Abstract
C14H16N6O7Cd, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 12.7095(3) Å, b = 17.4705(4) Å, c = 8.5763(3) Å, β = 93.292(10)°, Z = 4, V = 1901.15(9) Å3, Rgt(F) = 0.0263, wRref(F2) = 0.1047, T = 296(2) K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.18 × 0.14 × 0.12 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.20 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.5°, 99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 17257, 4347, 0.028 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3836 |
| N(param)refined: | 255 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], Olex2 [3], Diamond [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.9029 (3) | 0.85918 (17) | 0.5993 (4) | 0.0453 (7) |
| H1A | 0.864663 | 0.902448 | 0.638863 | 0.054* |
| H1B | 0.946804 | 0.837953 | 0.684911 | 0.054* |
| C2 | 0.8260 (2) | 0.79944 (15) | 0.5373 (4) | 0.0380 (6) |
| C3 | 0.6887 (2) | 0.68823 (14) | 0.4117 (3) | 0.0361 (6) |
| C4 | 0.7297 (2) | 0.82056 (15) | 0.4654 (4) | 0.0435 (7) |
| H4 | 0.710885 | 0.871952 | 0.458652 | 0.052* |
| C5 | 0.7850 (2) | 0.66764 (14) | 0.4814 (4) | 0.0429 (7) |
| H5 | 0.804352 | 0.616325 | 0.486235 | 0.051* |
| C6 | 0.85326 (19) | 0.72311 (16) | 0.5444 (4) | 0.0447 (7) |
| H6 | 0.917875 | 0.708625 | 0.591684 | 0.054* |
| C7 | 0.6619 (2) | 0.76522 (15) | 0.4040 (4) | 0.0429 (6) |
| H7 | 0.597279 | 0.779698 | 0.356769 | 0.051* |
| C8 | 0.6107 (3) | 0.62868 (14) | 0.3551 (4) | 0.0416 (7) |
| H8A | 0.566469 | 0.648854 | 0.268751 | 0.050* |
| H8B | 0.647602 | 0.584172 | 0.318381 | 0.050* |
| C9 | 0.4474 (2) | 0.63175 (13) | 0.5052 (4) | 0.0344 (6) |
| H9 | 0.408295 | 0.662706 | 0.435260 | 0.041* |
| C10 | 0.57615 (18) | 0.56456 (13) | 0.6113 (3) | 0.0348 (5) |
| H10 | 0.640917 | 0.540456 | 0.629791 | 0.042* |
| C11 | 0.49548 (19) | 0.56439 (13) | 0.7059 (3) | 0.0334 (5) |
| H11 | 0.494907 | 0.539529 | 0.801777 | 0.040* |
| C12 | 1.02184 (19) | 0.93879 (14) | 0.2643 (4) | 0.0394 (6) |
| H12 | 1.024478 | 0.969607 | 0.176239 | 0.047* |
