Abstract
C8H14Br2N2, monoclinic, I2/a (no. 15), a = 9.0331(9) Å, b = 13.4475(14) Å, c = 27.586(3) Å, β = 94.879(9)°, Z = 12, V = 3338.8(6) Å3, Rgt(F) = 0.0582, wRref = 0.0885, T = 290 K.
Tables 1 and 2 contain details on the crystal structure as well as measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless needle |
| Size: | 0.67 × 0.14 × 0.04 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 7.24 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Xcalibur, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.0°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique | 9870, 9870 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 6167 |
| N(param)refined: | 171 |
| Programs: | Diamond [1], CrysAlisPRO [2], SHELX [3], [4], [5] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Br1 | 0.34206 (7) | 0.65873 (5) | 0.59810 (3) | 0.0450 (2) |
| Br2 | 0.38821 (8) | 0.29498 (6) | 0.65036 (3) | 0.0508 (2) |
| Br3 | 0.81651 (7) | 0.00903 (5) | 0.57816 (3) | 0.0446 (2) |
| N1 | 0.1378 (5) | 0.4737 (4) | 0.64036 (19) | 0.0421 (17) |
| H11 | 0.173 (4) | 0.536 (2) | 0.6344 (6) | 0.063* |
| H12 | 0.061 (3) | 0.459 (3) | 0.6176 (8) | 0.063* |
| H13 | 0.213 (4) | 0.428 (3) | 0.6384 (5) | 0.063* |
| N2 | 0.4155 (5) | 0.3444 (4) | 0.87023 (19) | 0.0416 (17) |
| H21 | 0.320 (4) | 0.317 (3) | 0.8673 (2) | 0.062* |
| H22 | 0.413 (4) | 0.405 (2) | 0.8869 (8) | 0.062* |
| H23 | 0.481 (3) | 0.301 (3) | 0.8875 (8) | 0.062* |
| N3 | 0.5516 (5) | 0.1762 (4) | 0.5630 (2) | 0.0428 (18) |
| H31 | 0.474 (3) | 0.136 (3) | 0.5693 (6) | 0.064* |
| H32 | 0.558 (4) | 0.2278 (18) | 0.5847 (8) | 0.064* |
| H33 | 0.638 (4) | 0.140 (3) | 0.5661 (5) | 0.064* |
| C1 | 0.0842 (7) | 0.4706 (5) | 0.6899 (2) | 0.0418 (19) |
| H1A | 0.046393 | 0.404593 | 0.695782 | 0.050* |
| H1B | 0.002849 | 0.517270 | 0.691316 | 0.050* |
| C2 | 0.2040 (6) | 0.4957 (5) | 0.7292 (2) | 0.0321 (16) |
| C3 | 0.2424 (7) | 0.5936 (5) | 0.7388 (3) | 0.0418 (18) |
| H3 | 0.195975 | 0.644503 | 0.720399 | 0.050* |
| C4 | 0.3483 (8) | 0.6149 (5) | 0.7752 (3) | 0.0445 (19) |
| H4A | 0.373114 | 0.680905 | 0.781768 | 0.053* |
| C5 | 0.4195 (7) | 0.5411 (6) | 0.8024 (2) | 0.0420 (18) |
| H5A | 0.492474 | 0.557676 | 0.826850 | 0.050* |
| C6 | 0.3841 (7) | 0.4433 (5) | 0.7938 (2) | 0.0336 (17) |
| C7 | 0.2749 (7) | 0.4212 (5) | 0.7569 (2) | 0.0345 (17) |
| H7A | 0.249017 | 0.355192 | 0.750605 | 0.041* |
| C8 | 0.4656 (7) | 0.3617 (5) | 0.8211 (2) | 0.0434 (19) |
| H8A | 0.453020 | 0.300785 | 0.802428 | 0.052* |
| H8B | 0.570684 | 0.377590 | 0.824368 | 0.052* |
| C9 | 0.5275 (7) | 0.2154 (6) | 0.5133 (2) | 0.048 (2) |
| H9A | 0.526552 | 0.160767 | 0.490372 | 0.057* |
| H9B | 0.608955 | 0.259240 | 0.507076 | 0.057* |
| C10 | 0.3830 (7) | 0.2718 (6) | 0.5057 (2) | 0.0357 (17) |
| C11 | 0.3821 (8) | 0.3735 (6) | 0.5059 (3) | 0.057 (2) |
| H11A | 0.471775 | 0.407750 | 0.510117 | 0.069* |
| C12 | 0.250000 | 0.4268 (8) | 0.500000 | 0.066 (3) |
| H12A | 0.249998 | 0.495945 | 0.500001 | 0.079* |
| C13 | 0.250000 | 0.2213 (7) | 0.500000 | 0.037 (2) |
| H13A | 0.250001 | 0.152185 | 0.500000 | 0.044* |
Source of material
The title compound 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium dibromide was synthesized by the reaction of 63% aqueous hydrobromic acid and 1,3-phenylenedimethanamine at ambient conditions. In a typical experiment 1 mmol of 1,3-phenylenedimethanamine is reacted with an excess of hydrobromic acid. The resulting light-yellow solution was stored in a desiccator equipped with a small amount of molecular sieve. Clear colourless crystals were obtained after a few days.
