Abstract
C62H96Zn4N10O28, monoclinic, P21/c, a = 12.1072(11) Å, b = 27.878(3) Å, c = 11.4494(9) Å, β = 102.011(2)°, V = 3779.8(6) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0448, wRref(F2) = 0.1092, T = 298(2) K.
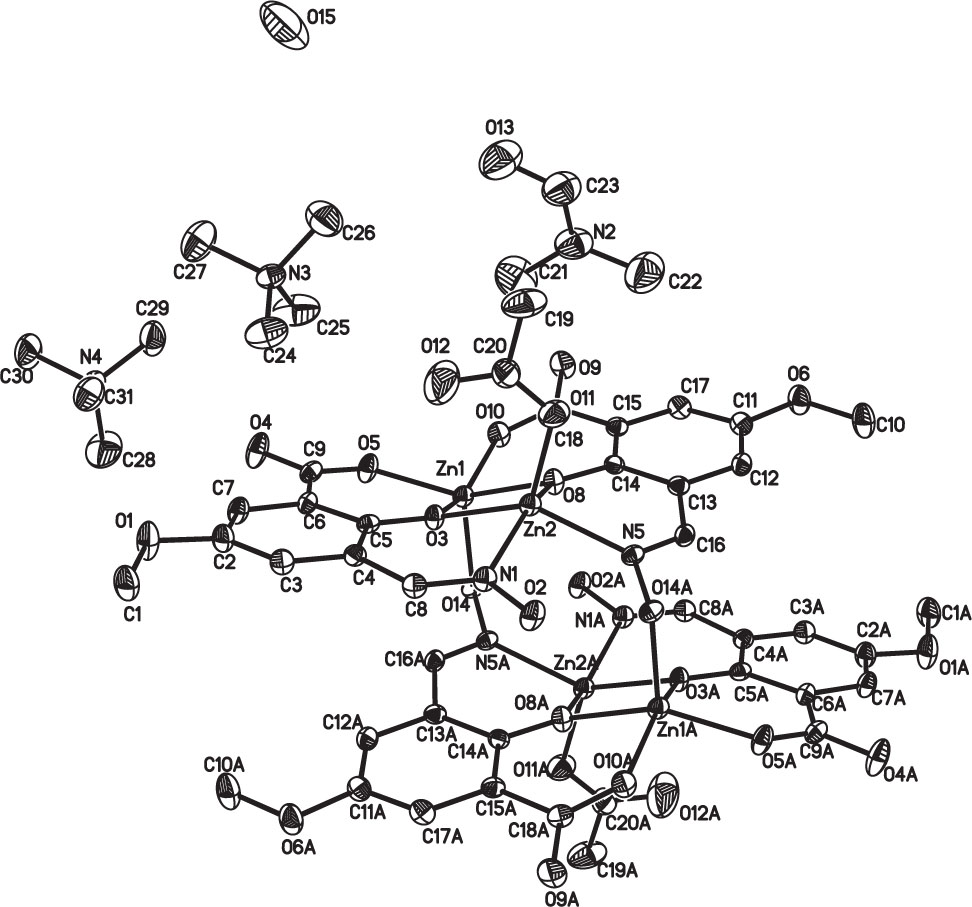
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Hydrogen atoms are omitted in the figure for clarity. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.42 × 0.31 × 0.30 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.34 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | APEX2, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.0°>, 97% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 18855, 6630, 0.045 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 4732 |
| N(param)refined: | 482 |
| Programs: | Bruker programs [1], SHELX [2] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn1 | 0.47791(4) | 0.10806(2) | 0.01684(4) | 0.03022(14) |
| Zn2 | 0.60193(4) | 0.02527(2) | 0.18594(4) | 0.02994(14) |
| O1 | 0.1971(3) | 0.10619(11) | 0.4927(3) | 0.0593(9) |
| O2 | 0.5393(2) | −0.06752(9) | 0.2949(3) | 0.0420(7) |
| O3 | 0.4660(2) | 0.06958(9) | 0.1671(2) | 0.0306(6) |
| O4 | 0.2989(3) | 0.20140(10) | 0.1820(3) | 0.0574(9) |
| O5 | 0.3961(2) | 0.16050(9) | 0.0768(3) | 0.0427(7) |
| O6 | 0.9488(3) | 0.05748(11) | −0.2225(3) | 0.0521(8) |
| N5 | 0.6568(3) | −0.03093(10) | 0.0917(3) | 0.0290(7) |
| O8 | 0.6141(2) | 0.06527(9) | 0.0394(2) | 0.0343(6) |
| O9 | 0.6971(3) | 0.18552(10) | −0.1420(3) | 0.0530(9) |
| O10 | 0.5605(2) | 0.15338(9) | −0.0700(3) | 0.0426(7) |
| O11 | 0.7417(3) | 0.03780(12) | 0.3044(3) | 0.0590(9) |
| O12 | 0.6606(4) | 0.0849(2) | 0.4003(5) | 0.163(3) |
| O13 | 0.9380(5) | 0.18877(19) | 0.4226(5) | 0.1163(17) |
| O14 | 0.3650(2) | 0.07828(9) | −0.1178(2) | 0.0331(6) |
| O15 | 0.9155(4) | 0.21518(19) | 0.9170(7) | 0.167(3) |
| H15C | 0.8464 | 0.2071 | 0.8984 | 0.200* |
| H15D | 0.9195 | 0.2456 | 0.9180 | 0.200* |
| C1 | 0.1674(4) | 0.06936(18) | 0.5643(4) | 0.0575(13) |
| H1A | 0.1337 | 0.0434 | 0.5144 | 0.086* |
| H1B | 0.1145 | 0.0815 | 0.6089 | 0.086* |
| H1C | 0.2338 | 0.0581 | 0.6185 | 0.086* |
| C2 | 0.2634(3) | 0.09390(15) | 0.4124(4) | 0.0398(10) |
| C3 | 0.3180(3) | 0.05087(14) | 0.4109(4) | 0.0365(10) |
| H3 | 0.3101 | 0.0272 | 0.4658 | 0.044* |
