Abstract
The Zhijin phosphorite (P)-bearing rare earth element (REE) deposit in Guizhou Province (China) hosts vast ore resources (P: 1.348 billion tonnes; REE: 1.44 Mt). Up to date, the Zhijin phosphorite resource has not been exploited because of the uncertain occurrence of the associated REEs, which hampers mineral processing and extraction. In this study, the structure, the valence state, and the coordination position of Y in the REE-yttrium-rich bioclastic samples from Zhijin were revealed by means of synchrotron radiation X-ray absorption fine structure analysis. The results show that the Y occurs as Y(iii) in the samples, and that the form of Y is different from the Y2O3 form in standard xenotime samples. Yttrium in the samples was in a complex coordination position without Y–O–Y bonding, and the Y–O bond lengths range widely without clear patterns. We suggest that Y in the samples is surrounded by organic or macro-molecular compounds, rather than in inorganic ones. Thus, Y in collophanite is unlikely to be in the form of isomorphism.
1 Introduction
Rare earth metal is a strategic material widely used in many high-tech industries and is critical to the future prosperity of humanity. At present, the global production of heavy rare earth elements (HREEs) comes mainly from the ion-adsorbed rare earth ore, and exploring HREEs in phosphorite represents a new way to tackle the global HREE supply challenge [1,2]. A large number of phosphate deposits [3] were discovered in the Ediacaran and Early Cambrian Yangtze platform in South China. Previous studies [4 5,6,7,8] showed that these phosphorite deposits are REE bearing (Figure 1), some of which containing relatively high total (∑) REE contents, such as the Xinhua (aka. Zhijin) (∑REE = 242.92–1059.59 ppm, avg. 611.27 ppm), Kaiyang (∑REE = 42.96–399.5 ppm, avg. 176.1 ppm), Wengan (∑REE = 11.89–223 ppm, avg. 67.4 ppm) [9], Kunyang (∑REE = 5.97–332.62 ppm, avg. 130.16 ppm) [10], as well as the Bahuang (in Tongren) (∑REE = 197.9–1013.35 ppm, avg. 768.08 ppm), Songlin (in Zunyi) (∑REE = 500.33 ppm) [11], and Jingxiang (∑REE = 27.73–157.97 ppm, avg. 93.86 ppm) [12]. According to statistics, the ∑REE content of the Xinhua deposit is higher than that of many Ediacaran to Early Cambrian deposits, especially for the Y content (accounting up to 45% of the total ∑REY). In addition, the ∑REE content is positively correlated with that of P2O5 [11,13].

Statistics of REE content in typical phosphate deposits (data source listed above).
The Xinhua ore district (in Zhijin P deposit) is located southwest of the Zhijin county with high transport accessibility. The ore bodies are mainly distributed along the west limb (close to the axis) of the northeast–southwest-trending Guohua anticline. Structural geology is dominated by transtensional faulting and local small structures. The ore district contains four ore sections, namely Gaoshan, Gezhongwu, Guohua, and Daga. These ore sections are all located on the limbs of the Guohua anticline, and the major prospect locations are shown in Figure 2. Stratigraphy (from bottom up) is the Dengying Formation (Fm.) dolomite, Gezhongwu Fm. sandy phosphorite, bioclastic dolomitic phosphorite, and Niutitang Fm. black shale.

Geographic location and simplified geologic map of the ZhijinXinhua P deposit. Numbers on the map: 1. Dengying Formation; 2. Gezhongwu Formation; 3. Niutitang-Mingxinxi Formation; 4. Dapu Formation; 5. Fault; 6. Roads; 7. Rivers; 8. Name locations; 9. Phosphate prospect; 10. Ore section in the Xinhua P deposit; 11. Guohua-Gezhongwu anticline.
In this study, we studied the profiles with large ore resources, including the Gezhongwu (Figure 3a and c), Guohua (Figure 3d–f), and Majiaqiao (Figure 3b). We observed the vertical change in lithology, color, and sedimentary structure, and performed the sampling in certain spacing.
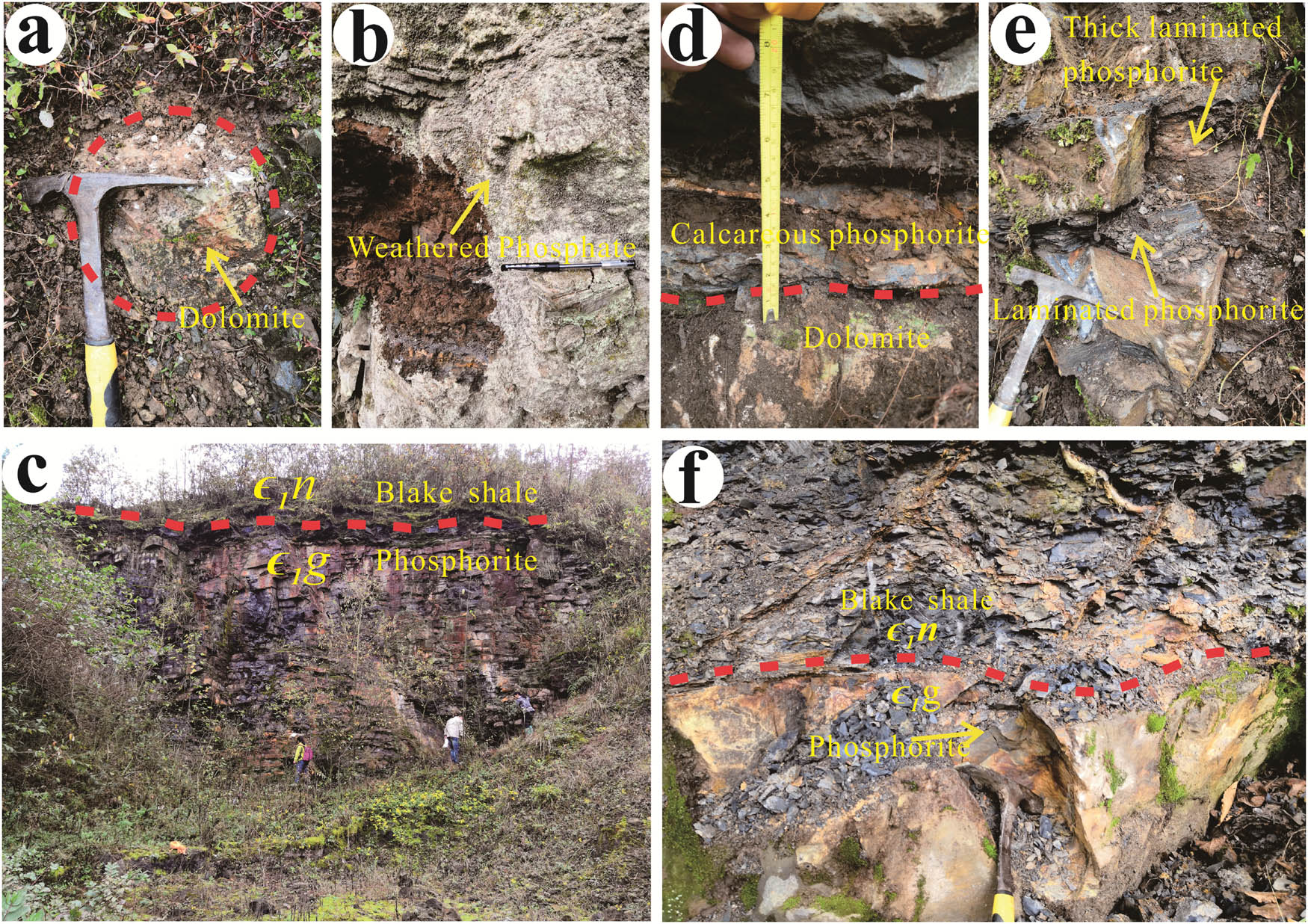
Field geological profile of the Zhijin deposit, Guizhou Province, China. (a) Basal dolomite (Gezhongwu profile). (b) Weathered phosphorite (Majiaqiao profile). (c) Banded dolomitic phosphorite and the overlying Niutitang Fm. black shale (Gezhongwu profile). (d) Basal dolomite in clear contact with calcareous phosphorite (Guohua profile). (e) Thin-medium-bedded cherty phosphorite with banded structure (Guohua profile). (f) Phosphorite in clear contact with the overlying Niutitang Fm. black shale (Guohua profile).