Experimental details
A crystal of the title compound was directly selected from the mother liquor and mounted on an Xcalibur four-circle diffractometer equipped with an EOS detector [2]. An empirical absorption correction using spherical harmonics based on multi-scans was applied [2]. The structure solution, completion and the refinement, succeeded using the SHELX program system [3], [4], [5]. All investigated crystals showed a systematic non-merohedral twinning with a systematic and perfect overlap of some groups of reflections. We finally selected a crystal with an approximate twin ratio of 1:1. The twin operation is a twofold axis around 0.000, 0.707, 0.707 in the reciprocal lattice (0.060, 0.970 0.234 for the direct lattice). The resulting twin matrix is: −1.000, 0.000, 0.000; 0.100, 0.612, 0.387; 0.100, 1.613, −0.613. Atomic coordinates of hydrogen atoms were added using the corresponding riding model with fixed Uiso parameters. The maximum residual electron density peaks (all > 0.66 e⋅Å−3) are right next to the bromide anions.
Comment
There is a longstanding interest of one of us (GJR) in the structural chemistry of diaminium salts and their hydrogen bonding schemes [6], [7], [8], [9].
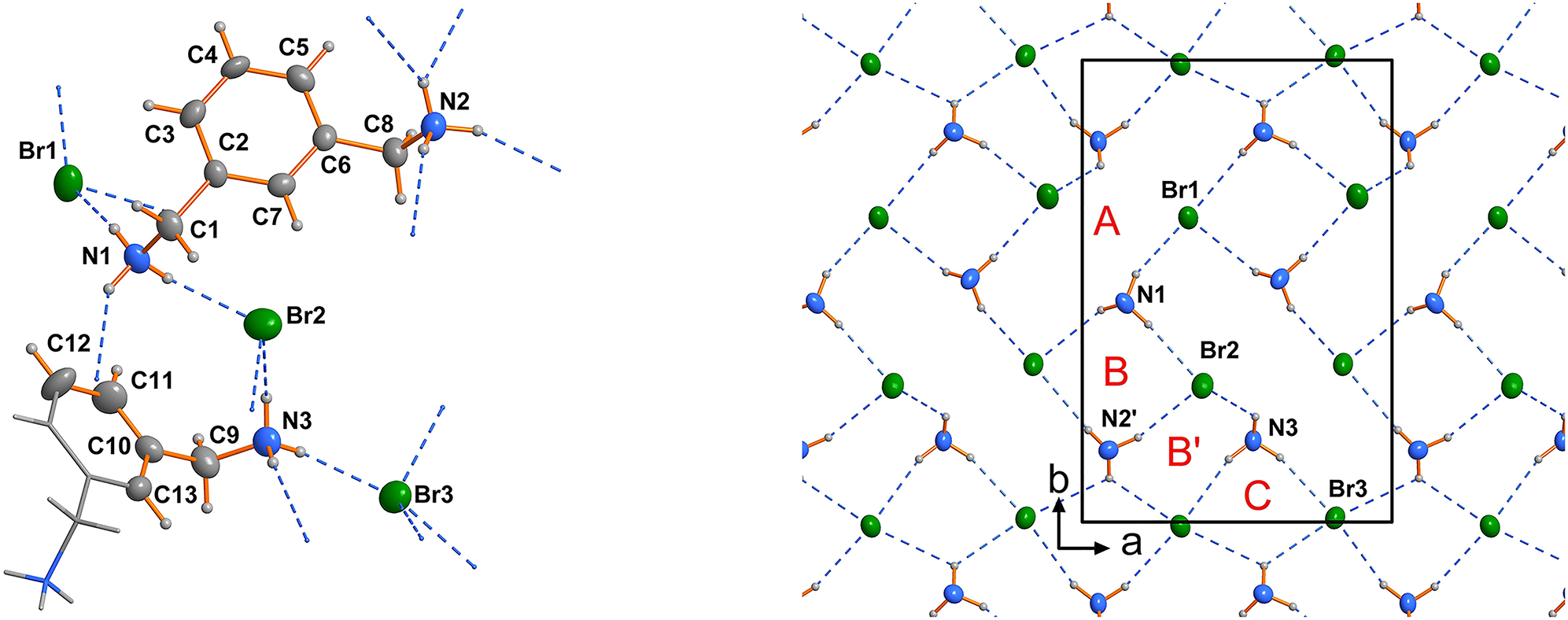
We have already shown that the lengths and shapes of organic cations influence or even determine the topology of the embedded polyhalogenide anions [6 and reference therein]. The final structural motif of such a system is a compromise between the accessible molecular conformations, hydrogen bonding and other weak intermolecular forces like van der Waals interactions of adjacent alkyl chains [8], [, 10]. In presence of aryl moieties CH–π and π-π interaction needs to be considered [11]. The 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium cation is a typical cationic, semi-flexible tecton, which can form hydrogen-bonded and cross-linked networks. In contrast to simple aliphatic diaminium cations the conformational adjustments are restricted to rotations about the CH2–aryl single bond (see the left part of the Figure).
There are already some 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium salt structures listed in The Cambrige Structural Database. A small share of these structures contain simple counter anions like: chloride [12], perchlorate [13], sulfate [14], nitrate [15], tetraiodide [16], which form hydrogen bonded networks with the 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium cation. Furthermore some 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium salts with complex counter anions are in the focus of current research [17], [, 18] because of their physical properties.
