Abstract
C28H28CuN6O16, triclinic, P1̅, (no. 2), a = 7.3118(7) Å, b = 10.0597(8) Å, c = 11.2579(10) Å, α = 92.109(7)°, β = 105.804(7)°, γ = 98.416(7)°, V = 785.63(12)Å3, Z = 1, Rgt(F) = 0.042, wRref(F2) = 0.095, T = 173(2) K.
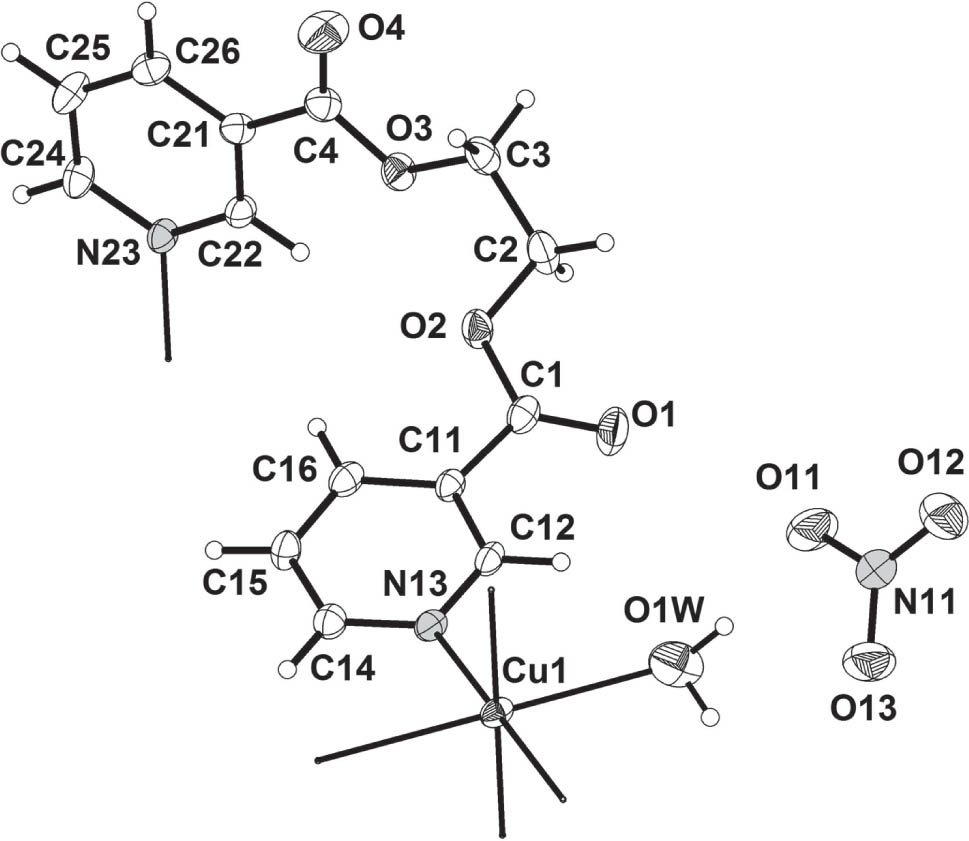
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Light blue plate |
| Size: | 0.25 × 0.19 × 0.09 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 7.8 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | IPDS II, ω-scans |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 51.2°, >98% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 8041, 2918, 0.066 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2226 |
| N(param)refined: | 235 |
| Programs: | SHELX [4], Stoe X-AREA [5], PLATON [6], Multi-scan absorption correction [7] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu1 | 0.5000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.02006(16) |
| C1 | 0.2579(4) | 0.2108(3) | 0.3625(3) | 0.0244(6) |
| O1 | 0.0967(3) | 0.1960(2) | 0.2954(2) | 0.0377(6) |
| O2 | 0.3206(3) | 0.2916(2) | 0.4681(2) | 0.0271(5) |
| C2 | 0.1811(5) | 0.3675(3) | 0.4964(3) | 0.0310(7) |
| H2A | 0.0840 | 0.3076 | 0.5246 | 0.037* |
| H2B | 0.1140 | 0.4095 | 0.4222 | 0.037* |
| C3 | 0.2928(5) | 0.4739(3) | 0.5973(3) | 0.0279(7) |
| H3A | 0.3963 | 0.5291 | 0.5710 | 0.033* |
| H3B | 0.2066 | 0.5340 | 0.6158 | 0.033* |
| O3 | 0.3749(3) | 0.40688(19) | 0.7058(2) | 0.0264(5) |
| O4 | 0.5727(4) | 0.5992(2) | 0.7885(3) | 0.0469(7) |
| C4 | 0.5167(5) | 0.4820(3) | 0.7940(3) | 0.0254(7) |
| C11 | 0.4137(4) | 0.1429(3) | 0.3400(3) | 0.0198(6) |
| C12 | 0.3929(4) | 0.0949(3) | 0.2188(3) | 0.0220(6) |
| H12 | 0.2796 | 0.1050 | 0.1564 | 0.026* |
| N13 | 0.5269(4) | 0.0348(2) | 0.1865(2) | 0.0219(5) |
| C14 | 0.6839(4) | 0.0180(3) | 0.2770(3) | 0.0239(6) |
| H14 | 0.7777 | −0.0269 | 0.2559 | 0.029* |
| C15 | 0.7138(5) | 0.0635(3) | 0.3991(3) | 0.0257(6) |
