Abstract
C20H23O3N2Bi, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 10.6897(5) Å, b = 10.5590(5) Å, c = 17.4099(9) Å, β = 105.491(2)°, V = 1893.71(16) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0253, wR(F2) = 0.0576, T = 296(2) K.
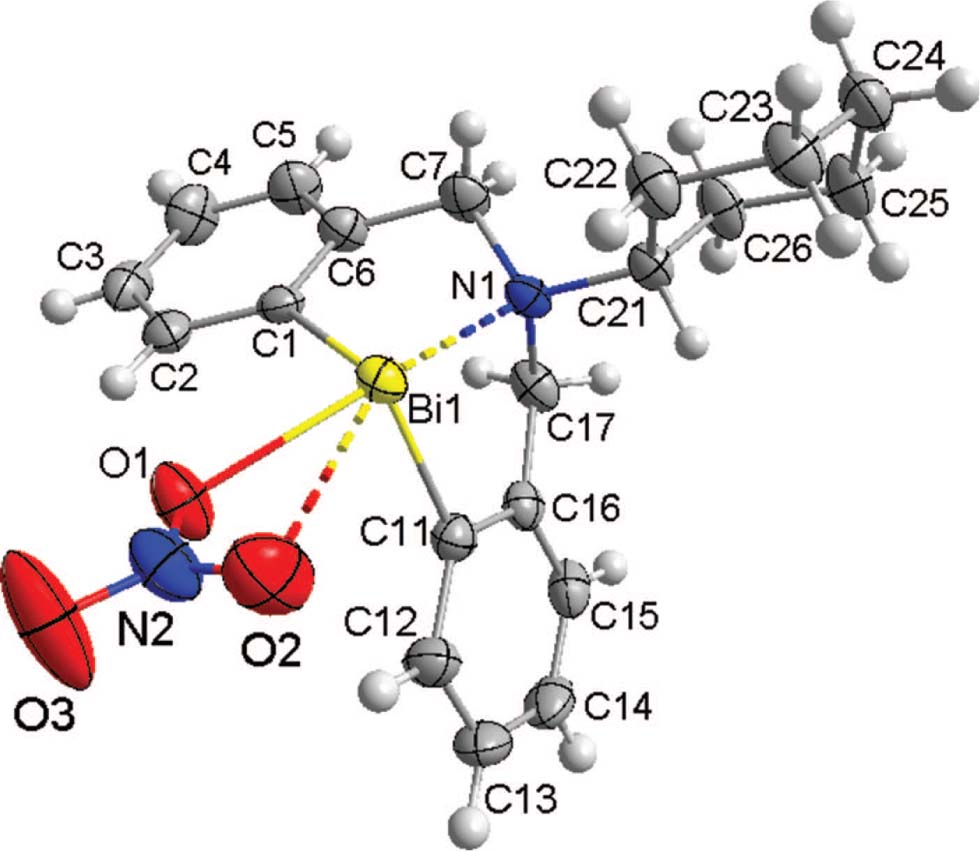
The asymmetric unit of the title crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.05 × 0.04 × 0.03 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 9.33 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.5°, 98% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 14351, 4174, 0.034 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3516 |
| N(param)refined: | 235 |
| Programs: | Bruker programs [1], SHELX programs [2], [3], Olex2 [2] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi1 | 0.99740(2) | 0.27546(2) | 0.04107(2) | 0.02798(6) |
| N1 | 0.7606(3) | 0.2827(3) | 0.0321(2) | 0.0278(7) |
| N2 | 1.2999(4) | 0.2434(4) | 0.0921(3) | 0.0468(10) |
| O1 | 1.2198(3) | 0.3143(4) | 0.1148(2) | 0.0489(8) |
| O2 | 1.2588(4) | 0.1543(4) | 0.0483(3) | 0.0654(11) |
| O3 | 1.4140(4) | 0.2673(6) | 0.1160(3) | 0.104(2) |
| C1 | 0.9601(4) | 0.4611(4) | 0.0942(2) | 0.0284(8) |
| C2 | 1.0537(4) | 0.5374(4) | 0.1441(2) | 0.0341(9) |
| H2 | 1.140489 | 0.513098 | 0.157202 | 0.041* |
| C3 | 1.0187(5) | 0.6488(4) | 0.1742(3) | 0.0408(11) |
| H3 | 1.080823 | 0.697209 | 0.209703 | 0.049* |
| C4 | 0.8908(5) | 0.6878(5) | 0.1515(3) | 0.0471(12) |
| H4 | 0.867252 | 0.764362 | 0.170084 | 0.057* |
| C5 | 0.7980(5) | 0.6137(4) | 0.1012(3) | 0.0433(11) |
| H5 | 0.711924 | 0.640368 | 0.086460 | 0.052* |
| C6 | 0.8313(4) | 0.5003(4) | 0.0726(2) | 0.0331(9) |
| C7 | 0.7285(4) | 0.4196(4) | 0.0175(3) | 0.0366(10) |
| H7A | 0.644519 | 0.437010 | 0.026526 | 0.044* |
| H7B | 0.723842 | 0.440334 | −0.037520 | 0.044* |
| C11 | 0.9738(4) | 0.1542(4) | 0.1411(2) | 0.0304(9) |
| C12 | 1.0714(4) | 0.0771(4) | 0.1870(3) | 0.0401(10) |
| H12 | 1.153524 | 0.077946 | 0.178304 | 0.048* |
| C13 | 1.0471(5) | −0.0001(5) | 0.2447(3) | 0.0466(11) |
| H13 | 1.112556 | −0.051772 | 0.274777 | 0.056* |
| C14 | 0.9258(5) | −0.0011(5) | 0.2582(3) | 0.0464(12) |
| H14 | 0.909919 | −0.052417 | 0.297985 | 0.056* |
| C15 | 0.8275(4) | 0.0740(4) | 0.2129(3) | 0.0401(10) |
| H15 | 0.745323 | 0.071621 | 0.221378 | 0.048* |
| C16 | 0.8517(4) | 0.1535(4) | 0.1541(2) | 0.0294(8) |
