Abstract
[Co(C11H11O2N2)2(H2O)2], monoclinic,
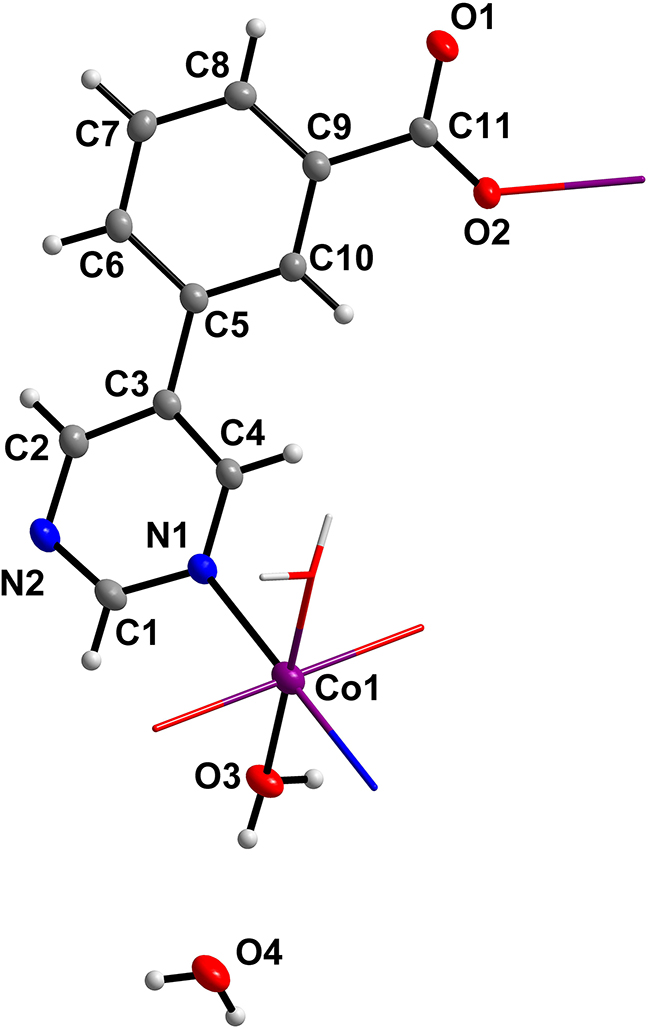
The asymmetric unit of the molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.13 × 0.11 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.82 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 28.3°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 6839, 2676, 0.018 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2340 |
| N(param)refined: | 172 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], [3], Diamond [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co1 | 0.500000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.02176 (9) |
| O1 | 0.85551 (13) | 0.61825 (15) | 0.62114 (7) | 0.0381 (3) |
| O2 | 0.61420 (13) | 0.55215 (14) | 0.63417 (7) | 0.0309 (2) |
| O3 | 0.30785 (14) | 0.05714 (15) | 1.04896 (8) | 0.0337 (3) |
| N1 | 0.58426 (15) | 0.23641 (14) | 1.02250 (8) | 0.0261 (3) |
| N2 | 0.66254 (16) | 0.42948 (16) | 1.13396 (8) | 0.0318 (3) |
| C1 | 0.59837 (18) | 0.29584 (18) | 1.10563 (10) | 0.0300 (3) |
| H1 | 0.559756 | 0.238383 | 1.147422 | 0.036* |
| C2 | 0.71720 (19) | 0.51054 (18) | 1.07325 (10) | 0.0295 (3) |
| H2 | 0.761698 | 0.605149 | 1.090892 | 0.035* |
| H3A | 0.273 (3) | 0.008 (2) | 1.0857 (15) | 0.044* |
| H3B | 0.240 (2) | 0.075 (2) | 1.0049 (15) | 0.044* |
| H4A | 0.089 (3) | −0.108 (2) | 1.1610 (14) | 0.044* |
| H4B | 0.225 (2) | −0.087 (3) | 1.2178 (14) | 0.044* |
| C3 | 0.71114 (17) | 0.46087 (17) | 0.98465 (10) | 0.0238 (3) |
| C4 | 0.64096 (17) | 0.31990 (17) | 0.96275 (9) | 0.0253 (3) |
| H4 | 0.632849 | 0.281685 | 0.904326 | 0.030* |
| C5 | 0.78163 (17) | 0.55104 (17) | 0.92096 (9) | 0.0231 (3) |
| C6 | 0.90470 (17) | 0.65317 (17) | 0.95550 (10) | 0.0259 (3) |
| H6 | 0.940460 | 0.664648 | 1.018269 | 0.031* |
| C7 | 0.97358 (17) | 0.73690 (18) | 0.89783 (10) | 0.0280 (3) |
| H7 | 1.052437 | 0.806847 | 0.921865 | 0.034* |
| C8 | 0.92587 (17) | 0.71724 (18) | 0.80447 (10) | 0.0278 (3) |
| H8 | 0.974695 | 0.771593 | 0.765835 | 0.033* |
| C9 | 0.80438 (17) | 0.61574 (17) | 0.76837 (9) | 0.0246 (3) |
| C10 | 0.73136 (17) | 0.53534 (17) | 0.82673 (10) | 0.0247 (3) |
| H10 | 0.647911 | 0.470317 | 0.802415 | 0.030* |
| C11 | 0.75461 (17) | 0.59345 (16) | 0.66665 (9) | 0.0251 (3) |
| O4 | 0.18901 (17) | −0.10870 (17) | 1.16861 (9) | 0.0438 (3) |
Source of material
All reagents and solvents employed were commercially available and used as received without further purification. The title compound was synthesized via the reaction of Co(NO3)2·6H2O (0.0125 mmol, 0.00375 g), 3-(pyrimidin-5-yl) benzoic acid (0.025 mmol, 0.005 g) in 1 mL dimethylformamide (DMF) and 0.5 mL water. The mixture was stirred for 0.5 h and then heated at 85 °C for 12 h to afford pink block crystals in a yield of 75%.
