Abstract
Five different solvents (petroleum ether, chloroform, ethyl acetate, acetone, and distilled water) were used to extract antibacterial compounds from pineapple leaf fiber. Compounds extracted using acetone showed the greatest antibacterial effect against Escherichia coli, measured by inhibition zone diameter. Three extraction parameters including temperature, time and solid-liquid ratio were optimized through orthogonal experiment based on single factor investigations for achieving maximum active substance extraction rate and bacteriostatic effect. Results showed that using acetone, the optimum extraction conditions for temperature, time and solid-liquid ratio were 45°C, 8 h, and 1:40 (g/ml), respectively.
1 Introduction
Pineapple (Ananas comosus), belonging to Bromeliaceae family, is a kind of perennial monocotyledon herbaceous plant as well as one of the most known tropical fruits [1]. In China, pineapple is mainly planted in 6 provinces including Hainan, Guangdong, Guangxi, Yunnan, Fujian, and Taiwan. In recent years, the average planting area of pineapple has been maintained at approximately 70 000 hm2[2]. The wasted leaves per mu is about 5~10t, thus national total wasted amount is accumulated to nearly 10,000,000 t per year, leading to large amount of resource waste and eco-environmental pollution [3]. The fiber content in pineapple leaf is only around 1.5% (dry basis). However, extricated fiber from the leaf has similar uses as hemp, and unique advantages. It is prescribed in “Chinese Materia Medica” that pineapple leaf has effects of promoting digestion and anti-diarrhea and is also used to treat summer diarrhea, dyspepsia and gastral cavity pain. There have been studies indicating that with three major functions including natural antimicrobial function, anti-mite function and dispelling unpleasant smells [4-5], the fiber has a stronger antibacterial property than existing bast-fibres, and this is the significance which lies in the qualitative and quantitative researches on effective chemical components included in pineapple leaf fiber. This experiment focuses on the optimization of extrication technology for antibacterial components in pineapple leaf fiber, providing a theoretical basis and basic data for separation and purification of the active substances from pineapple leaf fiber.
2 Material and Methods
2.1 Material
Pineapple leaves were obtained from a planting base in Xuwen County, Zhanjiang City. Fiber was extracted from the leaves using a self-developed semi-automatic extractor, and then dried and stored. Escherichia coli ATCC25922 was used to test suspected antibacterial substances from extracted fiber.
2.2 Experimental method
2.2.1 Preparation of polar crude extracts
Dry fibers were ground into powder and 10 g were placed in each of five 500 mL round-bottom flasks. 400 mL of a single solvent (one of: petroleum ether, chloroform, ethyl acetate, acetone, or distilled water) was added to each flask, which were placed in a water bath, heated for 2 h, and cooled to 25°C. The mixtures were filtered by qualitative filter paper and rotating evaporation concentrated into extractum which was put in 10 mL EP tubes and stored in 4°C refrigerator until needed for analysis.
2.2.2 Qualitative analysis and antibacterial tests of chemical components under different polarity sections
Bacteriostatic activity was measured by agar diffusion; qualitative analysis on the 5 extract samples was made using special color developing agents.
2.2.3 Determination of optimal parameter of extrication technology
In single factor experiment, only corresponding acetone solution is added in blank group; by successively changing temperature, reaction time, and solid-liquid ratio, based on Escherichia coli as indicator bacteria as well as extraction yield × bacteriostatic diameter as active tracking indicator, related research and analysis can be performed, moreover the optimal parameters of orthogonal experiment of three factors three levels can be determined.
3 Results and Discussion
3.1 Qualitative analysis and antibacterial test of chemical components under different polarity sections
Escherichia coli was used as an indicator in the antibacterial tests, and the antibacterial activity was measured with the agar diffusion method. Test results are shown in Table 1. Extracts obtained from ethyl acetate, acetone, and distilled water exhibited antibacterial activity, with acetone-extracted samples showing the largest inhibition zone (14.76 mm).
