Abstract
C30H30GeW12CuN8O41, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 12.095(2) Å, b = 13.488(3) Å, c = 19.220(4) Å, α = 90.221(3)°, β = 92.188(3)°, γ = 108.966(3)°, V = 2962.8(10) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0624, wRref(F2) = 0.1622, T = 296(2) K.
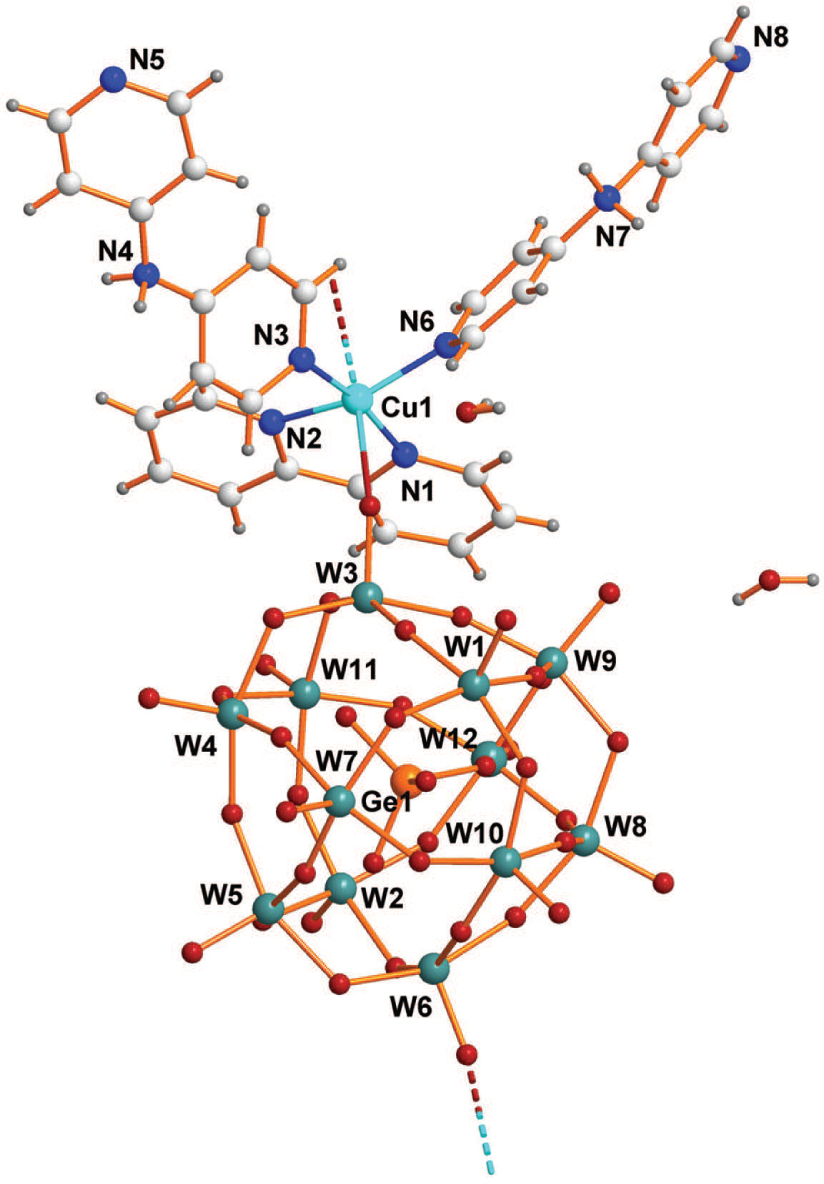
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Source of material
A mixture of K4[GeW12O40] ⋅ 14H2O (0.1 mmol), CuCl2 ⋅ 2 H2O (0.2 mmol), 4,4′-dipyridylamine (0.1 mmol), 2,2′-bipyridine (0.1 mmol), and H2O (10 mL) was stirred for 30 min at 25 °C, after the pH value of the solution was adjusted to 5.0 with diluted NaOH solution and then transferred to a 23 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel reactor. The solution was heated under autogenous pressure at 160 °C for 96 h. After the solution was slowly cooled to room termperature at a rate of 10 °C h−1, blue block-shaped crystals were filtered off, washed with distilled water and dried in air.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Blue block |
| Size: | 0.18 × 0.12 × 0.09 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 24.1 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 26.9°, 98% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 16457, 11935, 0.050 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 8794 |
| N(param)refined: | 848 |
| Programs: | Olex2 [1], SHELX [2] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 0.40968(6) | 1.01560(6) | 0.25592(3) | 0.01614(17) |
| W2 | 0.18792(7) | 1.43847(6) | 0.21179(4) | 0.02087(18) |
| W3 | 0.09213(6) | 0.96399(6) | 0.21505(4) | 0.01726(18) |
| W4 | 0.15391(6) | 1.11328(6) | 0.07249(3) | 0.01787(18) |
| W5 | 0.35750(6) | 1.38706(6) | 0.08883(3) | 0.01868(18) |
| W6 | 0.47650(7) | 1.48535(6) | 0.24480(4) | 0.02123(18) |
| W7 | 0.47307(6) | 1.16409(6) | 0.11303(3) | 0.01614(17) |
| W8 | 0.40702(7) | 1.32170(6) | 0.40380(3) | 0.02084(18) |
| W9 | 0.22299(6) | 1.07260(6) | 0.38941(3) | 0.01743(18) |
| W10 | 0.59278(6) | 1.26331(6) | 0.26990(4) | 0.01994(18) |
| W11 | −0.01308(6) | 1.16422(6) | 0.19447(4) | 0.02128(19) |
| W12 | 0.11872(7) | 1.27214(6) | 0.36868(4) | 0.02035(18) |
| Ge1 | 0.28985(15) | 1.22169(14) | 0.23592(8) | 0.0137(4) |