| C17 | 0.7498(4) | 0.2458(4) | 0.1123(3) | 0.0341(10) |
| H17A | 0.664900 | 0.208630 | 0.106965 | 0.041* |
| H17B | 0.755940 | 0.321317 | 0.144792 | 0.041* |
| C21 | 0.6808(4) | 0.1959(4) | −0.0309(2) | 0.0293(9) |
| H21 | 0.701868 | 0.108994 | −0.012014 | 0.035* |
| C22 | 0.7152(4) | 0.2078(5) | −0.1097(3) | 0.0414(11) |
| H22A | 0.807185 | 0.191697 | −0.101281 | 0.050* |
| H22B | 0.697792 | 0.293666 | −0.129509 | 0.050* |
| C23 | 0.6381(4) | 0.1156(5) | −0.1716(3) | 0.0435(11) |
| H23A | 0.657075 | 0.131380 | −0.222210 | 0.052* |
| H23B | 0.665158 | 0.029779 | −0.155355 | 0.052* |
| C24 | 0.4933(4) | 0.1273(5) | −0.1824(3) | 0.0454(11) |
| H24A | 0.463730 | 0.208979 | −0.205780 | 0.054* |
| H24B | 0.448588 | 0.062045 | −0.218711 | 0.054* |
| C25 | 0.4604(4) | 0.1142(5) | −0.1037(3) | 0.0435(11) |
| H25A | 0.482539 | 0.029721 | −0.082579 | 0.052* |
| H25B | 0.367883 | 0.126333 | −0.111571 | 0.052* |
| C26 | 0.5350(4) | 0.2120(5) | −0.0442(3) | 0.0416(11) |
| H26A | 0.509770 | 0.296561 | −0.064311 | 0.050* |
| H26B | 0.513188 | 0.202497 | 0.006064 | 0.050* |
Source of material
The compound C6H11N(CH2C6H4)2BiCl is prepared by the literature known synthesis [5]. To a solution of C6H11N(CH2C6H4)2BiCl (0.274 g, 0.5 mmol) in 20 mL CH2Cl2, a solution of AgNO3 (0.085 g, 0.5 mmol) in 10 mL distilled water was added. The mixture was stirred in the dark at room temperature for 12 h and then filtered. The organic phase was separated from aqueous phase and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. After removal of the solvent in vacuum, the compound C6H11N(CH2C6H4)2BiNO3 was obtained. Crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis were obtained by crystallization from CH2Cl2/n-hexane solution. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, TMS): δ = 8.19 (2H, s), 7.54 (4H, dd, J = 14.8, 7.6 Hz), 7.33 (2H, t, J = 7.6 Hz), 4.53 (2H, d, J = 15.2 Hz), 4.32 (2H, d, J = 15.2 Hz), 2.97 (1H, t, J = 11.2 Hz), 2.07 (2H, d, J = 11.6 Hz), 1.90 (2H, d, J = 12.8 Hz), 1.69 (1H, d, J = 12.8 Hz), 1.44−1.26 (4H, m), 1.17–1.08 (1H, m) ppm; 13C NMR (CDCl3, 100 MHz, TMS): δ = 150.65, 137.80, 131.10, 128.39, 128.15, 65.75, 62.40, 31.20, 25.62, 25.36 ppm.
Experimental details
All H atoms were generated geometrically and refined using the riding model, with C—H = 0.93 Å for aryl and 0.97 Å for methylene H atoms, respectively. Uiso(H) set to 1.2Ueq(C) for all H atoms.
