Abstract
High-quality development of sports competition performance industry in the Chengdu-Chongqing region is based on the improvement of the sports event system and the strengthening of market entities, and it promotes economic and social development by extending the industrial chain and enhancing the value chain. To effectively evaluate its development effect and promote high-quality development, based on the analysis of the opportunities and challenges faced by the sports competition performance industry in the Chengdu-Chongqing region, this article uses the literature research method and survey interview method to construct a performance evaluation index system from the perspective of performance evaluation theory. It also analyzes the strategic thinking of high-quality development from three aspects: guiding ideology, main principles, and development goals, and explores the strategic path for high-quality development from five aspects: integrated development of points and surfaces, priority development between regions, conditional step-by-step development within the region, selective key development of small cities, and layered development with emphasis on different stages.
1 Introduction
The sports competition performance industry is an important part of the sports industry, which is of great significance for tapping and unleashing consumer potential, safeguarding and improving people’s livelihoods, and creating new economic growth drivers. In recent years, the rapid development of the sports competition performance industry in the Chengdu-Chongqing region has become an important force for economic growth. However, there is still a large gap compared with developed countries. Therefore, how to promote high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry has become a hot topic in the industry and academia.
The Chengdu-Chongqing region refers to the region between Chengdu and Chongqing in Sichuan Province, including 15 cities in Sichuan Province such as Chengdu, Mianyang, Deyang, Meishan, Leshan, Ya’an, Ziyang, Neijiang, Zigong, Yibin, Luzhou, Suining, Nanchong, Guang’an, and Dazhou, as well as districts and counties in the Chongqing metropolitan area, such as Fuling, Jiangjin, Hechuan, Yongchuan, Tongnan, Tongliang, Dazu, Rongchang, and Bishan. The region covers an area of about 200,000 km2 and has a population of 87.24 million, accounting for 6.6% and 35% of the southwestern region of China, respectively. The region is the most developed area in western China and one of the important urban belts in China. With the implementation of a series of national policies and plans such as the “Western Development,” “Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone Regional Plan,” “Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Cluster Development Plan,” and “Outline of the Construction Plan for the Chengdu-Chongqing Dual-city Economic Circle,” the urbanization of the Chengdu-Chongqing region has developed rapidly, various undertakings have continuously progressed, and economic strength has significantly increased. In December 2022, the Office of the Sports Bureau of Sichuan Province released a draft of the “14th Five-Year Plan” for the Integrated Development of the Sports Industry in the Chengdu-Chongqing Twin City Economic Zone, which solicited opinions. The draft proposal aims to explore the institutional system and path model for regional sports integration, and accelerate the high-quality development of the sports industry in the Chengdu-Chongqing region. The high-quality development of sports competitions and performance industry in the Chengdu-Chongqing region refers to further improving the quality of sports competition and performance products, expanding the industry chain, and promoting the sustainable development of sports competitions and performance industry in the region while maintaining the essential characteristics of sports competitions and performances. Developing the sports competition performance industry in the region is beneficial for promoting the popularization of sports culture, driving local economic development, showcasing local culture, enhancing urban image and status, attracting more tourists to watch games, and promoting the development of the tourism industry.
In recent years, the study of sports competitions and performance industry has attracted close attention from many experts and research institutions at home and abroad. The sports competition performance industry originated from ancient Greece, passed through ancient Rome, and a long medieval period, and finally became an important cultural phenomenon in contemporary society with the rise of Western industrial civilization. Western scholars’ research on sports events mainly focuses on the demographic characteristics of audiences, the motives and demands for watching the games, the cognitive and consumption aspects of sports products, and the causal path relationships between multiple variables. The results present rich and three-dimensional research perspectives, empirical research paradigms, and diverse research methods (Luo, 2019). Foreign research on performance evaluation mainly discusses different evaluation methods to evaluate the performance of different enterprises or personnel. Some scholars have used Analytic hierarchy process and eigenvalue calculation by mathematical programming to evaluate teacher performance, thereby making the authorities aware of the quality and quantity of activities acceptable to the organization. It also creates a foundation for empowering human resources and reducing dissatisfaction and complaints (Movafaghpour, 2019). Some scholars have established a performance evaluation model of digital game industry by combining Analytic hierarchy process and Balanced score card (Moradi et al., 2018). Some scholars proposed that enhanced performance evaluation through Neutrosophic Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) leveraging pentagonal neutrosophic numbers, and the practicability and effectiveness of the proposed method are verified by numerical examples (Mohanta & Toragay, 2023). Some scholars use Fuzzy-DEA to study the performance evaluation of human capital management organization through cases (Tavakoli et al., 2017). Some scholars use Smart PLS3 software to conduct structural equation modeling to test the impact of innovation and strategic planning on organizational performance, and believe that both innovation and strategic planning have a positive impact on organizational performance (Osintsev & Khalilian, 2023). It can be seen that foreign research on performance evaluation mainly focuses on the combination of multiple research methods and empirical research. In China, experts and scholars started to research the sports competition performance industry relatively late. From the early 1990s to the present, the research on the sports competition performance industry has mainly focused on the sports competition and performance market, treating the sports competition performance industry as an industry that produces sports and competition performance products (Liu & Zhang, 1999). In December 2018, the General Office of the State Council of China issued the “Guiding Opinions on Accelerating the Development of Sports Performance Industry,” which pointed out the direction for the rapid development of China’s sports competition performance industry. Currently, there are few research results on the high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry, and only a few scholars have studied the theoretical connotations and prospects of high-quality development from the perspective of urban benefits (He & Xu, 2020). It can be seen that research on the high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry is still in its early stages. However, due to the intervention of national policies and the maturity of the sports competition performance industry, more and more research results on this topic are expected to emerge in the future. It can be said that the Chengdu-Chongqing region is at the forefront of research and practice in the high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry. As early as 2016, Chengdu proposed to build itself into a world-renowned sports events city and an international sports industry center city by 2025. In late 2018, the “Tianfu International Sports Events Research Center” was established, which is committed to research in two aspects: International sports event introduction and evaluation, and large-scale sports event openness and dissemination. Although the Chengdu-Chongqing region is at the forefront of innovative development in the sports competition performance industry, it should also be noted that there are still some challenges in this industry. For example, the marketization level is not high, regional development is imbalanced, there is a severe shortage of high-end talent, the ecological development of the upstream and downstream of the industrial chain is not perfect, and there is a prominent homogenous competition in the regional sports industry chain. To address these challenges and accelerate the high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry in the region, it is necessary to take urgent action. Overall, whether it is at the national or regional level, the development of the sports competition performance industry will continue to improve, but there is still a need to further enrich its completeness, systematism, and strategic high-quality development.
Nowadays, with the increasing demand of people, although the existing sports competition performance industry generates high income, there is always a loss. So, the sports competition performance industry needs a suitable performance evaluation system. Currently, both domestically and internationally, the application of performance evaluation theory in the development of sports competition performance industry is still in its preliminary stage. The research is limited to a single field or discipline, lacking comprehensiveness and synergy. At the same time, there are also many differences in understanding and application of the performance evaluation theory in different research fields. Therefore, this research will combine the actual situation of the sports competition performance industry in the Chengdu-Chongqing region, draw on domestic and foreign research results, and construct an application model and index system for performance evaluation theory in this industry. The goal is to provide more comprehensive and systematic research support for the high-quality development of this industry. This study aims to explore the relevant issues of high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry in the Chengdu-Chongqing region based on the performance evaluation theory, providing theoretical support and practical guidance for the high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry in the region, and making a positive contribution to the sustainable development of this industry.
2 Methods
2.1 Research Questions and Hypotheses
This study will address three main research questions: What are the opportunities and challenges facing the sports competition performance industry in the Chengdu-Chongqing region? How can we evaluate the development level and quality of the sports competition performance industry in the region based on the performance evaluation theory? In light of the existing problems, how can we promote the high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry in the region, and propose development ideas and paths? The hypothesis of this research is that through a scientific and reasonable performance evaluation method based on performance evaluation theory, it can promote the high-quality development of the sports and performing arts industry in area.
2.2 Research Design
For the research on the high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry in the Chengdu-Chongqing region based on performance evaluation theory, various methods can be used to collect and analyze data. One method is a questionnaire survey. A targeted questionnaire survey will be designed to obtain the opinions and views of the respondents on the sports competition performance industry in area, through face-to-face or online methods. The second method is field observation and in-depth interviews. Through field observation and in-depth interviews, the experiences, insights, and problems of the participants in the sports competition performance industry in area will be obtained. The third method is document analysis. Relevant documents and materials, such as policy documents and statistical data, will be collected, sorted, and analyzed to provide background and information support for the research. One or more of the above methods can be used to collect and analyze data depending on the research questions and hypotheses. During the data collection and analysis process, it is necessary to protect the confidentiality and privacy of the data, as well as ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data.
2.3 Sample Selection
Sample selection is one of the important steps in research. In the study of high-quality development of sports competitions and performances industry in the Chengdu-Chongqing region, we consider sample selection from the following aspects: first, selecting a total of 70 people, including responsible persons of local sports competition and performance-related institutions, professional practitioners in the industry, relevant government officials, cultural media personnel, etc., to obtain their views and suggestions on the high-quality development of the industry. Second, selecting local citizens, students, and other groups, using methods such as questionnaire surveys to obtain their understanding, participation, expectations, and other information about the sports competitions and performance industry in the region, in order to help us better understand public needs and attitudes. Third, for specific themes or issues, specific sample groups are selected for in-depth interviews or field research to obtain more detailed and in-depth information and insights. When determining sampling methods and sample sizes, various factors such as sample representativeness, feasibility, and efficiency are considered. Specifically, methods such as random sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling are used. At the same time, the sample size is determined based on the specific research type, accuracy requirements, population homogeneity, sampling methods, objective constraints, etc.
2.4 Data Collection and Analysis
In terms of data collection, we use the following methods: first, through research on existing literature, we collect statistical data and case materials related to the sports competition performance industry in the Chengdu-Chongqing region; second, we design questionnaires and conduct interviews to collect opinions and suggestions from industry practitioners, experts, scholars, and consumers; third, we obtain relevant data through official websites, newspapers, magazines, and other channels. In terms of data processing, we use the following methods (Deng & Xiang, 2016): first, we organize the collected data, and remove outliers and duplicate data; second, we use descriptive statistics to analyze the data materials, provide basic statistical descriptions and visual displays of the data; third, we use SWOT analysis to evaluate the development opportunities and challenges in the sports competition performance industry in the region.
3 Results
3.1 Opportunities and Challenges for the Development of Sports Competition Performance Industry in Chengdu-Chongqing Region
At present, the development momentum of sports competition performance industry in Chengdu-Chongqing region is good, and there are advantages in national policies, regional location, cultural tourism, sports consumption, event resources, and other aspects. However, some bottleneck problems do exist, such as low degree of marketization, unbalanced regional development, extreme shortage of high-end talents, imperfect development ecology of the upstream and downstream of the industrial chain, and prominent homogenous competition in the regional sports industrial chain.
3.1.1 Development Opportunities of Sports Competition Performance Industry in Chengdu-Chongqing Region
First, macro planning brings policy dividends. From a vertical perspective, Chengdu-Chongqing region has always played an important role in China’s regional development plate: In 2011, The State Council approved and the National Development and Reform Commission issued the Regional Plan for Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone; In 2016, the Development Plan for Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Agglomeration jointly issued by the National Development and Reform Commission and the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development made it clear that by 2020, the Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration should be basically built into a national-level urban agglomeration with vibrant economy, excellent quality of life, and beautiful ecological environment. In 2030, the Chengdu-Chongqing city cluster will complete its historic leap from a national city cluster to a world-class city cluster. In October 2021, the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and The State Council issued the Planning Outline for the Construction of the Chengdu-Chongqing Twin City Economic Circle. It pointed out that by 2025, the economic strength, development vitality, and international influence of the Chengdu-Chongqing Twin City Economic Circle will be greatly enhanced, the level of integrated development will be significantly improved, regional characteristics will be further demonstrated, and its role in supporting the national high-quality development will be significantly enhanced. By 2035, China aims to build a two-city economic circle with strong strengths and distinctive features, make Chongqing and Chengdu modern international cities, improve the urban system for coordinated development of large, medium, and small cities, basically realize infrastructure connectivity, basically complete the construction of a national science and technology innovation center, and take full advantage of world-class advanced manufacturing clusters. The modern industrial system is maturing, an open economic system integrated into the global economy is basically in place, the people’s quality of life has significantly improved, and the country’s ability to support and drive high-quality development has significantly increased. China has become an active growth pole and a strong source of power with international influence. Horizontally, the Key Tasks for New Urbanization Construction in 2019 issued by the National Development and Reform Commission clearly places the Chengdu-Chongqing City cluster alongside the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei City cluster, the Yangtze River Delta City cluster, and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao City cluster (The Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and The State Council, 2021). From the perspective of fields, in December 2018, in order to solve the problems of insufficient effective supply, small overall scale and inactive mass consumption in China’s sports competition performance industry, and accelerate the development of sports competition performance industry, The Guiding Opinions on Accelerating the Development of Sports Competition Performance Industry issued by The General Office of the State Council of China has pointed out the direction for the development of China’s sports competition performance industry from the aspects of overall requirements, competition system, market environment, platform construction, and fund guarantee. In 2022, the official website of Sichuan Sports Bureau asked for the opinion draft of the “14th Five-Year Plan” Sports Industry Integration Development Plan of Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Circle, which pointed out that top-level design and overall planning should be strengthened, the institutional system and path model of regional sports integration development should be explored, and the high-quality development of sports industry in Chongqing and Sichuan should be accelerated (Sichuan Provincial Sports Bureau Office, 2022). The frequent promulgation of these macro plans has brought policy dividends for the development of sports competition performance industry in the region.
