Abstract
C12H16N8O6V2Zn, triclinic,
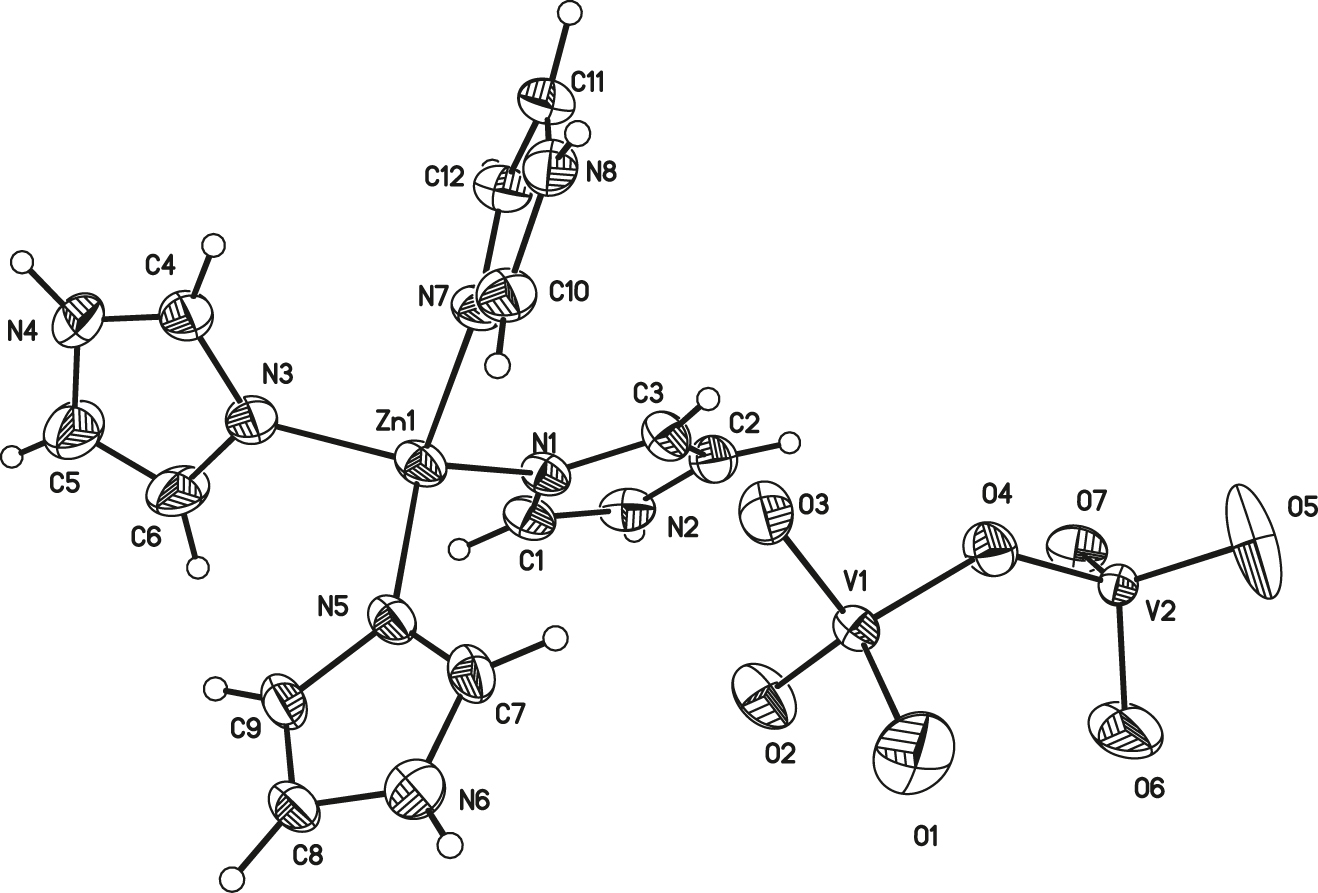
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Orange block |
| Size: | 0.21 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 2.13 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.0°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 9817, 3572, 0.019 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 3067 |
| N(param)refined: | 268 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], Shelx [2] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn1 | 0.48010 (5) | 0.84813 (4) | 0.76262 (4) | 0.04556 (14) |
| V1 | 0.91210 (6) | 0.58299 (5) | 0.86362 (5) | 0.03335 (15) |
| V2 | 1.06962 (6) | 0.46842 (5) | 0.65741 (5) | 0.03392 (15) |
| N1 | 0.4929 (3) | 0.7516 (3) | 0.6080 (3) | 0.0419 (7) |
| N2 | 0.4362 (4) | 0.6306 (3) | 0.4275 (3) | 0.0495 (8) |
| H2 | 0.384382 | 0.581912 | 0.358547 | 0.059* |
| N3 | 0.2878 (4) | 0.9350 (3) | 0.7158 (3) | 0.0543 (8) |
| N4 | 0.1374 (5) | 1.0892 (4) | 0.6948 (5) | 0.0814 (13) |
| H4 | 0.107018 | 1.166142 | 0.693676 | 0.098* |
| N5 | 0.4901 (3) | 0.7493 (3) | 0.9132 (3) | 0.0438 (7) |
| N6 | 0.5687 (4) | 0.6412 (3) | 1.0853 (3) | 0.0554 (8) |
| H6 | 0.627180 | 0.603630 | 1.148555 | 0.066* |
| N7 | 0.6497 (3) | 0.9927 (3) | 0.8100 (3) | 0.0455 (7) |
| N8 | 0.8536 (4) | 1.1216 (3) | 0.9108 (4) | 0.0550 (9) |
| H8 | 0.934249 | 1.155582 | 0.971217 | 0.066* |
| O1 | 1.000000 | 0.500000 | 1.000000 | 0.1030 (18) |
| O2 | 0.7409 (3) | 0.5159 (3) | 0.7918 (3) | 0.0688 (9) |
| O3 | 0.9048 (3) | 0.7365 (3) | 0.9077 (3) | 0.0619 (8) |