| C4 | 0.3850(3) | 0.04217(13) | 0.3281(3) | 0.0300(9) |
| C5 | 0.4006(3) | 0.07779(13) | 0.2443(3) | 0.0283(9) |
| C6 | 0.3410(3) | 0.12155(13) | 0.2453(3) | 0.0289(9) |
| C7 | 0.2745(3) | 0.12796(14) | 0.3294(4) | 0.0371(10) |
| H7 | 0.2356 | 0.1567 | 0.3293 | 0.044* |
| C8 | 0.4346(3) | −0.00567(14) | 0.3329(4) | 0.0339(10) |
| H8 | 0.4115 | −0.0279 | 0.3835 | 0.041* |
| C9 | 0.3450(3) | 0.16362(14) | 0.1627(4) | 0.0335(9) |
| C10 | 1.0052(4) | 0.01379(18) | −0.2309(5) | 0.0607(14) |
| H10A | 0.9531 | −0.0090 | −0.2747 | 0.091* |
| H10B | 1.0349 | 0.0016 | −0.1522 | 0.091* |
| H10C | 1.0660 | 0.0190 | −0.2716 | 0.091* |
| C11 | 0.8624(3) | 0.05670(15) | −0.1603(4) | 0.0362(10) |
| C12 | 0.8331(3) | 0.01717(14) | −0.1020(4) | 0.0352(10) |
| H12 | 0.8707 | −0.0117 | −0.1064 | 0.042* |
| C13 | 0.7480(3) | 0.01934(13) | −0.0361(3) | 0.0297(9) |
| C14 | 0.6900(3) | 0.06275(13) | −0.0290(3) | 0.0281(9) |
| C15 | 0.7155(3) | 0.10262(13) | −0.0953(3) | 0.0312(9) |
| C16 | 0.7197(3) | −0.02576(14) | 0.0149(3) | 0.0314(9) |
| H16 | 0.7501 | −0.0535 | −0.0106 | 0.038* |
| C17 | 0.8017(3) | 0.09860(14) | −0.1583(4) | 0.0363(10) |
| H17 | 0.8192 | 0.1251 | −0.2005 | 0.044* |
| C18 | 0.6539(3) | 0.15006(14) | −0.1025(4) | 0.0339(10) |
| C19 | 0.8459(5) | 0.0693(2) | 0.4819(5) | 0.088(2) |
| H19A | 0.8398 | 0.0504 | 0.5503 | 0.132* |
| H19B | 0.8545 | 0.1025 | 0.5043 | 0.132* |
| H19C | 0.9105 | 0.0590 | 0.4520 | 0.132* |
| C20 | 0.7412(4) | 0.06311(19) | 0.3865(5) | 0.0546(13) |
| C21 | 0.7993(6) | 0.1718(3) | 0.2006(7) | 0.127(3) |
| H21A | 0.7938 | 0.1862 | 0.1235 | 0.191* |
| H21B | 0.7856 | 0.1956 | 0.2563 | 0.191* |
| H21C | 0.7441 | 0.1467 | 0.1953 | 0.191* |
| C22 | 0.9523(7) | 0.1192(3) | 0.1621(7) | 0.129(3) |
| H22A | 0.9035 | 0.0918 | 0.1470 | 0.193* |
| H22B | 1.0271 | 0.1090 | 0.1992 | 0.193* |
| H22C | 0.9542 | 0.1350 | 0.0880 | 0.193* |
| C23 | 0.9681(6) | 0.1615(2) | 0.3485(7) | 0.094(2) |
| H23 | 1.0379 | 0.1466 | 0.3718 | 0.112* |
| C24 | 0.5394(5) | 0.15428(18) | 0.5636(5) | 0.0779(18) |
| H24A | 0.4583 | 0.1540 | 0.5435 | 0.117* |
| H24B | 0.5644 | 0.1505 | 0.6483 | 0.117* |
| H24C | 0.5681 | 0.1284 | 0.5233 | 0.117* |
| C25 | 0.5443(6) | 0.2073(2) | 0.3962(5) | 0.094(2) |
| H25A | 0.5692 | 0.1807 | 0.3551 | 0.141* |