Comment
The interest in the chemistry of hypervalent organobismuth compounds with intramolecular N, O, S → Bi interactions has increased in recent years owing to their fascinating chemistry, structure and uses in organic synthesis, catalysis and medicine [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13]. As part of our work on hypervalent organobismuth compounds with intramolecular N, O, S → Bi interactions, we report herein the crystal structure of a hypervalent organobismuth nitrate with intramolecular N → Bi coordinations.
In the molecular structure of organobismuth nitrate (cf. the figure), C6H11N(CH2C6H4)2BiNO3, the N → Bi coordination is observed, and the Bi(1)—N(1) distance [2.495(3) Å] is shorter than those of the organobismuth chloride and triphenylgermylpropionate with same framework, e.g. C6H11N(CH2C6H4)2BiCl (2.517(4) Å) [5] and C6H11N(CH2C6H4)2BiOC(O)CH2CH2GePh3 (2.563(3) Å) [5], while this distance is longer than those of the organobismuth perfluorooctanesulfonate and tetrafluoroborate with same framework, i.e. C6H11N(CH2C6H4)2BiOSO2C8F17 (2.397(5) Å) [6] and C6H11N(CH2C6H4)2BiBF4 (2.394(8) Å) [7]. The geometry around the central Bi atom can be described as a distorted pseudo-trigonal bipyramid. The N(1) and O(1) atoms occupy at the apical positions, and both the C(1) and C(11) atoms at the equatorial positions along with a lone electron pair of bismuth. The nitrate group in the title compound can be considered as acting as an asymmetric bidentate ligand (cf. the figure). One O atom of nitrate group is covalently bound to the bismuth [Bi(1)—O(1) 2.416(3) Å], while the other O atom is weakly coordinated to the bismuth [Bi(1)—O(2) 3.0451(4) Å vs. rvdW (Bi,O) 3.80 Å] [14]. Similar Bi—O distances were found for nitrate ligands in the related [2,6-(Me2NCH2)2C6H3]Bi(NO3)2 [8], [2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4]2BiNO3 [9], C6H5CH2N(CH2C6H4)2BiNO3 [10], O(CH2C6H4)2BiNO3 [12], S(CH2C6H4)2BiNO3 [13]. Taking in account these contacts and the increased coordination number of the bismuth, the title compound might be described as 12-Bi-5 hypervalent species [15], [16], [17].
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Province Education Department (No. 15A041), and Talent Research Startup Fund of Hunan Institute of Engineering (Nos. 14006 and 16RC001).
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2009).Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXT – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H.: OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 42 (2009) 339–341.10.1107/S0021889808042726Search in Google Scholar
5. Zhang, X. W.; Xia, J.; Yan, H. W.; Luo, S. L.; Yin, S. F.; Au, C. T.; Wong, W. Y.: Synthesis, structure, and in vitro antiproliferative activity of cyclic hypervalent organobismuth(III) chlorides and their triphenylgermylpropionate derivatives. J. Organomet. Chem. 694 (2009) 3019–3026.10.1016/j.jorganchem.2009.05.003Search in Google Scholar
6. Zhang, X. W.; Yin, S. F.; Qiu, R. H.; Xia, J.; Dai, W. L.; Yu, Z. Y.; Au, C. T.; Wong, W. Y.: Synthesis and structure of an air-stable hypervalent organobismuth(III) perfluorooctanesulfonate and its use as high-efficiency catalyst for Mannich-type reactions in water. J. Organomet. Chem. 694 (2009) 3559–3564.10.1016/j.jorganchem.2009.07.018Search in Google Scholar
7. Zhang, X. W.; Qiu, R. H.; Tan, N. Y.; Yin, S. F.; Xia, J.; Luo, S. L.; Au, C. T.: Air-stable hypervalent organobismuth(III) tetrafluoroborate as effective and reusable catalyst for the allylation of aldehyde with tetraallyltin. Tetrahedron Lett. 51 (2010) 153–156.10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.10.104Search in Google Scholar
8. Breunig, H. J.; Nema, M. G.; Silvestru, C.; Soran, A.; Varga, R. A.: Organobismuth compounds with the pincer ligand 2,6-(Me2NCH2)C6H3: monoorganobismuth(III) carbonate, sulfate, nitrate, and a diorganobismuthenium(III) salt. Dalton Trans. 39 (2010) 11277–11284.10.1039/c0dt00927jSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Nema, M. G.; Breunig, H. J.; Soran, A.; Silvestru, C.: Diorganobismuth(III) compounds with the pendant arm 2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4 ligand – isothiocyanate, trifluoracetate and nitrate. J. Organomet. Chem. 705 (2012) 23–29.10.1016/j.jorganchem.2012.01.011Search in Google Scholar
10. Toma, A.; Ra t, C. I.; Pavel, O.; Hardacre, C.; Rüffer, T.; Lang, H.; Mehring, M.; Silvestru, A.; Pârvulescu, V.: Heterocyclic bismuth(III) compounds with transannular N→Bi interactions as catalysts for the oxidation of thiophenol to diphenyldisulfide. Catal. Sci. Technol. 7 (2017) 5343–5353.10.1039/C7CY00521KSearch in Google Scholar
