Abstract
C24H20Cl2N4O2Zn, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 9.9265(6) Å, b = 15.368(1) Å, c = 16.636(1) Å, α = 102.760(1)°, β = 90.385(2)°, γ = 94.112(3)°, V = 2311.4(3) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0260, wRref(F2) = 0.0653, T = 100(2) K.
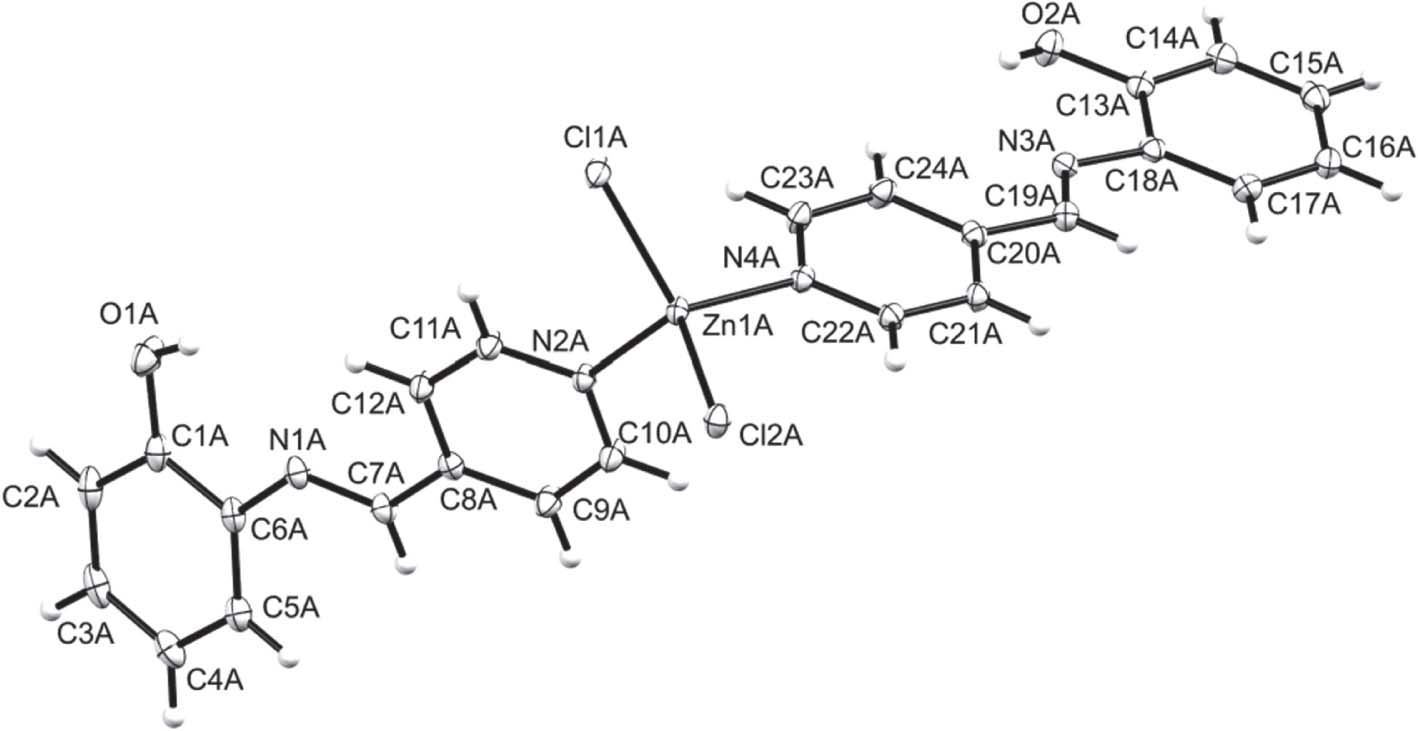
One of two crystallographically independent complexes present in the asymmetric unit of the title structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.32 × 0.24 × 0.13 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.32 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 28.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 42934, 11554, 0.022 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 9948 |
| N(param)refined: | 599 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], [4], Mercury [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn1A | 0.53123(2) | 0.50168(2) | 0.74864(2) | 0.01497(4) |
| Cl1A | 0.45239(4) | 0.39154(2) | 0.64279(2) | 0.02351(8) |
| Cl2A | 0.73240(4) | 0.48070(2) | 0.81512(2) | 0.01996(8) |
| O1A | 0.49354(14) | 0.81901(8) | 0.35948(7) | 0.0302(3) |
| H1A | 0.499361 | 0.779826 | 0.387227 | 0.045* |
| O2A | −0.32494(12) | 0.67340(8) | 0.94117(7) | 0.0234(2) |
| H2AA | −0.256651 | 0.648163 | 0.915162 | 0.035* |
| N1A | 0.61731(14) | 0.82862(8) | 0.51152(8) | 0.0188(3) |
| N2A | 0.56483(13) | 0.61225(8) | 0.69916(7) | 0.0164(2) |
| N3A | −0.07106(13) | 0.63077(8) | 0.99315(8) | 0.0171(2) |
| N4A | 0.37381(13) | 0.53458(8) | 0.83253(7) | 0.0160(2) |
| C1A | 0.57005(17) | 0.89563(11) | 0.39851(9) | 0.0223(3) |
| C2A | 0.58197(18) | 0.96709(12) | 0.35904(10) | 0.0261(4) |
| H2A | 0.535949 | 0.961743 | 0.306835 | 0.031* |
| C3A | 0.66073(18) | 1.04549(12) | 0.39602(10) | 0.0268(4) |
| H3A | 0.669072 | 1.093760 | 0.368774 | 0.032* |
| C4A | 0.72802(18) | 1.05465(11) | 0.47268(11) | 0.0267(3) |
| H4A | 0.783210 | 1.108511 | 0.497289 | 0.032* |
| C5A | 0.71398(17) | 0.98465(11) | 0.51289(10) | 0.0228(3) |
| H5A | 0.758939 | 0.991034 | 0.565532 | 0.027* |
| C6A | 0.63426(16) | 0.90468(10) | 0.47677(9) | 0.0190(3) |
| C7A | 0.62881(16) | 0.83752(10) | 0.58946(9) | 0.0178(3) |
| H7A | 0.648031 | 0.895443 | 0.623854 | 0.021* |
| C8A | 0.61255(15) | 0.75883(10) | 0.62664(9) | 0.0169(3) |
| C9A | 0.61682(18) | 0.76942(10) | 0.71207(9) | 0.0224(3) |
| H9A | 0.636919 | 0.827043 | 0.746871 | 0.027* |
| C10A | 0.59151(18) | 0.69517(10) | 0.74567(9) | 0.0223(3) |
| H10A | 0.593078 | 0.703219 | 0.803962 | 0.027* |
| C11A | 0.56507(17) | 0.60208(10) | 0.61674(9) | 0.0210(3) |
| H11A | 0.548607 | 0.543463 | 0.583267 | 0.025* |
| C12A | 0.58806(17) | 0.67262(10) | 0.57861(9) | 0.0208(3) |
| H12A | 0.587200 | 0.662495 | 0.520167 | 0.025* |
| C13A | −0.30638(16) | 0.67668(10) | 1.02341(9) | 0.0178(3) |
| C14A | −0.42056(17) | 0.69890(10) | 1.07575(10) | 0.0207(3) |