Second is the unique geographical advantages. Chengdu-Chongqing region is located at the intersection of the “two horizontal and three vertical” urbanization strategic patterns along the horizontal axis of the Yangtze River passage and the vertical axis of the Bao-Kunming Passage. As an important urbanization region in China, it has the geographical advantage of connecting the east with the west and the north with the south. It has excellent natural endowments, strong comprehensive carrying capacity and sound transportation system. The region has the best economic foundation and the strongest economic strength in western China, with strong industrial strength such as electronic information, equipment manufacturing and finance, and strong international and domestic influence. Chengdu-Chongqing cities are increasingly playing a leading role. A number of small and medium-sized cities are developing in a distinctive way. Counties (districts) and administrative towns are densely distributed. The region has the advantage of world-class outdoor natural resources endowment, which can promote the development of outdoor sports competition and performance industries such as mountain, water, ice and snow, aviation, automobile and motorcycle, bicycle, etc., and jointly promote the region to build world-class outdoor sports events, performances, and tourist destinations with international style, Chinese flavor, and Bashu charm.
Third are the rich and colorful cultural tourism resources. Cities in Chengdu-Chongqing are closely connected with mountains and rivers, people and culture, and have close economic and trade exchanges. Cooperation in transportation, agriculture, commerce, education, science and technology, sports, labor, and other fields has been strengthened, and cooperation between neighboring regions has been deepened. The cooperation process of Chengdu-Chongqing region is accelerating gradually, and the trend of integration development is increasingly obvious (National Development and Reform Commission and Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, 2016). It has abundant human resources, a sound environment for innovation and entrepreneurship, and rich experience in carrying out reforms such as coordinating comprehensive support for urban and rural areas. An open economic system is taking shape, with huge space and potential for future development. The region has a population of about 100 million, which is the most populous in China’s economic zone and the most densely populated area in western China. The region has two national central cities and several large and medium-sized cities. With a good industrial and technological foundation, the region is the largest industrial center and the main gathering place of technology industry in western China.
Fourth, the consciousness of sports consumption is constantly enhanced. With the continuous improvement of the living standard of residents in the region, as well as the extensive development of national fitness, people’s concept of sports consumption has changed, and the investment in sports consumption has generally increased. Especially after the epidemic, people have a strong demand for enhancing their physical fitness, pursuing physical and mental health, and improving immunity. People’s attitude and behavior toward fitness consumption are also quietly changing, and their exercise habits and modes are sinking. Compared with those who only pay attention to functional fitness in the past, people pay more attention to the improvement of physical and mental health brought by exercise. People also enjoy more exercise through social participation in fitness. Sports are becoming an attitude towards life and emotional management, and entering a healthy normal mode (China Youth Daily, 2020). At the same time, the competition performance market will also face a large-scale explosion.
Fifth are colorful competition performance activities. In recent years, Chengdu-Chongqing region has made full use of the hardware advantages of Liangjiang Football Game Center, International Small Ball Game Center, Chengdu Fenghuang Mountain Sports Park, Chengdu Donganhu Sports Park, and other large sports venues as well as the experience and ability to operate large-scale sports events, and negotiated to jointly host international and domestic large-scale sports events with high visibility, strong professionalism, and strong roots. These events not only demonstrate the region’s professional ability in organizing large-scale sports events, but also further enhance the international influence and global competitiveness of Chengdu-Chongqing twin city economic circle. For example, the 31st Summer University Games, the 2022 World Team Table Tennis Championships, the 2024 Tong Yu Cup Badminton Competition, the 2025 World Games, and other high-level international events were organized with high standards. It is reported that in the future, Chongqing Metropolitan Circle will enhance the influence of Chongqing International Marathon, Changshou Lake International Triathlon, Yongchuan International Women’s Soccer Invitational Tournament, “Black Valley Cup” International Badminton Challenge, and other competitions. Chengdu Metropolitan Circle will build the brand scale, brand and integrated development of Chengdu International Marathon, International Elite School Rowing Challenge, International Youth Soccer Game, and other events. These rich event resources and a series of international top brand events have been selected to settle in the region. High-quality events and wide brand awareness have injected infinite vitality into the high-quality development of sports competition performance industry in the region.
3.1.2 Challenges to the Development of Sports Competition Performance Industry in Chengdu-Chongqing Region
First, the degree of marketization is not high. Under the background of the development of sports industry in China, the low marketization degree of sports competition performance industry in Chengdu-Chongqing region affects its development, which is mainly reflected in three aspects (Li, 2018). First, the effective supply is not sufficient, the management level of sports events is not very high, and the grasp of the mass sports consumption demand and sports market is not good. In terms of competition performance, there are not many options that can meet the individual needs of the public. According to the survey, the independent innovation ability of sports competition performance enterprises is not very strong, the investment in research and development is not strong, the brand added value is relatively low, and the overall localization of the world-famous brand events is lacking. Second, the overall scale is not large. At present, although a few sports such as football, basketball and dance sports have embarked on the road of professional development in the region, the professional market for most sports has not yet formed. Third, the laws and regulations of sports competition performance market are not perfect. Due to the late start of the sports competition performance market, and immature laws and regulations, some operators in order to seek economic benefits or social value, under the condition of not having the right to operate, attract sponsorship, raise funds, organize sports competition performance activities of low quality, which endangers the healthy operation of the whole sports competition performance market. Sports competition performance market is the service market, and the quality of service determines the embodiment of its value. At present, the region is relatively lacking authoritative laws and regulations to supervise and manage the healthy operation of the whole market, which will restrict the industry to develop to high quality.
Second, regional development is unbalanced. Under the background of unbalanced regional social development in China, the sports competition performance market in Chengdu-Chongqing region also shows the huge gap between the relatively backward development of towns, cities, counties, and central cities and the highly developed metropolitan areas. Compared with the higher degree of marketization represented by Chengdu and Chongqing, the sports competition performance market of towns, cities, and counties has various deficiencies in terms of market scale, business philosophy, capital investment and infrastructure, etc. This gap directly affects the prospect of market cluster development. Take Chengdu as an example. In terms of domestic league, all professional clubs are at a relatively high level in terms of professionalism and competition level. Moreover, Chengdu vigorously introduces large international sports events and strives to build itself into a world-famous city for sports events, sports, and life, which cannot be accomplished in other regions at present. This kind of polarization phenomenon of market operation activities is very unfavorable to the high-quality development strategy of sports competition performance market in the region.
Third, there is an acute shortage of high-level talents. Due to the influence of region, education system, and income marketization, the reserve of professional senior technical personnel such as sports competition performance operation and management, sports events and data analysis is insufficient. In the reality that China's sports competition performance industry is facing a shortage of high-level professional talents such as operation management and product research and development, the current talent structure in the region is mainly concentrated in the traditional fields with sports knowledge, technology and skills, and there is a lack of high-level talents with overall planning and comprehensive research and development capabilities. This situation restricts the high quality development of sports competition performance industry. Sports competition performance market is a highly professional market, and high-quality professionals for the sustainable development of the market are particularly important. At present, there are some problems in sports competition performance market, such as a small number of managers, lack of experience, lack of talent with deep understanding of sports competition performance market, and practical experience; the lack of talent directly affects the interests and development of business enterprises. The introduction of high-level sports events is closely related to professional high-end sports agencies. At present, the level of sports agencies and brokers in the region is not the same, which is mainly due to the lack of formal management departments to provide relevant guidance and training, and lack of professional knowledge of sports competition performance. At the same time, the complex high-level talents with knowledge of market development, marketing planning, strategic planning, data analysis, and other aspects lead to the lag of sports intermediary professional services, which will restrict the development of sports competition performance market (Deng & Tang, 2020).
Fourth, the ecology of symbiotic development of the upstream and downstream of the industrial chain is not perfect. The sustainable development of famous international sports events is because they have established a dynamic and innovative industrial chain ecology. Football World Cup, Olympic Games, Wimbledon Tennis Championships, NBA, and other events have formed a fully closed ecological chain from event building, service promotion, product production, and sales. However, most of the sports events in the region are still pure games, with no products for the terminal market, and no binding design customers. At the same time, there is a big gap between the event packaging display and the development and application of cutting-edge technology and the international famous sports events. Technological innovation and market application are not well connected, and no closed industrial chain has been formed (Zhang, 2019). In terms of supporting the sports competition performance industry, there is still a lack of high-end public service platform, the construction of intelligent event service platform, and event bidding, and decision-making intelligent system is still weak. The professional service platform supporting the research and development, operation, and evaluation of the event still needs to be perfected, and the supporting enterprises supporting the key technologies needed for the high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry are lacking, leading to high costs related to the event. With the rapid development of the internet, if sports enterprises fail to establish an effective supply chain management information system and transfer information quickly and efficiently in the process of development, the speed of feedback information will be greatly reduced, thus reducing the efficiency, forcing the decline in consumer satisfaction, and ultimately leading to the reduction and loss of consumers.
Fifth, the phenomenon of homogeneous competition of regional sports industry chain is prominent. In recent years, the region has achieved positive results in promoting the cooperation of sports industry, and a number of landmark cooperation projects have been implemented. But the region has not formed the sports industry collaborative development mechanism based on gradient and differentiation (Huang et al., 2021). It is mainly manifested in the following aspects: first, there is a lack of division of labor planning based on each link of the industrial chain. In the selection of leading industries, Chengdu-Chongqing region has the convergence, and the industrial upstream and downstream supporting and complementarity are poor. Second, there are relatively many regional industrial undertaking platforms, but the lack of substantive contact and cooperation between enterprises makes it difficult to form industrial clusters and industrial chains. For example, many large sports enterprises have directly settled in Chengdu and Chongqing metropolitan areas, but few have landed in other areas. Third, the cross-regional industrial collaborative working mechanism has not been formed, and the cross-regional sports industry management and industrial chain layout have the problems of long consultation time and high decision-making cost.
3.2 Performance Evaluation Theory and Its Application in Sports Competition Performance Industry
As an effective way to improve and evaluate performance, performance evaluation has been recognized by people. This part mainly analyzes the concept and principle of performance evaluation theory, the application of performance evaluation in sports competition performance industry, and the construction of performance evaluation index system of sports competition performance industry in the region.
3.2.1 Concepts and Principles of Performance Evaluation Theory
Performance evaluation is an important concept in the field of modern management. It is a way to quantify and evaluate the performance of organizations, departments, and individuals in a certain period of time. The core principle of performance evaluation is to compare the performance of an organization or an individual with pre-set standards or goals to determine the degree or gap of achievement, and give corresponding feedback and rewards. The theory of performance evaluation mainly includes objective management theory, contribution and income theory, incentive theory, and so on. In short, the theory of performance evaluation can help organizations or individuals to effectively measure and improve performance levels, so as to achieve efficient operation and sustainable development. Specifically, the theory of performance evaluation includes the following concepts and principles.
3.2.1.1 Performance
Performance refers to the results or performance achieved by an organization or an individual in a specific period of time. Performance evaluation can be evaluated from many aspects, including quantity, quality, efficiency, benefit, innovation, and so on. Through the evaluation of these aspects, we can have a comprehensive understanding of the results or performance of an organization or an individual in a specific period of time, and can evaluate its performance level more objectively. For example, for a production firm, quantitative performance can measure the output of its products; Quality performance can measure the qualified rate of its products; Efficiency performance can measure its production efficiency and resource utilization efficiency; Effectiveness performance can measure sales and profit margins; Innovation performance can be measured by technological innovation and product research and development ability. The evaluation of these performance indicators can help enterprises understand their strengths and weaknesses, find out the problems, formulate reasonable and effective management measures, and promote the sustainable development of enterprises.
