenyl)amino)benzoate, C20H18F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)propane-1,3-diol, C6H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitrophenyl) hydrazine, C12H8N6O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)-1,2-dihydro-4H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-4-one, C19H14Cl2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-5-oxo-4-(1-oxo-4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)isoindolin-2-yl)pentanoic acid, C17H19N3O5
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(2-(((Z)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino) phenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C33H23Br2N5O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-methoxy-6-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C11H11N3O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-((tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)methyl)-5,5-diphenyl-6-(p-tolyl) tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-one, C41H42O2Si
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-5-(4-cyanophenoxy)benzyl 1-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carboxylate, C21H19BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C10H14F6N2P
- The crystal structure of 2,2-di(thiophen-3-yl)-1-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C24H19BN2O2S3
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-1-(2-iodobenzoyl)-1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde, C16H9BrINO2
- The crystal structure of monocarbonyl-2-carboxypyridinato-κ2N,O-triphenylphosphine-rhodium(I) acetonitrile solvate, C26H20.50N1.50O3PRh
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-tetrakis(1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ1N)manganese(II), C60H68O4N12Cl10Mn
- Crystal structure of 3-(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)-1-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-2,2-diphenylpropan-1-ol, C37H36Cl2OSi
- Crystal structure of langite from Mine du Pradet (France)
- The crystal structure of 5′-(furan-2-yl)-3′-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]-4′-carboxylic acid, C30H27NO5S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(((4-acetophenone)imino)methyl)-4-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C30H22F2N2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of poly[(tripyridine-κ3N,N′,N″) μ3-(pyridine-3,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N:O:O′) manganese(II)], C22H22N4O8Mn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15ClN2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino) ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II), C40H46CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-[(1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)cobalt(II)], C6H12CoN2O8
- (6R,7S)-2,3,13-trimethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[3′,4′]cycloocta [1′,2′:4,5]benzo[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-1-ol, C22H26O6
- Crystal structure of 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)amino)benzoic acid, C18H14Cl2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (5aS,6aS,8aR,9R,11aS, 11bS,13R,13aS)-1,1,8a,11a-tetramethyl-9-((S)-1-((S)-5-methyl-6-oxo-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-3-oxo-1,7,8,8a,9,10,11,11a,11b,12,13,13a-dodecahydro-3H,6H-cyclopenta[5,6]cyclopropa[1,8a]naphtho[2,1-c]oxepin-13-yl acetate, C32H44O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-O,O′:O″)cobalt(II)], C12H12N2O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)-amino]-2-(2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoyl)-acrylic acid ethyl ester, C17H13F4NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3-methoxybenzoate, C13H16O6
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile, C13H7BrClF3N2
- The crystal structure of triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O,O)nickel(II) monohydrate, C12H15NO9Ni
- Crystal structure of dihydroxy(2,4,6-triisopro-pylphenyl)telluronium trifluoromethanesulfonate, C16H25F3O5STe
- The crystal structure of 1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tris(dibromomethyl)benzene, C9H6Br6
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-N-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-imine, C25H21N5OS
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(phenylimino)-2,3-dihydrothiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C24H16N2O3S
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ4-3,3′-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate-N:N′:O:O′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N6O6Cd
- Crystal structure of (8R,8′S,13S,13′R)-8,8′-bis(hydroxymethyl)-9,9′,10,10′-tetramethoxy-5,5′,6,6′,8,8′,13,13′-octahydro-[13,13′-bi[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinoline]-7,7′-diium chloride-methanol (1/2), C46H58N2O14Cl2
- The crystal structure of 8-methoxy-2,2-diphenyl-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C29H25BN2O3S
- Crystal structure of aqua-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N‴)copper(II) 5-carboxyisophthalate tetrahydrate, C25H50N4CuO11
- The crystal structure of 1-(naphthalen-2-ylsulfonyl)-2,2-diphenyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ij]quinoline, C31H23BN2O2S