| H14A | −0.510347 | 0.710676 | 1.054344 | 0.025* |
| C15A | −0.40219(17) | 0.70370(10) | 1.15948(10) | 0.0231(3) |
| H15A | −0.479961 | 0.718605 | 1.195464 | 0.028* |
| C16A | −0.27063(17) | 0.68684(11) | 1.19116(10) | 0.0228(3) |
| H16A | −0.258339 | 0.691538 | 1.248739 | 0.027* |
| C17A | −0.15757(17) | 0.66321(10) | 1.13890(9) | 0.0210(3) |
| H17A | −0.068263 | 0.651272 | 1.160771 | 0.025* |
| C18A | −0.17425(15) | 0.65683(9) | 1.05397(9) | 0.0166(3) |
| C19A | 0.04993(16) | 0.60463(10) | 1.01075(9) | 0.0184(3) |
| H19A | 0.070786 | 0.601673 | 1.066025 | 0.022* |
| C20A | 0.15804(16) | 0.57893(10) | 0.94734(9) | 0.0168(3) |
| C21A | 0.29266(16) | 0.55769(10) | 0.97106(9) | 0.0182(3) |
| H21A | 0.312813 | 0.557966 | 1.027182 | 0.022* |
| C22A | 0.39695(16) | 0.53617(10) | 0.91255(9) | 0.0177(3) |
| H22A | 0.488413 | 0.521988 | 0.929680 | 0.021* |
| C23A | 0.24256(17) | 0.55403(11) | 0.80920(9) | 0.0207(3) |
| H23A | 0.225028 | 0.552593 | 0.752576 | 0.025* |
| C24A | 0.13278(16) | 0.57588(10) | 0.86374(9) | 0.0203(3) |
| H24A | 0.041638 | 0.588621 | 0.844836 | 0.024* |
| Zn1B | −0.09512(2) | 0.02925(2) | 0.74854(2) | 0.01920(5) |
| Cl1B | −0.03373(4) | −0.09137(2) | 0.65881(2) | 0.02339(8) |
| Cl2B | −0.30760(4) | 0.02279(3) | 0.80974(2) | 0.02481(8) |
| O1B | −0.09580(14) | 0.59846(8) | 0.69823(8) | 0.0308(3) |
| H1B | −0.114188 | 0.546258 | 0.704952 | 0.046* |
| O2B | 0.78118(13) | 0.20379(9) | 0.95782(7) | 0.0302(3) |
| H2BA | 0.713921 | 0.173824 | 0.927777 | 0.045* |
| N1B | 0.02106(14) | 0.44309(9) | 0.63420(8) | 0.0211(3) |
| N2B | −0.07254(14) | 0.13371(8) | 0.69008(8) | 0.0201(3) |
| N3B | 0.53289(14) | 0.12836(9) | 1.00096(8) | 0.0210(3) |
| N4B | 0.06352(14) | 0.06222(9) | 0.83847(8) | 0.0212(3) |
| C1B | 0.00852(18) | 0.59813(11) | 0.64173(10) | 0.0239(3) |
| C2B | 0.0507(2) | 0.67848(11) | 0.61925(11) | 0.0313(4) |
| H2B | 0.005424 | 0.731480 | 0.642592 | 0.038* |
| C3B | 0.1583(2) | 0.68019(12) | 0.56301(11) | 0.0329(4) |
| H3B | 0.187847 | 0.734991 | 0.548373 | 0.039* |
| C4B | 0.2243(2) | 0.60317(12) | 0.52733(12) | 0.0318(4) |
| H4B | 0.297735 | 0.605183 | 0.488205 | 0.038* |
| C5B | 0.18237(18) | 0.52359(12) | 0.54919(11) | 0.0273(4) |
| H5B | 0.227771 | 0.470890 | 0.525100 | 0.033* |
| C6B | 0.07372(16) | 0.51977(10) | 0.60645(10) | 0.0204(3) |
| C7B | 0.05899(17) | 0.36583(10) | 0.60088(10) | 0.0216(3) |
| H7B | 0.123060 | 0.359494 | 0.556057 | 0.026* |
| C8B | 0.00609(16) | 0.28590(10) | 0.63003(9) | 0.0202(3) |
| C9B | −0.10257(17) | 0.28683(11) | 0.68759(10) | 0.0230(3) |
| H9B | −0.151193 | 0.339458 | 0.707176 | 0.028* |
| C10B | −0.13855(17) | 0.20986(11) | 0.71577(10) | 0.0234(3) |
| H10B | −0.212850 | 0.210858 | 0.754816 | 0.028* |
| C11B | 0.02741(18) | 0.13200(11) | 0.63172(10) | 0.0243(3) |
| H11B | 0.071768 | 0.077900 | 0.611394 | 0.029* |