| C13 | 0.9418 (2) | 0.93711 (15) | 0.3623 (4) | 0.0429 (6) |
| H13 | 0.880219 | 0.965937 | 0.354111 | 0.052* |
| C14 | 1.0629 (2) | 0.85634 (16) | 0.4435 (4) | 0.0377 (6) |
| H14 | 1.098792 | 0.819168 | 0.503194 | 0.045* |
| Cd1 | 0.25711 (2) | 0.62897 (2) | 0.72705 (2) | 0.02835 (10) |
| N1 | 0.41389 (16) | 0.60684 (12) | 0.6385 (3) | 0.0321 (4) |
| N2 | 0.54515 (16) | 0.60664 (12) | 0.4835 (3) | 0.0321 (4) |
| N3 | 0.96953 (18) | 0.88494 (13) | 0.4746 (3) | 0.0364 (5) |
| N4 | 1.09821 (17) | 0.88791 (13) | 0.3157 (3) | 0.0355 (5) |
| N5 | 0.3246 (2) | 0.57681 (15) | 1.0379 (3) | 0.0462 (6) |
| N6 | 0.16370 (18) | 0.59363 (14) | 0.4187 (3) | 0.0400 (5) |
| O1 | 0.32005 (17) | 0.64621 (12) | 0.9937 (3) | 0.0421 (5) |
| O2 | 0.30656 (17) | 0.52576 (11) | 0.9374 (3) | 0.0518 (5) |
| O3 | 0.3462 (3) | 0.56272 (18) | 1.1748 (3) | 0.1005 (12) |
| O4 | 0.18826 (16) | 0.66020 (10) | 0.4704 (2) | 0.0397 (4) |
| O5 | 0.18496 (17) | 0.53760 (11) | 0.5036 (3) | 0.0452 (5) |
| O6 | 0.1208 (2) | 0.58865 (16) | 0.2886 (3) | 0.0815 (9) |
| O7 | 0.27372 (17) | 0.75953 (12) | 0.7364 (2) | 0.0565 (6) |
| H7A | 0.231101 | 0.783424 | 0.812925 | 0.12 (2)* |
| H7B | 0.293433 | 0.789077 | 0.645234 | 0.072 (12)* |
Source of material
All solvents and other reagents were of analytical grade. The method of synthesizing the title complex has been improved [5], [6], [7], [8]. A mixture of cadmium nitrate, 1,4-bis(1 H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene and water was introduced into a 25 mL Teflon lined reactor autoclave and heated to 115 °C for three days. After cooling to room temperature, colourless block crystals were obtained. Elemental analysis–Anal. Calcd. for C14H16N6O7Cd: C, 34.13%; H, 3.27%; N, 17.06%. Found: C, 34.19%; H, 3.31%; N, 16.98%.
Experimental details
Hydrogen atoms were placed in their geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms.
Comment
