Crystal structure of N1,N2-bis(2-fluorobenzyl)benzene-1,2-diamine,C20H18F2N2
-
Zhi Wei Ning
Abstract
C20H18F2N2, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 12.4233(11) Å, b = 7.3805(7) Å, c = 18.9531(16) Å, β = 104.109(3)°, V = 104.109(3) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0464, wRref(F2) = 0.1201, T = 296(2) K.
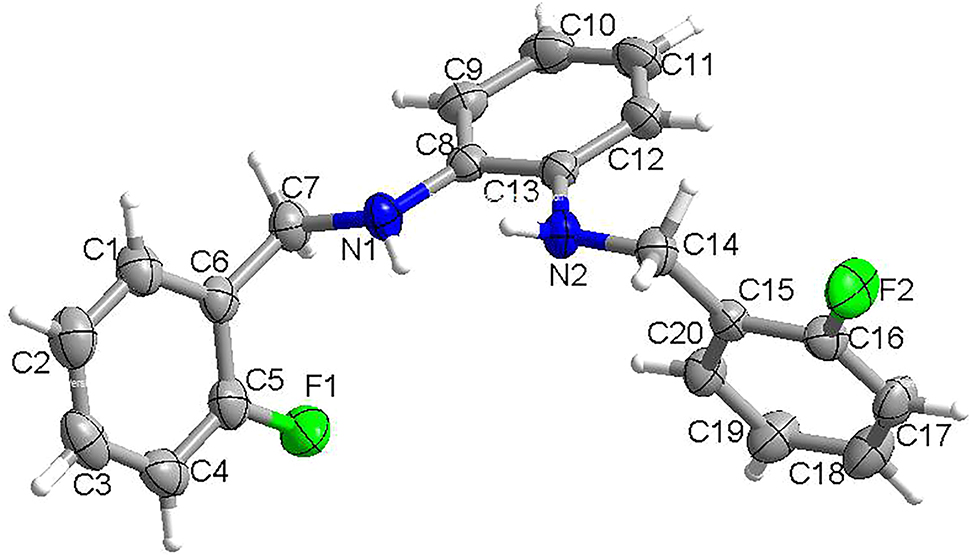
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless prism |
| Size: | 0.42 × 0.38 × 0.35 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.09 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SMART, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.0°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 8005, 2957, 0.104 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1455 |
| N(param)refined: | 236 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], [3], Olex2 [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.1777 (3) | 0.4570 (5) | 0.55252 (15) | 0.0748 (8) |
| H1a | 0.1486 | 0.5423 | 0.5788 | 0.090* |
| C2 | 0.1201 (3) | 0.2998 (5) | 0.53252 (16) | 0.0874 (10) |
| H2 | 0.0527 | 0.2806 | 0.5445 | 0.105* |
| C3 | 0.1624 (3) | 0.1705 (5) | 0.49465 (15) | 0.0862 (10) |
| H3 | 0.1244 | 0.0624 | 0.4813 | 0.103* |
| C4 | 0.2623 (3) | 0.2024 (4) | 0.47644 (14) | 0.0792 (9) |
| H4 | 0.2912 | 0.1173 | 0.4499 | 0.095* |
| C5 | 0.3174 (3) | 0.3599 (5) | 0.49794 (14) | 0.0701 (8) |
| H5b | 0.3855 | 0.3780 | 0.4869 | 0.084* |
| C6 | 0.2772 (2) | 0.4947 (4) | 0.53542 (12) | 0.0591 (7) |
| C7 | 0.3394 (2) | 0.6679 (4) | 0.55588 (12) | 0.0676 (8) |
| H7A | 0.3716 | 0.7063 | 0.5166 | 0.081* |
| H7B | 0.2886 | 0.7616 | 0.5634 | 0.081* |
| C8 | 0.5056 (2) | 0.7805 (4) | 0.64599 (12) | 0.0508 (6) |
| C9 | 0.4969 (2) | 0.9535 (4) | 0.61579 (13) | 0.0659 (8) |
| H9 | 0.4365 | 0.9826 | 0.5778 | 0.079* |
| C10 | 0.5774 (3) | 1.0823 (4) | 0.64200 (17) | 0.0771 (9) |
| H10 | 0.5709 | 1.1975 | 0.6215 | 0.093* |
| C11 | 0.6665 (3) | 1.0414 (4) | 0.69791 (18) | 0.0805 (9) |
| H11 | 0.7205 | 1.1287 | 0.7152 | 0.097* |
| C12 | 0.6766 (2) | 0.8709 (4) | 0.72870 (14) | 0.0660 (7) |
| H12 | 0.7375 | 0.8445 | 0.7667 | 0.079* |
| C13 | 0.5976 (2) | 0.7386 (3) | 0.70390 (12) | 0.0510 (6) |
