Abstract
This paper proposes a new face recognition system based on combining two feature extraction techniques: the Vander Lugt correlator (VLC) and Gabor ordinal measures (GOM). The proposed system relies on the execution speed of VLC and the robustness of GOM. In this system, we applied the Tan and Triggs and retina modeling enhancement techniques, which are well suited for VLC and GOM, respectively. We evaluated our system on the standard FERET probe data sets and on extended YaleB database. The obtained results exhibited better face recognition rates in a shorter execution time compared to the GOM technique.
1 Introduction
Because of the increase and complexity of criminal behavior in modern societies, robust and efficient authentication systems became vital. Compared to traditional token (Id Card, badge, …) and knowledge-based systems (PIN, Password, …), which can be either forgotten or stolen, biometric authentication systems offer a better solution for a wide range of applications like access control, criminal identification, etc.
Different modalities are used in biometric systems such as iris, fingerprint, voice, and face recognition. The latter is widely used for many factors. Interestingly, such a system is able to recognize people without their interaction. In addition, this makes the task more difficult due to some challenging factors such as pose variation, luminosity, facial expression in addition to the aging and the time-precision compromise. A face recognition system rests on four main steps: face detection, preprocessing, feature extraction, and classification.
The Gabor wavelet feature extraction techniques showed promising results in face recognition applications like the Gabor ordinal measures (GOM) [4], [9] and optic-based techniques like the Vander Lugt correlator (VLC) [1], [8], which represents a fast face recognition system.
In this paper, we propose combining these two techniques in order to take profit from the speed of VLC and the precision of GOM.
This work is outlined as follows: in Section 2, we describe the preprocessing techniques used in our system. Section 3 contains our proposed hybrid face recognition system. The experimental results are presented in Section 4. Finally, conclusions are drawn in Section 5.
2 Preprocessing
Preprocessing is a crucial step for feature extraction and then for the performance of the face recognition system. This preprocessing is composed of three steps as shown in Figure 1: landmark detection, image alignment and cropping, and Tan and Triggs [20], [21] preprocessing or retina modeling.

Preprocessing Step.
2.1 Landmark Detection
In general, there are three main methods to locate the facial landmarks from a face image: the first category performs a sliding window search based on local-patch classifiers, which encounters the problems of the ambiguity or corruption in local features [25]. The second category of methods is the well-known framework of the active shape model (ASM) [2] and the active appearance model (AAM) [5]. These methods fit a generative model for the global facial appearance and are, hence, robust to local corruptions. However, to estimate the parameters in the generative models, expensive iterative steps are required.
Recently, a new framework based on explicit regression methods was proposed [3], [18]. In this framework, the problem of landmark localization is considered directly as a regression task, and a holistic regression is used to compute the landmark coordinates from raw input pixels. Compared to the previous methods, this framework is more robust and stable as the global contextual information is incorporated at the beginning. It is also more efficient as no iterative fitting step or sliding window search is required. Instead of the random ferns (group of features) used in Ref. [3], Sun et al. [18] applied a more powerful deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) in the regression framework and achieved a state-of-the-art performance [25].
2.2 Tan and Triggs
The preprocessing technique proposed by Tan and Triggs consists of three steps [21]: gamma correction, Difference of Gaussian (DoG) filtering, and contrast equalization as shown in the Figure 2.

Tan and Triggs Preprocessing.
2.2.1 Gamma Correction
The gamma correction is a nonlinear gray-level transformation that replaces the gray-level I with IGC
where
2.2.2 DoG Filtering
This step is achieved by a convolutional product between the enhanced image I’ and the DoG filter. The DoG filter is a bandpass filter described by equation (2). The high-pass filtering simplifies the recognition by removing the incidental information and reducing the aliasing and noise without affecting the performance of the recognition system. Instead, in many cases, the high-pass filter increases the performance.
where the standard deviations of the two Gaussians are
2.2.3 Contrast Equalization
The contrast equalization is the final step of the preprocessing chain. This step consists in rescaling the image intensities to standardize a robust measurement of overall contrast or intensity variation. This contrast equalization is based on the application of the following equations consecutively.
With α is a strongly compressive exponent that reduces the influence of large values; τ is a threshold used to truncate large values after the first phase of normalization.
2.3 Retina Modeling
The retina modeling is a preprocessing technique for removing illumination variation [23]. It is based on two consecutive adaptive nonlinear operations that act as an efficient light adaptation filter followed by a DoG filtering as shown in Figure 3.

Retina Modeling.
For each pixel of the input image, the first nonlinear function is computed by performing a low-pass filter.
The computation of the adaptation factor
where G1 is a 2D Gaussian low-pass filter with standard deviation equal to 1 [23].
Using the adaptation factor F1, the first light-adapted image
where
The second light-adapted image
with
where G2 is a 2D Gaussian low-pass filter with standard deviation equal to 3.
The second light-adapted image
3 Proposed Face Recognition System
Our recognition system consists in combining two feature extraction techniques as shown in Figure 4: VLC and GOM. First, the biometric signature is verified using VLC as a feature extraction technique. If this signature is rejected, a second step is performed using GOM for feature extraction.
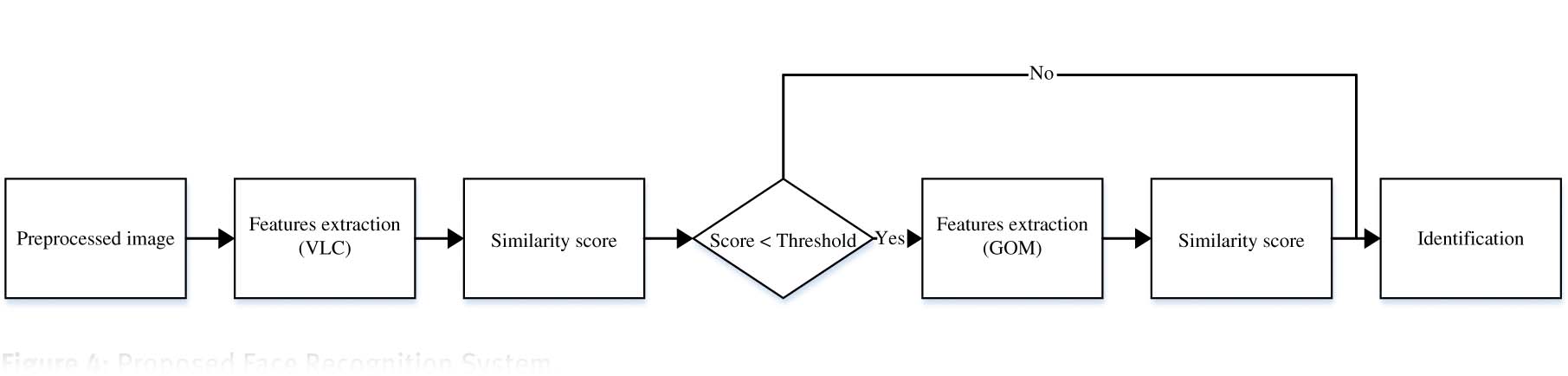
Proposed Face Recognition System.