Coordination polymers (CPs) not only exhibit novel structures and topologies, but also may possess magnetic, optical and catalytic properties, etc. [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14]. Organic ligands are important for constructing CPs, and flexible ligands have different conformations and can be used to construct CPs with different structures.
In this work, we used ((1 H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene (L1) as a flexible ligand, assembling with Cd(NO3)2 to obtain a perfect 1D structure. Li et al. [15] already used the same ligand (L1) with Cd(NO3)2 obtaining a 2D structure, and Xu et al. [16] used the ligand (L1) with Cd(NO3)2 obtaining a 3D 2-fold interpenetrating structure. It can be seen that L1 forms different structures at different temperatures and solvents.
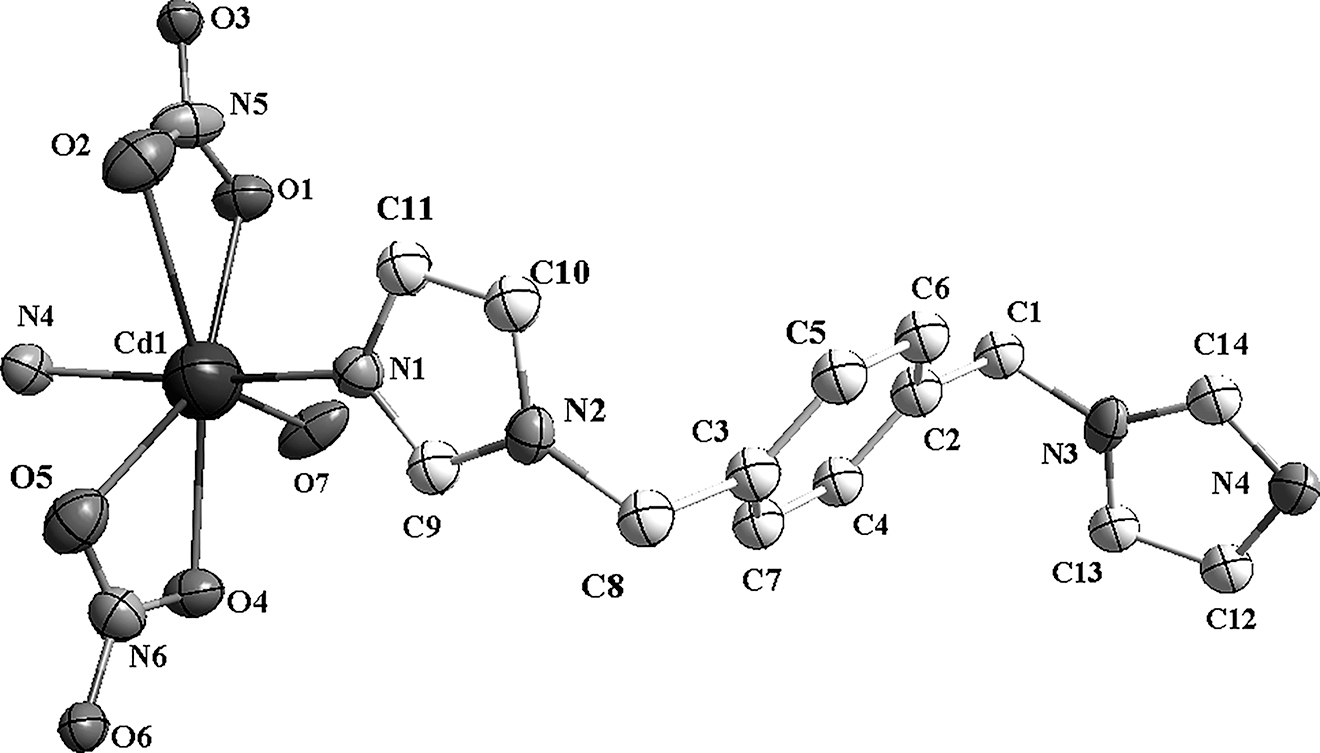
The crystal structure shows that the title complex consists of one Cd(II) atom, one L1 ligand, two nitrate anions and one coordinated water molecule. The Cd(II) atom is seven-coordinated with two nitrogen atoms (N1 and N4) from two L1 ligands four oxygen atoms (O1, O2, O4 and O5) from two nitrate ions and one oxygen atom (O7) from coordinated water. In the structure, Cd(II) is bridged by L1 ligands, forming a one-dimensional chain. Bond lengths and angles are all in the expected ranges [].
Funding source: Young Teacher Foundation of Lanzhou City University
Award Identifier / Grant number: LZCU-QN2017-17
Funding source: Young Teacher Foundation of Lanzhou City University
Award Identifier / Grant number: LZCU-QN2017-23
Funding source: Doctoral Research Initiation Fund
Award Identifier / Grant number: LZCU-BS2018-02
Funding source: Higher Education ResearchProject of Gansu Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2019B-171
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
Research funding: The research was financially supported by the Young Teacher Foundation of Lanzhou City University (LZCU-QN2017-17), the Young Teacher Foundation of Lanzhou City University (LZCU-QN2017-23), the Doctoral Research Initiation Fund (LZCU-BS2018-02), the Higher Education Research Project of Gansu Province (2019B-171).
