Abstract
Polyacrylate resin composite materials with the mineral exhibit super water absorbency and good degradation ability. In this work, expanded perlite and sodium polyacrylate resin composite materials have been prepared with ceric ammonium nitrate (CAN), N,N’-methylene bisacrylamide (MBA), tapioca starch, and expanded perlite. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and field emission scanning electron microscopy (SEM) are used to characterize the bonds absorption peaks and morphologies. The results suggest that the expanded perlite can graft on sodium polyacrylate resin, and the optimal distilled water and 0.9% NaCl absorbency are 1079 and 253 g/g when the expanded perlite content is 8 wt%, respectively. The swelling water model of the composite materials is firstly simulated to be Voigt-based model. In addition, the composite materials absorbency that is influenced by special characteristics of the expanded perlite has been shown.
1 Introduction
Polyacrylate resin is one of the important superabsorbent polymers (SAPs) because of their broad sources and super solution absorbency, which have the potential water absorbency of hundreds times that of their own weight with three-dimensionally net structure, and they can be always used in agriculture (i.e., water retention, soil nutrient reserves, and low soil compaction), sanitary products, food and drug preservation (1,2). However, the traditional polyacrylate resin has some drawbacks, such as not very fast swelling rates, weak mechanical properties, and poor degradation ability, which hinder their application in the field of agriculture distinctly (3). Therefore, many researchers had focused on polyacrylate resin composite materials with clay, montmorillonite, or kieselguhr mineral to overcome their disadvantages in recent years (4, 5, 6). Additionally, the starch could graft on polyacrylate resin by chains with their quantities of –OH for the three-dimensionally net structure, resulting in the super water absorbency and good degradation ability (1,7, 8, 9).
Expanded perlite, possessing a similar aluminosilicate structure like the other mineral, features two-dimensional layered and three-dimensional pore structure with through holes and thin walls (10). The expanded perlite and polyacrylate resin composite materials were seldom reported, although they might have potential larger water absorbency than the other mineral composite materials (~600 g/g) (4, 5, 6,11). Further, Voigt model was used to simulate creep process of superpolymer, but it was seldom fitted with the mineral and sodium polyacrylate resin composite materials, because the composite materials not featured linear viscoelastic behavior basically (12). Though the composite materials swelling water model was essential for their actual application, the Voigt-based model was rarely reported before (13).
In this paper, the expanded perlite and sodium polyacrylate resin composite materials were reported. The influences of various contents of expanded perlite on composite materials structure and solution absorbency were fully discussed. Moreover, the swelling water model was simulated under the swelling rate of composite materials with the optimum formula, which would give guidance on environmental friendly agricultural application.
2 Experimental
2.1 Preparation
The expanded perlite and sodium polyacrylate resin composite materials were synthesized by solution polymerization. The expanded perlite was prepared with perlite mineral by an expanded process under 1180°C, which was mined in Shangtianti, Xinyang, P. R. China. The starting raw materials were crylic acid monomer, ceric ammonium nitrate (CAN) initiator, N,N’-methylene bisacrylamide (MBA) cross-linking agent, grafted tapioca starch, NaOH neutralizer, and expanded perlite. Firstly, 62% neutralization of crylic acid was achieved by NaOH solution under −12°C. Secondly, the polycondensation of sodium acrylate was prepared with 0.10 wt% CAN, 1.6 wt% MBA, and 7 wt% tapioca starch under 25°C for 1 h, and then various contents of the expanded perlite (2–12 wt%; 200 mesh) were added into the aforementioned polycondensation under 65°C for 2.5 h in a container under a pressure of ~0.5 bar. Thirdly, the composite materials particles were obtained by shredding and drying process.
2.2 Characterization
The phase of the expanded perlite was characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD; X’Pert PRO) under a 2θ scanning rate of 0.05°/s with Cu-Kα radiation at room temperature. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (SEM; S-4800) was used to detect the composite materials fracture and surface morphologies. The FT-IR (Nicolet IS-50) spectra were investigated the bonds absorption peaks of the materials using KBr pellets. The solution absorbency (Q, g/g) was calculated by the equation, i.e., Q = (m2-m1)/m1, here m1 is the weight of dried composite materials particles, m2 represents the weight of the swelled solution samples after draining for 5 min, all the absorbency results were tested for 5 times in this study.