| H15 | 0.8258 | 0.0491 | 0.4605 | 0.031* |
| C16 | 0.5796(4) | 0.1302(3) | 0.4313(3) | 0.0245(6) |
| H16 | 0.6006 | 0.1664 | 0.5139 | 0.029* |
| C21 | 0.5991(4) | 0.4043(3) | 0.8991(3) | 0.0221(6) |
| C22 | 0.5277(4) | 0.2696(3) | 0.9040(3) | 0.0224(6) |
| H22 | 0.4199 | 0.2270 | 0.8391 | 0.027* |
| N23 | 0.6048(3) | 0.1977(2) | 0.9966(2) | 0.0214(5) |
| C24 | 0.7577(4) | 0.2598(3) | 1.0881(3) | 0.0270(7) |
| H24 | 0.8149 | 0.2091 | 1.1537 | 0.032* |
| C25 | 0.8345(5) | 0.3940(3) | 1.0905(3) | 0.0299(7) |
| H25 | 0.9403 | 0.4349 | 1.1573 | 0.036* |
| C26 | 0.7553(4) | 0.4676(3) | 0.9944(3) | 0.0254(7) |
| H26 | 0.8065 | 0.5598 | 0.9934 | 0.030* |
| N11 | −0.0596(4) | 0.2595(3) | −0.2635(3) | 0.0363(7) |
| O11 | 0.0037(5) | 0.2673(3) | −0.1473(2) | 0.0526(7) |
| O12 | −0.1320(4) | 0.3540(2) | −0.3170(3) | 0.0503(7) |
| O13 | −0.0446(5) | 0.1571(3) | −0.3224(3) | 0.0568(8) |
| O1W | 0.1524(5) | 0.0474(3) | −0.0595(2) | 0.0481(7) |
| H1WA | 0.094(5) | 0.111(3) | −0.092(4) | 0.072* |
| H1WBa | 0.0843 | 0.0018 | −0.0116 | 0.072* |
| H1WCa | 0.0885 | −0.0116 | −0.1145 | 0.072* |
aOccupancy: 0.50.
Source of material
A solution of Cu(NO3)2 (18.76 mg, 0.1 mmol) in water was slowly added to a solution of the ligand ethane-1,2-diyl-bis(pyridine-3-carboxylate) (27.2 mg, 0.1 mmol) in THF (4 mL). Light blue single crystals were obtained after a few days (65%).
Experimental details
All H atoms were located in the difference Fourier map, but refined with fixed individual displacement parameters, using a riding model with C—H distances of 0.95 Å (for aromatic rings), 0.99 Å (for CH2 groups), with Uiso(H) values of 1.2Ueq(C) (for CH in aromatic and CH2). One H atom of the water molecule was refined freely with O1W—H1WA distance of 0.864(10) Å but the other one is disordered with occupancy fixed at 50%. The O—H bond distances are O1W—H1WB 0.9206 Å and O1W—H1WC 0.8292 Å.