| C12B | 0.06801(18) | 0.20572(11) | 0.60023(10) | 0.0251(3) |
| H12B | 0.137899 | 0.201689 | 0.558425 | 0.030* |
| C13B | 0.77353(18) | 0.18657(10) | 1.03498(10) | 0.0222(3) |
| C14B | 0.89429(19) | 0.20876(11) | 1.08737(10) | 0.0257(3) |
| H14B | 0.980258 | 0.235198 | 1.069468 | 0.031* |
| C15B | 0.8883(2) | 0.19205(12) | 1.16568(11) | 0.0287(4) |
| H15B | 0.969914 | 0.207913 | 1.201992 | 0.034* |
| C16B | 0.7633(2) | 0.15214(14) | 1.19143(11) | 0.0339(4) |
| H16B | 0.760488 | 0.139886 | 1.244947 | 0.041* |
| C17B | 0.64268(19) | 0.13010(13) | 1.13964(11) | 0.0300(4) |
| H17B | 0.557601 | 0.102869 | 1.157711 | 0.036* |
| C18B | 0.64601(17) | 0.14791(10) | 1.06071(10) | 0.0211(3) |
| C19B | 0.40400(18) | 0.10979(11) | 1.01926(10) | 0.0238(3) |
| H19B | 0.382120 | 0.107049 | 1.074385 | 0.029* |
| C20B | 0.28787(17) | 0.09244(10) | 0.95603(10) | 0.0216(3) |
| C21B | 0.14505(19) | 0.08259(13) | 0.97796(11) | 0.0319(4) |
| H21B | 0.121667 | 0.085829 | 1.033994 | 0.038* |
| C22B | 0.03650(19) | 0.06801(13) | 0.91805(11) | 0.0307(4) |
| H22B | −0.060850 | 0.061894 | 0.934230 | 0.037* |
| C23B | 0.20125(18) | 0.07332(12) | 0.81689(10) | 0.0279(4) |
| H23B | 0.221218 | 0.070796 | 0.760526 | 0.033* |
| C24B | 0.31511(18) | 0.08825(12) | 0.87301(10) | 0.0263(3) |
| H24B | 0.411241 | 0.095614 | 0.855250 | 0.032* |
Source of material
The synthesis of the ligand (E)-2-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)phenol (pap) has been reported by us earlier [5], [6], [7]. This educt (2 mmol, 0.397 g) was dissolved in anhydrous ethanol (ca. 10 mL) and was added slowly to the solution of ZnCl2 (1 mmol, 0.136 g) in anhydrous ethanol (ca. 10 mL) and kept under stirring at ambient temperature for 6 h. A yellow precipitate was formed which was isolated in vacuo. The yellow precipitate was crystallized using DCM/toluene [8]. Yield = 0.456 g, 85.55%, m.p. = 226–227 °C, 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6, 25 °C, δ in ppm): δ = 9.19 (2H, s, Hj-OH), 8.78 (2H, s, Hc—C=N—), 8.74 (4H, d, J = 5.91 Hz, Hb—C5H4N—), 8.00 (4H, d, J = 5.44 Hz, Ha—C5H4N), 7.28 (2H, d, J = 7.26 Hz, Hd—C6H4), 7.14 (2H, t, J = 8.11, 7.26 Hz, Hf—C6H4), 6.92 (2H, d, J = 8.11 Hz, Hg—C6H4), 6.86 (2H, t, J = 7.69 Hz, He—C6H4). 13C-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6, 25 °C, δ in ppm): δ = 157.39 (—C=N—), 151.55 (—OH), 150.23 (C5H4N, 2C’s), 149.95 (C5H4N), 136.85 (C6H4), 128.49 (C6H4), 122.36 (C5H4N, 2C’s), 122.12 (C6H4), 119.47 (C6H4), 116.35 (C6H4). FT-IR (cm−1): (Ar-CH) 3055, (—C=N—) 1622, (pyridyl) 1483, (C—OH) 1139, 1056. MS (ESILC-MS): m/z Calcd. for [C24H20Cl2N4O2Zn]: 532.73; found [ZnL2 − Cl2 + 1L+ EtOH+ Na]+: 726 (21%), [Zn(L2) − Cl2 + 1L+ EtOH+ Na]+: 727 (10%). Anal. Calcd. (%) for [Zn(L)2Cl2]. C, 54.11; H, 3.78; N, 10.52; found (%): C, 54.11; H, 3.64; N, 10.71.
