Abstract
C12H8Cl2N2O5Cu, triclinic,
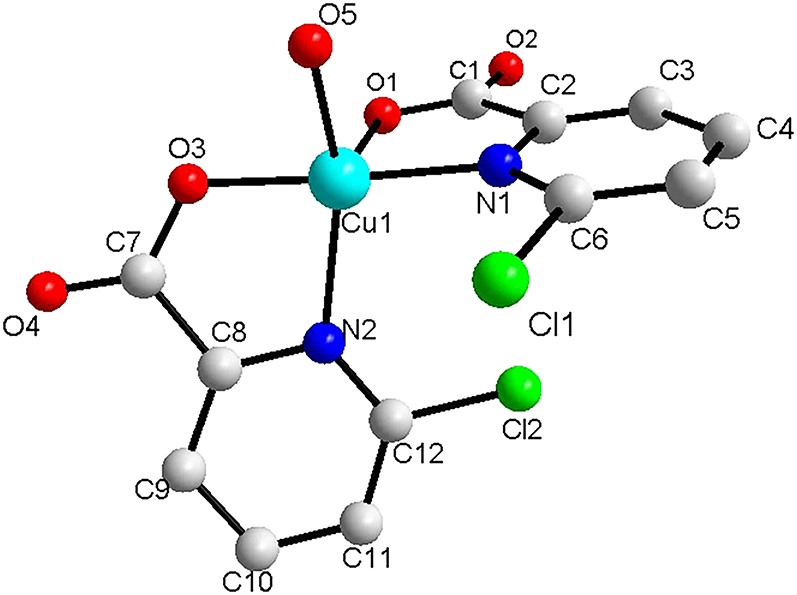
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Green block |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 2.02 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker Smart APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.1°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 4692, 2998, 0.013 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2704 |
| N(param)refined: | 205 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu1 | 0.63033 (4) | 0.79121 (3) | 0.65841 (2) | 0.02320 (8) |
| Cl1 | 0.33740 (9) | 0.64066 (7) | 0.85624 (5) | 0.03863 (14) |
| Cl2 | 0.89300 (9) | 0.47344 (7) | 0.83728 (5) | 0.03834 (14) |
| O1 | 0.8697 (2) | 0.89883 (18) | 0.67337 (13) | 0.0331 (3) |
| O2 | 1.0344 (2) | 0.97638 (18) | 0.81051 (14) | 0.0334 (3) |
| O3 | 0.6288 (2) | 0.79805 (16) | 0.48969 (12) | 0.0312 (3) |
| O4 | 0.6447 (3) | 0.6574 (2) | 0.33334 (13) | 0.0406 (4) |
| O5 | 0.3755 (3) | 0.9528 (2) | 0.66144 (16) | 0.0488 (5) |
| H5A | 0.2761 (12) | 0.9273 (13) | 0.6955 (15) | 0.073* |
| H5B | 0.366 (2) | 1.0096 (15) | 0.6026 (9) | 0.073* |
| N1 | 0.6219 (2) | 0.79432 (18) | 0.83367 (14) | 0.0220 (3) |
| N2 | 0.7572 (2) | 0.56074 (18) | 0.62878 (14) | 0.0219 (3) |
| C1 | 0.9011 (3) | 0.9177 (2) | 0.77804 (17) | 0.0243 (4) |
| C2 | 0.7600 (3) | 0.8614 (2) | 0.87388 (17) | 0.0236 (4) |
| C3 | 0.7757 (4) | 0.8727 (3) | 0.99272 (19) | 0.0335 (5) |
| H3 | 0.8731 | 0.9182 | 1.0185 | 0.040* |
| C4 | 0.6434 (4) | 0.8150 (3) | 1.07373 (19) | 0.0388 (5) |
| H4 | 0.6506 | 0.8220 | 1.1545 | 0.047* |
| C5 | 0.5017 (4) | 0.7473 (3) | 1.03286 (19) | 0.0347 (5) |
| H5 | 0.4105 | 0.7088 | 1.0852 | 0.042* |
| C6 | 0.4981 (3) | 0.7379 (2) | 0.91258 (18) | 0.0260 (4) |
| C7 | 0.6623 (3) | 0.6715 (2) | 0.43735 (17) | 0.0264 (4) |
| C8 | 0.7335 (3) | 0.5332 (2) | 0.51564 (17) | 0.0236 (4) |
| C9 | 0.7806 (3) | 0.3904 (3) | 0.4715 (2) | 0.0314 (5) |
| H9 | 0.7644 | 0.3764 | 0.3928 | 0.038* |
| C10 | 0.8525 (3) | 0.2682 (3) | 0.5461 (2) | 0.0358 (5) |
| H10 | 0.8798 | 0.1704 | 0.5194 | 0.043* |
| C11 | 0.8824 (3) | 0.2942 (2) | 0.6601 (2) | 0.0337 (5) |