Experimental details
Hydrogen atoms were placed in their geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms.
Comment
2-D metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and coordination polymers (CP) have drawn tremendous attentions because of their great enormous potential applications in energy storage [5], [6], catalysis [7], as well as sensor [8].
In this work, we synthesize a 2D CP constructed by central Co ions and the 3-(pyrimidin-5-yl)benzoato (L) ligand under solvothermal conditions. L is an efficient ligand which contains benzoate and pyrimidine functional groups. Surprisingly, compounds based on HL are reported uncommonly.
The structure of this compound is centrosymmetric with Co2+ on the inversion center. The Co center is coordinated by two N atoms from two L and four O atoms from two L and two coordinated water molecules (see the Figure). The distances of Co–O bonds are 2.00443(11) Å, 2.0856(10) Å, and the distances of the Co–N bonds are 2.2043(13) Å. Interestingly, the dihedral angle between the benzene ring and the pyrimidine ring is 24.7°. What’s more, there are π⋯π stacking interactions between the aromatic rings, to construct a three-dimensional architecture. Finally, it should be mentioned that an isomorphous structure is already known [9].
Funding source: Anyang Institute of Technology
Award Identifier / Grant number: 21801005
Funding source: National Natural Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 21901008
Award Identifier / Grant number: 51672204
Funding source: Key Scientific Research Project Plan of Henan Province Colleges and Universities
Award Identifier / Grant number: 19A150012
Award Identifier / Grant number: 19A480003
Funding source: Scientific and Technological Project of Henan Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: 192102310232
Funding source: Initiation Funds for Postdoctoral Scientific Research Projects in Henan Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: 1901020
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
Research funding: Foundation of Anyang Institute of Technology, National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21801005, 21901008, 51672204), Key scientific Research Project Plan of Henan Province Colleges and Universities (19A150012, 19A480003), Scientific and Technological Project of Henan Province (192102310232) and Initiation Funds for Postdoctoral Scientific Research Projects in Henan Province (1901020).