| Cu1 | −0.1781(2) | 0.71904(18) | 0.24552(10) | 0.0222(5) |
| O1 | 0.0130(10) | 1.1382(10) | 0.0991(5) | 0.019(3) |
| O2 | 0.3809(12) | 1.4366(10) | 0.0076(6) | 0.028(3) |
| O3 | 0.2305(12) | 1.2607(11) | 0.0684(6) | 0.026(3) |
| O4 | 0.1674(10) | 1.1406(10) | 0.1921(5) | 0.018(3) |
| O5 | 0.5168(11) | 1.2745(11) | 0.3526(6) | 0.025(3) |
| O6 | 0.3443(11) | 1.0426(10) | 0.3399(6) | 0.023(3) |
| O7 | 0.4055(10) | 1.1774(10) | 0.2224(5) | 0.017(2) |
| O8 | 0.2496(10) | 0.9670(9) | 0.2173(5) | 0.016(3) |
| O9 | 0.0262(10) | 1.1958(10) | 0.2914(6) | 0.021(3) |
| O10 | 0.2617(12) | 1.3420(10) | 0.4228(6) | 0.024(3) |
| O11 | 0.2681(10) | 1.2224(9) | 0.3232(5) | 0.011(2) |
| O12 | 0.3434(11) | 1.1806(11) | 0.4410(5) | 0.022(3) |
| O13 | 0.4348(11) | 1.4305(10) | 0.3358(6) | 0.025(3) |
| O14 | 0.3202(10) | 1.3463(9) | 0.2051(5) | 0.012(2) |
| O15 | 0.3108(10) | 1.1020(10) | 0.0848(5) | 0.018(3) |
| O16 | 0.2449(11) | 1.4525(9) | 0.1168(6) | 0.018(3) |
| O17 | 0.4319(12) | 0.8980(10) | 0.2722(6) | 0.026(3) |
| O18 | 0.5573(11) | 1.1148(11) | 0.2860(6) | 0.026(3) |
| O19 | 0.1105(13) | 1.5242(11) | 0.2087(7) | 0.033(3) |
| O20 | 0.4768(10) | 1.4895(10) | 0.1453(6) | 0.022(3) |
| O21 | 0.4586(10) | 1.0342(10) | 0.1623(5) | 0.018(3) |
| O22 | 0.0968(10) | 0.9763(9) | 0.1160(5) | 0.018(3) |
| O23 | −0.0336(11) | 1.0168(10) | 0.2116(6) | 0.023(3) |
| O24 | 0.0164(11) | 0.8330(11) | 0.2229(6) | 0.028(3) |
| O25 | 0.1244(11) | 1.0087(10) | 0.3113(5) | 0.019(3) |
| O26 | 0.1892(12) | 0.9760(10) | 0.4489(6) | 0.026(3) |
| O27 | 0.4502(10) | 1.2940(10) | 0.0954(5) | 0.018(3) |
| O28 | 0.5638(10) | 1.3897(10) | 0.2425(5) | 0.018(3) |
| O29 | 0.6079(11) | 1.2349(10) | 0.1724(5) | 0.019(3) |
| O30 | 0.5372(11) | 1.1427(11) | 0.0396(6) | 0.028(3) |
| O31 | 0.3420(12) | 1.5301(10) | 0.2419(6) | 0.029(3) |
| O32 | 0.5844(11) | 1.6026(10) | 0.2656(6) | 0.028(3) |
| O33 | 0.4913(12) | 1.3828(11) | 0.4738(6) | 0.030(3) |
| O34 | 0.1134(11) | 1.1435(11) | 0.4124(6) | 0.025(3) |
| O35 | 0.1223(10) | 1.0781(11) | −0.0118(6) | 0.027(3) |
| O36 | 0.7344(13) | 1.3097(12) | 0.2969(7) | 0.034(3) |
| O37 | −0.1555(12) | 1.1621(12) | 0.1871(7) | 0.038(4) |
| O38 | 0.0714(11) | 1.3092(10) | 0.1816(6) | 0.021(3) |
| O39 | 0.0164(13) | 1.3026(12) | 0.4171(7) | 0.037(4) |