11. Tan, N. Y.; Dang, L. M.; Lan, D. H.; Wu, S. S.; Au, C. T.; Yi, B.: Crystal structure of bis{5H-dibenzo[c,f][1,5]oxabismocin-12(7H)-yl} carbonate, C29H24O5Bi2. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 233 (2018) 875–877.10.1515/ncrs-2018-0067Search in Google Scholar
12. Liu, Y. P.; Lei, J.; Tang, L. W.; Peng, Y.; Au, C. T.; Chen, Y.; Yin, S. F.: Studies on the cytotoxicity and anticancer performance of heterocyclic hypervalent organobismuth(III) compounds. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 139 (2017) 826–835.10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.08.043Search in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Toma, A.; Ra t, C. I.; Silvestru, A.; Rüffer, T.; Lang, H.; Mehring, M.: Heterocyclic bismuth(III) compounds with transannular S→Bi interactions. An experimental and theoretical approach. J. Organomet. Chem. 806 (2016) 5–11.10.1016/j.jorganchem.2016.01.019Search in Google Scholar
14. Emsley, J.: Die Elemente. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin (1994).10.1515/9783110857054Search in Google Scholar
15. Perkins, C. W.; Martin, J. C.; Arduengo, A. J.; Lau, W.; Alegria, A.; Koch, K.: The N-X-L nomenclature system has been described previously: N valence shell electrons about a central atom X with L ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 102 (1980) 7753–7759.10.1021/ja00546a019Search in Google Scholar
16. Tan, N.; Zhang, X.: 6-Cyclohexyl-6,7-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,5]azabismocin-12(5H)-yl(N→Bi) trifluoromethanesulfonate. Acta Crystallogr. E67 (2011) m252.10.1107/S1600536811002510Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
17. Zhang, X.-W.; Fan, T.: 6-Phenyl-6,7-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,5]azabismocin-12(5H)-yl perchlorate. Acta Crystallogr. E67 (2011) m875.10.1107/S1600536811021039Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
©2019 Nianyuan Tan et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)-μ4-4′-methyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,5-dicarboxylato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)manganese(II)], C52H40N2O10Mn2
- Crystal structure of bis[2-(((3-aminopropyl)imino)methyl)-4-nitro-phenolato-κ3N,N′,O]nickel(II), C20H24N6NiO6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl) phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II) — ethanol (1/1), C34H36CoN4O5
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-{2,5-dichloro-3-hydroxy-4-[4-(1-methoxyimino-ethyl)-phenylamino]-6-methyl-phenylamino}-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime, C24H22Cl2N4O4
- The pseudosymmetric crystal structure of 2,4,6,8,10,12-hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane dimethyl carbonate (2/3), C21H30N24O33
- Crystal structure of (1,4-diazepane)4CuII2(μ-Cl)10CuI6, C20H48Cl10Cu8N8
- Crystal structure of methyl 2,7,7-trimethyl-4-(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H23NO3S
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(4-(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-6-yl)phenyl)acetate, C15H13N3O2
- Crystal structure of (1S,3aR,3bR,10aR,10bR,12aR)-8-amino-3a,3b,6,6,10a-pentamethyl-1-((S)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)-2,3,3a,3b,4,5,5a,6,10,10a,10b,11,12,12a-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[7,8]phenanthro[2,3-d]thiazol-12-ol – a panaxadiol dervative, C31H50N2O2S
- Crystal structure of bis[(((4-fluorophenyl)amino)methyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrachloridocobaltate(II), C50H44Cl4CoF2N2P2
- Crystal structure of 5,4′-dihydroxy-7,3′-dimethoxyflavanone, C17H16O6
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-cyclobis(1-(1,1′-ferrocenylmethyl)-4-butyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole) tetrafluoroborate, C21H25FeN6⋅BF4
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-diethylaminoethyl)-2,3-dihydro-2-thioxoquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C14H19N3OS
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl) ((methyldiphenylsilyl)oxy)methyl) pyrrolidine, C34H39NOSi
- The crystal structure of 1,4-dinitro-2,3,5,6-tetraacetoxy-piperazine, C12H16N4O12
- Crystal structure of rac-3,6-dimethyl-5-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-6-vinyl-1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2H-indol-2-one, C15H19NO
- Crystal structure of (Cu0.51In0.49)tet[Cr1.74In0.26]octSe4 selenospinel, Cu0.51In0.75Cr1.74Se4
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-5-methoxy-4,6-dimethylisobenzofuran-1(3H)-one, C11H12O4
- Crystal structure of trans-tetrakis(acetonitrile-κN)bis(triphenylphosphine-κP)ruthenium(II) dihexafluorophosphate - dichloroform (1/2), C46H44Cl6F12N4P4Ru
- Crystal structure of 2-((4-nitrophenyl)thio)ethan-1-ol, C8H9NO3S