| C14 | 0.7040 (2) | 0.5046 (3) | 0.78625 (12) | 0.0603 (7) |
| H14A | 0.6874 | 0.3922 | 0.8079 | 0.072* |
| H14B | 0.7201 | 0.5955 | 0.8244 | 0.072* |
| C15 | 0.8058 (2) | 0.4773 (3) | 0.75771 (11) | 0.0489 (6) |
| C16 | 0.9073 (2) | 0.4380 (4) | 0.80387 (12) | 0.0613 (7) |
| C17 | 1.0027 (2) | 0.4067 (4) | 0.78206 (15) | 0.0778 (9) |
| H17 | 1.0687 | 0.3803 | 0.8159 | 0.093* |
| C18 | 0.9990 (3) | 0.4149 (4) | 0.70898 (16) | 0.0838 (9) |
| H18 | 1.0627 | 0.3954 | 0.6925 | 0.101* |
| C19 | 0.9000 (3) | 0.4524 (4) | 0.66086 (14) | 0.0755 (9) |
| H19 | 0.8967 | 0.4566 | 0.6113 | 0.091* |
| C20 | 0.8048 (2) | 0.4841 (3) | 0.68435 (13) | 0.0609 (7) |
| H20 | 0.7389 | 0.5104 | 0.6504 | 0.073* |
| F1a | 0.4115 (3) | 0.3927 (5) | 0.48346 (14) | 0.0980 (14) |
| F1Ab | 0.1450 (4) | 0.5726 (6) | 0.5906 (3) | 0.113 (2) |
| F2 | 0.91046 (14) | 0.4293 (2) | 0.87692 (7) | 0.0986 (6) |
| N1 | 0.42681 (18) | 0.6445 (4) | 0.62191 (10) | 0.0590 (6) |
| H1A | 0.454 (2) | 0.539 (4) | 0.6348 (14) | 0.079 (10)* |
| N2 | 0.6066 (2) | 0.5608 (3) | 0.73116 (11) | 0.0560 (6) |
| H2A | 0.545 (3) | 0.527 (4) | 0.7344 (15) | 0.092 (11)* |
a Occupancy: 0.579(5), b Occupancy: 0.421(5).
Source of material
A mixture of o-phenylene diamine (0.541 g, 5 mmol), 1-bromopropane (0.615 g, 5 mmol) and potassium carbonate (0.828 g, 6 mmol) was stirred in ethanol at room temperature. After the reaction was completed (monitored by TLC, eluent, dichloromethane/petroleum ether, 1/1, v/v), the solvent was removed and the residue was extracted with dichloromethane (3 × 40 mL), dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and purified by silica gel column chromatography (eluent, dichloromethane/petroleum ether, 1/1, v/v) to afford the white solid. Yield, 645 mg, 40%. The title compound was dissolved in dichloromethane, and the solvent was evaporated slowly at room temperature. After three days, colorless crystals were obtained.
Experimental details
Data reduction was carried out using SAINT+ and SADABS [1]. The structure was determined by intrinsic phasing routines in the SHELXT program [2] and refined by full-matrix least-squares methods in SHELXL [3] by using Olex 2 [4]. All of the hydrogen atoms were placed in the calculated positions.