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar
3. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis programm. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
4. Brandenburg, K. DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Ver. 4.0; Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2015.Search in Google Scholar
5. Ma, J. C., Dong, X. Y., Dong, W. K., Zhang, Y., Zhu, L. C., Zhang, J. T. An unexpected dinuclear Cu(II) complex with a bis(Salamo) chelating ligand: synthesis, crystal structure, and photophysical properties. J. Coord. Chem. 2016, 69, 149–159; https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2015.1108410.Search in Google Scholar
6. Li, G., Zhou, W. M., Zhu, L. C., Wang, L. Crystal structure of (Z)-1-(((3-acetyl-2-hydroxyphenyl)amino)methylene)naphthalen- 2(1H)-one, C19H15NO3. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2016, 231, 315–317; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2015-0166.Search in Google Scholar
7. Wu, H. L., Bai, Y. C., Zhang, Y. H., Li, Z., Wu, M. C. Synthesis, crystal structure, antioxidation and DNA-binding properties of a dinuclear copper(II) complex with bis( N-salicylidene)-3-oxapentane- 1,5-diamine. J. Coord. Chem. 2014, 67, 3054–3066; https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2014.959507.Search in Google Scholar
8. Song, X. Q., Liu, P. P., Liu, Y. A., Zhou, J. J., Wang, X. L. Two dodecanuclear heterometallic [Zn6Ln6] clusters constructed by a multidentate salicylamide salen-like ligand: synthesis, structure, luminescence and magnetic properties. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 8154–8163; https://doi.org/10.1039/c6dt00212a.Search in Google Scholar
9. Dong, W. K., Ma, J. C., Dong, Y. J., Zhu, L. C., Zhang, Y. Di-and tetranuclear heterometallic 3d-4f cobalt(II)-lanthanide(III) complexes derived from a hexadentate bisoxime: syntheses, structures and magnetic properties. Polyhedron 2016, 115, 228–235; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2016.05.017.Search in Google Scholar
10. Zhang, H., Xu, Y. L., Wu, H. L., Aderinto, S. O., Fan, X. Y. Mono-, bi- and multi-nuclear silver complexes constructed from bis(benzimidazole)- 2-oxapropane ligands and methacrylate: syntheses, crystal structures, DNA- binding properties and antioxidant activities. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 83697–83708; https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra09733b.Search in Google Scholar
11. Sun, Y. X., Lu, R. E., Li, X. R., Zhao, Y. Y., Li, C. Y. A Schiff base ligand containing oxime group and its Cu(II) complex: syntheses and supramolecular structures. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 31, 1055–1062.Search in Google Scholar
12. Dong, W. K., Ma, J. C., Zhu, L. C., Sun, Y. X., Akogun, S. F., Zhang, Y. A series of heteromultinuclear zinc(II)-lanthanide(III) complexes based on 3-MeOsalamo: syntheses, structural characterizations, and luminescent properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 6903–6914; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.6b01067.Search in Google Scholar
13. Zheng, S. S., Dong, W. K., Zhang, Y., Chen, L., Ding, Y. J. Four salamo- type 3d-4f hetero-bimetallic [ZnIILnIII] complexes: syntheses, crystal structures, and luminescent and magnetic properties. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 4966–4973; https://doi.org/10.1039/c6nj04090j.Search in Google Scholar
14. Zhang, X. Y., Yang, Q. L., Yun, M., Si, C. D., An, N., Jia, M. M., Liu, J. C., Dong, X. Y. Seven novel metal-organic frameworks assembled from semi- rigid polycarboxylate and auxiliary N-donor ligands: syntheses, structures, and properties. Acta Crystallogr. 2020, B76, 1001–1017; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2052520620012834.Search in Google Scholar
15. Li, F. A., Yang, W. C., Hu, X. M. Crystal structure of bisnitrate- bis(1-(4-((1 H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzyl)-1 H-imidazole)cadmium(II), [Cd(NO3)2(C14H14N4)2]n. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2011, 226, 587–588; https://doi.org/10.1524/ncrs.2011.0263.Search in Google Scholar
16. Xu, B., Yang, Q. L., Yun, M., Zhang, X. Y., Wu, Y. F., Dong, X. Y. Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[(μ2-nitrato- κ4 O, O′:O′, O″)-nitrato-κ O-(-μ2 1,4-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2 N:N′) cadmium(II)], C14H14N6O6Cd. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2019, 234, 1181–1182; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2019-0311.Search in Google Scholar
