Abstract
C26H18N6ZnS4, triclinic,
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.22 × 0.21 × 0.18 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.26 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 28.3°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 9681, 6567, 0.093 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 5260 |
| N(param)refined: | 334 |
| Programs: | SHELX [1], Bruker [2] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.9451 (3) | 0.2105 (2) | 0.05814 (18) | 0.0456 (5) |
| C2 | 0.9456 (2) | 0.2330 (2) | 0.16656 (17) | 0.0416 (4) |
| C3 | 0.8896 (3) | 0.3176 (2) | 0.20736 (18) | 0.0427 (5) |
| C4 | 0.8312 (3) | 0.3768 (2) | 0.13851 (19) | 0.0517 (6) |
| C5 | 1.1081 (3) | 0.1708 (2) | 0.70883 (18) | 0.0462 (5) |
| C6 | 1.0242 (3) | 0.1611 (2) | 0.60428 (16) | 0.0398 (4) |
| C7 | 0.8665 (3) | 0.08420 (19) | 0.55806 (17) | 0.0402 (4) |
| C8 | 0.7812 (3) | 0.0135 (2) | 0.61560 (19) | 0.0456 (5) |
| C9 | 0.8185 (3) | 0.3409 (3) | 0.6839 (3) | 0.0652 (7) |
| H9 | 0.9070 | 0.3806 | 0.6648 | 0.078* |
| C10 | 0.8384 (4) | 0.3195 (3) | 0.7798 (3) | 0.0754 (9) |
| H10 | 0.9401 | 0.3441 | 0.8256 | 0.090* |
| C11 | 0.7076 (4) | 0.2615 (3) | 0.8076 (2) | 0.0656 (7) |
| H11 | 0.7197 | 0.2483 | 0.8733 | 0.079* |
| C12 | 0.5599 (3) | 0.2233 (3) | 0.7382 (2) | 0.0581 (6) |
| H12 | 0.4700 | 0.1823 | 0.7553 | 0.070* |
| C13 | 0.5450 (3) | 0.2456 (2) | 0.6431 (2) | 0.0508 (5) |
| H13 | 0.4442 | 0.2188 | 0.5952 | 0.061* |
| C14 | 0.6497 (4) | 0.3285 (3) | 0.5137 (2) | 0.0600 (7) |
| H14A | 0.5848 | 0.2492 | 0.4569 | 0.072* |
| H14B | 0.7521 | 0.3634 | 0.5030 | 0.072* |
| C15 | 0.5708 (3) | 0.4173 (2) | 0.50768 (19) | 0.0458 (5) |
| C16 | 0.6505 (3) | 0.5423 (2) | 0.5690 (2) | 0.0504 (5) |
| H16 | 0.7525 | 0.5712 | 0.6161 | 0.060* |
| C17 | 0.4190 (3) | 0.3753 (2) | 0.4385 (2) | 0.0494 (5) |
| H17 | 0.3636 | 0.2911 | 0.3969 | 0.059* |
| C18 | 0.3202 (3) | 0.3055 (3) | 0.0460 (2) | 0.0557 (6) |
| H18 | 0.2415 | 0.2608 | −0.0198 | 0.067* |
| C19 | 0.3896 (4) | 0.4352 (3) | 0.0796 (3) | 0.0688 (8) |
| H19 | 0.3565 | 0.4782 | 0.0372 | 0.083* |
| C20 | 0.5072 (3) | 0.4997 (3) | 0.1754 (3) | 0.0641 (7) |
| H20 | 0.5559 | 0.5869 | 0.1986 | 0.077* |
| C21 | 0.5525 (3) | 0.4348 (3) | 0.2370 (2) | 0.0611 (6) |
| H21 | 0.6326 | 0.4774 | 0.3025 | 0.073* |
| C22 | 0.4805 (3) | 0.3087 (2) | 0.20223 (18) | 0.0516 (5) |
| H22 | 0.5109 | 0.2649 | 0.2448 | 0.062* |
| C23 | 0.2920 (3) | 0.1048 (2) | 0.0721 (2) | 0.0613 (7) |
| H23A | 0.1937 | 0.0736 | 0.0139 | 0.074* |
| H23B | 0.2664 | 0.0767 | 0.1303 | 0.074* |
| C24 | 0.4017 (3) | 0.0515 (2) | 0.0355 (2) | 0.0462 (5) |
| C25 | 0.4100 (3) | 0.0389 (2) | −0.0667 (2) | 0.0539 (6) |
| H25 | 0.3491 | 0.0643 | −0.1124 | 0.065* |
| C26 | 0.4905 (3) | 0.0118 (2) | 0.1012 (2) | 0.0540 (6) |
| H26 | 0.4841 | 0.0188 | 0.1696 | 0.065* |
| N1 | 0.6731 (2) | 0.30538 (17) | 0.61782 (15) | 0.0449 (4) |
| N2 | 0.3663 (2) | 0.24471 (17) | 0.10803 (14) | 0.0407 (4) |
| N3 | 0.7826 (3) | 0.4239 (3) | 0.0834 (2) | 0.0769 (8) |
| N4 | 0.9460 (3) | 0.1911 (3) | −0.02791 (18) | 0.0636 (6) |
| N5 | 0.7066 (3) | −0.0423 (2) | 0.6590 (2) | 0.0623 (6) |
| N6 | 1.1847 (3) | 0.1848 (2) | 0.79231 (17) | 0.0673 (6) |
| S1 | 1.01499 (8) | 0.14502 (6) | 0.23146 (5) | 0.04983 (15) |
| S2 | 0.88203 (8) | 0.35786 (6) | 0.33647 (5) | 0.05154 (16) |
| S3 | 1.14199 (6) | 0.25819 (6) | 0.54831 (5) | 0.04838 (15) |
| S4 | 0.75176 (7) | 0.06525 (6) | 0.43227 (5) | 0.04942 (15) |
| Zn1 | 0.95002 (3) | 0.20276 (2) | 0.38601 (2) | 0.04353 (10) |
Source of material