The asymmetric unit of the title structure contains one 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium dication in general position and another half of a 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium dication located on a twofold axis (see the left part of the Figure). Consequently, there are three bromide counter anions in the asymmetric unit, which are all in general positions. Thus, the Z′ parameter [19] is 1.5, a finding which is not uncommon in chemical crystallography [20], [21], [22]. The same situation has been reported for the directly structurally related 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium dichloride [12]. Bond lengths and angles in the cation are in the range of expectations [12], [13], [14], [15], [16], [17], [18]. The 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium cations in the title structure use their conformational flexibility by a rotation about the C1–C2, C6–C8 and C9–C10 single bonds, respectively (left part of the Figure). A dihedral angle of −172.4(6)° for the atoms N1, C2, C8, N2 in this structure leads to the wellknown [16] double hook shape of the 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium dication. The 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium cation located on the twofold axis shows a significantly different conformation (N3–C9–C9′–N3′ = −136.9(8); ′ = −x + 1/2, y, −z + 1).
Cations and anions are connected via NH⃛Br hydrogen bonds (see the Figure). Each –NH3 group donates at least three hydrogen bonds and each bromide anion accepts at least three of them. All Br⃛H distances are significantly below the typical van der Waals distances [23]. These hydrogen bonds construct a 2D-network in the ab plane. In this network three different ring types (right part of the Figure) can be assigned {graph set descriptors [24]: A:
The title structure shows the ability of semiflexible organic cations to support the formation of an ordered crystalline material by its conformational adjustments to form a maximum of hydrogen bonds.
Funding source: Ministry of Innovation, Science and Research of North–Rhine Westphalia and the German Research Foundation (DFG)
Award Identifier / Grant number: INST 208/533–1, 162659349
Funding source: Heinrich–Heine–Universität Düsseldorf
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
Research funding: This research was funded by the Ministry of Innovation, Science and Research of North–Rhine Westphalia and the German Research Foundation – DFG (Xcalibur diffractometer; INST 208/533–1, project no. 162659349). Finally, funding by the open access fund of the Heinrich–Heine–Universität Düsseldorf is also gratefully acknowledged.