| O40 | 0.1674(10) | 1.3857(10) | 0.3036(6) | 0.020(3) |
| N1 | −0.1850(14) | 0.8330(13) | 0.3089(7) | 0.025(3) |
| N2 | −0.2759(13) | 0.7797(12) | 0.1849(7) | 0.019(3) |
| N3 | −0.1527(14) | 0.6235(13) | 0.1706(7) | 0.024(4) |
| N4 | −0.1713(15) | 0.4420(13) | −0.0078(7) | 0.028(4) |
| H4A | −0.2234 | 0.4606 | −0.0339 | 0.033* |
| H4B | −0.1033 | 0.4686 | −0.0281 | 0.033* |
| N5 | −0.2633(18) | 0.1220(17) | −0.0528(9) | 0.044(4) |
| N6 | −0.1455(15) | 0.6313(13) | 0.3237(7) | 0.026(4) |
| N7 | −0.1352(15) | 0.4036(14) | 0.4674(8) | 0.030(3) |
| H7A | −0.1417 | 0.3483 | 0.4401 | 0.036* |
| H7B | −0.0613 | 0.4256 | 0.4838 | 0.036* |
| N8 | −0.327(2) | 0.2658(16) | 0.6375(10) | 0.055(6) |
| C1 | −0.3266(19) | 0.7417(17) | 0.1226(9) | 0.032(5) |
| H1 | −0.3170 | 0.6808 | 0.1050 | 0.038* |
| C2 | −0.3943(19) | 0.7913(18) | 0.0827(9) | 0.031(5) |
| H2 | −0.4349 | 0.7606 | 0.0419 | 0.037* |
| C3 | −0.3977(17) | 0.8887(17) | 0.1074(10) | 0.030(4) |
| H3 | −0.4348 | 0.9270 | 0.0808 | 0.036* |
| C4 | −0.3447(18) | 0.9271(16) | 0.1721(10) | 0.029(5) |
| H4 | −0.3480 | 0.9906 | 0.1892 | 0.034* |
| C5 | −0.2859(16) | 0.8697(15) | 0.2119(8) | 0.021(4) |
| C6 | −0.2352(15) | 0.9001(15) | 0.2802(8) | 0.020(4) |
| C7 | −0.241(2) | 0.989(2) | 0.3176(11) | 0.047(6) |
| H7 | −0.2805 | 1.0324 | 0.2992 | 0.056* |
| C8 | −0.184(2) | 1.008(2) | 0.3851(10) | 0.043(6) |
| H8 | −0.1851 | 1.0654 | 0.4117 | 0.051* |
| C9 | −0.1264(18) | 0.9431(18) | 0.4106(9) | 0.032(5) |
| H9 | −0.0881 | 0.9559 | 0.4543 | 0.038* |
| C10 | −0.1262(17) | 0.8612(18) | 0.3721(8) | 0.030(5) |
| H10 | −0.0831 | 0.8199 | 0.3893 | 0.036* |
| C11 | −0.1970(16) | 0.5215(16) | 0.1738(10) | 0.029(5) |
| H11 | −0.2267 | 0.4933 | 0.2159 | 0.035* |
| C12 | −0.2031(18) | 0.4530(18) | 0.1199(9) | 0.030(4) |
| H12 | −0.2342 | 0.3808 | 0.1251 | 0.036* |
| C13 | −0.1589(16) | 0.4981(15) | 0.0545(8) | 0.019(4) |
| C14 | −0.1068(16) | 0.6071(15) | 0.0528(9) | 0.021(4) |
| H14 | −0.0718 | 0.6384 | 0.0126 | 0.026* |
| C15 | −0.1073(16) | 0.6674(15) | 0.1096(8) | 0.022(4) |
| H15 | −0.0760 | 0.7399 | 0.1069 | 0.027* |
| C16 | −0.209(2) | 0.1581(19) | 0.0075(13) | 0.045(6) |
| H16 | −0.1912 | 0.1117 | 0.0380 | 0.055* |
| C17 | −0.178(2) | 0.2648(19) | 0.0272(11) | 0.037(5) |