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker, SAXI. SADABS Bruker; Bruker: Madison, 2008.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Brandenburg, K. DIAMOND. Visual crystal structure information system (Version 4.0); Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2015.Search in Google Scholar
5. Park, J., Lee, M., Feng, D., Huang, Z., Hinckley, A. C., Yakovenko, A., Zou, X., Cui, Y., Bao, Z. Stabilization of hexaaminobenzene in a 2D conductive metalâ organic framework for high power sodium storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10315–10323; https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b06020.Search in Google Scholar
6. Sheberla, D., Bachman, J. C., Elias, J. S., Sun, C.-J., Yang, S.-H., Dincǎ, M. Conductive MOF electrodes for stable supercapacitors with high areal capacitance. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 220–224; https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4766.Search in Google Scholar
7. Wright, A. M., Sun, C., Dincǎ, M. Thermal cycling of a MOF-based NO disproportionation catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 681–686; https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c12134.Search in Google Scholar
8. Wang, J., Liu, S., Luo, J., Hou, S., Song, H., Niu, Y., Zhang, C. Conductive metal-organic frameworks for amperometric sensing of paracetamol. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 594093; https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.594093.Search in Google Scholar
9. Wang, Y., Tian, Y., Luo, J.-H. Two new d10 metal-directed coordination polymers based on an unsymmetrical ligand 3-pyrimidin-5-ylbenzoic acid. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2011, 14, 1258–1261; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2011.04.036.Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Jing Wang et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-aqua-tetraaqua-(μ3-glutarato-κ4O,O′:O′:O′′)-(μ5-glutarato-κ6O:O,O′:O′:O′′:O′′′)distrontium(II)], C10H22O13Sr2
- The crystal structure of acetato-κ1O-{(2-(2-(2-aminophenoxy)ethoxy)phenyl)(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)amido-κ2N,N′,O}copper(II), C26H26CuN2O5
- Crystal structure of dimethanolato-k2O:O-bis(1-((2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κN)-bis(thiocyanato-κN)dicopper(II), C34H32Cu2N12O2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-(pyrimidin-5-yl)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, [Co(C11H11O2N2)2(H2O)2]
- Crystal structure of bis(3,3-dimethyl-1-phenylbut-1-en-2-yl)(trimethylsilyl)amido-k1N)zinc(II), Zn(C15H24NSi)2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-methanolato-κ2O:O)-(μ2-1-((2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ2N:N′)-(thiocyanato-κ1N)copper(II)] 0.25 hydrate, C17H16CuN6OS ⋅ 0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-5-nitroanilinium iodide monohydrate, C6H8IN3O2
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium perchlorate monohydrate, C6H9ClN2O7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-2,4-dimethoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene from Arundina graminifolia, C16H16O3
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E, 1′E)-(((1R, 2R)-1,2-diphenylethane-1,2-diyl) bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-ethylphenol), C32H32N2O2
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide monohydrate, C6H9IN2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C16H11BF2N2
- Crystal structure of bis{(2-pyridinyl)-1-phenyl-1-isopropylmethanolato-κ2N,O}nickel, C30H32N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of poly[(m3-3-carboxyadamantane-1-carboxylato-κ3O:O′:O″)-(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)sodium(II)], C24H23N2NaO4
- Crystal structure of 2-phenylethynyl-1,3,6,8-tetramethylBOPHY (BOPHY = bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine), C22H20B2F4N4
- Crystal structure of 4-tert-butyl-2-N-(2-pyridylmethyl)aminophenol, C16H20N2O
- The crystal structure of (3Z,3′Z)-4,4′-((1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(azanediyl))bis(pent-3-en-2-one), C18H24N2O2
- Crystal structure of (morpholine-1-carbodithioato-κ2-S,S′)bis(triphenylphosphine-κ-P)gold(I), C41H38AuNOP2S2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(4-bromobenzyl)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C26H19Br2ClN2
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl (N′-benzoyl-N,N-diphenylcarbamimidothioato-κ2S,O)-(pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I) — methanol (1/1) C26H23O4N4SRe
