Abstract
C30H26N4O8, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 6.6363(7) Å, b = 9.0231(9) Å, c = 22.082(2) Å, β = 92.765(2)°, V =1320.7(2) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0455, wRref(F2) = 0.1234, T = 296(2) K.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.25 × 0.23 × 0.22 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.11 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | CCD area detector, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.0°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 6471, 2310, 0.030 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1664 |
| N(param)refined: | 191 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2, 3] |
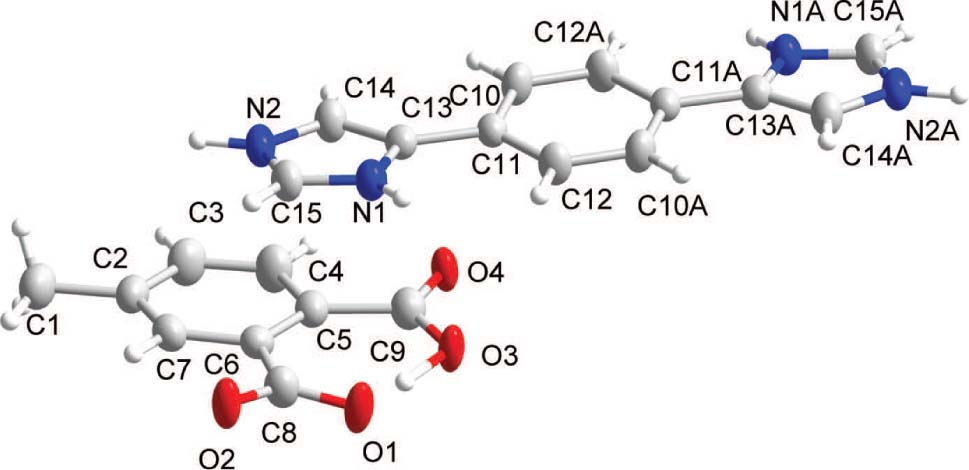
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | −0.2627(4) | 0.4076(3) | 0.29001(12) | 0.0540(7) |
| H1A | −0.348507 | 0.322246 | 0.285404 | 0.081* |
| H1B | −0.336858 | 0.494691 | 0.277660 | 0.081* |
| H1C | −0.216756 | 0.417168 | 0.331717 | 0.081* |
| C2 | −0.0847(3) | 0.3897(3) | 0.25135(10) | 0.0402(6) |
| C3 | 0.0631(3) | 0.2869(3) | 0.26601(11) | 0.0485(6) |
| H3 | 0.053044 | 0.228363 | 0.300389 | 0.058* |
| C4 | 0.2260(3) | 0.2701(3) | 0.23010(11) | 0.0466(6) |
| H4 | 0.321886 | 0.198302 | 0.240604 | 0.056* |
| C5 | 0.2527(3) | 0.3563(2) | 0.17876(10) | 0.0366(5) |
| C6 | 0.1025(3) | 0.4622(2) | 0.16302(10) | 0.0353(5) |
| C7 | −0.0619(3) | 0.4741(2) | 0.19960(10) | 0.0392(5) |
| H7 | −0.162115 | 0.542429 | 0.188724 | 0.047* |
| C8 | 0.0945(4) | 0.5663(3) | 0.10941(11) | 0.0438(6) |
| C9 | 0.4410(3) | 0.3189(3) | 0.14589(11) | 0.0424(6) |
| C10 | 0.4133(3) | −0.0578(2) | 0.04994(10) | 0.0392(5) |
| H10 | 0.355484 | −0.097786 | 0.083839 | 0.047* |
| C11 | 0.3224(3) | 0.0623(2) | 0.02077(9) | 0.0311(5) |
| C12 | 0.4120(3) | 0.1194(2) | −0.02970(10) | 0.0386(6) |
| H12 | 0.353701 | 0.200054 | −0.050076 | 0.046* |
| C13 | 0.1355(3) | 0.1243(2) | 0.04295(9) | 0.0323(5) |
| C14 | 0.0330(3) | 0.0930(3) | 0.09295(10) | 0.0400(6) |
| H14 | 0.069535 | 0.023308 | 0.122493 | 0.048* |
| C15 | −0.1350(3) | 0.2652(3) | 0.04348(10) | 0.0396(6) |
| H15 | −0.232934 | 0.335024 | 0.032212 | 0.048* |
| N1 | 0.0256(2) | 0.23360(19) | 0.01276(8) | 0.0384(5) |
| H1D | 0.047638 | 0.274144 | −0.024163 | 0.046* |
| N2 | −0.1346(3) | 0.1828(2) | 0.09228(8) | 0.0404(5) |
| H2A | −0.243234 | 0.189637 | 0.122182 | 0.049* |
| O1 | 0.2445(3) | 0.5781(2) | 0.07602(9) | 0.0763(7) |