3.2.1.2 Management by Objectives
Management by objectives refers to the definition and quantification of organizational or individual objectives in the formulation of performance evaluation standards for subsequent evaluation and feedback. In management by objectives, it is necessary to define specific work objectives and time nodes first, and then convert these objectives into quantifiable indicators, and formulate corresponding assessment standards and evaluation systems. In the evaluation process, it is necessary to evaluate the completion of the goal and the process of achieving the goal, so as to better guide and motivate the work of employees. Management by objectives is a scientific management method, which can help organizations and individuals understand their work objectives and expected results more clearly, so as to better realize the development and progress of individuals and organizations.
3.2.1.3 Feedback Mechanism
The feedback mechanism refers to the timely feedback of performance evaluation results to the appraised, so as to promote their improvement and enhancement of performance. Feedback can be either a positive reward or a negative punishment, depending on the outcome of the performance evaluation (Liu, 2006). Positive reward feedback can make the assessed feel that their efforts have been recognized and affirmed, and also enhance their work motivation and sense of belonging. Negative punishment feedback can help the evaluated person recognize their shortcomings and actively improve and enhance themselves. At the same time, the feedback mechanism also needs to have the characteristics of timeliness, fairness, and transparency to ensure the accuracy and credibility of the evaluation results, and prevent the abuse or misunderstanding of the evaluation results.
3.2.1.4 Reward Mechanism
Reward mechanism refers to encouraging and motivating the performance improvement of individuals or organizations through rewards. Rewards can be material rewards, such as salary and benefits, or spiritual rewards, such as praise and promotion. Material reward can directly motivate employees to work, and it is also a kind of recognition and reward for employees’ work achievements. Non-material rewards can motivate employees to work harder and innovate, improve their self-confidence and sense of belonging, and enhance their sense of identity and loyalty to the organization. For the organization, the establishment of a reasonable and effective reward mechanism can not only motivate the work enthusiasm of employees, but also improve the competitiveness and innovation ability of the organization, so as to achieve a win-win situation.
3.2.1.5 Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement means that performance evaluation is a dynamic process, which requires constant adjustment and improvement of evaluation standards and feedback mechanism to adapt to the needs of organizational or individual changes and development. With the passage of time, the goals, work content, and work characteristics of organizations and individuals will change, so the performance evaluation standards and feedback mechanisms need to be adjusted and improved accordingly. At the same time, with the continuous development of science and technology and the continuous progress of society, the methods and tools of performance evaluation are also constantly innovated and improved, and it is necessary to constantly update and apply the latest evaluation tools and technologies. Only continuous improvement of performance evaluation can better meet the needs of organizations and individuals, improve the effectiveness and reliability of performance evaluation.
3.2.2 Application of Performance Evaluation in Sports Competition Performance Industry
Sports Competition Performance Industry is a typical industry chain, involving many fields, such as event planning, venue construction, event promotion, event live broadcast, etc. In this industry chain, the performance evaluation of each link is very important. For example, in the event planning stage, the event planning scheme needs to be evaluated to determine whether it meets the market demand and the operation law of the event. In the stage of stadium construction, it is necessary to evaluate the stadium construction plan to determine whether it can meet the needs of spectators and athletes. In the stage of event promotion and live broadcast, it is necessary to evaluate the effect of promotion and live broadcast to determine whether it can attract more viewers and businesses.
3.2.2.1 Performance evaluation in the event planning stage
The event planning stage is the key to the success of the event, so it is necessary to evaluate the event planning scheme to determine whether it meets the market demand and the operation law of the event, including the following aspects. On the one hand, market demand assessment evaluates whether the event planning scheme meets the market demand, including considering whether it meets the interests and needs of local audience or event participants, and whether it can attract enough audience and participants to participate. It can be evaluated by means of market survey, questionnaire survey, etc. On the other hand, event operation law evaluation evaluates whether the event planning scheme conforms to the event operation law, including whether the setting of competition rules is reasonable, whether the reward mechanism is in place, whether the venue facilities meet the requirements, etc. This can be done by referring to the experience and success of existing events. Third, comprehensive evaluation: The overall comprehensive evaluation of the event planning scheme is carried out to determine the feasibility and implementation effect of the scheme by considering market demand, event operation rules, and other factors. It can be evaluated through expert review, meeting discussion, etc.
3.2.2.2 Performance Evaluation of Venue Construction Stage
The evaluation of stadium construction options is an important step to ensure that the stadium can meet the needs of spectators and athletes, and maximize the efficiency of the use of the stadium. In the stage of venue construction, the following aspects need to be evaluated: First, audience demand assessment: audience seat demand, safety demand, transportation demand, catering demand, etc., should be evaluated to determine whether the venue can meet the needs of the audience. The second is the assessment of athletes’ needs: the assessment of athletes’ needs for events, training, and accommodation to determine whether the venues can meet the needs of athletes. Third, facility evaluation: evaluate the infrastructure, site facilities, electrical equipment, communication equipment, etc., of the venue to ensure that the venue facilities meet the national standards and industry norms. Fourth, design evaluation: evaluate the design scheme of the venue, including architectural style, functional layout, lighting design, acoustic design, etc., to ensure that the design of the venue can meet the needs of sports and competition. Maintenance and maintenance evaluation: evaluate the maintenance and maintenance plan of the venue, including equipment maintenance, sanitation, safety inspection, etc., to ensure the long-term stable operation of the venue.
3.2.2.3 Performance Evaluation at the Stage of Event Promotion and Live Broadcast
The event promotion and live broadcast stage is an important part of the success of the event, and its performance needs to be evaluated. The evaluation at the stage of event promotion and live broadcast can be started from the following aspects: First, attractiveness evaluation: During the period of promotion and live broadcast, to understand whether there is a trend to attract more viewers and businesses compared with the same period in previous years, or to understand the audience’s interest and feedback on the event promotion and live broadcast through questionnaires and other means. Second, media exposure evaluation: The effect of promotion and live broadcasting can be judged by evaluating the media exposure, including the exposure of different platforms such as TV, Internet, and social media, as well as the distribution of exposure channels. Third, evaluation of marketing effect: Through the interactive effect and conversion rate of promotion and live broadcast activities, evaluate the marketing effect of the activity by comparing the relationship between input and output, as well as the income and effect obtained at each stage. Fourth, economic benefit evaluation: evaluate the impact of promotion and live broadcast on business and event economy, such as merchant participation, advertising income, ticket income, etc.
3.3 Construction of Performance Evaluation Index System for Sports Competitions and Performance Industry in Chengdu-Chongqing Region
The construction of performance evaluation index system of sports competition performance industry in Chengdu-Chongqing region needs to consider many factors, such as the status quo, characteristics and trends of industrial development, the principle of index selection and so on. Therefore, this part discusses the division of the development stages of the sports competition performance industry in the region, and analyzes the selection principles of performance evaluation indexes. On this basis, it constructs the performance evaluation indexes suitable for the sports competition performance industry in the region.
3.3.1 Division of Development Stages for Sports Competition Performance Industry in Chengdu-Chongqing Region
The high-quality development of sports competitions and performance industry can promote the coordinated development of sports competitions and performance industry among administrative divisions in the entire region, forming an industrial cluster with highly innovative networked structures. Therefore, it is an urgent choice for sports competitions and performance industry in the region to adapt to the development trends of knowledge economy, network economy, digital economy, and economic globalization. The spatial agglomeration body that is tightly connected through a network of cross-cutting relationships represents a new form of spatial economic organization between the market and hierarchy (Wang, 2001). The high-quality development of sports competitions and performance industry in the region can basically form nine industrial cluster areas. According to the requirements of the Outline of the Construction Plan for the Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Circle, and based on the development laws of sports competitions and performance industry, the high-quality development of sports competitions and performance industry follows the law of development from low to high. Through the analysis of multiple indicators such as the number of cities, sports population, industrialization rate, and proportion of sports competition performance industry in the regional economic total value in the region’s sports competition performance industry cluster areas, we conducted a comparative study and cluster analysis of the comprehensive strength of the regional sports competition performance industry. Based on this, we divided the sports competition performance industry cluster in the region into three categories: primary stage, intermediate stage, and advanced stage. Figure 1 shows the industrial cluster.
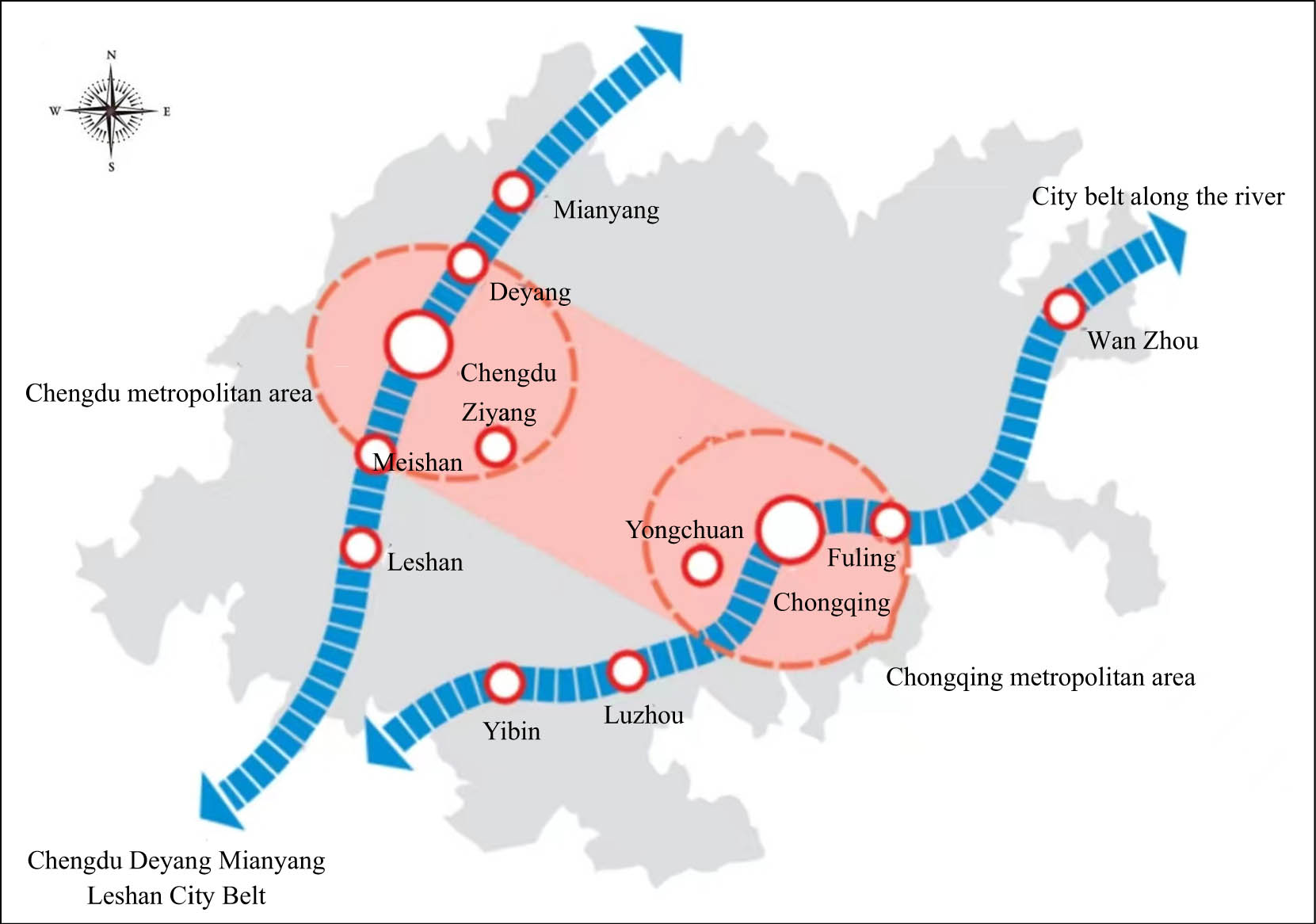
Sports competition performance industrial cluster in Chengdu-Chongqing region (Photo from Xinhuanet).