- Crystal structure of diaqua-dichlorido-bis(μ3-6,6′-(hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methanylylidene))bis(2-methoxyphenolato)κ6O,N:N′,O′,O′:O′′)trizinc(II) - ethanol (1/2), C36H44Cl2N4O12Zn3
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2-[(2-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid – 3-chlorobenzoic acid (2/1), C35H25ClO10S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenylamino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-ol, C15H11ClFN3O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl (E)-1-(3-ethoxy-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl)-2-(4-nitrophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-benzo[b][1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate, C23H23N3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-cyanophenyl)ethenesulfonyl fluoride, C9H6FNO2S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-bromo-2-(((3-chloropropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxidovanadium(IV), C20H20Br2Cl2N2O3V
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexaphenyldistannoxane – 2,2′-bipyridine (1/1), C46H38N2OSn2
- Crystal structure of coordination polymer catena-poly[diaqua-(2,6-dichloropyridine-4-carboxyliato-κ2O,O′)-bis(μ2-2,6-dichloropyridine-4-carboxyliato-κ2O:O′)terbium(III), C18H10Cl6N3O8Tb
- The crystal structure of 4-((2-(4,5-dihydro-1,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)anthracen-10-yl) methyl)morpholine, C34H31N3O
- The crystal structure of bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κO)-tetrakis(9H-xanthene-9-carboxylic-carboxylate-κ2O:O′)dicopper(II) - acetonitrile (1/2), C66H56Cu2N4O14
- Crystal structure of trans-dichlorido-(1,3-dimesityl-1H-imidazol-2(3H)-ylidene)-(5-methyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrrole-κN)palladium(II), C25H31Cl2N3OPd
- Crystal structure of 8,8′-di-p-tolyl-8′H-7,8′-biacenaphtho[1,2-d]imidazole, C40H26N4
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-(2,4-dioxopent-3-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-triazinium nitrate, C8H13N5O5
- Crystal structure of 4,4′,5,5′-tetraphenyl-2,2′-di-p-tolyl-2′H-1,2′-biimidazole, C44H34N4
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,10-phenanthroline – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (2/1), C30H14Br2F4I2N4
- Crystal structure of tris(1-phenyl-1,2-propanedione-2-oximato-κ2N,O)cobalt(III), C27H24N3O6Co
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(6,6′-((1,2-phenylenebis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-methoxyphenolato)-κ4O,N,N′,O′)iron(III), C22H18ClN2FeO4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-thenoyl-1H-pyrazol-5-olato-κ3O,O′:O′)-bis-(1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-thenoyl-1H-pyrazol-5-olato-κ2O,O)-bis(ethyl acetate-κO)dicadmium(II), C88H64Cl4N8O12S4Cd2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ2-3-(2-pyridyl)-4-(4-pyridyl)-5-(3-pyridyl)-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′)] copper(II), C17H12N6Cl2Cu
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-([2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine]-4′-carboxylic acid-κ3N,N′,N′′)copper(II) monohydrate, C16H13Cl2CuN3O3
- Crystal structure of triethylammonium(5-carboxypyridine-2-thiolato-κ2N,S)-bis(dimethylsulfoxide-κ1S)-(6-sulfidonicotinato-κ2N,S)ruthenium(II) trihydrate, C22H41N3O9RuS4
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ5-2,5-dicarboxy-benzoato-κ4O:O:O′:O′′,O′′′)silver(I)], C9H5AgO6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(thiophen-2-yl)-N-(5-((triphenylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)methanimine, C25H19N3S3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(3,5-dichloroisonicotinato-κ1O)-bis(1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ1N)cobalt(II), C38H36Cl4N6O6Co
- Crystal structure of dodecaaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(4,4′-((5-carboxylato-1,3-phenylene)bis(oxy))dibenzoato-κ1O)tricopper(II) - water (1/4), C62H70Cu3N4O32
- Crystal structure of bis(5-methoxy-2-(((2-oxidoethyl)imino)methyl)phenolate-κ3O,N,O′)manganes(IV), C20H22N2O6Mn
- Crystal structure of tetramethylammonium (2-(3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-1-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(III), C36H40N5O8Co
- Crystal structure of 6-cyclohexyl-6,7-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,5]azabismocin-12(5H)-yl nitrate, C20H23O3N2Bi
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-((2S,3S,4R,10R,13S, 17S)-17-(1-(dimethylamino) ethyl)-2,4-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl)-2-methylbut-2-enamide, C24H48N2O3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H12ClN3S
- Crystal structure of 1-benzyl-3-cyano-6-phenyl-1,2-dihydropyridine, C19H16N2