17. Wang, B., Wang, J. Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-bis(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)amine-κ2N:N′)-bis(nitrato-κO)cadmium(II)], C36H30CdN12O6. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2019, 234, 927–928.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0150Search in Google Scholar
18. Wang, B., Zhou, Y., Wang, Y., Chen, G.-H., Lian, Q.-X., Wang, H.-D. Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1,3-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)(nitrato-κO)cadmium(II)] - water (2/1), C28H32CdN10O7. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2019, 234, 817–818.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0126Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Cong-Cong Meng et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxidoethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ5N,O,O′:N′,O′′)hexkis(pyridine-κ1N)trinickel(II) - pyridine (1/1), C63H57Cl2N13Ni3O6
- Crystal structure of [(μ2-succinato κ3O,O′:O′′)-bis-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)]dinickel(II)] diperchlorate, dihydrate C36H82Cl2N8Ni2O15
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aquabis(3-nitrobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-pyrazine-N: N′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N4O9Cd
- Crystal structure of 4-(2,2-difluoroethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione, C14H15F2NO2
- The crystal structure of thioxanthen-9-one-10,10-dioxide, C13H8O3S – a second polymorph
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-methoxy-3-pyridyl)methylene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- The crystal structure of diaquahydrogen 2,5-dimethylbenzenesulphonate, C8H14O5S
- The crystal structure of N-(4-(cyclohexylimino)pent-2-en-2-yl)cyclohexanamine, C17H30N2
- The twinned crystal structure of 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium dibromide, C8H14Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2,4,7,9-tetranitro-10H-benzofuro[3,2-b]indole – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1), C16H11N5O10S
- Crystal structure of 2,6-bis(2-(pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)pyrrolo[3,4-f]isoindole-1,3,5,7(2H,6H)-tetraone, C24H18N4O4
- The crystal structure of 3,4-dichlorobenzoic acid chloride, C7H3Cl3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-k2S:S)zinc(II), C26H18N6ZnS4
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ-naphthalene-1-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)bis(methanol)copper(II), C46H36Cu2O10
- Crystal structure of 9-methyl-3-methylene-1,2,3,9-tetrahydro-4H-carbazol-4-one, C14H13NO
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(carbamothioylamino)methaniminium) 3-nitrophthalate monohydrate, C12H19N9O7S2
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,2-phenylene-bis(methylene))bis(1-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate), C18H24F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-6,8-dimethoxy-2-methyl-4H-benzo[g]chromen-4-one– rubrofusarin B, C16H14O5
- The crystal structure of bis(ethanol-kO)- bis(6-aminopicolinato-k2N,O)manganese(II), C16H22O6N4Mn
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-((carbonylbis(azanediyl))bis(ethane-2,1-diyl)) bis(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium) tetrafluoroborate monohydrate, C21H28N6O3B2F8
- Crystal structure of dimethanol-dichlorido-bis( μ2-2-(((1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2- phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato- κ4O:O,O′,N)dinickel (II), C20H24ClNiN3O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate, C7H6F3NO2
- Crystal structure of (OC‐6‐13)‐aqua‐tris (3‐bromopyridine‐κ1N)‐bis(trifluoroacetato‐κ1O)cadmium(II) C19H14Br3CdF6N3O5
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-3-(4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)phenyl) acrylate, C14H16O5
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of 2-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-3-bromo-5-chlorophenol, C13H8BrClN2O
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-N-(2-methyl-1-oxidopropylidene)-2-oxidobenzohydrazonate-κ5N,O,O′:N′,O′′)pentakis(pyridine-κ1N)tricopper(II), C47H45Cl2N9Cu3O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-bis(nitrato-κ2O:O′)- (μ2-((1 H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2 N,N′)-H2O-κ2O]cadmium(II), C14H16N6O7Cd
