Abstract
C14H8Br2N4O6⋅2(C2H6OS), triclinic,
CCDC no.: 2057510
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 3.40 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker photon 100, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 26.4°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 8435, 2602, 0.068 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 1586 |
| N(param)refined: | 167 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], [2], SHELX [3], [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Br1 | 0.80364 (7) | 0.88181 (6) | 0.37022 (4) | 0.0516 (2) |
| S1a | 0.1498 (8) | 0.7024 (7) | 0.1549 (4) | 0.098 (2) |
| S1Ab | 0.2235 (6) | 0.6030 (5) | 0.0933 (3) | 0.1053 (17) |
| O3 | 0.1045 (10) | 0.5372 (6) | 0.1930 (4) | 0.149 (2) |
| N1 | 0.6809 (8) | 0.8227 (6) | 0.7922 (4) | 0.0699 (13) |
| O1 | 0.3997 (5) | 0.7028 (4) | 0.3952 (2) | 0.0489 (8) |
| H1 | 0.297260 | 0.643909 | 0.401273 | 0.073* |
| N2 | 0.0921 (5) | 0.5454 (4) | 0.4953 (3) | 0.0393 (9) |
| O2 | 0.5654 (7) | 0.7917 (6) | 0.8726 (3) | 0.1033 (15) |
| O4 | 0.8570 (7) | 0.8809 (5) | 0.7921 (3) | 0.1037 (15) |
| C1 | 0.6473 (7) | 0.8123 (5) | 0.4991 (4) | 0.0378 (11) |
| C2 | 0.4607 (6) | 0.7271 (5) | 0.4921 (3) | 0.0338 (10) |
| C3 | 0.3478 (6) | 0.6703 (5) | 0.5883 (3) | 0.0363 (11) |
| C4 | 0.4199 (7) | 0.7021 (5) | 0.6864 (4) | 0.0428 (11) |
| H4 | 0.344511 | 0.666738 | 0.750255 | 0.051* |
| C5 | 0.6048 (7) | 0.7866 (5) | 0.6891 (4) | 0.0453 (12) |
| C6 | 0.7191 (7) | 0.8418 (5) | 0.5959 (4) | 0.0427 (12) |
| H6 | 0.843601 | 0.898375 | 0.599224 | 0.051* |
| C7 | 0.1569 (6) | 0.5777 (5) | 0.5845 (4) | 0.0388 (11) |
| H7 | 0.081932 | 0.541919 | 0.648422 | 0.047* |
| C9 | 0.0650 (12) | 0.7526 (11) | 0.0366 (7) | 0.170 (4) |
| H9A | 0.110755 | 0.669922 | −0.010857 | 0.255* |
| H9B | 0.125301 | 0.851714 | 0.008777 | 0.255* |
| H9C | −0.091628 | 0.766109 | 0.041511 | 0.255* |
| C10 | 0.4294 (12) | 0.7151 (10) | 0.1345 (5) | 0.143 (3) |
| H10A | 0.490694 | 0.724014 | 0.202445 | 0.215* |
| H10B | 0.460538 | 0.808077 | 0.087158 | 0.215* |
| H10C | 0.492417 | 0.620443 | 0.102721 | 0.215* |
aOccupancy: 0.418(7), bOccupancy: 0.582(7).
Source of materials
All chemicals were analytical reagent grade and used without further purification. The title compound was prepared according to the synthetic route as following. Into a 100 mL round-bottom flask with a reflux condenser, 3-bromo-5-nitro-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde (10 mmol, 2.4668 g) were dissolved in 40 mL ethanol and added hydrazine hydrate (1 mmol, 60 μL) into it, refluxing 2 h later, the pale yellow precipitate of the compound was obtained (yield 89%). A few days later, yellow block crystals were obtained from DMSO. 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO-d6) (ppm): 9.262 (s, 2H, –HC=N–), 8.658 (s, 2H, Ph–H), 8.551 (s, 2H, Ph–H).
Experimental details
Data integrations were performed by the SAINT program [1], and the absorption data were modified by using the multiscan program SADABS [2]. Structural solutions and refinements were performed by using the SHELXS [3] and SHELXL programs [4]. The H atoms attached to C atoms were placed in calculated idealized positions and refined by a riding model.
