Abstract
Random jammed dipole scatterers are natural composite and common byproducts of various chemical synthesis techniques. They often form complex aggregates with nontrivial correlations that influence the effective dielectric description of the medium. In this work, we investigate the packing dynamic of rectangular nanostructure under a close packing protocol and study its influence on the optical response of the medium. We show that the maximum packing densities, maximum scattering densities, and percolation threshold densities are all interconnected concepts that can be understood through the lens of Onsager’s exclusion area principle. The emerging positional and orientational correlations between the rectangular dipoles are studied, and various geometrical connections are drawn. The effective dielectric constants of the generated ensembles are then computed through the strong contrast expansion method, leading to several unintuitive results such as scattering suppression at maximum packing densities, as well as densities below the percolation threshold, and maximum scattering in between.
1 Introduction
Random packing persists to be an alluring topic, pertinent to fundamental questions in physics, chemistry, and biology [1], [2], [3]. Within the field of optics and photonics, in particular, understanding light–matter interactions in random packed media is crucial and urged by the growing usage of optical sensors and imaging systems in probing complex living cells, liquids, and granular media. In addition, the thriving genre of disordered photonics domesticates randomness toward various applications in light trapping [4], radiative cooling [5], and random lasing [6].
In this work, we investigate the optical response of packed rectangular nanostructures on a surface, as they are commonly employed as dipole scatterers in optical devices [7], [8], [9] for various applications including light harvesting [10] and biosensing [11]. However, a detailed electromagnetic simulation of such an ensemble is a computationally expensive task to perform and one rather seeks the effective medium description as an approximation. Many homogenization theories with varying degrees of applicability and complexity have been developed toward this aim [12], [13]. Bruggeman’s theory models aggregate structure with constituents that are treated on an equal footing and therefore cannot be applied in this case [14]. Maxwell–Garnett approximation, on the other hand, models inclusions dispersed in a continuous host medium. Its analytic simplicity