Abstract
C9H7FN2O3, triclinic, P1̅ (no. 2), a = 14.467(3) Å, b = 7.4629(14) Å, c = 8.9512(18) Å, α = 90°, β = 104.759(4)°, γ = 90°, V = 934.5(3) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0421, wRref(F2) = 0.1173, T = 273 K.
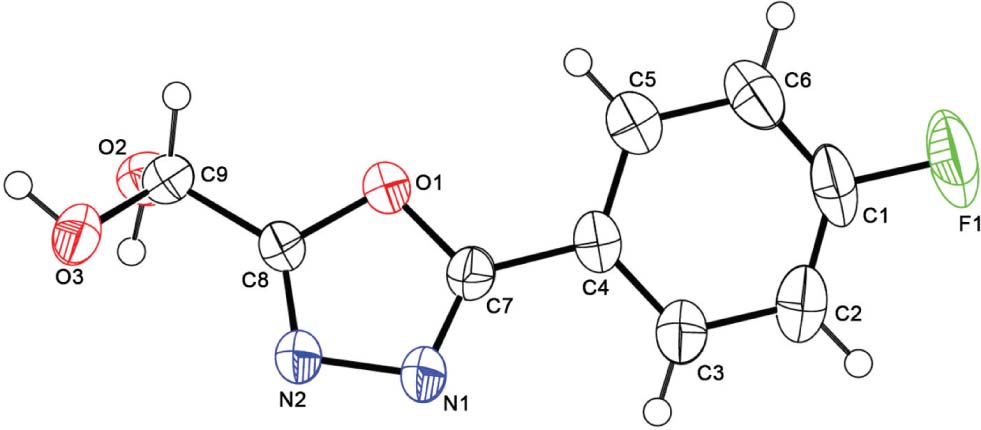
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.22 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.13 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SMART, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.6°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 5735, 1750, 0.036 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1243 |
| N(param)refined: | 142 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.58771(16) | 0.9348(4) | 0.4053(3) | 0.0609(7) |
| C2 | 0.60530(15) | 0.7679(3) | 0.4698(3) | 0.0569(6) |
| H2 | 0.5718 | 0.6682 | 0.4220 | 0.068* |
| C3 | 0.67422(14) | 0.7517(3) | 0.6080(2) | 0.0472(5) |
| H3 | 0.6885 | 0.6395 | 0.6532 | 0.057* |
| C4 | 0.72216(13) | 0.9023(3) | 0.6794(2) | 0.0403(5) |
| C5 | 0.70209(16) | 1.0690(3) | 0.6103(3) | 0.0540(6) |
| H5 | 0.7343 | 1.1700 | 0.6575 | 0.065* |
| C6 | 0.63378(18) | 1.0845(3) | 0.4707(3) | 0.0657(7) |
| H6 | 0.6199 | 1.1954 | 0.4229 | 0.079* |
| C7 | 0.79354(13) | 0.8830(2) | 0.8267(2) | 0.0365(4) |
| C8 | 0.88494(13) | 0.9647(2) | 1.0420(2) | 0.0357(4) |
| C9 | 0.92178(14) | 1.0911(2) | 1.1747(2) | 0.0401(5) |
| H9 | 0.9314 | 1.2096 | 1.1339 | 0.048* |
| F1 | 0.51945(11) | 0.9488(3) | 0.26892(17) | 0.0924(6) |
| N1 | 0.83987(11) | 0.7421(2) | 0.88672(18) | 0.0393(4) |
| N2 | 0.90022(11) | 0.7958(2) | 1.02942(18) | 0.0391(4) |
| O1 | 0.81784(9) | 1.02938(17) | 0.91916(15) | 0.0398(4) |
| O2 | 0.85449(11) | 1.10509(18) | 1.26279(18) | 0.0487(4) |
| H1O | 0.8515(15) | 1.003(2) | 1.308(3) | 0.058* |
| O3 | 1.00934(10) | 1.02487(19) | 1.25909(17) | 0.0499(4) |
| H2O | 1.0328(15) | 1.111(3) | 1.320(2) | 0.060* |
Source of material
All chemicals are of analytical grade and are commercially available. Preparation of 2-p-fluorophenyl-5-dihydroxymethyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole: a mixture of p-fluorobenzoic acid (30.0 g, 0.214 mol) and SOCl2 (30.5 g, 0.257 mol) in EtOH (150 mL) was reacted for 30 min. We slowly added hydrazine hydrate in reflux with stirring for 1 h. The white solid was filtered and washed with water and dried under vacuum to give the compound 4-fluorobenzohydrazide (32.3 g, yield 98%). To a mixture of 4-fluorobenzoyl hydrazide (30.0 g, 0.194 mol) and chloroacetic acid (18.3 mL, 0.194 mol) in xylene (200 mL), phosphorus oxychloride (20.08 mL) was dropped on the condition of ice bath, and stirred to reflux for 4 h. After cooling and evaporating the solvent under reduced pressure, saturated sodium bicarbonate solution was slowly added to the residue in ice bath. The product was filtered, and washed with water to neutrality to get the 2-(chloromethyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole (37.9 g, yield 92%). 