| O2 | −0.0588(3) | 0.6400(2) | 0.09838(9) | 0.0708(6) |
| O3 | 0.4922(3) | 0.3959(2) | 0.10041(9) | 0.0666(6) |
| H3A | 0.377273 | 0.490218 | 0.092488 | 0.080* |
| O4 | 0.5442(2) | 0.2134(2) | 0.16348(8) | 0.0583(5) |
Source of material
All reagents and solvents were used as obtained without further purification. The ethanol solution (5 mL) of 1,4-di(1H-imidazol-4-yl)benzene (L, 0.10 mmol, 0.021 g) was slowly added to an aqueous solution (25 mLs) of 4-methylphthalic acid (H2A, 0.1 mmol, 0.0181 g). The mixture was stirred for half an hour at 353 K. The solution was filtered, and the filtrate was kept at the room temperature. After two weeks later, colorless crystals of the title salt were obtained with a yield of 38%. Analysis calculated (%): C, 63.15; H, 4.59; N, 9.82. Found (%): C, 63.28; H, 4.38; N, 9.72.
Experimental details
Coordinates of hydrogen atoms were added using a riding model. Their Uiso values were set to 1.2Ueq of the parent atoms except H1A, H1B and H1C of the Uiso values were set to 1.5Ueq of the parent C1 atom.
Comment
Cocrystal is the type of multi-component crystalline supramolecular polymer that has attracted considerable attention in recent years because of their fascinating structural topologies and potential applications [4, 5] . Polyazaheteroaromatic compounds in their neutral and anionic forms have been widely exploited in the construction of intriguing metal-organic coordination architectures [6], [7], [8], [9], [10]. In addition to their favourable coordination abilities, the rich nitrogen atoms of polyazaheteroaromatic compounds can serve as weak base to accept protons from carboxylic acid or inorganic acid to form acid-base conjugate pair incorporating charge transfer interactions, which might potentially benefit the construction of cocrystals [11, 12] .
In this paper, we report the reaction product of the multi-nitrogen compound 1,4-di(1H-imidazol-4-yl)benzene (L) together with 4-methylphthalic acid (H2A). The asymmetric unit consists of one half of a dication and one monoanion (cf. the figure; a = 1 − x, −y, −z). As mentioned above, the nitrogen-rich molecule L can serve as weak base to accept protons from carboxylic acid to form HL+, and H2A are deprotonated to be HA− anion.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge support by the Natural Science Foundtion of Anhui Provincial Education Commission (No. KH2016B123).