Comment
Phenylamine derivatives are an important class of organic compounds, which have a wide range of applications in medicine and chemical industry [5], [6]. For instance, phenylamines are widely used as antimicrobial drugs, anti-inflammatory analgesics and antilipemic drugs in the field of medicine, and as insecticides and fungicides in the field of pesticides [7]. Additionally, phenylamines can also be used to synthesize some important medicinal intermediates and other chemicals with important application value in organic synthesis [8]. Although N1,N2-bis(2-fluorobenzyl)benzene-1,2-diamine is a known compound, its crystal structure has not been reported yet. Therefore, in consideration of the importance of this compound it was synthesized form commercial material, and also its crystal structure will be reported.
There is one molecule in the asymmetric unit (see the Figure). The bond lengths and angles in the title molecule are in normal ranges. In a word, the title compound was synthesized under mild conditions, which can be readily used as a key intermediate to develop new drugs, novel reagents and advanced materials.
Funding source: Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation
Award Identifier / Grant number: ZR2020QB167
Funding source: Key Research and Development project of Shandong Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2019GSF108216
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
Research funding: This work was supported by Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2020QB167) and Key Research and Development project of Shandong Province (No. 2019GSF108216).
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. SAINT+, version 7.60A (Includes XPREP and SADABS); Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
5. Lezama, J. O. G., Iriarte, A. G., Domínguez, R. E., Robles, N. L. Study of the structural and conformational properties of fluoro-substituted thioacetanilide derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1222, 128768; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128768.Search in Google Scholar
6. Giese, S., Klimov, K., Mikeházi, A., Kelemen, Z., Frost, D. S., Steinhauer, S., Müller, P., Nyulászi, L., Müller, C. 2-(Dimethylamino)phosphinine: a phosphorus-containing aniline derivative. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 60, 3581–3586; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202014423.Search in Google Scholar
7. Saad, M. M. I., Fumio, M. Influence of pesticides and neuroactive amines on cAMP levels of two-spotted spider mite (Acari: Tetranychidae). Insect Biochem. 2016, 19, 715–722.10.1016/0020-1790(89)90051-6Search in Google Scholar
8. Kesavan, S., Kumar, D. R., Baynosa, M. L., Shim, J. J. Potentiodynamic formation of diaminobenzene films on an electrochemically reduced graphene oxide surface: determination of nitrite in water samples. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 85, 97–106; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.12.004.Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Zhi Wei Ning et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-aqua-tetraaqua-(μ3-glutarato-κ4O,O′:O′:O′′)-(μ5-glutarato-κ6O:O,O′:O′:O′′:O′′′)distrontium(II)], C10H22O13Sr2
- The crystal structure of acetato-κ1O-{(2-(2-(2-aminophenoxy)ethoxy)phenyl)(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)amido-κ2N,N′,O}copper(II), C26H26CuN2O5
- Crystal structure of dimethanolato-k2O:O-bis(1-((2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κN)-bis(thiocyanato-κN)dicopper(II), C34H32Cu2N12O2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-(pyrimidin-5-yl)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, [Co(C11H11O2N2)2(H2O)2]
- Crystal structure of bis(3,3-dimethyl-1-phenylbut-1-en-2-yl)(trimethylsilyl)amido-k1N)zinc(II), Zn(C15H24NSi)2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-methanolato-κ2O:O)-(μ2-1-((2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ2N:N′)-(thiocyanato-κ1N)copper(II)] 0.25 hydrate, C17H16CuN6OS ⋅ 0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-5-nitroanilinium iodide monohydrate, C6H8IN3O2
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium perchlorate monohydrate, C6H9ClN2O7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-2,4-dimethoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene from Arundina graminifolia, C16H16O3
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E, 1′E)-(((1R, 2R)-1,2-diphenylethane-1,2-diyl) bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-ethylphenol), C32H32N2O2
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide monohydrate, C6H9IN2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C16H11BF2N2
- Crystal structure of bis{(2-pyridinyl)-1-phenyl-1-isopropylmethanolato-κ2N,O}nickel, C30H32N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of poly[(m3-3-carboxyadamantane-1-carboxylato-κ3O:O′:O″)-(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)sodium(II)], C24H23N2NaO4