| H25B | 0.5761 | 0.2365 | 0.3731 | 0.141* |
| H25C | 0.4634 | 0.2093 | 0.3759 | 0.141* |
| C26 | 0.7055(5) | 0.1995(2) | 0.5570(6) | 0.089(2) |
| H26A | 0.7304 | 0.1980 | 0.6421 | 0.134* |
| H26B | 0.7346 | 0.2281 | 0.5276 | 0.134* |
| H26C | 0.7325 | 0.1719 | 0.5213 | 0.134* |
| C27 | 0.5420(6) | 0.2406(2) | 0.5897(6) | 0.095(2) |
| H27A | 0.4613 | 0.2429 | 0.5668 | 0.142* |
| H27B | 0.5755 | 0.2698 | 0.5698 | 0.142* |
| H27C | 0.5635 | 0.2352 | 0.6743 | 0.142* |
| C28 | 0.0904(6) | 0.2847(3) | 0.1926(6) | 0.108(3) |
| H28A | 0.0823 | 0.3063 | 0.1261 | 0.162* |
| H28B | 0.0190 | 0.2811 | 0.2155 | 0.162* |
| H28C | 0.1156 | 0.2540 | 0.1702 | 0.162* |
| C29 | 0.2822(5) | 0.3149(2) | 0.2555(6) | 0.092(2) |
| H29A | 0.3058 | 0.2872 | 0.2170 | 0.138* |
| H29B | 0.3390 | 0.3229 | 0.3245 | 0.138* |
| H29C | 0.2713 | 0.3414 | 0.2010 | 0.138* |
| C30 | 0.1301(5) | 0.3479(2) | 0.3432(6) | 0.087(2) |
| H30A | 0.1063 | 0.3708 | 0.2805 | 0.131* |
| H30B | 0.1890 | 0.3615 | 0.4032 | 0.131* |
| H30C | 0.0673 | 0.3395 | 0.3783 | 0.131* |
| C31 | 0.1963(5) | 0.26706(19) | 0.3883(5) | 0.0712(16) |
| H31A | 0.1281 | 0.2602 | 0.4153 | 0.107* |
| H31B | 0.2526 | 0.2787 | 0.4539 | 0.107* |
| H31C | 0.2232 | 0.2383 | 0.3572 | 0.107* |
| N1 | 0.5070(3) | −0.01959(11) | 0.2736(3) | 0.0325(8) |
| N2 | 0.9103(4) | 0.15205(19) | 0.2405(5) | 0.0834(15) |
| N3 | 0.5814(3) | 0.20043(13) | 0.5262(3) | 0.0445(9) |
| N4 | 0.1734(3) | 0.30400(13) | 0.2931(4) | 0.0512(10) |
Source of material
H3L (H3L = 3-hydroxy-3-carboxyl-5-methoxybenzaldehyde oxime); systematic name: (E)-2-hydroxy-3-((hydroxyimino)methyl)-5-methoxybenzoic acid (0.0421 g, 0.2 mmol) in 10 mL DMF and Zn(OAc)2⋅H2O (0.0663 g, 0.3 mmol) in 10 mL DMF were mixed and stirred for 30 min at room temperature, eight drops of methanol solution of the tetramethylammonium hydroxide were added. The solution was kept stirring for 5 h, then filtered. The filtrate was evenly divided into 6 test tubes to diffuse with the help of the ethanol and ether. After 1 week, the light yellow crystals suitable for single crystal X-ray measurements were obtained with the yield of 0.028 g, 22.0% based on Zn. Infrared spectrum (KBr, cm−1): 3441 (s), 1652 (s), 1560 (s), 1488 (m), 1449 (w), 1420 (m), 1349 (s), 1265 (w), 1244 (w), 1152 (w), 1057 (m), 983 (m), 950 (m), 795 (s), 714 (w), 670 (w), 556 (w). Anal. calc. for C62H96Zn4N10O28: C 44.00, H 5.67, N 8.28; found: C 42.23, H 5.14, N 7.89%.