All reagents and chemicals were purchased from commercial sources and used without further purification. The starting materials disodium maleonitriledithiolate and 1,4-bis(methylpyridinium benzene bromide were synthesized following the literature procedures [3], [, 4]. An aqueous solution (10 mL) of 1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) dibromide (BisPyBr2) (0.0842 g, 0.2 mmol) was added slowly to an aqueous solution (15 mL) of disodium maleonitriledithiolate (0.0741 g, 0.4 mmol) and ZnCl2 (0.0277 g, 0.2 mmol). The mixture was stirred at room temperature for several minutes. A yellow precipitate was filtered off, washed by water and dried under vacuum. The precipitate was solved in DMF with ether diffusion yielding yellow crystals after two weeks.
Experimental details
Absorption corrections were applied by using the multi-scan method. Hydrogen atoms were located in difference electron density maps, and treated as riding atoms. The Uiso values of the hydrogen atoms were set to 1.2Ueq(C).
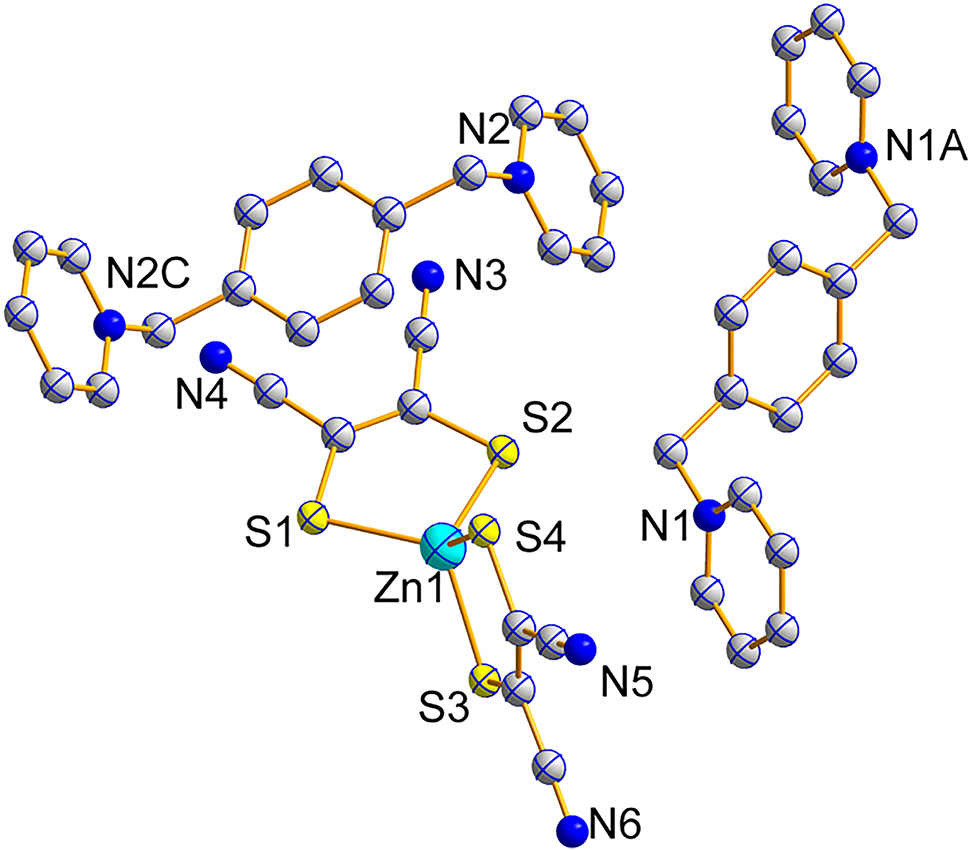
Comment
The maleonitriledithiolate (mnt) ligand is most often used for special structures and has great potential in diversified applications, such as conducting, magnetic materials, dyes and non-linear optics [5], [6], [7], [8], and so on. Compared with the [Ni(mnt)2]n− complexes [9], [10], [11], the [Zn(mnt)2]2− complexes are less studied.
The title complex crystallizes in triclinic
Funding source: Scientific and Technological Research Projects of Henan Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: 182102311077
Funding source: National Natural Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 21776063, U1704127
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
Research funding: The Scientific and Technological Research Projects of Henan Province (182102311077), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21776063, U1704127).
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
2. Bruker. SMART APEX–II CCD; Bruker AXS Inc: Madison, WI, USA, 2006.Search in Google Scholar
3. Simmons, H. E., Blomstrom, D. C., Vest, R. D. Thiacyanocarbons. II. chemistry of disodium dimercaptomaleonitrile. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1962, 84, 4756–4771; https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00883a029.Search in Google Scholar
4. Musilek, K., Komloova, M., Zavadova, V., Holas, O., Hrabinova, M., Pohanka, M., Dohnal, V., Nachon, F., Dolezal, M., Kuca, K., Jung, Y. S. Preparation and in vitro screening of symmetrical bispyridinium cholinesterase inhibitors bearing different connecting linkage-initial study for Myasthenia gravis implications. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 1763–1766; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.01.034.Search in Google Scholar
5. Mueller–Westerhoff, U. T., Vance, B., Ihl Yoon, D. The synthesis of dithiolene dyes with strong near–IR absorption. Tetrahedron 1991, 47, 909–932; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-4020(01)80932-7.Search in Google Scholar
6. Tanaka, H., Okano, Y., Kobayashi, H., Suzuki, W., Kobayashi, A. A three- dimensional synthetic metallic crystal composed of single-component molecules. Science 2001, 291, 285–287; https://doi.org/10.1126/science.291.5502.285.Search in Google Scholar
7. Bigoli, F., Chen, C. T., Wu, W. C., Deplano, P., Mercuri, M. L., Pellinghelli, M. A., Pilia, L., Pintus, G., Serpe, A., Trogu, E. F. [Ni(R2pipdt)2](BF4)2 (R2pipdt = 1,4-disubstituted-piperazine-3,2- dithione) as useful precursors of mixed-ligand dithiolenes of interest for non-linear optics. Chem. Commun. 2001, 2246–2247; https://doi.org/10.1039/b106064n.Search in Google Scholar
8. Robertson, N., Cronin, L. Metal bis-1,2-dithiolene complexes in conducting or magnetic crystalline assemblies. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 227, 93–127; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0010-8545(01)00457-x.Search in Google Scholar
