Abstract
In the Internet intelligent teaching platform, students’ demand for English cultural content is increasingly obvious. To help students quickly locate the overall content of resources in online autonomous learning, this study constructs a video annotation model for online teaching. This method classifies text by designing an optimized Bidirectional Encoder Representation from the Transformers model and designs a Text Rank keyword extraction model that integrates external knowledge and semantic feature weights. The extraction of knowledge points contained in audio and video resources can be realized. In the experimental data set, a relatively complete video content summary could be obtained by combining the first three sentences with the last two sentences. The F1 value of the classification model was up to 91.3%. In addition, the BERT-T model proposed in this article had the best effect on the experiment. Compared with the original BERT model, the macro-F1 was 0.8% higher and 0.5% higher than the Ro BERTA model. In the keyword extraction experiment, B-Text Rank was 2.19 and 2.85% higher than the traditional Text Rank in the two datasets. The experiment shows that the BERT-Text Rank network resource annotation model has excellent application performance in English online autonomous teaching and could guide students to learn.
1 Introduction
Online English education has brought diverse learning methods to teachers and students. In the past, students and teachers could only obtain paper-based learning materials by purchasing books. Now, the emergence of various learning platforms enables teachers and students to obtain various types of learning resources such as video, audio, pictures, PowerPoint for free, creating a good environment for students’ independent learning. The way of cultural teaching is therefore increasingly important on the Internet platform. However, the rapid expansion of digital education resources has not benefited everyone (Albiladi & Alshareef, 2019). Various schools and platforms are rich in teaching resources, but the storage method is relatively backward, and there is a lack of scientific and efficient management of massive resources in the digital teaching resource database. This makes it difficult for users to retrieve and use knowledge resources. Therefore, this article proposes an English network resource annotation model based on Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Transformers (BERT) Text Rank. This method converts video files into text through speech recognition and uses text classification method to classify resources. At the same time, a Text Rank keyword extraction model integrating external knowledge and semantic feature weights is designed. This model could realize the extraction of knowledge points contained in audio and video resources and use the classification label and keyword extraction results together as the label of audio and video resources. The significance of this study lies in the extension of the marking model to the marking methods of English teaching video resources. This method also solves the problem of English teaching and education informatization, and has important practical significance for realizing personalized and cultural content education. The contribution of the research is to help students achieve autonomous learning of English cultural knowledge and skills application on the online teaching platform.
2 Literature Review
Turan and Akdag-Cimen (2020) combined flipped classroom teaching methods with computer statistics. They analyzed the data in the database and found that the mixed and quantitative methods were the most widely used in English teaching. In the context of English blended learning, Richard Jegadeesan (2021) discussed the strategies of combining Internet technology factors with teachers. For example, the strategy content included applications such as increasing the richness of network knowledge teaching in the intelligent communication system, virtual classroom library of mobile devices, etc. The ultimate goal of the strategy was to improve students’ learning enthusiasm. Bai and Guo (2021) conducted various experiments on English teaching among primary school students in Hong Kong, mainly exploring the relationship between students’ interests, self-efficacy, and other psychological factors and their motivation for English writing. Their results showed that the growth mentality had the strongest and most significant correlation with all students’ motivation for English writing.
Wenyan (2021) constructed a face recognition method suitable for online teaching through the BERT model. This method helped teachers accurately identify students’ learning state in the application, thus optimizing the classroom strategy of online teaching. Alzamil (2022) analyzed the possibility of online classrooms replacing traditional teaching methods in English teaching. His experimental results showed that traditional teaching methods are more effective than online learning in teaching sentences, so traditional offline learning is still needed in current English teaching. Xu and Zhu (2023) used computer courses as an example to construct a new computer teaching model based on deep learning theory and constructed an intelligent testing database using the BERT model. The experimental results showed that this method improved students’ learning enthusiasm, problem-solving ability, and practical ability. Wulff et al. (2023) used a pre-trained language BERT model to classify written reflection fragments of pre-service physics teachers based on the elements of the reflection support model. The experimental results showed that BERT could improve the performance of language-related tasks in educational contexts such as classification.
To sum up, although all countries have found the importance of oral training in English teaching, the solutions that scholars seek remain in the aspects of teachers’ influence and students’ psychology. There are few views on the combination of English culture teaching and skill teaching. In English online teaching, technology development mostly focuses on the recognition of students’ state of attention and classroom quality in passive courses but ignores students’ ability of autonomous learning. Therefore, this study proposes an intelligent labeling model of online teaching resources from the perspective of autonomous learning of English culture.
3 Methodology
3.1 Explicit and Invisible Strategies of English Culture Teaching in the Network Platform
Since the reform and opening up, China’s English education has been in the process of development. It has made efforts to meet international standards. However, students and teachers pay less attention to communicative teaching in educational activities. In addition, students are also in a social environment where English is not often used. The influence of these factors has led to the low oral English ability of Chinese students (Kumayas & Lengkoan, 2023). Besides, the cultural knowledge in the current English textbooks of all stages in China is dominated by English-speaking countries, ignoring the communicative role of cross-cultural teaching. This leads to the insufficient ability of Chinese students to use English to express their local environment and culture. Therefore, students should be aware of the differences between Chinese and Western cultures and have a more thorough understanding when reading first-hand English materials. Mastering communication etiquette and taboos in life and work can effectively improve the ability of cross-cultural communication. The cultural aspect of English teaching usually includes the basic theories and knowledge of the history, politics, economy, diplomacy, social culture, literature, and other aspects of British and American countries. In cultural teaching, students can better accept the skills and knowledge of English listening, speaking, reading, writing, and translating. Combining technical knowledge and cultural content, the ultimate goal of English teaching is to cultivate high-quality, high-level students with the ability to engage in translation, research, teaching, and management work. The contents of English skills application teaching and cultural knowledge teaching are shown in Figure 1.