| H17 | −0.1415 | 0.2870 | 0.0706 | 0.045* |
| C18 | −0.2013(17) | 0.3362(15) | −0.0166(8) | 0.022(4) |
| C19 | −0.256(2) | 0.293(2) | −0.0839(10) | 0.042(6) |
| H19 | −0.2717 | 0.3373 | −0.1171 | 0.051* |
| C20 | −0.283(2) | 0.191(2) | −0.0982(12) | 0.050(6) |
| H20 | −0.3166 | 0.1656 | −0.1417 | 0.060* |
| C21 | −0.0608(16) | 0.5881(15) | 0.3251(9) | 0.021(4) |
| H21 | −0.0039 | 0.6086 | 0.2921 | 0.025* |
| C22 | −0.0533(18) | 0.5168(17) | 0.3716(10) | 0.031(5) |
| H22 | 0.0087 | 0.4903 | 0.3718 | 0.037* |
| C23 | −0.1418(17) | 0.4828(16) | 0.4201(10) | 0.026(4) |
| C24 | −0.2356(18) | 0.5229(18) | 0.4171(9) | 0.039(6) |
| H24 | −0.2974 | 0.4978 | 0.4466 | 0.047* |
| C25 | −0.235(2) | 0.5990(18) | 0.3704(10) | 0.038(5) |
| H25 | −0.2944 | 0.6291 | 0.3697 | 0.045* |
| C26 | −0.261(2) | 0.219(2) | 0.6012(12) | 0.054(6) |
| H26 | −0.2572 | 0.1547 | 0.6159 | 0.065* |
| C27 | −0.203(3) | 0.263(2) | 0.5454(13) | 0.069(10) |
| H27 | −0.1641 | 0.2261 | 0.5204 | 0.083* |
| C28 | −0.1986(18) | 0.3617(17) | 0.5240(9) | 0.028(4) |
| C29 | −0.259(2) | 0.4105(17) | 0.5635(8) | 0.035(5) |
| H29 | −0.2556 | 0.4784 | 0.5524 | 0.042* |
| C30 | −0.323(3) | 0.363(2) | 0.6190(10) | 0.058(8) |
| H30 | −0.3642 | 0.3979 | 0.6437 | 0.070* |
| O1Wa | −0.463(3) | 0.888(3) | 0.4476(15) | 0.052(9) |
| H1WAa | −0.5044 | 0.8959 | 0.4797 | 0.077* |
| H1WBa | −0.4108 | 0.8663 | 0.4667 | 0.077* |
| O2Wa | 0.405(3) | 0.903(3) | 0.5585(15) | 0.061(10) |
| H2WAa | 0.4220 | 0.9063 | 0.6003 | 0.091* |
| H2WBa | 0.3719 | 0.9433 | 0.5382 | 0.091* |
aOccupancy: 0.5.
Experimental details
The Olex2 program equipped with SHELXT and SHELXL were used for structure analysis [1], [2]. All the non-hydrogen atoms were located by SHELXT directly and refined anisotropicly by SHELXL with least squares methods. All the hydrogens on N and C were placed at calculated positions (0.93 Å) and refined with the riding model, with Uiso(H) set to 1.2 Ueq(C) or 1.2 Ueq(N). The H atoms of the solvent water molecule were located from the difference Fourier map and then allowed to ride on their parent O atom in the final cycles of refinement with d(O–H) = 0.850 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq(O). The occupancies of water molecules were refined as 0.5.