arises from the consideration of only the one-point probability function (density) where convergence is assured under the dilute and long wavelength limit. However, at large packing density, the positional and orientational correlations between the dipoles are not negligible anymore and can drastically alter the effective dielectric constant of the ensemble. The strong contrast expansion method presented in the study by Rechtsmanand and Torquato [13] is rather a generic and exact approach that includes the contribution of high-order point probability functions and thus captures the correction due to the emerged correlations.
In this article, we investigate the influence of the packing dynamic on the optical response of jammed rectangular nanostructures. A comprehensive workflow chart can be found in the supplementary material (section S1). In section 2, we define the packing protocol used in the study and compute the maximum achieved packing densities at various aspect ratios. We proceed in section 3 with point process statistical analysis to unravel the short-range ordering and spontaneous alignment between the packed rectangles. In section 4, we model the ensemble as a two-phase isotropic medium and estimate the effective dielectric constant
2 Random close packing
We consider the packing of hard rectangles of length l and width w on a square substrate, where the interaction potential
where
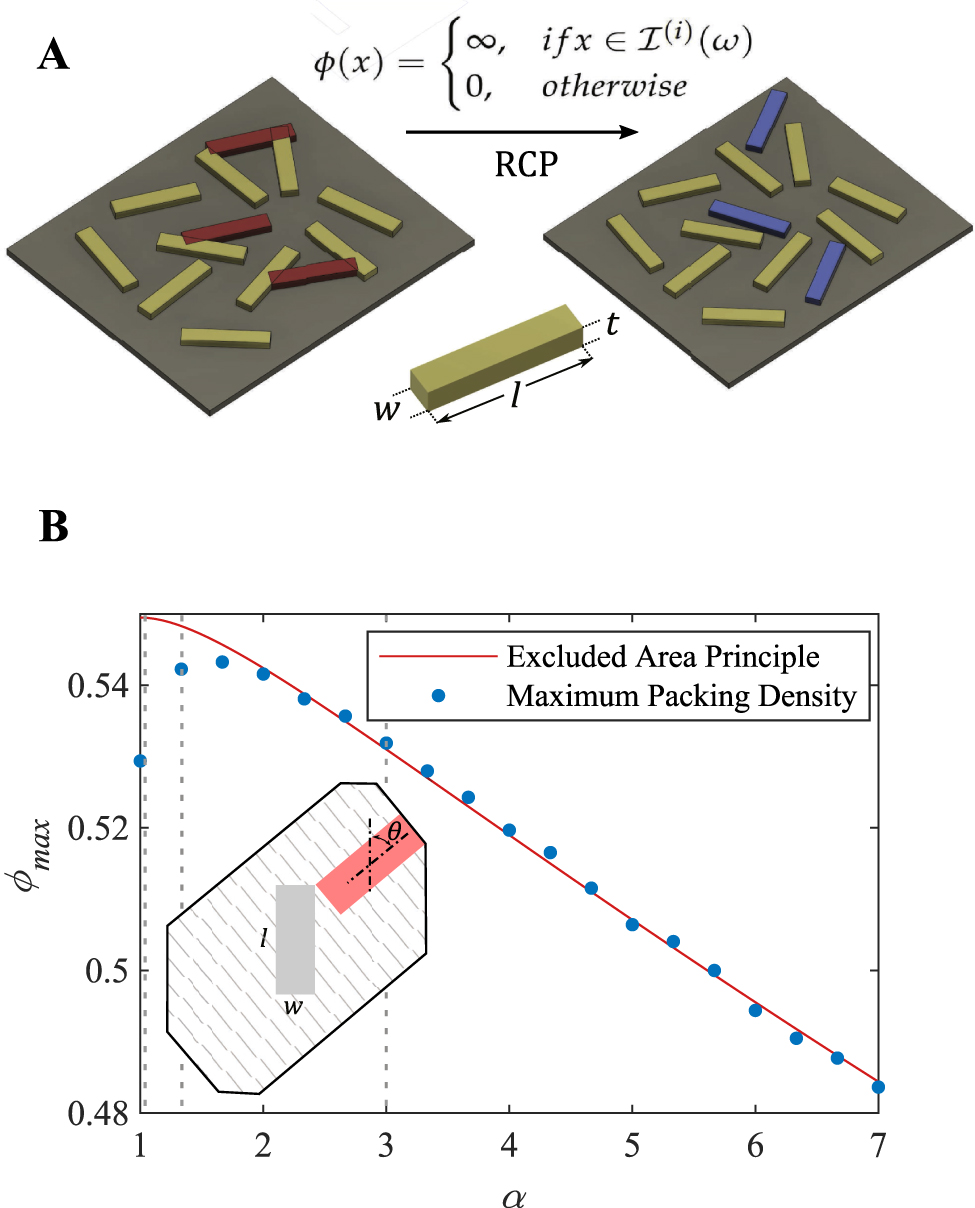
Random close packing of hard rectangles:
(A) illustration of the collective rearrangement packing protocol with
3 Point process statistical analysis
The collective rearrangement packing protocol produces a statistically homogeneous medium that we assume ergodic (any single realization of the ensemble is representative of the ensemble in the infinite area-limit). We start our investigation by performing a stochastic point process analysis. Each rectangle is represented by its two midpoint coordinates (x, y) and the angle
where
which is an average measure of the degree of alignment between two rectangles within a distance of r and r + dr. Thus,
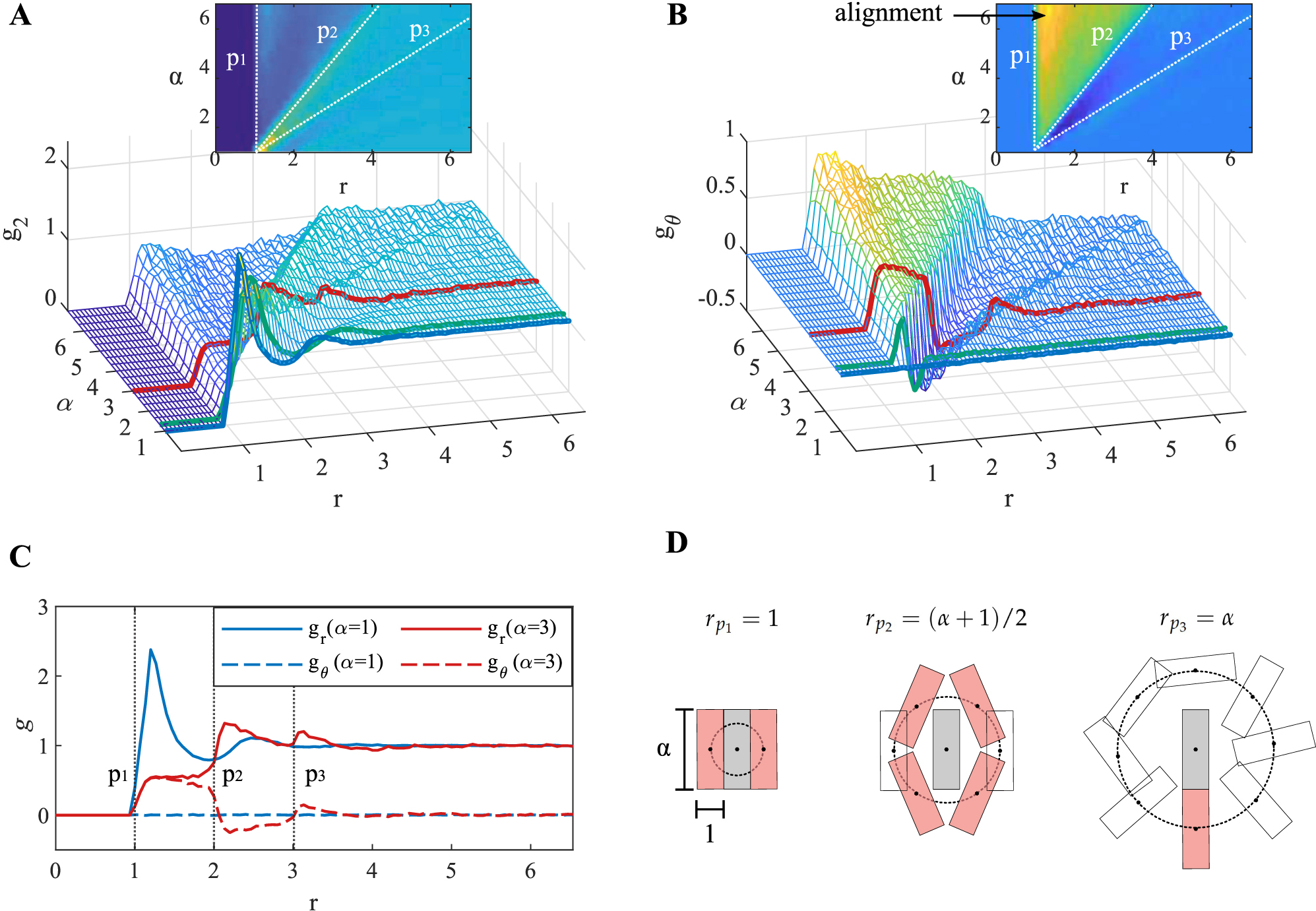
Point process analysis of maximally random packed rectangles:
(A) radial pair correlation functions
We conclude from this analysis the lack of long-range translational or nematic order in the ensemble. The effective permittivity in the 2D plane is thus macroscopically isotropic and polarization independent at all aspect ratios. In addition, high aspect ratios have a destructive behavior on short-range positional order, and therefore, their scattering features will be weaker. Furthermore, the average rectangle orientation after lifting the p2 constrain is approximately