Antibacterial effect of chemical composition of different polarity.
| Extraction agent | petroleum ether (A) | chloroform (B) | ethyl acetate (C) | acetone (D) | distilled water (E) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| diameter of inhibition | 0 | 0 | 10.20 | 14.76 | 12.32 |
| zone (mm) | |||||
| 0 | 0 | 10.10 | 13.56 | 12.10 | |
| 0 | 0 | 9.10 | 13.50 | 11.30 |
Note: inner diameter of Oxford cup is 7.8 mm, outer diameter of Oxford cup is 8.0 mm
Qualitative analysis was applied to the extracts at 5 polarity intervals (A, B, C, D, E) using a special color developing agent. Compounds identified from the extracts are shown in Table 2, and include flavonoid and phenols from samples B, C, D, and E, with D showing the greatest color response. According to related literature reports Cannabis sativa and Apocynum venetum contain flavonoid and phenols [6-7], and both compounds have antibacterial effects, from which we can infer that the antibacterial substances in pineapple leaf fiber were likely two such compounds [8-9].
Qualitative analysis results of pinealpple fiber extracts at 5 polarity intervals (A, B, C, D, E) treated with color developing agents.
| Substance | Reagent | Petroleum ether (A) | Chloroform (B) | Ethyl acetate (C) | Acetone (D) | Distilled water (E) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color development phenomenon | Conclusion | Color development phenomenon | Conclusion | Color development phenomenon | Conclusion | Color development phenomenon | Conclusion | Color development phenomenon | Conclusion | ||
| volatile oil | qualitative filter paper | none | — | oil spot | + | oil spot | + | none | — | oil spot | ++++ |
| anthraquinone | 1%sodium hydroxide | none | — | none | — | none | — | red, disappear after cidification | ++++ | none | — |
| alkaloid | bismuth potassium iodide | none | — | none | — | none | — | none | — | yellow precipitate | ++ |
| phenol | ferric trichloride - 1% potassium ferricyanide | blue spot | ++ | blue spot | ++ | blue spot | ++++ | blue spot | + | blue spot | ++ |
| lactone, coumarin | hydroxylamine hydrochloride | prunosus spot | + | prunosus spot | ++++ | none | — | prunosus spot | ++ | prunosus spot | ++++ |
| saponin | foam test | none | — | none | — | none | — | foam | ++ | none | — |
| cardiac glycosides | Kedde reagent | none | — | none | — | prunosus spot | ++++ | none | — | none | — |
| flavonoid | hydrochloric acid - magnesium powder | none | — | red spot | ++ | red spot | ++++ | red spot | ++ | red spot | ++ |
| organic acid | 0.05% bromophenol blue | none | — | none | — | none | — | blue | ++ | none | — |
| amino acid | ninhydrin | purple ringspot | + | purple ringspot | + | none | — | purple ringspot | ++ | none | — |
| reducing sugar, glycosides with polysaccharide | Fehling reagent | none | — | none | — | none | — | erythrine precipitate | + | none | — |
| steroid and terpenoid | concentrated sulfuric acid | none | — | brown ringspot | ++ | brown ringspot | ++ | brown ringspot | + | brown ringspot | ++ |
| cyanophoric glycoside | picric acid sodium test paper | none | — | none | — | none | — | none | — | none | — |
Note: “++++”—very significant color development, “++”—significant color development, “+”—insignificant color development, “—”no color development
3.2 Single factor experiment result and analysis
3.2.1 The effect of temperature extraction rates and antibacterial
As the acetone-extracted samples demonstrated the greatest antibacterial effect, this solvent was used to determine the effect of temperature on the extraction process. Different temperatures were set using a consistent extraction time of 8 h and a solid-liquid ratio of 1:40. The results are shown in Fig. 1a. The extraction rate increased with the temperature, reaching a peak value at 45°C and then decreasing with the continuous increase of temperature, leveling off at 65°C. Such variation was probably due to the overly high temperature which led to increasing evaporation rate of acetone, thus leading to the decrease of extraction efficiency. On the other hand, the antibacterial effect increased with the temperature, reached a peak value at 55°C, and then with the increase of temperature the inhibitory zone diameter (IZD) decreased, which may have been due to overly high temperature leading to the denaturation of antibacterial substance, and thus damping the antibacterial effect. This experiment was based on extraction rate × bacteriostatic diameter as active tracking indicator, and by comprehensively evaluating the two indexes, 45°C was selected as the optimal temperature for extraction [10-11].