| H11 | 0.9329 | 0.2146 | 0.7118 | 0.040* |
| C12 | 0.8358 (3) | 0.4417 (2) | 0.69683 (18) | 0.0256 (4) |
Source of material
To a solution of 6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylic acid (2 mmol) in anhydrous methanol (30 mL) was successively added copper acetate (1 mmol), and then maintained for 4 h at 55 °C with stirring, and then filtered at 55 °C. The filtrate was left to slowly evaporate at room temperature for 15 days, and then the precipitated green rod crystals of the title compound were filtered off. Yield: 31.5%. Anal. Calcd. for C12H8Cl2N2O5Cu: C, 36.52; H, 2.04; N, 7.10; found: C, 36.61; H, 2.03; N, 7.06.
Experimental details
A suitable crystal was selected and mounted on a Bruker Smart APEX-II CCD. Hydrogen atoms were placed in their geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms.
Comment
In the past Cisplatin, a representative of platinum metal complexes, played an important role in clinical chemotherapy for various cancers [3], [4], [5]. Nevertheless, these drugs have severe toxicity and drug resistance, which makes it urgent to design and synthesize new antitumor drugs with potential biological activity, high efficiency and low toxicity [6], [7], [8]. In the recent study, the chemical structures of thiophene and pyridine with heterocyclic compounds have antibacterial, anticancer and anti-inflammatory effects. Pyridine ring drugs have the ability to enhance the binding of drugs to biomacromolecules and resist cancer [8].
Single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis demonstrates that the asymmetric unit of the title structure contains one copper(II) cation, two 6-chloropyridine-2-carboxylate ligands and one H2O ligand. The bond distances of Cu–N are 1.9887(17) and 2.1167(17) Å, bond lengths of Cu–O are 1.9154(16) to 2.0980(16) Å, respectively, which are similar with reference []. In the title complex, the bond angles of O(3)-Cu(1)-N(1), O(5)-Cu(1)-N(2), O(3)-Cu(1)-O(1), N(1)-Cu(1)-O(1), O(5)-Cu(1)-O(1) and O(1)-Cu(1)-N(2) are 177.06(6)°, 145.02(8)°, 99.31(6)°, 80.70(6)°, 107.00(8)° and 107.53(7)°, respectively, which suggests a distorted square-pyramidal geometry [12].