Major ore types at Zhijin are dark-/light-gray bioclastic-bearing dolomitic phosphorite (dominant) and brecciated phosphorite [14,15], with the former displaying (inter)layered and banded structure (Figure 4a and b). Bioclasts in the biophosphorites are mainly dominated by small shells (Figure 5a–e), including Zhijinites and hyolithes spicules (Figure 5a) and algal biocide (Figure 5e). Samples from the top of the ore layer contain higher Si contents, and subrounded P-bearing lithics are occasionally found. This not only indicates the complex formation of the P deposit, but also demonstrates the major influence on the occurrence, enrichment environment, and distribution patterns of REEs.

Hand specimen photos of phosphate ores from Zhijin, Guizhou Province: (a) collophane-rich sample; (b) dolomite-rich sample.

Thin-section microphotographs of the Zhijin phosphate ore, showing microstructural features (plane-polarized transmitted light). (a) Bioclastics in concentric rings (XL-6-10, 5 × 10); (b) bioclastics in radial and drusy form (XD-6-2, 5 × 10); (c) bioclastics show lineation and zoning (XL-6-10, 5 × 10); (d) numerous stripped bioclastics (XL-L-1, 5 × 10); (e) rounded algae fossils in siliceous cement; (f) few bioclastics in this more silicic and phosphoric sample (W-X2, 10 × 10).
As aforementioned, the REE occurrence in the Zhijin P ores remains to be investigated. The REE occurrence refers to the physicochemical state and their combination with other coexisting elements in a particular stage of the REE migration history. The state of occurrence includes the phase (gas, liquid, solid), the type and form of compounds, the bond type, and the physicochemical features of the valence and coordination position in the crystal lattice.
Research on phosphorite-associated REE has attracted increasing attention in recent years. Previous studies suggested that REEs exist mainly as ion adsorption state (e.g., REE deposits in the Jiangxi granite weathering crust), independent minerals (Bayan Obo REE deposit), or isomorphism in minerals and rocks [16].
As supported by X-ray diffraction (XRD), electron probe microanalysis (EPMA), and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) analyses on the REE occurrence at Zhijin, it is concluded that the REEs in phosphorite exist mainly as isomorphism in the carbonate–fluorapatite lattice [10,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. The isomorphic occurrence is likely led by the phosphate–carbonate–fluorapatite crystals in phosphorite, which have open hexagonal columnar structure. In that case, the Ca2+ and REE ionic radii are similar and thus REE can enter the crystal via isomorphism. Meanwhile, REEs in phosphorite occur mainly in collophane, most of which exist in apatite as ions and minor adsorbed on clay minerals [4,20,24,25,26,27]. This indicates that the REEs in phosphorite do not occur predominantly in independent minerals. Duan et al. studied the Zhijin deposit by means of mineral processing experiment and concluded that the ores contain ion-adsorbing REEs, whose content is lower than those in the form of isomorphism. Besides, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy spectral analysis [19] and ICP-MS analysis [23] found that the REEs do not occur as independent minerals [23], although Liu et al. argued that REEs can occur as cerianite at Zhijin, based on EPMA data [28].
In this study, we applied synchrotron radiation X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) experiment to reveal the type of bonding, the valence state, and the coordination information of Y in REE-rich apatite crystals from Zhijin, as well as to elucidate the atomic-scale Y occurrence in phosphorite.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Sample preparation and standard selection
To achieve more meaningful data, REE-rich phosphorite samples (XL-6-10) from Zhijin (Figure 3a–c) were analyzed instead of whole-rock samples. Mineral trace element geochemistry of the Zhijin REE-bearing phosphorite suggests that the REE contents in both collophanite and bioclastics are high and are closely related to the collophanite content. Probably because of the limited number of samples, pure cellophane samples were not found, and 1#, 2#, and 3# bioclastic samples were selected under heavy fraction lens (Table 1 and Figure 6).
REE content of fossil and phosphorite in REE-bearing phosphorus rocks in Xinhua, Zhijin County, Guizhou (ppm)
| Minerals | Bioclast 2# | Bioclast 3# | Dolomite | Phosphate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| La | 117.50 | 113.70 | 127.30 | 316.10 |
| Ce | 75.64 | 66.59 | 73.68 | 184.35 |
| Pr | 17.93 | 18.32 | 20.64 | 51.84 |
| Nd | 78.60 | 80.23 | 90.93 | 25.96 |
| Sm | 13.86 | 13.95 | 15.77 | 39.72 |
| Eu | 3.21 | 3.26 | 3.60 | 8.83 |
| Gd | 16.50 | 16.50 | 18.40 | 46.50 |
| Tb | 2.31 | 2.36 | 2.57 | 6.46 |
| Dy | 14.31 | 14.75 | 16.30 | 8.69 |
| Ho | 3.08 | 2.97 | 3.51 | 8.21 |
| Er | 8.48 | 8.17 | 9.55 | 21.80 |
| Tm | 8.48 | 8.17 | 9.55 | 21.80 |
| Yb | 1.02 | 0.99 | 1.16 | 2.46 |
| Lu | 5.29 | 4.99 | 6.26 | 12.46 |
| Y | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.76 | 1.57 |
| ∑REE | 543.74 | 524.07 | 587.72 | 1431.50 |
Note: Individual minerals were analyzed with ICP–MS at the Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences [4].