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Brandenburg, K. diamond. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Ver. 4.5.2; Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2018.Search in Google Scholar
2. Oxford Diffraction. CrysAlisPRO. (version 1.171.33.42); Oxford Diffraction Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
5. Hübschle, C. B., Sheldrick, G. M., Dittrich, B. ShelXle: a Qt graphical user interface for SHELXL. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1281–1284; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889811043202.Search in Google Scholar
6. Megen van, M., Reiss, G. J. I62− Anion composed of two asymmetric triiodide moieties: a competition between halogen and hydrogen bond. Inorganics 2013, 1, 3–13; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics1010003.Search in Google Scholar
7. Reiss, G. J., van Megen, M. Two new polyiodides in the 4,4′-bipyridinium diiodide/iodine system. Z. Naturforsch. 2012, B67, 5–10; https://doi.org/10.1515/znb-2012-0102.Search in Google Scholar
8. Reiss, G. J., Engel, J. S. Hydrogen bonded 1,10-diammoniodecane - an example of an organo-template for the crystal engineering of polymeric polyiodides. CrystEngComm 2002, 4, 155–161; https://doi.org/10.1039/B203499A.Search in Google Scholar
9. van Megen, M., Jablonka, A., Reiss, G. J. Synthesis, structure and thermal decomposition of a new iodine inclusion compound in the 2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diamine/HI/I2 system. Z. Naturforsch. 2014, B69, 753–760; https://doi.org/10.5560/znb.2014-4088.Search in Google Scholar
10. Visi, M. Z., Knobler, C. B., Owen, J. J., Khan, M. I., Schubert, D. M. Structures of self-assembled nonmetal borates derived from α,ω-diaminoalkanes. Cryst. Growth Des. 2006, 6, 538–545; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg0504915.Search in Google Scholar
11. Dobrzycki, L., Woźniak, K. 1D vs 2D crystal architecture of hybrid inorganic-organic structures with benzidine dication. J. Mol. Struct. 2009, 921, 18–33; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2008.12.027.Search in Google Scholar
12. Cheng, H., Li, H. (m–Phenylenedimethylene)diammonium dichloride. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, E64, o2060; https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600536808031334.Search in Google Scholar
13. Guesmi, A., Roisnel, T., Marouani, H. Featuring non-covalent interactions in m-xylylenediaminium bis(perchlorate) monohydrate: synthesis, characterization and Hirshfeld surface analysis. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1194, 66–72; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.04.124.Search in Google Scholar
14. Guesmi, A., Gatfaoui, S., Roisnel, T., Marouani, H. m-Xylylenediaminium sulfate: crystal structure and Hirshfeld surface analysis. Acta Crystallogr. 2016, E72, 776–779; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2056989016006940.Search in Google Scholar
15. Gatfaoui, S., Dhaouadi, H., Roisnel, T., Rzaigui, M., Marouani, H. m-Xylylenediaminium dinitrate. Acta Crystallogr. 2014, E70, o398–o399; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536814004620.Search in Google Scholar
16. Reiss, G. J. Crystal structure of bis(1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium) bis(triiodide) tetraiodide - water (1/2), C8H16I5N2O. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2020, 235, 1047–1050; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020-0164.Search in Google Scholar
17. Su, B., Song, G., Molokeev, M. S., Lin, Z., Xia, Z. Synthesis, crystal structure and green luminescence in zero-dimensional tin halide (C8H14N2)2SnBr6. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 9962–9968; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c01103.Search in Google Scholar
18. Jomaa, I., Noureddine, O., Gatfaoui, S., Issaoui, N., Roisnel, T., Marouani, H. Experimental, computational, and in silico analysis of (C8H14N2)2[CdCl6] compound. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1213, 128186; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128186.Search in Google Scholar
19. Steed, K. M., Steed, J. W. Packing Problems: high Z′ crystal structures and their relationship to cocrystals, inclusion compounds, and polymorphism. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2895–2933; https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500564z.Search in Google Scholar