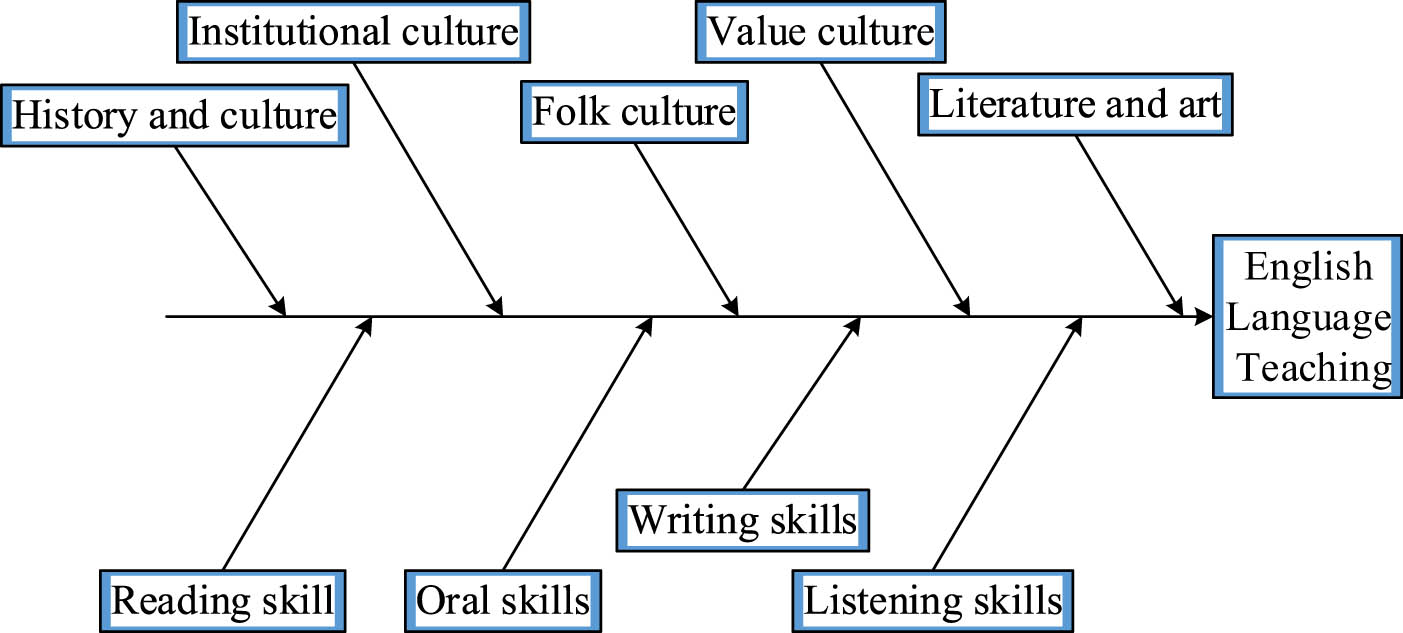
The content of English skill application teaching and cultural knowledge teaching.
As shown in Figure 1, students should be able to understand some Chinese and foreign cultures and ideas in teaching and improve their humanistic, artistic, and aesthetic qualities. To cultivate and improve the cultural quality of English majors, students should establish correct social, historical, and life values. From the dominant perspective, first of all, English education shows a trend of increasing knowledge application skills in the distribution of courses, while cultural and literature courses decrease. Second, English skill learning courses give too much attention to grammatical structure analysis, which makes the content difficult and reduces the interaction between teachers and students. This also led to an inactive learning atmosphere in the classroom. Finally, there is a lack of hierarchy in English teaching. Students have insufficient time to sort out and understand the teaching content. If culture is divided into utensil culture, institutional culture, and conceptual culture, the English culture teaching in China mostly stays on utensil and institutional culture. Its teaching rarely involves the content of the third stage. From the perspective of invisibility, first, it is difficult to give full play to students’ advantages of online autonomous learning. Second, student-oriented English culture teaching activities show the characteristics of shallow content, simple form, and passive acceptance by students. Finally, students in autonomous learning have few opportunities to practice. The difficulties faced by English culture teaching at the present stage are shown in Figure 2.

Difficulties in English culture teaching at the present stage.
With the rapid development and popularization of the Internet in the new century, podcasts, blogs, Massive Open Online Courses (MOOC), etc., provide new channels for digital and mobile English learning. In educational text data, there are a large number of academic terms that can reflect the current research content and theme of the text. These terms can usually be used as keywords to summarize an article. The keyword extraction method for word graphs is based on word nodes, calculating word weights to generate keywords. Compared to package and topic models, extracting keywords from the perspective of words is better. Therefore, this article chooses the text ranking graph model as the basic model for keyword extraction. With the rise of pre-trained language models, many researchers in the field of keyword extraction have combined pre-trained language modeling with unsupervised keyword extraction models, which not only ensures the performance of keyword extraction but also enriches semantic information, to some extent solving the problem of low accuracy in traditional unsupervised keyword extraction models. This article proposes an improved text ranking keyword extraction model based on pre-trained language models, aiming to improve the accuracy of educational text keyword extraction and enhance the efficiency of extraction tasks.
This also brings new opportunities for English learning. Relying on the gradually developing network technology, teaching resources on the network show the characteristics of wide richness and high convenience, which play an important role in English teaching. Internet English teaching supplements the cultural content that students learn in the classroom and can ensure the complete transmission of teaching information. Second, there are many forms of network resources, such as text, voice, video, and image. The presentation of network resources is more vivid and diverse. Knowledge is more easily accepted by students in this way. Teachers can arrange the teaching contents in a more orderly way by relying on the network platform to improve the coherence and systematization of English teaching. Finally, the network platform can strengthen the interactivity of English teaching and activate the classroom atmosphere.
3.2 Application of the BERT Model in the Standards of English Online Teaching Resources
This method classifies the text of audio and video resources by designing an optimized BERT model and designs a Text Rank keyword extraction model that integrates external knowledge and semantic feature weights to extract the knowledge points contained in the audio and video resources. Finally, the classification label and keyword extraction result are used together as the label of the audio and video resources.
Despite the growing importance of network resources for English culture teaching, the organization of the teaching resource database is still in a low efficiency and slow query application mode. Knowledge atlas has become a hot spot to improve the structure of English teaching. Representing resource content information through tags is the basis of building a knowledge map. This research will use the method of deep learning to build a label-generation model of English online teaching resources. The process of generating resource annotations from this model is shown in Figure 3.