- Isolation and crystal structure of 4-((2-(methoxycarbonyl)phenyl)amino)-2-methyl-4-oxobutanoic acid from Delphinium Grandiflorum, C13H15N1O5
- Crystal structure of tetraqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)benzoato-κO)nickel(II), C16H22O10Ni
- Crystal structure of ajacisine D monohydrate, C30H44N2O9
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(1-(2-aminophenylimino)ethyl)benzene-1,3-diol, C14H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)phenyl)acetato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)(formiato-κ1O)cobalt(II)], C11H9CoN3O4
- The crystal structure of bis tetrabutylammonium bis(μ3-2,2,2-tri(hydroxymethyl)ethyl-4-((3-methoxy-3-oxopropyl)amino)-4-oxobutanoato)-(μ6-oxido)-hexakis(μ2-oxido)-hexaoxido-hexavanadium(V), C58H112N4O29V6
- Crystal structure of (N-benzylpropane-1,3-diamine-κ2N, N′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)platinum(II) chloride, C20H24Cl2N4Pt
- Crystal structure of 5-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-N-phenyl-2-amine, C23H16ClN5O
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ2(carboxylatomethyl)((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)amido-κ3N: O:O′)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C18H14CuN4O6S
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ2-(carboxylatomethyl)((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)amido-κ3N:O:O′)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′) nickel(II)], C18H14NiN4O6S
- Crystal structure of N-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-17-((S)-1-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl)-N-methylbenzamide, C31H48N2O
- The crystal structure of dichloroido(1,3-bis(2,6-dimethyl-phenyl)-1H-3l4-imidazol-2-yl)(2-methyl-4,5-dihydrooxazol-κN)palladium(IV)-water (1/1), C23H29Cl2N3O2Pd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibromido-{μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O}zinc(II)], C34H32Br4N8O2Zn2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-dichlorido-bis(μ2-2-(((1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,N,O′)dicobalt(II), C36H36Cl2N6O6Co2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridinyl)ethyane-κ2N:N′)-(μ2–pyridazine-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)]dizinc(II) dihydrate, C12H12ZnN3O6
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-chloro-2,6-dinitrophenyl)-1-(4-chloro)diazene oxide, C12H6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of 2-isopropylthioxanthone, C16H14OS
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(4-(3-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-6-yl)phenyl)acetate, C19H17N5O2
- Crystal structure of 4,4-dimethyl-2-(trifluoromethyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole, C6H9F3N2
- Crystal structure of N-methylanilinium 5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-2-phenyl-4H-chromene-8-sulfonate monohydrate, C22H21NO8S
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxybenzoate, C10H10O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(μ-1,1′-[(5-methoxy-2,4,6-trimethyl-1,3-phenylene)bis(methylene)]bis(1H-1,2,4-triazole)-κ2N:N′)-bis(isothiocyanato-κN)manganese(II)], C34H40MnN14O2S2
- Crystal structure of N-(2-methylphenyl)(propan-2-yloxy)carbothioamide, C11H15NOS
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)-μ4-4′-methyl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,5-dicarboxylato-κ4O:O′:O′′:O′′′)manganese(II)], C52H40N2O10Mn2
- Crystal structure of bis[2-(((3-aminopropyl)imino)methyl)-4-nitro-phenolato-κ3N,N′,O]nickel(II), C20H24N6NiO6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl) phenolato-κ2N,O}cobalt(II) — ethanol (1/1), C34H36CoN4O5
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-{2,5-dichloro-3-hydroxy-4-[4-(1-methoxyimino-ethyl)-phenylamino]-6-methyl-phenylamino}-phenyl)-ethanone O-methyl-oxime, C24H22Cl2N4O4
- The pseudosymmetric crystal structure of 2,4,6,8,10,12-hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane dimethyl carbonate (2/3), C21H30N24O33
- Crystal structure of (1,4-diazepane)4CuII2(μ-Cl)10CuI6, C20H48Cl10Cu8N8
- Crystal structure of methyl 2,7,7-trimethyl-4-(3-methylthiophen-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H23NO3S
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(4-(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-6-yl)phenyl)acetate, C15H13N3O2
- Crystal structure of (1S,3aR,3bR,10aR,10bR,12aR)-8-amino-3a,3b,6,6,10a-pentamethyl-1-((S)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)-2,3,3a,3b,4,5,5a,6,10,10a,10b,11,12,12a-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[7,8]phenanthro[2,3-d]thiazol-12-ol – a panaxadiol dervative, C31H50N2O2S