20. Todd, A. M., Anderson, K. M., Byrne, P., Goeta, A. E., Steed, J. W. Helical or polar guest-dependent Z′ = 1.5 or Z′ = 2 forms of a sterically hindered bis(urea) clathrate. Cryst. Growth Des. 2006, 6, 1750–1752; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg060318o.Search in Google Scholar
21. Kirsop, P., Storey, J. M. D., Harrison, W. T. A. 2–Bromo-1,3-bis(bromomethyl)benzene, with Z′ = 1.5: whole-molecule disorder of one of the two independent molecules. Acta Crystallogr. 2006, C62, o376–o378; https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108270106017707.Search in Google Scholar
22. Lo Presti, L., Soave, R., Longhi, M., Ortoleva, E. Conformational polymorphism in a Schiff-base macrocyclic organic ligand: an experimental and theoretical study. Acta Crystallogr. 2010, B66, 527–543; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108768110029514.Search in Google Scholar
23. Hu, S.-Z., Zhou, Z.-H., Xie, Z.-X., Robertson, B. E. A comparative study of crystallographic van der Waals radii. Z. Kristallogr. CM 2014, 229, 517–523; https://doi.org/10.1515/zkri-2014-1726.Search in Google Scholar
24. Grell, J., Bernstein, J., Tinhofer, G. Investigation of hydrogen bond patterns. A review of mathematical tools for the graph set approach. Crystallogr. Rev. 2002, 8, 1–56; https://doi.org/10.1080/08893110211936.Search in Google Scholar
© 2020 Niklas Brandt and Guido J. Reiss, published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxidoethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ5N,O,O′:N′,O′′)hexkis(pyridine-κ1N)trinickel(II) - pyridine (1/1), C63H57Cl2N13Ni3O6
- Crystal structure of [(μ2-succinato κ3O,O′:O′′)-bis-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)]dinickel(II)] diperchlorate, dihydrate C36H82Cl2N8Ni2O15
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aquabis(3-nitrobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-pyrazine-N: N′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N4O9Cd
- Crystal structure of 4-(2,2-difluoroethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione, C14H15F2NO2
- The crystal structure of thioxanthen-9-one-10,10-dioxide, C13H8O3S – a second polymorph
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-methoxy-3-pyridyl)methylene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- The crystal structure of diaquahydrogen 2,5-dimethylbenzenesulphonate, C8H14O5S
- The crystal structure of N-(4-(cyclohexylimino)pent-2-en-2-yl)cyclohexanamine, C17H30N2
- The twinned crystal structure of 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium dibromide, C8H14Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2,4,7,9-tetranitro-10H-benzofuro[3,2-b]indole – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1), C16H11N5O10S
- Crystal structure of 2,6-bis(2-(pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)pyrrolo[3,4-f]isoindole-1,3,5,7(2H,6H)-tetraone, C24H18N4O4
- The crystal structure of 3,4-dichlorobenzoic acid chloride, C7H3Cl3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-k2S:S)zinc(II), C26H18N6ZnS4
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ-naphthalene-1-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)bis(methanol)copper(II), C46H36Cu2O10
- Crystal structure of 9-methyl-3-methylene-1,2,3,9-tetrahydro-4H-carbazol-4-one, C14H13NO
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(carbamothioylamino)methaniminium) 3-nitrophthalate monohydrate, C12H19N9O7S2
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,2-phenylene-bis(methylene))bis(1-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate), C18H24F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-6,8-dimethoxy-2-methyl-4H-benzo[g]chromen-4-one– rubrofusarin B, C16H14O5
- The crystal structure of bis(ethanol-kO)- bis(6-aminopicolinato-k2N,O)manganese(II), C16H22O6N4Mn
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-((carbonylbis(azanediyl))bis(ethane-2,1-diyl)) bis(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium) tetrafluoroborate monohydrate, C21H28N6O3B2F8
- Crystal structure of dimethanol-dichlorido-bis( μ2-2-(((1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2- phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato- κ4O:O,O′,N)dinickel (II), C20H24ClNiN3O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate, C7H6F3NO2
- Crystal structure of (OC‐6‐13)‐aqua‐tris (3‐bromopyridine‐κ1N)‐bis(trifluoroacetato‐κ1O)cadmium(II) C19H14Br3CdF6N3O5
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-3-(4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)phenyl) acrylate, C14H16O5
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of 2-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-3-bromo-5-chlorophenol, C13H8BrClN2O