4 Strong contrast expansion of the effective dielectric constant
The statistical properties of phase i in two-phase heterogeneous media can be specified by an infinite set of n-point probability functions
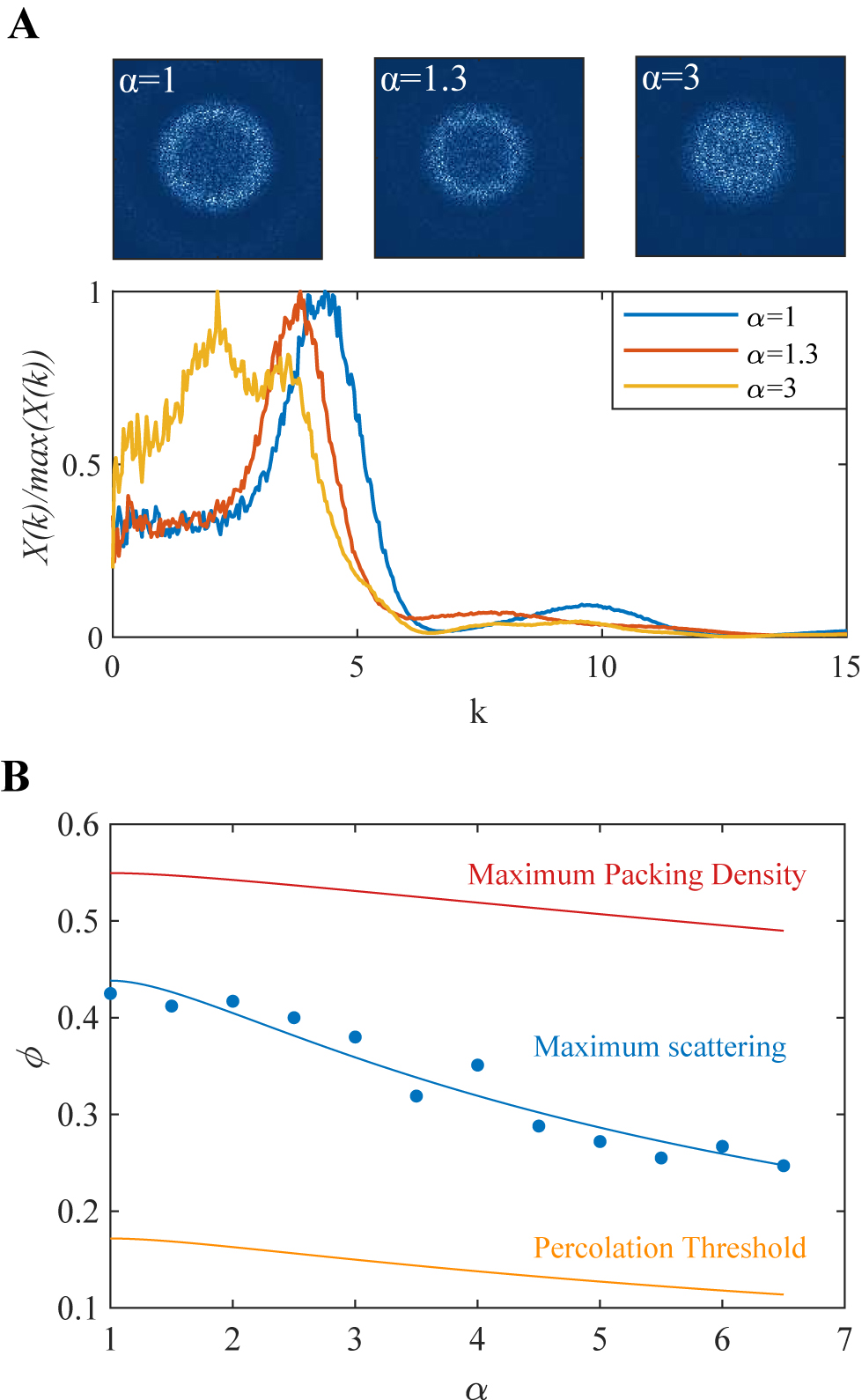
Two-phase heterogeneous analysis:
(A) spectral density images for
From the calculated autocovariance function, we can proceed in calculating the effective-dielectric constant by the strong contrast expansion method. The expressions presented in the study by Rechtsman and Torquato [13] were formulated for 3D random structures. We rederive the method for two-phase medium in 2D and truncate the expansions up to the second order to include the 2-point probability function
where
where
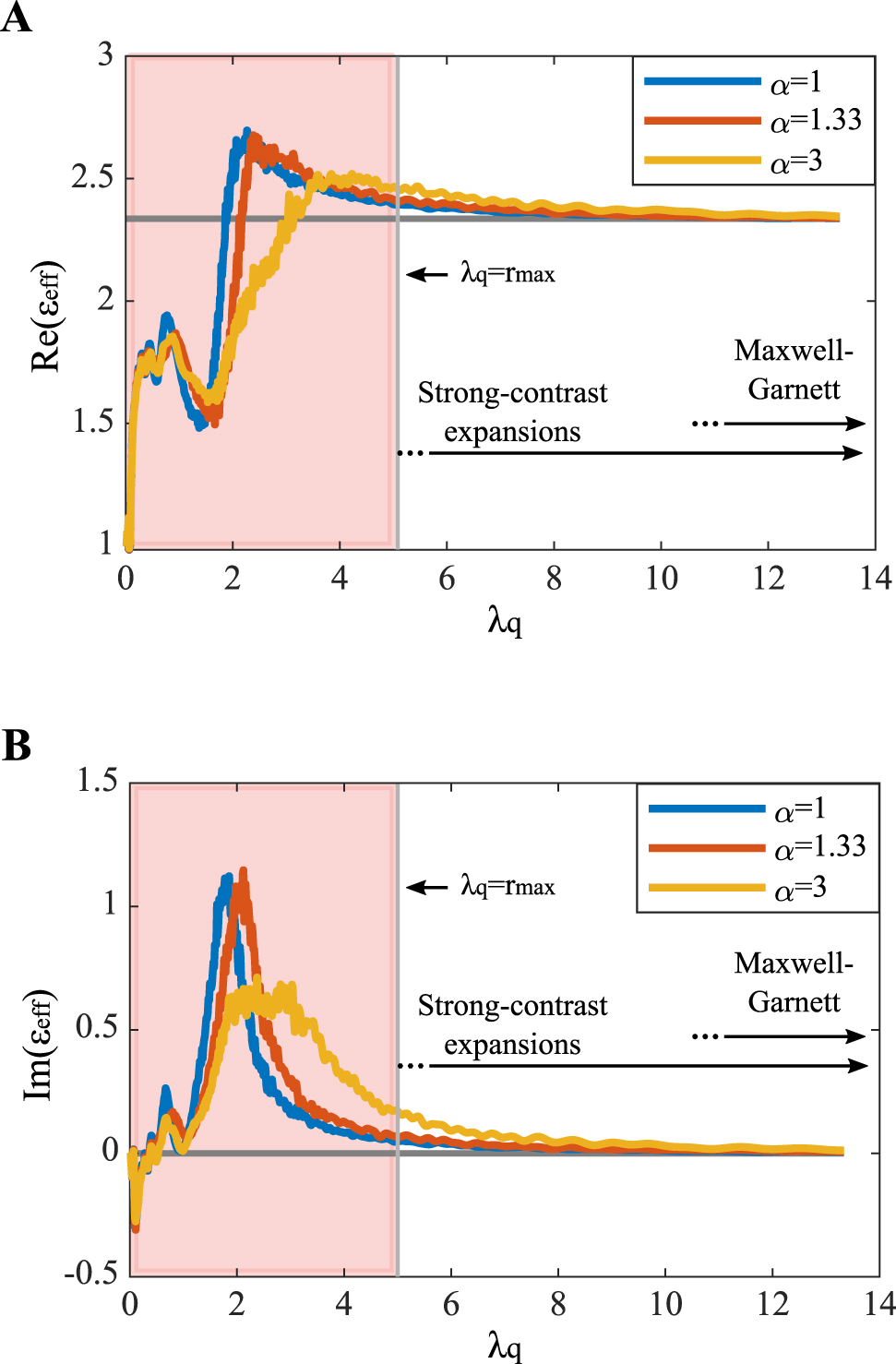
The complex effective dielectric constant
5 Conclusion
Random packed media are a ubiquitous and natural outcome of various chemical synthesis techniques. In the subwavelength limit, the complex inhomogeneous medium can be described by an effective homogeneous one with great accuracy. In this work, we statistically analyze jammed rectangular dipoles under the random close packing protocol for various densities and aspect ratios. The arising microscopic correlations were traced and shown to have direct and indirect consequences on the effective dielectric constant of the medium. Statistical tools and concepts such as Onsager’s excluded area principle, the positional correlation function, and the orientational correlation function, are of great utilities in describing the state of the ensemble and deduce some of the optical characteristics such as polarization dependence and spectral shifts. To study the influence of structural correlations on the macroscopic optical response, we accommodate the strong contrast expansion method to two-dimensional structure and use it to estimate the effective dielectric constant for the generated ensembles. This allows us to capture various effects beyond what Maxwell–Garnett approximation can, such as scattering enhancement and suppression as well as correlation-induced spectral shift. This work paves a systematic path toward engineering random medium with tailored optical properties.
Funding source: National Science Foundation Career Award
Award Identifier / Grant number: ECCS-1554021
Funding source: Office of Naval Research Young Investigator Award
Award Identifier / Grant number: N00014-17-1-2671