- The crystal structure of pentakis(carbonyl)-{μ-[2,3-bis(sulfanyl)propan-1-olato]}-(triphenylphosphane)diiron (Fe–Fe)C26H21Fe2O6PS2
- Crystal structure of ethyl-2-(3-benzoylthioureido)propanoate, C13H16N2O3S
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4b,5,14,15-tetrahydro-6H-isoquinolino[2′,1′:1,6] pyrazino[2,3-b]quinoxaline, C19H18N4O
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-[ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidenemethylylidene)]bis(6-chlorophenol), C16H14Cl2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-((2-(2-(2-aminophenoxy)ethoxy)phenyl)amino)-1-phenylbut-2-en-1-one, C24H24N2O3
- The crystal structure of 10-(3,5-di(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)-10H-phenoxazine dihydrate, C28H23N3O3
- Crystal structure of poly[dipoly[aqua-di(µ2-pyrazin-2-olato-κ2N:N′) zinc(II)], C8H8N4O3Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetra(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κO)-manganese(II)-platinum(II)], C10H14MnN6O2Pt
- The crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-6,6′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dichlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C16H12Cl5MnN2O3
- Crystal structure of [di(µ2-cyanido)-dicyanido-bis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)- bis(2,2′-(ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidenemethanylylidene))diphenolato-κ4,N,N′,O,O′)- dimanganese(III)-platinum(II)], C40H40Mn2N8O6PtS2
- The crystal structure of (azido)-κ1N-6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato-κ4N,N,O,O)-(methanol)-manganese(III)–methanol(1/1), C22H26Br2MnN5O4
- Crystal structure of 7-chloro-N-(4-iodobenzyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridin-9-amine, C20H18ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N′′′)-bis(μ2-thiocyanato-κ2N:S)-bis(thiocyanato-κS)-nickel(II)palladium(II)], C14H24N8NiPdS4
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-4-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)aniline monohydrate, C12H20ClN3O
- Crystal structure of the 2D coordination polymer poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3- methoxyisonicotinato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] — dimethylformamide (1/1), C20H30CoN4O10
- Crystal structure of 4-[(5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino]-3-propyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C12H13ClN4OS
- Crystal structure of N-(5-(2-(benzyl(1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-yl)amino)-1-hydroxyethyl)-2-(benzyloxy)phenyl)formamide, C33H36N2O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, C9H12O5
- The crystal structure of 1-((dimethylamino)(3-nitrophenyl)methyl)naphthalen-2-ol, C19H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)-dicyanido-tetrakis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)-manganese(II)-platinum(II)], C12H24MnN4O4PtS4
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-N-(2-pyrimidinyl)benzenesulfonamide–1,4-dioxane (1/1), C14H18N4O4S
- Crystal structure of bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,3-(2-methyl-imidazol)}di-chloridomercury(II), [Hg(C11H11N5)2Cl2], C22H22N10Cl2Hg
- Crystal structure of 2, 3-bis((4-methylbenzoyl)oxy) succinic acid–N, N-dimethylformamide (1/1), C23H25NO9
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(4-(4-carboxyphenoxy)benzoato-κ1O)-μ2-(1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C40H28N4O10Co
- Crystal structure of 1H-imidazol-3-ium poly[aqua-(μ4-glutarato-κ6O,O′:O′:O′′,O′′′:O′′′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)strontium(II)], C8H13N3O8Sr
- Crystal structure of (R)-6-(benzo[b]thiophen-5-yl)-2-methyl-2,6-dihydrobenzo [5,6] silino[4,3,2-cd]indole, C23H17NSSi
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-thiocyanato-κ2N:S)-(2-(5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)pyridine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)]–dioxane (1/1), C15H17CdN5O2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-1,4-bis(2′-carboxylatophenoxy)benzene-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridione-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)] monhydrate, C30H22CdN2O7⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-k2N:N′)-bis(μ2-4′-methyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,5-dicarboxylato-k4O,O′:O″,O′″)dicadmium(II)] dihydrate, C20H20NO7Cd