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-N-(2-methyl-1-oxidopropylidene)-2-oxidobenzohydrazonate-κ5N,O,O′:N′,O′′)pentakis(pyridine-κ1N)tricopper(II), C47H45Cl2N9Cu3O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-bis(nitrato-κ2O:O′)- (μ2-((1 H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2 N,N′)-H2O-κ2O]cadmium(II), C14H16N6O7Cd
- The crystal structure of pentakis(carbonyl)-{μ-[2,3-bis(sulfanyl)propan-1-olato]}-(triphenylphosphane)diiron (Fe–Fe)C26H21Fe2O6PS2
- Crystal structure of ethyl-2-(3-benzoylthioureido)propanoate, C13H16N2O3S
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4b,5,14,15-tetrahydro-6H-isoquinolino[2′,1′:1,6] pyrazino[2,3-b]quinoxaline, C19H18N4O
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-[ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidenemethylylidene)]bis(6-chlorophenol), C16H14Cl2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-((2-(2-(2-aminophenoxy)ethoxy)phenyl)amino)-1-phenylbut-2-en-1-one, C24H24N2O3
- The crystal structure of 10-(3,5-di(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)-10H-phenoxazine dihydrate, C28H23N3O3
- Crystal structure of poly[dipoly[aqua-di(µ2-pyrazin-2-olato-κ2N:N′) zinc(II)], C8H8N4O3Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetra(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κO)-manganese(II)-platinum(II)], C10H14MnN6O2Pt
- The crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-6,6′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dichlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C16H12Cl5MnN2O3
- Crystal structure of [di(µ2-cyanido)-dicyanido-bis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)- bis(2,2′-(ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidenemethanylylidene))diphenolato-κ4,N,N′,O,O′)- dimanganese(III)-platinum(II)], C40H40Mn2N8O6PtS2
- The crystal structure of (azido)-κ1N-6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato-κ4N,N,O,O)-(methanol)-manganese(III)–methanol(1/1), C22H26Br2MnN5O4
- Crystal structure of 7-chloro-N-(4-iodobenzyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridin-9-amine, C20H18ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N′′′)-bis(μ2-thiocyanato-κ2N:S)-bis(thiocyanato-κS)-nickel(II)palladium(II)], C14H24N8NiPdS4
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-4-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)aniline monohydrate, C12H20ClN3O
- Crystal structure of the 2D coordination polymer poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3- methoxyisonicotinato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] — dimethylformamide (1/1), C20H30CoN4O10
- Crystal structure of 4-[(5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino]-3-propyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C12H13ClN4OS
- Crystal structure of N-(5-(2-(benzyl(1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-yl)amino)-1-hydroxyethyl)-2-(benzyloxy)phenyl)formamide, C33H36N2O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, C9H12O5
- The crystal structure of 1-((dimethylamino)(3-nitrophenyl)methyl)naphthalen-2-ol, C19H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)-dicyanido-tetrakis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)-manganese(II)-platinum(II)], C12H24MnN4O4PtS4
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-N-(2-pyrimidinyl)benzenesulfonamide–1,4-dioxane (1/1), C14H18N4O4S
- Crystal structure of bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,3-(2-methyl-imidazol)}di-chloridomercury(II), [Hg(C11H11N5)2Cl2], C22H22N10Cl2Hg
- Crystal structure of 2, 3-bis((4-methylbenzoyl)oxy) succinic acid–N, N-dimethylformamide (1/1), C23H25NO9
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(4-(4-carboxyphenoxy)benzoato-κ1O)-μ2-(1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C40H28N4O10Co
- Crystal structure of 1H-imidazol-3-ium poly[aqua-(μ4-glutarato-κ6O,O′:O′:O′′,O′′′:O′′′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)strontium(II)], C8H13N3O8Sr
- Crystal structure of (R)-6-(benzo[b]thiophen-5-yl)-2-methyl-2,6-dihydrobenzo [5,6] silino[4,3,2-cd]indole, C23H17NSSi
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-thiocyanato-κ2N:S)-(2-(5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)pyridine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)]–dioxane (1/1), C15H17CdN5O2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-1,4-bis(2′-carboxylatophenoxy)benzene-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridione-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)] monhydrate, C30H22CdN2O7⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-k2N:N′)-bis(μ2-4′-methyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,5-dicarboxylato-k4O,O′:O″,O′″)dicadmium(II)] dihydrate, C20H20NO7Cd