2-(Chloromethyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole (35.0g, 0.164 mol) and sodium acetate (16.1 g, 0.197 mol) were stirred in N,N-dimethylformamide (150 mL) at ambient temperature for 24 h before partitioning between dichloromethane and water. The aqueous phase was extracted with dichloromethane, the combined organics washed with sat. dried (Na2SO4), and concentrated in vacuo to get the (5-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)methyl acetate (34.4 g, yield 89%). The product was used in the next reaction without purification. A mixture of (5-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)methyl acetate (30.0 g, 0.127 mol) and sodium hydroxide (14.2, 0.254 mol) in H2O:THF (1:1) at ambient temperature for 24 h. The mixture was concentrated in vacuo, followed by purification of the residue (24.6 g, yield 84%) by silica gel flash chromatography (gradient from n-hexane to n-hexane:ethyl acetate 1:1). The product was used in the next reaction without purification. A mixture of 2-p-fluorophenyl-5-dihydroxymethyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole (24.0 g, 0.137 mol) and MnO2 (10.8 g, 0.123 mol) in THF (9 mL) was stirred for 16 h. The reaction mixture was filtered through a pad of celite and the filtrate was evaporated to get the title compound (18.8 g, yield 80%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ [ppm] 8.08 (t, 2H), 7.46 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 2H), 7.29 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 2H), 6.01 (t, 1H). Crystals were grown in hexane at room temperature.
Experimental details
All hydrogen atoms were placed in geometrically calculated positions.
Comment
1,3,4-Oxadiazoles have shown broad biological activities [4], [5]. Antifungal activities against rice sheath blight (RSB) and sorghum anthracnose (SA) [6] are two examples. Some oxadiazole compounds are also good photosensitive materials and monomers for polymer liquid crystals and polymers [7]. The 1,3,4-oxadiazole ring is introduced into a different compound structure, and a series of compounds having a broad spectrum of biological activity and an electroluminescent material can be produced by structural modification [8]. Therefore, the synthesis of 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives has also become a hot spot of research. Oxadiazole derivatives, having been important intermediates in the fields of medicine and organic chemical industry [9], [10].
The structure of the title compound was elucidated by spectroscopic method and X-ray diffraction. The crystal structure shows that the 1,3,4-oxadiazole is linked to p-fluorophenyl via C7, and C8 is linked to dihydroxymethyl. All bond lengths and angles in the crystal structure are within the normal ranges [11]. The crystal structure indicates that the molecule shows intermolecular O3—H20 ⋯ N2 hydrogen bonds (distance = 2.00 Å), and O2—H10 ⋯ N1 hydrogen bonds (distance = 1.98 Å).
Acknowledgements
This work has been awarded the first-class construction project number of Guizhou Province: (Chinese Pharmacy) (GNYL [2017]), Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Plan ([2017] 1049) and Guizhou Province 2017 first-class University (Phase I)) Key Construction Project – Pharmacy Support for the experimental teaching center platform construction project ([2017] No. 158).