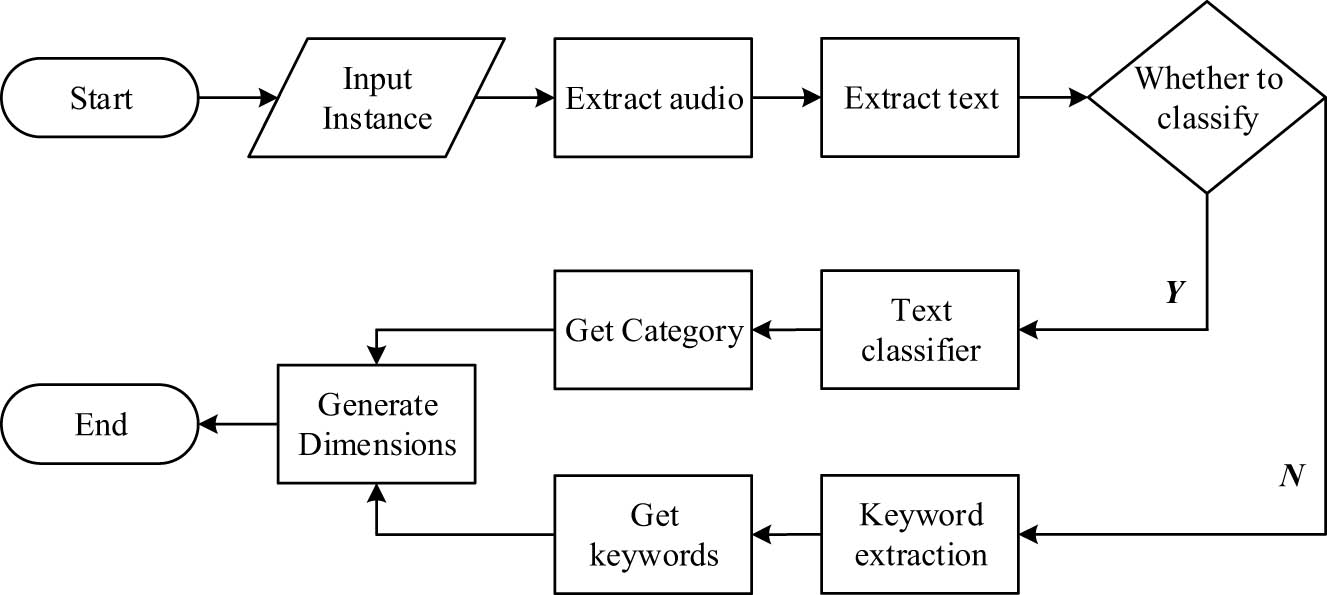
Model flow of tagging generation of English teaching network resources.
Figure 3 shows that the educational resource annotation model built in this study mainly relies on two tasks: keyword extraction and classification, which are completed by Text Rank and BERT models, respectively. BERT is a pre-training language model for two-way feature representation, which can simultaneously obtain the context feature representation of text. The core of BERT is the transformer structure. The bidirectional transformer encoder is composed of multiple layers. The characteristics of the basic transformer encoder enable BERT to better learn the context information in text data. The bidirectional network structure ensures that BERT can mine more semantic information. The structure of the transformer is shown in Figure 4.

Transformer structure.
As shown in Figure 4, the transformer encoder is composed of a multi-head attention mechanism (MHAM) and a fully connected feed-forward network (FCFFN). Each layer has a residual connection and normalization layer. Assuming that the input of each sub-layer is x, the output of the sub-layer is expressed as equation (1)
The MHAM model is composed of multiple scaled dot product attention (SDPA) models, and its mathematical expression is shown in equation (2)
In equation (2), the input of attention is queries (
First, a linear mapping is performed for the matrix with input dimension
To apply the BERT model to video resource annotation, it is necessary to preprocess the teaching videos first. After converting the audio of the video into text data, this study used the Chardet tool to detect the text data format and unified the text data into UTF-8 encoding. After text preprocessing, text vectors are extracted from the BRT model. If the word vector matrix is used as input to the model, the relationship between the original text sentence and the vector matrix is expressed as follows (5):
where
3.3 Research on the Model of Educational Resources Labeling in English Online Media
To achieve the key word extraction of the tagging model of English online teaching resources, the Text Rank model used in this study is essentially a weighted undirected graph model. It is assumed that any sentence in the sentence set
In equation (6),
In equation (7),
In equation (8),
The formula after improving the weight transfer matrix is equation (10):
After the probability transfer matrix is obtained, the Text Rank value of the word node can be finally calculated, as shown in equation (11):
Finally, when the research and construction of the English teaching network resource labeling method is applied to the online teaching platform, the relationship between administrators, teachers, and students and the system functions are shown in Figure 5.

Application scenario of resource annotation model in online teaching platform.
In Figure 5, the model built by the research takes into account the actual needs of teaching tasks. The design of educational video resource marking systems can provide users with convenient educational video annotation, result display, data storage, and other services. Thus, various personalized online teaching platforms can make better use of educational video data. The educational video resource tagging model includes module design and function construction, including data preprocessing, text classification, keyword extraction, and result display functions.
4 Results
4.1 BERT Classification Model Experiment Based on Network Education Resources
To test the constructed annotation model of English teaching resources, the research took all English course teaching videos in the online teaching resources platform of a university as raw data. The audio in the video was extracted and stored separately. The experiment used the format factory audio and video conversion tool to save the audio track as a wav file. Intelligent speech recognition service was used to convert teachers’ teaching content into text data. The model parameters of the experiment are shown in Table 1.
Model parameters of the experiment
| Project | Parameter | Parameter name | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-training covering method | Whole-word covering | Max_seq_len | 510 |
| Model type | Base | Batch_size | 64 |
| Pre-training word vector | 5.4B | Learning_rate | 5 × 10−5 |
| Optimizer | LAMB | Num_epoch | 15 |
| Cover vocabulary | 11,045 | Num_labels | — |
In the experiment, the structure of the BERT classification model was composed of a 12-layer bidirectional transformer decoder. Its hidden layer dimension was 768 with 12 attention mechanisms, and the overall parameter quantity was about 110 M. The maximum length of the text sentence was 510 words, and the learning rate was 5 × 10−5. The number of samples for each batch during training was 64. To verify the effectiveness of the BERT classification model in English teaching network resources, that experiment first sets up the classification performance of the model in different teaching text interceptions. Since the length of text in the teaching video resources was generally more than 510 words, the study adopted three methods to obtain text data of different lengths. They were the first segment interception method, the first and last combination interception method, and the direct interception method. The macro precision of the classification model under different interception methods is shown in Table 2.