- Crystal structure of 2-phenylethynyl-1,3,6,8-tetramethylBOPHY (BOPHY = bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine), C22H20B2F4N4
- Crystal structure of 4-tert-butyl-2-N-(2-pyridylmethyl)aminophenol, C16H20N2O
- The crystal structure of (3Z,3′Z)-4,4′-((1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(azanediyl))bis(pent-3-en-2-one), C18H24N2O2
- Crystal structure of (morpholine-1-carbodithioato-κ2-S,S′)bis(triphenylphosphine-κ-P)gold(I), C41H38AuNOP2S2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(4-bromobenzyl)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C26H19Br2ClN2
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl (N′-benzoyl-N,N-diphenylcarbamimidothioato-κ2S,O)-(pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I) — methanol (1/1) C26H23O4N4SRe
- The crystal structure of Ba2Mn(SeO3)2Cl2 containing 1∞[Mn(SeO3)2Cl2]4− chains
- Crystal structure of 3,3′,3″-((1E,1′E,1″E)-((nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(azaneylylidene)) tris(methaneylylidene))tris(4-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde) monohydrate, C42H36N4O6·H2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(6-acetyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-yl)benzonitrile, C14H12N6O
- Crystal structure of benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18O5
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5-methyl-7-(4-(phenylthio)phenyl)-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C20H19N5O2S
- Crystal structure of N′,N‴-((propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2-diyl))bis(methaneylylidene))-di(isonicotinohydrazide)– water – dimethylformamide (1/4/2), C25H24N8O2·4H2O·2C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(2,4-dinitrophenoxy)benzaldehyde, C13H8N2O6
- The crystal structure of 1-dodecylpyridin-1-ium bromide monohydrate, C17H32BrNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(4-(dimethylamino)benzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium nitrate, C10H16N6O3
- Crystal structure of (E)-(2-((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazineyl)(amino)methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C6H12N6O4
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-propylimidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H60Cl2CuN12
- The crystal structure of bis{(μ2-3,3-dimethyl-1-phenylbut-1-en-2-yl)((dimethylamino)dimethylsilyl)amido-κ3N,N′:N′}dilithium, C32H54Li2N4Si2
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinin-2(3H)-yl)benzoate, C18H15BN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-(1-((2-chlorothiazol-5-yl)methyl)pyridin-2(1H)-ylidene)-2,2,2-trifluoroacetamide, C11H7ClF3N3OS
- Crystal structure of N′, N‴-((propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2-diyl))bis (methaneylylidene))di(picolinohydrazide) – water – methanol (1/1/1), C25H24N8O2·H2O·CH3OH
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-chloro-benzyl)-7-[4-(2-chloro-benzyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-5,6,8-trifluoro-3H-quinazolin-4-one, C26H21Cl2F3N4O
- Crystal structure of N1,N2-bis(2-fluorobenzyl)benzene-1,2-diamine,C20H18F2N2
- The crystal structure of 2-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C17H13BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methaneylylidene)) bis(2-bromo-4-nitrophenol) — dimethylsulfoxide (1/2), C14H8Br2N4O6⋅2(C2H6OS)
- Selective biocatalytic synthesis and crystal structure of (2R,6R)-hydroxyketaminium chloride, C13H17Cl2NO2
- Crystal structure of bis{tetraaqua-[μ3-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O′,O″] [μ2-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylate-κ3N,O:O]dicobalt(II)} dihydrate, C36H44Co4N8O26
- Crystal structure of diethyl-2,2′-naphthalene-2,3-diylbis(oxy)diacetate, C18H20O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxylato-κO,O′:O′;:O″, O″′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1Himidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C27H18CdN6O4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)benzoato-κ2O:O')zinc(II)], C32H30N4O8Zn
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho [1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C18H17BN2O2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)nickel(II) dichloride – 1-ethylimidazole (1/2), C40H64Cl2NiN16
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2,4-dinitrophenolato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) 1.5 hydrate, C12H13CuN4O13.5
- Crystal structure of N′,N‴-((1E,1′E)-((decane-1,10-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene)) bis(methaneylylidene))di(isonicotinohydrazide), C36H40N6O4