References
1. BRUKER. SMART APEX software (5.624) for SMART APEX detector. Bruker Axs Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2001).Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXTL, Version 6.10. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2000).Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
4. Al-Talib, M.; Tashtoush, H.; Odeh, N.: A convenient synthesis of alkyl and aryl substituted bis-1,3,4-oxadiazoles. Synth. Commun. 20 (1990) 1811–1817.10.1080/00397919008053105Search in Google Scholar
5. Rodrigues, G. C.; Feijó, D. F.; Bozza, M. T.; Pan, P.; Vullo, D.; Parkkila, S.; Supuran, C. T.; Capasso, C.; Aguiar, A. P.; Vermelho, A. B.: Design, synthesis, and evaluation of hydroxamic acid derivatives as promising agents for the management of chagas disease. J. Med. Chem. 57 (2013) 298–308.10.1021/jm400902ySearch in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Yu, F.; Guan, A.; Li, M.; Hu, L.; Li, X.: Design, synthesis, and fungicidal activity of novel 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives. Chin. Chem. Lett. 29 (2018) 915–918.10.1016/j.cclet.2018.01.050Search in Google Scholar
7. Goel, R.; Luxami, V.; Paul, K.: Recent advances in development of imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazines: synthesis, reactivity and their biological applications. Org. Biomol. Chem. 12 (2015) 3525–3555.10.1039/C4OB01380HSearch in Google Scholar
8. Hewings, D. S.; Fedorov, O.; Filippakopoulos, P.; Martin, S.; Picaud, S.; Tumber, A.; Wells, C.; Olcina, M. M.; Freeman, K.; Gill, A.; Ritchie, A. J.; Sheppard, D. W.; Russell, A. J.; Hammond, E. M.; Knapp, S.; Brennan, P. E.; Conway, S. J.: Optimization of 3,5-dimethylisoxazole derivatives as potent bromodomain ligands. J. Med. Chem. 56 (2013) 3217–3227.10.1021/jm301588rSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Zhao, J. S.; Jin, P.; Xi, N.; Wei, D. D.; Li, J.; Deng, W.; Hu, C. H.; He, D.: Design, synthesis and crystal structure of the antitumor agent N1-(2-(4-methoxy-2-nitrophenoxy)-2-dimethyl acyloxymethyl)-5-fluorouracil. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 36 (2017) 937–942.Search in Google Scholar
10. Li, H.; Kang, S.; Xing, Z.; Zeng, H.; Wang, H.: The synthesis, optical properties and X-ray crystal structure of novel 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives carrying a thiophene unit. Dyes Pigments 80 (2009) 163–167.10.1016/j.dyepig.2008.06.008Search in Google Scholar
11. Zhou, Z.; Long, D.; Wu, Q.-M.; Yu, D.-H.; Lu, H.-G.: The crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C8H5FN2O. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 234 (2018) 153–154.10.1515/ncrs-2018-0242Search in Google Scholar
©2020 Yong-Li Zhao et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2N:O)silver(I)], C15H8AgNO4S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium) bis(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)succinato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) tetrahydrate, C48H70CuN8O12, [C10H14N2]2[Cu(C14H17N2O4)2] ⋅ 4 H2O
- Crystal structure of triaqua-bis(2-(6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-1-(2-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-3-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-κ2O,O′)calcium(II) – ethanol (1/2), C44H76CaO19S2
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5-(4-(diphenylamino)phenyl)thiophene-2-carboxylate, C25H21NO2S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(2-methyl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- The crystal structure of (E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N′-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H13ClN2O4
- The crystal structure of (2Z,2′Z)-N′,N′′′′-(pyridine-2,6-dicarbonyl)dipicolinohydrazonamide, C19H17N9O2
- Photochromic properties and crystal structure of 3,3′-(perfluorocyclopent-1-ene-1,2-diyl)bis(5-(4-(azidomethyl)phenyl)-2-methylthiophene), C29H20F6N6S2
- Crystal structure of aqua-dichlorido-(4-(((3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)hydrazono)(oxido)methyl)pyridin-1-ium-κ3N,O,O′)iron(III), C15H16Cl2N3O4Fe
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrabromo-6-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-nickel(II)], C26H14Br8NiN2O10
- Crystal structure of diethanol-κ1O-bis(μ2-N-((2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)pyrazine-2-carbohydrazonato-κ5N,O,O′:O′:N′)-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dieuropium(III), C36H32N10O12Eu2
- The crystal structure of 2-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-((3,4-difluorobenzyl)oxy)styryl)-4,6-dimethoxybenzaldehyde, C24H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoylpyrene, C23H14O
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6-p-cymene)-(N-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) – acetone (1/1), C22H23ClN2F7OPRu