Funding source: ONR JTO MRI Award
Award Identifier / Grant number: N00014-17-1-2442
Funding source: DARPA DSO-NLM
Award Identifier / Grant number: HR00111820038
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
Research funding: This work was supported by the National Science Foundation Career Award (ECCS-1554021), the Office of Naval Research Young Investigator Award (N00014-17-1-2671), the ONR JTO MRI Award (N00014-17-1-2442), and the DARPA DSO-NLM Program no. HR00111820038.
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
[1] J. D. Bernal, “A geometrical approach to the structure of liquids,” Nature, vol. 183, pp. 141–147, 1959. https://doi.org/10.1038/183141a0.Search in Google Scholar
[2] P. Schaaf and J. Talbot, “Kinetics of random sequential adsorption,” Phys. Rev. Lett., vol. 62, pp. 175–178, 1989. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.62.175.Search in Google Scholar
[3] J. Feder, “Random sequential adsorption,” J. Theor. Biol., vol. 87, pp. 237–254, 1980. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-5193(80)90358-6.Search in Google Scholar
[4] H. Atwater and A. Polman, “Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices,” Nat. Mater., vol. 9, pp. 205–213, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2629.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Y. Zhail, Y. Ma, S. David, et al., “Scalable-manufactured randomized glasspolymer hybrid metamaterial for daytime radiative cooling,” Science, vol. 355, pp. 1062–1066, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aai7899.Search in Google Scholar
[6] N. Lawandy, R. Balachandran, A. Gomes, et al., “Laser action in strongly scattering media,” Nature, vol. 368, pp. 436–438, 1994. https://doi.org/10.1038/368436a0.Search in Google Scholar
[7] M. Dupre, L. Hsu, and B. Kante, “On the design of random metasurface based devices,” Sci. Rep., vol. 8, p. 7162, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25488-4.Search in Google Scholar
[8] H. Nasari, M. Dupré, and B. Kanté, “Efficient design of random metasurfaces,” Opt. Lett., vol. 43, pp. 5829–5832, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1364/ol.43.005829.Search in Google Scholar
[9] J. Park, A. Ndao, W. Cai, et al., “Symmetry-breaking-induced plasmonic exceptional points and nanoscale sensing,” Nat. Phys., vol. 16, pp. 462–468, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-020-0796-x.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Y.-Z. Zheng, X. Tao, J.-W. Zhang, et al., “Plasmonic enhancement of light-harvesting efficiency in tandem dye-sensitized solar cells using multiplexed gold core/silica shell nanorods,” J. Power Sources, vol. 376, pp. 26–32, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.11.072.Search in Google Scholar