Experimental details
The H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with C—H = 0.93 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C), respectively [19]. The highest peak is located 0.361 Å from Cu1 and the deepest hole is situated −0.233 Å3.
Comment
The Zn coordination polymers have drawn intense attention in recent decades owing to their special structures [3] and unique properties [4], which have potential applications in luminescence [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], gas absorption [11], [12], [13], photoluminescence [14, 15] and heterogeneous catalysis [16]. Especially, the tetranuclear Zn complexes are often used as catalysts. Copolymerization of CO2 [17] and cyclohexene oxide and electrode posited precursor for ZnO nanosheets [18]. The 2-hydroxy-3-carboxyl-5-methoxybenzaldehyde oxime (L) acts as a N/O bridging ligand and has proven to be an excellent ligand in the synthesis of metal-organic complexes [19, 20] in the past. Therefore, we herein report the construction of a novel tetranuclear Zn compound with L as ligand. The syntheses and structures of the compound are described in this paper.
The asymmetric unit consists of two ZnII ions, two HL ligands, one acetate, two tetramethyl ammonium cations, one DMF molecule and one water molecule. Each ZnII ion exhibits a five-coordinated tetragonal pyramid configuration. For Zn1, the coordination atoms are from five oxygen atoms of three HL ligands to form a O5 coordination environment. The coordination atoms of Zn2 are supplied by three oxygen atoms and two nitrogen atoms to display a N2O3 coordination environment. The bond length range of Zn—O bonds and Zn—N bonds are 1.967–2.091 Å and 2.091–2.088 Å, respectively. Four Zn atoms are connected by O atoms to form the core of the complex. The bond angles of Zn(2)—O(3)—Zn(1), Zn(1)—O(8)—Zn(2) are 102.1° and 103.45°, respectively. Bond lengths and angles are all in the expected ranges.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for financial support of this work from the Natural Science Foundation of China (21701078).