Comment
The significant contemporary interest in the crystal engineering of inorganic-organic hybrid materials not only originates from their diversely structural flexibility, but also from their widely promising potential applications in catalysis, medicine, photochemistry and electromagnetism [3], [4], [5]. Up to now, although a number of inorganic-organic hybrid compounds containing polyoxomolybdates have been reported [6, 7] . Design and synthesis of novel hybrid materials with highly specific and cooperative functions are still a challenging work. A widely used approach to the synthesis of these materials is the hydrothermal crystallization in the presence of organic amines, which are used as templates or structure-directing agents to facilitate the formation of various networks [8, 9] .
The title crystal structure is composed of [GeW12O40]4− Keggin-type polyoxoanions, [Cu(C10H8N2)(C10H10N3)2]4+ copper complex cations and water molecules. The polyoxoanion [GeW12O40]4− is a well known α-Keggin structure composed of 12 corner- or edge-sharing WO6 octahedra with the central germanium ordered and coordinated to four oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral fashion (cf. the figure). The Ge—O distances are in the range of 1.708(9)–1.718(11) Å and the O—Ge—O angles are in the range of 108.9(5)–110.5(5)°. The W—O distances can be grouped into three sets according to the kind of oxygen atoms bound to the tungsten atoms: W—Ot = 1.681(12)−1.726(13) Å, W—Ob = 1.877(12)−1.964(11) Å and W—Oc = 2.291(12)−2.331(12) Å. The O—W—O angles are between 71.2(5) and 170.6(5)° and are in accord with the literature [10]. In the copper complex [Cu(C10H8N2)(C10H10N3)2]4+, each of the Cu2+ is six-coordinated by two nitrogen atoms from two 4,4′-dipyridylaminium cations (dpa) (N3 and N6), two nitrogen atoms from one 2,2′-bipyridine molecule (bipy, N1 and N2) and two oxygen atoms from adjacent POMs anions (O24 and O32), respectively, resulting a distorted octahedral geometry. The Cu—O distances were in the ranges of 2.412(13)−2.833(14) Å, and the Cu—N distances ranges from 1.982(16) to 2.026(14) Å. The dpa and bpy molecules act as a monodentate and bidentate ligand respectively coordinated to a copper atom with its nitrogen atoms. The most remarkable structural feature of the title compound is that the adjacent Keggin [GeW12O40]4− clusters are interconnected through [Cu(C10H8N2)(C10H10N3)2]4+ bridging groups to form a one-dimensional infinite anionic chain (cf. the figure; dashed lines). Furthermore, the adjacent one-dimensional chains are linked up by extensive hydrogen bonding interactions of the polyoxoanions, 4,4′-dipyridylamine, 2,2′-bipyridine and lattice water molecules to form a three-dimensional supramolecules framework. There are three types of intermolecular hydrogen bonds (O—H⋯O, C—H⋯O, N—H⋯O).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Education Commission of Shaanxi Province (17JK0017), the Funded Projects of Ankang University (2013AYPYZR02, 2016AYQDZR13), and the training Programs of Innovation and Entrepreneurship of Ankang University Undergraduates (2016akxy038, 2017sxjy019).