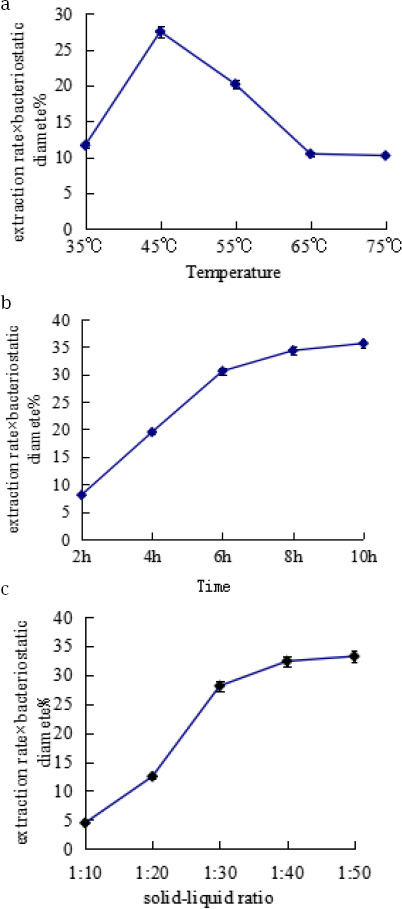
A) Effect of temperature, B) Effect of extracting time C) Effect of solid-liquid ratio on the extraction rate and antibacterial activity of bacteriostatic material from pineapple leaf fiber.
3.2.2 The effect of time on extraction rates and antibacterial
Different extraction times were set using acetone at 45°C and a solid-liquid ratio of 1:40. The results are shown in Fig. 1b. The antibacterial activity reached and maintained a peak at 6h, while extraction rates peaked at 6 h and decreased after 8 h. Through comprehensive consideration of both indexes, the optimal extrication time was determined as 8 h [12].
3.2.3 The influence of solid-liquid ratio extraction rate and antibacterial effect of antibacterial active substances extricated from pineapple leaf fiber
Different solid-liquid ratios were set using acetone at 45°C and 8 h. The results are shown in Fig. 1c. The extraction rate increased with the solid-liquid ratios, reaching a peak value at 1:40 (g/mL). Although the extrication rate continued to increase with the solid-liquid ratio, increases slowed after 1:40. According to Table 3 (b), the active tracking indicator is positively related to solidliquid ratio, and the active tracking indicator remains unchanged when solid-liquid ratio reaches 1:40. Through comprehensive consideration of both indexes, the optimal solid-liquid ratio was determined as 1:40 (g/mL) [13].
Results of orthogonal test for the extrication effect and antibacterial effect of fiber antibacterial material.
| Factor | Temperature (W) | Solid-liquid ratio (L) | Time (T) | IZD (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9.44 | ||
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 10.65 | ||
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 10.9 | ||
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 12.29 | ||
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 10.5 | ||
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 11.5 | ||
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 10.3 | ||
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 9.3 | ||
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 9.0 | ||
| k1 | 10.297 | 10.230 | 10.320 | |||
| k2 | 11.050 | 10.310 | 10.200 | |||
| k3 | 9.700 | 10.507 | 10.527 | |||
| Maximum | 1.350 | 0.277 | 0.327 | |||
| difference | ||||||
| Order of | W > T > L | |||||
| importance | ||||||
| Optimal level | W2 | L3 | T3 | |||
| Optimal | W2T3L3 | |||||
| combination |
3.3 Optimization of extrication condition by orthogonal experiment
Based on the theory of second order regression current rotation design, and through comprehensive analysis of single factor experiment, acetone solution was selected as extraction agent. In the experiment, the three factors (temperature, extrication time, and solid-liquid ration) that significantly influenced the extrication effect and antibacterial effect of fiber antibacterial material were selected, the interaction effects were not considered, and L9 (33) design was selected. The results are shown in Table 3. Through comparing the maximum difference among the three factor including temperature, extraction time, and solid-liquid ratio, it can be concluded that temperature exhibits the greatest effect followed by time and then solid-liquid ratio [14].
Antibacterial test of extract under optimal process condition. To further verify the reliability of optimal process, 10 g fiber was taken and ground into powder, under the condition that solid-liquid ratio was 1:40, temperature was 45°C and extrication time was 8 h. Through agar diffusion method, the antibacterial activity of the extract was measured, and the IZD was measured as 30.15 mm. Therefore, it indicated that the extrication condition optimized by orthogonal experiment was suitable for the extrication of antibacterial substance from pineapple leaf fiber, providing theoretical basis and basic data for future studies on separation and purification [15].
4 Conclusion
This experiment investigated the influences of different solvents on the extraction of antibacterial compounds from pineapple leaf fiber. Through comprehensively considering the antibacterial activity of each extract and relative qualitative analysis, acetone was finally selected as extraction solvent.