- The crystal structure of Ba2Mn(SeO3)2Cl2 containing 1∞[Mn(SeO3)2Cl2]4− chains
- Crystal structure of 3,3′,3″-((1E,1′E,1″E)-((nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(azaneylylidene)) tris(methaneylylidene))tris(4-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde) monohydrate, C42H36N4O6·H2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(6-acetyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-yl)benzonitrile, C14H12N6O
- Crystal structure of benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18O5
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5-methyl-7-(4-(phenylthio)phenyl)-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C20H19N5O2S
- Crystal structure of N′,N‴-((propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2-diyl))bis(methaneylylidene))-di(isonicotinohydrazide)– water – dimethylformamide (1/4/2), C25H24N8O2·4H2O·2C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(2,4-dinitrophenoxy)benzaldehyde, C13H8N2O6
- The crystal structure of 1-dodecylpyridin-1-ium bromide monohydrate, C17H32BrNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(4-(dimethylamino)benzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium nitrate, C10H16N6O3
- Crystal structure of (E)-(2-((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazineyl)(amino)methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C6H12N6O4
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-propylimidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H60Cl2CuN12
- The crystal structure of bis{(μ2-3,3-dimethyl-1-phenylbut-1-en-2-yl)((dimethylamino)dimethylsilyl)amido-κ3N,N′:N′}dilithium, C32H54Li2N4Si2
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinin-2(3H)-yl)benzoate, C18H15BN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-(1-((2-chlorothiazol-5-yl)methyl)pyridin-2(1H)-ylidene)-2,2,2-trifluoroacetamide, C11H7ClF3N3OS
- Crystal structure of N′, N‴-((propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2-diyl))bis (methaneylylidene))di(picolinohydrazide) – water – methanol (1/1/1), C25H24N8O2·H2O·CH3OH
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-chloro-benzyl)-7-[4-(2-chloro-benzyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-5,6,8-trifluoro-3H-quinazolin-4-one, C26H21Cl2F3N4O
- Crystal structure of N1,N2-bis(2-fluorobenzyl)benzene-1,2-diamine,C20H18F2N2
- The crystal structure of 2-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C17H13BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methaneylylidene)) bis(2-bromo-4-nitrophenol) — dimethylsulfoxide (1/2), C14H8Br2N4O6⋅2(C2H6OS)
- Selective biocatalytic synthesis and crystal structure of (2R,6R)-hydroxyketaminium chloride, C13H17Cl2NO2
- Crystal structure of bis{tetraaqua-[μ3-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O′,O″] [μ2-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylate-κ3N,O:O]dicobalt(II)} dihydrate, C36H44Co4N8O26
- Crystal structure of diethyl-2,2′-naphthalene-2,3-diylbis(oxy)diacetate, C18H20O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxylato-κO,O′:O′;:O″, O″′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1Himidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C27H18CdN6O4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)benzoato-κ2O:O')zinc(II)], C32H30N4O8Zn
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho [1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C18H17BN2O2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)nickel(II) dichloride – 1-ethylimidazole (1/2), C40H64Cl2NiN16
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2,4-dinitrophenolato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) 1.5 hydrate, C12H13CuN4O13.5
- Crystal structure of N′,N‴-((1E,1′E)-((decane-1,10-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene)) bis(methaneylylidene))di(isonicotinohydrazide), C36H40N6O4
- The crystal structure of 2-[(R)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-2,3,7,7a-tetrahydro-3a,6-epoxyisoindol-1(6H)-one, C19H20NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (1E,2E)-3-(anthracen-9-yl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one oxime, C24H19NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (2E,2′E)-3,3′-(1,3-phenylene)bis(1-(3-bromophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one), C24H16Br2O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(µ2-1,2-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene- κ2N:N′)-bis(nitrato-κO)copper(II)], C28H28N10O6Cu