Macro precision of classification model under different interception methods
| Data interception method | Macro-P (%) | Macro-R (%) | Macro-F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Five sentences in the beginning | 90.4 | 89.7 | 90.1 |
| First 4 + last 1 | 90.6 | 90.4 | 90.5 |
| First 3 + last 2 | 91.4 | 91.1 | 91.3 |
| First 2 + last 3 | 91.0 | 90.6 | 90.8 |
| First 1 + last 4 | 90.3 | 89.5 | 89.9 |
| The first 510 characters | 90.5 | 90.1 | 90.3 |
| The last 510 characters | 90.4 | 90 | 90.2 |
Macro-P, Macro-R, and Macro-F1 in the table represented the precision rate, recall rate, and F1 value of performance indicators. The data in Table 2 showed that under the same model, different data interception methods directly affected the final effect of the model. From the two results of the direct interception method, both the beginning and the end of the document contained information that could summarize the document. The interception method that combined the first three sentences and the last two sentences performed better, reaching a macro-F1 value of 91.3%. Meanwhile, its precision and recall rates were 91.4 and 91.1%, respectively, which were also higher than other data interceptions. In summary, the article believed that in the text data of English education in a university, most of the course content was contained in the teacher’s opening remarks. At the end of the course, the teacher would also review and summarize this lesson. The course content could be highly summarized by combining the first three sentences and the last two sentences. The number of text characters obtained varied from the original article, ranging from 200 to 350 words. After the experiment of text interception strategy, this study compared the performance of different classification models.
Figure 6 shows that the classification results of the Fast Text model were only second to those of Text convolutional neural network (CNN) and BERT series models. Its F1 value was 87.8%. The F1 value of Text CNN was only 0.5% different from the original BERT model. The long short-term memory (LSTM) model had the worst performance. The F1 value of Binary LSTM was 1.4% higher than the original LSTM model but still 4.1% lower than the original BERT model. The BERT-T model proposed in the article had the best effect in the experiment, with the macro-F1 reaching 91.2%. It was 0.8% higher than the macro-F1 of the original BERT model and 0.5% higher than the macro-F1 of the Ro BERTA model. The reason was that the CNN structure had excellent ability in local information extraction, which could more effectively extract the information in the BERT output word vector. In order to highlight the accuracy of the BERT-Text Rank model in video text classification and recognition, 50 data samples were randomly selected from the university course text data set to compare the classification accuracy of traditional classification methods and the BERT-Text Rank model studied, as shown in Figure 7.

Performance comparison of different classification models.

Comparison of classification accuracy between traditional clustering algorithm and BERT-Text Rank model studied.
The traditional clustering algorithm in Figure 7 was a single K-means algorithm, with computer, physics, history, and others numbered 1–4. From Figure 7, it can be seen that out of 50 test samples, the traditional method made 16 judgments with a recognition accuracy of only 68%, while the BERT-Text Rank model made only two judgments with an accuracy of 96%. The data showed that the BERT-Text Rank model had higher accuracy in determining the category of video text samples.
4.2 B-Text Rank Keyword Extraction Application Experiment of Online Education Resources
This research took the Wiley InterScience (WIS) database and the English literature data of a university as the experimental objects and validated the semantic weighted keyword extraction model. The WIS database contained social science and natural science journals in English. This experiment first compared the B-Text Rank keyword extraction model built in the study with term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF), Yet Another Keyword Extractor (YAKE), the original Text Rank, and EmbedRank models. Table 3 shows the comparison of macro precision values of 3, 5, and 7 keywords extracted from two data sets by different models.
Macro precision values of 3, 5, and 7 keywords extracted from two data sets by different models
| Macro precision | College English Literature Database | Willey science database | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | TOP3 (%) | TOP5 (%) | TOP7 (%) | Model | TOP3 (%) | TOP5 (%) | TOP7 (%) | |
| Macro-P | TF-IDF | 23.60 | 20.30 | 16.70 | TF-IDF | 24.21 | 20.68 | 15.46 |
| YAKE | 23.54 | 21.06 | 16.90 | YAKE | 23.71 | 20.36 | 15.31 | |
| Text Rank | 24.77 | 21.32 | 18.36 | Text Rank | 24.43 | 21.13 | 16.30 | |
| Embed Rank | 23.78 | 19.63 | 15.34 | Embed Rank | 23.84 | 20.45 | 15.73 | |
| B-Text Rank | 25.61 | 21.77 | 18.44 | B-Text Rank | 25.11 | 21.30 | 16.94 | |
| Macro-R | TF-IDF | 23.60 | 20.30 | 16.70 | TF-IDF | 24.21 | 20.68 | 15.46 |
| YAKE | 23.54 | 21.06 | 16.90 | YAKE | 23.71 | 20.36 | 15.31 | |
| Text Rank | 24.77 | 21.32 | 18.36 | Text Rank | 24.43 | 21.13 | 16.30 | |
| Embed Rank | 23.78 | 19.63 | 15.34 | Embed Rank | 23.84 | 20.45 | 15.73 | |
| B-Text Rank | 25.61 | 21.77 | 18.44 | B-Text Rank | 25.11 | 21.30 | 16.94 | |
The comparison of macro recall rate values in Table 3 showed that the more keywords extracted, the greater the value of each model. In the two datasets, the keyword extraction method with external knowledge weight proposed in this article was superior to other baseline models in obtaining the macro-R value. When the number of keywords extracted was 7, the B-Text Rank model proposed in this article was 0.47% higher than the original Text Rank model. From the comparison results of macro precision in the table, it could be found that the keyword extraction method proposed in this article with external knowledge weights on the two datasets had macro P values of 25.61, 21.77, and 18.44% in the TOP3, TOP5, and TOP7 cases, respectively, which were better than other baseline models. When the number of keyword extractions was set to 3, the Text Rank model with external knowledge weight proposed was 0.84% higher than the original model. Finally, the F1 value of different algorithms is shown in Figure 8.