The extrication technology was optimized through single factor test and orthogonal experiment, and the optimal extrication condition was determined as 45°C for extrication temperature, 8 h for extrication time, and solid-liquid ratio for 1:40. In addition, the orthogonal experiment was proved to be reasonable and reliable, and can effectively extricate the antibacterial substance from pineapple leaf fiber. The antibacterial test result showed that IZD was as large as 30.15 mm. The order of influence of the three factors is: temperature> time> solid-liquid ratio.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Hainan Natural Science Foundation (No. 20152026), the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (No. 201203021) and the Fundamental Scientific Research Funds for Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences (No. 1630062015014).
Conflict of interest: Authors declare nothing to disclose.
References
[1] Ashraf M.A., Maah M.J., Yusoff I., Study of mango biomass (Mangifera indica L.) as cationic bio-sorbent, Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol, 2010, 7, 581-590.10.1007/BF03326167Search in Google Scholar
[2] Appendino G., Gibbons S., Giana S., Antibacterial cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa: a structure-activity study, J. Nat. Prod, 2008, 71,1427-1430.10.1021/np8002673Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Chen J.H., Zang G.G., Zhao L.N., Li Y.J., Tang H.J., The progress of studies on cannabinoids and suggestion of exploiting hemp resource in China, China Fiber Prod., 2003, 25, 266-271.Search in Google Scholar
[4] Ashraf M.A., Maah M.J., Yusoff I., Mahmood K., Wajid A., Study of biosorptive potential in the peel of Citris reticulatae, Punica grantum, Daucus carota and Momordica charantia, Res. J. Biotechnol., 2011, 6, 51-56.10.5897/AJB11.1090Search in Google Scholar
[5] Deng G.R., Zhang J., Ou Z.Q., Li M.F., Lian W.W., Noise analysis and control of pineapple leaf fiber extractor., Trans. Chinese Soc. Agri. Eng., 2009, 25, 99-104.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Feng D.C., Liu X.L., Yang Q., Li G.X., Progress in antibacterial agents and antibacterial fibers, China Synth. Fiber Indus, 2005, 28, 40-42.Search in Google Scholar
[7] Han G.T., Study on fiber structure and knitting technology of Apocynum, Donghua Uni., 2006, 210-220.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Ashraf M.A., Yusoff I., Yusof I., Alias Y., Removal of acid yellow17 dye from aqueous solution using eco-friendly biosorbent, Desalin. Water Treat., 2013, 51, 4530-454010.1080/19443994.2012.747187Search in Google Scholar
[9] Liu C. H., Liu, Y., Current status of pineapple production and research in China, Guang. Agri. Sci., 2010, 10, 65-68.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Wang J.L., Jiang J.M., Lian W.W., Huang T., Zhang J., Deng Y.G., Bacteria resistant property of pineapple leaf fiber, Chinese J. Trop. Crops, 2009, 30,1694-1697.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Wang J.P., Wang H.Y., Du L.J., Ding Y., Xing D.M., Wang W., New cerebroside from leaves of pineapple, J. Chinese Mater. Medica, 2007, 32, 401-403.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Ashraf M.A., Yusoff I., Yusof I., Alias Y., Removal of Cd (II) onto Raphanus sativus peels biomass: Equlibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics, Desalin. Water Treat., 2013, 51, 4402-441210.1080/19443994.2012.752333Search in Google Scholar
[13] Xie W.D., Xing D.M., Sun H., The effect of Ananas comosus L. leaves on diabetic-dyslipidemic rats induced by alloxan and a high-fat/high-cholesterol diet, Am. J. Chin. Med., 2005, 33, 80-95.10.1142/S0192415X05002692Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Ashraf M.A., Maah M.J., Yusoff I., Removal of lead from synthetic solutions by protonted teleosts biomass, E. J. Chem., 2012, 9, 345-353.10.1155/2012/769180Search in Google Scholar
[15] Zhou Y.K., Zhang J.C., Zhang H., Bacteria resistant property of hemp fiber and its anti-bacterial mechanism, J. Text. Res, 2007, 28, 12-15.Search in Google Scholar
© 2016 Zhikai Zhuang et al., published by De Gruyter Open
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular article
- Purification of polyclonal IgG specific for Camelid’s antibodies and their recombinant nanobodies
- Regular article
- Antioxidative defense mechanism of the ruderal Verbascum olympicum Boiss. against copper (Cu)-induced stress
- Regular article
- Polyherbal EMSA ERITIN Promotes Erythroid Lineages and Lymphocyte Migration in Irradiated Mice
- Regular article
- Expression and characterization of a cutinase (AnCUT2) from Aspergillus niger
- Regular article
- The Lytic SA Phage Demonstrate Bactericidal Activity against Mastitis Causing Staphylococcus aureus
- Regular article
- MafB, a target of microRNA-155, regulates dendritic cell maturation
- Regular article
- Plant regeneration from protoplasts of Gentiana straminea Maxim
- Regular article
- The effect of radiation of LED modules on the growth of dill (Anethum graveolens L.)