Discussion
The design of polymeric organic-inorganic materials with novel topologies and structural motifs is of current interest in the field of coordination chemistry [1]. This paper forms part of our continuing study of the synthesis, structural characterization and physical properties of coordination polymers [2]. The Cu atom exists in a square-planar CuN4 coordination geometry; it lies on an inversion center. The bond distances and angles Cu—N and N—Cu—N ranging from 2.030(2)–2.066(2) Å; 88.90(9)–180.00(13)° respectively. The ligand has a gauche conformation and links two Cu(II) atoms using its two pyridine groups to give a 1D helical structure. The most obvious difference between the ligand of the title compound and the uncoordinated ligand [3] is the angle between the planes of pyridine rings [77.08(15)° and 44.71(19)°], respectively which is a consequence of the flexible organic components of the title compound. One intramolecular and one intermolecular hydrogen bond interactions is observed between the water ligand and nitrate anion; O1W—H1WA ⋯O1WBi and O1W—H1WA ⋯O11 [symmetry code (i) −x, −y, −z].
References
1 Blake, A. J.; Champness, N. R.; Chung, S. S.; Li, W. S.; Schröder, M.: In situ ligand synthesis and construction of an unprecedented three-dimensional array with silver(I): a new approach to inorganic crystal engineering. Chem. Commun. (1997) 1675–1676.10.1039/a702972aSearch in Google Scholar
2 Vallejos, J.; Brito, I.; Cárdenas, A.; Bolte, M.; Conejeros, S.; Alemany, P.; Llanos, J.: Self-assembly of discrete metallocycles versus coordination polymers based on Cu(I) and Ag(I) ions and flexible ligands: structural diversification and luminescent properties. Polymers 8 (2016) 2–16.10.3390/polym8020046Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3 Brito, I.; Vallejos, J.; López-Rodríguez, M.; Cárdenas, A.: Ethane-1,2-diylbis(pyridine-3-carboxylate). Acta Crystallogr. E66 (2010) o114.10.1107/S1600536809052106Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4 Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5 Stoe & Cie. X-AREA. Stoe & Cie, Darmstadt, Germany, 2001.Search in Google Scholar
6 Spek, A. L.: Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D65 (2009) 148–155.10.1107/S090744490804362XSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
7 Blessing, R. H.: An empirical correction for absorption anisotropy. Acta Crystallogr. A51 (1995) 33–38.10.1107/S0108767394005726Search in Google Scholar PubMed
©2017 Iván Brito et al., published by De Gruyter.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- The crystal structure of triphenylphosphineoxide – 2,5-dichloro-3,6-dihydroxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione (2/1), C42H32Cl2O6P2
- Crystal structure of poly-[diaqua-[bis(μ2-hydroxy)-bis(μ4-3,4,5,6-tetrachlorophthalato-κ3O,O′:O′; κ2O′′:O′′′)dilanthanum(III)], C8H3Cl4LaO6
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(3,4-diphenylthieno[2,3-b]thiophene-2,5-diyl)bis[1-phenyl-methanone], C32H20O2S2
- Crystal structure of 4a-hydroxy-9-(3,5-dibromo-phenyl)-3,4,4a,5,6,7,9,9a-octahydro-2H-xanthene-1,8-dione, C19H18Br2O4
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-4,6,9,10-tetramethyl-1-oxo-6-vinyldecahydro-3a,9-propanocyclopenta[8]annulen-8-yl 2-((2-methyl-1-(3-methylbenzamido)propan-2-yl)thio)acetate, C34H49NO5S
- Crystal structure of pyridinium bis(naphthalane-2,3-diolato-κ2O,O′)borate monohydrate, C25H20BNO5
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-((1E,1′E)-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(naphthalen-2-olato)nickel(II), C72H52N4O8Ni2
- The crystal structure of 3-(2-acetyl-4-butyramido-phenoxy)-2-hydroxy-N-isopropylpropan-1-aminium tetraphenylborate, C42H49BN2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl (Z)-N′-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-phenylpiperazine-1-carbothioimidate, C28H34BrN3S
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ6-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)-(μ2-1,2-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)dicobalt(II)], Co2C24H16N4O8
- Crystal structure of catena-(bis(μ2-1, 2-bis(imidazole-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κN:N′)-dichlororido-nickel(II)), C28H28Cl2N8Ni
- Crystal structure of (Z)-1-(1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-3-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C15H16N2O3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-1-(1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-3-hydroxy-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C14H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)-6-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H18O4