References
BRUKER. SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2009).Search in Google Scholar
Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXT – Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Han, L. L.; Li, Z. H.; Chen, J. S.; Wang, X. P.; Sun, D.: Solution and mechanochemical syntheses of two novel cocrystals: ligand length modulated interpenetration of hydrogen-bonded 2D 63-hcb networks based on a robust trimeric heterosynthon. Cryst. Growth Des. 14 (2014) 1221–1226.10.1021/cg4017454Search in Google Scholar
Wang, L.; Wen, X.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Yang, P.; Zhang, H.; Deng, Z.: 2:1 5-Fluorocytosine-acesulfame CAB cocrystal and 1:1 5-fluorocytosine- acesulfame salt hydrate with enhanced stability against hydration. CrystEngComm 16 (2014) 8537–8545.10.1039/C4CE01150CSearch in Google Scholar
Chen, S. S.; Wang, P.; Takamizawa, S.; Okamura, T. A.; Chen, M.; Sun, W. Y.: Zinc(II) and cadmium(II) metal-organic frameworks with 4-imidazole containing tripodal ligand: sorption and anion exchange properties. Dalton Trans. 43 (2014) 6012–6020.10.1039/c3dt53388cSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
Zhang, Z. Y.; Xiao, L.; Chen, S. S.; Qiao, R.; Yang, S.: A novel Zn(II) complex with 4-connected umc topology: synthesis, crystal structure and luminescent property. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 36 (2017) 819–824.Search in Google Scholar
Chen, S. S.: The roles of imidazole ligands in coordination supramolecular systems. CrystEngComm 18 (2016) 6543–6565.10.1039/C6CE01258BSearch in Google Scholar
Zhu, M. A.; Guo, X. Z.; Chen, S. S.: Synthesis, crystal structure and luminescent property of a new Zn(II) complex based on 4-imidazole-carboxylate ligand. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 36 (2017) 1348–1354.Search in Google Scholar
Chen, S. S.; Sheng, L. Q.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z. D.; Qiao, R.; Yang, S.: Syntheses, structures, and properties of a series of polyazaheteroaromatic core-based Zn(II) coordination polymers together with carboxylate auxiliary ligands. Cryst. Growth Des. 16 (2016) 229–241.10.1021/acs.cgd.5b01133Search in Google Scholar
Zhu, M. A.; Guo, X. Z.; Xiao, L.; Chen, S. S.: A new Cd(II) coordination compound based on 4-(1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)phenylacetic acid: synthesis, structure and photoluminescence property. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 37 (2018) 437–444.Search in Google Scholar
Li, W. D.; Fang, X.; Qiao, R.; Chen, S. S.: Non-covalent bonded 3D supramolecular architectures based on acid-base adducts. Chinese J. Struct. Chem. 35 (2016) 46–54.Search in Google Scholar
©2018 Liang-Quan Sheng, published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of di-μ2-aqua-tetraaqua-bis(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)disodium(I) C18H24N6Na2O10
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2-bromo-4-chloro-6-formylphenolato-κ2O,O′)cobalt(II), C16H16Cl2CrN3O7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-(4-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl)ethan-1-one-κ2N:O)-bis(1,1,1-trifluoro-4-oxo-4-(thiophen-2-yl)but-2-en-2-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II)], C27H18CuF6N2O5S2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carboxylate, C18H15F2NO5
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-dimethoxy-2,2′-[1,1′-(ethylenedioxydinitrilo)diethylidyne]diphenol, C20H24N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H14Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,3,9,10,16,17,23,24-octakis(2,6-dimethylphenoxy)phthalocyanine - trichloromethane (1/2), C98H84Cl6N8O8
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-((1-(2-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methoxy)-1-naphthoate, C24H21N3O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3,3′-thiodipropionato-κ2O:O′)-(bipyridine-κ2N,N′)copper(II)] C16H16CuN2O4S
- Crystal structure of [4-chloro-2-(((2-((3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)phenyl)imino)(phenyl)methyl)phenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′}nickel(II) - ethyl acetate (1/1), C32H29ClN2NiO5
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C29H52Cl2N4NiO9
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carboxylate, C20H21NO5
- Structure and photochromism of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(3-quinolyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C33H20F6N2S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3,5-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoate-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II))] 2.5 hydrate, C22H23CoN12O8.50
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(1,3-dimesityl-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl)(morpholine-κN)palladium(IV), C25H33Cl2N3OPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(4,4′-dipyridylaminium-kN)-(μ2-germanowolframato-κ2O:O′)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)copper(II)] with a Keggin-type heteropolyoxoanion, [Cu(C10H8N2)(C10H10N3)2][GeW12O40] ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridin-1-ium-4-carbohydrazonate-κ3N,N′,O)-tris[nitrato-κ2O,O′)lanthanum(III), C12H15N8O12La