- Regular article
- ELF-EMF exposure decreases the peroxidase catalytic efficiency in vitro
- Regular article
- Cold hardening protects cereals from oxidative stress and necrotrophic fungal pathogenesis
- Regular article
- MC1R gene variants involvement in human OCA phenotype
- Regular article
- Chondrogenic potential of canine articular cartilage derived cells (cACCs)
- Regular article
- Cloning, expression, purification and characterization of Leishmania tropica PDI-2 protein
- Regular article
- High potential of sub-Mediterranean dry grasslands for sheep epizoochory
- Regular article
- Identification of drought, cadmium and root-lesion nematode infection stress-responsive transcription factors in ramie
- Regular article
- Herbal supplement formula of Elephantopus scaber and Sauropus androgynus promotes IL-2 cytokine production of CD4+T cells in pregnant mice with typhoid fever
- Regular article
- Caffeine effects on AdoR mRNA expression in Drosophila melanogaster
- Regular article
- Effects of MgCl2 supplementation on blood parameters and kidney injury of rats exposed to CCl4
- Regular article
- Effective onion leaf fleck management and variability of storage pathogens
- Regular article
- Improving aeration for efficient oxygenation in sea bass sea cages. Blood, brain and gill histology
- Regular article
- Biogenic amines and hygienic quality of lucerne silage
- Regular article
- Isolation and characterization of lytic phages TSE1-3 against Enterobacter cloacae
- Regular article
- Effects of pH on antioxidant and prooxidant properties of common medicinal herbs
- Regular article
- Relationship between cytokines and running economy in marathon runners
- Regular article
- Anti-leukemic activity of DNA methyltransferase inhibitor procaine targeted on human leukaemia cells
- Regular article
- Research Progress in Oncology. Highlighting and Exploiting the Roles of Several Strategic Proteins in Understanding Cancer Biology
- Regular article
- Ectomycorrhizal communities in a Tuber aestivum Vittad. orchard in Poland
- Regular article
- Impact of HLA-G 14 bp polymorphism and soluble HLA-G level on kidney graft outcome
- Regular article
- In-silico analysis of non-synonymous-SNPs of STEAP2: To provoke the progression of prostate cancer
- Regular article
- Presence of sequence and SNP variation in the IRF6 gene in healthy residents of Guangdong Province
- Regular article
- Environmental and economic aspects of Triticum aestivum L. and Avena sativa growing
- Regular article
- A molecular survey of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato in central-eastern Europe
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Molecular genetics related to non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Roles of long noncoding RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Advancement of Wnt signal pathway and the target of breast cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- A tumor suppressive role of lncRNA GAS5 in human colorectal cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- The role of E-cadherin - 160C/A polymorphism in breast cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- The proceedings of brain metastases from lung cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Newly-presented potential targeted drugs in the treatment of renal cell cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Decreased expression of miR-132 in CRC tissues and its inhibitory function on tumor progression
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- The unusual yin-yang fashion of RIZ1/RIZ2 contributes to the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Human papillomavirus infection mechanism and vaccine of vulva carcinoma
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Abnormal expressed long non-coding RNA IRAIN inhibits tumor progression in human renal cell carcinoma cells
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- UCA1, a long noncoding RNA, promotes the proliferation of CRC cells via p53/p21 signaling
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Forkhead box 1 expression is upregulatedin non-small cell lung cancer and correlateswith pathological parameters
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- The development of potential targets in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Low expression of miR-192 in NSCLC and its tumor suppressor functions in metastasis via targeting ZEB2
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Downregulation of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 induces tumor progression of human breast cancer through regulating CCND1 expression
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Post-translational modifications of EMT transcriptional factors in cancer metastasis
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- EZH2 Expression and its Correlation with Clinicopathological Features in Patients with Colorectal Carcinoma
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- The association between EGFR expression and clinical pathology characteristics in gastric cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- The peiminine stimulating autophagy in human colorectal carcinoma cells via AMPK pathway by SQSTM1
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Activating transcription factor 3 is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating cyclin D1
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Progress toward resistance mechanism to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Effect of miRNAs in lung cancer suppression and oncogenesis