- Crystal structure of (Z)-1-(1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-3-(4-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxyprop-2-en-1-one, C16H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-1-(1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-3-hydroxy-3-(p-toly)prop-2-en-1-one, C15H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1-acetyl-3-(3-chlorophenyl)-5-(4-isopropylphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-(1H)-pyrazole, C20H21ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-2,4-dinitro-5-iodoimidazole, C4H3IN4O4
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-3,5-dinitroaniline, C6H4ClN3O4
- Crystal structure of N,N-dimethyl-N′-(2-methyl-4-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-3(4H)-yl)formimidamide, C14H18N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-bis[μ3-4-chloro-2,6-bis((methylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O:O,N′]-(μ4-oxido)tetracopper(II), C28H32Cl2Cu4N4O11
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-ethane-1,2-diyl-bis(pyridine-3-carboxylate-κ2N:N′))copper(II)] dinitrate, C28H28CuN6O16
- Synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-nicotinato-κ2O,O′: κ1N)-(nitrato-κ1O)-(bis(2-benzimidazol-ylmethyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N′′)lead(II)], C22H18N7O5Pb
- The twinned crystal structure of (4SR)-7-benzyl-2,4,8,8-tetramethyl-7,8-dihydroimidazo[5,1-c][1,2,4]triazine-3,6(2H,4H)-dione, C16H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C15H13NO3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H12Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-butane-1,4-diyl-bis(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κN))silver(I)] tetrafluoroborate, C16H16AgN2O4BF4
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-2,5-dihydroxytere-phthalato)-bis(μ4-2,5-dihydroxyterephthalato)dicerium(III)], C24H16CeN2O10
- Crystal structure of 5,7,4′-trihydroxy-3,8,3′-trymethoxyflavone, C18H16O8
- Crystal structure of N-(3,4-dichlorobenzylidene)-4-methylaniline, C14H11Cl2N
- Crystal structure of 4-(3-Methoxy-phenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester, C22H27NO4
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13FN2O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1,(3,4-dihydroxythieno[2,3-b] thiophene-2,5-diyl)bis(2-bromoethanone), C10H6Br2O4S2
- The crystal structure of N,N′-(4,4′-oxydibenzyl)-bisisonicotinamide 3.5 hydrate, C24H24N4O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[hexakis(μ2-chlorido)-hexakis(4-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine-κN)tricadmium(II)], Cd3C48H42Cl6N18
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C21H22I1N3
- Crystal structure of 4-(1,3-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidin-2-yl)benzonitrile, C20H17N3
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-bis(2,2′-sulfonyldipyrazine-κ1N)dicopper(II), C24H24Cu2N8O12S2
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-6,8-diphenyl-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-c]quinoline, C28H18ClN3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-((1-(2-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methoxy)-2-naphthoate, C24H21N3O5
- Crystal structure of (tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′′)-chloranilato-κO,O′-zinc(II) – methanol (1/1), C25H22Cl2N4O5Zn
- Crystal structure of 1,1-dimethyl-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)urea, C10H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4a-Hydroxy-9-(2-nitro-phenyl)-3,4,4a,5,6,7,9,9a-octahydro-2H-xanthene-1,8-dione, C19H19NO6
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6–1-isopropyl-4-methyl benzene)-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)-N-(p-tolyl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate(V), C23H26ClF6N2PRu
- Crystal structure of phenyl(2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidin-2-yl)methanone, C24H18N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-methyl-4-((3-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5(4H)-one, C29H23N7O
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(2-butyl-1,3-dioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-6-yl)piperazin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyldiethylcarbamodithioate, C27H34N4O3S2
- Crystal structure of poly-[diaqua-bis(μ-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] bis(4-chlorobenzenesulfonate) – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/1/2), C42H40Cl2CoN6O10S2
- Crystal structure of (η6-benzene)-(N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C20H20Cl2N2O5Ru
- Crystal structure of 4,10,16,22-tetrahydroxy-6,12,18,24-tetramethoxy-2,8,14,20-tetraethylphenylresorcin[4]arene – ethyl acetate (1/1), C68H72O10