Experimental details
The structure was solved by the direct method using the SHELXS [2] program and refined. The visual crystal structure information was performed using Mercury [3] system software. The C—H and O—H distances were restrainted to 0.950 Å and 0.84 Å, respectively with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(O).
Comment
Schiff base metal complexes are known to be widely studied mainly because of their numerous applications. Most importantly, most Schiff bases are biologically active and the activity can be further enhanced when complexed with transition metals [9]. Reports have shown that Zn is one of the twenty four essential elements in life [10] and it has found usage in medicine for the treatment of ailments such as athletes foot [11], eczema [11], rheumatoid arthritis [12], diabetes [13], ringworms [9], fungi [9], [14] and cancer [15]. Zn2+ is a redox-stable ion with the ability to interact with amino acid residues side chain in proteins [16] by involving in direct chemical catalysis or by maintaining protein structure and stability [16]. This is only possible when in complexed form according to de Fátima et al. [16]. Zn2+ ion showed insignificant activity as anti-urease agents but when complexed with a ligand especially those containing N-donor atom [89], its activity was improved. As such, its coordination to Schiff base ligands will further improve its role as part of a metalloenzymes [17] by contributing to metalloproteins structure and activity.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound contains two symmetrically independent complexes. Each complex contains two pap ligands and two chlorido ligands coordinating to a Zn2+ ion. The two pyridinyl moieties in each molecule coordinate to Zn2+ through the nitrogen atom. Furthermore, the conformation of the coordinated ligands is best described by the dihedral angles between pyridinyl and anilinyl rings in each pap ligand which were found to range between 1.15(5)° and 27.43(6)°. The metal centres adopt a distorted tetrahedral geometry with Npy—Zn—Npy, Cl—Zn—Cl and Npy—Zn—Cl bond angles of 102.69(5)–104.14(5)°, 116.61(1)–118.42(2)° and 104.87(4)–111.66(4)°, respectively. These are in agreement with closely related Zn(II) complexes reported [10], [15], [18], [19]. Intermolecular π⋯π and O—H⋯Cl interactions exist in the crystal.
Funding source: National Research Foundation of South Africa
Award Identifier / Grant number: 119342
Funding statement: We appreciate the University of KwaZulu-Natal and the National Research Foundation of South Africa (Grant number: 119342) for their financial assistance for Ms Adesola A. Adeleke.
References
1. Bruker. APEXII. Bruker AXS Inc, Madison, WI, USA (2009).Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Macrae, C. F.; Bruno, I. J.; Chisholm, J. A.; Edgington, P. R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Rodriguez-Monge, L.; Taylor, R.; van de Streek, J.; Wood, P. A.: Mercury CSD 2.0 – new features for the visualization and investigation of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 41 (2008) 466–470.10.1107/S0021889807067908Search in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Njogu, E. M.; Omondi, B.; Nyamori, V. O.: Silver(I)-pyridinyl Schiff base complexes: synthesis, characterisation and antimicrobial studies. J. Mol. Struct. 1135 (2017) 118–128.10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.01.061Search in Google Scholar
6. Njogu, E. M.; Omondi, B.; Nyamori, V. O.: Silver(I)-pyridinyl Schiff base complexes: synthesis, structural characterization and reactivity in ring-opening polymerisation of ϵ-caprolactone. Inorg. Chim. Acta 457 (2017) 160–170.10.1016/j.ica.2016.12.019Search in Google Scholar
7. Njogu, E. M.; Omondi, B.; Nyamori, V. O.: Coordination polymers and discrete complexes of Ag(I)-N-(pyridylmethylene)anilines: synthesis, crystal structures and photophysical properties. J. Coord. Chem. 70 (2017) 2796–2814.10.1080/00958972.2017.1370088Search in Google Scholar
8. Arafat, Y.; Ali, S.; Shahzadi, S.; Shahid, M.: Preparation, characterization, and antimicrobial activities of bimetallic complexes of sarcosine with Zn(II) and Sn(IV). Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2013 (2013) 351262.10.1155/2013/351262Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Gyanakumari, C.; Mounika, K.; Pragathi, A.: Synthesis, characterization and biological activity of a Schiff base derived from 3-ethoxy salicylaldehyde and 2-amino benzoic acid and its transition metal complexes. J. Sci. Res. 2 (2010) 513–524.10.3329/jsr.v2i3.4899Search in Google Scholar
10. Wriedt, M.; Jeß, I.; Näther, C.: Synthesis, crystal structures, and thermal properties of new [ZnX2(2,5-dimethylpyrazine)] (X = Cl, Br, I) coordination compounds. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009 (2009) 363–372.10.1002/ejic.200800646Search in Google Scholar
11. Chohan, Z. H.; Pervez, H.; Rauf, A.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C. T.: Antibacterial Co(II), Cu(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes of thiadiazole derived furanyl, thiophenyl and pyrrolyl Schiff bases. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 17 (2002) 117–122.10.1080/14756360290024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Yamgar, R. S.; Nivid, Y.; Nalawade, S.; Mandewale, M.; Atram, R. G.; Sawant, S. S.: Novel zinc(II) complexes of heterocyclic ligands as antimicrobial agents: synthesis, characterisation, and antimicrobial studies. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2014 (2014) 276598.10.1155/2014/276598Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
13. Asri-Rezaei, S.; Tamaddonfard, E.; Ghasemsoltani-Momtaz, B.; Erfanparast, A.; Gholamalipour, S.: Effects of crocin and zinc chloride on blood levels of zinc and metabolic and oxidative parameters in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 5 (2015) 403–412.Search in Google Scholar