Comment
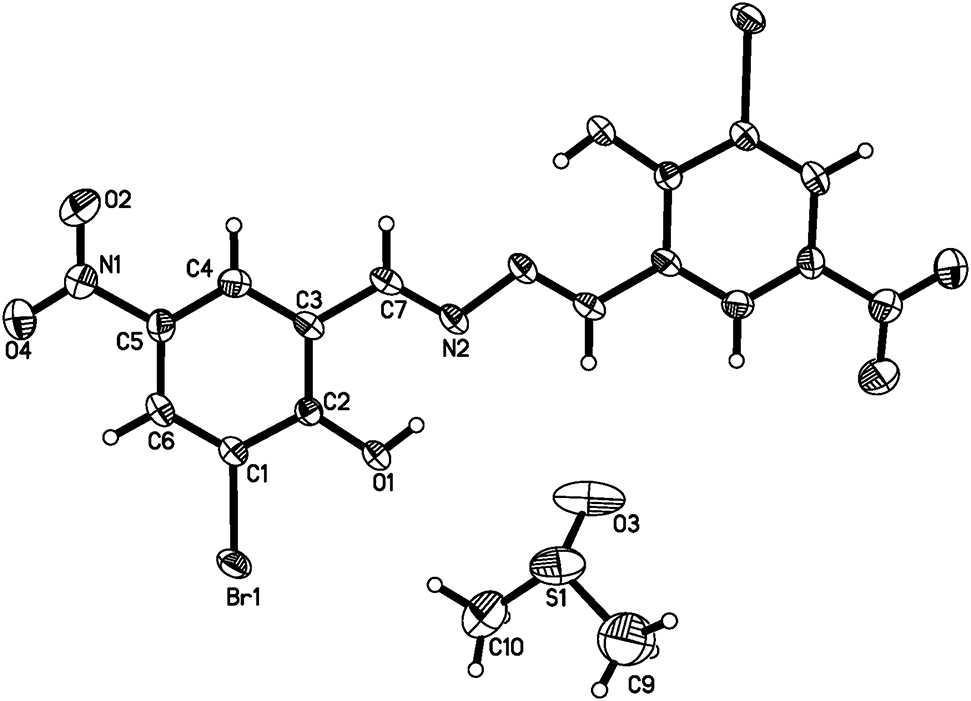
Salicylaldehyde azine (SAA) consists of salicylaldehyde and hydrazine, is a Schiff base with ESIPT process and its derivatives exhibit obvious aggregation-induced emission (AIE) characters with recognizable fluorescence performance which have been used widely in bioimaging and ions detection [5], [6]. Different SAA derivatives with specific spectral properties can be obtained [7], [8]. In this report a SA derivative, named 3-bromo-2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde which has an electron drawing group (–NO2) para to the hydroxyl group, was chosen to study the fluorescence properties and we got the crystal structure of the title compound unexpectedly.
The single-crystal X-ray diffraction revealed that title compound crystallized in the triclinic space group and it contains one dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) molecule and one half of the hydrazine compound in the asymmetric unit. The aromatic carbon-carbon bond lengths deviate significantly, that the values of the C(3)–C(4) and C(1)–C(6) bond-distances are 1.380(6) and 1.359(6) Å respectively, which are shorter than the values of the remaining bond distances [9], [10]. The length of double bond C(7)–N(2), 1.261(5) Å, is very consistent with the value of 1.259(5) Å given by Safin for the length of carbon-nitrogen double bond of N,N′-bis(5-bromosalicylidene)diamines [10]. The two benzene rings are in trans configuration connected by N2–N2A bond, and are nearly coplanar (C6–C1–C2–O1: 179.9(4)°, O1–C2–C3–C7: 1.2(6)°, C3–C7–N2–N2A: 179.5(4)°, C4–C3–C7–N2: 178.6(4)°. In addition, there are weak interactions in the structure. Firstly, the intramolecular O1–H1···N2 hydrogen bonds form a six-membered ring, generating a S(6) ring motif [11]. Secondly, π···π interactions between aromatic rings are also contained in the structure. The molecules are nearly planar and are arranged in parallel packing, meanwhile the distance between atom N2 and Cg (C1–C2–C3–C7–Br1–O1–N2) is 3.33 Å.