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,3,5,7-tetraphenyl-8-(N-phenylformamido)-2-oxa-5-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct -3-en-7-yl benzoate, C44H34N2O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(3-acetyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-7-(diethylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C21H21N3O4S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-κ2O:O′)nickel(II)], C18H12F4NiN2O6
- Crystal structure of 4-hydroxynaphtho[2,3-b]benzofuran-6,11-dione, C16H8O4
- The crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]dodecane – acetone (1/1), C45H48N2O5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)iminio)methyl)-6-bromophenolate, C17H15N2BrO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-oxalyl dihydrazide-κ4N,O:N′,O′)-bis(μ2-pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)dicadmium(II)] hexahydrate, C16H28O18N6Cd2
- Crystal structure of poly[tetra-(μ4-naphthalene-1,8-dicarboxylato-κ4O:O,O′: O′′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ4-oxo-κ4O:O:O:O) penta-lead(II)], C48H24O17Pb5
- Crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[c,f][1,5]oxabismocin-12 (7H)-yl acetate, C16H15O3Bi
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-chloro-6-nitrophenyl)-1-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl)diazene 1-oxide, C12H6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of bis(3-methyl-N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)nickel(II), C28H26N8O2Ni
- Crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]-dodecane, C40H36Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis[(μ2-4⋯O,O′:O′)-(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)]-di-lead(II)μ-4-hydroxybenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′;κ3O,O′:O′-bis-[(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)di-lead(II)] monohydrate, C52H36N4O12Pb2 ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ3-3,4,5,6-tetrafluoro-phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethene-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C14H9CoF4NO6
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-4-phenyl-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H10O3
- Crystal structure of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(5-oxohexyl)-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C20H24N4O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O)-bis(nitrato-κ1O)zinc(II)], C17H16N6O7Zn
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(6-aminopicolinato-κ2N,O)magnesium(II), C12H14O6N4Mg
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxamide-κ2N,O)-[tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′]nickel(II) diperchlorate — methanol (1/3), C33H39Cl2N9NiO12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3-(4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-acrylato-κO1)-(μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N3:N3′)cobalt(II)], C32H26CoF6N4O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate monohydrate, C22H25NO5S⋅H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(N-oxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl) acetamide κ2O,O′)-diaqua-zinc(II), C6H12ZnN10O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-chlorophenylimino)methyl)pyridinium 3,5-dinitrobenzoate, C19H13ClN4O6
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis((E)-2-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)phenol)zinc(II), C24H20Cl2N4O2Zn
- Crystal structure of cyclo-[tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-p-xylylenediamine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(II)] dimethyl sulfoxide solvate, C20H36Cl4N4O2Pd2S2
- Crystal structure of 4-(3-fluorophenyl)-7-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H9FO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-(pyrimidin-2-yl)hydrazono)methyl)quinolin-1-ium perchlorate – methanol (1/1), C15H16N5O5Cl
- The crystal structure of bis(N-(amino(pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)zinc(II) – methanol (2/5), C57H60Cl2N16O13Zn2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4,4′-di(4-pyridyl)-6,6′-di(tert-butyl)-2,2′-[propylenedioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenol, C35H40N4O4
- Crystal structure of (3E,3′E)-3,3′-((1,3,4-thiadiazole-2,5-diyl)bis(sulfanediyl))bis(4-hydroxy-4-phenylbut-3-en-2-one), C22H18N2O4S3
- Crystal structure of (N-benzyl-N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)di(4-chlorobenzyl)chloridotin(IV), C23H22Cl3NS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) sodium bromide hydrate, [Na(18-crown-6)]Br ⋅ H2O, C12H26BrNaO7
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H13F2N1O4
- Crystal structure of chlorido (2-(4-ethylphenyl)pyrimidine-k2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-kP) palladium(II), C30H26ClN2PPd
- Crystal structure of 18-crown-6 – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene – acetonitrile (1/1/2), C22H30F4I2N2O6