9. Duan, H. B., Ren, X. M., Meng, Q. J. One-dimensional (1D) [Ni(mnt)2]− based spin–Peierls-like complexes: structural, magnetic and transition properties. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 1509–1522; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2009.12.021.Search in Google Scholar
10. Wang, P. Crystal structure of Mn(II)(H2O)(2,13-dimethyl-3,6,9,12,18- pentaazabicyclo[12.3.1]octadeca-1(18),2,12,14,16-pentaene)-bis(maleonitriledithiolate)nickel(II), C23H25MnN9NiOS4. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2012, 227, 511–512; https://doi.org/10.1524/ncrs.2012.0244.Search in Google Scholar
11. Yan, W. H., Pan, H. Y. Crystal structure of 1,4- bis(methylpyridinium benzene) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2S:S)nickel(II), C26H18N6NiS4. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2021, 236, 107–108. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020–0407.10.1515/ncrs-2020-0407Search in Google Scholar
12. Liu, X., Liu, J. L., Cai, B., Ren, X. M. A charge transfer salt consisted of bis(maleonitriledithiolato)zincate dianion and 1,1′-didecyl- 4,4′-bipyridinium exhibiting uncommon nematic mesophase behavior. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2011, 14, 1428–1431; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2011.05.038.Search in Google Scholar
13. Jeffrey, G. A. Hydrogen-bonding: an update. Crystallogr. Rev. 2003, 9, 135–176; https://doi.org/10.1080/08893110310001621754.Search in Google Scholar
© 2020 Wei-Hong Yan et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxidoethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ5N,O,O′:N′,O′′)hexkis(pyridine-κ1N)trinickel(II) - pyridine (1/1), C63H57Cl2N13Ni3O6
- Crystal structure of [(μ2-succinato κ3O,O′:O′′)-bis-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)]dinickel(II)] diperchlorate, dihydrate C36H82Cl2N8Ni2O15
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aquabis(3-nitrobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-pyrazine-N: N′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N4O9Cd
- Crystal structure of 4-(2,2-difluoroethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione, C14H15F2NO2
- The crystal structure of thioxanthen-9-one-10,10-dioxide, C13H8O3S – a second polymorph
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-methoxy-3-pyridyl)methylene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- The crystal structure of diaquahydrogen 2,5-dimethylbenzenesulphonate, C8H14O5S
- The crystal structure of N-(4-(cyclohexylimino)pent-2-en-2-yl)cyclohexanamine, C17H30N2
- The twinned crystal structure of 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium dibromide, C8H14Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2,4,7,9-tetranitro-10H-benzofuro[3,2-b]indole – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1), C16H11N5O10S
- Crystal structure of 2,6-bis(2-(pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)pyrrolo[3,4-f]isoindole-1,3,5,7(2H,6H)-tetraone, C24H18N4O4
- The crystal structure of 3,4-dichlorobenzoic acid chloride, C7H3Cl3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-k2S:S)zinc(II), C26H18N6ZnS4
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ-naphthalene-1-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)bis(methanol)copper(II), C46H36Cu2O10
- Crystal structure of 9-methyl-3-methylene-1,2,3,9-tetrahydro-4H-carbazol-4-one, C14H13NO
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(carbamothioylamino)methaniminium) 3-nitrophthalate monohydrate, C12H19N9O7S2