14. Shankar, A. H.; Prasad, A. S.: Zinc and immune function: the biological basis of altered resistance to infection. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 68 (1998) 447S–463S.10.1093/ajcn/68.2.447SSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
15. Čobeljić, B.; Pevec, A.; Turel, I.; Swart, M.; Mitić, D.; Milenković, M.; Marković, I.; Jovanović, M.; Sladić, D.; Jeremić, M.; Anđelković, K.: Synthesis, characterization, DFT calculations and biological activity of derivatives of 3-acetylpyridine and the zinc(II) complex with the condensation product of 3-acetylpyridine and semicarbazide. Inorg. Chim. Acta 404 (2013) 5–12.10.1016/j.ica.2013.04.017Search in Google Scholar
16. de Fátima, A.; de Paula Pereira, C.; Olímpio, C. R. S. D. G.; de Freitas Oliveira, B. G.; Franco, L. L.; da Silva, P. H. C.: Schiff bases and their metal complexes as urease inhibitors–a brief review. J. Adv. Res. 13 (2018) 113–126.10.1016/j.jare.2018.03.007Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
17. McCall, K. A.; Huang, C.-C.; Fierke, C. A.: Function and mechanism of zinc metalloenzymes. Nutr. J. 130 (2000) 1437S–1446S.10.1093/jn/130.5.1437SSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
18. Abu Ali, H.; Maloul, S.; Abu Ali, I.; Akkawi, M.; Jaber, S.: Dichloro-bis-(pyridine-2-yl-undecyl-amine)zinc(II), [ZnCl2(C16N2H26)2]: synthesis, characterization and antimalarial activity. J. Coord. Chem. 69 (2016) 2514–2522.10.1080/00958972.2016.1204443Search in Google Scholar
19. Li, L.; Clarkson, G. J.; Evans, D. J.; Lees, M. R.; Turner, S. S.; Scott, P.: Isomeric Fe(II) MOFs: from a diamond-framework spin-crossover material to a 2D hard magnet. Chem. Commun. 47 (2011) 12646–12648.10.1039/c1cc15574aSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
©2020 Adesola A. Adeleke et al., published by De Gruyter.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2N:O)silver(I)], C15H8AgNO4S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium) bis(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)succinato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) tetrahydrate, C48H70CuN8O12, [C10H14N2]2[Cu(C14H17N2O4)2] ⋅ 4 H2O
- Crystal structure of triaqua-bis(2-(6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-1-(2-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-3-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-κ2O,O′)calcium(II) – ethanol (1/2), C44H76CaO19S2
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5-(4-(diphenylamino)phenyl)thiophene-2-carboxylate, C25H21NO2S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(2-methyl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- The crystal structure of (E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N′-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H13ClN2O4
- The crystal structure of (2Z,2′Z)-N′,N′′′′-(pyridine-2,6-dicarbonyl)dipicolinohydrazonamide, C19H17N9O2
- Photochromic properties and crystal structure of 3,3′-(perfluorocyclopent-1-ene-1,2-diyl)bis(5-(4-(azidomethyl)phenyl)-2-methylthiophene), C29H20F6N6S2
- Crystal structure of aqua-dichlorido-(4-(((3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)hydrazono)(oxido)methyl)pyridin-1-ium-κ3N,O,O′)iron(III), C15H16Cl2N3O4Fe
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrabromo-6-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-nickel(II)], C26H14Br8NiN2O10
- Crystal structure of diethanol-κ1O-bis(μ2-N-((2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)pyrazine-2-carbohydrazonato-κ5N,O,O′:O′:N′)-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dieuropium(III), C36H32N10O12Eu2
- The crystal structure of 2-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-((3,4-difluorobenzyl)oxy)styryl)-4,6-dimethoxybenzaldehyde, C24H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoylpyrene, C23H14O
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6-p-cymene)-(N-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) – acetone (1/1), C22H23ClN2F7OPRu
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,3,5,7-tetraphenyl-8-(N-phenylformamido)-2-oxa-5-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct -3-en-7-yl benzoate, C44H34N2O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(3-acetyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-7-(diethylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C21H21N3O4S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-κ2O:O′)nickel(II)], C18H12F4NiN2O6
- Crystal structure of 4-hydroxynaphtho[2,3-b]benzofuran-6,11-dione, C16H8O4
- The crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]dodecane – acetone (1/1), C45H48N2O5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)iminio)methyl)-6-bromophenolate, C17H15N2BrO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-oxalyl dihydrazide-κ4N,O:N′,O′)-bis(μ2-pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)dicadmium(II)] hexahydrate, C16H28O18N6Cd2
- Crystal structure of poly[tetra-(μ4-naphthalene-1,8-dicarboxylato-κ4O:O,O′: O′′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ4-oxo-κ4O:O:O:O) penta-lead(II)], C48H24O17Pb5
- Crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[c,f][1,5]oxabismocin-12 (7H)-yl acetate, C16H15O3Bi
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-chloro-6-nitrophenyl)-1-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl)diazene 1-oxide, C12H6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of bis(3-methyl-N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)nickel(II), C28H26N8O2Ni
- Crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]-dodecane, C40H36Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis[(μ2-4⋯O,O′:O′)-(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)]-di-lead(II)μ-4-hydroxybenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′;κ3O,O′:O′-bis-[(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)di-lead(II)] monohydrate, C52H36N4O12Pb2 ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ3-3,4,5,6-tetrafluoro-phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethene-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C14H9CoF4NO6