| O4 | 1.0136 (3) | 0.5810 (3) | 0.7559 (3) | 0.0554 (7) |
| O5 | 1.2476 (4) | 0.4875 (6) | 0.7011 (4) | 0.1244 (18) |
| O6 | 1.0218 (7) | 0.3230 (3) | 0.6759 (7) | 0.166 (3) |
| O7a | 0.9534 (6) | 0.4587 (5) | 0.4966 (5) | 0.0547 (13) |
| C1 | 0.3836 (4) | 0.6822 (4) | 0.5133 (3) | 0.0479 (9) |
| H1 | 0.283811 | 0.671083 | 0.507696 | 0.057* |
| C2 | 0.5858 (5) | 0.6679 (4) | 0.4673 (4) | 0.0529 (10) |
| H2A | 0.651107 | 0.646329 | 0.425407 | 0.063* |
| C3 | 0.6209 (4) | 0.7418 (4) | 0.5786 (4) | 0.0487 (9) |
| H3 | 0.716451 | 0.780393 | 0.628210 | 0.058* |
| C4 | 0.2778 (6) | 1.0624 (4) | 0.7221 (5) | 0.0683 (13) |
| H4A | 0.359562 | 1.125741 | 0.743231 | 0.082* |
| C5 | 0.0510 (6) | 0.9745 (5) | 0.6690 (7) | 0.0916 (18) |
| H5 | −0.052855 | 0.963278 | 0.646560 | 0.110* |
| C6 | 0.1423 (5) | 0.8793 (4) | 0.6816 (6) | 0.0758 (15) |
| H6A | 0.112086 | 0.789665 | 0.669284 | 0.091* |
| C7 | 0.6083 (4) | 0.7016 (4) | 0.9971 (4) | 0.0502 (9) |
| H7 | 0.704855 | 0.709595 | 0.994268 | 0.060* |
| C8 | 0.4195 (4) | 0.6492 (4) | 1.0581 (4) | 0.0469 (9) |
| H8A | 0.361504 | 0.615157 | 1.103732 | 0.056* |
| C9 | 0.3721 (4) | 0.7158 (4) | 0.9527 (4) | 0.0506 (9) |
| H9 | 0.274206 | 0.736123 | 0.912586 | 0.061* |
| C10 | 0.7612 (4) | 1.0218 (4) | 0.9202 (4) | 0.0528 (10) |
| H10 | 0.773735 | 0.978660 | 0.994485 | 0.063* |
| C11 | 0.7994 (5) | 1.1603 (4) | 0.7907 (5) | 0.0597 (11) |
| H11 | 0.840753 | 1.228679 | 0.757536 | 0.072* |
| C12 | 0.6731 (5) | 1.0803 (4) | 0.7279 (4) | 0.0526 (9) |
| H12 | 0.611684 | 1.083950 | 0.642412 | 0.063* |
-
aOccupancy: 0.5.