Photos of (from left to right) Nos. 1, 2, and 3 bioclastic samples.
Sample preparation: The bioclastic samples were first grinded to 400 mesh and then spread uniformly on a 20 cm adhesive tape (1–2 cm wide). The thickness was adjusted by folding the adhesive tape.
In this study, standard samples were analytical reagents from the Beijing Fangzheng Rare Earth Science and Technology and the content of Y2O3 is 100%. Results of the measured elements were compared with the standard sample data.
2.2 Synchrotron radiation XAFS experiment
The experiment was conducted at the Laboratory of Biomacromolecules (1W1B) of Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility, with 2.5-GeV electron storage ring and 150 mA current. Exit-fixed Si (111) double-crystal monochromator was adopted. K-absorption edge (17,038 eV) of Y in Y-bearing minerals was analyzed by using the fluorescence XAFS analysis. Pure Ar gas was used as the absorbing gas in the pre- and post-ionization chambers and Lytle ionization chamber. The fluorescence XAFS technique is highly sensitive and can measure trace element contents down to ppm, Zhang and Chen concluded that the La and Y contents account for about 1–5% (qualitative analysis) of individual mineral dolomite, as determined by SEM analysis of the REE-bearing Zhijin phosphate ores [18 19,20,21,22]. Thus, the REE requirements of fluorescence XAFS experiment can be met in our phosphate ores.
For the fluorescence extended XAFS analysis, the elemental compositions of the standard (REE oxides) were compared with those of the samples. The fluorescence XAFS data were processed with the Athena software to generate the X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) spectra. The spectra were compared with those of the standard, and the structural characteristics of the REE materials were obtained. After processing the XANES spectra with the Athena software (via first derivative), the REE valence features were obtained. Afterward, analysis of the form of REEs was conducted on the XANES spectra, which yielded partial REE structural features of the samples.
Since 1993, various reports were made on the XAFS and XANES spectra [29,30,31,32,33,34], which emphasized the application of XAFS and XANES spectra in mineralogy, petrology, and metallogeny. Besides, Peng et al. (1999) also investigated the geochemical application of synchrotron radiation X-ray absorption spectra. These authors considered that for the type of trace REE compositions in minerals, the valence state, the coordination position, and the bond features are critical but also very hard to constrain (e.g., Au, Ag, As, and P occurrence). This issue, nonetheless, can be resolved with synchrotron radiation X-ray absorption spectra. Amhed and Thomas conducted synchrotron radiation X-ray absorption spectral analysis on the CeO2 structure features and yielded values for parameters such as the Ce–O bond length [35]. Similar XANES analysis was conducted on the As occurrence in the tailing of a particular mine, and showed the three As valence states [33,36]. Meanwhile, Manceau et al. conducted synchrotron radiation XAFS on the REE occurrence in manganese nodules and suggested that the Ce occurs as Ce(iv) instead of Ce(iii) [37].
All in all, previous synchrotron radiation XANES studies have yielded certain achievements, suggesting that this technique can differentiate and quantitatively analyze the mineral trace REE composition types, valence state, coordination position, and bonding features. This can be used to investigate the REY occurrence in the Zhijin REE-bearing P ores.
XAFS experimental principle, shown in Figure 7, I 0 is the incident X-ray intensity, X-ray permeates the front detector to the sample of thickness d. The detector D f and the sample is set at 45°, fluorescence signal is received with uniform thick sample (u T d < 1), the fluorescence intensity can be expressed as
(Note: w fA = fluorescence yield, Ω = stereoscopic acceptance angle of fluorescent detector (D f ), E = energy of the incident X-ray, E f = energy of the fluorescent X-ray, u A (E) = absorption coefficient of the element A to be measured, u B (E) = absorption coefficient of all the other atoms in the sample and the absorbed atoms, μ T(E f ) = total absorption coefficient at the fluorescence energy).

Schematic diagram of the fluorescence method.
The signal contains not only the XAFS signal of the structural information of the measured elements, but also the fluorescence spectra of the other elements in the sample and the background signal scattered by the elastic and inelastic X-rays. However, the background signal and the fluorescence spectrum were separated on the energy axis. During the incident light scanning, the fluorescence energy spectrum is constant and the intensity changes with the incident light energy to form a scattered peak. The scattered peak shifts to the high-energy end with increasing incident light energy. Fluorescence detection mode inhibits the background signal and increases the ratio of the measured element fluorescence signal, to obtain the absorption spectrum of the structural information of the measured elements in the sample.
3 Results
Owing to the low Y content of the samples (below 1,000 ppm), only the XANES data were obtained by the fluorescence analysis. Compared with standard Y2O3 oxides, the first peak value is offset from the main peak, indicating that the structural form of REYs in the samples differs from that of the standard (Figure 8). The second peak value shows that the corresponding peak values of the Y2O3 in these three samples are clearly lower than those of the standard. Although the Y2O3 peak value in No. 1 sample is closest to that of the standard, the spectral lines disappear gradually and are jagged. The corresponding spectra of Y2O3 in No. 2 sample are more distinct but jagged, implying that both Nos. 1 and 2 samples contain impurities. The spectral lines of No. 3 sample are close to those of the standard and are smooth and show strong extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) signals. This indicates that the sample is relatively pure.

Y-K-edge XANES spectra.
Figure 9 illustrates the EXAFS results of No. 3 bioclastic sample, and shows that the Y valence in the samples do not change much and is similar to that of the standard. This indicates that the Y in our samples occurs as Y(iii).

EXAFS plot (a and b).
In Figure 8, it is shown that the local structure of Y in the samples is quite different from the Y2O3 form in the standard. The Y in the samples is in a complex coordination environment without such Y–O–Y bonding, and the Y–O bond length is slightly shorter with a wider distribution, which indicates that the internal local environment of Y in the samples is markedly different from that of Y2O3 in the standard, and its coordination environment of the former is more complex. There are several Y–O bonds with various lengths close to 2.1 A, and the peak corresponding to the Y–O–Y bond length position disappears. This indicates that the ambient local environment of Y in the samples is clearly different from that of Y2O3 in the standard, and that no similar long-order range of crystals is present. This is consistent with the XANES results, which demonstrates that the REYs in the Zhijin REE-bearing phosphate ores do not occur in an inorganic form.