- Crystal structure of iodido-(η6-benzene) (1-(pyridin-2-yl)-N-(p-fluoro-methanamine)-κ2N,Nʹ)ruthenium(II) hexaflourophosphate, (C18H15F7IN2RuP)
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-3-(p-tolyl) propylidene)-1,3-dihydro-2H-inden-2-one, C25H20O2
- Crystal structure of tricyclohexyl[4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-benzoato-κO]tin(IV), C27H39N3O2Sn
- Crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)cadmium(II)]monohydrate, C12H15NO9Cd
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)-2,6-difluorophenyl)amino)benzoate, C20H18F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)propane-1,3-diol, C6H11N3O3
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitrophenyl) hydrazine, C12H8N6O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)-1,2-dihydro-4H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-4-one, C19H14Cl2N2O3
- The crystal structure of 5-amino-5-oxo-4-(1-oxo-4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)isoindolin-2-yl)pentanoic acid, C17H19N3O5
- Crystal structure of N2,N6-bis(2-(((Z)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino) phenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C33H23Br2N5O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-methoxy-6-(((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C11H11N3O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-((tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)methyl)-5,5-diphenyl-6-(p-tolyl) tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-one, C41H42O2Si
- Crystal structure of 9-fluoro-4-(6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)-5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine, C18H15FN4O
- The crystal structure of 2-bromo-5-(4-cyanophenoxy)benzyl 1-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carboxylate, C21H19BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate(V)), C10H14F6N2P
- The crystal structure of 2,2-di(thiophen-3-yl)-1-tosyl-1,2-dihydro-2λ4,3λ4-[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ig]quinoline, C24H19BN2O2S3
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-1-(2-iodobenzoyl)-1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde, C16H9BrINO2
- The crystal structure of monocarbonyl-2-carboxypyridinato-κ2N,O-triphenylphosphine-rhodium(I) acetonitrile solvate, C26H20.50N1.50O3PRh
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-tetrakis(1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ1N)manganese(II), C60H68O4N12Cl10Mn
- Crystal structure of 3-(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)-1-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-2,2-diphenylpropan-1-ol, C37H36Cl2OSi
- Crystal structure of langite from Mine du Pradet (France)
- The crystal structure of 5′-(furan-2-yl)-3′-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)-3′,4′,5′,6′-tetrahydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]-4′-carboxylic acid, C30H27NO5S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(((4-acetophenone)imino)methyl)-4-fluorophenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C30H22F2N2O4Zn
- The crystal structure of poly[(tripyridine-κ3N,N′,N″) μ3-(pyridine-3,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N:O:O′) manganese(II)], C22H22N4O8Mn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-chloro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15ClN2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino) ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II), C40H46CoN4O4
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-[(1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)cobalt(II)], C6H12CoN2O8
- (6R,7S)-2,3,13-trimethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[3′,4′]cycloocta [1′,2′:4,5]benzo[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-1-ol, C22H26O6
- Crystal structure of 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)amino)benzoic acid, C18H14Cl2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (5aS,6aS,8aR,9R,11aS, 11bS,13R,13aS)-1,1,8a,11a-tetramethyl-9-((S)-1-((S)-5-methyl-6-oxo-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-3-oxo-1,7,8,8a,9,10,11,11a,11b,12,13,13a-dodecahydro-3H,6H-cyclopenta[5,6]cyclopropa[1,8a]naphtho[2,1-c]oxepin-13-yl acetate, C32H44O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-O,O′:O″)cobalt(II)], C12H12N2O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-[(furan-2-ylmethyl)-amino]-2-(2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-benzoyl)-acrylic acid ethyl ester, C17H13F4NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)-3-methoxybenzoate, C13H16O6
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile, C13H7BrClF3N2
- The crystal structure of triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O,O)nickel(II) monohydrate, C12H15NO9Ni
- Crystal structure of dihydroxy(2,4,6-triisopro-pylphenyl)telluronium trifluoromethanesulfonate, C16H25F3O5STe
- The crystal structure of 1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-imidazole 3-oxide
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tris(dibromomethyl)benzene, C9H6Br6
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-N-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-imine, C25H21N5OS
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(phenylimino)-2,3-dihydrothiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C24H16N2O3S