References
BRUKER. SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA (2009).Search in Google Scholar
Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Ma, L. F.; Qin, J. H.; Han, M. L.; Wang, L. Y.; Du, M.: A unique 3-D Zn(II) coordination framework with 1,2,3-benzenetricarboxyl and 4,4′-bipyridyl tectons showing 4-connected self-penetrating network and helical character. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 14 (2011) 1584–1587.10.1016/j.inoche.2011.06.008Search in Google Scholar
Li, M. Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.: Synthesis, structure and proton conductivity of a metal-organic framework with rich hydrogen-bonds between the layers. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 79 (2017) 37–40.10.1016/j.inoche.2017.03.022Search in Google Scholar
Chen, X. L.; Zhang, X. G.; Gao, L. J.; Ma, H. Y.: New examples of d10 metal-organic frameworks based on 4,4′-(hexafluoroisopropylidene)diphthalic acid: Synthesis crystal structure and luminesence. J. Mol. Struct. 1085 (2015) 45–51.10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.12.040Search in Google Scholar
Zhang, S. Q.; Jiang, F. L.; Wu, M. Y.; Feng, R.; Ma, J.; Xu, W. T.; Hong, M. C.: The Zn(II)-organic coordination polymers based on 2-(pyridin-4-yl)-1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylate ligands: crystal structure and luminescent properties. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 14 (2011) 1400–1405.10.1016/j.inoche.2011.05.032Search in Google Scholar
Bu, X. Z.; Wei, Z. W.; Zhang, C. H.; Ren, S. F.: Employing tetrahedral {Zn4O} clusters as building subunits to construct a new acentric metal-organic framework. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 48 (2014) 158–160.10.1016/j.inoche.2014.08.017Search in Google Scholar
Liu, B.; Yang, G. P.; Wang, Y. Y.; Liu, R. T.; Hou, L.; Shi, Q. Z.: Two new pH-controlled metal-organic frameworks based on polynuclear secondary building units with conformation-flexible cyclohexane-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylate ligand. Inorg. Chim. Acta 367 (2011) 127–134.10.1016/j.ica.2010.12.023Search in Google Scholar
Lv, C. W.; Li, J.; Hou, Z.; Li, M. K.: Synthesis, structure and luminescent property of a new Zn(II) coordination polymer with isolated tetrahedral {Zn4O} clusters as building subunits. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 36 (2013) 1–3.10.1016/j.inoche.2013.07.001Search in Google Scholar
Wang, D. Z.: Zinc(II) and cadmium(II) coordination polymers with bis(tetrazole) ligands: synthesis, structures and luminescent properties. Polyhedron 35 (2012) 142–148.10.1016/j.poly.2012.01.012Search in Google Scholar
He, W. W.; Li, N.; Wang, X.; Hu, T. L.; Bu, X. H.: A cationic metal-organic framework based on {Zn4} cluster for rapid and selective adsorption of dyes. Chin. Chem. Lett. 29 (2018) 857–860.10.1016/j.cclet.2017.10.003Search in Google Scholar
Du, J.; Zou, G. L.: A novel microporous zinc(II) metal-organic framework with highly selectivity adsorption of CO2 over CH4. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 69 (2016) 20–23.10.1016/j.inoche.2016.04.015Search in Google Scholar
Moradpour, T.; Abbasi, A.; Hecke, K. V.: A nanoporous 3D zinc(II) metal-organic framework for selective adsorption of benzaldehyde and formaldehyde. J. Solid State Chem. 228 (2015) 36–41.10.1016/j.jssc.2015.04.013Search in Google Scholar
Liu, B.; Guo, K.; Feng, H. J.; Miao, W. N.; He, T. T.; Xu, L.: Mixed sulfoisophthalate and 1,2,4-triazole directed d10 metal coordination polymers: synthesis, property and structural diversity. J. Solid State Chem. 254 (2017) 47–54.10.1016/j.jssc.2017.07.001Search in Google Scholar
Guo, Y. Y.; Ma, P. T.; Wang, J. P.; Niu, J. Y.: Two multi-dimensional frameworks constructed from zinc coordination polymers with pyridine carboxylic acids. J. Solid State Chem. 184 (2011) 3121–3127.10.1016/j.jssc.2011.09.030Search in Google Scholar
Zhang, S. X.; He, H. M.; Sun, F. X.; Zhao, N.; Du, J. S.; Pan, Q. H.; Zhu, G. S.: A novel adenine-based zinc(II) metal-organic framework featuring the lewis basic sites for heterogeneous catalysis. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 79 (2017) 55–59.10.1016/j.inoche.2016.11.011Search in Google Scholar
Kröger, M.; Folli, C.; Walter, O.; Döring, M.: A new amidoimidomalonate zinc complex with a sedecameric solid state structure catalyzing the copolymerization of CO2 and cyclohexene oxide. J. Organomet. Chem. 691 (2006) 3397–3402.10.1016/j.jorganchem.2006.04.018Search in Google Scholar