- Crystal structure of 1‐tert‐butyl‐3‐(2,6‐diisopropyl‐4‐phenoxyphenyl)‐2-methylisothiourea, C24H34N2OS
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-(4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — N,N′-dimethylformamide (1/1), C28H34N8O8Co
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ1N)manganese(II) 2,3-dihydroxyterephthalate, C32H32MnN8O10
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxidoethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ5N,O,O′:N′,O′′)hexkis(pyridine-κ1N)trinickel(II) - pyridine (1/1), C63H57Cl2N13Ni3O6
- Crystal structure of [(μ2-succinato κ3O,O′:O′′)-bis-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane)]dinickel(II)] diperchlorate, dihydrate C36H82Cl2N8Ni2O15
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aquabis(3-nitrobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-pyrazine-N: N′)cadmium(II)], C18H14N4O9Cd
- Crystal structure of 4-(2,2-difluoroethyl)-2,4,6-trimethylisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione, C14H15F2NO2
- The crystal structure of thioxanthen-9-one-10,10-dioxide, C13H8O3S – a second polymorph
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-methoxy-3-pyridyl)methylene)-7-fluoro-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H14FNO2
- The crystal structure of diaquahydrogen 2,5-dimethylbenzenesulphonate, C8H14O5S
- The crystal structure of N-(4-(cyclohexylimino)pent-2-en-2-yl)cyclohexanamine, C17H30N2
- The twinned crystal structure of 1,3-phenylenedimethanaminium dibromide, C8H14Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2,4,7,9-tetranitro-10H-benzofuro[3,2-b]indole – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1), C16H11N5O10S
- Crystal structure of 2,6-bis(2-(pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)pyrrolo[3,4-f]isoindole-1,3,5,7(2H,6H)-tetraone, C24H18N4O4
- The crystal structure of 3,4-dichlorobenzoic acid chloride, C7H3Cl3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-k2S:S)zinc(II), C26H18N6ZnS4
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ-naphthalene-1-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)bis(methanol)copper(II), C46H36Cu2O10
- Crystal structure of 9-methyl-3-methylene-1,2,3,9-tetrahydro-4H-carbazol-4-one, C14H13NO
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(carbamothioylamino)methaniminium) 3-nitrophthalate monohydrate, C12H19N9O7S2
- Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,2-phenylene-bis(methylene))bis(1-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate), C18H24F12N4P2
- The crystal structure of 5-hydroxy-6,8-dimethoxy-2-methyl-4H-benzo[g]chromen-4-one– rubrofusarin B, C16H14O5
- The crystal structure of bis(ethanol-kO)- bis(6-aminopicolinato-k2N,O)manganese(II), C16H22O6N4Mn
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-((carbonylbis(azanediyl))bis(ethane-2,1-diyl)) bis(1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium) tetrafluoroborate monohydrate, C21H28N6O3B2F8
- Crystal structure of dimethanol-dichlorido-bis( μ2-2-(((1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2- phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato- κ4O:O,O′,N)dinickel (II), C20H24ClNiN3O4
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate, C7H6F3NO2
- Crystal structure of (OC‐6‐13)‐aqua‐tris (3‐bromopyridine‐κ1N)‐bis(trifluoroacetato‐κ1O)cadmium(II) C19H14Br3CdF6N3O5
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-3-(4-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethoxy)phenyl) acrylate, C14H16O5
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of 2-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-3-bromo-5-chlorophenol, C13H8BrClN2O
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-N-(2-methyl-1-oxidopropylidene)-2-oxidobenzohydrazonate-κ5N,O,O′:N′,O′′)pentakis(pyridine-κ1N)tricopper(II), C47H45Cl2N9Cu3O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-bis(nitrato-κ2O:O′)- (μ2-((1 H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2 N,N′)-H2O-κ2O]cadmium(II), C14H16N6O7Cd
- The crystal structure of pentakis(carbonyl)-{μ-[2,3-bis(sulfanyl)propan-1-olato]}-(triphenylphosphane)diiron (Fe–Fe)C26H21Fe2O6PS2
- Crystal structure of ethyl-2-(3-benzoylthioureido)propanoate, C13H16N2O3S
- Crystal structure of 2-methoxy-4b,5,14,15-tetrahydro-6H-isoquinolino[2′,1′:1,6] pyrazino[2,3-b]quinoxaline, C19H18N4O