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Role and inhibition of Src signaling in the progression of liver cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- The antitumor effects of mitochondria-targeted 6-(nicotinamide) methyl coumarin
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Characterization of particle shape, zeta potential, loading efficiency and outdoor stability for chitosan-ricinoleic acid loaded with rotenone
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Genetic diversity and population structure of ginseng in China based on RAPD analysis
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Optimizing the extraction of antibacterial compounds from pineapple leaf fiber
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Identification of residual non-biodegradable organic compounds in wastewater effluent after two-stage biochemical treatment
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Remediation of deltamethrin contaminated cotton fields: residual and adsorption assessment
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- A best-fit probability distribution for the estimation of rainfall in northern regions of Pakistan
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Artificial Plant Root System Growth for Distributed Optimization: Models and Emergent Behaviors
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- The complete mitochondrial genomes of two weevils, Eucryptorrhynchus chinensis and E. brandti: conserved genome arrangement in Curculionidae and deficiency of tRNA-Ile gene
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Characteristics and coordination of source-sink relationships in super hybrid rice
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Construction of a Genetic Linkage Map and QTL Analysis of Fruit-related Traits in an F1 Red Fuji x Hongrou Apple Hybrid
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Effects of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Dilong on Airway Remodeling in Rats with OVA-induced-Asthma
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- The effect of sewage sludge application on the growth and absorption rates of Pb and As in water spinach
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Effectiveness of mesenchymal stems cells cultured by hanging drop vs. conventional culturing on the repair of hypoxic-ischemic-damaged mouse brains, measured by stemness gene expression
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular article
- Purification of polyclonal IgG specific for Camelid’s antibodies and their recombinant nanobodies
- Regular article
- Antioxidative defense mechanism of the ruderal Verbascum olympicum Boiss. against copper (Cu)-induced stress
- Regular article
- Polyherbal EMSA ERITIN Promotes Erythroid Lineages and Lymphocyte Migration in Irradiated Mice
- Regular article
- Expression and characterization of a cutinase (AnCUT2) from Aspergillus niger
- Regular article
- The Lytic SA Phage Demonstrate Bactericidal Activity against Mastitis Causing Staphylococcus aureus
- Regular article
- MafB, a target of microRNA-155, regulates dendritic cell maturation
- Regular article
- Plant regeneration from protoplasts of Gentiana straminea Maxim
- Regular article
- The effect of radiation of LED modules on the growth of dill (Anethum graveolens L.)
- Regular article
- ELF-EMF exposure decreases the peroxidase catalytic efficiency in vitro
- Regular article
- Cold hardening protects cereals from oxidative stress and necrotrophic fungal pathogenesis
- Regular article
- MC1R gene variants involvement in human OCA phenotype
- Regular article
- Chondrogenic potential of canine articular cartilage derived cells (cACCs)
- Regular article
- Cloning, expression, purification and characterization of Leishmania tropica PDI-2 protein
- Regular article
- High potential of sub-Mediterranean dry grasslands for sheep epizoochory
- Regular article
- Identification of drought, cadmium and root-lesion nematode infection stress-responsive transcription factors in ramie
- Regular article
- Herbal supplement formula of Elephantopus scaber and Sauropus androgynus promotes IL-2 cytokine production of CD4+T cells in pregnant mice with typhoid fever
- Regular article
- Caffeine effects on AdoR mRNA expression in Drosophila melanogaster
- Regular article
- Effects of MgCl2 supplementation on blood parameters and kidney injury of rats exposed to CCl4
- Regular article
- Effective onion leaf fleck management and variability of storage pathogens
- Regular article
- Improving aeration for efficient oxygenation in sea bass sea cages. Blood, brain and gill histology
- Regular article
- Biogenic amines and hygienic quality of lucerne silage
- Regular article
- Isolation and characterization of lytic phages TSE1-3 against Enterobacter cloacae
- Regular article
- Effects of pH on antioxidant and prooxidant properties of common medicinal herbs
- Regular article
- Relationship between cytokines and running economy in marathon runners
- Regular article
- Anti-leukemic activity of DNA methyltransferase inhibitor procaine targeted on human leukaemia cells
- Regular article
- Research Progress in Oncology. Highlighting and Exploiting the Roles of Several Strategic Proteins in Understanding Cancer Biology
- Regular article
- Ectomycorrhizal communities in a Tuber aestivum Vittad. orchard in Poland
- Regular article
- Impact of HLA-G 14 bp polymorphism and soluble HLA-G level on kidney graft outcome
- Regular article
- In-silico analysis of non-synonymous-SNPs of STEAP2: To provoke the progression of prostate cancer
- Regular article
- Presence of sequence and SNP variation in the IRF6 gene in healthy residents of Guangdong Province
- Regular article