Source of materials
Imidazole (2 mmol), Zn(OAc)2 (0.25 mmol), V2O5 (0.3 mmol) and Et4NOH (0.3 mmol) were successively added to 10 mL water in a 25 mL flask, the mixture was ground together for 24 h. After the reaction was finished, the mixture was filtered and the filtrate was slowly evaporated at room temperature. The orange crystals were obtained, yield: 47%.
Experimental details
In the title compound, all non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically. All hydrogen atomic positions were taken from a difference Fourier map. They were refined with variable isotropic displacement parameters. Their U iso values were set to 1.2U eq (C, N of imidazole ring) of the parent atoms, respectively. All the H atoms were refined as riding on their parent atom.
Comment
At present, transition metal zinc complexes have gained widespread attention in many fields due to their excellent thermodynamic stability, abundance, low-cost and non-toxic nature [3], [4], [5], [6]. Various ligands are used to synthesize zinc complexes with varying coordination numbers and geometries [7], [8], [9]. Particularly, the research and development of imidazole derivatives have continuously expanded in the last decades [10], [11], [12]. For instance, the related study reported the synthesis of a series of polyoxometalate complexes with imidazole derivatives as organic ligands and further investigated their electrocatalytic and photocatalytic activities [10]. However, there are only few reports available involving the study of imidazole-zinc polyoxovandates [13].
Single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis shows that the title compound contains one tetra-imidazole-zinc cation, and two crystallographically distinct V atoms. In the crystal structure, the Zn(II) atom is coordinated by four nitrogen atoms from four imidazole ligands, and the bond lengths of Zn–N are 1.974(3) Å, 1.982(3) Å, 2.013(3) Å and 2.016(3) Å, respectively. Additionally, the bond angles of N(5)–Zn(1)–N(1), N(5)–Zn(1)–N(7), N(1)–Zn(1)–N(7), N(5)–Zn(1)–N(3), N(1)–Zn(1)–N(3) and N(7)–Zn(1)–N(3) are 118.25(12)°, 110.71(13)°, 104.02(12)°, 106.24(13)°, 110.23(13)° and 106.94(13)°, respectively, which confirmed that the Zn center forms a tetrahedral coordination geometry. Clearly, the bond lengths and angles are normal and correspond to those discussed in Zn(C18H37-im)2Cl2 (im = imidazole) [14] and Zn(sac)2(im)2 (sac = saccharinate anion) [15]. It can be speculated that the tetrahedral Zn complex exhibits weak intermolecular core interactions due to steric effects of imidazole ligands. The bond lengths of V–O range from 1.569(4) Å to 1.848(5) Å and the O–V–O angles range from 92.1(3)° to 127.2(3)°, which are consistent with previously reported vanadates [16]. The V(1)O4 and V(2)O4 tetrahedra and their crystallographic partners formed the 1D chain by sharing the corners, alternately.
Additionally, the three dimensional supramolecular network of title compound was constructed by intermolecular weak C–H⋯O and N–H⋯O hydrogen-bonding interaction between the adjacent molecules.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge support by the Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students of Liaocheng University (CXCY2022039).