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,2-phenylene-bis(methylene))bis(1-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate), C18H24F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-6,8-dimethoxy-2-methyl-4H-benzo[g]chromen-4-one– rubrofusarin B, C16H14O5
- The crystal structure of bis(ethanol-kO)- bis(6-aminopicolinato-k2N,O)manganese(II), C16H22O6N4Mn
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-((carbonylbis(azanediyl))bis(ethane-2,1-diyl)) bis(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium) tetrafluoroborate monohydrate, C21H28N6O3B2F8
- Crystal structure of dimethanol-dichlorido-bis( μ2-2-(((1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2- phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato- κ4O:O,O′,N)dinickel (II), C20H24ClNiN3O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate, C7H6F3NO2
- Crystal structure of (OC‐6‐13)‐aqua‐tris (3‐bromopyridine‐κ1N)‐bis(trifluoroacetato‐κ1O)cadmium(II) C19H14Br3CdF6N3O5
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-3-(4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)phenyl) acrylate, C14H16O5
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of 2-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-3-bromo-5-chlorophenol, C13H8BrClN2O
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-N-(2-methyl-1-oxidopropylidene)-2-oxidobenzohydrazonate-κ5N,O,O′:N′,O′′)pentakis(pyridine-κ1N)tricopper(II), C47H45Cl2N9Cu3O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-bis(nitrato-κ2O:O′)- (μ2-((1 H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2 N,N′)-H2O-κ2O]cadmium(II), C14H16N6O7Cd
- The crystal structure of pentakis(carbonyl)-{μ-[2,3-bis(sulfanyl)propan-1-olato]}-(triphenylphosphane)diiron (Fe–Fe)C26H21Fe2O6PS2
- Crystal structure of ethyl-2-(3-benzoylthioureido)propanoate, C13H16N2O3S
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4b,5,14,15-tetrahydro-6H-isoquinolino[2′,1′:1,6] pyrazino[2,3-b]quinoxaline, C19H18N4O
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-[ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidenemethylylidene)]bis(6-chlorophenol), C16H14Cl2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-((2-(2-(2-aminophenoxy)ethoxy)phenyl)amino)-1-phenylbut-2-en-1-one, C24H24N2O3
- The crystal structure of 10-(3,5-di(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)-10H-phenoxazine dihydrate, C28H23N3O3
- Crystal structure of poly[dipoly[aqua-di(µ2-pyrazin-2-olato-κ2N:N′) zinc(II)], C8H8N4O3Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetra(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κO)-manganese(II)-platinum(II)], C10H14MnN6O2Pt
- The crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-6,6′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dichlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C16H12Cl5MnN2O3
- Crystal structure of [di(µ2-cyanido)-dicyanido-bis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)- bis(2,2′-(ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidenemethanylylidene))diphenolato-κ4,N,N′,O,O′)- dimanganese(III)-platinum(II)], C40H40Mn2N8O6PtS2
- The crystal structure of (azido)-κ1N-6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato-κ4N,N,O,O)-(methanol)-manganese(III)–methanol(1/1), C22H26Br2MnN5O4
- Crystal structure of 7-chloro-N-(4-iodobenzyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridin-9-amine, C20H18ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N′′′)-bis(μ2-thiocyanato-κ2N:S)-bis(thiocyanato-κS)-nickel(II)palladium(II)], C14H24N8NiPdS4
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-4-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)aniline monohydrate, C12H20ClN3O