3.1 Vander Lugt Correlator
The VLC is one of the optical correlation techniques (OCT) that are based on the all-optical setup and are characterized by their discrimination capability and their ability of instantly detecting and estimating target objects [2], [25].
As shown in Figure 5, the VLC is composed by three planes and two lenses: the input plane, the Fourier plane, and the correlation plane. Each two planes are separated by a convergent lens. The first lens performs the Fourier transform FT of the target image. The second performs the inverse Fourier transform

4f Setup.
The VLC, as shown in Figure 6, is based on the multiplication of the spectrum of the target image by a correlation filter made from a reference image. The inverse Fourier transform is then applied to the obtained image.

VLC Face Recognition System.
The similarity degree between the target and the reference images is then provided by the correlation result, which is characterized by the central correlation peak.
To evaluate the correlation, the peak-to-correlation energy (PCE) is defined by equation (9) as the energy of the peak correlation normalized to the total energy of the correlation plane.
where N and M refer to the size of the peak correlation spot and the size of the correlation plane, respectively.
We opted for a phase-only filter: HPOF, where the POF is an optimized filter defined by:
where
As all optical implementations are rather complex to develop, many researchers were interested in the numerical implementation of the correlation [25], which shows a good compromise between performance and simplicity. In this work, we used the numerical implementation of VLC.
3.2 Gabor Ordinal Measures
The GOM is a local feature extraction technique that showed a good performance in pattern recognition applications due to the discrimination capability of the Gabor wavelet [15], [17] and the robustness of the ordinal measures [10], [19].
As shown in Figure 7, the process of GOM feature extraction consists mainly of five steps: 1) applying multiresolution and orientation Gabor filters to the input image, 2) deriving ordinal measures from Gabor filter responses, 3) encoding multiple ordinal measures, 4) concatenating histograms of the encoded images, and 5) applying the linear discriminant analysis to reduce the feature vector size.

GOM Face Recognition System.
3.2.1 Gabor Filters
Gabor filters are based on the Gabor wavelet [6], [7], [17], which are widely used in pattern recognition applications due to their performance that could be explained by their similarity with the visual cortex in the mammalian brain.
A family of 2D Gabor filters composed of five scales and eight orientations as shown in Figure 8 is described by equation (11) [12]:

Gabor Wavelet Filter Bank: (A) Real Parts, (B) Magnitude.
where
The response of the input image (I) to the Gabor filter family is obtained by the convolution of the image I with each filter
The Gabor filtering provides four types of images: Gabor magnitude feature images, Gabor phase feature images, real Gabor feature images, and imaginary Gabor feature images.
3.2.2 Ordinal Measures
Ordinal measure is a qualitative relationship between the average intensity values of two or more image regions [19].
Ordinal measures can be defined as multi-lobe differential filters (MLDF) [4]:
where ω and δ represent the central position and the scale of a 2D Gaussian filter, Np and Nn are the numbers of positive and negative lobes, respectively. Cp and Cn are two constants used to maintain the balance between positive and negative lobes (
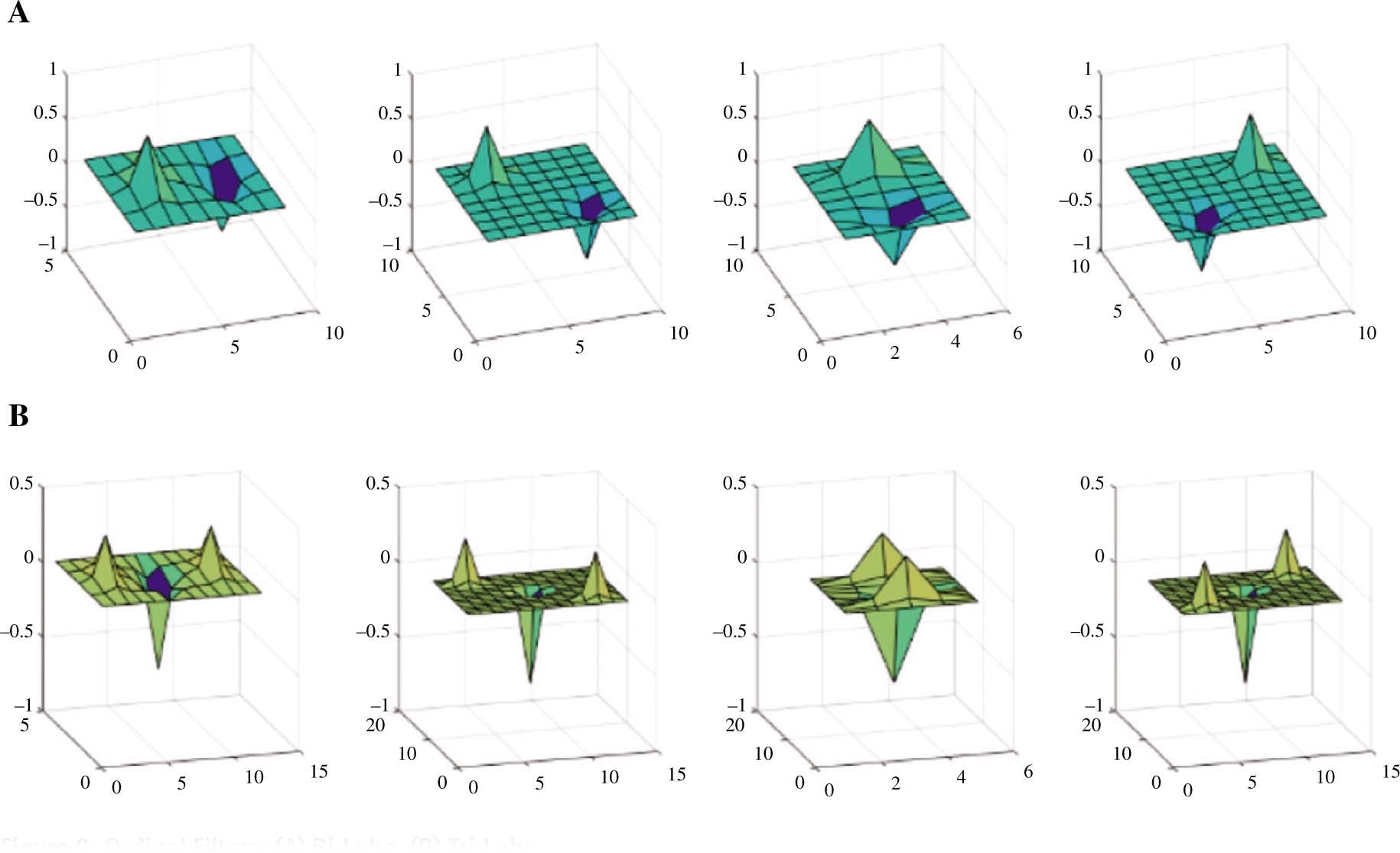
Ordinal Filters: (A) Bi-Lobe, (B) Tri-Lobe.