4 Discussion
We have used XRD, SEM, phase analysis, and other means to search the local environment of Y in phosphate ore, during my master’s degree study with my teacher, Professor Zhang Jie, but did not get the expected results. Therefore, this study adopts XAFS innovative experiment for quantitative research and finds some differences with previous research results. The results show that the local form of Y was different from the Y2O3 form in complex coordination environment and that Y–O–Y bonding is absent. Besides, the Y–O bond length has no obvious change but has a wide distribution, which indicates that Y in the samples is surrounded by organic or macromolecular compounds instead of inorganic materials. Thus, the organic extraction can be an effective method in the separation and extraction of the REY resource in the Zhijin REE-bearing phosphate ores.
Our results on the REY occurrence in phosphorites differ from those reported by previous studies, in that the REEs exist in collophanite in the form of isomorphism. However, it does not preclude the other forms of REE occurrences as proposed in previous studies.
5 Conclusion
The results show that the valence of Y in the samples was 3+, and the local form of Y is different from the Y2O3 form in standard xenotime. Yttrium in the samples is in a complex coordination environment without Y–O–Y bonding, and the Y–O bond length has no obvious change but a disperse distribution. It is indicated that Y in the samples is surrounded by organic or macromolecular compounds, but not by inorganic materials. Through microscopic investigation of Y (occurrence, valence state, and local environment) in P ore minerals, it is found that organic extraction is more effective for REEs in the Zhijin REE-bearing phosphate deposit. Shortfalls of this work are the limitation of the sample separation conditions. This early-stage experiment has only picked bioclastic samples, and the REY-related dolomite and collophane single-mineral samples are yet to be separated or analyzed.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Professor Zheng Lirong from the Beijing Electron Positron Collider National Laboratory (Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for helping with the experiment.
-
Funding information: The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41862002).
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Emsbo P, Mclaughlin PI, Breit GN. Rare earth elements in sedimentary phosphate deposits: solution to the global REE crisis? Gondwana Res. 2015;27(2):776–85.10.1016/j.gr.2014.10.008Search in Google Scholar
[2] Hein JR, Koschinsky A, Mikesell M, Mizell K, Glenn CR, Wood R. Marine phosphorites as potential resources for heavy rare earth elements and Yttrium. Minerals. 2016;88(6):1–22.10.3390/min6030088Search in Google Scholar
[3] Huan C, Shuhai X, Chuanming Z, Yongbo P. Phosphogenesis associated with the Shuram excursion: petrographic and geochemical observations from the Ediacaran Doushantuo formation of South China. Sediment Geol. 2016;341(1):134–46.10.1016/j.sedgeo.2016.05.008Search in Google Scholar
[4] Chen JY, Yang RD. Analysis on REE geochemical characteristics of three types of REE-rich soil in Guizhou Province, China. J Rare Earths. 2010;28:517–22.10.1016/S1002-0721(10)60271-2Search in Google Scholar
[5] Mao T, Yang RD, Mao JR. Research on carbon and oxygen isotopes in phosphorus-bearing rock series of the late Neoproterozoic-early Cambrian Taozichong formation in Qingzhen City, Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Chin J Geochem. 2014;33(4):439–49.10.1007/s11631-014-0710-2Search in Google Scholar
[6] Chen JY, Yang RD, Wei HR, Gao JB. Rare earth element geochemistry of Cambrian phosphorites from the Yangtze region. J Rare Earths. 2013;31:101–10.10.1016/S1002-0721(12)60242-7Search in Google Scholar
[7] Yang BQ, Zhang XP. Analysis of global rare earth production and consumption structure. Chin Rare Earths. 2014;35(1):110–8.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Xiao CY, Zhang ZW, He CZ. The depositional environment of Ediacaran phosphorite deposits, South China. Bull Mineral Petrol Geochem. 2018;37(1):121–37.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Shi CH. Formation of phosphorite deposit, breakup of Rodinia supercontinent and biological explosion. Guiyang: Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences; 2005. p. 25–6.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Yang WD, Qi L. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of rare earth elements in early Cambrian phosphorite series in eastern Yunnan. Bull Mineral Petrol Geochem. 1995;14(4):224–7.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Xie H, Zhu LJ. The modes of occurrence of rare earth element in phosphorite of Meishucun stage of Cambrian in Guizhou. China Min Mag. 2012;21:65–70.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Luo DK. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of Jingxiang phosphorite deposit in Hubei Province. Beijing: China University of Geosciences; 2011. p. 39–9.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Zhang YB, Gong ML, Li H. The modes of occurrence of rare earth elements in phosphorite of Meishucun stage of Cambrian in Guizhou. J Earth Sci Environ. 2007;29:362–8.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Liu XQ, Zhang H, Tang Y, Liu YL. REE geochemical characteristic of apatite: implications for ore genesis of the Zhijin phosphorite. Minerals. 2020;1012(10):3–22.10.3390/min10111012Search in Google Scholar
[15] Han YC, Xia XH, Xiao RG, Wei XS. Phosphorus deposits in China. Beijing: Geological Publishing House; 2012. p. 410–513.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Neary CR, Highly DE. Chapter 12 – The Economic Importance of the Rare Earth Elements. In: Henderson PBT, editor. Developments in Geochemistry. Elsevier; 1984. p. 423–66.10.1016/B978-0-444-42148-7.50017-4Search in Google Scholar
[17] Kazutaka Y, Hanjie L, Koichiro F, Shiki M, Satoru H. Geochemistry and mineralogy of REY-rich mud in the eastern Indian Ocean. J Asian Earth Sci. 2014;93:25–36.10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.005Search in Google Scholar
[18] Zhang J, Chen DL. Scanning electron microscope study of the ore-bearing REE in Xinhua phosphorite, Zhijin, Guizhou. J Mineral Petrol. 2000;20:59–64.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Zhang J, Zhang Q, Chen DL. REE geochemistry of the ore-bearing REE in Xinhua phosphorite, Zhijin, Guizhou. J Mineral Petrol. 2003;23:35–8.Search in Google Scholar
[20] Zhang J, Shun CM, Yang GF, Xie F. Separation and enrichment of rare earth elements in phosphorite in Xinhua, Zhijin, Guizhou. J Rare Earths. 2006;24:413–8.10.1016/S1002-0721(07)60415-3Search in Google Scholar
[21] Zhang J, Sun CM, Gong ML, Zhang T, Chen DL, Chen JY. Geochemical characteristics and occurrence states of the REE elements of the phosphorite in Xinhua, Zhijin, Guizhou. Chin Rare Earths. 2007;28:75–9.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Zhang J, Zhang T, Chen JY. Rare earth elements geochemical characteristics of early phosphorite in Cambrian, Guizhou. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press; 2008. p. 1–117.Search in Google Scholar