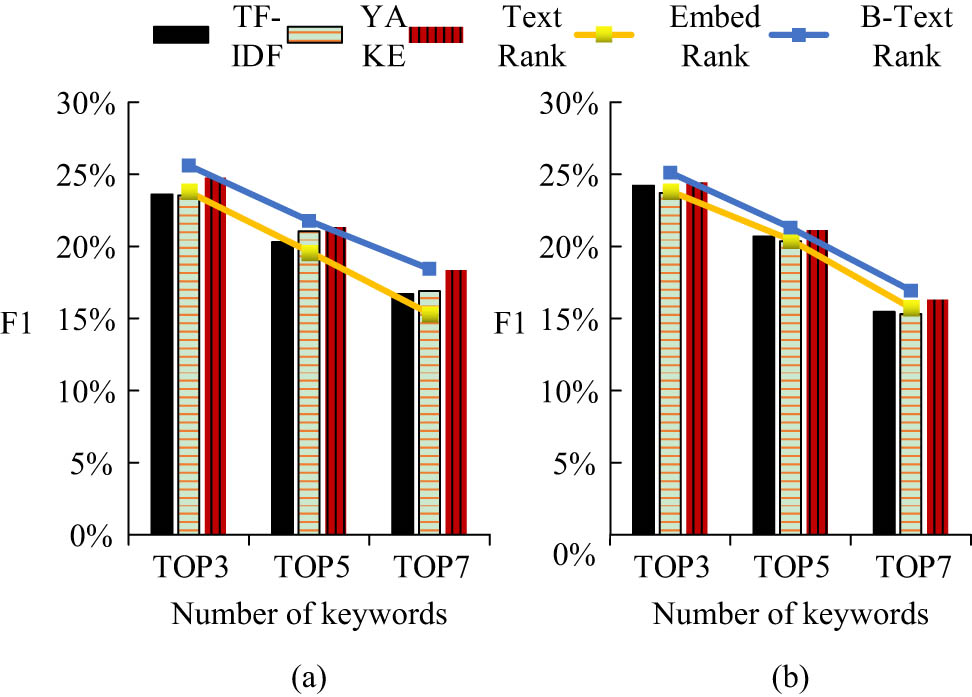
F1 value of different algorithms. (a) College English literature database and (b) Wiley science database.
The two datasets in Figure 8 showed that the keyword extraction method with external knowledge weights was better than other baseline models. When five keywords were selected, the B-Text Rank model was 0.56 and 0.69% higher than the TF-IDF and YAKE based on statistical methods and 0.19% higher than the original Text Rank model. This group of experiments set up two control groups to verify the feasibility and efficiency of the interception method proposed in keyword extraction. The setting purpose of control group 1 was to verify the feasibility and effectiveness of the text rank model integrating semantic weight. Control group 2 was to verify the impact of data interception methods on the keyword extraction process. The specific results are shown in Table 4.
Macro-F1 of models in different control groups on two data sets
| Data set | Groups | Model | TOP3 (%) | TOP5 (%) | TOP7 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| College English Literature Database | Control group 1 | TF-IDF | 19.29 | 20.51 | 19.94 |
| YAKE | 19.14 | 20.85 | 20.01 | ||
| Text Rank | 20.28 | 21.39 | 21.17 | ||
| Embed Rank | 19.08 | 19.87 | 18.71 | ||
| Control group 2 | TF-IDF | 19.70 | 20.56 | 19.79 | |
| YAKE | 19.53 | 20.99 | 19.97 | ||
| Text Rank | 20.58 | 20.95 | 20.65 | ||
| Embed Rank | 19.76 | 20.69 | 18.95 | ||
| W2V-Text Rank | 20.99 | 21.97 | 20.69 | ||
| ELMO-Text Rank | 21.75 | 23.58 | 21.68 | ||
| Experimental group | B-Text Rank | 21.81 | 23.48 | 21.56 | |
| Willey science database | Control group 1 | TF-IDF | 19.58 | 20.86 | 18.99 |
| YAKE | 19.48 | 20.73 | 18.93 | ||
| Text Rank | 19.92 | 21.23 | 19.78 | ||
| Embed Rank | 19.24 | 20.66 | 19.12 | ||
| Control group 2 | TF-IDF | 19.71 | 20.30 | 19.21 | |
| YAKE | 19.85 | 20.72 | 19.64 | ||
| Text Rank | 20.38 | 21.00 | 20.27 | ||
| Embed Rank | 20.18 | 20.76 | 19.81 | ||
| W2V-Text Rank | 21.46 | 21.99 | 20.93 | ||
| ELMO-Text Rank | 22.24 | 23.81 | 22.11 | ||
| Experimental group | B-Text Rank | 22.60 | 24.08 | 22.29 |
In Table 4, the performance of the B-Text Rank was improved compared with other baseline models in terms of macro-F1 value indicators. In the experiment of control group 1, the B-Text Rank was 2.19 and 2.85% higher than the traditional Text Rank in the two models. This showed that the fusion of semantic weights was feasible and improved the performance of the model. In control group experiment 2, this study showed the best performance in extracting three keywords, with macro-F1 values of 21.81 and 22.6% in the two datasets. In conclusion, B-Text Rank performed well under the comprehensive consideration of model extraction performance and efficiency. At last, the experiment applied the B-Text Rank resource annotation model proposed in the study to the MOOC forum management of the university. It also analyzed satisfaction evaluation from the feedback of the teacher administrator. Details are shown in Figure 9.

MOOC administrator’s satisfaction evaluation on traditional classification methods and optimized management methods.
The new MOOC intelligent management labeling method fed back its satisfaction evaluation through the administrator’s scoring behavior. The average satisfaction of teachers’ overall service was 84.95%, higher than 5.68% in the old system. It meant that the staff generally recognized the effect of model classification on the classification of comments in MOOC forums. In terms of teaching effect, the satisfaction of teachers in the new system was 82.64 ± 1.86%, while that in the old system was 80.41 ± 0.79%. In terms of teaching feedback and communication effect, teachers’ average satisfaction increased by 11.6 and 7.9%. In terms of fault resolution, the satisfaction of teachers in the new system was 84.95 ± 1.34%, and that in the old system was 79.27 ± 1.83%.