Liang, W. T.; Li, W. P.; Chen, H. N.; Liu, H. C.; Zhu, L. Q.: Exploiting electrodeposited flower-like Zn4(OH)6SO4⋅4H2O nanosheets as precursor for porous ZnO nanosheets. Electrochim. Acta 156 (2015) 171–178.10.1016/j.electacta.2015.01.022Search in Google Scholar
Pandey, J.; Mishra, M.; Bisht, S. S.; Sharma, A.; Tripathi, R. P.: An efficient chemoselective etherification of phenols in polyfunctional aromatic compounds. Tetrahedron Lett. 4 (2018) 695–698.10.1016/j.tetlet.2007.11.129Search in Google Scholar
Cai, J.; Liu, L. G.; Hong, K. H.; Wang, P.; Li, L. S.; Cao, M.; Sun, C. L.; Wu, X. Q.; Zong, X.; Chen, J. Q.; Ji, M.: Discovery of phenoxybutanoic acid derivatives as potent endothelin antagonists with antithpentensive activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 23 (2015) 657–667.10.1016/j.bmc.2015.01.003Search in Google Scholar PubMed
©2018 Xue L. Niu et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of di-μ2-aqua-tetraaqua-bis(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)disodium(I) C18H24N6Na2O10
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2-bromo-4-chloro-6-formylphenolato-κ2O,O′)cobalt(II), C16H16Cl2CrN3O7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-(4-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl)ethan-1-one-κ2N:O)-bis(1,1,1-trifluoro-4-oxo-4-(thiophen-2-yl)but-2-en-2-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II)], C27H18CuF6N2O5S2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carboxylate, C18H15F2NO5
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-dimethoxy-2,2′-[1,1′-(ethylenedioxydinitrilo)diethylidyne]diphenol, C20H24N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H14Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,3,9,10,16,17,23,24-octakis(2,6-dimethylphenoxy)phthalocyanine - trichloromethane (1/2), C98H84Cl6N8O8
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-((1-(2-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methoxy)-1-naphthoate, C24H21N3O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3,3′-thiodipropionato-κ2O:O′)-(bipyridine-κ2N,N′)copper(II)] C16H16CuN2O4S
- Crystal structure of [4-chloro-2-(((2-((3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)phenyl)imino)(phenyl)methyl)phenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′}nickel(II) - ethyl acetate (1/1), C32H29ClN2NiO5
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C29H52Cl2N4NiO9
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carboxylate, C20H21NO5
- Structure and photochromism of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(3-quinolyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C33H20F6N2S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3,5-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoate-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II))] 2.5 hydrate, C22H23CoN12O8.50
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(1,3-dimesityl-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl)(morpholine-κN)palladium(IV), C25H33Cl2N3OPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(4,4′-dipyridylaminium-kN)-(μ2-germanowolframato-κ2O:O′)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)copper(II)] with a Keggin-type heteropolyoxoanion, [Cu(C10H8N2)(C10H10N3)2][GeW12O40] ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridin-1-ium-4-carbohydrazonate-κ3N,N′,O)-tris[nitrato-κ2O,O′)lanthanum(III), C12H15N8O12La
- The crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-4-((2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-3,6-dimethylbenzoyl)oxy)-3,6-dimethylbenzoic acid–methanol (1/1), C20H24O8
- Crystal structure of guanidinium tetrapropylammonium bis(hydrogencarbonate) dihydrate, C15H40N4O8
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-bromo-3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H27BrO2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)phenyl)acetic acid, C10H9N3O4
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazol-3-ium)bis(2-carboxybenzoate), C30H26N4O8
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(4,10-diphenyl-4,10-dihydropyreno[4,5-d:9,10-d′]diimidazole-5,11-diyl)bis(N,N-diphenylaniline), C66H44N6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C20H18CoN12O2
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide 1.5 hydrate, C20H22IN2O1.5
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromane, C16H16O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-carboxy-5-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-4-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)pyridine-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C18H12N4O8Zn
- Crystal structure of bis(1-((2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ2N:N′)tetraiodidodicadmium(II), [Cd2(C13H15N5)2I4]