- The crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-4-((2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-3,6-dimethylbenzoyl)oxy)-3,6-dimethylbenzoic acid–methanol (1/1), C20H24O8
- Crystal structure of guanidinium tetrapropylammonium bis(hydrogencarbonate) dihydrate, C15H40N4O8
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-bromo-3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H27BrO2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)phenyl)acetic acid, C10H9N3O4
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazol-3-ium)bis(2-carboxybenzoate), C30H26N4O8
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(4,10-diphenyl-4,10-dihydropyreno[4,5-d:9,10-d′]diimidazole-5,11-diyl)bis(N,N-diphenylaniline), C66H44N6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C20H18CoN12O2
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide 1.5 hydrate, C20H22IN2O1.5
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromane, C16H16O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-carboxy-5-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-4-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)pyridine-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C18H12N4O8Zn
- Crystal structure of bis(1-((2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ2N:N′)tetraiodidodicadmium(II), [Cd2(C13H15N5)2I4]
- Crystal structure of tetramethylammonium bis(acetato-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ3-3-((hydroxyimino)methyl)-5-methoxy-2-oxidobenzoate-κ5O,O′:O′,N:O′′)tetrazinc(II) — N,N′-dimethylformamide — water (1/2/2), C62H96Zn4N10O28
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-5-tert-butylisophthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone-κO)zinc(II)] C17H22N2O5Zn
- Crystal structure of [tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′]-[(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,N)]cadmium(II)–methanol (1:3) C34H36CdN8O7
- The crystal structure of bis(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-amine-κN)-diiodidocadmium(II), C14H14CdI2N6
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(1H-benzimidazol-2-amine)-κN)-bis(μ2-sulfonato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C30H36N12O10S2Zn2
- Crystal structure of 3β-methoxy-20α-dimethylamino-pregn-5-ene, C24H41NO
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-oxydibenzoate, C16H14O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-3-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- Crystal structure of 4-((E)-((E)-5-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-oxopiperidin-3-ylidene)methyl)benzonitrile, C26H18F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetato-κ1O)-bis(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-one oxime-κ2N,N′)zinc(II), C18H22N4O6Zn
- The crystal structure of 9-butoxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2H-imidazo[1,5-a]quinolin-10-ium bromide, C17H21O2N2Br
- Crystal stucture of 2-(tert-butyl)-6-(hydroxymethyl)-4-methylphenol, C12H18O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(2-(5-chloroquinolin-8-yloxy)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethan-1-one-κ3N,O,O′)-(dinitrato-κ2O,O′)mercury(II)], C15H15N4O8ClHg
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (3aS,6R,6aS,7S)-1H,3H,6H,7H-3a,6:7,9a-diepoxybenzo[de]isochromene-3a1,6a-dicarboxylate, C16H16O7
- The crystal structure of 2-(dimethoxymethyl)-4-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-imidazole—petroleum ether-chloroform (3/1), C27H33Cl3N4O4
- Crystal structure of 8-(trifluoromethyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-carbaldehyde, C9H5F3N2O
- The crystal structure of N,N-diethyl-4,6-bis(naphthalen-2-yloxy)-1,3,5-triazin-2-amine, C27H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-7-chloro-3,3a-dihydrocyclopenta[b]chromen-1(2H)-one, C12H8BrClO2
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(4-fluorophenyl)methylene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H11F2N3S
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of di-μ2-aqua-tetraaqua-bis(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)disodium(I) C18H24N6Na2O10
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2-bromo-4-chloro-6-formylphenolato-κ2O,O′)cobalt(II), C16H16Cl2CrN3O7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-(4-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl)ethan-1-one-κ2N:O)-bis(1,1,1-trifluoro-4-oxo-4-(thiophen-2-yl)but-2-en-2-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II)], C27H18CuF6N2O5S2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carboxylate, C18H15F2NO5
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-dimethoxy-2,2′-[1,1′-(ethylenedioxydinitrilo)diethylidyne]diphenol, C20H24N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H14Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,3,9,10,16,17,23,24-octakis(2,6-dimethylphenoxy)phthalocyanine - trichloromethane (1/2), C98H84Cl6N8O8
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-((1-(2-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methoxy)-1-naphthoate, C24H21N3O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3,3′-thiodipropionato-κ2O:O′)-(bipyridine-κ2N,N′)copper(II)] C16H16CuN2O4S