5 Conclusion
To realize the effective marking of educational video resources on the video resource platform, the BERT-Text Rank video annotation model is proposed and applied in the English culture teaching and skill teaching. In the classification technology of video teaching resources, experiments on text interception methods and different classification models are studied. The conclusion is that the extraction method of the first three sentences + the last two sentences could better summarize the overall content of the English teaching video. In the comparison of classification models, the BERT-T model showed the best effect in the experiment. Macro-F1 reached 91.2%, which was 0.8% higher than that of the original BERT model and 0.5% higher than that of the Ro BERTA model. In addition, the performance of different extraction models was compared in the experimental video keyword extraction. When the number of keywords extracted was 7, the B-Text Rank model was 0.47% higher than the original Text Rank model. The comparison results of macro precision in the table found that the macro-P value of the keyword extraction method with external knowledge weight on the two datasets is better than other baseline models. When the number of keyword extractions was set to three, the Text Rank model with external knowledge weight was 0.84% higher than the original model. The deficiency of this study is that the B-Text Rank method is only applicable to English online teaching video resources. It cannot analyze audio files. As a result, a computer vision model and multi-modal educational video resource labeling model can be constructed to process such videos in subsequent research.
-
Funding information: The author states no funding involved.
-
Conflict of interest: The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The data used to support the findings of the research are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
-
Article note: As part of the open assessment, reviews and the original submission are available as supplementary files on our website.
References
Albiladi, W. S., & Alshareef, K. K. (2019). Blended learning in English teaching and learning: A review of the current literature. Journal of Language Teaching and Research, 10(2), 232–238.10.17507/jltr.1002.03Search in Google Scholar
Alzamil, A. (2022). L2 learning of English conditionals: Online versus traditional classroom teaching. Sino-US English Teaching, 19(3), 79–87.10.17265/1539-8072/2022.03.001Search in Google Scholar
Bai, B., & Guo, W. (2021). Motivation and self-regulated strategy use: Relationships to primary school students’ English writing in Hong Kong. Language Teaching Research, 25(3), 378–399.10.1177/1362168819859921Search in Google Scholar
Guo, W., Liu, X., Wang, S., Gao, H., Sankar, A., Yang, Z., & Agarwal, D. (2020). Detext: A deep text ranking framework with BERT. Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management (pp. 2509–2516).10.1145/3340531.3412699Search in Google Scholar
Jiao, X., Chang, H., Yin, Y., Shang, L., Jian, X., Chen, X., & Liu, Q. (2023). SKDBERT: Compressing BERT via stochastic knowledge distillation. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 37(6), 7414–7422.10.1609/aaai.v37i6.25902Search in Google Scholar
Kumayas, T., & Lengkoan, F. (2023). The challenges of teaching grammar at the university level: Learning From the experience of English lecturer. Journal of English Culture, Language, Literature and Education, 11(1), 98–105.10.53682/eclue.v11i1.6058Search in Google Scholar
Richard Jegadeesan, P. (2021). English language teaching and learning with technology: A study. International Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology, 11(2), 131–134.Search in Google Scholar
Turan, Z., & Akdag-Cimen, B. (2020). Flipped classroom in English language teaching: A systematic review. Computer Assisted Language Learning, 33(5–6), 590–606.10.1080/09588221.2019.1584117Search in Google Scholar
Wenyan, N. (2021). Construction of network open teaching platform of analytical chemistry based on facial recognition and artificial intelligence. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems: Applications in Engineering and Technology, 40(4), 7435–7445.10.3233/JIFS-189566Search in Google Scholar
Wulff, P., Mientus, L., & Nowak, A. (2023). Utilizing a pretrained language model (BERT) to classify preservice physics teachers’ written reflections. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 33(3), 439–466.10.1007/s40593-022-00290-6Search in Google Scholar
Xu, Z., & Zhu, P. (2023). Using BERT-based textual analysis to design a smarter classroom mode for computer teaching in higher education institutions. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 18(19), 114–127.10.3991/ijet.v18i19.42483Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Political Turnover and Public Health Provision in Brazilian Municipalities
- Examining the Effects of Trade Liberalisation Using a Gravity Model Approach
- Operating Efficiency in the Capital-Intensive Semiconductor Industry: A Nonparametric Frontier Approach
- Does Health Insurance Boost Subjective Well-being? Examining the Link in China through a National Survey
- An Intelligent Approach for Predicting Stock Market Movements in Emerging Markets Using Optimized Technical Indicators and Neural Networks
- Analysis of the Effect of Digital Financial Inclusion in Promoting Inclusive Growth: Mechanism and Statistical Verification
- Effective Tax Rates and Firm Size under Turnover Tax: Evidence from a Natural Experiment on SMEs
- Re-investigating the Impact of Economic Growth, Energy Consumption, Financial Development, Institutional Quality, and Globalization on Environmental Degradation in OECD Countries
- A Compliance Return Method to Evaluate Different Approaches to Implementing Regulations: The Example of Food Hygiene Standards
- Panel Technical Efficiency of Korean Companies in the Energy Sector based on Digital Capabilities
- Time-varying Investment Dynamics in the USA
- Preferences, Institutions, and Policy Makers: The Case of the New Institutionalization of Science, Technology, and Innovation Governance in Colombia
- The Impact of Geographic Factors on Credit Risk: A Study of Chinese Commercial Banks
- The Heterogeneous Effect and Transmission Paths of Air Pollution on Housing Prices: Evidence from 30 Large- and Medium-Sized Cities in China
- Analysis of Demographic Variables Affecting Digital Citizenship in Turkey
- Green Finance, Environmental Regulations, and Green Technologies in China: Implications for Achieving Green Economic Recovery
- Coupled and Coordinated Development of Economic Growth and Green Sustainability in a Manufacturing Enterprise under the Context of Dual Carbon Goals: Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality
- Revealing the New Nexus in Urban Unemployment Dynamics: The Relationship between Institutional Variables and Long-Term Unemployment in Colombia
- The Roles of the Terms of Trade and the Real Exchange Rate in the Current Account Balance
- Cleaner Production: Analysis of the Role and Path of Green Finance in Controlling Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollution
