Abstract
C13H9N3O2, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 3.7375(1) Å, b = 27.9680(6) Å, c = 10.2595(2) Å, β = 95.5120(10)°, V = 1067.47(4) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.0370, wR ref (F 2) = 0.0975, T = 100 K.
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
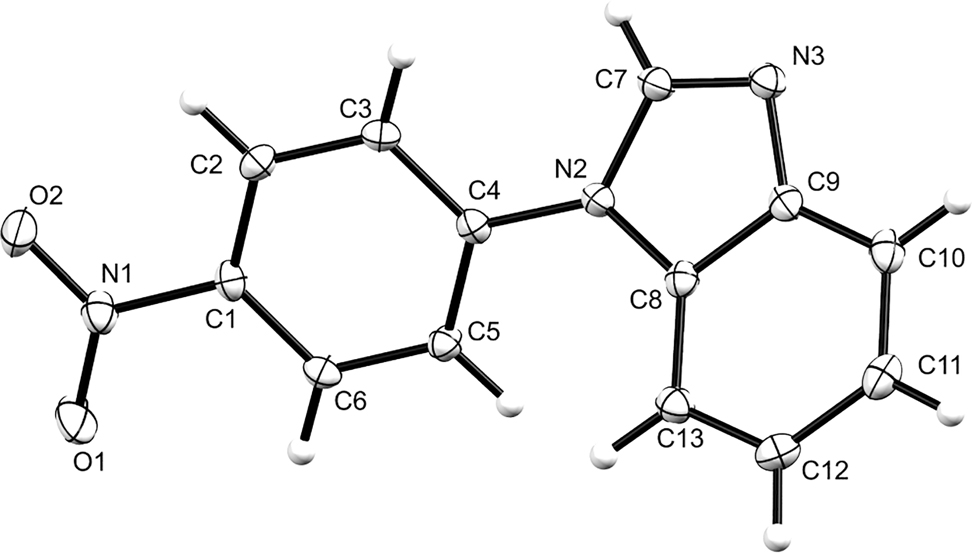
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Block, colourless |
| Size: | 0.35 × 0.22 × 0.14 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.11 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω-scans |
| θ max, completeness: | 28.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 16,686, 2678, 0.022 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 2340 |
| N(param)refined: | 163 |
| Programs: | Bruker programs [1], SHELX [2, 3], Mercury [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| x | y | z | U iso*/U eq | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | 0.5825 (3) | 0.23558 (3) | −0.28700 (10) | 0.0359 (3) |
| O2 | 0.4120 (3) | 0.29322 (3) | −0.41760 (9) | 0.0307 (2) |
| N1 | 0.5643 (3) | 0.27807 (4) | −0.31499 (10) | 0.0190 (2) |
| N2 | 1.1115 (3) | 0.40974 (3) | 0.06625 (9) | 0.0142 (2) |
| N3 | 1.3137 (3) | 0.48000 (3) | 0.15102 (10) | 0.0168 (2) |
| C1 | 0.7257 (3) | 0.31238 (4) | −0.21878 (11) | 0.0150 (2) |
| C6 | 0.9016 (3) | 0.29518 (4) | −0.10301 (11) | 0.0157 (2) |
| H6 | 0.928437 | 0.261777 | −0.088348 | 0.019* |
| C5 | 1.0370 (3) | 0.32772 (4) | −0.00933 (11) | 0.0148 (2) |
| H5 | 1.161927 | 0.316828 | 0.070135 | 0.018* |
| C4 | 0.9892 (3) | 0.37661 (4) | −0.03204 (10) | 0.0137 (2) |
| C8 | 1.0857 (3) | 0.40654 (4) | 0.20120 (11) | 0.0141 (2) |
| C9 | 1.2102 (3) | 0.45074 (4) | 0.25120 (11) | 0.0153 (2) |
| C10 | 1.2101 (3) | 0.46071 (4) | 0.38404 (12) | 0.0188 (2) |
| H10 | 1.290473 | 0.490731 | 0.418927 | 0.023* |
| C11 | 1.0890 (3) | 0.42547 (4) | 0.46370 (11) | 0.0199 (2) |
| H11 | 1.089811 | 0.431278 | 0.554958 | 0.024* |
| C2 | 0.6871 (3) | 0.36085 (4) | −0.24519 (11) | 0.0159 (2) |
| H2 | 0.572419 | 0.371569 | −0.326602 | 0.019* |
| C3 | 0.8191 (3) | 0.39332 (4) | −0.15052 (11) | 0.0151 (2) |
| H3 | 0.794037 | 0.426691 | −0.166046 | 0.018* |
| C13 | 0.9582 (3) | 0.37116 (4) | 0.27998 (11) | 0.0168 (2) |
| H13 | 0.870739 | 0.341494 | 0.244845 | 0.020* |
| C12 | 0.9652 (3) | 0.38140 (4) | 0.41247 (11) | 0.0189 (2) |
| H12 | 0.884150 | 0.357961 | 0.469864 | 0.023* |
| C7 | 1.2482 (3) | 0.45461 (4) | 0.04498 (11) | 0.0158 (2) |
| H7 | 1.290807 | 0.465953 | −0.039429 | 0.019* |
Source of material
The title compound was synthesized according to literature [5]. Colourless, block crystals were obtained by slow evaporation of its dichloromethane solution.
Experimental details
Crystal evaluation and data collection were done on a Bruker Smart APEX2 diffractometer [1]. The structure was solved by the direct method using the SHELXS [2] program. The visual crystal structure information was performed using MERCURY [4] system software. All C–Haromatic bond distances were restrained to 0.95 Å with U iso(Haromatic) = 1.2U eq of the parent atom.