The ordinal features
For Gabor magnitude feature images
For Gabor phase features image
For real Gabor features image
For imaginary Gabor features image
with
3.2.3 Encoding G O M _ α
The
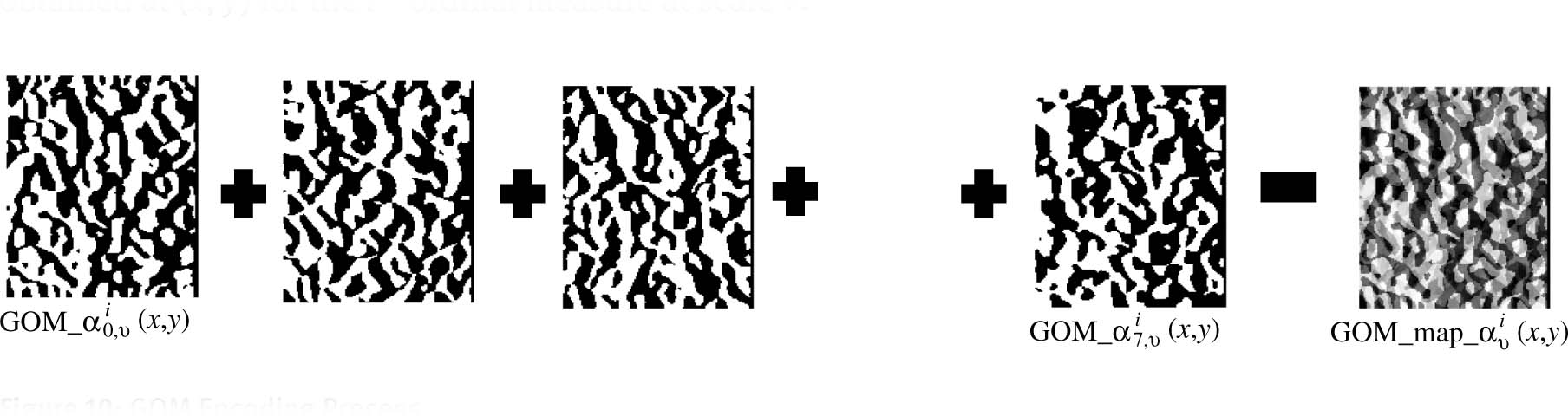
GOM Encoding Process.
The encoding is described by equation (18):
where α ∈ {m: magnitude, p: phase, r: real, i: imaginary} and
3.2.4 Histogram Representation
The obtained
3.2.5 Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)
The LDA is a statistical approach widely used in dimensionality reduction and supervised classification to find the set of projection vectors, which maximize the between-class and minimize the within-class. This technique is used to reduce the feature vector dimension of each block.
4 Experiments
4.1 FERET Database
The performance of the proposed technique is evaluated using the FERET database [14], which is one of the most used databases in face recognition research community. It contains standard partitions: a gallery (Fa) and two probe sets (Fb) and (Fc), where the gallery (Fa) contains 1196 frontal face images as shown in Figure 11 with one image per person, the (Fb) probe set contains 1195 images with different facial expressions, and the (Fc) probe set contains 194 images with variations of lighting.

Examples of FERET Database Images.
To evaluate our system, we used the gallery for the identification stage and the training set, which contains 1002 images for 429 subjects, for the LDA.
4.2 Extended YaleB Database
This database contains frontal face images under various illumination and expression conditions for 38 persons. In total, it has 2412 images. We used one image per person for the training and the rest for the evaluation [13].
4.3 Experimental Settings
A preprocessing step is performed before the evaluation of the different algorithms. A geometrical normalization of the images consists in resizing the image to a 128 × 160 region of interest according to the position of the eyes. In order to reduce the effect of the illumination variation, local shadowing, and highlights, the two preprocessing sequences proposed by Tan and Triggs [20] and Son Vu and Caplier [23] are performed.
For the proposed recognition system, as shown in Table 1, we performed eight tests with the two preprocessing techniques. For the first four tests, we used only one feature extraction technique.
Test Scenarios.
| Preprocessing technique | Feature extraction | |
|---|---|---|
| Test 1 | Tan and Triggs | VLC |
| Test 2 | Retina modeling | VLC |
| Test 3 | Tan and Triggs | GOM |
| Test 4 | Retina modeling | GOM |
| Test 5 | Tan and Triggs | VLC and GOM |
| Test 6 | Retina modeling | VLC and GOM |
| Test 7 | Retina modeling | VLC |
| Tan and Triggs | GOM | |
| Test 8 | Tan and Triggs | VLC |
| Retina modeling | GOM |
In the first and second tests, we, respectively, performed Tan and Triggs and retina modeling as a preprocessing method and VLC for feature extraction.
In the third and fourth tests, we, respectively, performed Tan and Triggs and retina modeling as a preprocessing method and GOM for feature extraction.
For the fifth, sixth, seventh, and eighth tests, we combined the two feature extraction techniques.
For the fifth test, we first performed the Tan and Triggs test for both VLC and GOM.
For the sixth test, we first performed the retina modeling for both VLC and GOM.
For the seventh test, we performed the retina modeling for the VLC and Tan and Triggs for the GOM.
Finally, we performed Tan and Triggs for the VLC and the retina modeling for the GOM.
In the GOM method, we used only the Gabor magnitude features. We reduced the dimension of each block feature vector from 2560 to 260 using LDA. The cosine distance is then used for the classification.
4.4 Results and Discussion
From test 1 and test 2 in Table 2, we can see that the VLC technique gives better results when using Tan and Triggs techniques. This can be explained by the fact that the spectrum of the preprocessed image using the Tan and Triggs method is richer than the retina modeling as shown in Figure 12.