- The crystal structure of 2-[(R)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-2,3,7,7a-tetrahydro-3a,6-epoxyisoindol-1(6H)-one, C19H20NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (1E,2E)-3-(anthracen-9-yl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one oxime, C24H19NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (2E,2′E)-3,3′-(1,3-phenylene)bis(1-(3-bromophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one), C24H16Br2O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(µ2-1,2-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene- κ2N:N′)-bis(nitrato-κO)copper(II)], C28H28N10O6Cu
- Synthesis and crystal structure of the novel chiral acetyl-3-thiophene-5-(9-anthryl)-2-pyrazoline, C23H18N2OS
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(thiophen-3-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C9H11NOS
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-4-amino-4H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) copper(II)], C9H8N5O5CuI
- Crystal structure of cyclopropane-1,2,3-triyltris(phenylmethanone), C24H18O3
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(thioureido)methaniminium) terephthalate, C12H18N8O4S2
- A three-dimensional Eu(III) framework in the crystal structure of dimethylaminium poly[dimethylformamide-κ1N)bis(μ4-terephthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)europium(III)] monohydrate, C21H25EuN2O10
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxyphenyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H20O4
- The crystal structure of Hexakis(diethylamido)dimolybdenum, Mo2(NEt2)6
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-aqua-tetraaqua-(μ3-glutarato-κ4O,O′:O′:O′′)-(μ5-glutarato-κ6O:O,O′:O′:O′′:O′′′)distrontium(II)], C10H22O13Sr2
- The crystal structure of acetato-κ1O-{(2-(2-(2-aminophenoxy)ethoxy)phenyl)(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)amido-κ2N,N′,O}copper(II), C26H26CuN2O5
- Crystal structure of dimethanolato-k2O:O-bis(1-((2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κN)-bis(thiocyanato-κN)dicopper(II), C34H32Cu2N12O2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-(pyrimidin-5-yl)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, [Co(C11H11O2N2)2(H2O)2]
- Crystal structure of bis(3,3-dimethyl-1-phenylbut-1-en-2-yl)(trimethylsilyl)amido-k1N)zinc(II), Zn(C15H24NSi)2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-methanolato-κ2O:O)-(μ2-1-((2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ2N:N′)-(thiocyanato-κ1N)copper(II)] 0.25 hydrate, C17H16CuN6OS ⋅ 0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-5-nitroanilinium iodide monohydrate, C6H8IN3O2
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium perchlorate monohydrate, C6H9ClN2O7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-2,4-dimethoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene from Arundina graminifolia, C16H16O3
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E, 1′E)-(((1R, 2R)-1,2-diphenylethane-1,2-diyl) bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-ethylphenol), C32H32N2O2
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide monohydrate, C6H9IN2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C16H11BF2N2
- Crystal structure of bis{(2-pyridinyl)-1-phenyl-1-isopropylmethanolato-κ2N,O}nickel, C30H32N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of poly[(m3-3-carboxyadamantane-1-carboxylato-κ3O:O′:O″)-(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)sodium(II)], C24H23N2NaO4
- Crystal structure of 2-phenylethynyl-1,3,6,8-tetramethylBOPHY (BOPHY = bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine), C22H20B2F4N4
- Crystal structure of 4-tert-butyl-2-N-(2-pyridylmethyl)aminophenol, C16H20N2O
- The crystal structure of (3Z,3′Z)-4,4′-((1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(azanediyl))bis(pent-3-en-2-one), C18H24N2O2
- Crystal structure of (morpholine-1-carbodithioato-κ2-S,S′)bis(triphenylphosphine-κ-P)gold(I), C41H38AuNOP2S2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(4-bromobenzyl)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C26H19Br2ClN2
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl (N′-benzoyl-N,N-diphenylcarbamimidothioato-κ2S,O)-(pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I) — methanol (1/1) C26H23O4N4SRe
- The crystal structure of Ba2Mn(SeO3)2Cl2 containing 1∞[Mn(SeO3)2Cl2]4− chains
- Crystal structure of 3,3′,3″-((1E,1′E,1″E)-((nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(azaneylylidene)) tris(methaneylylidene))tris(4-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde) monohydrate, C42H36N4O6·H2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(6-acetyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-yl)benzonitrile, C14H12N6O
- Crystal structure of benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18O5