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(N-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)(η6-1-isopropyl-4-methyl benzene) ruthenium (II) tetrafluoroborate, C22H22Cl3N2BF4Ru
- Crystal structure of 3-(5-methyl-1-p-tolyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carbaldehyde, a rare Z′ = 3 structure, C20H17N5O
- Crystal structure of 5-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-N-phenyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-amine, C23H16ClN5S
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one-N,N-dimethylformamide (1/1), C18H17NO5
- Crystal structure of halogen-bonded 2-chloro-1,10-phenanthroline—1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (2/1), C30H14Cl2F4I2N4
- Crystal structure of 1-(4,4-dimethyl-2,6-dithioxo-1,3,5-triazinan-1-yl)-3-(diethylaminocarbonyl)thiourea, C11H20N6OS3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate, C18H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1-dimethyl-3-(4-methylphenyl)urea, C10H14N2O
- Crystal structure of yttrium gallium antimonide, Y5Ga1.24Sb2.77
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-2-oxoacetic acid, C16H15NO5
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- The crystal structure of triphenylphosphineoxide – 2,5-dichloro-3,6-dihydroxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione (2/1), C42H32Cl2O6P2
- Crystal structure of poly-[diaqua-[bis(μ2-hydroxy)-bis(μ4-3,4,5,6-tetrachlorophthalato-κ3O,O′:O′; κ2O′′:O′′′)dilanthanum(III)], C8H3Cl4LaO6
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(3,4-diphenylthieno[2,3-b]thiophene-2,5-diyl)bis[1-phenyl-methanone], C32H20O2S2
- Crystal structure of 4a-hydroxy-9-(3,5-dibromo-phenyl)-3,4,4a,5,6,7,9,9a-octahydro-2H-xanthene-1,8-dione, C19H18Br2O4
- Crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-4,6,9,10-tetramethyl-1-oxo-6-vinyldecahydro-3a,9-propanocyclopenta[8]annulen-8-yl 2-((2-methyl-1-(3-methylbenzamido)propan-2-yl)thio)acetate, C34H49NO5S
- Crystal structure of pyridinium bis(naphthalane-2,3-diolato-κ2O,O′)borate monohydrate, C25H20BNO5
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-((1E,1′E)-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(naphthalen-2-olato)nickel(II), C72H52N4O8Ni2
- The crystal structure of 3-(2-acetyl-4-butyramido-phenoxy)-2-hydroxy-N-isopropylpropan-1-aminium tetraphenylborate, C42H49BN2O4
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl (Z)-N′-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-phenylpiperazine-1-carbothioimidate, C28H34BrN3S
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ6-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)-(μ2-1,2-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)dicobalt(II)], Co2C24H16N4O8
- Crystal structure of catena-(bis(μ2-1, 2-bis(imidazole-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κN:N′)-dichlororido-nickel(II)), C28H28Cl2N8Ni
- Crystal structure of (Z)-1-(1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-3-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C15H16N2O3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-1-(1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-3-hydroxy-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C14H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)-6-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H18O4
- Crystal structure of (Z)-1-(1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-3-(4-ethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxyprop-2-en-1-one, C16H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-1-(1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-3-hydroxy-3-(p-toly)prop-2-en-1-one, C15H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1-acetyl-3-(3-chlorophenyl)-5-(4-isopropylphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-(1H)-pyrazole, C20H21ClN2O
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-2,4-dinitro-5-iodoimidazole, C4H3IN4O4
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-3,5-dinitroaniline, C6H4ClN3O4
- Crystal structure of N,N-dimethyl-N′-(2-methyl-4-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-3(4H)-yl)formimidamide, C14H18N4OS
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-bis[μ3-4-chloro-2,6-bis((methylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O:O,N′]-(μ4-oxido)tetracopper(II), C28H32Cl2Cu4N4O11
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-ethane-1,2-diyl-bis(pyridine-3-carboxylate-κ2N:N′))copper(II)] dinitrate, C28H28CuN6O16
- Synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-nicotinato-κ2O,O′: κ1N)-(nitrato-κ1O)-(bis(2-benzimidazol-ylmethyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N′′)lead(II)], C22H18N7O5Pb