Funding source: Talent Introduction Program of Dezhou University
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2016kjrc17
Funding source: Bidding subject of Dezhou University
Award Identifier / Grant number: 3010040205
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This study was supported by the Talent Introduction Program of Dezhou University (No. 2016kjrc17) and the Bidding subject of Dezhou University (No. 3010040205).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2004.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Yarnell, A., Oh, S., Reinberg, D., Lippard, S. Interaction of FACT, SSRP1, and the high mobility group (HMG) domain of SSRP1 with DNA damaged by the anticancer drug cisplatin. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 25736–25741; https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m101208200.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
4. Hou, X., Zhang, X., Wei, K., Ji, C., Dou, S., Wang, W., Li, M., Wang, P. Cisplatin induces loop structures and condensation of single DNA molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1400–1410; https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn933.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Patrick, S., Turchi, J. Replication protein A (RPA) binding to duplex cisplatin-damaged DNA is mediated through the generation of single-stranded DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 14972–149728; https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.21.14972.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Schmitt, N., Rubel, E. Osteopontin does not mitigate Cisplatin ototoxicity or nephrotoxicity in adult mice. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 149, 614–620; https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599813498218.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Sandeep, S., Debashree, M., Rybak, L., Vickram, R. Mechanisms of cisplatin- induced ototoxicity and otoprotection. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 338–350.10.3389/fncel.2017.00338Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. Wei, M., Peng, X., Xing, L., Dai, Y., Huang, R., Geng, M., Zhang, A., Ai, J., Song, Z. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of a series of novel 2-benzamide-4-(6-oxy-n-methyl-1-naphthamide)-pyridine derivatives as potent fibroblast growth factor receptor (fgfr) inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 154, 9–28; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.05.005.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Takasaki, S., Takamizawa, S. Reversible crystal deformation of a single-crystal host of copper(II) 1-naphthoate-pyrazine through crystal phase transition induced by methanol vapor sorption. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 5024–5027; https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cc09948f.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Kukovec, B.-M., Popovic, Z., Kozlevcar, B., Jaglicic, Z. 3D supramolecular architectures of copper(II) complexes with 6-methylpicolinic and 6-bromopicolinic acid: synthesis, spectroscopic, thermal and magnetic properties. Polyhedron 2008, 27, 3631–3638; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2008.09.011.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Karthik, K., Qadir, A. Synthesis and crystal structure of a new binuclear copper(II) carboxylate complex as precursor for copper(II) xide nanoparticles. J. Struct. Chem. 2019, 60, 1126–1132; https://doi.org/10.1134/s002247661907014x.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Addison, A., Rao, T., Reedijk, J., Rijn, J., Verschoor, G. Synthesis, structure, and spectroscopic properties of copper (II) compounds containing nitrogen-sulphur donor ligands; the crystal and molecular structure of aqua [1,7-bis(N-methylbenzimidazol--yl)-2,6-dithiaheptane]copper(II) perchlorate. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1984, 7, 1349–1356; https://doi.org/10.1039/dt9840001349.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2021 Zhongyu Zhang et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of [aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3 O,N,O′)-(1,10-phenanothroline-κ2 N,N′)copper(II)] dihydrate, C19H16O7N3CuI
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazolium) octamolybdate, C24H44Mo8N8O26
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(µ2-3,5-bis(1-imidazolyl)pyridine-κ2 N:N′)-(µ2-3-nitrophthalato-k3 O,O′:O″)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C30H25N11O8Cd
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2-(3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)pyridine-κ2 N:N′)-bis(3,5-dicarboxybenzoato-κ1 O)cobalt(II), C38H30CoN12O14
- Crystal structure of the nickel(II) complex aqua-(2,6-di(pyrazin-2-yl)-4,4′-bipyridine-κ3 N,N′,N′′)-(phthalato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II) tetrahydrate, C26H26N6O9Ni
- The crystal structure of 1-[5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridine-3-sulfonyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]-N-methylmethanaminium 3-carboxyprop-2-enoate, C21H20FN3O6S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane - 4,4-dihydroxydiphenylmethane (1/1), C25H21N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-((E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium trifluoroacetate dihydrate, C34H36Cl4N10O12