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-[ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidenemethylylidene)]bis(6-chlorophenol), C16H14Cl2N2O2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-((2-(2-(2-aminophenoxy)ethoxy)phenyl)amino)-1-phenylbut-2-en-1-one, C24H24N2O3
- The crystal structure of 10-(3,5-di(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)-10H-phenoxazine dihydrate, C28H23N3O3
- Crystal structure of poly[dipoly[aqua-di(µ2-pyrazin-2-olato-κ2N:N′) zinc(II)], C8H8N4O3Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[tetra(μ2-cyanido-κ2N:O)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κO)-manganese(II)-platinum(II)], C10H14MnN6O2Pt
- The crystal structure of aqua-chlorido-6,6′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dichlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III), C16H12Cl5MnN2O3
- Crystal structure of [di(µ2-cyanido)-dicyanido-bis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)- bis(2,2′-(ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidenemethanylylidene))diphenolato-κ4,N,N′,O,O′)- dimanganese(III)-platinum(II)], C40H40Mn2N8O6PtS2
- The crystal structure of (azido)-κ1N-6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato-κ4N,N,O,O)-(methanol)-manganese(III)–methanol(1/1), C22H26Br2MnN5O4
- Crystal structure of 7-chloro-N-(4-iodobenzyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridin-9-amine, C20H18ClIN2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N″,N′′′)-bis(μ2-thiocyanato-κ2N:S)-bis(thiocyanato-κS)-nickel(II)palladium(II)], C14H24N8NiPdS4
- Crystal structure of 3-chloro-4-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)aniline monohydrate, C12H20ClN3O
- Crystal structure of the 2D coordination polymer poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3- methoxyisonicotinato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] — dimethylformamide (1/1), C20H30CoN4O10
- Crystal structure of 4-[(5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino]-3-propyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C12H13ClN4OS
- Crystal structure of N-(5-(2-(benzyl(1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-yl)amino)-1-hydroxyethyl)-2-(benzyloxy)phenyl)formamide, C33H36N2O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, C9H12O5
- The crystal structure of 1-((dimethylamino)(3-nitrophenyl)methyl)naphthalen-2-ol, C19H18N2O3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)-dicyanido-tetrakis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)-manganese(II)-platinum(II)], C12H24MnN4O4PtS4
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-N-(2-pyrimidinyl)benzenesulfonamide–1,4-dioxane (1/1), C14H18N4O4S
- Crystal structure of bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,3-(2-methyl-imidazol)}di-chloridomercury(II), [Hg(C11H11N5)2Cl2], C22H22N10Cl2Hg
- Crystal structure of 2, 3-bis((4-methylbenzoyl)oxy) succinic acid–N, N-dimethylformamide (1/1), C23H25NO9
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(4-(4-carboxyphenoxy)benzoato-κ1O)-μ2-(1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C40H28N4O10Co
- Crystal structure of 1H-imidazol-3-ium poly[aqua-(μ4-glutarato-κ6O,O′:O′:O′′,O′′′:O′′′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)strontium(II)], C8H13N3O8Sr
- Crystal structure of (R)-6-(benzo[b]thiophen-5-yl)-2-methyl-2,6-dihydrobenzo [5,6] silino[4,3,2-cd]indole, C23H17NSSi
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-thiocyanato-κ2N:S)-(2-(5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)pyridine-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)]–dioxane (1/1), C15H17CdN5O2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-1,4-bis(2′-carboxylatophenoxy)benzene-κ2O:O′)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridione-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)] monhydrate, C30H22CdN2O7⋅H2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetraaqua-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-k2N:N′)-bis(μ2-4′-methyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,5-dicarboxylato-k4O,O′:O″,O′″)dicadmium(II)] dihydrate, C20H20NO7Cd
- Crystal structure of 1‐tert‐butyl‐3‐(2,6‐diisopropyl‐4‐phenoxyphenyl)‐2-methylisothiourea, C24H34N2OS
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)-(4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ1O)cobalt(II)] — N,N′-dimethylformamide (1/1), C28H34N8O8Co
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene-κ1N)manganese(II) 2,3-dihydroxyterephthalate, C32H32MnN8O10