- Synthesis and crystal structure of the novel chiral acetyl-3-thiophene-5-(9-anthryl)-2-pyrazoline, C23H18N2OS
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(thiophen-3-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C9H11NOS
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-4-amino-4H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) copper(II)], C9H8N5O5CuI
- Crystal structure of cyclopropane-1,2,3-triyltris(phenylmethanone), C24H18O3
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(thioureido)methaniminium) terephthalate, C12H18N8O4S2
- A three-dimensional Eu(III) framework in the crystal structure of dimethylaminium poly[dimethylformamide-κ1N)bis(μ4-terephthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)europium(III)] monohydrate, C21H25EuN2O10
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxyphenyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H20O4
- The crystal structure of Hexakis(diethylamido)dimolybdenum, Mo2(NEt2)6
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-aqua-tetraaqua-(μ3-glutarato-κ4O,O′:O′:O′′)-(μ5-glutarato-κ6O:O,O′:O′:O′′:O′′′)distrontium(II)], C10H22O13Sr2
- The crystal structure of acetato-κ1O-{(2-(2-(2-aminophenoxy)ethoxy)phenyl)(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)amido-κ2N,N′,O}copper(II), C26H26CuN2O5
- Crystal structure of dimethanolato-k2O:O-bis(1-((2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κN)-bis(thiocyanato-κN)dicopper(II), C34H32Cu2N12O2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-(pyrimidin-5-yl)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, [Co(C11H11O2N2)2(H2O)2]
- Crystal structure of bis(3,3-dimethyl-1-phenylbut-1-en-2-yl)(trimethylsilyl)amido-k1N)zinc(II), Zn(C15H24NSi)2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-methanolato-κ2O:O)-(μ2-1-((2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ2N:N′)-(thiocyanato-κ1N)copper(II)] 0.25 hydrate, C17H16CuN6OS ⋅ 0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-5-nitroanilinium iodide monohydrate, C6H8IN3O2
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium perchlorate monohydrate, C6H9ClN2O7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-2,4-dimethoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene from Arundina graminifolia, C16H16O3
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E, 1′E)-(((1R, 2R)-1,2-diphenylethane-1,2-diyl) bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-ethylphenol), C32H32N2O2
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide monohydrate, C6H9IN2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C16H11BF2N2
- Crystal structure of bis{(2-pyridinyl)-1-phenyl-1-isopropylmethanolato-κ2N,O}nickel, C30H32N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of poly[(m3-3-carboxyadamantane-1-carboxylato-κ3O:O′:O″)-(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)sodium(II)], C24H23N2NaO4
- Crystal structure of 2-phenylethynyl-1,3,6,8-tetramethylBOPHY (BOPHY = bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine), C22H20B2F4N4
- Crystal structure of 4-tert-butyl-2-N-(2-pyridylmethyl)aminophenol, C16H20N2O
- The crystal structure of (3Z,3′Z)-4,4′-((1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(azanediyl))bis(pent-3-en-2-one), C18H24N2O2
- Crystal structure of (morpholine-1-carbodithioato-κ2-S,S′)bis(triphenylphosphine-κ-P)gold(I), C41H38AuNOP2S2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(4-bromobenzyl)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C26H19Br2ClN2
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl (N′-benzoyl-N,N-diphenylcarbamimidothioato-κ2S,O)-(pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I) — methanol (1/1) C26H23O4N4SRe
- The crystal structure of Ba2Mn(SeO3)2Cl2 containing 1∞[Mn(SeO3)2Cl2]4− chains
- Crystal structure of 3,3′,3″-((1E,1′E,1″E)-((nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(azaneylylidene)) tris(methaneylylidene))tris(4-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde) monohydrate, C42H36N4O6·H2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(6-acetyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-yl)benzonitrile, C14H12N6O
- Crystal structure of benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18O5
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5-methyl-7-(4-(phenylthio)phenyl)-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C20H19N5O2S
- Crystal structure of N′,N‴-((propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2-diyl))bis(methaneylylidene))-di(isonicotinohydrazide)– water – dimethylformamide (1/4/2), C25H24N8O2·4H2O·2C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(2,4-dinitrophenoxy)benzaldehyde, C13H8N2O6