- Crystal structure of tetramethylammonium bis(acetato-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ3-3-((hydroxyimino)methyl)-5-methoxy-2-oxidobenzoate-κ5O,O′:O′,N:O′′)tetrazinc(II) — N,N′-dimethylformamide — water (1/2/2), C62H96Zn4N10O28
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-5-tert-butylisophthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone-κO)zinc(II)] C17H22N2O5Zn
- Crystal structure of [tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′]-[(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,N)]cadmium(II)–methanol (1:3) C34H36CdN8O7
- The crystal structure of bis(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-amine-κN)-diiodidocadmium(II), C14H14CdI2N6
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(1H-benzimidazol-2-amine)-κN)-bis(μ2-sulfonato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C30H36N12O10S2Zn2
- Crystal structure of 3β-methoxy-20α-dimethylamino-pregn-5-ene, C24H41NO
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-oxydibenzoate, C16H14O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-3-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- Crystal structure of 4-((E)-((E)-5-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-oxopiperidin-3-ylidene)methyl)benzonitrile, C26H18F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetato-κ1O)-bis(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-one oxime-κ2N,N′)zinc(II), C18H22N4O6Zn
- The crystal structure of 9-butoxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2H-imidazo[1,5-a]quinolin-10-ium bromide, C17H21O2N2Br
- Crystal stucture of 2-(tert-butyl)-6-(hydroxymethyl)-4-methylphenol, C12H18O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(2-(5-chloroquinolin-8-yloxy)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethan-1-one-κ3N,O,O′)-(dinitrato-κ2O,O′)mercury(II)], C15H15N4O8ClHg
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (3aS,6R,6aS,7S)-1H,3H,6H,7H-3a,6:7,9a-diepoxybenzo[de]isochromene-3a1,6a-dicarboxylate, C16H16O7
- The crystal structure of 2-(dimethoxymethyl)-4-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-imidazole—petroleum ether-chloroform (3/1), C27H33Cl3N4O4
- Crystal structure of 8-(trifluoromethyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-carbaldehyde, C9H5F3N2O
- The crystal structure of N,N-diethyl-4,6-bis(naphthalen-2-yloxy)-1,3,5-triazin-2-amine, C27H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-7-chloro-3,3a-dihydrocyclopenta[b]chromen-1(2H)-one, C12H8BrClO2
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(4-fluorophenyl)methylene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H11F2N3S
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of di-μ2-aqua-tetraaqua-bis(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)disodium(I) C18H24N6Na2O10
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2-bromo-4-chloro-6-formylphenolato-κ2O,O′)cobalt(II), C16H16Cl2CrN3O7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-(4-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl)ethan-1-one-κ2N:O)-bis(1,1,1-trifluoro-4-oxo-4-(thiophen-2-yl)but-2-en-2-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II)], C27H18CuF6N2O5S2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carboxylate, C18H15F2NO5
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-dimethoxy-2,2′-[1,1′-(ethylenedioxydinitrilo)diethylidyne]diphenol, C20H24N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H14Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,3,9,10,16,17,23,24-octakis(2,6-dimethylphenoxy)phthalocyanine - trichloromethane (1/2), C98H84Cl6N8O8
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-((1-(2-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methoxy)-1-naphthoate, C24H21N3O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3,3′-thiodipropionato-κ2O:O′)-(bipyridine-κ2N,N′)copper(II)] C16H16CuN2O4S
- Crystal structure of [4-chloro-2-(((2-((3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)phenyl)imino)(phenyl)methyl)phenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′}nickel(II) - ethyl acetate (1/1), C32H29ClN2NiO5
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C29H52Cl2N4NiO9
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carboxylate, C20H21NO5
- Structure and photochromism of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(3-quinolyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C33H20F6N2S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3,5-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoate-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II))] 2.5 hydrate, C22H23CoN12O8.50