3 Results and discussion
Figure 1 shows XRD pattern of the expanded perlite. It could be observed the majority phase of the expanded perlite main peaks was SiO2 with hexagonal phase, which was in line with the information of PDF # 79-1910. The impurity phases in the figure were speculated as aluminosilicate compounds in the structure. The expanded perlite fracture SEM image is displayed in Figure 1a It could be seen, the expanded perlite possessed through holes and thin wall characteristics. The special characteristics and phase implied the expanded perlite could elevate the sodium polyacrylate resin water absorbency and enhance mechanic strength after grafting reaction (14).
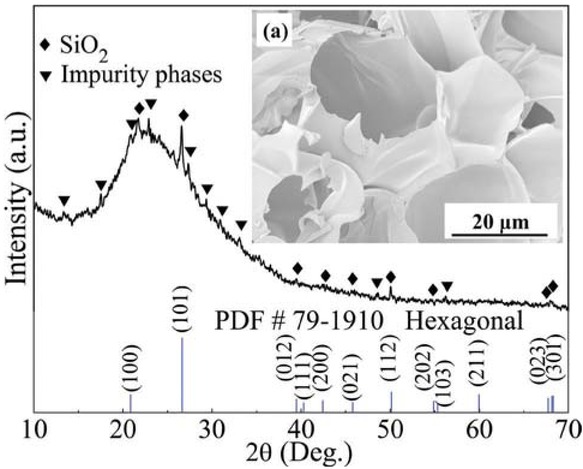
XRD pattern of the expanded perlite. The inset (a) is SEM image of the expanded perlite fracture.
FT-IR spectra of the expanded perlite, sodium polyacrylate resin, and composite materials are given in the Figure 2. From the figure, the characteristic of –OH bond absorbed around 3748 and 2924 cm−1, suggesting all the samples had a capacity for dehydration condensation with –COOH. The absorption peaks around 1541 and 1675 cm−1 indicated the existence of C=O bond in the resin and composite materials. The absorption peaks around 771, 852, and 1040 cm−1 revealed the unique cyclical glucose units in the structure (7,15). In addition, the unique Si–O bonds absorption peaks could be observed around 811 and 1156 cm−1 in the expanded perlite and composite materials. Figures 2a and b show SEM images for the composite materials surface and fracture surface, respectively. It could be observed the expanded perlite was tightly sealed with the resin in the Figure 2a, the holes were highly filled with the resin and two sides of thin walls were also bonded with the resin in the Figure 2b All the detected bonds reaction information and microstructure message implied the expanded perlite grafted on sodium polyacrylate resin, which was in agreement with literature report (15).
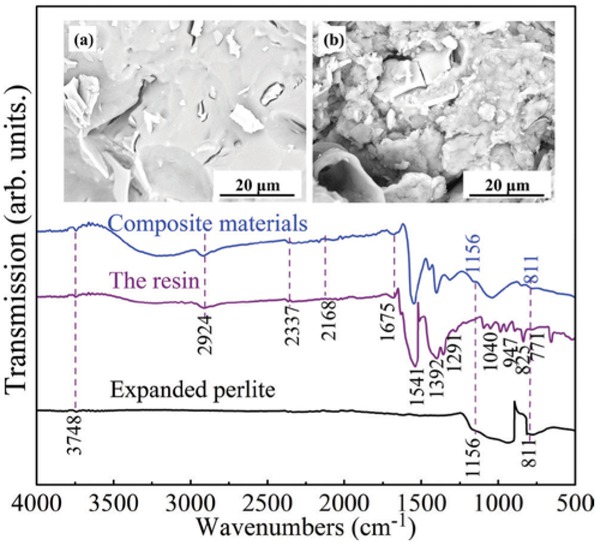
FT-IR patterns of the expanded perlite, sodium polyacrylate resin, and composite materials. SEM images for the inset (a) the composite materials surface and (b) fracture surface.
Figure 3 shows solution absorbency (g/g) of the composite materials under various contents of expanded perlite. The distilled water and 0.9% NaCl absorbency firstly elevated and then decreased with increasing addition of expanded perlite. The optimal distilled water absorbency was 1079 g/g, and the 0.9% NaCl absorbency was 253 g/g when the expanded perlite was 8 wt%. The reason for the varying absorbency was attributed to the varied osmotic pressure in different solution. The elevated solution absorbency of the composite materials with a small addition of expanded perlite was due to its porous structure and their bonding reactions (15). However, the decreased solution absorbency was attributed to the inadequate filled resin in the through holes, formed cracks, or punched channels in the structure of the composite materials.