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-4-phenyl-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H10O3
- Crystal structure of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(5-oxohexyl)-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C20H24N4O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O)-bis(nitrato-κ1O)zinc(II)], C17H16N6O7Zn
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(6-aminopicolinato-κ2N,O)magnesium(II), C12H14O6N4Mg
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxamide-κ2N,O)-[tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′]nickel(II) diperchlorate — methanol (1/3), C33H39Cl2N9NiO12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3-(4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-acrylato-κO1)-(μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N3:N3′)cobalt(II)], C32H26CoF6N4O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate monohydrate, C22H25NO5S⋅H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(N-oxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl) acetamide κ2O,O′)-diaqua-zinc(II), C6H12ZnN10O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-chlorophenylimino)methyl)pyridinium 3,5-dinitrobenzoate, C19H13ClN4O6
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis((E)-2-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)phenol)zinc(II), C24H20Cl2N4O2Zn
- Crystal structure of cyclo-[tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-p-xylylenediamine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(II)] dimethyl sulfoxide solvate, C20H36Cl4N4O2Pd2S2
- Crystal structure of 4-(3-fluorophenyl)-7-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H9FO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-(pyrimidin-2-yl)hydrazono)methyl)quinolin-1-ium perchlorate – methanol (1/1), C15H16N5O5Cl
- The crystal structure of bis(N-(amino(pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)zinc(II) – methanol (2/5), C57H60Cl2N16O13Zn2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4,4′-di(4-pyridyl)-6,6′-di(tert-butyl)-2,2′-[propylenedioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenol, C35H40N4O4
- Crystal structure of (3E,3′E)-3,3′-((1,3,4-thiadiazole-2,5-diyl)bis(sulfanediyl))bis(4-hydroxy-4-phenylbut-3-en-2-one), C22H18N2O4S3
- Crystal structure of (N-benzyl-N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)di(4-chlorobenzyl)chloridotin(IV), C23H22Cl3NS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) sodium bromide hydrate, [Na(18-crown-6)]Br ⋅ H2O, C12H26BrNaO7
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H13F2N1O4
- Crystal structure of chlorido (2-(4-ethylphenyl)pyrimidine-k2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-kP) palladium(II), C30H26ClN2PPd
- Crystal structure of 18-crown-6 – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene – acetonitrile (1/1/2), C22H30F4I2N2O6
- Crystal structure of diisobutyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C16H24O6
- Crystal structure of poly[[tris(μ2-cis-1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylato)-κ2O, O′]-bis[μ3-1,3,5-tris[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzene-κ3N, N′,N′′]-trizinc(II)] – water (1/20), C60H106N12O32Zn3
- The synthesis and crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide–tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C16H14N4Cl2F6O3S
- Crystal structure of dimethylbis(diisopropyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C16H34N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of diisopropyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C14H20O6
- The synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl (E)-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-5-((2-methoxybenzylidene)amino)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C22H15N3Cl2F6O4S
- The crystal structure of a matrine derivative, 13-(methylamine-1-yl) carbodithioate matrine, C17H27N3OS2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxy-6-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C26H20CuN2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-p-fluorophenyl-5-dihydroxymethyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C9H7FN2O3
- Crystal structure of dichloridobis(4-chlorophenyl-κC1)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tin(IV), C24H16Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of bis{bromido-triphenyltin(IV)}(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′), C46H38Br2N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-chloro-quinolin-8-yloxy)-N-quinolin-8-yl-acetamide, C20H14N3O2Cl
- Crystal structure of bis(N-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(II) — dimethylformamide (1/1), C41H41N9O5Co
- Crystal structure of bis[2-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-1-tosylhydrazin-1-ido-κ3-N,N′,O]copper(II), C30H34N8O4S2Cu
- Crystal structure of (2-p-tolylpyrimidine-κ2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-κP) palladium(II), C29H24ClN2PPd
- Halogen bonding in crystal structure of bis(1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium triiodide, C16H32CsI3O8
- The synthesis and crystal structure of N-(3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfinyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-2-phenylacetamide, C20H10N4Cl2F6O2S
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)nicotinic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-methylbenzyl)thiazolidin-2-one, C11H13ONS
- The crystal structure of 2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(isoquinolin-1-yl)ethane-1,1-diol, C11H8F3NO2
- The crystal structure of 3-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- The crystal structure of 5-nitropicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 3-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-1,5-dioxaspiro[5.5]undecane-2,4-dione, C16H18O5