References
Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H.: OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 42 (2009) 339–341.10.1107/S0021889808042726Search in Google Scholar
Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar
Dolbecq, A.; Dumas, E.; Mayer, C. R.; Mialane, P.: Hybrid organic-inorganic polyoxometalate compounds: from structural diversity to applications. Chem. Rev. 41 (2010) 6009–6048.10.1021/cr1000578Search in Google Scholar
Sun, C. Y.; Liu, S. X.; Liang, D. D.; Shao, K. Z.; Ren, Y. H.; Su, Z. M.: Highly stable crystalline catalysts based on a microporous metal organic framework and polyoxometalates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 (2009) 1883–1888.10.1021/ja807357rSearch in Google Scholar
Mitchell, S. G.; Streb, C.; Miras, H. N.; Boyd, T.; Long, D. L.; Cronin, L.: Face-directed self-assembly of an electronically active Archimedean polyoxometalate architecture. Nat. Chem. 2 (2010) 308–312.10.1038/nchem.581Search in Google Scholar
Hagrman, P. J.; Hagrman, D.; Zubieta, J.: Organic-inorganic hybrid materials: from “simple” coordination polymers to organodiamine-templated molybdenum oxides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 38 (1999) 2638–2684.10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19990917)38:18<2638::AID-ANIE2638>3.0.CO;2-4Search in Google Scholar
Dolbecq, A.; Mialane, P.; Lisnard, L.; Marrot, J.; Secheresse, F.: Hybrid organic-inorganic 1D and 2D frameworks with epsilon-Keggin polyoxomolybdates as building blocks. Chem. Eur. J. 9 (2003) 2914–2920.10.1002/chem.200204670Search in Google Scholar
Liu, X. Y.; Ma, X. H.; Cen, P. P.; Wu, Y. W.; Zhang, C. C.; Shi, Q.; Song, W. M.; Xie, G.; Chen, S. P.: A substituent effect of phenylacetic acid coligand perturbed structures and magnetic properties observed in two triple-bridged azido-Cu(II) chain compounds with ferromagnetic ordering and slow magnetic relaxation. Dalton Trans. 46 (2017) 7556–7566.10.1039/C7DT01338HSearch in Google Scholar
Lin, Z. E.; Yao, Y. W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G. Y.: Isolation of a monomeric hybrid zinc phosphateand its one-dimensional relative. Dalton Trans. 32 (2003) 3160–3164.10.1039/b304778dSearch in Google Scholar
Han, Q.-X.; Wang, J.-P.; Song, L.-H.: K2NaH[GeW12O40] ⋅ 7H2O, with a Keggin-type heteropolyoxoanion. Acta Crystallogr. E 62 (2006) i201–i203.10.1107/S1600536806034362Search in Google Scholar
©2018 Li-Zhou Wu, published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of di-μ2-aqua-tetraaqua-bis(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)disodium(I) C18H24N6Na2O10
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2-bromo-4-chloro-6-formylphenolato-κ2O,O′)cobalt(II), C16H16Cl2CrN3O7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-(4-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl)ethan-1-one-κ2N:O)-bis(1,1,1-trifluoro-4-oxo-4-(thiophen-2-yl)but-2-en-2-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II)], C27H18CuF6N2O5S2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carboxylate, C18H15F2NO5
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-dimethoxy-2,2′-[1,1′-(ethylenedioxydinitrilo)diethylidyne]diphenol, C20H24N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H14Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,3,9,10,16,17,23,24-octakis(2,6-dimethylphenoxy)phthalocyanine - trichloromethane (1/2), C98H84Cl6N8O8
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-((1-(2-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methoxy)-1-naphthoate, C24H21N3O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3,3′-thiodipropionato-κ2O:O′)-(bipyridine-κ2N,N′)copper(II)] C16H16CuN2O4S
- Crystal structure of [4-chloro-2-(((2-((3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)phenyl)imino)(phenyl)methyl)phenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′}nickel(II) - ethyl acetate (1/1), C32H29ClN2NiO5
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C29H52Cl2N4NiO9
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carboxylate, C20H21NO5
- Structure and photochromism of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(3-quinolyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C33H20F6N2S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3,5-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoate-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II))] 2.5 hydrate, C22H23CoN12O8.50
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(1,3-dimesityl-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl)(morpholine-κN)palladium(IV), C25H33Cl2N3OPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(4,4′-dipyridylaminium-kN)-(μ2-germanowolframato-κ2O:O′)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)copper(II)] with a Keggin-type heteropolyoxoanion, [Cu(C10H8N2)(C10H10N3)2][GeW12O40] ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridin-1-ium-4-carbohydrazonate-κ3N,N′,O)-tris[nitrato-κ2O,O′)lanthanum(III), C12H15N8O12La
- The crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-4-((2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-3,6-dimethylbenzoyl)oxy)-3,6-dimethylbenzoic acid–methanol (1/1), C20H24O8
- Crystal structure of guanidinium tetrapropylammonium bis(hydrogencarbonate) dihydrate, C15H40N4O8