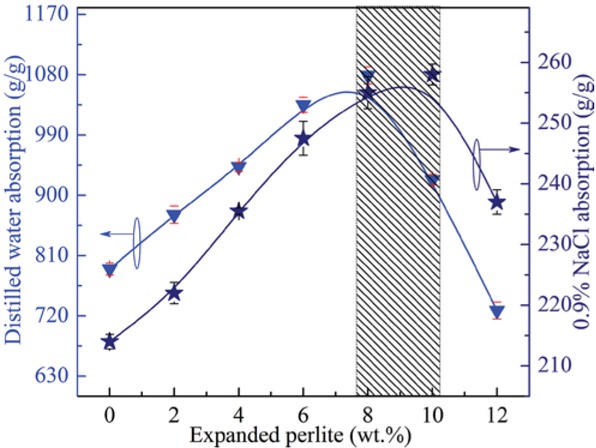
Distilled water and 0.9% NaCl absorbency (g/g) of the composite materials with varying contents of expanded perlite.
The composite materials were prepared with the expanded perlite content was 8 wt%, and their swelling rate (g/g) of the composite materials in distilled water is shown in Figure 4. It could be observed the swelling rate initially exponential growth, and then basically unchanged (1079 g/g) with increasing addition of expanded perlite. The detected swelling property was firstly simulated to be Voigt-based swelling model, the equation and some meanings of the parameters are displayed in the Figure 4, the water swelling rate (S; g/g) of the composite materials water absorbency (P, g/g) at a certain time was also calculated by the solution absorbency in the Experimental section (16). The Voigt-based swelling model of the composite materials could provide guidance on their practical application in swelling and plugging process.
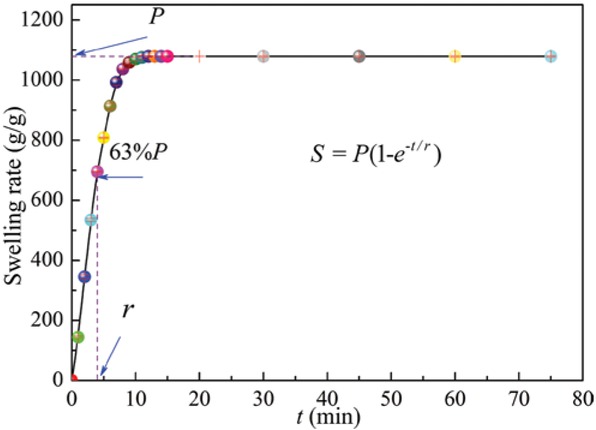
The swelling rate (g/g) of the composite materials in distilled water with expanded perlite content was 8 wt%.
4 Conclusions
The super water and 0.9% NaCl absorbency composite materials were successfully synthesized by solution polymerization with expanded perlite and sodium polyacrylate resin. The composite materials solution absorbency initially enhanced and then deteriorated with increasing expanded perlite contents, and the optimal solution absorbency (i.e., distilled water: 1079 g/g; 0.9% NaCl: 253 g/g) was obtained when the expanded perlite content was 8 wt%, showing a more excellent absorbability than the mineral composite materials. FT-IR and SEM results indicated the expanded perlite could graft on sodium polyacrylate resin for the composite materials. Under the optimum formula, the swelling water model of expanded perlite and sodium polyacrylate resin composite materials was firstly simulated to be Voigt-based model, which could provide guidance in their practical application.
Acknowledgements
The authors are very thankful to the Key Project of Henan Province Colleges and Universities (19A430021), the Special Innovation and Application Project of Xinyang (20180008), the Youth Scholar Sustentation Fund of XYNU (2018-QN-040), and Nanhu Scholars Program for Young Scholars of XYNU for their financial support.