[23] Duan KB, Wang DH, Xiong XX. A review of a preliminary quantitative study and genetic analysis for rare earth elements of ionic adsorption state in phosphate ore deposit in Zhijin, Guizhou Province. Rock Miner Anal. 2014;28:517–22.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Zhang J, Ni Y, Liang JT. Characteristics of mineralogical technology about medium-low grade bio-chip containing the rare earth dolomitic phosphorite in Xinhua, Zhijin, Guizhou. J Rare Earths. 2010;28:525–7.10.1016/S1002-0721(10)60333-XSearch in Google Scholar
[25] Zhang YB, Zhang BY, Yang SQ, Zhong ZG, Zhou HP, Luo XP. Enhancing the leaching effect of an ion-absorbed rare earth ore by ameliorating the seepage effect with sodium dodecyl sulfate surfactant. Int J Min Sci Technol. 2021;31(6):995–1002.10.1016/j.ijmst.2021.06.002Search in Google Scholar
[26] Chelgani SC, Rudolph M, Leistner T, Gutzmer J, Peuker UA. A review of rare earth minerals flotation: Monazite and xenotime. Int J Min Sci Technol. 2015;25(6):877–83.10.1016/j.ijmst.2015.09.002Search in Google Scholar
[27] Moldoveanu AG, Vladimiros GP. Recovery of rare earth elements adsorbed on clay minerals: II. Leaching with ammonium sulfate. Hydrometallurgy. 2013;131–132:158–66.10.1016/j.hydromet.2012.10.011Search in Google Scholar
[28] Liu SR, Hu RZ, Zhou GF, Gong GH, Jin ZS, Zheng WQ. Study on the mineral composition of the clastic phosphate in Zhijin phosphate deposits, China. Acta Mineralogica Sin. 2008;28:244–50.Search in Google Scholar
[29] Hu TD, Xie AL, Huang DX. Application of XAFSin mineralogy. New research on mineral physics and mineral materials. Beijing: Seismological Press; 1993. p. 16–7.Search in Google Scholar
[30] Peng MN, Li DN. K-edge XANES study on Si and Al from silicate minerals. Guangzhou: Sun Yat-Sen University Press; 1995. p. 6–8.Search in Google Scholar
[31] Peng MN, Li DN, Lin B, Liang JL. Synchrotron radiation X-ray absorption spectra and its application in mineralogy and geochemistry. Bull Mineral Petrol Geochem. 1999;18(1):33–7.Search in Google Scholar
[32] Li DN, Peng MN. K-edge XANES study in silicate glass. Synchrotron radiation technique and application. Beijing: Sciences Press; 1996. p. 122–5.Search in Google Scholar
[33] Li DN, Peng MN. K-edge XANES study on Al from Al2SiO5 polytype minerals. Bull Mineral Petrol Geochem. 1997;16:97–8.Search in Google Scholar
[34] Chu BB, Luo LQ, Xu T. XANES study of lead speciation in Duckweed. Spectrosc Spectr Anal. 2012;32(7):1975–8.Search in Google Scholar
[35] Amhed M, Thomas P. Cerium LIII EXAFS investigation structure of crystallization and amorphous cerium oxides. Fuel Chem. 2004;49(2):759–61.Search in Google Scholar
[36] Zhu XY, Wang RC, Lu XC, Huang SY. Occurrence of arsenic in shallow shale sulfide ore tailings of Yangshan, Tongling, Anhui Province. Acta Petrolog et Mineralog. 2013;32(6):918–24.Search in Google Scholar
[37] Manceau A, Lanson M, Takahashi Y. Mineralogy and crystal chemistry of Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu in a deep-sea Pacific polymetallic nodule. Am Mineralogist. 2014;99:2068–83.10.2138/am-2014-4742Search in Google Scholar
© 2022 Jiyan Chen et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Study on observation system of seismic forward prospecting in tunnel: A case on tailrace tunnel of Wudongde hydropower station
- The behaviour of stress variation in sandy soil
- Research on the current situation of rural tourism in southern Fujian in China after the COVID-19 epidemic
- Late Triassic–Early Jurassic paleogeomorphic characteristics and hydrocarbon potential of the Ordos Basin, China, a case of study of the Jiyuan area
- Application of X-ray fluorescence mapping in turbiditic sandstones, Huai Bo Khong Formation of Nam Pat Group, Thailand
- Fractal expression of soil particle-size distribution at the basin scale
- Study on the changes in vegetation structural coverage and its response mechanism to hydrology
- Spatial distribution analysis of seismic activity based on GMI, LMI, and LISA in China
- Rock mass structural surface trace extraction based on transfer learning
- Hydrochemical characteristics and D–O–Sr isotopes of groundwater and surface water in the northern Longzi county of southern Tibet (southwestern China)
- Insights into origins of the natural gas in the Lower Paleozoic of Ordos basin, China
- Research on comprehensive benefits and reasonable selection of marine resources development types
- Embedded deformation of the rubble-mound foundation of gravity-type quay walls and influence factors
- Activation of Ad Damm shear zone, western Saudi Arabian margin, and its relation to the Red Sea rift system
- A mathematical conjecture associates Martian TARs with sand ripples
- Study on spatio-temporal characteristics of earthquakes in southwest China based on z-value
- Sedimentary facies characterization of forced regression in the Pearl River Mouth basin
- High-precision remote sensing mapping of aeolian sand landforms based on deep learning algorithms
- Experimental study on reservoir characteristics and oil-bearing properties of Chang 7 lacustrine oil shale in Yan’an area, China
- Estimating the volume of the 1978 Rissa quick clay landslide in Central Norway using historical aerial imagery
- Spatial accessibility between commercial and ecological spaces: A case study in Beijing, China
- Curve number estimation using rainfall and runoff data from five catchments in Sudan
- Urban green service equity in Xiamen based on network analysis and concentration degree of resources
- Spatio-temporal analysis of East Asian seismic zones based on multifractal theory
- Delineation of structural lineaments of Southeast Nigeria using high resolution aeromagnetic data
- 3D marine controlled-source electromagnetic modeling using an edge-based finite element method with a block Krylov iterative solver
- A comprehensive evaluation method for topographic correction model of remote sensing image based on entropy weight method
- Quantitative discrimination of the influences of climate change and human activity on rocky desertification based on a novel feature space model
- Assessment of climatic conditions for tourism in Xinjiang, China
- Attractiveness index of national marine parks: A study on national marine parks in coastal areas of East China Sea
- Effect of brackish water irrigation on the movement of water and salt in salinized soil
- Mapping paddy rice and rice phenology with Sentinel-1 SAR time series using a unified dynamic programming framework
- Analyzing the characteristics of land use distribution in typical village transects at Chinese Loess Plateau based on topographical factors
- Management status and policy direction of submerged marine debris for improvement of port environment in Korea
- Influence of Three Gorges Dam on earthquakes based on GRACE gravity field
- Comparative study of estimating the Curie point depth and heat flow using potential magnetic data
- The spatial prediction and optimization of production-living-ecological space based on Markov–PLUS model: A case study of Yunnan Province
- Major, trace and platinum-group element geochemistry of harzburgites and chromitites from Fuchuan, China, and its geological significance
- Vertical distribution of STN and STP in watershed of loess hilly region
- Hyperspectral denoising based on the principal component low-rank tensor decomposition