- Crystal structure of the 2D coordination polymer poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3- methoxyisonicotinato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] — dimethylformamide (1/1), C20H30CoN4O10
- Crystal structure of 4-[(5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino]-3-propyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C12H13ClN4OS
- Crystal structure of N-(5-(2-(benzyl(1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-yl)amino)-1-hydroxyethyl)-2-(benzyloxy)phenyl)formamide, C33H36N2O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, C9H12O5
- The crystal structure of 1-((dimethylamino)(3-nitrophenyl)methyl)naphthalen-2-ol, C19H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)-dicyanido-tetrakis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)-manganese(II)-platinum(II)], C12H24MnN4O4PtS4
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-N-(2-pyrimidinyl)benzenesulfonamide–1,4-dioxane (1/1), C14H18N4O4S
- Crystal structure of bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,3-(2-methyl-imidazol)}di-chloridomercury(II), [Hg(C11H11N5)2Cl2], C22H22N10Cl2Hg
- Crystal structure of 2, 3-bis((4-methylbenzoyl)oxy) succinic acid–N, N-dimethylformamide (1/1), C23H25NO9
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(4-(4-carboxyphenoxy)benzoato-κ1O)-μ2-(1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C40H28N4O10Co
- Crystal structure of 1H-imidazol-3-ium poly[aqua-(μ4-glutarato-κ6O,O′:O′:O′′,O′′′:O′′′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)strontium(II)], C8H13N3O8Sr
- Crystal structure of (R)-6-(benzo[b]thiophen-5-yl)-2-methyl-2,6-dihydrobenzo [5,6] silino[4,3,2-cd]indole, C23H17NSSi
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-thiocyanato-κ2N:S)-(2-(5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)pyridine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)]–dioxane (1/1), C15H17CdN5O2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-1,4-bis(2′-carboxylatophenoxy)benzene-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridione-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)] monhydrate, C30H22CdN2O7⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-k2N:N′)-bis(μ2-4′-methyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,5-dicarboxylato-k4O,O′:O″,O′″)dicadmium(II)] dihydrate, C20H20NO7Cd
- Crystal structure of 1‐tert‐butyl‐3‐(2,6‐diisopropyl‐4‐phenoxyphenyl)‐2-methylisothiourea, C24H34N2OS
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-(4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — N,N′-dimethylformamide (1/1), C28H34N8O8Co
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ1N)manganese(II) 2,3-dihydroxyterephthalate, C32H32MnN8O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxidoethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ5N,O,O′:N′,O′′)hexkis(pyridine-κ1N)trinickel(II) - pyridine (1/1), C63H57Cl2N13Ni3O6
- Crystal structure of [(μ2-succinato κ3O,O′:O′′)-bis-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)]dinickel(II)] diperchlorate, dihydrate C36H82Cl2N8Ni2O15
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aquabis(3-nitrobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-pyrazine-N: N′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N4O9Cd
- Crystal structure of 4-(2,2-difluoroethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione, C14H15F2NO2
- The crystal structure of thioxanthen-9-one-10,10-dioxide, C13H8O3S – a second polymorph
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-methoxy-3-pyridyl)methylene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- The crystal structure of diaquahydrogen 2,5-dimethylbenzenesulphonate, C8H14O5S
- The crystal structure of N-(4-(cyclohexylimino)pent-2-en-2-yl)cyclohexanamine, C17H30N2