Funding source: Construction Plan of ‘1331 Engineering’ Fluorescent Probe Team
Award Identifier / Grant number: jzxycktd2019038
Funding source: National Natural Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 21671124
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
Research funding: Research Fund for Construction Plan of ‘1331 Engineering’ Fluorescent Probe Team (jzxycktd2019038) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 21671124).
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. SAINT; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
2. Bruker. SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2001.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
5. Lu, W., Chen, J. C., Shi, J. Z., Xu, L., Yang, S. L., Gao, B. H. A novel quinoline-based turn-on fuorescent probe for the highly selective detection of Al(III) and its bioimaging in living cells, plants tissues and zebrafsh. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2021; https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-020-01836-6.10.1007/s00775-020-01836-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Gupta, A. S., Paul, K., Luxami, V. A fluorescent probe with “AIE + ESIPT” characteristics for Cu2+ and F− ions estimation. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 246, 653–661.10.1016/j.snb.2017.02.080Search in Google Scholar
7. Guo, S. W., Song, Y. S., He, Y. L., Hu, X. Y., Wang, L. Y. Highly efficient artificial light-harvesting systems constructed in aqueous solution based on supramolecular self-assembly. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3163–3167; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201800175.Search in Google Scholar
8. Chai, J., Wu, Y. B., Yang, B. S., Liu, B. The photochromism, light harvesting and self-assembly activity of a multi-function Schiff-base compound based on the AIE effect. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 4057–4064. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8tc00509e.Search in Google Scholar
9. Arcovito, G., Bonamico, M., Dornenicano, A., Vaciago, A. Crystal and molecular structure of salicylaldehyde azine. J. Chem. Soc. B 1969, 733–741; https://doi.org/10.1039/j29690000733.Search in Google Scholar
10. Safin, D. A., Robeyns, K., Garcia, Y. Solid-state thermo- and photochromism in N,N′-bis(5-X-salicylidene)diamines (X = H, Br). RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 11379–11388; https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ra21631k.Search in Google Scholar
11. Wang, L., Su, Q., Wu, Q. L., Gao, W., Mu, Y. Synthesis of new substituted benzaldazine derivatives, hydrogen bonding-induced supramolecular structures and luminescent properties. C. R. Chimie 2012, 15, 463–470; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2011.12.006.Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Ling Ma et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-aqua-tetraaqua-(μ3-glutarato-κ4O,O′:O′:O′′)-(μ5-glutarato-κ6O:O,O′:O′:O′′:O′′′)distrontium(II)], C10H22O13Sr2
- The crystal structure of acetato-κ1O-{(2-(2-(2-aminophenoxy)ethoxy)phenyl)(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)amido-κ2N,N′,O}copper(II), C26H26CuN2O5
- Crystal structure of dimethanolato-k2O:O-bis(1-((2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κN)-bis(thiocyanato-κN)dicopper(II), C34H32Cu2N12O2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-(pyrimidin-5-yl)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, [Co(C11H11O2N2)2(H2O)2]
- Crystal structure of bis(3,3-dimethyl-1-phenylbut-1-en-2-yl)(trimethylsilyl)amido-k1N)zinc(II), Zn(C15H24NSi)2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-methanolato-κ2O:O)-(μ2-1-((2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ2N:N′)-(thiocyanato-κ1N)copper(II)] 0.25 hydrate, C17H16CuN6OS ⋅ 0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-5-nitroanilinium iodide monohydrate, C6H8IN3O2
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium perchlorate monohydrate, C6H9ClN2O7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-2,4-dimethoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene from Arundina graminifolia, C16H16O3
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E, 1′E)-(((1R, 2R)-1,2-diphenylethane-1,2-diyl) bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-ethylphenol), C32H32N2O2
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide monohydrate, C6H9IN2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C16H11BF2N2
- Crystal structure of bis{(2-pyridinyl)-1-phenyl-1-isopropylmethanolato-κ2N,O}nickel, C30H32N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of poly[(m3-3-carboxyadamantane-1-carboxylato-κ3O:O′:O″)-(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)sodium(II)], C24H23N2NaO4