- Crystal structure of 1-cyclopropyl-7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C15H13F2NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinin-2(3H)-yl)benzoate, C18H15BN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C14H11ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of Al-rich fluorophlogopite, K1.0(Mg2.8Al0.2)(Si2.8Al1.2)O10F2
- The crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium hexafluoridoantimonate(V), C20H22F6I2N3Sb
- Crystal structure of tris(3-iodopyridin-1-ium) catena-poly[(hexachlorido-κ1 Cl)-(μ2-trichlorido-κ2 Cl:Cl)diantimony(III)], C15H15Cl9I3N3Sb2
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1.3.2]diazaborinin-2(3H-yl)benzoate C18H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(4-methoxybenzoyl)naphthalene-2,7-diyl dibenzoate, C40H28O8
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3,6,8-tetramethylBOPHY (BOPHY = bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine), C14H15B2BrF4N4
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(2-fluorobenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C12H9ClFN3
- Crystal structure of bis(µ2- 4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O:N:O′)-bis(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O:N:O′)-bis(µ2-1-(4-pyridyl)piperazine-κ2N:N′)-hexa-aqua-tetra-copper(II), C46H46Cu4I4N10O22
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-2,5-dihydroxyterephthalato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-bis(4-pyridylformyl)piperazine-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C24H28CdN4O12
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-(μ3-2,3,5,6-tetrafluoroterephthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)cadmium(II)], C17H14N4O5F4Cd
- Crystal structure of 6-(quinolin-8-yl)benzo[a]phenanthridin-5(6H)-one, C26H16N2O
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis(6-chloropicolinato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C12H8Cl2N2O5Cu
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κ2N:N′) disilver(I)] 4-oxidopyridine-3-sulfonate trihydrate, C25H29Ag2N5O9S
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-bromophenyl)pyrimidin-2-amine, C10H8BrN3
- Crystal structure of 6-oxo-4-phenyl-1-propyl-1,6-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C15H14N2O
- Crystal structure of 4-(2,2-difluoroethyl)-2,4-dimethyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)isoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione, C14H12F5NO2
- Crystal structure of dibromido-(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)-(3-(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-1-yl)propanoato-κ1O)zinc(II), C11H16Br2N4O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(((2 (dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene)) bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)- titanium(IV) ─ dichloromethane (2/1), C33H29N3O6Ti
- The layered crystal structure of bis(theophyllinium) hexachloridostannate (IV), C14H18N8O8SnCl6
- The crystal structre of 3-(1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-3-yl)propane-1-sulfonate, C8H12N2O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of di-tert-butyl 1″-acetyl-2,2″,9′-trioxo-4a′,9a′-dihydro-1′H,3′H,9′H-dispiro[indoline-3,2′-xanthene-4′,3″-indoline]-1,3′-dicarboxylate, C39H38N2O9
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-(quinolin-8-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-fluoro-4-(p-tolylethynyl)benzene, C15H11F
- The crystal structure of bis[4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl) phenolato-κ2N,O] copper(II), C18H12Br2CuN4O2
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 3-imidazolato-κ 3 N:N:N′)(tetrahydrofuran- κ 1 O)lithium(I)], C7H11LiN2O
- Crystal structure of N′,N′′′-((1E,1′E)-(propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2diyl))bis(methaneylylidene))di(nicotinohydrazide) pentahydrate, C25H24N8O2·5H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-1-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophos-phate(V), C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C22H14N2O4S2Cu
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-3-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide hemihydrate, C6H8IN2O2.5
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-tetralone, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of [μ-hydroxido-bis[(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tricarbonylrhenium(I)] bromide hemihydrate, C30H26N4O9Re2Br
- The crystal structure of 2,5-bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)thiazolo[5,4-d]thiazole, C20H18N2S2
- The crystal structure of 5-benzoyl-1-[(E)-(4-fluorobenzylidene)amino]-4-phenylpyrimidin-2(1H)-one, C24H16FN3O2
- Crystal structure of monocarbonyl(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O′)(tricyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C25H39N2O3PRh
- Crystal structure of poly[bis[μ3-1,3,5-tris[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzene-κ3N:N′:N″]nickel(II)] hexafluorosilicate, C36H36N12NiSiF6
- The crystal structure of 13-(pyrazole-1-yl-4-carbonitrile)-matrine, C19H25N5O