[11] A. Abbas, L. Tian, J. J. Morrissey, et al., “Hot spot‐localized artificial antibodies for label‐free plasmonic biosensing,” Adv. Funct. Mater., vol. 23, pp. 1789–1797, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201202370.Search in Google Scholar
[12] M. Safdari, M. Baniassadi, H. Garmestani, et al., “A modified strong-contrast expansion for estimating the effective thermal conductivity of multiphase heterogeneous materials,” J. Appl. Phys., vol. 112, p. 114318, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4768467.Search in Google Scholar
[13] M. Rechtsman and S. Torquato, “Effective dielectric tensor for electromagnetic wave propagation in random media,” J. Appl. Phys., vol. 103, pp. 1–15, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2906135.Search in Google Scholar
[14] G. A. Niklasson, C. G. Granqvist, and O. Hunderi, “Effective medium models for the optical properties of inhomogeneous materials,” Appl. Opt., vol. 20, pp. 26–30, 1981. https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.20.000026.Search in Google Scholar
[15] A. Bertei, C. C. Chueh, J. G. Pharoah, et al., “Modified collective rearrangement sphere-assembly algorithm for random packings of nonspherical particles: towards engineering applications,” Powder Technol., vol. 253, pp. 311–324, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2013.11.034.Search in Google Scholar
[16] J. Perez-Justea, I. Pastoriza-Santosa, L. Liz-Marzana, et al., “Gold nanorods: synthesis, characterization and applications,” Coord. Chem. Rev., vol. 249, pp. 1870–1901, 2005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2005.01.030.Search in Google Scholar
[17] L. Onsager, “The effects of shape on the interaction of colloidal particles,” Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., vol. 51, pp. 627–659, 1949. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1949.tb27296.x.Search in Google Scholar
[18] I. Balberg, C. H. Anderson, S. Alexander, et al., “Excluded volume and its relation to the onset of percolation,” Phys. Rev. B, vol. 30, pp. 3933–3943, 1984. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.30.3933.Search in Google Scholar
[19] A. Donev, I. Cisse, D. Sachs, et al., “Improving the density of jammed disordered packings using ellipsoids,” Science, vol. 303, pp. 990–993, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1093010.Search in Google Scholar