FERET Data Sets Result.
| Enhancement techniques | Feature extraction | Fb | Fc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test 1 | Tan and Triggs | VLC | 77.41 | 85.57 |
| Test 2 | Retina modeling | VLC | 73.72 | 81.96 |
| Test 3 | Tan and Triggs | GOM | 98.16 | 99.48 |
| Test 4 | Retina modeling | GOM | 99.00 | 99.48 |
| Test 5 | Tan and Triggs | VLC and GOM | 98.16 | 99.48 |
| Test 6 | Retina modeling | VLC and GOM | 99.00 | 99.48 |
| Test 7 | Tan and Triggs | VLC | 99.00 | 99.48 |
| Retina modeling | GOM | |||
| Test 8 | Retina modeling | VLC | 98.16 | 99.48 |
| Tan and Triggs | GOM |

Image Spectrum Using (A) Tan and Triggs, (B) Retina Modeling.
However, the retina processing contains a low-pass filtering step, which eliminates high frequencies containing information useful for the recognition.
From tests 3 and 4 in Table 2, we deduce that for the GOM feature extraction, the two preprocessing techniques give almost the same results for Fb and Fc.
From the last four tests (test 5 to test 8), in which we combined the two feature extraction techniques VLC and GOM, we deduce that test 7 gives a better recognition rate when using, respectively, Tan and Triggs and retina modeling for image enhancement.
Table 3 shows the mean computation time for each data set using the proposed system. This time is computed as follows:
Mean Computation Time per Image.
| Data set | Proposed method (ms) | GOM (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| Fb | 107 | 486 |
| Fc | 69 | 486 |
where WCVLC is the number of well-classified images using VLC, TVLC is the mean computational time of VLC, MCVLC is the number of misclassified images using VLC, and TGOM is the mean computational time of GOM.
Figure 13 shows that the proposed system based on the combination of VLC and GOM almost outperforms the GOM algorithm on each probe set.

Examples of Extended YaleB Database Images.
Figure 14 shows that the proposed system based on the combination of VLC and GOM almost outperforms the GOM algorithm on the whole FERET database (see Figure 15).

Results on Each Probe Set of FERET.
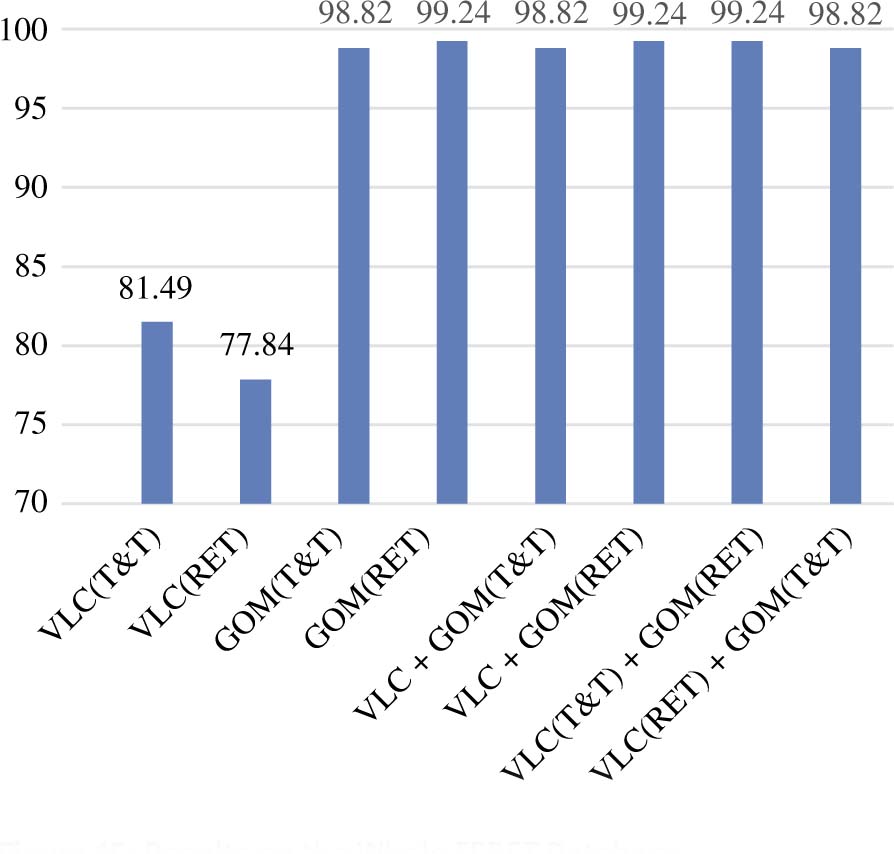
Results on the Whole FERET Database.
Table 4 shows the recognition rate of the proposed technique on the extended YaleB database using one image for the training and the rest for the testing. This table shows that our system outperforms other systems, although we only used one image for the training stage.
5 Conclusion
We combined the VLC and GOM feature extraction techniques in order to reduce the computational time and improve the accuracy of our face recognition system. Before each extraction technique, a preprocessing step was performed. We processed eight test scenarios to compare the effect of the preprocessing techniques on the performance of our system.
The results clearly showed that combining Tan and Triggs with the VLC and retina modeling with the GOM outperformed the other combinations on all the probe sets of the FERET database.
In this work, we proposed a new face recognition system that combines the VLC and GOM as feature extractions. This system outperforms systems based on the GOM technique in recognition rate and computation time.
Despite combining the GOM and VLC, the computation time for the system was still important due to the use of the Gabor wavelet. Our next work shall consist in a face recognition system that maintains the recognition rate performed by GOM and VLC and reduce the computation time.