- Environmental and economic aspects of Triticum aestivum L. and Avena sativa growing
- Regular article
- A molecular survey of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato in central-eastern Europe
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Molecular genetics related to non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Roles of long noncoding RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Advancement of Wnt signal pathway and the target of breast cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- A tumor suppressive role of lncRNA GAS5 in human colorectal cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- The role of E-cadherin - 160C/A polymorphism in breast cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- The proceedings of brain metastases from lung cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Newly-presented potential targeted drugs in the treatment of renal cell cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Decreased expression of miR-132 in CRC tissues and its inhibitory function on tumor progression
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- The unusual yin-yang fashion of RIZ1/RIZ2 contributes to the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Human papillomavirus infection mechanism and vaccine of vulva carcinoma
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Abnormal expressed long non-coding RNA IRAIN inhibits tumor progression in human renal cell carcinoma cells
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- UCA1, a long noncoding RNA, promotes the proliferation of CRC cells via p53/p21 signaling
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Forkhead box 1 expression is upregulatedin non-small cell lung cancer and correlateswith pathological parameters
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- The development of potential targets in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Low expression of miR-192 in NSCLC and its tumor suppressor functions in metastasis via targeting ZEB2
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Downregulation of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 induces tumor progression of human breast cancer through regulating CCND1 expression
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Post-translational modifications of EMT transcriptional factors in cancer metastasis
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- EZH2 Expression and its Correlation with Clinicopathological Features in Patients with Colorectal Carcinoma
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- The association between EGFR expression and clinical pathology characteristics in gastric cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- The peiminine stimulating autophagy in human colorectal carcinoma cells via AMPK pathway by SQSTM1
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Activating transcription factor 3 is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating cyclin D1
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Progress toward resistance mechanism to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Effect of miRNAs in lung cancer suppression and oncogenesis
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- Role and inhibition of Src signaling in the progression of liver cancer
- Topical Issue on Cancer Signaling, Metastasis and Target Therapy
- The antitumor effects of mitochondria-targeted 6-(nicotinamide) methyl coumarin
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Characterization of particle shape, zeta potential, loading efficiency and outdoor stability for chitosan-ricinoleic acid loaded with rotenone
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Genetic diversity and population structure of ginseng in China based on RAPD analysis
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Optimizing the extraction of antibacterial compounds from pineapple leaf fiber
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Identification of residual non-biodegradable organic compounds in wastewater effluent after two-stage biochemical treatment
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Remediation of deltamethrin contaminated cotton fields: residual and adsorption assessment
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- A best-fit probability distribution for the estimation of rainfall in northern regions of Pakistan
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Artificial Plant Root System Growth for Distributed Optimization: Models and Emergent Behaviors
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- The complete mitochondrial genomes of two weevils, Eucryptorrhynchus chinensis and E. brandti: conserved genome arrangement in Curculionidae and deficiency of tRNA-Ile gene
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Characteristics and coordination of source-sink relationships in super hybrid rice
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Construction of a Genetic Linkage Map and QTL Analysis of Fruit-related Traits in an F1 Red Fuji x Hongrou Apple Hybrid
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Effects of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Dilong on Airway Remodeling in Rats with OVA-induced-Asthma
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- The effect of sewage sludge application on the growth and absorption rates of Pb and As in water spinach
- Special Issue on CleanWAS 2015
- Effectiveness of mesenchymal stems cells cultured by hanging drop vs. conventional culturing on the repair of hypoxic-ischemic-damaged mouse brains, measured by stemness gene expression