- The twinned crystal structure of 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium dibromide, C8H14Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2,4,7,9-tetranitro-10H-benzofuro[3,2-b]indole – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1), C16H11N5O10S
- Crystal structure of 2,6-bis(2-(pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)pyrrolo[3,4-f]isoindole-1,3,5,7(2H,6H)-tetraone, C24H18N4O4
- The crystal structure of 3,4-dichlorobenzoic acid chloride, C7H3Cl3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-k2S:S)zinc(II), C26H18N6ZnS4
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ-naphthalene-1-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)bis(methanol)copper(II), C46H36Cu2O10
- Crystal structure of 9-methyl-3-methylene-1,2,3,9-tetrahydro-4H-carbazol-4-one, C14H13NO
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(carbamothioylamino)methaniminium) 3-nitrophthalate monohydrate, C12H19N9O7S2
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,2-phenylene-bis(methylene))bis(1-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate), C18H24F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-6,8-dimethoxy-2-methyl-4H-benzo[g]chromen-4-one– rubrofusarin B, C16H14O5
- The crystal structure of bis(ethanol-kO)- bis(6-aminopicolinato-k2N,O)manganese(II), C16H22O6N4Mn
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-((carbonylbis(azanediyl))bis(ethane-2,1-diyl)) bis(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium) tetrafluoroborate monohydrate, C21H28N6O3B2F8
- Crystal structure of dimethanol-dichlorido-bis( μ2-2-(((1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2- phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato- κ4O:O,O′,N)dinickel (II), C20H24ClNiN3O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate, C7H6F3NO2
- Crystal structure of (OC‐6‐13)‐aqua‐tris (3‐bromopyridine‐κ1N)‐bis(trifluoroacetato‐κ1O)cadmium(II) C19H14Br3CdF6N3O5
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-3-(4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)phenyl) acrylate, C14H16O5
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of 2-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-3-bromo-5-chlorophenol, C13H8BrClN2O
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-N-(2-methyl-1-oxidopropylidene)-2-oxidobenzohydrazonate-κ5N,O,O′:N′,O′′)pentakis(pyridine-κ1N)tricopper(II), C47H45Cl2N9Cu3O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-bis(nitrato-κ2O:O′)- (μ2-((1 H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2 N,N′)-H2O-κ2O]cadmium(II), C14H16N6O7Cd
- The crystal structure of pentakis(carbonyl)-{μ-[2,3-bis(sulfanyl)propan-1-olato]}-(triphenylphosphane)diiron (Fe–Fe)C26H21Fe2O6PS2
- Crystal structure of ethyl-2-(3-benzoylthioureido)propanoate, C13H16N2O3S
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4b,5,14,15-tetrahydro-6H-isoquinolino[2′,1′:1,6] pyrazino[2,3-b]quinoxaline, C19H18N4O
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-[ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidenemethylylidene)]bis(6-chlorophenol), C16H14Cl2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-((2-(2-(2-aminophenoxy)ethoxy)phenyl)amino)-1-phenylbut-2-en-1-one, C24H24N2O3
- The crystal structure of 10-(3,5-di(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)-10H-phenoxazine dihydrate, C28H23N3O3
- Crystal structure of poly[dipoly[aqua-di(µ2-pyrazin-2-olato-κ2N:N′) zinc(II)], C8H8N4O3Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetra(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κO)-manganese(II)-platinum(II)], C10H14MnN6O2Pt