- Crystal structure of [[Mo3Se7(S2CNEt2)3]2(μ-Se)] ⋅ 2(C6H4Cl2), C42H68Cl4Mo6N6S12Se15
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-hydroxy-3-((5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)thio)pent-3-en-2-one, C13H12N2O3S
- The crystal structure of (2,3-dioxo-5,6:13,14-dibenzo-9,10-benzo-1,4,8,11-7, 11-diene-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-nickel(II), Ni(C22H14N4O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-(1-benzyl-2-ethyl-4-nitro-1H-imidazol-5-ylthio)-propanoic acid, C15H17N3O4S
- The crystal structure of dichlorobis(2-(dicyclohexylphosphino)-2′,4′,6′-tri-i-propyl-1,1′-biphenyl) palladium(II)-dichloroform, C68H100Cl8P2Pd
- Crystal structure and antimicrobial properties of (1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium(I) pentaiodide, C16H32CsI5O8
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-carboxybenzoato-κ2N:O)silver(I)], C15H8AgNO4S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-phenylpiperazin-1-ium) bis(2-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)succinato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) tetrahydrate, C48H70CuN8O12, [C10H14N2]2[Cu(C14H17N2O4)2] ⋅ 4 H2O
- Crystal structure of triaqua-bis(2-(6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)-1-(2-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-3-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-κ2O,O′)calcium(II) – ethanol (1/2), C44H76CaO19S2
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5-(4-(diphenylamino)phenyl)thiophene-2-carboxylate, C25H21NO2S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromo-2-(2-methyl-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridine, C7H6BrN5
- The crystal structure of (E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N′-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H13ClN2O4
- The crystal structure of (2Z,2′Z)-N′,N′′′′-(pyridine-2,6-dicarbonyl)dipicolinohydrazonamide, C19H17N9O2
- Photochromic properties and crystal structure of 3,3′-(perfluorocyclopent-1-ene-1,2-diyl)bis(5-(4-(azidomethyl)phenyl)-2-methylthiophene), C29H20F6N6S2
- Crystal structure of aqua-dichlorido-(4-(((3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)hydrazono)(oxido)methyl)pyridin-1-ium-κ3N,O,O′)iron(III), C15H16Cl2N3O4Fe
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrabromo-6-carboxybenzoato-κ1O)-nickel(II)], C26H14Br8NiN2O10
- Crystal structure of diethanol-κ1O-bis(μ2-N-((2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)pyrazine-2-carbohydrazonato-κ5N,O,O′:O′:N′)-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)dieuropium(III), C36H32N10O12Eu2
- The crystal structure of 2-aminoisophthalic acid, C8H7NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-((3,4-difluorobenzyl)oxy)styryl)-4,6-dimethoxybenzaldehyde, C24H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoylpyrene, C23H14O
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6-p-cymene)-(N-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) – acetone (1/1), C22H23ClN2F7OPRu
- The crystal structure of 2-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,3,5,7-tetraphenyl-8-(N-phenylformamido)-2-oxa-5-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct -3-en-7-yl benzoate, C44H34N2O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(3-acetyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-7-(diethylamino)-2H-chromen-2-one, C21H21N3O4S
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-κ2O:O′)nickel(II)], C18H12F4NiN2O6
- Crystal structure of 4-hydroxynaphtho[2,3-b]benzofuran-6,11-dione, C16H8O4
- The crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]dodecane – acetone (1/1), C45H48N2O5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)iminio)methyl)-6-bromophenolate, C17H15N2BrO
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-oxalyl dihydrazide-κ4N,O:N′,O′)-bis(μ2-pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)dicadmium(II)] hexahydrate, C16H28O18N6Cd2
- Crystal structure of poly[tetra-(μ4-naphthalene-1,8-dicarboxylato-κ4O:O,O′: O′′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ4-oxo-κ4O:O:O:O) penta-lead(II)], C48H24O17Pb5
- Crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[c,f][1,5]oxabismocin-12 (7H)-yl acetate, C16H15O3Bi
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-chloro-6-nitrophenyl)-1-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl)diazene 1-oxide, C12H6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of bis(3-methyl-N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)nickel(II), C28H26N8O2Ni
- Crystal structure of 3,10-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-6,12-dibenzyl-2,9-acetyl-6,12-diazapentacyclo[6.3.1.02,7.04,11.05,9]-dodecane, C40H36Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis[(μ2-4⋯O,O′:O′)-(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)]-di-lead(II)μ-4-hydroxybenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′;κ3O,O′:O′-bis-[(4-hydroxybenzoato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)di-lead(II)] monohydrate, C52H36N4O12Pb2 ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ3-3,4,5,6-tetrafluoro-phthalato-κ3O:O′:O′′)-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethene-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C14H9CoF4NO6
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-4-phenyl-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H10O3
- Crystal structure of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(5-oxohexyl)-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C20H24N4O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O)-bis(nitrato-κ1O)zinc(II)], C17H16N6O7Zn
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(6-aminopicolinato-κ2N,O)magnesium(II), C12H14O6N4Mg
- Crystal structure of (pyridine-2-carboxamide-κ2N,O)-[tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′]nickel(II) diperchlorate — methanol (1/3), C33H39Cl2N9NiO12