3.3.1.1 Sports Competition Performance Industry Cluster in the Early Stage of Development
There are four sports competition performance industrial clusters in the primary development stage in the region: The sports competition performance industrial cluster in northeast Chongqing (including urban clusters in Wanzhou, Dazhou, and Kaizhou), southeast Chongqing (Qianjiang area), northeast Sichuan (including urban clusters in Nanchong, Suining, and Guang’an), and south Sichuan (Yibin, Luzhou, Zigong, and Neijiang). The obvious characteristics of this kind of sports competition performance industrial intensive area are that the region occupied by sports facilities, the total number of sports population and the total number of sports employed population, the development scale of sports competition performance industry, and the proportion of sports competition performance industry in the total regional economic value are significantly lower than the sports competition performance industrial cluster in Chengdu metropolitan area, Chongqing metropolitan area, and Chengdu Plain region. In fact, although the sports population in northeast Chongqing and south Sichuan sports competition performance industry cluster area is large, the sports competition performance industry development scale is large, the sports competition performance industry accounts for a high proportion of the total regional economic value, but its industrialization level is too low, the sports competition performance industry level scale order seriously presents polarization. Therefore, it also belongs to the primary stage of high-quality development of sports competition performance industry.
3.3.1.2 Sports Competition Performance Industry Cluster in the Intermediate Stage of Development
There are three sports competition performance industrial clusters in the intermediate development stage in the region: Chengdu metropolitan area (including Deyang, Meishan, and Ziyang), Chongqing metropolitan area (including Fuling, Changshou, Jiangjin, Hechuan, Yongchuan, Nanchuan, Qijiang-Wansheng Economic Development Zone, Dazu, Bishan, Tongliang, Tongnan, and Rongchang), Chengdu Plain region sports competition performance industrial cluster (including Mianyang and Leshan concentrated urban areas). The region occupied by the sports facilities, the total number of the sports population and sports working population, the development scale of the sports competition performance industry and the proportion of the sports competition performance industry in the total regional economic value are all much higher than the four major sports competition performance industry clusters in the initial stage of development. However, it is obviously smaller than the sports competition performance industrial clusters in Chengdu and Chongqing.
3.3.1.3 Sports Competition Performance Industry Cluster in the Advanced Stage of Development
There are two sports competition performance industrial clusters in the advanced development stage in the region: Chengdu sports competition performance industrial cluster and Chongqing sports competition performance industrial cluster. The region of high-quality sports facilities and places, the total number of sports population and sports employed population, the development scale of sports competition performance industry, and the proportion of sports competition performance industry in the total regional economic value are significantly higher than any other sports competition performance industry clusters in the region. The number of sports population, the number of sports fitness and leisure places, the total amount of sports competition performance industry, and the professional talents in the operation and management of sports competition performance industry can even be compared with the four major cities in the eastern region.
3.3.2 Principles for Selecting Performance Evaluation Indicators for Sports Competition Performance Industry in Chengdu-Chongqing Region
The selection of performance evaluation indicators for sports competition performance industry in the region needs to follow certain principles in order to develop an evaluation indicator system that is in line with the characteristics and actual situation of the sports competition performance industry in the region.
3.3.2.1 Principle of Objectivity
The performance evaluation indicators for sports competition performance industry in the region must be objective, scientific, and comprehensive, reflecting the real situation of the sports competition performance industry. Here are several indicators that can be used to evaluate the industry: First, economic contribution: This indicator can be reflected by statistics such as the total revenue, employment rate, and tax revenue of the sports competition performance industry in the local area, which can reflect its contribution to the local economy. The second is social impact: This indicator can be measured by conducting surveys, public feedback, and other methods to assess the image and reputation of the sports competition performance industry in society, reflecting its influence on society. The third is cultural inheritance: This indicator can be evaluated by investigating the local cultural inheritance situation of the sports competition performance industry, its promotion of local culture, and its external exchanges in the cultural aspect. Fourth, popularity and brand value: This indicator can be reflected by statistics such as the popularity, influence, and brand value of the sports competition performance industry, which can reflect its competitiveness in the market. These are just some possible indicators that can be used to evaluate the sports competition performance industry in the region. Specific indicators still need to be selected and formulated based on the local actual situation.
3.3.2.2 Principle of Operability
The performance evaluation indicators for sports competition performance industry in the region must be quantifiable and measurable, and able to provide effective information for policy-making and decision-making. Here are some possible performance evaluation indicators: First, economic benefits indicators: They include revenue, profit, return on investment, production efficiency, etc., these indicators can reflect the economic benefits of the industry. Second, social benefits indicators: They include employment creation, contribution rate, tax revenue, etc., these indicators can reflect the industry’s influence on and contribution to the society. Third, competitiveness indicators: They include market share, brand influence, product quality, etc., these indicators can reflect the industry’s competitiveness in the market. Four, sustainable development indicators: They include resource utilization efficiency, environmental protection, social responsibility, etc., these indicators can reflect the contribution of the industry to sustainable development. These indicators are all quantifiable and easy to measure, can provide effective information for policy-making and decision-making, and can help enterprises to clarify their own strengths and weaknesses, promote the sustainable development of the industry.
3.3.2.3 Comprehensive Principles
For the performance evaluation of the sports competition performance industry in the region, it is necessary to consider various factors, including economic benefits, social benefits, environmental benefits, etc. Economic benefits are one of the important aspects, mainly including economic indicators such as the revenue of sports events and performances, and the profit of venue operations. Additionally, social benefit is also one of the factors that must be considered, including the impact of sports events and performance activities on social recognition, influence, promotion of city image and cultural construction, etc. At the same time, environmental benefit is also indispensable, and it is necessary to consider the extent to which the sports competition performance industry impact the environment, such as the impact on water sources, air quality and other aspects. In the process of formulating evaluation indicators, corresponding evaluation indicator systems should be established based on the above multiple factors, and the proportion of economic, social, and environmental benefits evaluation should be reasonably allocated to achieve comprehensive evaluation. Only by considering these factors comprehensively can we more effectively evaluate the performance of the sports competition performance industry in the region and provide reference for its sustainable development.
3.3.2.4 Timeliness Principle
The performance evaluation indicators of the sports competition performance industry in the region must be able to reflect the development changes and trends of the industry in a timely manner, so as to adjust policies and measures in a timely manner. Here are some indicators that may be used to reflect the industry’s development changes and trends in a timely manner: First, annual growth rate: this indicator can reflect the growth or decline of the sports competition performance industry over a period of time by comparing data from different years. The second indicator is competitiveness, which can be reflected by comparing market share, brand value, and other data among different regions or enterprises to show the status and advantages and disadvantages of the sports competition performance industry in competition. The third indicator is the investment scale, which can reflect the investment status and trend of the industry through statistics of the total investment in the sports competition performance industry and the distribution of investment. The fourth indicator is government support: this indicator can reflect the industry’s advantages and disadvantages in policies by comparing the level of government support for the sports competition performance industry in different regions. The above are just some of the indicators that may be used to reflect the changes and trends in the development of the sports competition performance industry in the region. In fact, there are many other indicators that can be used.
3.3.2.5 Comparability Principle
The performance evaluation indicators of the sports competition performance industry in the region need to be comparable, in order to conduct cross-sectional and longitudinal comparative analysis. To achieve this, reference can be made to the evaluation indicators of relevant industries at home and abroad, summarized and adjusted according to the characteristics of the sports competition performance industry in the region, making it more in line with the actual situation of the sports competition performance industry in the region. By comparing with the indicators of related industries at home and abroad, we can better understand the strengths, weaknesses, level, and trends of the sports competition performance industry in the region, and provide reference for the formulation of scientific and reasonable industrial policies. In addition, we can also compare the performance evaluation indicators of the sports competition performance industry in the region with similar industries in other regions to further understand the differences and development status between regions.
3.3.3 Constructing the Performance Evaluation Indicator System for the Sports Competition Performance Industry in the Chengdu-Chongqing Region
The construction of performance evaluation indicators system for sports competition performance industry in the region needs to start from the perspective of industrial development, comprehensively considering the current situation, characteristics, and development trends of the sports competition performance industry in the region. Based on this, performance evaluation indicators applicable to the sports competition performance industry in the region can be designed. In order to construct the performance evaluation indicators for the sports competition performance industry in the region, the following aspects can be considered. According to two rounds of expert consultation and comprehensive consideration, the performance evaluation index of sports competition performance industry in the region is constructed, including 5 first-level indicators, 13 second-level indicators, and 42 third-level indicators. According to the results of the index system established above, the authors conducted an empirical test to verify the feasibility of the index system. The hierarchy analysis questionnaire was designed according to the established index system, the hierarchy analysis matrix was constructed, the questionnaire was sent to the experts participating in the second round of consultation, ten expert questionnaires were collected within the deadline, and the expert data were imported into YAAHP software to calculate the weight of the index system (as shown in Table 1).
Performance evaluation indexes of sports competition performance industry in Chengdu-Chongqing region
| Primary indicators (weight) | Secondary indicators (weight) | Tertiary indicators (weight) | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial performance (0.2132) | Output value (0.0942) | Direct output value (0.0506) | Direct output value refers to the economic activities directly related to the sports competition performance, such as ticket sales, advertising revenue, sponsorship, copyright income, etc |
| Indirect output value (0.0436) | Indirect output value refers to the supporting economic activities related to sports competition performance, such as tourism, accommodation, catering, transportation, logistics, etc | ||
| Profit (0.0656) | Sports event organization and management (0.0158) | Profits from ticket sales, sponsor investment, and advertising revenue | |
| Hotel and catering services (0.0139) | Profits generated by demand for accommodation and meals during the event | ||
| Logistics and support services (0.0166) | Profits generated by logistics, transportation, security, cleaning, medical care, etc | ||
| Media communication and broadcasting Services (0.0193) | Advertising revenue, membership fees, and other profits. | ||
| Sales of sporting goods and souvenirs (0.0126) | Profit from sales of sporting goods and souvenirs related to the event | ||
| Return on investment (0.0534) | Overall return on investment (0.0321) | Total return on investment reflects the profitability and economic efficiency of the entire industry, and refers to the ratio of annual profit or annual average profit to the total investment | |
| Return on investment for individual investments (0.0213) | The return on individual investment evaluates the return on a specific project and refers to the ratio of the return on a specific project to the investment | ||
| Market performance (0.2903) | Market occupancy (0.1347) | High or low market share (0.1347) | Market share refers to the proportion of a company or brand’s sales or sales in a particular market to the total sales or sales in that market |
| Market share (0.0946) | Sports organization and management (0.0272) | The proportion of sales (or sales) of ticket sales, sponsor investment, advertising revenue, etc., in the market for similar products | |