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5-methyl-7-(4-(phenylthio)phenyl)-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C20H19N5O2S
- Crystal structure of N′,N‴-((propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2-diyl))bis(methaneylylidene))-di(isonicotinohydrazide)– water – dimethylformamide (1/4/2), C25H24N8O2·4H2O·2C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(2,4-dinitrophenoxy)benzaldehyde, C13H8N2O6
- The crystal structure of 1-dodecylpyridin-1-ium bromide monohydrate, C17H32BrNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(4-(dimethylamino)benzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium nitrate, C10H16N6O3
- Crystal structure of (E)-(2-((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazineyl)(amino)methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C6H12N6O4
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-propylimidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H60Cl2CuN12
- The crystal structure of bis{(μ2-3,3-dimethyl-1-phenylbut-1-en-2-yl)((dimethylamino)dimethylsilyl)amido-κ3N,N′:N′}dilithium, C32H54Li2N4Si2
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinin-2(3H)-yl)benzoate, C18H15BN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-(1-((2-chlorothiazol-5-yl)methyl)pyridin-2(1H)-ylidene)-2,2,2-trifluoroacetamide, C11H7ClF3N3OS
- Crystal structure of N′, N‴-((propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2-diyl))bis (methaneylylidene))di(picolinohydrazide) – water – methanol (1/1/1), C25H24N8O2·H2O·CH3OH
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-chloro-benzyl)-7-[4-(2-chloro-benzyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-5,6,8-trifluoro-3H-quinazolin-4-one, C26H21Cl2F3N4O
- Crystal structure of N1,N2-bis(2-fluorobenzyl)benzene-1,2-diamine,C20H18F2N2
- The crystal structure of 2-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C17H13BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methaneylylidene)) bis(2-bromo-4-nitrophenol) — dimethylsulfoxide (1/2), C14H8Br2N4O6⋅2(C2H6OS)
- Selective biocatalytic synthesis and crystal structure of (2R,6R)-hydroxyketaminium chloride, C13H17Cl2NO2
- Crystal structure of bis{tetraaqua-[μ3-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O′,O″] [μ2-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylate-κ3N,O:O]dicobalt(II)} dihydrate, C36H44Co4N8O26
- Crystal structure of diethyl-2,2′-naphthalene-2,3-diylbis(oxy)diacetate, C18H20O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxylato-κO,O′:O′;:O″, O″′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1Himidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C27H18CdN6O4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)benzoato-κ2O:O')zinc(II)], C32H30N4O8Zn
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho [1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C18H17BN2O2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)nickel(II) dichloride – 1-ethylimidazole (1/2), C40H64Cl2NiN16
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2,4-dinitrophenolato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) 1.5 hydrate, C12H13CuN4O13.5
- Crystal structure of N′,N‴-((1E,1′E)-((decane-1,10-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene)) bis(methaneylylidene))di(isonicotinohydrazide), C36H40N6O4
- The crystal structure of 2-[(R)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-2,3,7,7a-tetrahydro-3a,6-epoxyisoindol-1(6H)-one, C19H20NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (1E,2E)-3-(anthracen-9-yl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one oxime, C24H19NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (2E,2′E)-3,3′-(1,3-phenylene)bis(1-(3-bromophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one), C24H16Br2O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(µ2-1,2-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene- κ2N:N′)-bis(nitrato-κO)copper(II)], C28H28N10O6Cu
- Synthesis and crystal structure of the novel chiral acetyl-3-thiophene-5-(9-anthryl)-2-pyrazoline, C23H18N2OS
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(thiophen-3-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C9H11NOS
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-4-amino-4H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) copper(II)], C9H8N5O5CuI
- Crystal structure of cyclopropane-1,2,3-triyltris(phenylmethanone), C24H18O3
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(thioureido)methaniminium) terephthalate, C12H18N8O4S2
- A three-dimensional Eu(III) framework in the crystal structure of dimethylaminium poly[dimethylformamide-κ1N)bis(μ4-terephthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)europium(III)] monohydrate, C21H25EuN2O10
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxyphenyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H20O4
- The crystal structure of Hexakis(diethylamido)dimolybdenum, Mo2(NEt2)6