[20] P. Chaikin, A. Donev, W. Man, et al., “Some observations on the random packing of hard ellipsoids,” Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., vol. 45, pp. 6960–6965, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie060032g.Search in Google Scholar
[21] Z. Ma and S. Torquato, “Hyperuniformity of generalized random organization models,” Phys. Rev. E, vol. 99, p. 022115, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1103/physreve.99.022115.Search in Google Scholar
[22] S. Torquato, Random Heterogeneous Materials, Berlin, Springer, 2002.10.1007/978-1-4757-6355-3Search in Google Scholar
[23] S. Torquato, “Hyperuniform states of matter,” Phys. Rep., vol. 745, pp. 1–95, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2018.03.001.Search in Google Scholar
[24] W. Man, M. Florescu, K. Matsuyama, et al., “Photonic band gap in isotropic hyperuniform disordered solids with low dielectric contrast,” Opt. Express, vol. 21, pp. 19972–19981, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.21.019972.Search in Google Scholar
[25] W. Man, M. Florescu, E. P. Williamson, et al., “Isotropic band gaps and freeform waveguides observed in hyperuniform disordered photonic solids,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., vol. 40, pp. 15886–15891, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1307879110.Search in Google Scholar
[26] O. Leseur, R. Pierrat, and R. Carminati, “High-density hyperuniform materials can be transparent,” Optica, vol. 3, pp. 763–767, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1364/optica.3.000763.Search in Google Scholar
[27] F. Bigourdan, R. Pierrat, and R. Carminati, “Enhanced absorption of waves in stealth hyperuniform disordered media,” Opt. Express, vol. 27, pp. 8666–8682, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.27.008666.Search in Google Scholar
[28] S. Torquato and J. Kim, “Nonlocal effective electromagnetic wave characteristics of composite media: beyond the quasistatic regime,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.00701.Search in Google Scholar
Supplementary Material
The online version of this article offers supplementary material (https://doi.org/10.1515/nanoph-2020-0431).
© 2020 Mutasem Odeh et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Editorial
- Editorial
- Optoelectronics and Integrated Photonics
- Disorder effects in nitride semiconductors: impact on fundamental and device properties
- Ultralow threshold blue quantum dot lasers: what’s the true recipe for success?