- Crystal structure of diisobutyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C16H24O6
- Crystal structure of poly[[tris(μ2-cis-1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylato)-κ2O, O′]-bis[μ3-1,3,5-tris[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzene-κ3N, N′,N′′]-trizinc(II)] – water (1/20), C60H106N12O32Zn3
- The synthesis and crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide–tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C16H14N4Cl2F6O3S
- Crystal structure of dimethylbis(diisopropyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C16H34N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of diisopropyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C14H20O6
- The synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl (E)-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-5-((2-methoxybenzylidene)amino)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C22H15N3Cl2F6O4S
- The crystal structure of a matrine derivative, 13-(methylamine-1-yl) carbodithioate matrine, C17H27N3OS2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxy-6-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C26H20CuN2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-p-fluorophenyl-5-dihydroxymethyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C9H7FN2O3
- Crystal structure of dichloridobis(4-chlorophenyl-κC1)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tin(IV), C24H16Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of bis{bromido-triphenyltin(IV)}(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′), C46H38Br2N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-chloro-quinolin-8-yloxy)-N-quinolin-8-yl-acetamide, C20H14N3O2Cl
- Crystal structure of bis(N-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(II) — dimethylformamide (1/1), C41H41N9O5Co
- Crystal structure of bis[2-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-1-tosylhydrazin-1-ido-κ3-N,N′,O]copper(II), C30H34N8O4S2Cu
- Crystal structure of (2-p-tolylpyrimidine-κ2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-κP) palladium(II), C29H24ClN2PPd
- Halogen bonding in crystal structure of bis(1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium triiodide, C16H32CsI3O8
- The synthesis and crystal structure of N-(3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfinyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-2-phenylacetamide, C20H10N4Cl2F6O2S
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)nicotinic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-methylbenzyl)thiazolidin-2-one, C11H13ONS
- The crystal structure of 2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(isoquinolin-1-yl)ethane-1,1-diol, C11H8F3NO2
- The crystal structure of 3-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- The crystal structure of 5-nitropicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 3-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-1,5-dioxaspiro[5.5]undecane-2,4-dione, C16H18O5
- Crystal structure of [[Mo3Se7(S2CNEt2)3]2(μ-Se)] ⋅ 2(C6H4Cl2), C42H68Cl4Mo6N6S12Se15
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-hydroxy-3-((5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)thio)pent-3-en-2-one, C13H12N2O3S
- The crystal structure of (2,3-dioxo-5,6:13,14-dibenzo-9,10-benzo-1,4,8,11-7, 11-diene-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-nickel(II), Ni(C22H14N4O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-(1-benzyl-2-ethyl-4-nitro-1H-imidazol-5-ylthio)-propanoic acid, C15H17N3O4S
- The crystal structure of dichlorobis(2-(dicyclohexylphosphino)-2′,4′,6′-tri-i-propyl-1,1′-biphenyl) palladium(II)-dichloroform, C68H100Cl8P2Pd
- Crystal structure and antimicrobial properties of (1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium(I) pentaiodide, C16H32CsI5O8
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2N:O)silver(I)], C15H8AgNO4S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium) bis(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)succinato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) tetrahydrate, C48H70CuN8O12, [C10H14N2]2[Cu(C14H17N2O4)2] ⋅ 4 H2O
- Crystal structure of triaqua-bis(2-(6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-1-(2-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-3-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-κ2O,O′)calcium(II) – ethanol (1/2), C44H76CaO19S2
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5-(4-(diphenylamino)phenyl)thiophene-2-carboxylate, C25H21NO2S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(2-methyl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- The crystal structure of (E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N′-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H13ClN2O4
- The crystal structure of (2Z,2′Z)-N′,N′′′′-(pyridine-2,6-dicarbonyl)dipicolinohydrazonamide, C19H17N9O2