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students of Liaocheng University (CXCY2022039).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. Apex2, Saint and Sadabs; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2004.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
3. Gusev, A. N., Kiskin, M. A., Braga, E. V., Chapran, M., Wiosna-Salyga, G., Baryshnikov, G. V., Minaeva, V. A., Minaev, B. F., Ivaniuk, K., Stakhira, P., Agren, H., Linert, W. Novel Zinc complex with an ethylenediamine Schiff base for high-luminance blue fluorescent OLED applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 11850–11859; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b02171.Search in Google Scholar
4. Kundu, B. K., Mobin, P. S. M. M., Mukhopadhyay, S. Studies on the influence of the nuclearity of zinc(II) hemi-salen complexes on some pivotal biological applications. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 15481–15503; https://doi.org/10.1039/d0dt02941f.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Liu, Z., Pulletikurthi, G., Lahiri, A., Cui, T., Endres, F. Suppressing the dendritic growth of zinc in an ionic liquid containing cationic and anionic zinc complexes for battery applications. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 8089–8098; https://doi.org/10.1039/c6dt00969g.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Sinha, A. K., Vigalok, A., Rawat, V. Catalytic application of zinc complex of oxygen depleted 1,3-bis(pyrazole)-p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene. Tetrahedron Lett. 2019, 60, 796–799; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2019.02.017.Search in Google Scholar
7. Asadi, M., Asadi, Z., Torabi, S., Lotfi, N. Synthesis, characterization and thermodynamics of complex formation of some new Schiff base ligands with some transition metal ions and the adduct formation of zinc Schiff base complexes with some organotin chlorides. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2012, 94, 372–377; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2012.03.061.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Keypour, H., Shooshtari, A., Rezaeivala, M., Mohsenzadeh, F., Rudbari, H. A. Synthesis and characterization of transition metal complexes of a hexadentate N4O2 donor Schiff base ligand: X-ray crystal structures of the copper(II) and zinc(II) complexes and their antibacterial properties. Transition Met. Chem. 2015, 40, 715–722; https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-015-9966-6.Search in Google Scholar
9. Kendur, U., Chimmalagi, G. H., Patil, S. M., Gudasi, K. B., Frampton, C. S. Synthesis, structural characterization and biological evaluation of mononuclear transition metal complexes of zwitterionic dehydroacetic acid N-aroylhydrazone ligand. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4278; https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4278.Search in Google Scholar
10. Huang, X., Gu, X., Zhang, H., Shen, G., Gong, S., Yang, B., Wang, Y., Chen, Y. Decavanadate-based clusters as bifunctional catalysts for efficient treatment of carbon dioxide and simulant sulfur mustard. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 45, 101419; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2020.101419.Search in Google Scholar
11. Huang, X., Gu, X., Qi, Y., Zhang, Y., Shen, G., Yang, B., Duan, W., Gong, S., Xue, Z., Chen, Y. Decavanadate-based transition metal hybrids as bifunctional catalysts for sulfide oxidation and C–C bond construction. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 2495–2503; https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.202100145.Search in Google Scholar
12. Huang, X., Gui, Y., Zhou, J., Zhang, Y., Shen, G., Yao, Q., Li, J., Xue, Z., Yang, G. Self-assembly of three Ag-polyoxovanadates frameworks for their efficient construction of C–N bond and detoxification of simulant sulfur mustard. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 2605–2610; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2021.09.042.Search in Google Scholar
13. Wang, H., Yang, X. Y., Ma, Y. Q., Cui, W. B., Li, Y. H., Tian, W. G., Yao, S., Gao, Y., Dang, S., Zhu, W. Imidazole-based zinc(II) complexes: highly selective fluorescent probes for acetone detection. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2014, 416, 63–68; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2014.03.017.Search in Google Scholar
14. Lee, C. K., Ling, M. J., Lin, I. J. B. Organic-inorganic hybrids of imidazole complexes of palladium(II), copper(II) and zinc(II). Crystals and liquid crystals. Dalton Trans. 2003, 24, 4731–4737; https://doi.org/10.1039/b308648h.Search in Google Scholar
15. Williams, P. A. M., Ferrer, E. G., Correa, M. J., Baran, E. J., Castellano, E. E., Piro, O. E. Characterization of two new zinc(II) complexes with saccharinate and imidazole or benzimidazole as ligands. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2004, 34, 285–290; https://doi.org/10.1023/b:jocc.0000022430.80438.63.10.1023/B:JOCC.0000022430.80438.63Search in Google Scholar
16. Huang, X., Qi, Y., Gu, X., Gong, S., Shen, G., Li, Q., Li, J. Imidazole- directed fabrication of three polyoxovanadate-based copper frameworks as efficient catalysts for constructing C–N bonds. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 10970–10976; https://doi.org/10.1039/d0dt02162h.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of undecacalcium decaarsenide, Ca11As10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4- ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H -pyrazol-3-one-κ2 N: O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)porphyrin-21,23-diido-κ4 N 4-naphthalocyanido-κ4 N 4-neodymium(IV) - chloroform (1/6) C114H90N12Cl18Nd