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(1,3-dimesityl-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl)(morpholine-κN)palladium(IV), C25H33Cl2N3OPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(4,4′-dipyridylaminium-kN)-(μ2-germanowolframato-κ2O:O′)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)copper(II)] with a Keggin-type heteropolyoxoanion, [Cu(C10H8N2)(C10H10N3)2][GeW12O40] ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridin-1-ium-4-carbohydrazonate-κ3N,N′,O)-tris[nitrato-κ2O,O′)lanthanum(III), C12H15N8O12La
- The crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-4-((2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-3,6-dimethylbenzoyl)oxy)-3,6-dimethylbenzoic acid–methanol (1/1), C20H24O8
- Crystal structure of guanidinium tetrapropylammonium bis(hydrogencarbonate) dihydrate, C15H40N4O8
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-bromo-3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H27BrO2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)phenyl)acetic acid, C10H9N3O4
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazol-3-ium)bis(2-carboxybenzoate), C30H26N4O8
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(4,10-diphenyl-4,10-dihydropyreno[4,5-d:9,10-d′]diimidazole-5,11-diyl)bis(N,N-diphenylaniline), C66H44N6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C20H18CoN12O2
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide 1.5 hydrate, C20H22IN2O1.5
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromane, C16H16O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-carboxy-5-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-4-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)pyridine-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C18H12N4O8Zn
- Crystal structure of bis(1-((2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ2N:N′)tetraiodidodicadmium(II), [Cd2(C13H15N5)2I4]
- Crystal structure of tetramethylammonium bis(acetato-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ3-3-((hydroxyimino)methyl)-5-methoxy-2-oxidobenzoate-κ5O,O′:O′,N:O′′)tetrazinc(II) — N,N′-dimethylformamide — water (1/2/2), C62H96Zn4N10O28
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-5-tert-butylisophthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone-κO)zinc(II)] C17H22N2O5Zn
- Crystal structure of [tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′]-[(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,N)]cadmium(II)–methanol (1:3) C34H36CdN8O7
- The crystal structure of bis(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-amine-κN)-diiodidocadmium(II), C14H14CdI2N6
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(1H-benzimidazol-2-amine)-κN)-bis(μ2-sulfonato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C30H36N12O10S2Zn2
- Crystal structure of 3β-methoxy-20α-dimethylamino-pregn-5-ene, C24H41NO
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-oxydibenzoate, C16H14O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-3-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- Crystal structure of 4-((E)-((E)-5-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-oxopiperidin-3-ylidene)methyl)benzonitrile, C26H18F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetato-κ1O)-bis(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-one oxime-κ2N,N′)zinc(II), C18H22N4O6Zn
- The crystal structure of 9-butoxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2H-imidazo[1,5-a]quinolin-10-ium bromide, C17H21O2N2Br
- Crystal stucture of 2-(tert-butyl)-6-(hydroxymethyl)-4-methylphenol, C12H18O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(2-(5-chloroquinolin-8-yloxy)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethan-1-one-κ3N,O,O′)-(dinitrato-κ2O,O′)mercury(II)], C15H15N4O8ClHg
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (3aS,6R,6aS,7S)-1H,3H,6H,7H-3a,6:7,9a-diepoxybenzo[de]isochromene-3a1,6a-dicarboxylate, C16H16O7
- The crystal structure of 2-(dimethoxymethyl)-4-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-imidazole—petroleum ether-chloroform (3/1), C27H33Cl3N4O4
- Crystal structure of 8-(trifluoromethyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-carbaldehyde, C9H5F3N2O
- The crystal structure of N,N-diethyl-4,6-bis(naphthalen-2-yloxy)-1,3,5-triazin-2-amine, C27H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-7-chloro-3,3a-dihydrocyclopenta[b]chromen-1(2H)-one, C12H8BrClO2
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(4-fluorophenyl)methylene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H11F2N3S