- The Research on the Impact of Regional Trade Network Relationships on Value Chain Resilience in China’s Service Industry
- Social Support and Suicidal Ideation among Children of Cross-Border Married Couples
- Asymmetrical Monetary Relations and Involuntary Unemployment in a General Equilibrium Model
- Job Crafting among Airport Security: The Role of Organizational Support, Work Engagement and Social Courage
- Does the Adjustment of Industrial Structure Restrain the Income Gap between Urban and Rural Areas
- Optimizing Emergency Logistics Centre Locations: A Multi-Objective Robust Model
- Geopolitical Risks and Stock Market Volatility in the SAARC Region
- Trade Globalization, Overseas Investment, and Tax Revenue Growth in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Can Government Expenditure Improve the Efficiency of Institutional Elderly-Care Service? – Take Wuhan as an Example
- Media Tone and Earnings Management before the Earnings Announcement: Evidence from China
- Review Articles
- Economic Growth in the Age of Ubiquitous Threats: How Global Risks are Reshaping Growth Theory
- Efficiency Measurement in Healthcare: The Foundations, Variables, and Models – A Narrative Literature Review
- Rethinking the Theoretical Foundation of Economics I: The Multilevel Paradigm
- Financial Literacy as Part of Empowerment Education for Later Life: A Spectrum of Perspectives, Challenges and Implications for Individuals, Educators and Policymakers in the Modern Digital Economy
- Special Issue: Economic Implications of Management and Entrepreneurship - Part II
- Ethnic Entrepreneurship: A Qualitative Study on Entrepreneurial Tendency of Meskhetian Turks Living in the USA in the Context of the Interactive Model
- Bridging Brand Parity with Insights Regarding Consumer Behavior
- The Effect of Green Human Resources Management Practices on Corporate Sustainability from the Perspective of Employees
- Special Issue: Shapes of Performance Evaluation in Economics and Management Decision - Part II
- High-Quality Development of Sports Competition Performance Industry in Chengdu-Chongqing Region Based on Performance Evaluation Theory
- Analysis of Multi-Factor Dynamic Coupling and Government Intervention Level for Urbanization in China: Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt
- The Impact of Environmental Regulation on Technological Innovation of Enterprises: Based on Empirical Evidences of the Implementation of Pollution Charges in China
- Environmental Social Responsibility, Local Environmental Protection Strategy, and Corporate Financial Performance – Empirical Evidence from Heavy Pollution Industry
- The Relationship Between Stock Performance and Money Supply Based on VAR Model in the Context of E-commerce
- A Novel Approach for the Assessment of Logistics Performance Index of EU Countries
- The Decision Behaviour Evaluation of Interrelationships among Personality, Transformational Leadership, Leadership Self-Efficacy, and Commitment for E-Commerce Administrative Managers
- Role of Cultural Factors on Entrepreneurship Across the Diverse Economic Stages: Insights from GEM and GLOBE Data
- Performance Evaluation of Economic Relocation Effect for Environmental Non-Governmental Organizations: Evidence from China
- Functional Analysis of English Carriers and Related Resources of Cultural Communication in Internet Media
- The Influences of Multi-Level Environmental Regulations on Firm Performance in China
- Exploring the Ethnic Cultural Integration Path of Immigrant Communities Based on Ethnic Inter-Embedding
- Analysis of a New Model of Economic Growth in Renewable Energy for Green Computing
- An Empirical Examination of Aging’s Ramifications on Large-scale Agriculture: China’s Perspective
- The Impact of Firm Digital Transformation on Environmental, Social, and Governance Performance: Evidence from China
- Accounting Comparability and Labor Productivity: Evidence from China’s A-Share Listed Firms
- An Empirical Study on the Impact of Tariff Reduction on China’s Textile Industry under the Background of RCEP
- Top Executives’ Overseas Background on Corporate Green Innovation Output: The Mediating Role of Risk Preference
- Neutrosophic Inventory Management: A Cost-Effective Approach
- Mechanism Analysis and Response of Digital Financial Inclusion to Labor Economy based on ANN and Contribution Analysis
- Asset Pricing and Portfolio Investment Management Using Machine Learning: Research Trend Analysis Using Scientometrics
- User-centric Smart City Services for People with Disabilities and the Elderly: A UN SDG Framework Approach
- Research on the Problems and Institutional Optimization Strategies of Rural Collective Economic Organization Governance
- The Impact of the Global Minimum Tax Reform on China and Its Countermeasures
- Sustainable Development of Low-Carbon Supply Chain Economy based on the Internet of Things and Environmental Responsibility
- Measurement of Higher Education Competitiveness Level and Regional Disparities in China from the Perspective of Sustainable Development
- Payment Clearing and Regional Economy Development Based on Panel Data of Sichuan Province
- Coordinated Regional Economic Development: A Study of the Relationship Between Regional Policies and Business Performance
- A Novel Perspective on Prioritizing Investment Projects under Future Uncertainty: Integrating Robustness Analysis with the Net Present Value Model
- Research on Measurement of Manufacturing Industry Chain Resilience Based on Index Contribution Model Driven by Digital Economy
- Special Issue: AEEFI 2023
- Portfolio Allocation, Risk Aversion, and Digital Literacy Among the European Elderly
- Exploring the Heterogeneous Impact of Trade Agreements on Trade: Depth Matters
- Import, Productivity, and Export Performances
- Government Expenditure, Education, and Productivity in the European Union: Effects on Economic Growth
- Replication Study
- Carbon Taxes and CO2 Emissions: A Replication of Andersson (American Economic Journal: Economic Policy, 2019)
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Political Turnover and Public Health Provision in Brazilian Municipalities
- Examining the Effects of Trade Liberalisation Using a Gravity Model Approach
- Operating Efficiency in the Capital-Intensive Semiconductor Industry: A Nonparametric Frontier Approach
- Does Health Insurance Boost Subjective Well-being? Examining the Link in China through a National Survey
- An Intelligent Approach for Predicting Stock Market Movements in Emerging Markets Using Optimized Technical Indicators and Neural Networks
- Analysis of the Effect of Digital Financial Inclusion in Promoting Inclusive Growth: Mechanism and Statistical Verification
- Effective Tax Rates and Firm Size under Turnover Tax: Evidence from a Natural Experiment on SMEs
- Re-investigating the Impact of Economic Growth, Energy Consumption, Financial Development, Institutional Quality, and Globalization on Environmental Degradation in OECD Countries
- A Compliance Return Method to Evaluate Different Approaches to Implementing Regulations: The Example of Food Hygiene Standards
- Panel Technical Efficiency of Korean Companies in the Energy Sector based on Digital Capabilities
- Time-varying Investment Dynamics in the USA