- Crystal structure of 2-phenylethynyl-1,3,6,8-tetramethylBOPHY (BOPHY = bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine), C22H20B2F4N4
- Crystal structure of 4-tert-butyl-2-N-(2-pyridylmethyl)aminophenol, C16H20N2O
- The crystal structure of (3Z,3′Z)-4,4′-((1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(azanediyl))bis(pent-3-en-2-one), C18H24N2O2
- Crystal structure of (morpholine-1-carbodithioato-κ2-S,S′)bis(triphenylphosphine-κ-P)gold(I), C41H38AuNOP2S2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(4-bromobenzyl)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C26H19Br2ClN2
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl (N′-benzoyl-N,N-diphenylcarbamimidothioato-κ2S,O)-(pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I) — methanol (1/1) C26H23O4N4SRe
- The crystal structure of Ba2Mn(SeO3)2Cl2 containing 1∞[Mn(SeO3)2Cl2]4− chains
- Crystal structure of 3,3′,3″-((1E,1′E,1″E)-((nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(azaneylylidene)) tris(methaneylylidene))tris(4-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde) monohydrate, C42H36N4O6·H2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(6-acetyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-yl)benzonitrile, C14H12N6O
- Crystal structure of benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18O5
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5-methyl-7-(4-(phenylthio)phenyl)-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C20H19N5O2S
- Crystal structure of N′,N‴-((propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2-diyl))bis(methaneylylidene))-di(isonicotinohydrazide)– water – dimethylformamide (1/4/2), C25H24N8O2·4H2O·2C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(2,4-dinitrophenoxy)benzaldehyde, C13H8N2O6
- The crystal structure of 1-dodecylpyridin-1-ium bromide monohydrate, C17H32BrNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(4-(dimethylamino)benzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium nitrate, C10H16N6O3
- Crystal structure of (E)-(2-((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazineyl)(amino)methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C6H12N6O4
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-propylimidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H60Cl2CuN12
- The crystal structure of bis{(μ2-3,3-dimethyl-1-phenylbut-1-en-2-yl)((dimethylamino)dimethylsilyl)amido-κ3N,N′:N′}dilithium, C32H54Li2N4Si2
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinin-2(3H)-yl)benzoate, C18H15BN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-(1-((2-chlorothiazol-5-yl)methyl)pyridin-2(1H)-ylidene)-2,2,2-trifluoroacetamide, C11H7ClF3N3OS
- Crystal structure of N′, N‴-((propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2-diyl))bis (methaneylylidene))di(picolinohydrazide) – water – methanol (1/1/1), C25H24N8O2·H2O·CH3OH
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-chloro-benzyl)-7-[4-(2-chloro-benzyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-5,6,8-trifluoro-3H-quinazolin-4-one, C26H21Cl2F3N4O
- Crystal structure of N1,N2-bis(2-fluorobenzyl)benzene-1,2-diamine,C20H18F2N2
- The crystal structure of 2-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C17H13BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methaneylylidene)) bis(2-bromo-4-nitrophenol) — dimethylsulfoxide (1/2), C14H8Br2N4O6⋅2(C2H6OS)
- Selective biocatalytic synthesis and crystal structure of (2R,6R)-hydroxyketaminium chloride, C13H17Cl2NO2
- Crystal structure of bis{tetraaqua-[μ3-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O′,O″] [μ2-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylate-κ3N,O:O]dicobalt(II)} dihydrate, C36H44Co4N8O26
- Crystal structure of diethyl-2,2′-naphthalene-2,3-diylbis(oxy)diacetate, C18H20O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxylato-κO,O′:O′;:O″, O″′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1Himidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C27H18CdN6O4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)benzoato-κ2O:O')zinc(II)], C32H30N4O8Zn
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho [1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C18H17BN2O2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)nickel(II) dichloride – 1-ethylimidazole (1/2), C40H64Cl2NiN16
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2,4-dinitrophenolato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) 1.5 hydrate, C12H13CuN4O13.5
- Crystal structure of N′,N‴-((1E,1′E)-((decane-1,10-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene)) bis(methaneylylidene))di(isonicotinohydrazide), C36H40N6O4