Bibliography
[1] A. Alfalou and C. Brosseau, Understanding correlation techniques for face recognition: from basics to applications, in: Oravec, M. (ed.), Face Recognition, IntechOpen, Rijeka, Croatia, 2010. doi: 10.5772/8935. Available from: https://www.intechopen.com/books/face-recognition/understanding-correlation-techniques-for-face-recognition-from-basics-to-applications.10.5772/8935Search in Google Scholar
[2] A. Blake and M. Isard, Active shape models. In: Active Contours. Springer, London, 1998.10.1007/978-1-4471-1555-7_2Search in Google Scholar
[3] X. Cao, Y. Wei, F. Wen and J. Sun, Face alignment by explicit shape regression, Int. J. Comput. Vis. 107 (2013), 177–190.10.1007/s11263-013-0667-3Search in Google Scholar
[4] Z. Chai, Z. Sun, H. Mendez-Vazquez, R. He and T. Tan, Gabor ordinal measures for face recognition, IEEE Trans. Inf. Foren. Sec. 9 (2014), 14–26.10.1109/TIFS.2013.2290064Search in Google Scholar
[5] T. Cootes, G. Edwards and C. Taylor, Active appearance models, IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 23 (2001), 681–685.10.1007/BFb0054760Search in Google Scholar
[6] J. Daugman, Two-dimensional spectral analysis of cortical receptive field profiles, Vis. Res. 20 (1980), 847–856.10.1016/0042-6989(80)90065-6Search in Google Scholar
[7] J. Daugman, Uncertainty relation for resolution in space, spatial frequency, and orientation optimized by two-dimensional visual cortical filters, J. Opt. Soc. Am A 2 (1985), 1160.10.1364/JOSAA.2.001160Search in Google Scholar
[8] M. Elbouz, F. Bouzidi, A. Alfalou, C. Brosseau, I. Leonard and B. Benkelfat, Adapted all-numerical correlator for face recognition applications, Opt. l Pattern Recognit. XXIV (2013), 874807-1–874807-8.10.1117/12.2014383Search in Google Scholar
[9] A. Ghorbel, I. Tajouri, W. Aydi and N. Masmoudi, A comparative study of GOM, uLBP, VLC and fractional Eigenfaces for face recognition, in: 2016 International Image Processing, Applications And Systems (IPAS), pp. 1–5, IEEE, Hammamet, Tunisia, 2016.10.1109/IPAS.2016.7880143Search in Google Scholar
[10] R. He, T. Tan, L. Davis and Z. Sun, Learning structured ordinal measures for video based face recognition, Pattern Recognit. 75 (2018), 4–14.10.1016/j.patcog.2017.02.005Search in Google Scholar
[11] Z. Jiang, Z. Lin and L. Davis, Label Consistent K-SVD: learning a discriminative dictionary for recognition, IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35 (2013), 2651–2664.10.1109/TPAMI.2013.88Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] M. Lades, J. Vorbruggen, J. Buhmann, J. Lange, C. von der Malsburg, R. Wurtz and W. Konen, Distortion invariant object recognition in the dynamic link architecture, IEEE Trans. Comput. 42 (1993), 300–311.10.1109/12.210173Search in Google Scholar
[13] K. Lee, J. Ho and D. Kriegman, Acquiring linear subspaces for face recognition under variable lighting, IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 27 (2005), 684–698.10.1109/TPAMI.2005.92Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] P. Phillips, H. Moon, S. Rizvi and P. Rauss, The FERET evaluation methodology for face-recognition algorithms, IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 22 (2000), 1090–1104.10.6028/NIST.IR.6264Search in Google Scholar
[15] Á. Serrano, I. de Diego C. Conde and E. Cabello, Recent advances in face biometrics with Gabor wavelets: a review, Pattern Recognit. Lett. 31 (2010), 372–381.10.1016/j.patrec.2009.11.002Search in Google Scholar
[16] S. Shekhar, V. M. Patel and R. Chellappa, Analysis sparse coding models for image-based classification, in: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 5207–5211, IEEE, 2014. doi: 10.1109/icip.2014.7026054.doi: 10.1109/icip.2014.7026054Search in Google Scholar
[17] L. Shen and L. Bai, A review on Gabor wavelets for face recognition, Pattern Anal. App. 9 (2006), 273–292.10.1007/s10044-006-0033-ySearch in Google Scholar
[18] Y. Sun, X. Wang and X. Tang, Deep convolutional network cascade for facial point detection, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3476–3483, IEEE, Portland, OR, 2013.10.1109/CVPR.2013.446Search in Google Scholar
[19] T. Tan and Z. Sun, Ordinal representations for biometrics recognition, in: 15th European Signal Processing Conference, IEEE, Paris, France, 2007.Search in Google Scholar
[20] X. Tan and B. Triggs, Fusing Gabor and LBP feature sets for kernel-based face recognition, in: International Workshop on Analysis and Modeling of Faces and Gestures, pp. 235–249, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2007.10.1007/978-3-540-75690-3_18Search in Google Scholar
[21] X. Tan and B. Triggs, Enhanced local texture feature sets for face recognition under difficult lighting conditions, IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19 (2010), 1635–1650.10.1007/978-3-540-75690-3_13Search in Google Scholar
[22] W. Tang, A. Panahi, H. Krim and L. Dai, Structured analysis dictionary learning for image classification (2018). http://arxiv.org/1805.00597.10.1109/ICASSP.2018.8461613Search in Google Scholar
[23] N.-S. Vu and A. Caplier, Illumination-robust face recognition using retina modeling, in: 2009 16th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 3289–3292, IEEE, Cairo, Egypt, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
[24] J. Wright, A. Yang, A. Ganesh, S. Sastry and Y. Ma, Robust face recognition via sparse representation, IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 31 (2009), 210–227.10.1109/AFGR.2008.4813404Search in Google Scholar
[25] E. Zhou, H. Fan, Z. Cao, Y. Jiang and Q. Yin, Extensive facial landmark localization with coarse-to-fine convolutional network cascade, in: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, pp. 386–391, IEEE, Sydney, NSW, 2013.10.1109/ICCVW.2013.58Search in Google Scholar
©2020 Walter de Gruyter GmbH, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- An Optimized K-Harmonic Means Algorithm Combined with Modified Particle Swarm Optimization and Cuckoo Search Algorithm
- Texture Feature Extraction Using Intuitionistic Fuzzy Local Binary Pattern
- Leaf Disease Segmentation From Agricultural Images via Hybridization of Active Contour Model and OFA
- Deadline Constrained Task Scheduling Method Using a Combination of Center-Based Genetic Algorithm and Group Search Optimization
- Efficient Classification of DDoS Attacks Using an Ensemble Feature Selection Algorithm
- Distributed Multi-agent Bidding-Based Approach for the Collaborative Mapping of Unknown Indoor Environments by a Homogeneous Mobile Robot Team
- An Efficient Technique for Three-Dimensional Image Visualization Through Two-Dimensional Images for Medical Data