Conflict of interest
Conflict of interest statement: The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
References
1 Fanta G.F., Burr R.C., Russell C.R., Rist C.E., Graft copolymers of starch I Copolymerization of gelatinized wheat starch with acrylonitrile Fractionation of copolymer and effect of solvent on copolymer composition. J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 1966, 10(6), 929-937.10.1002/app.1966.070100610Search in Google Scholar
2 Stout E.I., Trimnell D., Doane W.M., Russell C.R., Graft copolymers of starch-polyacrylonitrile prepared by ferrous ion-hydrogen peroxide initiation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 1977, 21(9), 2565-2573.10.1002/app.1977.070210922Search in Google Scholar
3 Ding R., Gong K., Super-absorbent resin preparation utilizing spent mushroom substrates. J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2013, 130(2), 1098-1103.10.1002/app.39285Search in Google Scholar
4 Bulut Y., Akçay G., Elma D., Serhatli I.E., Synthesis of clay-based superabsorbent composite and its sorption capability. J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 171(1-3), 717-723.10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.067Search in Google Scholar
5 Lee W.F., Yang L.G., Superabsorbent polymeric materials XII Effect of montmorillonite on water absorbency for poly (sodium acrylate) and montmorillonite nanocomposite superabsorbents. J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2010, 92(5), 3422-3429.10.1002/app.20370Search in Google Scholar
6 Pourjavadi A., Ghasemzadeh H., Soleyman R., Synthesis, characterization, and swelling behavior of alginate-g-poly (sodium acrylate)/kaolin superabsorbent hydrogel composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2010, 105(5), 2631-2639.10.1002/app.26345Search in Google Scholar
7 Huang Z.Q., Lu J.P., Li X.H., Tong Z.F., Effect of mechanical activation on physico-chemical properties and structure of cassava starch. Carbohyd. Polym., 2007, 68(1), 128-135.10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.07.017Search in Google Scholar
8 Liu R., Sun W., Zhang Y., Huang Z., Hu H., Zhao M., Preparation of starch dough using damaged cassava starch induced by mechanical activation to develop staple foods: application in crackers. Food Chem., 2019, 271, 284-290.10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.07.202Search in Google Scholar
9 Gilet A., Quettier C., Wiatz V., Bricout H., Ferreira M., Rousseau C., et al., Unconventional media and technologies for starch etherification and esterification. Green Chem., 2018, 20, 1152-1168.10.1039/C7GC03135ASearch in Google Scholar
10 Demirboğa R., Gül R., The effects of expanded perlite aggregate, silica fume and fly ash on the thermal conductivity of lightweight concrete. Cement Concrete. Res., 2003, 33(5), 723-727.10.1016/S0008-8846(02)01032-3Search in Google Scholar
11 Wu J., Wei Y., Lin J., Lin S., Study on starch-graft-acrylamide/mineral powder superabsorbent composite. Polymer, 2003, 44(21), 6513-6520.10.1016/S0032-3861(03)00728-6Search in Google Scholar
12 Li W., Liao P., Oldham T., Pan C., Yuan S., Fortner J.D., Real-time evaluation of natural organic matter deposition processes onto model environmental surfaces. Water Res., 2018, 129, 231-239.10.1016/j.watres.2017.11.024Search in Google Scholar PubMed
13 Ren W., Zhang Y., Peng Z., Zhang Y., Investigation on the water-swelling properties of chlorinated polyethylene modified by in situ formed sodium acrylate. Polym. Test., 2004, 23(7), 809-816.10.1016/j.polymertesting.2004.03.002Search in Google Scholar
14 Barnett D.L., Christie P.A., Eckert L.W., Composites of metal-modified urea-melamine-formaldehyde resins and fillers. US Patent 1978, 4128524.Search in Google Scholar
15 Mohammadzadeh P.P., Peighambardoust S.J., A review on acrylic based hydrogels and their applications in wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manage., 2018, 217, 123-143.10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.03.076Search in Google Scholar PubMed
16 Xia Y., Yang P., Sun Y., Wu Y., Mayers B., Gates B., et al., One-dimensional nanostructures: synthesis, characterization, and applications. Adv. Mater., 2003, 15(5), 353-389.10.1002/adma.200390087Search in Google Scholar
© 2019 Tian et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Special Issue: Polymers and Composite Materials / Guest Editor: Esteban Broitman
- A novel chemical-consolidation sand control composition: Foam amino resin system
- Bottom fire behaviour of thermally thick natural rubber latex foam
- Preparation of polymer–rare earth complexes based on Schiff-base-containing salicylic aldehyde groups attached to the polymer and their fluorescence emission properties