- The crystal structure of 2-[(R)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-2,3,7,7a-tetrahydro-3a,6-epoxyisoindol-1(6H)-one, C19H20NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (1E,2E)-3-(anthracen-9-yl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one oxime, C24H19NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (2E,2′E)-3,3′-(1,3-phenylene)bis(1-(3-bromophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one), C24H16Br2O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(µ2-1,2-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene- κ2N:N′)-bis(nitrato-κO)copper(II)], C28H28N10O6Cu
- Synthesis and crystal structure of the novel chiral acetyl-3-thiophene-5-(9-anthryl)-2-pyrazoline, C23H18N2OS
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(thiophen-3-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C9H11NOS
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-4-amino-4H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) copper(II)], C9H8N5O5CuI
- Crystal structure of cyclopropane-1,2,3-triyltris(phenylmethanone), C24H18O3
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(thioureido)methaniminium) terephthalate, C12H18N8O4S2
- A three-dimensional Eu(III) framework in the crystal structure of dimethylaminium poly[dimethylformamide-κ1N)bis(μ4-terephthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)europium(III)] monohydrate, C21H25EuN2O10
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxyphenyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H20O4
- The crystal structure of Hexakis(diethylamido)dimolybdenum, Mo2(NEt2)6
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-aqua-tetraaqua-(μ3-glutarato-κ4O,O′:O′:O′′)-(μ5-glutarato-κ6O:O,O′:O′:O′′:O′′′)distrontium(II)], C10H22O13Sr2
- The crystal structure of acetato-κ1O-{(2-(2-(2-aminophenoxy)ethoxy)phenyl)(4-oxo-4-phenylbut-2-en-2-yl)amido-κ2N,N′,O}copper(II), C26H26CuN2O5
- Crystal structure of dimethanolato-k2O:O-bis(1-((2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κN)-bis(thiocyanato-κN)dicopper(II), C34H32Cu2N12O2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3-(pyrimidin-5-yl)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, [Co(C11H11O2N2)2(H2O)2]
- Crystal structure of bis(3,3-dimethyl-1-phenylbut-1-en-2-yl)(trimethylsilyl)amido-k1N)zinc(II), Zn(C15H24NSi)2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-methanolato-κ2O:O)-(μ2-1-((2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κ2N:N′)-(thiocyanato-κ1N)copper(II)] 0.25 hydrate, C17H16CuN6OS ⋅ 0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-5-nitroanilinium iodide monohydrate, C6H8IN3O2
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium perchlorate monohydrate, C6H9ClN2O7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-2,4-dimethoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene from Arundina graminifolia, C16H16O3
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E, 1′E)-(((1R, 2R)-1,2-diphenylethane-1,2-diyl) bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-ethylphenol), C32H32N2O2
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide monohydrate, C6H9IN2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C16H11BF2N2
- Crystal structure of bis{(2-pyridinyl)-1-phenyl-1-isopropylmethanolato-κ2N,O}nickel, C30H32N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of poly[(m3-3-carboxyadamantane-1-carboxylato-κ3O:O′:O″)-(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)sodium(II)], C24H23N2NaO4
- Crystal structure of 2-phenylethynyl-1,3,6,8-tetramethylBOPHY (BOPHY = bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine), C22H20B2F4N4
- Crystal structure of 4-tert-butyl-2-N-(2-pyridylmethyl)aminophenol, C16H20N2O
- The crystal structure of (3Z,3′Z)-4,4′-((1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(azanediyl))bis(pent-3-en-2-one), C18H24N2O2
- Crystal structure of (morpholine-1-carbodithioato-κ2-S,S′)bis(triphenylphosphine-κ-P)gold(I), C41H38AuNOP2S2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(4-bromobenzyl)-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carbonitrile, C26H19Br2ClN2
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl (N′-benzoyl-N,N-diphenylcarbamimidothioato-κ2S,O)-(pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I) — methanol (1/1) C26H23O4N4SRe
- The crystal structure of Ba2Mn(SeO3)2Cl2 containing 1∞[Mn(SeO3)2Cl2]4− chains
- Crystal structure of 3,3′,3″-((1E,1′E,1″E)-((nitrilotris(ethane-2,1-diyl))tris(azaneylylidene)) tris(methaneylylidene))tris(4-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde) monohydrate, C42H36N4O6·H2O
- The crystal structure of 4-(6-acetyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-yl)benzonitrile, C14H12N6O
- Crystal structure of benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H18O5
- The crystal structure of ethyl 5-methyl-7-(4-(phenylthio)phenyl)-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C20H19N5O2S