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(3-(4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-acrylato-κO1)-(μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N3:N3′)cobalt(II)], C32H26CoF6N4O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate monohydrate, C22H25NO5S⋅H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(N-oxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl) acetamide κ2O,O′)-diaqua-zinc(II), C6H12ZnN10O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-((4-chlorophenylimino)methyl)pyridinium 3,5-dinitrobenzoate, C19H13ClN4O6
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis((E)-2-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)phenol)zinc(II), C24H20Cl2N4O2Zn
- Crystal structure of cyclo-[tetrachlorido-bis(μ2-p-xylylenediamine-κ2N:N′)dipalladium(II)] dimethyl sulfoxide solvate, C20H36Cl4N4O2Pd2S2
- Crystal structure of 4-(3-fluorophenyl)-7-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H9FO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-(pyrimidin-2-yl)hydrazono)methyl)quinolin-1-ium perchlorate – methanol (1/1), C15H16N5O5Cl
- The crystal structure of bis(N-(amino(pyridin-2-yl)methylene)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)zinc(II) – methanol (2/5), C57H60Cl2N16O13Zn2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4,4′-di(4-pyridyl)-6,6′-di(tert-butyl)-2,2′-[propylenedioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenol, C35H40N4O4
- Crystal structure of (3E,3′E)-3,3′-((1,3,4-thiadiazole-2,5-diyl)bis(sulfanediyl))bis(4-hydroxy-4-phenylbut-3-en-2-one), C22H18N2O4S3
- Crystal structure of (N-benzyl-N-methyl-dithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)di(4-chlorobenzyl)chloridotin(IV), C23H22Cl3NS2Sn
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6) sodium bromide hydrate, [Na(18-crown-6)]Br ⋅ H2O, C12H26BrNaO7
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H13F2N1O4
- Crystal structure of chlorido (2-(4-ethylphenyl)pyrimidine-k2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-kP) palladium(II), C30H26ClN2PPd
- Crystal structure of 18-crown-6 – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene – acetonitrile (1/1/2), C22H30F4I2N2O6
- Crystal structure of diisobutyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C16H24O6
- Crystal structure of poly[[tris(μ2-cis-1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylato)-κ2O, O′]-bis[μ3-1,3,5-tris[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]benzene-κ3N, N′,N′′]-trizinc(II)] – water (1/20), C60H106N12O32Zn3
- The synthesis and crystal structure of 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide–tetrahydrofuran (1/1), C16H14N4Cl2F6O3S
- Crystal structure of dimethylbis(diisopropyldithiocarbamato-κ2S,S′)tin(IV), C16H34N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of diisopropyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C14H20O6
- The synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl (E)-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-5-((2-methoxybenzylidene)amino)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C22H15N3Cl2F6O4S
- The crystal structure of a matrine derivative, 13-(methylamine-1-yl) carbodithioate matrine, C17H27N3OS2
- Crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxy-6-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)copper(II), C26H20CuN2O4
- The crystal structure of 2-p-fluorophenyl-5-dihydroxymethyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C9H7FN2O3
- Crystal structure of dichloridobis(4-chlorophenyl-κC1)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)tin(IV), C24H16Cl4N2Sn
- Crystal structure of bis{bromido-triphenyltin(IV)}(μ2-[4,4′-bipyridine]1,1′-dioxide-κ2O:O′), C46H38Br2N2O2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-chloro-quinolin-8-yloxy)-N-quinolin-8-yl-acetamide, C20H14N3O2Cl
- Crystal structure of bis(N-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-3-hydroxy-2-naphthohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(II) — dimethylformamide (1/1), C41H41N9O5Co
- Crystal structure of bis[2-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)-1-tosylhydrazin-1-ido-κ3-N,N′,O]copper(II), C30H34N8O4S2Cu
- Crystal structure of (2-p-tolylpyrimidine-κ2C,N)(triphenylphosphane-κP) palladium(II), C29H24ClN2PPd
- Halogen bonding in crystal structure of bis(1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium triiodide, C16H32CsI3O8
- The synthesis and crystal structure of N-(3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(trifluoromethylsulfinyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-2-phenylacetamide, C20H10N4Cl2F6O2S
- The crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)nicotinic acid, C7H4F3NO2
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-methylbenzyl)thiazolidin-2-one, C11H13ONS
- The crystal structure of 2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(isoquinolin-1-yl)ethane-1,1-diol, C11H8F3NO2
- The crystal structure of 3-bromoisonicotinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- The crystal structure of 5-nitropicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 3-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-1,5-dioxaspiro[5.5]undecane-2,4-dione, C16H18O5
- Crystal structure of [[Mo3Se7(S2CNEt2)3]2(μ-Se)] ⋅ 2(C6H4Cl2), C42H68Cl4Mo6N6S12Se15
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-hydroxy-3-((5-phenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)thio)pent-3-en-2-one, C13H12N2O3S
- The crystal structure of (2,3-dioxo-5,6:13,14-dibenzo-9,10-benzo-1,4,8,11-7, 11-diene-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)-nickel(II), Ni(C22H14N4O2)
- Crystal structure of 3-(1-benzyl-2-ethyl-4-nitro-1H-imidazol-5-ylthio)-propanoic acid, C15H17N3O4S
- The crystal structure of dichlorobis(2-(dicyclohexylphosphino)-2′,4′,6′-tri-i-propyl-1,1′-biphenyl) palladium(II)-dichloroform, C68H100Cl8P2Pd
- Crystal structure and antimicrobial properties of (1,4,7,10-tetraoxacyclododecane-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)cesium(I) pentaiodide, C16H32CsI5O8