- Waiting for Act 2: what lies beyond organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays for organic electronics?
- Waveguide combiners for mixed reality headsets: a nanophotonics design perspective
- On-chip broadband nonreciprocal light storage
- High-Q nanophotonics: sculpting wavefronts with slow light
- Thermoelectric graphene photodetectors with sub-nanosecond response times at terahertz frequencies
- High-performance integrated graphene electro-optic modulator at cryogenic temperature
- Asymmetric photoelectric effect: Auger-assisted hot hole photocurrents in transition metal dichalcogenides
- Seeing the light in energy use
- Lasers, Active optical devices and Spectroscopy
- A high-repetition rate attosecond light source for time-resolved coincidence spectroscopy
- Fast laser speckle suppression with an intracavity diffuser
- Active optics with silk
- Nanolaser arrays: toward application-driven dense integration
- Two-dimensional spectroscopy on a THz quantum cascade structure
- Homogeneous quantum cascade lasers operating as terahertz frequency combs over their entire operational regime
- Toward new frontiers for terahertz quantum cascade laser frequency combs
- Soliton dynamics of ring quantum cascade lasers with injected signal
- Fiber Optics and Optical Communications
- Propagation stability in optical fibers: role of path memory and angular momentum
- Perspective on using multiple orbital-angular-momentum beams for enhanced capacity in free-space optical communication links
- Biomedical Photonics
- A fiber optic–nanophotonic approach to the detection of antibodies and viral particles of COVID-19
- Plasmonic control of drug release efficiency in agarose gel loaded with gold nanoparticle assemblies
- Metasurfaces for biomedical applications: imaging and sensing from a nanophotonics perspective
- Hyperbolic dispersion metasurfaces for molecular biosensing
- Fundamentals of Optics
- A Tutorial on the Classical Theories of Electromagnetic Scattering and Diffraction
- Reflectionless excitation of arbitrary photonic structures: a general theory
- Optimization Methods
- Multiobjective and categorical global optimization of photonic structures based on ResNet generative neural networks
- Machine learning–assisted global optimization of photonic devices
- Artificial neural networks for inverse design of resonant nanophotonic components with oscillatory loss landscapes
- Adjoint-optimized nanoscale light extractor for nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond
- Topological Photonics
- Non-Hermitian and topological photonics: optics at an exceptional point
- Topological photonics: Where do we go from here?
- Topological nanophotonics for photoluminescence control
- Anomalous Anderson localization behavior in gain-loss balanced non-Hermitian systems
- Quantum computing, Quantum Optics, and QED
- Quantum computing and simulation
- NIST-certified secure key generation via deep learning of physical unclonable functions in silica aerogels
- Thomas–Reiche–Kuhn (TRK) sum rule for interacting photons
- Macroscopic QED for quantum nanophotonics: emitter-centered modes as a minimal basis for multiemitter problems
- Generation and dynamics of entangled fermion–photon–phonon states in nanocavities
- Polaritonic Tamm states induced by cavity photons
- Recent progress in engineering the Casimir effect – applications to nanophotonics, nanomechanics, and chemistry
- Enhancement of rotational vacuum friction by surface photon tunneling
- Plasmonics and Polaritonics
- Shrinking the surface plasmon
- Polariton panorama
- Scattering of a single plasmon polariton by multiple atoms for in-plane control of light
- A metasurface-based diamond frequency converter using plasmonic nanogap resonators
- Selective excitation of individual nanoantennas by pure spectral phase control in the ultrafast coherent regime
- Semiconductor quantum plasmons for high frequency thermal emission
- Origin of dispersive line shapes in plasmon-enhanced stimulated Raman scattering microscopy
- Epitaxial aluminum plasmonics covering full visible spectrum
- Metaoptics
- Metamaterials with high degrees of freedom: space, time, and more
- The road to atomically thin metasurface optics
- Active nonlocal metasurfaces
- Giant midinfrared nonlinearity based on multiple quantum well polaritonic metasurfaces
- Near-field plates and the near zone of metasurfaces
- High-efficiency metadevices for bifunctional generations of vectorial optical fields
- Printing polarization and phase at the optical diffraction limit: near- and far-field optical encryption
- Optical response of jammed rectangular nanostructures
- Dynamic phase-change metafilm absorber for strong designer modulation of visible light
- Arbitrary polarization conversion for pure vortex generation with a single metasurface
- Enhanced harmonic generation in gases using an all-dielectric metasurface
- Monolithic metasurface spatial differentiator enabled by asymmetric photonic spin-orbit interactions
Articles in the same Issue
- Editorial
- Editorial
- Optoelectronics and Integrated Photonics
- Disorder effects in nitride semiconductors: impact on fundamental and device properties
- Ultralow threshold blue quantum dot lasers: what’s the true recipe for success?