| Media communication and broadcasting services (0.0215) | The proportion of accommodation and meal sales (or sales) in the market for similar products during the event | ||
| Sports goods and souvenir sales (0.0167) | The proportion of sales (or sales) of logistics, transportation, security, cleaning, medical, etc., in the market of similar products | ||
| Hotel and catering services (0.0153) | The proportion of sales (or sales) of advertising revenue, membership fees, etc., in the market for similar products | ||
| Logistics and support services (0.0139) | The proportion of sales (or sales) of sporting goods and souvenirs related to the event in the market of similar products | ||
| New product development capability (0.0610) | Technological innovation capability (0.0231) | Technological innovation ability refers to the ability of the industry in technological research and development, including technological innovation awareness, technological research and development investment and technological research and development level | |
| Product design capability (0.0199) | Product design capability refers to the ability of the industry in product design, including product form design, function design, user demand analysis, and product testing | ||
| Market research capability (0.0089) | Market research ability refers to the ability of the industry in market research, including market demand analysis, competition analysis, and marketing | ||
| Quick response capability (0.0091) | Rapid response ability refers to the industry’s response speed in response to market changes and customer needs, including production speed, logistics speed, and after-sales service | ||
| Innovation performance (0.1351) | Technological innovation capability (0.0501) | Match data statistics and analysis (0.0131) | Statistics and analysis of athletes’ training and competition data based on big data and other technologies |
| Live broadcast technology (0.0176) | The events are broadcast live on the Internet during the games, and information about the games is transmitted to the audience via the Internet | ||
| Mobile applications (0.0104) | Develop targeted mobile applications to display competition information to users through mobile devices and enhance user experience | ||
| Stadium construction and operation management technology (0.0090) | In the venue design, the use of some emerging technologies, such as LED screen and 3D projection, to enhance the visual effect of the audience; In terms of operation management, some Internet technologies, such as online ticket purchase and mobile payment, have been adopted to improve the service quality and efficiency of the venue | ||
| Product innovation capability (0.0432) | Innovation of match format and rules (0.0107) | The competition format and rules are constantly innovated to meet the different needs of consumers | |
| Innovation of match venues and facilities (0.0118) | Innovation in the event venues and facilities to enhance the experience of the game, such as smart venue construction | ||
| Innovation of technology application (0.0105) | Innovation in video live broadcasting and VR technology application | ||
| Innovation of marketing strategy (0.0102) | Launch different forms of tickets, event theme peripheral products, etc | ||
| Service innovation capability (0.0418) | Service mode innovation (0.0148) | To provide more professional, personalized, differentiated services, such as the use of customized service model, according to the needs of different athletes, fans, and enterprises, to provide personalized services | |
| Service content innovation (0.0137) | Provide more rich and diversified service content, such as increasing interaction and participation, so that the audience can participate in the game, and improve the entertainment and attraction of the game | ||
| Service method innovation (0.0133) | Provide more convenient and efficient service methods, such as the use of information service methods, through mobile terminal, Internet and Internet of Things technology, to achieve the digitalization of the whole process of services, and provide all online services, convenient users to enjoy services anytime and anywhere | ||
| Social performance (0.2463) | Employment rate (0.1425) | Provision of employment opportunities (0.1425) | To promote the vigorous development of related industries, investment in technological innovation and talent introduction have increased more job opportunities |
| Social contribution (0.1038) | Driving economic growth (0.0307) | Drive the development of many related industries, such as catering, accommodation, transportation, tourism, etc., to promote local economic growth | |
| Paying taxes (0.0252) | Pay all kinds of taxes, such as venue rent, wages and benefits, taxes, etc., the generation of these taxes is crucial to support local governments in providing infrastructure construction, public services, and livelihood security | ||
| Promoting social and cultural exchanges (0.0266) | The promotion of local sports culture and brand provides an opportunity for foreigners and tourists to better understand the local culture. At the same time, international sports competitions also provide a platform for cultural exchanges with other countries and regions | ||
| Participating in public welfare activities (0.0213) | The organizers of the sports competition performance industry also actively participate in public welfare activities, such as fundraising to support charitable causes, poverty alleviation, etc., and have made positive contributions to social public welfare undertakings | ||
| Ecological performance (0.1151) | Efficiency of resource utilization (0.0627) | Efficiency of venue resource utilization (0.0212) | The industry in this region needs to make full use of venue resources and improve the utilization rate of venue resources through venue sharing and venue multi-function |
| Efficiency of human resource utilization (0.0165) | The industry in this region needs to rationally allocate human resources, improve the ability level of employees and improve the utilization efficiency of human resources through recruitment and training | ||
| Efficiency of financial resource utilization (0.0181) | The industry in this region needs to reasonably manage financial resources and maximize the use of financial resources through budgeting and cost control | ||
| Efficiency of environmental resource utilization (0.0069) | The industry in the region needs to pay attention to environmental protection, reduce the waste of energy, and water resources in the operation process, and improve the efficiency of environmental protection resources | ||
| Environmental protection (0.0524) | Venue design and construction (0.0192) | In the design and construction process of sports venues in the region, environmental factors are paid attention to, such as the selection of environmentally friendly materials in the construction of venues, improving energy conservation standards, and installing solar photovoltaic panels | |
| Environmental responsibility promotion (0.0179) | The region has also been improving its social responsibility, organizing various activities and public welfare actions to let more people join the ranks of environmental protection. For example, in the event, the garbage will be sorted and recycled, and the environmentally friendly tableware and paper will be used at the event site to reduce the impact on the environment | ||
| Specific environmental measures (0.0153) | According to the climate characteristics of the region, it is indispensable to take special environmental protection measures. For example, in the high temperature season, appropriate measures are taken to maintain the balance of humidity and temperature inside and outside the venue to reduce energy consumption and waste of resources |
3.4 Strategic Thinking for the High-quality Development of Sports Competition Performance Industry in the Chengdu-Chongqing Region from the Perspective of Performance Evaluation
To further advance the high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry in the region, it is necessary to strengthen top-level design and overall coordination, firmly establish the concept of industrial cluster development, fully leverage the advantages of performance evaluation, and create a high-level model for regional cooperation and high-quality development of the industry. This will play a supporting role in promoting the construction of a sports power province (city) in the new era of the region, take a leading role in building a city renowned for sports events, and serve as a demonstration role in promoting green economic development in the region. The performance evaluation of the sports competition performance industry is a complex network system that connects the interests of all parties in the industry chain of the sports competition performance industry through the integration of logistics, capital flow, and information flow by core sports enterprises. In the perspective of industrial clusters, the performance evaluation subjects in various links form a symbiotic and complementary relationship through industrial agglomeration, and optimize the effective division of labor between the subjects inside and outside the cluster to enhance the industry competitiveness. Figure 2 shows a simple structural model.
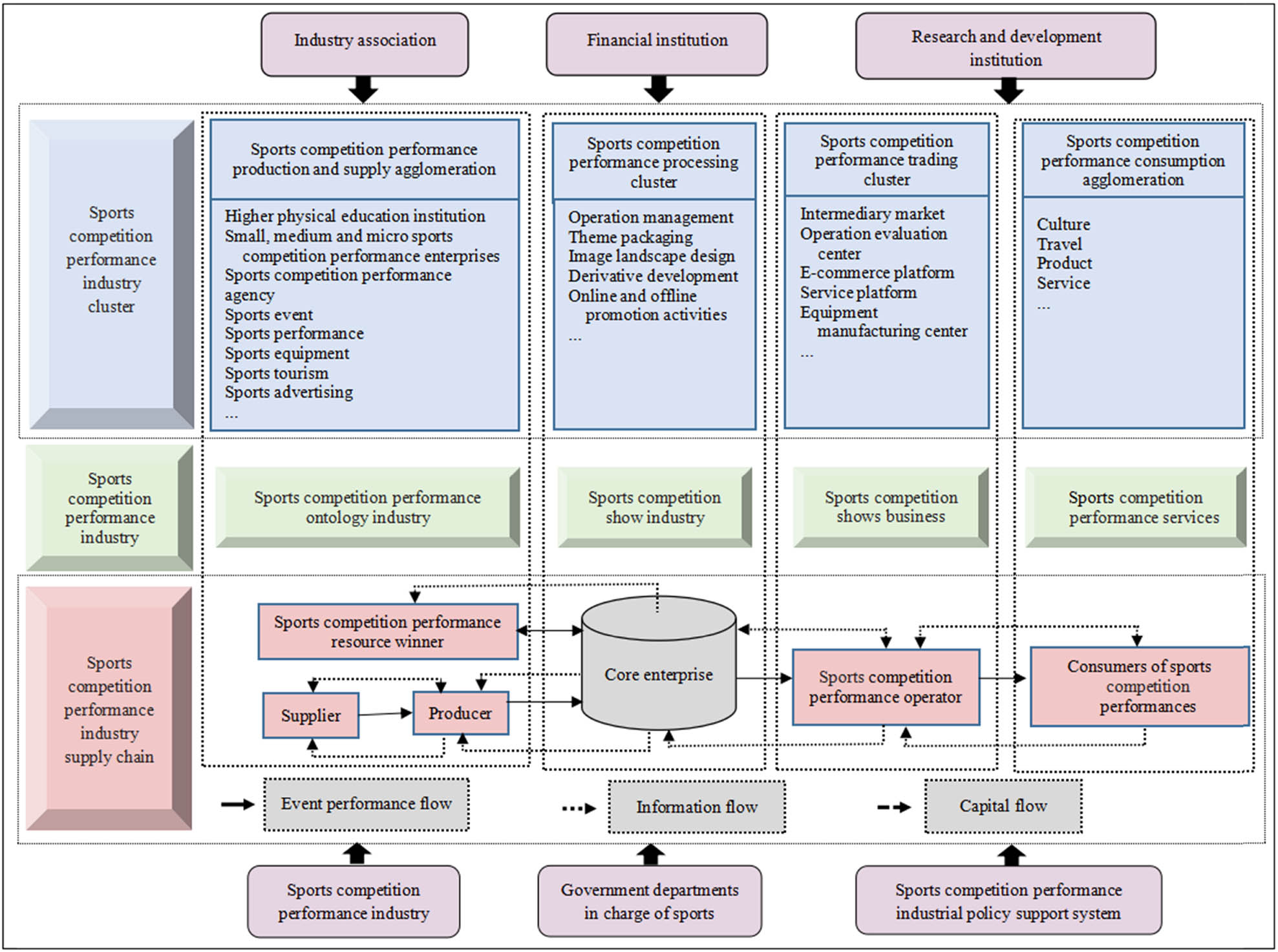
A simple model for the high-quality cluster development of the sports competition performance industry from the perspective of performance evaluation (Liu, 2020).
3.4.1 Guiding Ideology
Guided by Xi Jinping thoughts on socialism with Chinese characteristics for a new era, firmly implement the new development concept, take performance evaluation as the basis, promote high-quality development as the theme, deepen regional collaborative governance as the main line, based on the construction of a new development pattern of mutual promotion in the region, focus on promoting the formation of regional sports industry layout with complementary advantages and high-quality development, strengthen the leading role of Chongqing and Chengdu central cities. To lead and drive the overall and coordinated development of the sports industry in Chengdu-Chongqing, promote the efficient agglomeration of sports competition and performance industries, accelerate the formation of new driving forces for high-quality development, accelerate the shaping of new advantages in innovation and development, accelerate the construction of a new situation of cooperation and interaction in Chengdu-Chongqing, and actively promote the professional, branded, and integrated development of the sports competition performance industry in Chengdu-Chongqing. To promote the formation of a powerful and distinctive twin city sports competition performance industry cluster in the region, create an important pole of growth and a new source of power to drive the high-quality development of the national sports competition performance industry, and enhance people’s sense of gain and happiness.
3.4.2 Main Principles
The dual-core of Chengdu and Chongqing will lead the way, and regional linkage will be established. We aim to enhance the international competitiveness of the sports competition performance industry in the central cities of Chongqing and Chengdu, manage the relationship between central and regional development, strengthen the synergistic driving effect, promote the accelerated growth of the sports competition performance industry in small and medium-sized cities by leveraging the strengths of larger cities, and promote balanced development of the sports competition performance industry in the region by highlighting key cities. We will also promote the development of the rural sports competition performance industry effectively through the urban-rural integration, and to form a regional sports competition performance industry development pattern with distinct characteristics, reasonable layout, and intensive and efficient operation.
Share and include to improve people’s livelihoods: We adhere to the development concept centered on the people, increase the supply of high-quality sports competition performance industry products and services, continuously improve people’s physical fitness and health levels, construct a diverse and inclusive social governance pattern, enable the sports competition performance industry to benefit more people fairly, meet the diverse needs of the people’s lives, and improve the sense of gain and happiness of the masses.
To coordinate and cooperate while building together: We will adhere to the concept of “Chuan-Yu as a whole” and leverage our strengths to promote coordinated development. We will optimize and integrate regional resources, strengthen policy coordination, and docking for the sports competition performance industry, and achieve unified planning, integrated deployment, mutual cooperation, and joint implementation. The development of surrounding areas will also benefit from this effort, which will significantly enhance the overall competitiveness of the regional sports competition performance industry.
3.4.3 Development Objectives
Respect objective laws, leverage comparative advantages, rely on comprehensive transportation hubs and multi-dimensional open channels, improve the ability to participate in the global sports event resources allocation, promote the formation of a powerful and distinctive dual-city sports competition performance industry cluster in the region. We strive to build a higher-level and Sichuan-Chongqing characteristic national fitness public service system, practice the concept of “holding competitions, building cities, promoting industries, and benefiting the people,” continue to construct world-class event cities with high standards, and develop the sports competition performance industry in the region into an important highland with national and even global influence.
By 2025, the international influence of the sports competition performance industry in the region will be significantly enhanced, the regional characteristics will be further highlighted, and its role in supporting the high-quality development of the national sports competition performance industry will be significantly strengthened.
By 2030, a spatial pattern led by the dual-city of Chengdu-Chongqing will be formed. Chongqing and Chengdu have significantly increased their contribution to the national sports competition performance industry, the regional driving force and international competitiveness have been significantly enhanced, and significant breakthroughs have been made in the sports competition performance industry of the urban agglomeration. The development of small- and medium-sized cities and counties has accelerated, and a new pattern of complementary advantages, reasonable division of labor, benign interaction, and coordinated development between large, medium, and small cities and small towns has been formed, and the “Chengdu-Chongqing World Sports Events Circle” with international influence has been built.