- Combined Multi-Agent Method to Control Inter-Department Common Events Collision for University Courses Timetabling
- An Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Global Multidimensional Optimization
- A Kernel Probabilistic Model for Semi-supervised Co-clustering Ensemble
- Pythagorean Hesitant Fuzzy Information Aggregation and Their Application to Multi-Attribute Group Decision-Making Problems
- Using an Efficient Optimal Classifier for Soil Classification in Spatial Data Mining Over Big Data
- A Bayesian Multiresolution Approach for Noise Removal in Medical Magnetic Resonance Images
- Gbest-Guided Artificial Bee Colony Optimization Algorithm-Based Optimal Incorporation of Shunt Capacitors in Distribution Networks under Load Growth
- Graded Soft Expert Set as a Generalization of Hesitant Fuzzy Set
- Universal Liver Extraction Algorithm: An Improved Chan–Vese Model
- Software Effort Estimation Using Modified Fuzzy C Means Clustering and Hybrid ABC-MCS Optimization in Neural Network
- Handwritten Indic Script Recognition Based on the Dempster–Shafer Theory of Evidence
- An Integrated Intuitionistic Fuzzy AHP and TOPSIS Approach to Evaluation of Outsource Manufacturers
- Automatically Assess Day Similarity Using Visual Lifelogs
- A Novel Bio-Inspired Algorithm Based on Social Spiders for Improving Performance and Efficiency of Data Clustering
- Discriminative Training Using Noise Robust Integrated Features and Refined HMM Modeling
- Self-Adaptive Mussels Wandering Optimization Algorithm with Application for Artificial Neural Network Training
- A Framework for Image Alignment of TerraSAR-X Images Using Fractional Derivatives and View Synthesis Approach
- Intelligent Systems for Structural Damage Assessment
- Some Interval-Valued Pythagorean Fuzzy Einstein Weighted Averaging Aggregation Operators and Their Application to Group Decision Making
- Fuzzy Adaptive Genetic Algorithm for Improving the Solution of Industrial Optimization Problems
- Approach to Multiple Attribute Group Decision Making Based on Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Aggregation Operators
- Cubic Ordered Weighted Distance Operator and Application in Group Decision-Making
- Fault Signal Recognition in Power Distribution System using Deep Belief Network
- Selector: PSO as Model Selector for Dual-Stage Diabetes Network
- Oppositional Gravitational Search Algorithm and Artificial Neural Network-based Classification of Kidney Images
- Improving Image Search through MKFCM Clustering Strategy-Based Re-ranking Measure
- Sparse Decomposition Technique for Segmentation and Compression of Compound Images
- Automatic Genetic Fuzzy c-Means
- Harmony Search Algorithm for Patient Admission Scheduling Problem
- Speech Signal Compression Algorithm Based on the JPEG Technique
- i-Vector-Based Speaker Verification on Limited Data Using Fusion Techniques
- Prediction of User Future Request Utilizing the Combination of Both ANN and FCM in Web Page Recommendation
- Presentation of ACT/R-RBF Hybrid Architecture to Develop Decision Making in Continuous and Non-continuous Data
- An Overview of Segmentation Algorithms for the Analysis of Anomalies on Medical Images
- Blind Restoration Algorithm Using Residual Measures for Motion-Blurred Noisy Images
- Extreme Learning Machine for Credit Risk Analysis
- A Genetic Algorithm Approach for Group Recommender System Based on Partial Rankings
- Improvements in Spoken Query System to Access the Agricultural Commodity Prices and Weather Information in Kannada Language/Dialects
- A One-Pass Approach for Slope and Slant Estimation of Tri-Script Handwritten Words
- Secure Communication through MultiAgent System-Based Diabetes Diagnosing and Classification
- Development of a Two-Stage Segmentation-Based Word Searching Method for Handwritten Document Images
- Pythagorean Fuzzy Einstein Hybrid Averaging Aggregation Operator and its Application to Multiple-Attribute Group Decision Making
- Ensembles of Text and Time-Series Models for Automatic Generation of Financial Trading Signals from Social Media Content
- A Flame Detection Method Based on Novel Gradient Features
- Modeling and Optimization of a Liquid Flow Process using an Artificial Neural Network-Based Flower Pollination Algorithm
- Spectral Graph-based Features for Recognition of Handwritten Characters: A Case Study on Handwritten Devanagari Numerals
- A Grey Wolf Optimizer for Text Document Clustering
- Classification of Masses in Digital Mammograms Using the Genetic Ensemble Method
- A Hybrid Grey Wolf Optimiser Algorithm for Solving Time Series Classification Problems
- Gray Method for Multiple Attribute Decision Making with Incomplete Weight Information under the Pythagorean Fuzzy Setting
- Multi-Agent System Based on the Extreme Learning Machine and Fuzzy Control for Intelligent Energy Management in Microgrid
- Deep CNN Combined With Relevance Feedback for Trademark Image Retrieval
- Cognitively Motivated Query Abstraction Model Based on Associative Root-Pattern Networks
- Improved Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System Using Gray Wolf Optimization: A Case Study in Predicting Biochar Yield
- Predict Forex Trend via Convolutional Neural Networks
- Optimizing Integrated Features for Hindi Automatic Speech Recognition System
- A Novel Weakest t-norm based Fuzzy Fault Tree Analysis Through Qualitative Data Processing and Its Application in System Reliability Evaluation
- FCNB: Fuzzy Correlative Naive Bayes Classifier with MapReduce Framework for Big Data Classification
- A Modified Jaya Algorithm for Mixed-Variable Optimization Problems
- An Improved Robust Fuzzy Algorithm for Unsupervised Learning
- Hybridizing the Cuckoo Search Algorithm with Different Mutation Operators for Numerical Optimization Problems
- An Efficient Lossless ROI Image Compression Using Wavelet-Based Modified Region Growing Algorithm
- Predicting Automatic Trigger Speed for Vehicle-Activated Signs
- Group Recommender Systems – An Evolutionary Approach Based on Multi-expert System for Consensus
- Enriching Documents by Linking Salient Entities and Lexical-Semantic Expansion
- A New Feature Selection Method for Sentiment Analysis in Short Text
- Optimizing Software Modularity with Minimum Possible Variations
- Optimizing the Self-Organizing Team Size Using a Genetic Algorithm in Agile Practices
- Aspect-Oriented Sentiment Analysis: A Topic Modeling-Powered Approach
- Feature Pair Index Graph for Clustering
- Tangramob: An Agent-Based Simulation Framework for Validating Urban Smart Mobility Solutions
- A New Algorithm Based on Magic Square and a Novel Chaotic System for Image Encryption
- Video Steganography Using Knight Tour Algorithm and LSB Method for Encrypted Data