- Crystal structure of N′,N‴-((propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2-diyl))bis(methaneylylidene))-di(isonicotinohydrazide)– water – dimethylformamide (1/4/2), C25H24N8O2·4H2O·2C3H7NO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(2,4-dinitrophenoxy)benzaldehyde, C13H8N2O6
- The crystal structure of 1-dodecylpyridin-1-ium bromide monohydrate, C17H32BrNO
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(4-(dimethylamino)benzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium nitrate, C10H16N6O3
- Crystal structure of (E)-(2-((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazineyl)(amino)methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C6H12N6O4
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-propylimidazole-κ1N)copper(II) dichloride, C36H60Cl2CuN12
- The crystal structure of bis{(μ2-3,3-dimethyl-1-phenylbut-1-en-2-yl)((dimethylamino)dimethylsilyl)amido-κ3N,N′:N′}dilithium, C32H54Li2N4Si2
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-(1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinin-2(3H)-yl)benzoate, C18H15BN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-(1-((2-chlorothiazol-5-yl)methyl)pyridin-2(1H)-ylidene)-2,2,2-trifluoroacetamide, C11H7ClF3N3OS
- Crystal structure of N′, N‴-((propane-2,2-diylbis(1H-pyrrole-5,2-diyl))bis (methaneylylidene))di(picolinohydrazide) – water – methanol (1/1/1), C25H24N8O2·H2O·CH3OH
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-chloro-benzyl)-7-[4-(2-chloro-benzyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-5,6,8-trifluoro-3H-quinazolin-4-one, C26H21Cl2F3N4O
- Crystal structure of N1,N2-bis(2-fluorobenzyl)benzene-1,2-diamine,C20H18F2N2
- The crystal structure of 2-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C17H13BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-((1E,1′E)-hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methaneylylidene)) bis(2-bromo-4-nitrophenol) — dimethylsulfoxide (1/2), C14H8Br2N4O6⋅2(C2H6OS)
- Selective biocatalytic synthesis and crystal structure of (2R,6R)-hydroxyketaminium chloride, C13H17Cl2NO2
- Crystal structure of bis{tetraaqua-[μ3-1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O′,O″] [μ2-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylate-κ3N,O:O]dicobalt(II)} dihydrate, C36H44Co4N8O26
- Crystal structure of diethyl-2,2′-naphthalene-2,3-diylbis(oxy)diacetate, C18H20O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxylato-κO,O′:O′;:O″, O″′)-(μ2-1-(4-(1Himidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazole-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C27H18CdN6O4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-((2-(2-phenylacetyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl)benzoato-κ2O:O')zinc(II)], C32H30N4O8Zn
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho [1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborinine, C18H17BN2O2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)nickel(II) dichloride – 1-ethylimidazole (1/2), C40H64Cl2NiN16
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(2,4-dinitrophenolato-κ2O,O′)copper(II) 1.5 hydrate, C12H13CuN4O13.5
- Crystal structure of N′,N‴-((1E,1′E)-((decane-1,10-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene)) bis(methaneylylidene))di(isonicotinohydrazide), C36H40N6O4
- The crystal structure of 2-[(R)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-2,3,7,7a-tetrahydro-3a,6-epoxyisoindol-1(6H)-one, C19H20NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (1E,2E)-3-(anthracen-9-yl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one oxime, C24H19NO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (2E,2′E)-3,3′-(1,3-phenylene)bis(1-(3-bromophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one), C24H16Br2O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(µ2-1,2-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene- κ2N:N′)-bis(nitrato-κO)copper(II)], C28H28N10O6Cu
- Synthesis and crystal structure of the novel chiral acetyl-3-thiophene-5-(9-anthryl)-2-pyrazoline, C23H18N2OS
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(thiophen-3-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C9H11NOS
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-4-amino-4H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′) copper(II)], C9H8N5O5CuI
- Crystal structure of cyclopropane-1,2,3-triyltris(phenylmethanone), C24H18O3
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(thioureido)methaniminium) terephthalate, C12H18N8O4S2
- A three-dimensional Eu(III) framework in the crystal structure of dimethylaminium poly[dimethylformamide-κ1N)bis(μ4-terephthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)europium(III)] monohydrate, C21H25EuN2O10
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxyphenyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H20O4
- The crystal structure of Hexakis(diethylamido)dimolybdenum, Mo2(NEt2)6