- Study on the unsaturated hydrogen bond behavior of bio-based polyamide 56
- Effect of different nucleating agent on crystallization kinetics and morphology of polypropylene
- Effect of surface modifications on the properties of UHMWPE fibres and their composites
- Thermal degradation kinetics investigation on Nano-ZnO/IFR synergetic flame retarded polypropylene/ethylene-propylene-diene monomer composites processed via different fields
- Properties of carbon black-PEDOT composite prepared via in-situ chemical oxidative polymerization
- Regular articles
- Polyarylene ether nitrile and boron nitride composites: coating with sulfonated polyarylene ether nitrile
- Influence of boric acid on radial structure of oxidized polyacrylonitrile fibers
- Preparing an injectable hydrogel with sodium alginate and Type I collagen to create better MSCs growth microenvironment
- Application of calcium montmorillonite on flame resistance, thermal stability and interfacial adhesion in polystyrene nanocomposites
- Modifications of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC), and nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) for antimicrobial and wound healing applications
- Polycation-globular protein complex: Ionic strength and chain length effects on the structure and properties
- Improving the flame retardancy of ethylene vinyl acetate composites by incorporating layered double hydroxides based on Bayer red mud
- N, N’-sebacic bis(hydrocinnamic acid) dihydrazide: A crystallization accelerator for poly(L-lactic acid)
- The fabrication and characterization of casein/PEO nanofibrous yarn via electrospinning
- Waterborne poly(urethane-urea)s films as a sustained release system for ketoconazole
- Polyimide/mica hybrid films with low coefficient of thermal expansion and low dielectric constant
- Effects of cylindrical-electrode-assisted solution blowing spinning process parameters on polymer nanofiber morphology and microstructure
- Stimuli-responsive DOX release behavior of cross-linked poly(acrylic acid) nanoparticles
- Continuous fabrication of near-infrared light responsive bilayer hydrogel fibers based on microfluidic spinning
- A novel polyamidine-grafted carboxymethylcellulose: Synthesis, characterization and flocculation performance test
- Synthesis of a DOPO-triazine additive and its flame-retardant effect in rigid polyurethane foam
- Novel chitosan and Laponite based nanocomposite for fast removal of Cd(II), methylene blue and Congo red from aqueous solution
- Enhanced thermal oxidative stability of silicone rubber by using cerium-ferric complex oxide as thermal oxidative stabilizer
- Long-term durability antibacterial microcapsules with plant-derived Chinese nutgall and their applications in wound dressing
- Fully water-blown polyisocyanurate-polyurethane foams with improved mechanical properties prepared from aqueous solution of gelling/ blowing and trimerization catalysts
- Preparation of rosin-based polymer microspheres as a stationary phase in high-performance liquid chromatography to separate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and alkaloids
- Effects of chemical modifications on the rheological and the expansion behavior of polylactide (PLA) in foam extrusion
- Enhanced thermal conductivity of flexible h-BN/polyimide composites films with ethyl cellulose
- Maize-like ionic liquid@polyaniline nanocomposites for high performance supercapacitor
- γ-valerolactone (GVL) as a bio-based green solvent and ligand for iron-mediated AGET ATRP
- Revealing key parameters to minimize the diameter of polypropylene fibers produced in the melt electrospinning process
- Preliminary market analysis of PEEK in South America: opportunities and challenges
- Influence of mid-stress on the dynamic fatigue of a light weight EPS bead foam
- Manipulating the thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of polydicyclopentadiene via tuning the stiffness of the incorporated monomers
- Voigt-based swelling water model for super water absorbency of expanded perlite and sodium polyacrylate resin composite materials
- Simplified optimal modeling of resin injection molding process
- Synthesis and characterization of a polyisocyanide with thioether pendant caused an oxidation-triggered helix-to-helix transition
- A glimpse of biodegradable polymers and their biomedical applications
- Development of vegetable oil-based conducting rigid PU foam
- Conetworks on the base of polystyrene with poly(methyl methacrylate) paired polymers
- Effect of coupling agent on the morphological characteristics of natural rubber/silica composites foams
- Impact and shear properties of carbon fabric/ poly-dicyclopentadiene composites manufactured by vacuum‐assisted resin transfer molding