- The crystal structure of 1-dodecylpyridin-1-ium bromide monohydrate, C17H32BrNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(4-(dimethylamino)benzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium nitrate, C10H16N6O3
- Crystal structure of (E)-(2-((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazineyl)(amino)methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C6H12N6O4
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-propylimidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H60Cl2CuN12
- The crystal structure of bis{(μ2-3,3-dimethyl-1-phenylbut-1-en-2-yl)((dimethylamino)dimethylsilyl)amido-κ3N,N′:N′}dilithium, C32H54Li2N4Si2
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinin-2(3H)-yl)benzoate, C18H15BN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-(1-((2-chlorothiazol-5-yl)methyl)pyridin-2(1H)-ylidene)-2,2,2-trifluoroacetamide, C11H7ClF3N3OS
- Crystal structure of N′, N‴-((propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2-diyl))bis (methaneylylidene))di(picolinohydrazide) – water – methanol (1/1/1), C25H24N8O2·H2O·CH3OH
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-chloro-benzyl)-7-[4-(2-chloro-benzyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-5,6,8-trifluoro-3H-quinazolin-4-one, C26H21Cl2F3N4O
- Crystal structure of N1,N2-bis(2-fluorobenzyl)benzene-1,2-diamine,C20H18F2N2
- The crystal structure of 2-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C17H13BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methaneylylidene)) bis(2-bromo-4-nitrophenol) — dimethylsulfoxide (1/2), C14H8Br2N4O6⋅2(C2H6OS)
- Selective biocatalytic synthesis and crystal structure of (2R,6R)-hydroxyketaminium chloride, C13H17Cl2NO2
- Crystal structure of bis{tetraaqua-[μ3-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O′,O″] [μ2-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylate-κ3N,O:O]dicobalt(II)} dihydrate, C36H44Co4N8O26
- Crystal structure of diethyl-2,2′-naphthalene-2,3-diylbis(oxy)diacetate, C18H20O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxylato-κO,O′:O′;:O″, O″′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1Himidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C27H18CdN6O4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)benzoato-κ2O:O')zinc(II)], C32H30N4O8Zn
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho [1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C18H17BN2O2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)nickel(II) dichloride – 1-ethylimidazole (1/2), C40H64Cl2NiN16
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2,4-dinitrophenolato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) 1.5 hydrate, C12H13CuN4O13.5
- Crystal structure of N′,N‴-((1E,1′E)-((decane-1,10-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene)) bis(methaneylylidene))di(isonicotinohydrazide), C36H40N6O4
- The crystal structure of 2-[(R)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-2,3,7,7a-tetrahydro-3a,6-epoxyisoindol-1(6H)-one, C19H20NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (1E,2E)-3-(anthracen-9-yl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one oxime, C24H19NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (2E,2′E)-3,3′-(1,3-phenylene)bis(1-(3-bromophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one), C24H16Br2O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(µ2-1,2-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene- κ2N:N′)-bis(nitrato-κO)copper(II)], C28H28N10O6Cu
- Synthesis and crystal structure of the novel chiral acetyl-3-thiophene-5-(9-anthryl)-2-pyrazoline, C23H18N2OS
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(thiophen-3-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C9H11NOS
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-4-amino-4H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) copper(II)], C9H8N5O5CuI
- Crystal structure of cyclopropane-1,2,3-triyltris(phenylmethanone), C24H18O3
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(thioureido)methaniminium) terephthalate, C12H18N8O4S2
- A three-dimensional Eu(III) framework in the crystal structure of dimethylaminium poly[dimethylformamide-κ1N)bis(μ4-terephthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)europium(III)] monohydrate, C21H25EuN2O10
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxyphenyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H20O4
- The crystal structure of Hexakis(diethylamido)dimolybdenum, Mo2(NEt2)6