- Preferences, Institutions, and Policy Makers: The Case of the New Institutionalization of Science, Technology, and Innovation Governance in Colombia
- The Impact of Geographic Factors on Credit Risk: A Study of Chinese Commercial Banks
- The Heterogeneous Effect and Transmission Paths of Air Pollution on Housing Prices: Evidence from 30 Large- and Medium-Sized Cities in China
- Analysis of Demographic Variables Affecting Digital Citizenship in Turkey
- Green Finance, Environmental Regulations, and Green Technologies in China: Implications for Achieving Green Economic Recovery
- Coupled and Coordinated Development of Economic Growth and Green Sustainability in a Manufacturing Enterprise under the Context of Dual Carbon Goals: Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality
- Revealing the New Nexus in Urban Unemployment Dynamics: The Relationship between Institutional Variables and Long-Term Unemployment in Colombia
- The Roles of the Terms of Trade and the Real Exchange Rate in the Current Account Balance
- Cleaner Production: Analysis of the Role and Path of Green Finance in Controlling Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollution
- The Research on the Impact of Regional Trade Network Relationships on Value Chain Resilience in China’s Service Industry
- Social Support and Suicidal Ideation among Children of Cross-Border Married Couples
- Asymmetrical Monetary Relations and Involuntary Unemployment in a General Equilibrium Model
- Job Crafting among Airport Security: The Role of Organizational Support, Work Engagement and Social Courage
- Does the Adjustment of Industrial Structure Restrain the Income Gap between Urban and Rural Areas
- Optimizing Emergency Logistics Centre Locations: A Multi-Objective Robust Model
- Geopolitical Risks and Stock Market Volatility in the SAARC Region
- Trade Globalization, Overseas Investment, and Tax Revenue Growth in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Can Government Expenditure Improve the Efficiency of Institutional Elderly-Care Service? – Take Wuhan as an Example
- Media Tone and Earnings Management before the Earnings Announcement: Evidence from China
- Review Articles
- Economic Growth in the Age of Ubiquitous Threats: How Global Risks are Reshaping Growth Theory
- Efficiency Measurement in Healthcare: The Foundations, Variables, and Models – A Narrative Literature Review
- Rethinking the Theoretical Foundation of Economics I: The Multilevel Paradigm
- Financial Literacy as Part of Empowerment Education for Later Life: A Spectrum of Perspectives, Challenges and Implications for Individuals, Educators and Policymakers in the Modern Digital Economy
- Special Issue: Economic Implications of Management and Entrepreneurship - Part II
- Ethnic Entrepreneurship: A Qualitative Study on Entrepreneurial Tendency of Meskhetian Turks Living in the USA in the Context of the Interactive Model
- Bridging Brand Parity with Insights Regarding Consumer Behavior
- The Effect of Green Human Resources Management Practices on Corporate Sustainability from the Perspective of Employees
- Special Issue: Shapes of Performance Evaluation in Economics and Management Decision - Part II
- High-Quality Development of Sports Competition Performance Industry in Chengdu-Chongqing Region Based on Performance Evaluation Theory
- Analysis of Multi-Factor Dynamic Coupling and Government Intervention Level for Urbanization in China: Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt
- The Impact of Environmental Regulation on Technological Innovation of Enterprises: Based on Empirical Evidences of the Implementation of Pollution Charges in China
- Environmental Social Responsibility, Local Environmental Protection Strategy, and Corporate Financial Performance – Empirical Evidence from Heavy Pollution Industry
- The Relationship Between Stock Performance and Money Supply Based on VAR Model in the Context of E-commerce
- A Novel Approach for the Assessment of Logistics Performance Index of EU Countries
- The Decision Behaviour Evaluation of Interrelationships among Personality, Transformational Leadership, Leadership Self-Efficacy, and Commitment for E-Commerce Administrative Managers
- Role of Cultural Factors on Entrepreneurship Across the Diverse Economic Stages: Insights from GEM and GLOBE Data
- Performance Evaluation of Economic Relocation Effect for Environmental Non-Governmental Organizations: Evidence from China
- Functional Analysis of English Carriers and Related Resources of Cultural Communication in Internet Media
- The Influences of Multi-Level Environmental Regulations on Firm Performance in China
- Exploring the Ethnic Cultural Integration Path of Immigrant Communities Based on Ethnic Inter-Embedding
- Analysis of a New Model of Economic Growth in Renewable Energy for Green Computing
- An Empirical Examination of Aging’s Ramifications on Large-scale Agriculture: China’s Perspective
- The Impact of Firm Digital Transformation on Environmental, Social, and Governance Performance: Evidence from China
- Accounting Comparability and Labor Productivity: Evidence from China’s A-Share Listed Firms
- An Empirical Study on the Impact of Tariff Reduction on China’s Textile Industry under the Background of RCEP
- Top Executives’ Overseas Background on Corporate Green Innovation Output: The Mediating Role of Risk Preference
- Neutrosophic Inventory Management: A Cost-Effective Approach
- Mechanism Analysis and Response of Digital Financial Inclusion to Labor Economy based on ANN and Contribution Analysis
- Asset Pricing and Portfolio Investment Management Using Machine Learning: Research Trend Analysis Using Scientometrics
- User-centric Smart City Services for People with Disabilities and the Elderly: A UN SDG Framework Approach
- Research on the Problems and Institutional Optimization Strategies of Rural Collective Economic Organization Governance
- The Impact of the Global Minimum Tax Reform on China and Its Countermeasures
- Sustainable Development of Low-Carbon Supply Chain Economy based on the Internet of Things and Environmental Responsibility
- Measurement of Higher Education Competitiveness Level and Regional Disparities in China from the Perspective of Sustainable Development
- Payment Clearing and Regional Economy Development Based on Panel Data of Sichuan Province
- Coordinated Regional Economic Development: A Study of the Relationship Between Regional Policies and Business Performance
- A Novel Perspective on Prioritizing Investment Projects under Future Uncertainty: Integrating Robustness Analysis with the Net Present Value Model
- Research on Measurement of Manufacturing Industry Chain Resilience Based on Index Contribution Model Driven by Digital Economy
- Special Issue: AEEFI 2023
- Portfolio Allocation, Risk Aversion, and Digital Literacy Among the European Elderly
- Exploring the Heterogeneous Impact of Trade Agreements on Trade: Depth Matters
- Import, Productivity, and Export Performances
- Government Expenditure, Education, and Productivity in the European Union: Effects on Economic Growth
- Replication Study
- Carbon Taxes and CO2 Emissions: A Replication of Andersson (American Economic Journal: Economic Policy, 2019)