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(2-chlorobenzyl)urea, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis[benzyl(methyl)carbamodithioato-κ 2 S,S′]-di-n-butyltin(IV), C26H38N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate – methanol (1/2), C25H32N2O4S⋅2CH3OH
- Synthesis and crystal structure of {(N′,N″-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))-bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato)-κ6 N 2 O 4}copper(II), C30H24CuN4O6
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((5-(nitro)-2-oxidophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Br2MnN5O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta-[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C13H10N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ3-2-aminonicotinato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O′″)-(μ4-oxalato-κ6 N:N′:O,O′:O″,O′″)dicopper(I)-disamarium(III)], [SmCu(C6N2H5O2)2(C2O4)] n
- The crystal structure of 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoic- acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide—water (1/1/1), C12H13N3O7
- Crystal structure of N-ethyl-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-phenyl]piperazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H18F3N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-anilino-1,4-diphenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ium iodide, C20H17N4I
- The crystal structure of (tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine)-benzoato-copper(II) perchlorate monohydrate, CuC31H28N7O7Cl
- Crystal structure of [2-hydroxy-3-methyl-benzoato-k1 O-triphenyltin(IV)], C26H22O3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)-benzoato-k1 O)zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- The crystal structure of dicarbonyl-(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O)-rhodium(I), C8H5N2O4Rh
- The crystal structure of oxalic acid – 2-ethoxybenzamide (2/1), C20H24N2O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 7-ethyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C10H15N5O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(N,N-dimethylacetamide-κO) (μ4-2-nitroisophthalato-κ 4 O:O′:O″:O′″)manganese(II)], C11H10N2O7Mn
- Crystal structure of 14-O-acetyldelcosine, C26H41NO8
- The crystal structure of poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-(μ 4-2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5 O:O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H13CdClN2O5
- Crystal structure of propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphine sulfide) ethanol solvate, C27H26P2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{[(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)-hydrazinocarbonylmethyl]-trimethylammonium} tetrabromozincate, C32H54N8O4ZnBr4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2′-(2,5-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-3,4-diyl)dibenzoate, C34H30O7
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H12O3
- The crystal structure of tetra(imidazole-κ1 N)zinc(II) μ2-oxido-hexaoxido-divanadium(VI) C12H16N8O6V2Zn
- Crystal structure of S-2-(1-(5-methylpyridin-2-ylamino)octyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione, C24H28N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxido-2-oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-oktakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) – methanol – pyridine (1/1/1) C76H65N13Cl2Ni3O9
- The crystal structure of methyl 3,5-diaminobenzoate, C8H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 10-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-5H-dibenzo[a,d][7]annelen-5-one, C27H17NO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C16H20N2O5
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19BrN2O
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl)-3,6-bis ((4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)methylene)-1,4-dialuminacyclohexane – benzene (1/2), C50H72Al2B2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ 3-diphenylphosphinato)-tetrakis(μ 2-diphenylphosphinato)-bis(diphenylphosphinato)-bis(μ 2-hydroxo)dicopper(II)-ditin(IV), C104H100O18P8Cu2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 3-((3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)methoxy)benzo[d] isothiazole 1,1-dioxide, C11H6Cl2N2O3S2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H11FO3
- The crystal structure of tris(carbonyl)-bis(carbonyl)-[μ-propane-1,2- dithiolato]-(benzyldiphenylphosphine)diiron (Fe—Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenethyl)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium nitrate, C16H23N4O4Cl
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-disulfanediyldi(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine) monohydrate, C4H8N8OS2
- The crystal structure of trans-[bis(4-methylpyridine-κN)bis(quinoline-2-carboxylato- κ 2 N,O)cadmium(II)], C32H26CdN4O4
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2′-hydroxy-4′,6′-dimethoxy-3-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C28H28O7