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis((E)-4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-1-methylpiperidin-4-one, C24H21F6NO3
- The crystal structure of N,N′-(Disulfanediyldi-2,1-phenylene)di(6′-methylpyridine)-2-carboxamide, C26H22N4O2S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C19H16FNO2
- The crystal structure of cis-diaqua-bis (N-butyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)pyridin-2-amine-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride trihydrate, C28H44Cl2N6O5Co
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- The crystal structure of 6-bromohexanoic acid, C6H11BrO2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-thiophenol, C6H5ClS
- The crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl chloride, C7H6BrCl
- The crystal structure of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate, C10H18O5
- The crystal structure of (2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol, C12H15ClO3
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal: 2-hydroxybenzoic acid – N′-(butan-2-ylidene)pyridine-4-carbohydrazide, C10H13N3O·C7H6O3
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((5-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(butane-1,4-diyl)bis(3-propyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C32H56F24N8P4
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2)-cadmium(II), C14H20CdCl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-cyanobenzyl)-3-cyano-4-phenyl-4-(2-cyanobenzyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine monohydrate, C56H42N8O
- The crystal structure of 3-(carboxymethyl)-1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride, C7H9N2O2Cl
- The crystal structure of adamantylmethoxydiphenylsilane, C23H28OSi
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of (2E,4Z,13E,15Z)-3,5,14,16-tetramethyl-2,6,13,17-tetraazatricyclo[16.4.0.07,12]docosa-1(22),2,4,7,9,11,13,15,18,20-decaene, C22H24N4
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2 N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C18H28N10O8Co
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of [aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3 O,N,O′)-(1,10-phenanothroline-κ2 N,N′)copper(II)] dihydrate, C19H16O7N3CuI
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1-isopropyl-1H-imidazolium) octamolybdate, C24H44Mo8N8O26
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(µ2-3,5-bis(1-imidazolyl)pyridine-κ2 N:N′)-(µ2-3-nitrophthalato-k3 O,O′:O″)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C30H25N11O8Cd
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2-(3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)pyridine-κ2 N:N′)-bis(3,5-dicarboxybenzoato-κ1 O)cobalt(II), C38H30CoN12O14
- Crystal structure of the nickel(II) complex aqua-(2,6-di(pyrazin-2-yl)-4,4′-bipyridine-κ3 N,N′,N′′)-(phthalato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II) tetrahydrate, C26H26N6O9Ni
- The crystal structure of 1-[5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridine-3-sulfonyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]-N-methylmethanaminium 3-carboxyprop-2-enoate, C21H20FN3O6S
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane - 4,4-dihydroxydiphenylmethane (1/1), C25H21N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-((E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium trifluoroacetate dihydrate, C34H36Cl4N10O12
- Crystal structure of 1-cyclopropyl-7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C15H13F2NO4
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinin-2(3H)-yl)benzoate, C18H15BN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C14H11ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of Al-rich fluorophlogopite, K1.0(Mg2.8Al0.2)(Si2.8Al1.2)O10F2
- The crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium hexafluoridoantimonate(V), C20H22F6I2N3Sb
- Crystal structure of tris(3-iodopyridin-1-ium) catena-poly[(hexachlorido-κ1 Cl)-(μ2-trichlorido-κ2 Cl:Cl)diantimony(III)], C15H15Cl9I3N3Sb2
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1.3.2]diazaborinin-2(3H-yl)benzoate C18H15BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(4-methoxybenzoyl)naphthalene-2,7-diyl dibenzoate, C40H28O8
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,3,6,8-tetramethylBOPHY (BOPHY = bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine), C14H15B2BrF4N4
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(2-fluorobenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C12H9ClFN3
- Crystal structure of bis(µ2- 4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O:N:O′)-bis(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O:N:O′)-bis(µ2-1-(4-pyridyl)piperazine-κ2N:N′)-hexa-aqua-tetra-copper(II), C46H46Cu4I4N10O22
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-2,5-dihydroxyterephthalato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-bis(4-pyridylformyl)piperazine-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C24H28CdN4O12
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-(μ3-2,3,5,6-tetrafluoroterephthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)cadmium(II)], C17H14N4O5F4Cd
- Crystal structure of 6-(quinolin-8-yl)benzo[a]phenanthridin-5(6H)-one, C26H16N2O
- The crystal structure of aqua-bis(6-chloropicolinato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C12H8Cl2N2O5Cu