- Effect of resins on the salt spray resistance and wet adhesion of two component waterborne polyurethane coating
- Modifying potato starch by glutaraldehyde and MgCl2 for developing an economical and environment-friendly electrolyte system
- Effect of curing degree on mechanical and thermal properties of 2.5D quartz fiber reinforced boron phenolic composites
- Preparation and performance of polypropylene separator modified by SiO2/PVA layer for lithium batteries
- A simple method for the production of low molecular weight hyaluronan by in situ degradation in fermentation broth
- Curing behaviors, mechanical properties, dynamic mechanical analysis and morphologies of natural rubber vulcanizates containing reclaimed rubber
- Developing an epoxy resin with high toughness for grouting material via co-polymerization method
- Application of antioxidant and ultraviolet absorber into HDPE: Enhanced resistance to UV irradiation
- Study on the synthesis of hexene-1 catalyzed by Ziegler-Natta catalyst and polyhexene-1 applications
- Fabrication and characterization of conductive microcapsule containing phase change material
- Desorption of hydrolyzed poly(AM/DMDAAC) from bentonite and its decomposition in saltwater under high temperatures
- Synthesis, characterization and properties of biomass and carbon dioxide derived polyurethane reactive hot-melt adhesives
- The application of a phosphorus nitrogen flame retardant curing agent in epoxy resin
- High performance polyimide films containing benzimidazole moieties for thin film solar cells
- Rigid polyurethane/expanded vermiculite/ melamine phenylphosphate composite foams with good flame retardant and mechanical properties
- A novel film-forming silicone polymer as shale inhibitor for water-based drilling fluids
- Facile droplet microfluidics preparation of larger PAM-based particles and investigation of their swelling gelation behavior
- Effect of salt and temperature on molecular aggregation behavior of acrylamide polymer
- Dynamics of asymmetric star polymers under coarse grain simulations
- Experimental and numerical analysis of an improved melt-blowing slot-die
Articles in the same Issue
- Special Issue: Polymers and Composite Materials / Guest Editor: Esteban Broitman
- A novel chemical-consolidation sand control composition: Foam amino resin system
- Bottom fire behaviour of thermally thick natural rubber latex foam
- Preparation of polymer–rare earth complexes based on Schiff-base-containing salicylic aldehyde groups attached to the polymer and their fluorescence emission properties
- Study on the unsaturated hydrogen bond behavior of bio-based polyamide 56
- Effect of different nucleating agent on crystallization kinetics and morphology of polypropylene
- Effect of surface modifications on the properties of UHMWPE fibres and their composites
- Thermal degradation kinetics investigation on Nano-ZnO/IFR synergetic flame retarded polypropylene/ethylene-propylene-diene monomer composites processed via different fields
- Properties of carbon black-PEDOT composite prepared via in-situ chemical oxidative polymerization
- Regular articles
- Polyarylene ether nitrile and boron nitride composites: coating with sulfonated polyarylene ether nitrile
- Influence of boric acid on radial structure of oxidized polyacrylonitrile fibers
- Preparing an injectable hydrogel with sodium alginate and Type I collagen to create better MSCs growth microenvironment
- Application of calcium montmorillonite on flame resistance, thermal stability and interfacial adhesion in polystyrene nanocomposites
- Modifications of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC), and nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) for antimicrobial and wound healing applications
- Polycation-globular protein complex: Ionic strength and chain length effects on the structure and properties
- Improving the flame retardancy of ethylene vinyl acetate composites by incorporating layered double hydroxides based on Bayer red mud
- N, N’-sebacic bis(hydrocinnamic acid) dihydrazide: A crystallization accelerator for poly(L-lactic acid)
- The fabrication and characterization of casein/PEO nanofibrous yarn via electrospinning
- Waterborne poly(urethane-urea)s films as a sustained release system for ketoconazole
- Polyimide/mica hybrid films with low coefficient of thermal expansion and low dielectric constant
- Effects of cylindrical-electrode-assisted solution blowing spinning process parameters on polymer nanofiber morphology and microstructure
- Stimuli-responsive DOX release behavior of cross-linked poly(acrylic acid) nanoparticles
- Continuous fabrication of near-infrared light responsive bilayer hydrogel fibers based on microfluidic spinning