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of undecacalcium decaarsenide, Ca11As10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4- ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H -pyrazol-3-one-κ2 N: O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)porphyrin-21,23-diido-κ4 N 4-naphthalocyanido-κ4 N 4-neodymium(IV) - chloroform (1/6) C114H90N12Cl18Nd
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(2-chlorobenzyl)urea, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis[benzyl(methyl)carbamodithioato-κ 2 S,S′]-di-n-butyltin(IV), C26H38N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate – methanol (1/2), C25H32N2O4S⋅2CH3OH
- Synthesis and crystal structure of {(N′,N″-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))-bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato)-κ6 N 2 O 4}copper(II), C30H24CuN4O6
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((5-(nitro)-2-oxidophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Br2MnN5O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta-[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C13H10N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ3-2-aminonicotinato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O′″)-(μ4-oxalato-κ6 N:N′:O,O′:O″,O′″)dicopper(I)-disamarium(III)], [SmCu(C6N2H5O2)2(C2O4)] n
- The crystal structure of 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoic- acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide—water (1/1/1), C12H13N3O7
- Crystal structure of N-ethyl-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-phenyl]piperazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H18F3N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-anilino-1,4-diphenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ium iodide, C20H17N4I
- The crystal structure of (tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine)-benzoato-copper(II) perchlorate monohydrate, CuC31H28N7O7Cl
- Crystal structure of [2-hydroxy-3-methyl-benzoato-k1 O-triphenyltin(IV)], C26H22O3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)-benzoato-k1 O)zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- The crystal structure of dicarbonyl-(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O)-rhodium(I), C8H5N2O4Rh
- The crystal structure of oxalic acid – 2-ethoxybenzamide (2/1), C20H24N2O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 7-ethyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C10H15N5O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(N,N-dimethylacetamide-κO) (μ4-2-nitroisophthalato-κ 4 O:O′:O″:O′″)manganese(II)], C11H10N2O7Mn
- Crystal structure of 14-O-acetyldelcosine, C26H41NO8
- The crystal structure of poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-(μ 4-2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5 O:O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H13CdClN2O5
- Crystal structure of propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphine sulfide) ethanol solvate, C27H26P2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{[(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)-hydrazinocarbonylmethyl]-trimethylammonium} tetrabromozincate, C32H54N8O4ZnBr4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2′-(2,5-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-3,4-diyl)dibenzoate, C34H30O7
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H12O3
- The crystal structure of tetra(imidazole-κ1 N)zinc(II) μ2-oxido-hexaoxido-divanadium(VI) C12H16N8O6V2Zn
- Crystal structure of S-2-(1-(5-methylpyridin-2-ylamino)octyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione, C24H28N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxido-2-oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-oktakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) – methanol – pyridine (1/1/1) C76H65N13Cl2Ni3O9
- The crystal structure of methyl 3,5-diaminobenzoate, C8H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 10-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-5H-dibenzo[a,d][7]annelen-5-one, C27H17NO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C16H20N2O5
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19BrN2O
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl)-3,6-bis ((4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)methylene)-1,4-dialuminacyclohexane – benzene (1/2), C50H72Al2B2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ 3-diphenylphosphinato)-tetrakis(μ 2-diphenylphosphinato)-bis(diphenylphosphinato)-bis(μ 2-hydroxo)dicopper(II)-ditin(IV), C104H100O18P8Cu2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 3-((3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)methoxy)benzo[d] isothiazole 1,1-dioxide, C11H6Cl2N2O3S2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H11FO3
- The crystal structure of tris(carbonyl)-bis(carbonyl)-[μ-propane-1,2- dithiolato]-(benzyldiphenylphosphine)diiron (Fe—Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenethyl)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium nitrate, C16H23N4O4Cl
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-disulfanediyldi(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine) monohydrate, C4H8N8OS2
- The crystal structure of trans-[bis(4-methylpyridine-κN)bis(quinoline-2-carboxylato- κ 2 N,O)cadmium(II)], C32H26CdN4O4
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2′-hydroxy-4′,6′-dimethoxy-3-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C28H28O7