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl-κ2N:N′) disilver(I)] 4-oxidopyridine-3-sulfonate trihydrate, C25H29Ag2N5O9S
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-bromophenyl)pyrimidin-2-amine, C10H8BrN3
- Crystal structure of 6-oxo-4-phenyl-1-propyl-1,6-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C15H14N2O
- Crystal structure of 4-(2,2-difluoroethyl)-2,4-dimethyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)isoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione, C14H12F5NO2
- Crystal structure of dibromido-(1-methyl-1H-imidazole-κ1N)-(3-(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-1-yl)propanoato-κ1O)zinc(II), C11H16Br2N4O2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1,1′-(((2 (dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene)) bis(naphthalen-2-olato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)- titanium(IV) ─ dichloromethane (2/1), C33H29N3O6Ti
- The layered crystal structure of bis(theophyllinium) hexachloridostannate (IV), C14H18N8O8SnCl6
- The crystal structre of 3-(1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-3-yl)propane-1-sulfonate, C8H12N2O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of di-tert-butyl 1″-acetyl-2,2″,9′-trioxo-4a′,9a′-dihydro-1′H,3′H,9′H-dispiro[indoline-3,2′-xanthene-4′,3″-indoline]-1,3′-dicarboxylate, C39H38N2O9
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-2-(quinolin-8-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-fluoro-4-(p-tolylethynyl)benzene, C15H11F
- The crystal structure of bis[4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl) phenolato-κ2N,O] copper(II), C18H12Br2CuN4O2
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 3-imidazolato-κ 3 N:N:N′)(tetrahydrofuran- κ 1 O)lithium(I)], C7H11LiN2O
- Crystal structure of N′,N′′′-((1E,1′E)-(propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2diyl))bis(methaneylylidene))di(nicotinohydrazide) pentahydrate, C25H24N8O2·5H2O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-1-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophos-phate(V), C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O′)copper(II), C22H14N2O4S2Cu
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-3-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide hemihydrate, C6H8IN2O2.5
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-tetralone, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of [μ-hydroxido-bis[(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)-tricarbonylrhenium(I)] bromide hemihydrate, C30H26N4O9Re2Br
- The crystal structure of 2,5-bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl)thiazolo[5,4-d]thiazole, C20H18N2S2
- The crystal structure of 5-benzoyl-1-[(E)-(4-fluorobenzylidene)amino]-4-phenylpyrimidin-2(1H)-one, C24H16FN3O2
- Crystal structure of monocarbonyl(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O′)(tricyclohexylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), C25H39N2O3PRh
- Crystal structure of poly[bis[μ3-1,3,5-tris[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzene-κ3N:N′:N″]nickel(II)] hexafluorosilicate, C36H36N12NiSiF6
- The crystal structure of 13-(pyrazole-1-yl-4-carbonitrile)-matrine, C19H25N5O
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis((E)-4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-1-methylpiperidin-4-one, C24H21F6NO3
- The crystal structure of N,N′-(Disulfanediyldi-2,1-phenylene)di(6′-methylpyridine)-2-carboxamide, C26H22N4O2S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-methoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C19H16FNO2
- The crystal structure of cis-diaqua-bis (N-butyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)pyridin-2-amine-κ2N,N′)cobalt(II)] dichloride trihydrate, C28H44Cl2N6O5Co
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- The crystal structure of 6-bromohexanoic acid, C6H11BrO2
- The crystal structure of 4-chloro-thiophenol, C6H5ClS
- The crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl chloride, C7H6BrCl
- The crystal structure of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate, C10H18O5
- The crystal structure of (2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol, C12H15ClO3
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal: 2-hydroxybenzoic acid – N′-(butan-2-ylidene)pyridine-4-carbohydrazide, C10H13N3O·C7H6O3
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((5-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(butane-1,4-diyl)bis(3-propyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C32H56F24N8P4
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2)-cadmium(II), C14H20CdCl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-cyanobenzyl)-3-cyano-4-phenyl-4-(2-cyanobenzyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine monohydrate, C56H42N8O
- The crystal structure of 3-(carboxymethyl)-1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride, C7H9N2O2Cl
- The crystal structure of adamantylmethoxydiphenylsilane, C23H28OSi
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of (2E,4Z,13E,15Z)-3,5,14,16-tetramethyl-2,6,13,17-tetraazatricyclo[16.4.0.07,12]docosa-1(22),2,4,7,9,11,13,15,18,20-decaene, C22H24N4
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2 N:N′)cobalt(II)] dinitrate, C18H28N10O8Co