- Clay-Based Brick Porosity Estimation Using Image Processing Techniques
- AGCS Technique to Improve the Performance of Neural Networks
- A Color Image Encryption Technique Based on Bit-Level Permutation and Alternate Logistic Maps
- A Hybrid of Deep CNN and Bidirectional LSTM for Automatic Speech Recognition
- Database Creation and Dialect-Wise Comparative Analysis of Prosodic Features for Punjabi Language
- Trapezoidal Linguistic Cubic Fuzzy TOPSIS Method and Application in a Group Decision Making Program
- Histopathological Image Segmentation Using Modified Kernel-Based Fuzzy C-Means and Edge Bridge and Fill Technique
- Proximal Support Vector Machine-Based Hybrid Approach for Edge Detection in Noisy Images
- Early Detection of Parkinson’s Disease by Using SPECT Imaging and Biomarkers
- Image Compression Based on Block SVD Power Method
- Noise Reduction Using Modified Wiener Filter in Digital Hearing Aid for Speech Signal Enhancement
- Secure Fingerprint Authentication Using Deep Learning and Minutiae Verification
- The Use of Natural Language Processing Approach for Converting Pseudo Code to C# Code
- Non-word Attributes’ Efficiency in Text Mining Authorship Prediction
- Design and Evaluation of Outlier Detection Based on Semantic Condensed Nearest Neighbor
- An Efficient Quality Inspection of Food Products Using Neural Network Classification
- Opposition Intensity-Based Cuckoo Search Algorithm for Data Privacy Preservation
- M-HMOGA: A New Multi-Objective Feature Selection Algorithm for Handwritten Numeral Classification
- Analogy-Based Approaches to Improve Software Project Effort Estimation Accuracy
- Linear Regression Supporting Vector Machine and Hybrid LOG Filter-Based Image Restoration
- Fractional Fuzzy Clustering and Particle Whale Optimization-Based MapReduce Framework for Big Data Clustering
- Implementation of Improved Ship-Iceberg Classifier Using Deep Learning
- Hybrid Approach for Face Recognition from a Single Sample per Person by Combining VLC and GOM
- Polarity Analysis of Customer Reviews Based on Part-of-Speech Subcategory
- A 4D Trajectory Prediction Model Based on the BP Neural Network
- A Blind Medical Image Watermarking for Secure E-Healthcare Application Using Crypto-Watermarking System
- Discriminating Healthy Wheat Grains from Grains Infected with Fusarium graminearum Using Texture Characteristics of Image-Processing Technique, Discriminant Analysis, and Support Vector Machine Methods
- License Plate Recognition in Urban Road Based on Vehicle Tracking and Result Integration
- Binary Genetic Swarm Optimization: A Combination of GA and PSO for Feature Selection
- Enhanced Twitter Sentiment Analysis Using Hybrid Approach and by Accounting Local Contextual Semantic
- Cloud Security: LKM and Optimal Fuzzy System for Intrusion Detection in Cloud Environment
- Power Average Operators of Trapezoidal Cubic Fuzzy Numbers and Application to Multi-attribute Group Decision Making
Articles in the same Issue
- An Optimized K-Harmonic Means Algorithm Combined with Modified Particle Swarm Optimization and Cuckoo Search Algorithm
- Texture Feature Extraction Using Intuitionistic Fuzzy Local Binary Pattern
- Leaf Disease Segmentation From Agricultural Images via Hybridization of Active Contour Model and OFA
- Deadline Constrained Task Scheduling Method Using a Combination of Center-Based Genetic Algorithm and Group Search Optimization
- Efficient Classification of DDoS Attacks Using an Ensemble Feature Selection Algorithm
- Distributed Multi-agent Bidding-Based Approach for the Collaborative Mapping of Unknown Indoor Environments by a Homogeneous Mobile Robot Team
- An Efficient Technique for Three-Dimensional Image Visualization Through Two-Dimensional Images for Medical Data
- Combined Multi-Agent Method to Control Inter-Department Common Events Collision for University Courses Timetabling
- An Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Global Multidimensional Optimization
- A Kernel Probabilistic Model for Semi-supervised Co-clustering Ensemble
- Pythagorean Hesitant Fuzzy Information Aggregation and Their Application to Multi-Attribute Group Decision-Making Problems
- Using an Efficient Optimal Classifier for Soil Classification in Spatial Data Mining Over Big Data
- A Bayesian Multiresolution Approach for Noise Removal in Medical Magnetic Resonance Images
- Gbest-Guided Artificial Bee Colony Optimization Algorithm-Based Optimal Incorporation of Shunt Capacitors in Distribution Networks under Load Growth
- Graded Soft Expert Set as a Generalization of Hesitant Fuzzy Set
- Universal Liver Extraction Algorithm: An Improved Chan–Vese Model
- Software Effort Estimation Using Modified Fuzzy C Means Clustering and Hybrid ABC-MCS Optimization in Neural Network
- Handwritten Indic Script Recognition Based on the Dempster–Shafer Theory of Evidence
- An Integrated Intuitionistic Fuzzy AHP and TOPSIS Approach to Evaluation of Outsource Manufacturers
- Automatically Assess Day Similarity Using Visual Lifelogs
- A Novel Bio-Inspired Algorithm Based on Social Spiders for Improving Performance and Efficiency of Data Clustering
- Discriminative Training Using Noise Robust Integrated Features and Refined HMM Modeling
- Self-Adaptive Mussels Wandering Optimization Algorithm with Application for Artificial Neural Network Training
- A Framework for Image Alignment of TerraSAR-X Images Using Fractional Derivatives and View Synthesis Approach
- Intelligent Systems for Structural Damage Assessment
- Some Interval-Valued Pythagorean Fuzzy Einstein Weighted Averaging Aggregation Operators and Their Application to Group Decision Making
- Fuzzy Adaptive Genetic Algorithm for Improving the Solution of Industrial Optimization Problems
- Approach to Multiple Attribute Group Decision Making Based on Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Aggregation Operators
- Cubic Ordered Weighted Distance Operator and Application in Group Decision-Making
- Fault Signal Recognition in Power Distribution System using Deep Belief Network
- Selector: PSO as Model Selector for Dual-Stage Diabetes Network
- Oppositional Gravitational Search Algorithm and Artificial Neural Network-based Classification of Kidney Images
- Improving Image Search through MKFCM Clustering Strategy-Based Re-ranking Measure
- Sparse Decomposition Technique for Segmentation and Compression of Compound Images
- Automatic Genetic Fuzzy c-Means
- Harmony Search Algorithm for Patient Admission Scheduling Problem
- Speech Signal Compression Algorithm Based on the JPEG Technique
- i-Vector-Based Speaker Verification on Limited Data Using Fusion Techniques
- Prediction of User Future Request Utilizing the Combination of Both ANN and FCM in Web Page Recommendation