- The twinned crystal structure of (4SR)-7-benzyl-2,4,8,8-tetramethyl-7,8-dihydroimidazo[5,1-c][1,2,4]triazine-3,6(2H,4H)-dione, C16H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C15H13NO3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H12Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-butane-1,4-diyl-bis(pyridine-3-carboxylato-κN))silver(I)] tetrafluoroborate, C16H16AgN2O4BF4
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-2,5-dihydroxytere-phthalato)-bis(μ4-2,5-dihydroxyterephthalato)dicerium(III)], C24H16CeN2O10
- Crystal structure of 5,7,4′-trihydroxy-3,8,3′-trymethoxyflavone, C18H16O8
- Crystal structure of N-(3,4-dichlorobenzylidene)-4-methylaniline, C14H11Cl2N
- Crystal structure of 4-(3-Methoxy-phenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester, C22H27NO4
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3-fluorophenyl)-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile, C16H13FN2O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1,(3,4-dihydroxythieno[2,3-b] thiophene-2,5-diyl)bis(2-bromoethanone), C10H6Br2O4S2
- The crystal structure of N,N′-(4,4′-oxydibenzyl)-bisisonicotinamide 3.5 hydrate, C24H24N4O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[hexakis(μ2-chlorido)-hexakis(4-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine-κN)tricadmium(II)], Cd3C48H42Cl6N18
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C21H22I1N3
- Crystal structure of 4-(1,3-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidin-2-yl)benzonitrile, C20H17N3
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-bis(2,2′-sulfonyldipyrazine-κ1N)dicopper(II), C24H24Cu2N8O12S2
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-6,8-diphenyl-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-c]quinoline, C28H18ClN3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-((1-(2-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methoxy)-2-naphthoate, C24H21N3O5
- Crystal structure of (tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′′)-chloranilato-κO,O′-zinc(II) – methanol (1/1), C25H22Cl2N4O5Zn
- Crystal structure of 1,1-dimethyl-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)urea, C10H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4a-Hydroxy-9-(2-nitro-phenyl)-3,4,4a,5,6,7,9,9a-octahydro-2H-xanthene-1,8-dione, C19H19NO6
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6–1-isopropyl-4-methyl benzene)-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)-N-(p-tolyl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate(V), C23H26ClF6N2PRu
- Crystal structure of phenyl(2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidin-2-yl)methanone, C24H18N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-methyl-4-((3-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5(4H)-one, C29H23N7O
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(2-butyl-1,3-dioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-6-yl)piperazin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyldiethylcarbamodithioate, C27H34N4O3S2
- Crystal structure of poly-[diaqua-bis(μ-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] bis(4-chlorobenzenesulfonate) – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/1/2), C42H40Cl2CoN6O10S2
- Crystal structure of (η6-benzene)-(N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C20H20Cl2N2O5Ru
- Crystal structure of 4,10,16,22-tetrahydroxy-6,12,18,24-tetramethoxy-2,8,14,20-tetraethylphenylresorcin[4]arene – ethyl acetate (1/1), C68H72O10
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(N-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)(η6-1-isopropyl-4-methyl benzene) ruthenium (II) tetrafluoroborate, C22H22Cl3N2BF4Ru
- Crystal structure of 3-(5-methyl-1-p-tolyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carbaldehyde, a rare Z′ = 3 structure, C20H17N5O
- Crystal structure of 5-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-N-phenyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-amine, C23H16ClN5S
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one-N,N-dimethylformamide (1/1), C18H17NO5
- Crystal structure of halogen-bonded 2-chloro-1,10-phenanthroline—1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (2/1), C30H14Cl2F4I2N4
- Crystal structure of 1-(4,4-dimethyl-2,6-dithioxo-1,3,5-triazinan-1-yl)-3-(diethylaminocarbonyl)thiourea, C11H20N6OS3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate, C18H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1-dimethyl-3-(4-methylphenyl)urea, C10H14N2O
- Crystal structure of yttrium gallium antimonide, Y5Ga1.24Sb2.77
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-2-oxoacetic acid, C16H15NO5