By 2035, a strong and distinct dual-city sports circle will be established, and Chongqing and Chengdu will enter the ranks of modern sports powerhouse provinces (cities). The urban system for the coordinated development of sports in large, medium, and small cities will be further improved, with basic interconnectivity of infrastructure realized, and the “World Sports Center” with international influence will be basically built. Sports will become a bridge and link between cities and the world, and the physical literacy and health level of the people will be greatly improved, significantly enhancing the support and driving force for the high-quality development of the national sports industry. It will become an active growth pole and a strong source of power with international influence.
3.5 Strategic Path for the High-quality Development of Sports Competition Performance Industry in Chengdu-Chongqing Region from the Perspective of Performance Evaluation
To accelerate the high-quality development of sports competition and performance industries in the region, a spatial concentration strategy should be adopted, with a focus on developing sports competition and performance industries in cities and towns within the region with high levels of industrial spatial agglomeration and urban-regional agglomeration. Therefore, the basic strategic path for the high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry in the region should be to implement spatial concentration and key promotion strategies, vigorously promote the concentration of sports competition and performance industries in key areas with superior location conditions, strong spatial accessibility, high industrial agglomeration degree and urban agglomeration degree, and prioritize the development of sports competition and performance industries in key areas. Expand the scale of sports competition performance industry, strengthen the division of labor and cooperation and the integration of the industry between Chengdu, Chongqing metropolitan areas, and urban clusters, and between the eight regional central cities and urban agglomerations, and improve the spatial aggregation capacity of the sports competition performance industry, and promote the development of new spatial forms of sports competition and performance industries, such as sports competition performance industry circles, belts, and clusters, and to form an organic combination of high-quality development of sports competition and performance industries in urban agglomerations, regional central cities, and densely populated towns in new spatial forms of sports competition and performance industries. This will expand the scale of high-quality development of sports competition and performance industries in densely populated areas. This will enable the sports competition performance industry in the region to reach the advanced level of the sports competition performance industry in the developed coastal cities, and further drive the high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry in the region. The strategic path is shown in Figure 3.
Strategic path of high-quality development of sports competition performance industry.
3.5.1 Strategy for Integrated Development through the Combination of Points and Surfaces
This strategy aims to promote the high-quality development of sports competition performance industry in the region, increase the spatial agglomeration of sports competition performance industry, and promote the formation of new spatial organizational forms such as urban sports competition performance industry circle, urban sports competition performance industry belt, and urban sports competition performance industry group. In the process of urbanization, the sports competition performance industry should shift from the traditional model of clustering around a single city as the core “point” to a new model of clustering around sports competition performance industry circles, belts, groups, and other spatial organizational forms centered on the industry. This will create a more extensive area for the concentration of the sports competition performance industry. It is important to strengthen the high-quality integrated development of sports competition performance industry between large- and medium-sized cities and small towns within key areas. This will promote the coordinated development of sports competition performance industry in county-level administrative units and small towns, and expand the industry chain of sports competition and performance. While enhancing the agglomeration capacity of sports competition performance industry in large- and medium-sized cities in the region, we should also accelerate the high-quality integration of sports competition performance industry between these cities and surrounding towns through external demand generated by the industry, as well as the diffusion of capital and technology. This will transmit the influence of industrialization and urbanization to the sports competition performance industry in smaller towns around the region. The sports competition performance industry in surrounding small towns should be organized into clusters, forming a reasonable division of labor with the sports competition performance industry in central and large cities. This will create an integrated urban-rural spatial structure system for the high-quality development of sports competition performance industry (Deng, 2012).
3.5.2 Priority Development Strategy between Regions
To prioritize the development of sports competition performance industry in the 15 cities in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic zone construction plan, which includes Chengdu, Zigong, Luzhou, Deyang, Mianyang, Suining, Neijiang, Leshan, Nanchong, Meishan, Yibin, Guangan, Dazhou, Ya’an, and Ziyang. Priority should be given to the development of sports competition performance industry in 21 districts in Chongqing, including Yuzhong, Dadukou, Jiangbei, Shapingba, Jiulongpo, Nan’an, Beibei, Yubei, Banan, Fuling, Changshou, Jiangjin, Hechuan, Yongchuan, Nanchuan, Qijiang-Wansheng Economic Development Zone, Dazu, Bishan, Tongliang, Tongnan, and Rongchang. Further, strengthen the functions of cities such as Chengdu, Chongqing, Mianyang, and Yibin, which have a significant impact on the region’s sports competition performance industry. This will better leverage their roles as economic, information, trade, financial, and cultural centers, as well as their role in providing services, radiating and driving development in the high-quality development of sports competition performance industry. They will become the core and strategic support points for the concentration of sports competition performance industry and sports population in the region in the new era. Encourage the development of industry clusters for sports competitions and performance enterprises, with tourism, transportation, catering, and other industries as support, and advertising, printing, on-site services, etc., as supporting industries, to form an efficient service system for the sports competition performance industry with industry matching, industry linkage, and high operation efficiency. Cultivate a number of sports competition performance industry agglomeration areas (General Office of the State Council, 2021).
3.5.3 Gradual Development Strategy with Conditions in the Region
Cultivate and develop the sports competition performance industry in the Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration and regional central cities, promote the formation of high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry in the region, and conditionally develop a good situation in a gradual manner. By adjusting and optimizing the structure of the sports competition performance industry, improving its ability to gather and radiate to surrounding areas, these cities’ sports competition and performance industries can fully leverage their important roles in regional economic development. They will become key industries in the region and high-quality cluster development centers for sports competition and performance industries facing provincial and municipal border areas.
3.5.4 Selective Key Development Strategy for Small Cities
We should actively support the sports competition performance industry in small cities, and select targeted areas for key development. In this process, it is possible to strengthen its industrial functions and expand its scale, strengthen its connection with the sports competition performance industry in large and medium-sized cities, and promote the small city sports competition performance industry cluster to move towards the medium-sized city sports competition performance industry cluster. The development of sports competition performance industry in small towns should change the situation of excessive dispersion and low-level development, accelerate the transformation from dispersed to concentrated development, increase the gathering scale between the sports competition performance industry and sports population, gradually promote the upgrading of the sports competition performance industry in small towns, and make some small town’s sports competition performance industry catch up with the development level of sports competition performance industry in small cities (Li, 2011). To achieve high-quality development of sports competition and performance industries in small towns in the region, we should make use of their unique regional sports resources, natural resources, ethnic customs in different seasons, and abundant high-quality ecological tourism resources. We should focus on promoting the development of sports tourism industry, sports manufacturing industry, fitness and entertainment industry, sports equipment industry, and other sports-related industries derived from sports events and performances.
3.5.5 Layered Development Strategy with Emphasis on Different Stages
To promote high-quality development of sports competition performance industry in the primary stage, the key is to accelerate the coordinated development between the sports competition performance industry clusters in regional central cities and town clusters. The construction of sports infrastructure in the region is urgently needed, and it is necessary to fully utilize the historical opportunity of funding and policy tilt in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle. Utilizing the task objectives of the “Outline of the Plan for the Construction of Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Zone” and the “Guiding Opinions on Accelerating the Development of sports competition performance industry,” as well as the opportunity of constructing a strong sports nation strategy, the government can play a leading role in investment, providing key support for development and exerting its promoting role to accelerate the development of sports competition performance industry. To expand the development space of sports competition performance industry, it is important to adopt a multi-party financing model through cooperation between associations and clubs, associations and enterprises (companies), and joint investment with clubs. More importantly, it is necessary to coordinate the construction of regional sports infrastructure and the development of regional economy, creating a favorable environment for promoting high-quality development of sports competition performance industry clusters in regional central cities and town clusters. It is important to vigorously support the social public sports industry, accelerate the development of key sports events and performance industries, and guide other cities in the region to actively interact with central cities for development, in order to achieve high-quality development of sports competition performance industry clusters.
To promote the high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry in the intermediate stage, the main goal is to use development as the driving force and give full play to the market-oriented role. This will facilitate the integration of the sports competition performance industry in Chengdu metropolitan area and Chengdu plain region. Through integrated development within the region, it is important to guide the construction of urban sports facilities, the layout of sports competition and performance industries, and flow of resources in the industry. We need to break down artificial barriers and administrative boundaries, and establish an integrated market mechanism for sports competition performance industry (Liu & Zheng, 2004). We need to promote the efficient flow of production factors such as talents, capital, technology, and information, as well as various tangible sports products within the sports competition performance industry in the Chengdu metropolitan area and Chengdu plain region. This will facilitate the construction of a shared market system for sports competition performance industry. We also need to collaborate with sports manufacturing, sports service, sports fitness, and leisure industries to form a competitive and driving force for the sports competition performance industry. We need to coordinate the construction of regional sports public services within the region and between cities, and work together to build world-renowned sports event cities to enhance the overall competitive advantage of the sports competition performance industry.
In order to achieve high-quality development of sports competition performance industry in the advanced stage of Chengdu and Chongqing metropolitan areas, there are significant differences compared to the first two categories of high-quality development in the sports competition performance industry. This is reflected in the highly concentrated sports competition performance industry, large urban sports population, and the formation of a relatively complete market network system for sports competition performance industry. The entire sports competition performance industry cluster has strong development strength and is in a period of rapid development. The sports competition performance industry cluster area has a strong collaborative division of labor, but there are also serious contradictions such as redundant construction of sports infrastructure and similar structure of sports competition performance industry in the process of development. Therefore, we need to coordinate the sports competition performance industry resources in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle, while adhering to the principles of collaborative construction, mutual complementarity, industrial integration, and balanced development. Driven by the dual cores of Chengdu and Chongqing metropolitan areas, we will focus on building the dual-core sports competition performance industry, which will drive the overall optimization of spatial layout, improvement of functional systems, and overall upgrading of the development level of the sports competition performance industry in the region. Chengdu city will focus on building the park-city demonstration zone that practices the new development concept, implement the action of building a world famous event city, and accelerate the construction of a fitness and dynamic capital that highlights the park-city background, a world-class international event capital, a sports innovation resource allocation center that radiates globally, a fashionable and charming sports consumption center, an outdoor sports and leisure center with international appeal, a sports and cultural exchange center that showcases the unique Tianfu culture, and an open and collaborative sports growth pole in the Chengdu metropolitan area. Chongqing’s metropolitan area focuses on building a new model of high-quality development and high-quality life, and vigorously promotes the coordinated and rapid development of the sports industry in the central city and the main urban area. It aims to create it as the core area of the national sports tourism demonstration zone, and accelerate the construction of a sports event city, a smart sports city, a leading edge for national fashion sports consumption, and a western sports finance highland. This will form a high-quality development pattern for the sports competition performance industry, which is led by consumption, driven by innovation, characterized by active entities, optimized structure, and efficient governance (Sichuan Provincial Sports Bureau Office, 2022).
4 Conclusion
Currently, there are not many research results on the high-quality development of sports competition performance industry in Chengdu-Chongqing region, and there are even fewer studies based on performance evaluation. From the perspective of performance evaluation theory, the sports competition performance industry in the region has shown a trend of annual growth, with Chongqing and Chengdu developing their sports competition performance industry most rapidly. The sports competition performance industry in the region has brought significant economic and social benefits, playing a positive role in promoting local economic growth, improving employment rates, and promoting the city’s image. Government support and investment are important factors in promoting high-quality development of the sports competition performance industry in the region. Market-oriented operation is also a key element in the high-quality development of this industry. At present, there are still some problems in the sports competition performance industry in the region, such as insufficient support for niche sports events, the influence of sports events needs to be further improved, the lack of regional characteristics and brand advantages, and the agglomeration advantage of sports competition performance industry has not been really established. High quality development is the only way to develop the sports competition performance industry in the region. At present, benefiting from the gradual release of policy dividends such as China’s Guiding Opinions on Accelerating the Development of Sports Performance Industry, the Construction Plan of Chengdu-Chongqing Twin City Economic Circle, the 14th Five-Year Plan for the Integrated Development of Sports Industry of Chengdu-Chongqing Twin City Economic Circle, the sports competition performance industry in the region is facing a historical opportunity of rapid development. However, how to transform the policy dividend into the competitiveness of the industry, how to deal with the increasingly complex industrial environment, how to grasp the new opportunities brought by new business forms and new technologies are the difficult problems that the development of sports competition performance industry must solve (Deng et al., 2019).