- Crystal structure of [4-chloro-2-(((2-((3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)phenyl)imino)(phenyl)methyl)phenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′}nickel(II) - ethyl acetate (1/1), C32H29ClN2NiO5
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C29H52Cl2N4NiO9
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carboxylate, C20H21NO5
- Structure and photochromism of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(3-quinolyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C33H20F6N2S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3,5-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoate-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II))] 2.5 hydrate, C22H23CoN12O8.50
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(1,3-dimesityl-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl)(morpholine-κN)palladium(IV), C25H33Cl2N3OPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(4,4′-dipyridylaminium-kN)-(μ2-germanowolframato-κ2O:O′)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)copper(II)] with a Keggin-type heteropolyoxoanion, [Cu(C10H8N2)(C10H10N3)2][GeW12O40] ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridin-1-ium-4-carbohydrazonate-κ3N,N′,O)-tris[nitrato-κ2O,O′)lanthanum(III), C12H15N8O12La
- The crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-4-((2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-3,6-dimethylbenzoyl)oxy)-3,6-dimethylbenzoic acid–methanol (1/1), C20H24O8
- Crystal structure of guanidinium tetrapropylammonium bis(hydrogencarbonate) dihydrate, C15H40N4O8
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-bromo-3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H27BrO2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)phenyl)acetic acid, C10H9N3O4
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazol-3-ium)bis(2-carboxybenzoate), C30H26N4O8
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(4,10-diphenyl-4,10-dihydropyreno[4,5-d:9,10-d′]diimidazole-5,11-diyl)bis(N,N-diphenylaniline), C66H44N6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C20H18CoN12O2
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide 1.5 hydrate, C20H22IN2O1.5
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromane, C16H16O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-carboxy-5-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-4-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)pyridine-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C18H12N4O8Zn
- Crystal structure of bis(1-((2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ2N:N′)tetraiodidodicadmium(II), [Cd2(C13H15N5)2I4]
- Crystal structure of tetramethylammonium bis(acetato-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ3-3-((hydroxyimino)methyl)-5-methoxy-2-oxidobenzoate-κ5O,O′:O′,N:O′′)tetrazinc(II) — N,N′-dimethylformamide — water (1/2/2), C62H96Zn4N10O28
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-5-tert-butylisophthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone-κO)zinc(II)] C17H22N2O5Zn
- Crystal structure of [tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′]-[(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,N)]cadmium(II)–methanol (1:3) C34H36CdN8O7
- The crystal structure of bis(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-amine-κN)-diiodidocadmium(II), C14H14CdI2N6
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(1H-benzimidazol-2-amine)-κN)-bis(μ2-sulfonato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C30H36N12O10S2Zn2
- Crystal structure of 3β-methoxy-20α-dimethylamino-pregn-5-ene, C24H41NO
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-oxydibenzoate, C16H14O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-3-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- Crystal structure of 4-((E)-((E)-5-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-oxopiperidin-3-ylidene)methyl)benzonitrile, C26H18F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetato-κ1O)-bis(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-one oxime-κ2N,N′)zinc(II), C18H22N4O6Zn
- The crystal structure of 9-butoxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2H-imidazo[1,5-a]quinolin-10-ium bromide, C17H21O2N2Br
- Crystal stucture of 2-(tert-butyl)-6-(hydroxymethyl)-4-methylphenol, C12H18O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(2-(5-chloroquinolin-8-yloxy)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethan-1-one-κ3N,O,O′)-(dinitrato-κ2O,O′)mercury(II)], C15H15N4O8ClHg
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (3aS,6R,6aS,7S)-1H,3H,6H,7H-3a,6:7,9a-diepoxybenzo[de]isochromene-3a1,6a-dicarboxylate, C16H16O7
- The crystal structure of 2-(dimethoxymethyl)-4-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-imidazole—petroleum ether-chloroform (3/1), C27H33Cl3N4O4
- Crystal structure of 8-(trifluoromethyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-carbaldehyde, C9H5F3N2O
- The crystal structure of N,N-diethyl-4,6-bis(naphthalen-2-yloxy)-1,3,5-triazin-2-amine, C27H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-7-chloro-3,3a-dihydrocyclopenta[b]chromen-1(2H)-one, C12H8BrClO2
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(4-fluorophenyl)methylene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H11F2N3S