- Waiting for Act 2: what lies beyond organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays for organic electronics?
- Waveguide combiners for mixed reality headsets: a nanophotonics design perspective
- On-chip broadband nonreciprocal light storage
- High-Q nanophotonics: sculpting wavefronts with slow light
- Thermoelectric graphene photodetectors with sub-nanosecond response times at terahertz frequencies
- High-performance integrated graphene electro-optic modulator at cryogenic temperature
- Asymmetric photoelectric effect: Auger-assisted hot hole photocurrents in transition metal dichalcogenides
- Seeing the light in energy use
- Lasers, Active optical devices and Spectroscopy
- A high-repetition rate attosecond light source for time-resolved coincidence spectroscopy
- Fast laser speckle suppression with an intracavity diffuser
- Active optics with silk
- Nanolaser arrays: toward application-driven dense integration
- Two-dimensional spectroscopy on a THz quantum cascade structure
- Homogeneous quantum cascade lasers operating as terahertz frequency combs over their entire operational regime
- Toward new frontiers for terahertz quantum cascade laser frequency combs
- Soliton dynamics of ring quantum cascade lasers with injected signal
- Fiber Optics and Optical Communications
- Propagation stability in optical fibers: role of path memory and angular momentum
- Perspective on using multiple orbital-angular-momentum beams for enhanced capacity in free-space optical communication links
- Biomedical Photonics
- A fiber optic–nanophotonic approach to the detection of antibodies and viral particles of COVID-19
- Plasmonic control of drug release efficiency in agarose gel loaded with gold nanoparticle assemblies
- Metasurfaces for biomedical applications: imaging and sensing from a nanophotonics perspective
- Hyperbolic dispersion metasurfaces for molecular biosensing
- Fundamentals of Optics
- A Tutorial on the Classical Theories of Electromagnetic Scattering and Diffraction
- Reflectionless excitation of arbitrary photonic structures: a general theory
- Optimization Methods
- Multiobjective and categorical global optimization of photonic structures based on ResNet generative neural networks
- Machine learning–assisted global optimization of photonic devices
- Artificial neural networks for inverse design of resonant nanophotonic components with oscillatory loss landscapes
- Adjoint-optimized nanoscale light extractor for nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond
- Topological Photonics
- Non-Hermitian and topological photonics: optics at an exceptional point
- Topological photonics: Where do we go from here?
- Topological nanophotonics for photoluminescence control
- Anomalous Anderson localization behavior in gain-loss balanced non-Hermitian systems
- Quantum computing, Quantum Optics, and QED
- Quantum computing and simulation
- NIST-certified secure key generation via deep learning of physical unclonable functions in silica aerogels
- Thomas–Reiche–Kuhn (TRK) sum rule for interacting photons
- Macroscopic QED for quantum nanophotonics: emitter-centered modes as a minimal basis for multiemitter problems
- Generation and dynamics of entangled fermion–photon–phonon states in nanocavities
- Polaritonic Tamm states induced by cavity photons
- Recent progress in engineering the Casimir effect – applications to nanophotonics, nanomechanics, and chemistry
- Enhancement of rotational vacuum friction by surface photon tunneling
- Plasmonics and Polaritonics
- Shrinking the surface plasmon
- Polariton panorama
- Scattering of a single plasmon polariton by multiple atoms for in-plane control of light
- A metasurface-based diamond frequency converter using plasmonic nanogap resonators
- Selective excitation of individual nanoantennas by pure spectral phase control in the ultrafast coherent regime
- Semiconductor quantum plasmons for high frequency thermal emission
- Origin of dispersive line shapes in plasmon-enhanced stimulated Raman scattering microscopy
- Epitaxial aluminum plasmonics covering full visible spectrum
- Metaoptics
- Metamaterials with high degrees of freedom: space, time, and more
- The road to atomically thin metasurface optics
- Active nonlocal metasurfaces
- Giant midinfrared nonlinearity based on multiple quantum well polaritonic metasurfaces
- Near-field plates and the near zone of metasurfaces
- High-efficiency metadevices for bifunctional generations of vectorial optical fields
- Printing polarization and phase at the optical diffraction limit: near- and far-field optical encryption
- Optical response of jammed rectangular nanostructures
- Dynamic phase-change metafilm absorber for strong designer modulation of visible light
- Arbitrary polarization conversion for pure vortex generation with a single metasurface
- Enhanced harmonic generation in gases using an all-dielectric metasurface
- Monolithic metasurface spatial differentiator enabled by asymmetric photonic spin-orbit interactions