- Photochromic properties and crystal structure of 3,3′-(perfluorocyclopent-1-ene-1,2-diyl)bis(5-(4-(azidomethyl)phenyl)-2-methylthiophene), C29H20F6N6S2
- Crystal structure of aqua-dichlorido-(4-(((3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)hydrazono)(oxido)methyl)pyridin-1-ium-κ3N,O,O′)iron(III), C15H16Cl2N3O4Fe
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrabromo-6-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-nickel(II)], C26H14Br8NiN2O10
- Crystal structure of diethanol-κ1O-bis(μ2-N-((2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)pyrazine-2-carbohydrazonato-κ5N,O,O′:O′:N′)-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dieuropium(III), C36H32N10O12Eu2
- The crystal structure of 2-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-((3,4-difluorobenzyl)oxy)styryl)-4,6-dimethoxybenzaldehyde, C24H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoylpyrene, C23H14O
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6-p-cymene)-(N-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) – acetone (1/1), C22H23ClN2F7OPRu
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,3,5,7-tetraphenyl-8-(N-phenylformamido)-2-oxa-5-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct -3-en-7-yl benzoate, C44H34N2O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(3-acetyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-7-(diethylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C21H21N3O4S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-κ2O:O′)nickel(II)], C18H12F4NiN2O6
- Crystal structure of 4-hydroxynaphtho[2,3-b]benzofuran-6,11-dione, C16H8O4
- The crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]dodecane – acetone (1/1), C45H48N2O5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)iminio)methyl)-6-bromophenolate, C17H15N2BrO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-oxalyl dihydrazide-κ4N,O:N′,O′)-bis(μ2-pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)dicadmium(II)] hexahydrate, C16H28O18N6Cd2
- Crystal structure of poly[tetra-(μ4-naphthalene-1,8-dicarboxylato-κ4O:O,O′: O′′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ4-oxo-κ4O:O:O:O) penta-lead(II)], C48H24O17Pb5
- Crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[c,f][1,5]oxabismocin-12 (7H)-yl acetate, C16H15O3Bi
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-chloro-6-nitrophenyl)-1-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl)diazene 1-oxide, C12H6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of bis(3-methyl-N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)nickel(II), C28H26N8O2Ni
- Crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]-dodecane, C40H36Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis[(μ2-4⋯O,O′:O′)-(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)]-di-lead(II)μ-4-hydroxybenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′;κ3O,O′:O′-bis-[(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)di-lead(II)] monohydrate, C52H36N4O12Pb2 ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ3-3,4,5,6-tetrafluoro-phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethene-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C14H9CoF4NO6
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-4-phenyl-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H10O3
- Crystal structure of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(5-oxohexyl)-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C20H24N4O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O)-bis(nitrato-κ1O)zinc(II)], C17H16N6O7Zn
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(6-aminopicolinato-κ2N,O)magnesium(II), C12H14O6N4Mg
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxamide-κ2N,O)-[tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′]nickel(II) diperchlorate — methanol (1/3), C33H39Cl2N9NiO12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3-(4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-acrylato-κO1)-(μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N3:N3′)cobalt(II)], C32H26CoF6N4O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate monohydrate, C22H25NO5S⋅H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(N-oxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl) acetamide κ2O,O′)-diaqua-zinc(II), C6H12ZnN10O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-chlorophenylimino)methyl)pyridinium 3,5-dinitrobenzoate, C19H13ClN4O6
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis((E)-2-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)phenol)zinc(II), C24H20Cl2N4O2Zn
- Crystal structure of cyclo-[tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-p-xylylenediamine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(II)] dimethyl sulfoxide solvate, C20H36Cl4N4O2Pd2S2
- Crystal structure of 4-(3-fluorophenyl)-7-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H9FO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-(pyrimidin-2-yl)hydrazono)methyl)quinolin-1-ium perchlorate – methanol (1/1), C15H16N5O5Cl