- A novel polyamidine-grafted carboxymethylcellulose: Synthesis, characterization and flocculation performance test
- Synthesis of a DOPO-triazine additive and its flame-retardant effect in rigid polyurethane foam
- Novel chitosan and Laponite based nanocomposite for fast removal of Cd(II), methylene blue and Congo red from aqueous solution
- Enhanced thermal oxidative stability of silicone rubber by using cerium-ferric complex oxide as thermal oxidative stabilizer
- Long-term durability antibacterial microcapsules with plant-derived Chinese nutgall and their applications in wound dressing
- Fully water-blown polyisocyanurate-polyurethane foams with improved mechanical properties prepared from aqueous solution of gelling/ blowing and trimerization catalysts
- Preparation of rosin-based polymer microspheres as a stationary phase in high-performance liquid chromatography to separate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and alkaloids
- Effects of chemical modifications on the rheological and the expansion behavior of polylactide (PLA) in foam extrusion
- Enhanced thermal conductivity of flexible h-BN/polyimide composites films with ethyl cellulose
- Maize-like ionic liquid@polyaniline nanocomposites for high performance supercapacitor
- γ-valerolactone (GVL) as a bio-based green solvent and ligand for iron-mediated AGET ATRP
- Revealing key parameters to minimize the diameter of polypropylene fibers produced in the melt electrospinning process
- Preliminary market analysis of PEEK in South America: opportunities and challenges
- Influence of mid-stress on the dynamic fatigue of a light weight EPS bead foam
- Manipulating the thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of polydicyclopentadiene via tuning the stiffness of the incorporated monomers
- Voigt-based swelling water model for super water absorbency of expanded perlite and sodium polyacrylate resin composite materials
- Simplified optimal modeling of resin injection molding process
- Synthesis and characterization of a polyisocyanide with thioether pendant caused an oxidation-triggered helix-to-helix transition
- A glimpse of biodegradable polymers and their biomedical applications
- Development of vegetable oil-based conducting rigid PU foam
- Conetworks on the base of polystyrene with poly(methyl methacrylate) paired polymers
- Effect of coupling agent on the morphological characteristics of natural rubber/silica composites foams
- Impact and shear properties of carbon fabric/ poly-dicyclopentadiene composites manufactured by vacuum‐assisted resin transfer molding
- Effect of resins on the salt spray resistance and wet adhesion of two component waterborne polyurethane coating
- Modifying potato starch by glutaraldehyde and MgCl2 for developing an economical and environment-friendly electrolyte system
- Effect of curing degree on mechanical and thermal properties of 2.5D quartz fiber reinforced boron phenolic composites
- Preparation and performance of polypropylene separator modified by SiO2/PVA layer for lithium batteries
- A simple method for the production of low molecular weight hyaluronan by in situ degradation in fermentation broth
- Curing behaviors, mechanical properties, dynamic mechanical analysis and morphologies of natural rubber vulcanizates containing reclaimed rubber
- Developing an epoxy resin with high toughness for grouting material via co-polymerization method
- Application of antioxidant and ultraviolet absorber into HDPE: Enhanced resistance to UV irradiation
- Study on the synthesis of hexene-1 catalyzed by Ziegler-Natta catalyst and polyhexene-1 applications
- Fabrication and characterization of conductive microcapsule containing phase change material
- Desorption of hydrolyzed poly(AM/DMDAAC) from bentonite and its decomposition in saltwater under high temperatures
- Synthesis, characterization and properties of biomass and carbon dioxide derived polyurethane reactive hot-melt adhesives
- The application of a phosphorus nitrogen flame retardant curing agent in epoxy resin
- High performance polyimide films containing benzimidazole moieties for thin film solar cells
- Rigid polyurethane/expanded vermiculite/ melamine phenylphosphate composite foams with good flame retardant and mechanical properties
- A novel film-forming silicone polymer as shale inhibitor for water-based drilling fluids
- Facile droplet microfluidics preparation of larger PAM-based particles and investigation of their swelling gelation behavior
- Effect of salt and temperature on molecular aggregation behavior of acrylamide polymer
- Dynamics of asymmetric star polymers under coarse grain simulations
- Experimental and numerical analysis of an improved melt-blowing slot-die