- Crystal structure of bis[(((4-fluorophenyl)amino)methyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrachloridocobaltate(II), C50H44Cl4CoF2N2P2
- Crystal structure of 5,4′-dihydroxy-7,3′-dimethoxyflavanone, C17H16O6
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-cyclobis(1-(1,1′-ferrocenylmethyl)-4-butyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole) tetrafluoroborate, C21H25FeN6⋅BF4
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-diethylaminoethyl)-2,3-dihydro-2-thioxoquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C14H19N3OS
- Crystal structure of 2-(bis(3,5-dimethylphenyl) ((methyldiphenylsilyl)oxy)methyl) pyrrolidine, C34H39NOSi
- The crystal structure of 1,4-dinitro-2,3,5,6-tetraacetoxy-piperazine, C12H16N4O12
- Crystal structure of rac-3,6-dimethyl-5-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-6-vinyl-1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2H-indol-2-one, C15H19NO
- Crystal structure of (Cu0.51In0.49)tet[Cr1.74In0.26]octSe4 selenospinel, Cu0.51In0.75Cr1.74Se4
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-5-methoxy-4,6-dimethylisobenzofuran-1(3H)-one, C11H12O4
- Crystal structure of trans-tetrakis(acetonitrile-κN)bis(triphenylphosphine-κP)ruthenium(II) dihexafluorophosphate - dichloroform (1/2), C46H44Cl6F12N4P4Ru
- Crystal structure of 2-((4-nitrophenyl)thio)ethan-1-ol, C8H9NO3S
- Crystal structure of diaqua-dichlorido-bis(μ3-6,6′-(hydrazine-1,2-diylidenebis(methanylylidene))bis(2-methoxyphenolato)κ6O,N:N′,O′,O′:O′′)trizinc(II) - ethanol (1/2), C36H44Cl2N4O12Zn3
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 2-[(2-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid – 3-chlorobenzoic acid (2/1), C35H25ClO10S4
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenylamino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-ol, C15H11ClFN3O2
- Crystal structure of ethyl (E)-1-(3-ethoxy-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl)-2-(4-nitrophenyl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-benzo[b][1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate, C23H23N3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-cyanophenyl)ethenesulfonyl fluoride, C9H6FNO2S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-bromo-2-(((3-chloropropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxidovanadium(IV), C20H20Br2Cl2N2O3V
- The crystal structure of 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexaphenyldistannoxane – 2,2′-bipyridine (1/1), C46H38N2OSn2
- Crystal structure of coordination polymer catena-poly[diaqua-(2,6-dichloropyridine-4-carboxyliato-κ2O,O′)-bis(μ2-2,6-dichloropyridine-4-carboxyliato-κ2O:O′)terbium(III), C18H10Cl6N3O8Tb
- The crystal structure of 4-((2-(4,5-dihydro-1,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)anthracen-10-yl) methyl)morpholine, C34H31N3O
- The crystal structure of bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κO)-tetrakis(9H-xanthene-9-carboxylic-carboxylate-κ2O:O′)dicopper(II) - acetonitrile (1/2), C66H56Cu2N4O14
- Crystal structure of trans-dichlorido-(1,3-dimesityl-1H-imidazol-2(3H)-ylidene)-(5-methyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrrole-κN)palladium(II), C25H31Cl2N3OPd
- Crystal structure of 8,8′-di-p-tolyl-8′H-7,8′-biacenaphtho[1,2-d]imidazole, C40H26N4
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-(2,4-dioxopent-3-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-triazinium nitrate, C8H13N5O5
- Crystal structure of 4,4′,5,5′-tetraphenyl-2,2′-di-p-tolyl-2′H-1,2′-biimidazole, C44H34N4
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 2-bromo-1,10-phenanthroline – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (2/1), C30H14Br2F4I2N4
- Crystal structure of tris(1-phenyl-1,2-propanedione-2-oximato-κ2N,O)cobalt(III), C27H24N3O6Co
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(6,6′-((1,2-phenylenebis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-methoxyphenolato)-κ4O,N,N′,O′)iron(III), C22H18ClN2FeO4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-thenoyl-1H-pyrazol-5-olato-κ3O,O′:O′)-bis-(1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-thenoyl-1H-pyrazol-5-olato-κ2O,O)-bis(ethyl acetate-κO)dicadmium(II), C88H64Cl4N8O12S4Cd2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ2-3-(2-pyridyl)-4-(4-pyridyl)-5-(3-pyridyl)-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N′)] copper(II), C17H12N6Cl2Cu
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-([2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine]-4′-carboxylic acid-κ3N,N′,N′′)copper(II) monohydrate, C16H13Cl2CuN3O3
- Crystal structure of triethylammonium(5-carboxypyridine-2-thiolato-κ2N,S)-bis(dimethylsulfoxide-κ1S)-(6-sulfidonicotinato-κ2N,S)ruthenium(II) trihydrate, C22H41N3O9RuS4