- Evaluation of fractures using conventional and FMI logs, and 3D seismic interpretation in continental tight sandstone reservoir
- U–Pb zircon dating of the Paleoproterozoic khondalite series in the northeastern Helanshan region and its geological significance
- Quantitatively determine the dominant driving factors of the spatial-temporal changes of vegetation-impacts of global change and human activity
- Can cultural tourism resources become a development feature helping rural areas to revitalize the local economy under the epidemic? An exploration of the perspective of attractiveness, satisfaction, and willingness by the revisit of Hakka cultural tourism
- A 3D empirical model of standard compaction curve for Thailand shales: Porosity in function of burial depth and geological time
- Attribution identification of terrestrial ecosystem evolution in the Yellow River Basin
- An intelligent approach for reservoir quality evaluation in tight sandstone reservoir using gradient boosting decision tree algorithm
- Detection of sub-surface fractures based on filtering, modeling, and interpreting aeromagnetic data in the Deng Deng – Garga Sarali area, Eastern Cameroon
- Influence of heterogeneity on fluid property variations in carbonate reservoirs with multistage hydrocarbon accumulation: A case study of the Khasib formation, Cretaceous, AB oilfield, southern Iraq
- Designing teaching materials with disaster maps and evaluating its effectiveness for primary students
- Assessment of the bender element sensors to measure seismic wave velocity of soils in the physical model
- Appropriated protection time and region for Qinghai–Tibet Plateau grassland
- Identification of high-temperature targets in remote sensing based on correspondence analysis
- Influence of differential diagenesis on pore evolution of the sandy conglomerate reservoir in different structural units: A case study of the Upper Permian Wutonggou Formation in eastern Junggar Basin, NW China
- Planting in ecologically solidified soil and its use
- National and regional-scale landslide indicators and indexes: Applications in Italy
- Occurrence of yttrium in the Zhijin phosphorus deposit in Guizhou Province, China
- The response of Chudao’s beach to typhoon “Lekima” (No. 1909)
- Soil wind erosion resistance analysis for soft rock and sand compound soil: A case study for the Mu Us Sandy Land, China
- Investigation into the pore structures and CH4 adsorption capacities of clay minerals in coal reservoirs in the Yangquan Mining District, North China
- Overview of eco-environmental impact of Xiaolangdi Water Conservancy Hub on the Yellow River
- Response of extreme precipitation to climatic warming in the Weihe river basin, China and its mechanism
- Analysis of land use change on urban landscape patterns in Northwest China: A case study of Xi’an city
- Optimization of interpolation parameters based on statistical experiment
- Late Cretaceous adakitic intrusive rocks in the Laimailang area, Gangdese batholith: Implications for the Neo-Tethyan Ocean subduction
- Tectonic evolution of the Eocene–Oligocene Lushi Basin in the eastern Qinling belt, Central China: Insights from paleomagnetic constraints
- Geographic and cartographic inconsistency factors among different cropland classification datasets: A field validation case in Cambodia
- Distribution of large- and medium-scale loess landslides induced by the Haiyuan Earthquake in 1920 based on field investigation and interpretation of satellite images
- Numerical simulation of impact and entrainment behaviors of debris flow by using SPH–DEM–FEM coupling method
- Study on the evaluation method and application of logging irreducible water saturation in tight sandstone reservoirs
- Geochemical characteristics and genesis of natural gas in the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the Sichuan Basin
- Wehrlite xenoliths and petrogenetic implications, Hosséré Do Guessa volcano, Adamawa plateau, Cameroon
- Changes in landscape pattern and ecological service value as land use evolves in the Manas River Basin
- Spatial structure-preserving and conflict-avoiding methods for point settlement selection
- Fission characteristics of heavy metal intrusion into rocks based on hydrolysis
- Sequence stratigraphic filling model of the Cretaceous in the western Tabei Uplift, Tarim Basin, NW China
- Fractal analysis of structural characteristics and prospecting of the Luanchuan polymetallic mining district, China
- Spatial and temporal variations of vegetation coverage and their driving factors following gully control and land consolidation in Loess Plateau, China
- Assessing the tourist potential of cultural–historical spatial units of Serbia using comparative application of AHP and mathematical method
- Urban black and odorous water body mapping from Gaofen-2 images
- Geochronology and geochemistry of Early Cretaceous granitic plutons in northern Great Xing’an Range, NE China, and implications for geodynamic setting
- Spatial planning concept for flood prevention in the Kedurus River watershed
- Geophysical exploration and geological appraisal of the Siah Diq porphyry Cu–Au prospect: A recent discovery in the Chagai volcano magmatic arc, SW Pakistan
- Possibility of using the DInSAR method in the development of vertical crustal movements with Sentinel-1 data
- Using modified inverse distance weight and principal component analysis for spatial interpolation of foundation settlement based on geodetic observations
- Geochemical properties and heavy metal contents of carbonaceous rocks in the Pliocene siliciclastic rock sequence from southeastern Denizli-Turkey
- Study on water regime assessment and prediction of stream flow based on an improved RVA
- A new method to explore the abnormal space of urban hidden dangers under epidemic outbreak and its prevention and control: A case study of Jinan City
- Milankovitch cycles and the astronomical time scale of the Zhujiang Formation in the Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China
- Shear strength and meso-pore characteristic of saturated compacted loess
- Key point extraction method for spatial objects in high-resolution remote sensing images based on multi-hot cross-entropy loss
- Identifying driving factors of the runoff coefficient based on the geographic detector model in the upper reaches of Huaihe River Basin
- Study on rainfall early warning model for Xiangmi Lake slope based on unsaturated soil mechanics
- Extraction of mineralized indicator minerals using ensemble learning model optimized by SSA based on hyperspectral image
- Lithofacies discrimination using seismic anisotropic attributes from logging data in Muglad Basin, South Sudan
- Three-dimensional modeling of loose layers based on stratum development law
- Occurrence, sources, and potential risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in southern Xinjiang, China
- Attribution analysis of different driving forces on vegetation and streamflow variation in the Jialing River Basin, China
- Slope characteristics of urban construction land and its correlation with ground slope in China
- Limitations of the Yang’s breaking wave force formula and its improvement under a wider range of breaker conditions
- The spatial-temporal pattern evolution and influencing factors of county-scale tourism efficiency in Xinjiang, China