- Presentation of ACT/R-RBF Hybrid Architecture to Develop Decision Making in Continuous and Non-continuous Data
- An Overview of Segmentation Algorithms for the Analysis of Anomalies on Medical Images
- Blind Restoration Algorithm Using Residual Measures for Motion-Blurred Noisy Images
- Extreme Learning Machine for Credit Risk Analysis
- A Genetic Algorithm Approach for Group Recommender System Based on Partial Rankings
- Improvements in Spoken Query System to Access the Agricultural Commodity Prices and Weather Information in Kannada Language/Dialects
- A One-Pass Approach for Slope and Slant Estimation of Tri-Script Handwritten Words
- Secure Communication through MultiAgent System-Based Diabetes Diagnosing and Classification
- Development of a Two-Stage Segmentation-Based Word Searching Method for Handwritten Document Images
- Pythagorean Fuzzy Einstein Hybrid Averaging Aggregation Operator and its Application to Multiple-Attribute Group Decision Making
- Ensembles of Text and Time-Series Models for Automatic Generation of Financial Trading Signals from Social Media Content
- A Flame Detection Method Based on Novel Gradient Features
- Modeling and Optimization of a Liquid Flow Process using an Artificial Neural Network-Based Flower Pollination Algorithm
- Spectral Graph-based Features for Recognition of Handwritten Characters: A Case Study on Handwritten Devanagari Numerals
- A Grey Wolf Optimizer for Text Document Clustering
- Classification of Masses in Digital Mammograms Using the Genetic Ensemble Method
- A Hybrid Grey Wolf Optimiser Algorithm for Solving Time Series Classification Problems
- Gray Method for Multiple Attribute Decision Making with Incomplete Weight Information under the Pythagorean Fuzzy Setting
- Multi-Agent System Based on the Extreme Learning Machine and Fuzzy Control for Intelligent Energy Management in Microgrid
- Deep CNN Combined With Relevance Feedback for Trademark Image Retrieval
- Cognitively Motivated Query Abstraction Model Based on Associative Root-Pattern Networks
- Improved Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System Using Gray Wolf Optimization: A Case Study in Predicting Biochar Yield
- Predict Forex Trend via Convolutional Neural Networks
- Optimizing Integrated Features for Hindi Automatic Speech Recognition System
- A Novel Weakest t-norm based Fuzzy Fault Tree Analysis Through Qualitative Data Processing and Its Application in System Reliability Evaluation
- FCNB: Fuzzy Correlative Naive Bayes Classifier with MapReduce Framework for Big Data Classification
- A Modified Jaya Algorithm for Mixed-Variable Optimization Problems
- An Improved Robust Fuzzy Algorithm for Unsupervised Learning
- Hybridizing the Cuckoo Search Algorithm with Different Mutation Operators for Numerical Optimization Problems
- An Efficient Lossless ROI Image Compression Using Wavelet-Based Modified Region Growing Algorithm
- Predicting Automatic Trigger Speed for Vehicle-Activated Signs
- Group Recommender Systems – An Evolutionary Approach Based on Multi-expert System for Consensus
- Enriching Documents by Linking Salient Entities and Lexical-Semantic Expansion
- A New Feature Selection Method for Sentiment Analysis in Short Text
- Optimizing Software Modularity with Minimum Possible Variations
- Optimizing the Self-Organizing Team Size Using a Genetic Algorithm in Agile Practices
- Aspect-Oriented Sentiment Analysis: A Topic Modeling-Powered Approach
- Feature Pair Index Graph for Clustering
- Tangramob: An Agent-Based Simulation Framework for Validating Urban Smart Mobility Solutions
- A New Algorithm Based on Magic Square and a Novel Chaotic System for Image Encryption
- Video Steganography Using Knight Tour Algorithm and LSB Method for Encrypted Data
- Clay-Based Brick Porosity Estimation Using Image Processing Techniques
- AGCS Technique to Improve the Performance of Neural Networks
- A Color Image Encryption Technique Based on Bit-Level Permutation and Alternate Logistic Maps
- A Hybrid of Deep CNN and Bidirectional LSTM for Automatic Speech Recognition
- Database Creation and Dialect-Wise Comparative Analysis of Prosodic Features for Punjabi Language
- Trapezoidal Linguistic Cubic Fuzzy TOPSIS Method and Application in a Group Decision Making Program
- Histopathological Image Segmentation Using Modified Kernel-Based Fuzzy C-Means and Edge Bridge and Fill Technique
- Proximal Support Vector Machine-Based Hybrid Approach for Edge Detection in Noisy Images
- Early Detection of Parkinson’s Disease by Using SPECT Imaging and Biomarkers
- Image Compression Based on Block SVD Power Method
- Noise Reduction Using Modified Wiener Filter in Digital Hearing Aid for Speech Signal Enhancement
- Secure Fingerprint Authentication Using Deep Learning and Minutiae Verification
- The Use of Natural Language Processing Approach for Converting Pseudo Code to C# Code
- Non-word Attributes’ Efficiency in Text Mining Authorship Prediction
- Design and Evaluation of Outlier Detection Based on Semantic Condensed Nearest Neighbor
- An Efficient Quality Inspection of Food Products Using Neural Network Classification
- Opposition Intensity-Based Cuckoo Search Algorithm for Data Privacy Preservation
- M-HMOGA: A New Multi-Objective Feature Selection Algorithm for Handwritten Numeral Classification
- Analogy-Based Approaches to Improve Software Project Effort Estimation Accuracy
- Linear Regression Supporting Vector Machine and Hybrid LOG Filter-Based Image Restoration
- Fractional Fuzzy Clustering and Particle Whale Optimization-Based MapReduce Framework for Big Data Clustering
- Implementation of Improved Ship-Iceberg Classifier Using Deep Learning
- Hybrid Approach for Face Recognition from a Single Sample per Person by Combining VLC and GOM
- Polarity Analysis of Customer Reviews Based on Part-of-Speech Subcategory
- A 4D Trajectory Prediction Model Based on the BP Neural Network
- A Blind Medical Image Watermarking for Secure E-Healthcare Application Using Crypto-Watermarking System
- Discriminating Healthy Wheat Grains from Grains Infected with Fusarium graminearum Using Texture Characteristics of Image-Processing Technique, Discriminant Analysis, and Support Vector Machine Methods
- License Plate Recognition in Urban Road Based on Vehicle Tracking and Result Integration
- Binary Genetic Swarm Optimization: A Combination of GA and PSO for Feature Selection
- Enhanced Twitter Sentiment Analysis Using Hybrid Approach and by Accounting Local Contextual Semantic
- Cloud Security: LKM and Optimal Fuzzy System for Intrusion Detection in Cloud Environment
- Power Average Operators of Trapezoidal Cubic Fuzzy Numbers and Application to Multi-attribute Group Decision Making