In order to improve these problems, the government of Chengdu-Chongqing region should attach great importance to the construction of sports competition performance industry agglomeration, make scientific planning, and actively promote industry agglomeration. It should discuss with sports industry leaders and large enterprises, formulate clear, scientific, and distinctive industrial agglomeration development strategy planning, and then launch a series of policies to cultivate industrial agglomeration, guide related enterprises to enter, promote the formation of agglomeration advantages, and create a distinctive and competitive sports competition performance industry cluster. We should build a good infrastructure and service platform for the agglomeration of sports competition performance industry, provide open conditions for the innovation of enterprises within the cluster, guide enterprises to jointly promote the strategic adjustment and industrial upgrading of sports competition performance industry in the region, and jointly promote the building of advantages of sports competition performance industry in the region. It is necessary to promote the improvement of various service systems of sports competition performance related industry technology and intermediary in area (Li, 2014). From the perspective of performance evaluation, the unique structural characteristics of the high-quality development of sports competition performance industry put forward new requirements for collaborative management. On this basis, the collaborative management system of sports competition performance industry from the perspective of performance evaluation can be constructed by establishing collaborative management mechanism, reconstructing business process system, and optimizing functional collaborative mode, which will be conducive to the transformation and upgrading of industrial clusters of sports competition performance industry and the improvement of the overall competitiveness of sports competition performance industry (Liu, 2020).
Although this study studies the high-quality development of sports competition performance industry in Chengdu-Chongqing region based on the theory of performance evaluation, there are still some shortcomings: First, the scope of investigation and interview in this study is relatively limited, and only the data of some areas in Chengdu-Chongqing are selected for analysis, so the research conclusions have certain limitations. Second, the performance evaluation index of this study can be further improved and optimized. For example, indicators such as talent training benefits can be added to fully reflect the influence of the industry. In the future research, we will further expand the scope of sample data, and continue to improve the performance evaluation index based on the actual situation, explore how to improve the quality and influence of the event, and promote high-quality development of sports competition performance industry in the region.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to the authors for their efforts in this article, especially to the authors of the papers cited by us in the article.
-
Funding information: This research was supported by Sichuan Provincial Key Research Base of Philosophy and Social Sciences: Tianfu Research Center of International Sports Events (Grant No. YJY2021B09).
-
Author contributions: Q.Y. and C.D. conceived the research framework of this study and drafted and revised it. Y.Y. and J.W. participated in the exchange and discussion of this study. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
-
Article note: As part of the open assessment, reviews and the original submission are available as supplementary files on our website.
-
Data availability statement: Data are contained within the article.
References
China Youth Daily. (2020). “Exercise to fight the epidemic” has led the people to upgrade their awareness, and sports have become a new normal of healthy life. China Youth Daily Client. https//baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1667296685039651245&wfr=spider&for=pc (accessed on 21 May 2020).Search in Google Scholar
Deng, C. L. (2012). Development thinking and model exploration of China’s great gymnastics industry. Chengdu Sport University. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C475KOm_zrgu4lQARvep2SAkVR3-_UaYGQCi3Eil_xtLb0nM2BElg-cOxEvxonBUhyUCUCBq2PAmucbIW9CKdvMJ&uniplatform=NZKPT (No documentation number).Search in Google Scholar
Deng, C., & Tang, Z. (2020). Historical opportunity and structural transformation of sports industry development under the background of new information technology. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1575, 1–6. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1575/1/012170.Search in Google Scholar
Deng, C., Tang, Z., & Zhao, Z. (2019). Countermeasures for the innovative development of China’s sports industry under the background of big data. Big Data Analytics for Cyber-Physical System in Smart City, 1117, 1223–1229. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-2568-1_170.Search in Google Scholar
Deng, E., & Xiang, Z. Q. (2016). Research on the mechanism of influence factors of internet finance brand image communication effect – An empirical analysis based on data from six provinces in central China. Hubei Social Sciences, 4, 58–65. doi: 10.13660/j.cnki.42-1112/c.013561.Search in Google Scholar
General Office of the State Council. (2021). Guiding opinions on accelerating the development of sports competition performance industry. Official website of central people’s government of the People’s Republic of China. http//www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2018-12/21/content_5350734.htm (accessed on 21 October 2021).Search in Google Scholar
He, Q., & Xu, G. H. (2020). Connotation and direction of the high-quality development of the sports performance industry from the perspective of urban efficiency. Journal of Shanghai University of Sport, 44, 55–65. doi: 10.16099/j.sus.2020.11.007.Search in Google Scholar
Huang, H. Q., Sheng, C. X., & Yi, Y. (2021). The pain points, blocking points and countermeasures of ensuring the safety of industrial chain and supply chain. The official hundred number of national development and reform commission of the People’s Republic of China. https//author.baidu.com/home?from=bjh_article&app_id=1631862049687989 (accessed on 15 March 2021).Search in Google Scholar
Li, C. Y. (2018). The total scale of sports competition performance industry will reach 2 trillion yuan by 2025. People’s Daily. https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1620524960028391187&wfr=spider&for=pc.Search in Google Scholar
Li, L. (2011). Theoretical exploration on the development path of sports industrial clusters in the western cities of China. Communications in Computer and Information Science, 2, 362–369. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-23020-2_53.Search in Google Scholar
Li, X. K. (2014). Analysis of development of Chinese sports industrial cluster based on supply chain management. Logistics Technology, 33, 159–161. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C44YLTlOAiTRKibYlV5Vjs7ir5D84hng_y4D11vwp0rrtYI9NektMkKZI2zYk-KQbPjWRNRHswoDBfWcYABwcQX0&uniplatform=NZKPT (No documentation number).Search in Google Scholar
Liu, B. L., & Zhang, Y. (1999). Development and problems on the sports competition market in China. Journal of Chengdu Physical Education Institute, 4, 4–9. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C44YLTlOAiTRKjkpgKvIT9Nkm5tS6uBYqSHqTAgSazl_cxZwfQlst0NznVe_wi-xDWJ-9MCMuU_W4PTvoaRvTOYX&uniplatform=NZKPT (No documentation number).Search in Google Scholar
Liu, L. L. (2006). Research on performance evaluation system and incentive mechanism for telecommunication enterprises based on EVA. Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C475KOm_zrgu4h_jQYuCnj_co8vp4jCXSivDpWurecxFtAcAcIi6JRKWR-uTQTs5-jKRCw6EFQlHZqSD61VNctmv&uniplatform=NZKPT (No documentation number).Search in Google Scholar
Liu, X. Y., & Zheng, C. D. (2004). The development strategy of small towns in the less developed areas of Western China and its advantages of late development: A case study of Sichuan. Journal of Southwest University for Nationalities∙Humanities& Social Sciences, 25, 1–5. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C44YLTlOAiTRKgchrJ08w1e7eeyE9jLkqq-e56JR9VD9N_5TqB_XohIbtDZlD2rw89hqIgA-OM956Y1ao4pmrpK1&uniplatform=NZKPT (No documentation number).Search in Google Scholar
Liu, Z. (2020). Research on construction of Chinese medicinal materials supply chain collaborative management system from perspective of industrial clusters. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 51, 3601–3608. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=3uoqIhG8C44YLTlOAiTRKibYlV5Vjs7i8oRR1PAr7RxjuAJk4dHXomDMAykjOojxUsZ1cfXX24Q6jDbLVXoYK3ppGnbzQPyJ&uniplatform=NZKPT (No documentation number).Search in Google Scholar
Luo, L. (2019). A literature review on spectator sports conducting by Western scholars. China Sport Science and Technology, 55, 41–51. doi: 10.16470/j.csst.2019073.Search in Google Scholar
Mohanta, K. K., & Toragay, O. (2023). Enhanced performance evaluation through neutrosophic data envelopment analysis leveraging pentagonal neutrosophic numbers. Journal of Operational and Strategic Analytics, 1, 70–80. doi: 10.56578/josa010204.Search in Google Scholar
Moradi, N., Malekmohammad, H., & Jamalzadeh, S. (2018). A model for performance evaluation of digital game industry using integrated AHP and BSC. International Journal of Research in Industrial Engineering, 5, 97–109. doi: 10.22105/riej.2019.169895.1074.Search in Google Scholar
Movafaghpour, M. A. (2019). Developing 360 degree performance evaluation method for school teachers. International Journal of Research in Industrial Engineering, 8, 28–39. doi: 10.22105/riej.2019.169895.1074.Search in Google Scholar
National Development and Reform Commission and Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development. (2016). Notice on printing and distributing the development plan of Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration. National Development and Reform Commission of the People’s Republic of China Website. https//www.ndrc.gov.cn/fggz/fzzlgh/gjjzxgh/201605/t20160504_1196728.html?code=&state=123 (accessed on 27 April 2016).Search in Google Scholar
Osintsev, N., & Khalilian, B. (2023). Does organizational performance increase with innovation and strategic planning? Journal of Operational and Strategic Analytics, 1, 25–33. doi: 10.56578/josa010104.Search in Google Scholar
Sichuan Provincial Sports Bureau Office. (2022). The “14th Five-Year” sports industry integration development plan of Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle. Sichuan Sports Bureau Official Website. http//tyj.sc.gov.cn/sctyj/tzgg/2022/12/27/28dc9e02fe9840e1af1a7b696901cfe8.shtml (accessed on 27 December 2022).Search in Google Scholar
Tavakoli, M. M., Molavi, B., & Shirouyehzad, H. (2017). Organizational performance evaluation considering human capital management approach by Fuzzy-DEA: A case study. International Journal of Research in Industrial Engineering, 6, 1–16. doi: 10.22105/riej.2017.48022.Search in Google Scholar
The Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and The State Council. (2021). Outline of planning for the construction of Chengdu-Chongqing twin city economic circle. Chinese Government Website. http//www.gov.cn/zhengce/2021-10/21/content_5643875.htm (accessed on 21 October 2021).Search in Google Scholar
Wang, J. C. (2001). Space of innovation, enterprise cluster and regional development, (pp. 3–4). Peking University Press.Search in Google Scholar
Zhang, B. L. (2019). Governance of sports competition performance industry chain. Central China Normal University. doi: 10.27159/d.cnki.ghzsu.2019.002727.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Political Turnover and Public Health Provision in Brazilian Municipalities
- Examining the Effects of Trade Liberalisation Using a Gravity Model Approach
- Operating Efficiency in the Capital-Intensive Semiconductor Industry: A Nonparametric Frontier Approach
- Does Health Insurance Boost Subjective Well-being? Examining the Link in China through a National Survey
- An Intelligent Approach for Predicting Stock Market Movements in Emerging Markets Using Optimized Technical Indicators and Neural Networks
- Analysis of the Effect of Digital Financial Inclusion in Promoting Inclusive Growth: Mechanism and Statistical Verification
- Effective Tax Rates and Firm Size under Turnover Tax: Evidence from a Natural Experiment on SMEs
- Re-investigating the Impact of Economic Growth, Energy Consumption, Financial Development, Institutional Quality, and Globalization on Environmental Degradation in OECD Countries
- A Compliance Return Method to Evaluate Different Approaches to Implementing Regulations: The Example of Food Hygiene Standards
- Panel Technical Efficiency of Korean Companies in the Energy Sector based on Digital Capabilities
- Time-varying Investment Dynamics in the USA
- Preferences, Institutions, and Policy Makers: The Case of the New Institutionalization of Science, Technology, and Innovation Governance in Colombia
- The Impact of Geographic Factors on Credit Risk: A Study of Chinese Commercial Banks
- The Heterogeneous Effect and Transmission Paths of Air Pollution on Housing Prices: Evidence from 30 Large- and Medium-Sized Cities in China
- Analysis of Demographic Variables Affecting Digital Citizenship in Turkey
- Green Finance, Environmental Regulations, and Green Technologies in China: Implications for Achieving Green Economic Recovery
- Coupled and Coordinated Development of Economic Growth and Green Sustainability in a Manufacturing Enterprise under the Context of Dual Carbon Goals: Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality
- Revealing the New Nexus in Urban Unemployment Dynamics: The Relationship between Institutional Variables and Long-Term Unemployment in Colombia
- The Roles of the Terms of Trade and the Real Exchange Rate in the Current Account Balance
- Cleaner Production: Analysis of the Role and Path of Green Finance in Controlling Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollution
- The Research on the Impact of Regional Trade Network Relationships on Value Chain Resilience in China’s Service Industry