- The crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-6,6′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dichlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C16H12Cl5MnN2O3
- Crystal structure of [di(µ2-cyanido)-dicyanido-bis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)- bis(2,2′-(ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidenemethanylylidene))diphenolato-κ4,N,N′,O,O′)- dimanganese(III)-platinum(II)], C40H40Mn2N8O6PtS2
- The crystal structure of (azido)-κ1N-6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato-κ4N,N,O,O)-(methanol)-manganese(III)–methanol(1/1), C22H26Br2MnN5O4
- Crystal structure of 7-chloro-N-(4-iodobenzyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridin-9-amine, C20H18ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N′′′)-bis(μ2-thiocyanato-κ2N:S)-bis(thiocyanato-κS)-nickel(II)palladium(II)], C14H24N8NiPdS4
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-4-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)aniline monohydrate, C12H20ClN3O
- Crystal structure of the 2D coordination polymer poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3- methoxyisonicotinato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] — dimethylformamide (1/1), C20H30CoN4O10
- Crystal structure of 4-[(5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino]-3-propyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C12H13ClN4OS
- Crystal structure of N-(5-(2-(benzyl(1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-yl)amino)-1-hydroxyethyl)-2-(benzyloxy)phenyl)formamide, C33H36N2O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, C9H12O5
- The crystal structure of 1-((dimethylamino)(3-nitrophenyl)methyl)naphthalen-2-ol, C19H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)-dicyanido-tetrakis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)-manganese(II)-platinum(II)], C12H24MnN4O4PtS4
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-N-(2-pyrimidinyl)benzenesulfonamide–1,4-dioxane (1/1), C14H18N4O4S
- Crystal structure of bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,3-(2-methyl-imidazol)}di-chloridomercury(II), [Hg(C11H11N5)2Cl2], C22H22N10Cl2Hg
- Crystal structure of 2, 3-bis((4-methylbenzoyl)oxy) succinic acid–N, N-dimethylformamide (1/1), C23H25NO9
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(4-(4-carboxyphenoxy)benzoato-κ1O)-μ2-(1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C40H28N4O10Co
- Crystal structure of 1H-imidazol-3-ium poly[aqua-(μ4-glutarato-κ6O,O′:O′:O′′,O′′′:O′′′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)strontium(II)], C8H13N3O8Sr
- Crystal structure of (R)-6-(benzo[b]thiophen-5-yl)-2-methyl-2,6-dihydrobenzo [5,6] silino[4,3,2-cd]indole, C23H17NSSi
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-thiocyanato-κ2N:S)-(2-(5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)pyridine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)]–dioxane (1/1), C15H17CdN5O2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-1,4-bis(2′-carboxylatophenoxy)benzene-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridione-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)] monhydrate, C30H22CdN2O7⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-k2N:N′)-bis(μ2-4′-methyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,5-dicarboxylato-k4O,O′:O″,O′″)dicadmium(II)] dihydrate, C20H20NO7Cd
- Crystal structure of 1‐tert‐butyl‐3‐(2,6‐diisopropyl‐4‐phenoxyphenyl)‐2-methylisothiourea, C24H34N2OS
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-(4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — N,N′-dimethylformamide (1/1), C28H34N8O8Co
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ1N)manganese(II) 2,3-dihydroxyterephthalate, C32H32MnN8O10