- Crystal structure of 1‐tert‐butyl‐3‐(2,6‐diisopropyl‐4‐phenoxyphenyl)‐2-methylisothiourea, C24H34N2OS
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-(4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — N,N′-dimethylformamide (1/1), C28H34N8O8Co
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ1N)manganese(II) 2,3-dihydroxyterephthalate, C32H32MnN8O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxidoethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ5N,O,O′:N′,O′′)hexkis(pyridine-κ1N)trinickel(II) - pyridine (1/1), C63H57Cl2N13Ni3O6
- Crystal structure of [(μ2-succinato κ3O,O′:O′′)-bis-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)]dinickel(II)] diperchlorate, dihydrate C36H82Cl2N8Ni2O15
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aquabis(3-nitrobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-pyrazine-N: N′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N4O9Cd
- Crystal structure of 4-(2,2-difluoroethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione, C14H15F2NO2
- The crystal structure of thioxanthen-9-one-10,10-dioxide, C13H8O3S – a second polymorph
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-methoxy-3-pyridyl)methylene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- The crystal structure of diaquahydrogen 2,5-dimethylbenzenesulphonate, C8H14O5S
- The crystal structure of N-(4-(cyclohexylimino)pent-2-en-2-yl)cyclohexanamine, C17H30N2
- The twinned crystal structure of 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium dibromide, C8H14Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2,4,7,9-tetranitro-10H-benzofuro[3,2-b]indole – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1), C16H11N5O10S
- Crystal structure of 2,6-bis(2-(pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)pyrrolo[3,4-f]isoindole-1,3,5,7(2H,6H)-tetraone, C24H18N4O4
- The crystal structure of 3,4-dichlorobenzoic acid chloride, C7H3Cl3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-k2S:S)zinc(II), C26H18N6ZnS4
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ-naphthalene-1-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)bis(methanol)copper(II), C46H36Cu2O10
- Crystal structure of 9-methyl-3-methylene-1,2,3,9-tetrahydro-4H-carbazol-4-one, C14H13NO
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(carbamothioylamino)methaniminium) 3-nitrophthalate monohydrate, C12H19N9O7S2
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,2-phenylene-bis(methylene))bis(1-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate), C18H24F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-6,8-dimethoxy-2-methyl-4H-benzo[g]chromen-4-one– rubrofusarin B, C16H14O5
- The crystal structure of bis(ethanol-kO)- bis(6-aminopicolinato-k2N,O)manganese(II), C16H22O6N4Mn
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-((carbonylbis(azanediyl))bis(ethane-2,1-diyl)) bis(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium) tetrafluoroborate monohydrate, C21H28N6O3B2F8
- Crystal structure of dimethanol-dichlorido-bis( μ2-2-(((1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2- phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato- κ4O:O,O′,N)dinickel (II), C20H24ClNiN3O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate, C7H6F3NO2
- Crystal structure of (OC‐6‐13)‐aqua‐tris (3‐bromopyridine‐κ1N)‐bis(trifluoroacetato‐κ1O)cadmium(II) C19H14Br3CdF6N3O5
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-3-(4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)phenyl) acrylate, C14H16O5
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of 2-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-3-bromo-5-chlorophenol, C13H8BrClN2O
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-N-(2-methyl-1-oxidopropylidene)-2-oxidobenzohydrazonate-κ5N,O,O′:N′,O′′)pentakis(pyridine-κ1N)tricopper(II), C47H45Cl2N9Cu3O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-bis(nitrato-κ2O:O′)- (μ2-((1 H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2 N,N′)-H2O-κ2O]cadmium(II), C14H16N6O7Cd
- The crystal structure of pentakis(carbonyl)-{μ-[2,3-bis(sulfanyl)propan-1-olato]}-(triphenylphosphane)diiron (Fe–Fe)C26H21Fe2O6PS2
- Crystal structure of ethyl-2-(3-benzoylthioureido)propanoate, C13H16N2O3S