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ5-2,5-dicarboxy-benzoato-κ4O:O:O′:O′′,O′′′)silver(I)], C9H5AgO6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(thiophen-2-yl)-N-(5-((triphenylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)methanimine, C25H19N3S3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(3,5-dichloroisonicotinato-κ1O)-bis(1,3-di(pyridin-4-yl)propane-κ1N)cobalt(II), C38H36Cl4N6O6Co
- Crystal structure of dodecaaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(4,4′-((5-carboxylato-1,3-phenylene)bis(oxy))dibenzoato-κ1O)tricopper(II) - water (1/4), C62H70Cu3N4O32
- Crystal structure of bis(5-methoxy-2-(((2-oxidoethyl)imino)methyl)phenolate-κ3O,N,O′)manganes(IV), C20H22N2O6Mn
- Crystal structure of tetramethylammonium (2-(3-ethoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)-1-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O)cobalt(III), C36H40N5O8Co
- Crystal structure of 6-cyclohexyl-6,7-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,5]azabismocin-12(5H)-yl nitrate, C20H23O3N2Bi
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-((2S,3S,4R,10R,13S, 17S)-17-(1-(dimethylamino) ethyl)-2,4-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl)-2-methylbut-2-enamide, C24H48N2O3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-((4-chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methylene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H12ClN3S
- Crystal structure of 1-benzyl-3-cyano-6-phenyl-1,2-dihydropyridine, C19H16N2
- Isolation and crystal structure of 4-((2-(methoxycarbonyl)phenyl)amino)-2-methyl-4-oxobutanoic acid from Delphinium Grandiflorum, C13H15N1O5
- Crystal structure of tetraqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)benzoato-κO)nickel(II), C16H22O10Ni
- Crystal structure of ajacisine D monohydrate, C30H44N2O9
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(1-(2-aminophenylimino)ethyl)benzene-1,3-diol, C14H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)phenyl)acetato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)(formiato-κ1O)cobalt(II)], C11H9CoN3O4
- The crystal structure of bis tetrabutylammonium bis(μ3-2,2,2-tri(hydroxymethyl)ethyl-4-((3-methoxy-3-oxopropyl)amino)-4-oxobutanoato)-(μ6-oxido)-hexakis(μ2-oxido)-hexaoxido-hexavanadium(V), C58H112N4O29V6
- Crystal structure of (N-benzylpropane-1,3-diamine-κ2N, N′)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)platinum(II) chloride, C20H24Cl2N4Pt
- Crystal structure of 5-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-N-phenyl-2-amine, C23H16ClN5O
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ2(carboxylatomethyl)((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)amido-κ3N: O:O′)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)copper(II)], C18H14CuN4O6S
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ2-(carboxylatomethyl)((3-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)amido-κ3N:O:O′)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′) nickel(II)], C18H14NiN4O6S
- Crystal structure of N-((3R,10S,13S,17S)-17-((S)-1-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl)-N-methylbenzamide, C31H48N2O
- The crystal structure of dichloroido(1,3-bis(2,6-dimethyl-phenyl)-1H-3l4-imidazol-2-yl)(2-methyl-4,5-dihydrooxazol-κN)palladium(IV)-water (1/1), C23H29Cl2N3O2Pd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dibromido-{μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one-κ2N:O}zinc(II)], C34H32Br4N8O2Zn2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-dichlorido-bis(μ2-2-(((1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ4O:O,N,O′)dicobalt(II), C36H36Cl2N6O6Co2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridinyl)ethyane-κ2N:N′)-(μ2–pyridazine-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)]dizinc(II) dihydrate, C12H12ZnN3O6
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-chloro-2,6-dinitrophenyl)-1-(4-chloro)diazene oxide, C12H6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of 2-isopropylthioxanthone, C16H14OS
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(4-(3-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-6-yl)phenyl)acetate, C19H17N5O2
- Crystal structure of 4,4-dimethyl-2-(trifluoromethyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole, C6H9F3N2
- Crystal structure of N-methylanilinium 5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-2-phenyl-4H-chromene-8-sulfonate monohydrate, C22H21NO8S
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxybenzoate, C10H10O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(μ-1,1′-[(5-methoxy-2,4,6-trimethyl-1,3-phenylene)bis(methylene)]bis(1H-1,2,4-triazole)-κ2N:N′)-bis(isothiocyanato-κN)manganese(II)], C34H40MnN14O2S2
- Crystal structure of N-(2-methylphenyl)(propan-2-yloxy)carbothioamide, C11H15NOS