- Evaluation and analysis of observed soil temperature data over Northwest China
- Agriculture and aquaculture land-use change prediction in five central coastal provinces of Vietnam using ANN, SVR, and SARIMA models
- Leaf color attributes of urban colored-leaf plants
- Application of statistical and machine learning techniques for landslide susceptibility mapping in the Himalayan road corridors
- Sediment provenance in the Northern South China Sea since the Late Miocene
- Drones applications for smart cities: Monitoring palm trees and street lights
- Double rupture event in the Tianshan Mountains: A case study of the 2021 Mw 5.3 Baicheng earthquake, NW China
- Review Article
- Mobile phone indoor scene features recognition localization method based on semantic constraint of building map location anchor
- Technical Note
- Experimental analysis on creep mechanics of unsaturated soil based on empirical model
- Rapid Communications
- A protocol for canopy cover monitoring on forest restoration projects using low-cost drones
- Landscape tree species recognition using RedEdge-MX: Suitability analysis of two different texture extraction forms under MLC and RF supervision
- Special Issue: Geoethics 2022 - Part I
- Geomorphological and hydrological heritage of Mt. Stara Planina in SE Serbia: From river protection initiative to potential geotouristic destination
- Geotourism and geoethics as support for rural development in the Knjaževac municipality, Serbia
- Modeling spa destination choice for leveraging hydrogeothermal potentials in Serbia
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Study on observation system of seismic forward prospecting in tunnel: A case on tailrace tunnel of Wudongde hydropower station
- The behaviour of stress variation in sandy soil
- Research on the current situation of rural tourism in southern Fujian in China after the COVID-19 epidemic
- Late Triassic–Early Jurassic paleogeomorphic characteristics and hydrocarbon potential of the Ordos Basin, China, a case of study of the Jiyuan area
- Application of X-ray fluorescence mapping in turbiditic sandstones, Huai Bo Khong Formation of Nam Pat Group, Thailand
- Fractal expression of soil particle-size distribution at the basin scale
- Study on the changes in vegetation structural coverage and its response mechanism to hydrology
- Spatial distribution analysis of seismic activity based on GMI, LMI, and LISA in China
- Rock mass structural surface trace extraction based on transfer learning
- Hydrochemical characteristics and D–O–Sr isotopes of groundwater and surface water in the northern Longzi county of southern Tibet (southwestern China)
- Insights into origins of the natural gas in the Lower Paleozoic of Ordos basin, China
- Research on comprehensive benefits and reasonable selection of marine resources development types
- Embedded deformation of the rubble-mound foundation of gravity-type quay walls and influence factors
- Activation of Ad Damm shear zone, western Saudi Arabian margin, and its relation to the Red Sea rift system
- A mathematical conjecture associates Martian TARs with sand ripples
- Study on spatio-temporal characteristics of earthquakes in southwest China based on z-value
- Sedimentary facies characterization of forced regression in the Pearl River Mouth basin
- High-precision remote sensing mapping of aeolian sand landforms based on deep learning algorithms
- Experimental study on reservoir characteristics and oil-bearing properties of Chang 7 lacustrine oil shale in Yan’an area, China
- Estimating the volume of the 1978 Rissa quick clay landslide in Central Norway using historical aerial imagery
- Spatial accessibility between commercial and ecological spaces: A case study in Beijing, China
- Curve number estimation using rainfall and runoff data from five catchments in Sudan
- Urban green service equity in Xiamen based on network analysis and concentration degree of resources
- Spatio-temporal analysis of East Asian seismic zones based on multifractal theory
- Delineation of structural lineaments of Southeast Nigeria using high resolution aeromagnetic data
- 3D marine controlled-source electromagnetic modeling using an edge-based finite element method with a block Krylov iterative solver
- A comprehensive evaluation method for topographic correction model of remote sensing image based on entropy weight method
- Quantitative discrimination of the influences of climate change and human activity on rocky desertification based on a novel feature space model
- Assessment of climatic conditions for tourism in Xinjiang, China
- Attractiveness index of national marine parks: A study on national marine parks in coastal areas of East China Sea
- Effect of brackish water irrigation on the movement of water and salt in salinized soil
- Mapping paddy rice and rice phenology with Sentinel-1 SAR time series using a unified dynamic programming framework
- Analyzing the characteristics of land use distribution in typical village transects at Chinese Loess Plateau based on topographical factors
- Management status and policy direction of submerged marine debris for improvement of port environment in Korea
- Influence of Three Gorges Dam on earthquakes based on GRACE gravity field
- Comparative study of estimating the Curie point depth and heat flow using potential magnetic data
- The spatial prediction and optimization of production-living-ecological space based on Markov–PLUS model: A case study of Yunnan Province
- Major, trace and platinum-group element geochemistry of harzburgites and chromitites from Fuchuan, China, and its geological significance
- Vertical distribution of STN and STP in watershed of loess hilly region
- Hyperspectral denoising based on the principal component low-rank tensor decomposition
- Evaluation of fractures using conventional and FMI logs, and 3D seismic interpretation in continental tight sandstone reservoir
- U–Pb zircon dating of the Paleoproterozoic khondalite series in the northeastern Helanshan region and its geological significance
- Quantitatively determine the dominant driving factors of the spatial-temporal changes of vegetation-impacts of global change and human activity
- Can cultural tourism resources become a development feature helping rural areas to revitalize the local economy under the epidemic? An exploration of the perspective of attractiveness, satisfaction, and willingness by the revisit of Hakka cultural tourism
- A 3D empirical model of standard compaction curve for Thailand shales: Porosity in function of burial depth and geological time
- Attribution identification of terrestrial ecosystem evolution in the Yellow River Basin
- An intelligent approach for reservoir quality evaluation in tight sandstone reservoir using gradient boosting decision tree algorithm
- Detection of sub-surface fractures based on filtering, modeling, and interpreting aeromagnetic data in the Deng Deng – Garga Sarali area, Eastern Cameroon
- Influence of heterogeneity on fluid property variations in carbonate reservoirs with multistage hydrocarbon accumulation: A case study of the Khasib formation, Cretaceous, AB oilfield, southern Iraq
- Designing teaching materials with disaster maps and evaluating its effectiveness for primary students
- Assessment of the bender element sensors to measure seismic wave velocity of soils in the physical model