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-bromo-3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H27BrO2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)phenyl)acetic acid, C10H9N3O4
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazol-3-ium)bis(2-carboxybenzoate), C30H26N4O8
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(4,10-diphenyl-4,10-dihydropyreno[4,5-d:9,10-d′]diimidazole-5,11-diyl)bis(N,N-diphenylaniline), C66H44N6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C20H18CoN12O2
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide 1.5 hydrate, C20H22IN2O1.5
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromane, C16H16O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-carboxy-5-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-4-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)pyridine-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C18H12N4O8Zn
- Crystal structure of bis(1-((2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ2N:N′)tetraiodidodicadmium(II), [Cd2(C13H15N5)2I4]
- Crystal structure of tetramethylammonium bis(acetato-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ3-3-((hydroxyimino)methyl)-5-methoxy-2-oxidobenzoate-κ5O,O′:O′,N:O′′)tetrazinc(II) — N,N′-dimethylformamide — water (1/2/2), C62H96Zn4N10O28
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-5-tert-butylisophthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone-κO)zinc(II)] C17H22N2O5Zn
- Crystal structure of [tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′]-[(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,N)]cadmium(II)–methanol (1:3) C34H36CdN8O7
- The crystal structure of bis(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-amine-κN)-diiodidocadmium(II), C14H14CdI2N6
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(1H-benzimidazol-2-amine)-κN)-bis(μ2-sulfonato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C30H36N12O10S2Zn2
- Crystal structure of 3β-methoxy-20α-dimethylamino-pregn-5-ene, C24H41NO
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-oxydibenzoate, C16H14O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-3-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- Crystal structure of 4-((E)-((E)-5-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-oxopiperidin-3-ylidene)methyl)benzonitrile, C26H18F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetato-κ1O)-bis(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-one oxime-κ2N,N′)zinc(II), C18H22N4O6Zn
- The crystal structure of 9-butoxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2H-imidazo[1,5-a]quinolin-10-ium bromide, C17H21O2N2Br
- Crystal stucture of 2-(tert-butyl)-6-(hydroxymethyl)-4-methylphenol, C12H18O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(2-(5-chloroquinolin-8-yloxy)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethan-1-one-κ3N,O,O′)-(dinitrato-κ2O,O′)mercury(II)], C15H15N4O8ClHg
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (3aS,6R,6aS,7S)-1H,3H,6H,7H-3a,6:7,9a-diepoxybenzo[de]isochromene-3a1,6a-dicarboxylate, C16H16O7
- The crystal structure of 2-(dimethoxymethyl)-4-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-imidazole—petroleum ether-chloroform (3/1), C27H33Cl3N4O4
- Crystal structure of 8-(trifluoromethyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-carbaldehyde, C9H5F3N2O
- The crystal structure of N,N-diethyl-4,6-bis(naphthalen-2-yloxy)-1,3,5-triazin-2-amine, C27H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-7-chloro-3,3a-dihydrocyclopenta[b]chromen-1(2H)-one, C12H8BrClO2
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(4-fluorophenyl)methylene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H11F2N3S
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of di-μ2-aqua-tetraaqua-bis(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κN)disodium(I) C18H24N6Na2O10
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2-bromo-4-chloro-6-formylphenolato-κ2O,O′)cobalt(II), C16H16Cl2CrN3O7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-(4-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl)ethan-1-one-κ2N:O)-bis(1,1,1-trifluoro-4-oxo-4-(thiophen-2-yl)but-2-en-2-olato-κ2O,O′)copper(II)], C27H18CuF6N2O5S2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carboxylate, C18H15F2NO5
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-dimethoxy-2,2′-[1,1′-(ethylenedioxydinitrilo)diethylidyne]diphenol, C20H24N2O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C16H14Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,3,9,10,16,17,23,24-octakis(2,6-dimethylphenoxy)phthalocyanine - trichloromethane (1/2), C98H84Cl6N8O8
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-((1-(2-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methoxy)-1-naphthoate, C24H21N3O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3,3′-thiodipropionato-κ2O:O′)-(bipyridine-κ2N,N′)copper(II)] C16H16CuN2O4S
- Crystal structure of [4-chloro-2-(((2-((3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)phenyl)imino)(phenyl)methyl)phenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′}nickel(II) - ethyl acetate (1/1), C32H29ClN2NiO5
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate, C29H52Cl2N4NiO9
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carboxylate, C20H21NO5