Discussion
N-substituted azoles bearing imidazole or benzimidazole have generated attention as common heterocyclic moieties in various pharmaceutical compounds [6]. Their mode of synthesis includes incorporating an azole ring into the framework of a pharmaceutical candidate compound [7, 8] and following advanced protocols to achieve more stereo- and regio-selective control of the product [9]. A greener route to N-substituted azoles is to alkylate/arylate the azole nitrogen with appropriate electrophiles, such as alkyl halides [1, 10, 11]. This involves basic deprotonation of the N atom in a suitable aprotic solvent and subsequent nucleophilic displacement of the halide from the alkyl halide. Polymorphs of N-substituted azoles are rare [12], [13], [14]. However, solid state structural study of the different crystalline forms of available compounds is important especially, due to the variety of the biological and pharmacological activities of different polymorphs [15].
The title compound crystallizes in the P21/c space group and is a polymorph of the C2/c -type structure (CCDC number: 1565535; CSD refcode: PESNEJ) [16]. The new polymorph reported herein consists of one molecule in the asymmetric unit compared to the former which has two. Though the magnitude of the b axis in the new polymorph (27.9680(6) Å) is significantly larger than that of the former (7.1422(8) Å), the other unit cell dimensions of the new polymorph are much smaller than those of PESNEJ. Hence, the new polymorph has a lower unit cell volume (1067.47(4) Å3) and a higher packing coefficient (0.738) than the former (cell volume = 1067.47(4) Å3; packing coefficient = 0.719). The molecular geometries of the two polymorphs are similar based on the root mean square deviation values (0.0576–0.0680 Å) obtained from the molecular overlays. This is an indication that intermolecular interactions are solely responsible for the formation of the different polymorphs. In the title compound, intermolecular C–H⃛N hydrogen bonds with the
Funding source: University of KwaZulu-Natal
Funding source: National Research Foundation http://dx.doi.org/10.13039/501100001321
Acknowledgement
HI thanks FCET Gusau.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This study was financially supported by University of KwaZulu-Natal and the National Research Foundation (NRF).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEXII; Bruker AXS Inc: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J., Wood, P. A. Mercury CSD 2.0-new features for the visualization and investigation of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2008, 41, 466–470; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889807067908.Search in Google Scholar
5. Lee, H. M., Lu, C. Y., Chen, C. Y., Chen, W. L., Lin, H. C., Chiu, P. L., Cheng, P. Y. Palladium complexes with ethylene-bridged bis(N-heterocyclic carbene) for C–C coupling reactions. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 5807–5825; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2004.04.070.Search in Google Scholar
6. Menge, W. M. P. B., Timmerman, H. Substituted imidazoles, the key to histaminergic receptors. In Pharmacochemistry Library; Leurs, R., Timmerman, H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 1998; pp. 145–158.10.1016/S0165-7208(98)80028-7Search in Google Scholar
7. Green, G., Evans, J., Vong, A., Katritzky, A., Rees, C., Scriven, E. Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry II; Pergamon Press: Oxford, 1995; p. 469.Search in Google Scholar
8. Taylor, A. P., Robinson, R. P., Fobian, Y. M., Blakemore, D. C., Jones, L. H., Fadeyi, O. Modern advances in heterocyclic chemistry in drug discovery. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 6611–6637; https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ob00936k.Search in Google Scholar
9. Xi, N., Xu, S., Cheng, Y., Tasker, A. S., Hungate, R. W., Reider, P. J. Regio-controlled synthesis of N-substituted imidazoles. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 7315–7319; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2005.08.138.Search in Google Scholar
10. Ibrahim, H., Bala, M. D., Omondi, B. 1-[4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl]ethanone monohydrate. Acta Crystallogr. 2012, 68, o2305; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536812029157.Search in Google Scholar
11. Ibrahim, H., Bala, M. D. 1-(4-Nitrophenyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium chloride. Acta Crystallogr. 2013, E69, o114; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536812050878.Search in Google Scholar
12. Albelo, L. M. R., Ruiz-Salvador, A. R., Lewis, D. W., Gómez, A., Mialane, P., Marrot, J., Dolbecq, A., Sampieri, A., Mellot-Draznieks, C. Zeolitic polyoxometalates metal organic frameworks (Z-POMOF) with imidazole ligands and ε-Keggin ions as building blocks; computational evaluation of hypothetical polymorphs and a synthesis approach. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 8632–8639; https://doi.org/10.1039/c004234j.Search in Google Scholar
13. Karaseva, I., Karasev, M., Kurbatova, S. Structure and polymorphism of imidazole derivatives. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2021, 95, 119–126; https://doi.org/10.1134/s0036024421010118.Search in Google Scholar
14. Desiraju, G. R. crystal engineering: a holistic view. Angew. Chem. 2007, 46, 8342–8356; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200700534.Search in Google Scholar
15. Aljamali, N. M., Alsabri, I. K. A. Development of trimethoprim drug and innovation of sulfazane-trimethoprim derivatives as anticancer agents. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2020, 13, 613–625; https://doi.org/10.13005/bpj/1925.Search in Google Scholar
16. Garcia-Aranda, M. I., Gomez-Castro, C. Z., Garcia-Baez, E. V., Gomez, Y. G., Castrejon-Flores, J. L., Padilla-Martinez, I. I. Acta Crystallogr. 2018, C74, 428.Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Halliru Ibrahim et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO