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4b,5,14,15-tetrahydro-6H-isoquinolino[2′,1′:1,6] pyrazino[2,3-b]quinoxaline, C19H18N4O
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-[ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidenemethylylidene)]bis(6-chlorophenol), C16H14Cl2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-((2-(2-(2-aminophenoxy)ethoxy)phenyl)amino)-1-phenylbut-2-en-1-one, C24H24N2O3
- The crystal structure of 10-(3,5-di(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)-10H-phenoxazine dihydrate, C28H23N3O3
- Crystal structure of poly[dipoly[aqua-di(µ2-pyrazin-2-olato-κ2N:N′) zinc(II)], C8H8N4O3Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetra(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κO)-manganese(II)-platinum(II)], C10H14MnN6O2Pt
- The crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-6,6′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dichlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C16H12Cl5MnN2O3
- Crystal structure of [di(µ2-cyanido)-dicyanido-bis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)- bis(2,2′-(ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidenemethanylylidene))diphenolato-κ4,N,N′,O,O′)- dimanganese(III)-platinum(II)], C40H40Mn2N8O6PtS2
- The crystal structure of (azido)-κ1N-6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato-κ4N,N,O,O)-(methanol)-manganese(III)–methanol(1/1), C22H26Br2MnN5O4
- Crystal structure of 7-chloro-N-(4-iodobenzyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridin-9-amine, C20H18ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N′′′)-bis(μ2-thiocyanato-κ2N:S)-bis(thiocyanato-κS)-nickel(II)palladium(II)], C14H24N8NiPdS4
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-4-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)aniline monohydrate, C12H20ClN3O
- Crystal structure of the 2D coordination polymer poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3- methoxyisonicotinato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] — dimethylformamide (1/1), C20H30CoN4O10
- Crystal structure of 4-[(5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino]-3-propyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C12H13ClN4OS
- Crystal structure of N-(5-(2-(benzyl(1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-yl)amino)-1-hydroxyethyl)-2-(benzyloxy)phenyl)formamide, C33H36N2O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, C9H12O5
- The crystal structure of 1-((dimethylamino)(3-nitrophenyl)methyl)naphthalen-2-ol, C19H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)-dicyanido-tetrakis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)-manganese(II)-platinum(II)], C12H24MnN4O4PtS4
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-N-(2-pyrimidinyl)benzenesulfonamide–1,4-dioxane (1/1), C14H18N4O4S
- Crystal structure of bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,3-(2-methyl-imidazol)}di-chloridomercury(II), [Hg(C11H11N5)2Cl2], C22H22N10Cl2Hg
- Crystal structure of 2, 3-bis((4-methylbenzoyl)oxy) succinic acid–N, N-dimethylformamide (1/1), C23H25NO9
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(4-(4-carboxyphenoxy)benzoato-κ1O)-μ2-(1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C40H28N4O10Co
- Crystal structure of 1H-imidazol-3-ium poly[aqua-(μ4-glutarato-κ6O,O′:O′:O′′,O′′′:O′′′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)strontium(II)], C8H13N3O8Sr
- Crystal structure of (R)-6-(benzo[b]thiophen-5-yl)-2-methyl-2,6-dihydrobenzo [5,6] silino[4,3,2-cd]indole, C23H17NSSi
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-thiocyanato-κ2N:S)-(2-(5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)pyridine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)]–dioxane (1/1), C15H17CdN5O2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-1,4-bis(2′-carboxylatophenoxy)benzene-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridione-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)] monhydrate, C30H22CdN2O7⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-k2N:N′)-bis(μ2-4′-methyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,5-dicarboxylato-k4O,O′:O″,O′″)dicadmium(II)] dihydrate, C20H20NO7Cd
- Crystal structure of 1‐tert‐butyl‐3‐(2,6‐diisopropyl‐4‐phenoxyphenyl)‐2-methylisothiourea, C24H34N2OS
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-(4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — N,N′-dimethylformamide (1/1), C28H34N8O8Co
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ1N)manganese(II) 2,3-dihydroxyterephthalate, C32H32MnN8O10