- Structure and photochromism of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(3-quinolyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C33H20F6N2S2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3,5-di(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoate-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II))] 2.5 hydrate, C22H23CoN12O8.50
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(1,3-dimesityl-1H-3λ4-imidazol-2-yl)(morpholine-κN)palladium(IV), C25H33Cl2N3OPd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(4,4′-dipyridylaminium-kN)-(μ2-germanowolframato-κ2O:O′)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)copper(II)] with a Keggin-type heteropolyoxoanion, [Cu(C10H8N2)(C10H10N3)2][GeW12O40] ⋅ H2O
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)pyridin-1-ium-4-carbohydrazonate-κ3N,N′,O)-tris[nitrato-κ2O,O′)lanthanum(III), C12H15N8O12La
- The crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-4-((2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-3,6-dimethylbenzoyl)oxy)-3,6-dimethylbenzoic acid–methanol (1/1), C20H24O8
- Crystal structure of guanidinium tetrapropylammonium bis(hydrogencarbonate) dihydrate, C15H40N4O8
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-bromo-3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H27BrO2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)phenyl)acetic acid, C10H9N3O4
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazol-3-ium)bis(2-carboxybenzoate), C30H26N4O8
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(4,10-diphenyl-4,10-dihydropyreno[4,5-d:9,10-d′]diimidazole-5,11-diyl)bis(N,N-diphenylaniline), C66H44N6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5-(3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)phenyl)tetrazol-2-ido-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C20H18CoN12O2
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-2-(p-tolyl)-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide 1.5 hydrate, C20H22IN2O1.5
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromane, C16H16O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-2-carboxy-5-nitroisophthalato-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-4-((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)pyridine-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C18H12N4O8Zn
- Crystal structure of bis(1-((2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ2N:N′)tetraiodidodicadmium(II), [Cd2(C13H15N5)2I4]
- Crystal structure of tetramethylammonium bis(acetato-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ3-3-((hydroxyimino)methyl)-5-methoxy-2-oxidobenzoate-κ5O,O′:O′,N:O′′)tetrazinc(II) — N,N′-dimethylformamide — water (1/2/2), C62H96Zn4N10O28
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-5-tert-butylisophthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)-(1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone-κO)zinc(II)] C17H22N2O5Zn
- Crystal structure of [tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′]-[(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ2O,N)]cadmium(II)–methanol (1:3) C34H36CdN8O7
- The crystal structure of bis(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-amine-κN)-diiodidocadmium(II), C14H14CdI2N6
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(1H-benzimidazol-2-amine)-κN)-bis(μ2-sulfonato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II) - methanol (1/1), C30H36N12O10S2Zn2
- Crystal structure of 3β-methoxy-20α-dimethylamino-pregn-5-ene, C24H41NO
- Crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-oxydibenzoate, C16H14O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-3-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- Crystal structure of 4-((E)-((E)-5-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-4-oxopiperidin-3-ylidene)methyl)benzonitrile, C26H18F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure of bis(acetato-κ1O)-bis(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-one oxime-κ2N,N′)zinc(II), C18H22N4O6Zn
- The crystal structure of 9-butoxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2H-imidazo[1,5-a]quinolin-10-ium bromide, C17H21O2N2Br
- Crystal stucture of 2-(tert-butyl)-6-(hydroxymethyl)-4-methylphenol, C12H18O2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(2-(5-chloroquinolin-8-yloxy)-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethan-1-one-κ3N,O,O′)-(dinitrato-κ2O,O′)mercury(II)], C15H15N4O8ClHg
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (3aS,6R,6aS,7S)-1H,3H,6H,7H-3a,6:7,9a-diepoxybenzo[de]isochromene-3a1,6a-dicarboxylate, C16H16O7
- The crystal structure of 2-(dimethoxymethyl)-4-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-imidazole—petroleum ether-chloroform (3/1), C27H33Cl3N4O4
- Crystal structure of 8-(trifluoromethyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-carbaldehyde, C9H5F3N2O
- The crystal structure of N,N-diethyl-4,6-bis(naphthalen-2-yloxy)-1,3,5-triazin-2-amine, C27H24N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5-bromo-7-chloro-3,3a-dihydrocyclopenta[b]chromen-1(2H)-one, C12H8BrClO2
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(4-fluorophenyl)methylene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H11F2N3S