- Social Support and Suicidal Ideation among Children of Cross-Border Married Couples
- Asymmetrical Monetary Relations and Involuntary Unemployment in a General Equilibrium Model
- Job Crafting among Airport Security: The Role of Organizational Support, Work Engagement and Social Courage
- Does the Adjustment of Industrial Structure Restrain the Income Gap between Urban and Rural Areas
- Optimizing Emergency Logistics Centre Locations: A Multi-Objective Robust Model
- Geopolitical Risks and Stock Market Volatility in the SAARC Region
- Trade Globalization, Overseas Investment, and Tax Revenue Growth in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Can Government Expenditure Improve the Efficiency of Institutional Elderly-Care Service? – Take Wuhan as an Example
- Media Tone and Earnings Management before the Earnings Announcement: Evidence from China
- Review Articles
- Economic Growth in the Age of Ubiquitous Threats: How Global Risks are Reshaping Growth Theory
- Efficiency Measurement in Healthcare: The Foundations, Variables, and Models – A Narrative Literature Review
- Rethinking the Theoretical Foundation of Economics I: The Multilevel Paradigm
- Financial Literacy as Part of Empowerment Education for Later Life: A Spectrum of Perspectives, Challenges and Implications for Individuals, Educators and Policymakers in the Modern Digital Economy
- Special Issue: Economic Implications of Management and Entrepreneurship - Part II
- Ethnic Entrepreneurship: A Qualitative Study on Entrepreneurial Tendency of Meskhetian Turks Living in the USA in the Context of the Interactive Model
- Bridging Brand Parity with Insights Regarding Consumer Behavior
- The Effect of Green Human Resources Management Practices on Corporate Sustainability from the Perspective of Employees
- Special Issue: Shapes of Performance Evaluation in Economics and Management Decision - Part II
- High-Quality Development of Sports Competition Performance Industry in Chengdu-Chongqing Region Based on Performance Evaluation Theory
- Analysis of Multi-Factor Dynamic Coupling and Government Intervention Level for Urbanization in China: Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt
- The Impact of Environmental Regulation on Technological Innovation of Enterprises: Based on Empirical Evidences of the Implementation of Pollution Charges in China
- Environmental Social Responsibility, Local Environmental Protection Strategy, and Corporate Financial Performance – Empirical Evidence from Heavy Pollution Industry
- The Relationship Between Stock Performance and Money Supply Based on VAR Model in the Context of E-commerce
- A Novel Approach for the Assessment of Logistics Performance Index of EU Countries
- The Decision Behaviour Evaluation of Interrelationships among Personality, Transformational Leadership, Leadership Self-Efficacy, and Commitment for E-Commerce Administrative Managers
- Role of Cultural Factors on Entrepreneurship Across the Diverse Economic Stages: Insights from GEM and GLOBE Data
- Performance Evaluation of Economic Relocation Effect for Environmental Non-Governmental Organizations: Evidence from China
- Functional Analysis of English Carriers and Related Resources of Cultural Communication in Internet Media
- The Influences of Multi-Level Environmental Regulations on Firm Performance in China
- Exploring the Ethnic Cultural Integration Path of Immigrant Communities Based on Ethnic Inter-Embedding
- Analysis of a New Model of Economic Growth in Renewable Energy for Green Computing
- An Empirical Examination of Aging’s Ramifications on Large-scale Agriculture: China’s Perspective
- The Impact of Firm Digital Transformation on Environmental, Social, and Governance Performance: Evidence from China
- Accounting Comparability and Labor Productivity: Evidence from China’s A-Share Listed Firms
- An Empirical Study on the Impact of Tariff Reduction on China’s Textile Industry under the Background of RCEP
- Top Executives’ Overseas Background on Corporate Green Innovation Output: The Mediating Role of Risk Preference
- Neutrosophic Inventory Management: A Cost-Effective Approach
- Mechanism Analysis and Response of Digital Financial Inclusion to Labor Economy based on ANN and Contribution Analysis
- Asset Pricing and Portfolio Investment Management Using Machine Learning: Research Trend Analysis Using Scientometrics
- User-centric Smart City Services for People with Disabilities and the Elderly: A UN SDG Framework Approach
- Research on the Problems and Institutional Optimization Strategies of Rural Collective Economic Organization Governance
- The Impact of the Global Minimum Tax Reform on China and Its Countermeasures
- Sustainable Development of Low-Carbon Supply Chain Economy based on the Internet of Things and Environmental Responsibility
- Measurement of Higher Education Competitiveness Level and Regional Disparities in China from the Perspective of Sustainable Development
- Payment Clearing and Regional Economy Development Based on Panel Data of Sichuan Province
- Coordinated Regional Economic Development: A Study of the Relationship Between Regional Policies and Business Performance
- A Novel Perspective on Prioritizing Investment Projects under Future Uncertainty: Integrating Robustness Analysis with the Net Present Value Model
- Research on Measurement of Manufacturing Industry Chain Resilience Based on Index Contribution Model Driven by Digital Economy
- Special Issue: AEEFI 2023
- Portfolio Allocation, Risk Aversion, and Digital Literacy Among the European Elderly
- Exploring the Heterogeneous Impact of Trade Agreements on Trade: Depth Matters
- Import, Productivity, and Export Performances
- Government Expenditure, Education, and Productivity in the European Union: Effects on Economic Growth
- Replication Study
- Carbon Taxes and CO2 Emissions: A Replication of Andersson (American Economic Journal: Economic Policy, 2019)
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Political Turnover and Public Health Provision in Brazilian Municipalities
- Examining the Effects of Trade Liberalisation Using a Gravity Model Approach
- Operating Efficiency in the Capital-Intensive Semiconductor Industry: A Nonparametric Frontier Approach
- Does Health Insurance Boost Subjective Well-being? Examining the Link in China through a National Survey
- An Intelligent Approach for Predicting Stock Market Movements in Emerging Markets Using Optimized Technical Indicators and Neural Networks
- Analysis of the Effect of Digital Financial Inclusion in Promoting Inclusive Growth: Mechanism and Statistical Verification
- Effective Tax Rates and Firm Size under Turnover Tax: Evidence from a Natural Experiment on SMEs
- Re-investigating the Impact of Economic Growth, Energy Consumption, Financial Development, Institutional Quality, and Globalization on Environmental Degradation in OECD Countries
- A Compliance Return Method to Evaluate Different Approaches to Implementing Regulations: The Example of Food Hygiene Standards
- Panel Technical Efficiency of Korean Companies in the Energy Sector based on Digital Capabilities
- Time-varying Investment Dynamics in the USA
- Preferences, Institutions, and Policy Makers: The Case of the New Institutionalization of Science, Technology, and Innovation Governance in Colombia
- The Impact of Geographic Factors on Credit Risk: A Study of Chinese Commercial Banks
- The Heterogeneous Effect and Transmission Paths of Air Pollution on Housing Prices: Evidence from 30 Large- and Medium-Sized Cities in China
- Analysis of Demographic Variables Affecting Digital Citizenship in Turkey
- Green Finance, Environmental Regulations, and Green Technologies in China: Implications for Achieving Green Economic Recovery
- Coupled and Coordinated Development of Economic Growth and Green Sustainability in a Manufacturing Enterprise under the Context of Dual Carbon Goals: Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality
- Revealing the New Nexus in Urban Unemployment Dynamics: The Relationship between Institutional Variables and Long-Term Unemployment in Colombia
- The Roles of the Terms of Trade and the Real Exchange Rate in the Current Account Balance
- Cleaner Production: Analysis of the Role and Path of Green Finance in Controlling Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollution
- The Research on the Impact of Regional Trade Network Relationships on Value Chain Resilience in China’s Service Industry
- Social Support and Suicidal Ideation among Children of Cross-Border Married Couples
- Asymmetrical Monetary Relations and Involuntary Unemployment in a General Equilibrium Model
- Job Crafting among Airport Security: The Role of Organizational Support, Work Engagement and Social Courage
- Does the Adjustment of Industrial Structure Restrain the Income Gap between Urban and Rural Areas
- Optimizing Emergency Logistics Centre Locations: A Multi-Objective Robust Model
- Geopolitical Risks and Stock Market Volatility in the SAARC Region
- Trade Globalization, Overseas Investment, and Tax Revenue Growth in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Can Government Expenditure Improve the Efficiency of Institutional Elderly-Care Service? – Take Wuhan as an Example
- Media Tone and Earnings Management before the Earnings Announcement: Evidence from China
- Review Articles
- Economic Growth in the Age of Ubiquitous Threats: How Global Risks are Reshaping Growth Theory
- Efficiency Measurement in Healthcare: The Foundations, Variables, and Models – A Narrative Literature Review
- Rethinking the Theoretical Foundation of Economics I: The Multilevel Paradigm
- Financial Literacy as Part of Empowerment Education for Later Life: A Spectrum of Perspectives, Challenges and Implications for Individuals, Educators and Policymakers in the Modern Digital Economy
- Special Issue: Economic Implications of Management and Entrepreneurship - Part II
- Ethnic Entrepreneurship: A Qualitative Study on Entrepreneurial Tendency of Meskhetian Turks Living in the USA in the Context of the Interactive Model
- Bridging Brand Parity with Insights Regarding Consumer Behavior
- The Effect of Green Human Resources Management Practices on Corporate Sustainability from the Perspective of Employees
- Special Issue: Shapes of Performance Evaluation in Economics and Management Decision - Part II
- High-Quality Development of Sports Competition Performance Industry in Chengdu-Chongqing Region Based on Performance Evaluation Theory
- Analysis of Multi-Factor Dynamic Coupling and Government Intervention Level for Urbanization in China: Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt
- The Impact of Environmental Regulation on Technological Innovation of Enterprises: Based on Empirical Evidences of the Implementation of Pollution Charges in China
- Environmental Social Responsibility, Local Environmental Protection Strategy, and Corporate Financial Performance – Empirical Evidence from Heavy Pollution Industry
- The Relationship Between Stock Performance and Money Supply Based on VAR Model in the Context of E-commerce
- A Novel Approach for the Assessment of Logistics Performance Index of EU Countries
- The Decision Behaviour Evaluation of Interrelationships among Personality, Transformational Leadership, Leadership Self-Efficacy, and Commitment for E-Commerce Administrative Managers
- Role of Cultural Factors on Entrepreneurship Across the Diverse Economic Stages: Insights from GEM and GLOBE Data
- Performance Evaluation of Economic Relocation Effect for Environmental Non-Governmental Organizations: Evidence from China
- Functional Analysis of English Carriers and Related Resources of Cultural Communication in Internet Media
- The Influences of Multi-Level Environmental Regulations on Firm Performance in China
- Exploring the Ethnic Cultural Integration Path of Immigrant Communities Based on Ethnic Inter-Embedding
- Analysis of a New Model of Economic Growth in Renewable Energy for Green Computing
- An Empirical Examination of Aging’s Ramifications on Large-scale Agriculture: China’s Perspective
- The Impact of Firm Digital Transformation on Environmental, Social, and Governance Performance: Evidence from China
- Accounting Comparability and Labor Productivity: Evidence from China’s A-Share Listed Firms
- An Empirical Study on the Impact of Tariff Reduction on China’s Textile Industry under the Background of RCEP
- Top Executives’ Overseas Background on Corporate Green Innovation Output: The Mediating Role of Risk Preference
- Neutrosophic Inventory Management: A Cost-Effective Approach
- Mechanism Analysis and Response of Digital Financial Inclusion to Labor Economy based on ANN and Contribution Analysis
- Asset Pricing and Portfolio Investment Management Using Machine Learning: Research Trend Analysis Using Scientometrics
- User-centric Smart City Services for People with Disabilities and the Elderly: A UN SDG Framework Approach
- Research on the Problems and Institutional Optimization Strategies of Rural Collective Economic Organization Governance
- The Impact of the Global Minimum Tax Reform on China and Its Countermeasures
- Sustainable Development of Low-Carbon Supply Chain Economy based on the Internet of Things and Environmental Responsibility
- Measurement of Higher Education Competitiveness Level and Regional Disparities in China from the Perspective of Sustainable Development
- Payment Clearing and Regional Economy Development Based on Panel Data of Sichuan Province
- Coordinated Regional Economic Development: A Study of the Relationship Between Regional Policies and Business Performance
- A Novel Perspective on Prioritizing Investment Projects under Future Uncertainty: Integrating Robustness Analysis with the Net Present Value Model
- Research on Measurement of Manufacturing Industry Chain Resilience Based on Index Contribution Model Driven by Digital Economy
- Special Issue: AEEFI 2023
- Portfolio Allocation, Risk Aversion, and Digital Literacy Among the European Elderly
- Exploring the Heterogeneous Impact of Trade Agreements on Trade: Depth Matters
- Import, Productivity, and Export Performances
- Government Expenditure, Education, and Productivity in the European Union: Effects on Economic Growth
- Replication Study
- Carbon Taxes and CO2 Emissions: A Replication of Andersson (American Economic Journal: Economic Policy, 2019)