- Appropriated protection time and region for Qinghai–Tibet Plateau grassland
- Identification of high-temperature targets in remote sensing based on correspondence analysis
- Influence of differential diagenesis on pore evolution of the sandy conglomerate reservoir in different structural units: A case study of the Upper Permian Wutonggou Formation in eastern Junggar Basin, NW China
- Planting in ecologically solidified soil and its use
- National and regional-scale landslide indicators and indexes: Applications in Italy
- Occurrence of yttrium in the Zhijin phosphorus deposit in Guizhou Province, China
- The response of Chudao’s beach to typhoon “Lekima” (No. 1909)
- Soil wind erosion resistance analysis for soft rock and sand compound soil: A case study for the Mu Us Sandy Land, China
- Investigation into the pore structures and CH4 adsorption capacities of clay minerals in coal reservoirs in the Yangquan Mining District, North China
- Overview of eco-environmental impact of Xiaolangdi Water Conservancy Hub on the Yellow River
- Response of extreme precipitation to climatic warming in the Weihe river basin, China and its mechanism
- Analysis of land use change on urban landscape patterns in Northwest China: A case study of Xi’an city
- Optimization of interpolation parameters based on statistical experiment
- Late Cretaceous adakitic intrusive rocks in the Laimailang area, Gangdese batholith: Implications for the Neo-Tethyan Ocean subduction
- Tectonic evolution of the Eocene–Oligocene Lushi Basin in the eastern Qinling belt, Central China: Insights from paleomagnetic constraints
- Geographic and cartographic inconsistency factors among different cropland classification datasets: A field validation case in Cambodia
- Distribution of large- and medium-scale loess landslides induced by the Haiyuan Earthquake in 1920 based on field investigation and interpretation of satellite images
- Numerical simulation of impact and entrainment behaviors of debris flow by using SPH–DEM–FEM coupling method
- Study on the evaluation method and application of logging irreducible water saturation in tight sandstone reservoirs
- Geochemical characteristics and genesis of natural gas in the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the Sichuan Basin
- Wehrlite xenoliths and petrogenetic implications, Hosséré Do Guessa volcano, Adamawa plateau, Cameroon
- Changes in landscape pattern and ecological service value as land use evolves in the Manas River Basin
- Spatial structure-preserving and conflict-avoiding methods for point settlement selection
- Fission characteristics of heavy metal intrusion into rocks based on hydrolysis
- Sequence stratigraphic filling model of the Cretaceous in the western Tabei Uplift, Tarim Basin, NW China
- Fractal analysis of structural characteristics and prospecting of the Luanchuan polymetallic mining district, China
- Spatial and temporal variations of vegetation coverage and their driving factors following gully control and land consolidation in Loess Plateau, China
- Assessing the tourist potential of cultural–historical spatial units of Serbia using comparative application of AHP and mathematical method
- Urban black and odorous water body mapping from Gaofen-2 images
- Geochronology and geochemistry of Early Cretaceous granitic plutons in northern Great Xing’an Range, NE China, and implications for geodynamic setting
- Spatial planning concept for flood prevention in the Kedurus River watershed
- Geophysical exploration and geological appraisal of the Siah Diq porphyry Cu–Au prospect: A recent discovery in the Chagai volcano magmatic arc, SW Pakistan
- Possibility of using the DInSAR method in the development of vertical crustal movements with Sentinel-1 data
- Using modified inverse distance weight and principal component analysis for spatial interpolation of foundation settlement based on geodetic observations
- Geochemical properties and heavy metal contents of carbonaceous rocks in the Pliocene siliciclastic rock sequence from southeastern Denizli-Turkey
- Study on water regime assessment and prediction of stream flow based on an improved RVA
- A new method to explore the abnormal space of urban hidden dangers under epidemic outbreak and its prevention and control: A case study of Jinan City
- Milankovitch cycles and the astronomical time scale of the Zhujiang Formation in the Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China
- Shear strength and meso-pore characteristic of saturated compacted loess
- Key point extraction method for spatial objects in high-resolution remote sensing images based on multi-hot cross-entropy loss
- Identifying driving factors of the runoff coefficient based on the geographic detector model in the upper reaches of Huaihe River Basin
- Study on rainfall early warning model for Xiangmi Lake slope based on unsaturated soil mechanics
- Extraction of mineralized indicator minerals using ensemble learning model optimized by SSA based on hyperspectral image
- Lithofacies discrimination using seismic anisotropic attributes from logging data in Muglad Basin, South Sudan
- Three-dimensional modeling of loose layers based on stratum development law
- Occurrence, sources, and potential risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in southern Xinjiang, China
- Attribution analysis of different driving forces on vegetation and streamflow variation in the Jialing River Basin, China
- Slope characteristics of urban construction land and its correlation with ground slope in China
- Limitations of the Yang’s breaking wave force formula and its improvement under a wider range of breaker conditions
- The spatial-temporal pattern evolution and influencing factors of county-scale tourism efficiency in Xinjiang, China
- Evaluation and analysis of observed soil temperature data over Northwest China
- Agriculture and aquaculture land-use change prediction in five central coastal provinces of Vietnam using ANN, SVR, and SARIMA models
- Leaf color attributes of urban colored-leaf plants
- Application of statistical and machine learning techniques for landslide susceptibility mapping in the Himalayan road corridors
- Sediment provenance in the Northern South China Sea since the Late Miocene
- Drones applications for smart cities: Monitoring palm trees and street lights
- Double rupture event in the Tianshan Mountains: A case study of the 2021 Mw 5.3 Baicheng earthquake, NW China
- Review Article
- Mobile phone indoor scene features recognition localization method based on semantic constraint of building map location anchor
- Technical Note
- Experimental analysis on creep mechanics of unsaturated soil based on empirical model
- Rapid Communications
- A protocol for canopy cover monitoring on forest restoration projects using low-cost drones
- Landscape tree species recognition using RedEdge-MX: Suitability analysis of two different texture extraction forms under MLC and RF supervision
- Special Issue: Geoethics 2022 - Part I
- Geomorphological and hydrological heritage of Mt. Stara Planina in SE Serbia: From river protection initiative to potential geotouristic destination
- Geotourism and geoethics as support for rural development in the Knjaževac municipality, Serbia
- Modeling spa destination choice for leveraging hydrogeothermal potentials in Serbia