- The crystal structure of bis(N-(amino(pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)zinc(II) – methanol (2/5), C57H60Cl2N16O13Zn2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4,4′-di(4-pyridyl)-6,6′-di(tert-butyl)-2,2′-[propylenedioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenol, C35H40N4O4
- Crystal structure of (3E,3′E)-3,3′-((1,3,4-thiadiazole-2,5-diyl)bis(sulfanediyl))bis(4-hydroxy-4-phenylbut-3-en-2-one), C22H18N2O4S3
- Crystal structure of (N-benzyl-N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)di(4-chlorobenzyl)chloridotin(IV), C23H22Cl3NS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) sodium bromide hydrate, [Na(18-crown-6)]Br ⋅ H2O, C12H26BrNaO7
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H13F2N1O4
- Crystal structure of chlorido (2-(4-ethylphenyl)pyrimidine-k2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-kP) palladium(II), C30H26ClN2PPd
- Crystal structure of 18-crown-6 – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene – acetonitrile (1/1/2), C22H30F4I2N2O6
- Crystal structure of diisobutyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C16H24O6
- Crystal structure of poly[[tris(μ2-cis-1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylato)-κ2O, O′]-bis[μ3-1,3,5-tris[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzene-κ3N, N′,N′′]-trizinc(II)] – water (1/20), C60H106N12O32Zn3
- The synthesis and crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide–tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C16H14N4Cl2F6O3S
- Crystal structure of dimethylbis(diisopropyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C16H34N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of diisopropyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C14H20O6
- The synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl (E)-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-5-((2-methoxybenzylidene)amino)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C22H15N3Cl2F6O4S
- The crystal structure of a matrine derivative, 13-(methylamine-1-yl) carbodithioate matrine, C17H27N3OS2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxy-6-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C26H20CuN2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-p-fluorophenyl-5-dihydroxymethyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C9H7FN2O3
- Crystal structure of dichloridobis(4-chlorophenyl-κC1)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tin(IV), C24H16Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of bis{bromido-triphenyltin(IV)}(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′), C46H38Br2N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-chloro-quinolin-8-yloxy)-N-quinolin-8-yl-acetamide, C20H14N3O2Cl
- Crystal structure of bis(N-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(II) — dimethylformamide (1/1), C41H41N9O5Co
- Crystal structure of bis[2-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-1-tosylhydrazin-1-ido-κ3-N,N′,O]copper(II), C30H34N8O4S2Cu
- Crystal structure of (2-p-tolylpyrimidine-κ2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-κP) palladium(II), C29H24ClN2PPd
- Halogen bonding in crystal structure of bis(1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium triiodide, C16H32CsI3O8
- The synthesis and crystal structure of N-(3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfinyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-2-phenylacetamide, C20H10N4Cl2F6O2S
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)nicotinic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-methylbenzyl)thiazolidin-2-one, C11H13ONS
- The crystal structure of 2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(isoquinolin-1-yl)ethane-1,1-diol, C11H8F3NO2
- The crystal structure of 3-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- The crystal structure of 5-nitropicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 3-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-1,5-dioxaspiro[5.5]undecane-2,4-dione, C16H18O5
- Crystal structure of [[Mo3Se7(S2CNEt2)3]2(μ-Se)] ⋅ 2(C6H4Cl2), C42H68Cl4Mo6N6S12Se15
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-hydroxy-3-((5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)thio)pent-3-en-2-one, C13H12N2O3S
- The crystal structure of (2,3-dioxo-5,6:13,14-dibenzo-9,10-benzo-1,4,8,11-7, 11-diene-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-nickel(II), Ni(C22H14N4O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-(1-benzyl-2-ethyl-4-nitro-1H-imidazol-5-ylthio)-propanoic acid, C15H17N3O4S
- The crystal structure of dichlorobis(2-(dicyclohexylphosphino)-2′,4′,6′-tri-i-propyl-1,1′-biphenyl) palladium(II)-dichloroform, C68H100Cl8P2Pd
- Crystal structure and antimicrobial properties of (1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium(I) pentaiodide, C16H32CsI5O8


