Abstract
C9H13NO4, orthorhombic, P212121 (no. 19), a = 5.8406(1) Å, b = 7.0840(1) Å, c = 24.3697(3) Å, V = 1,008.29(3) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0148, wRref(F2) = 0.0381, T = 100.0(1) K.
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
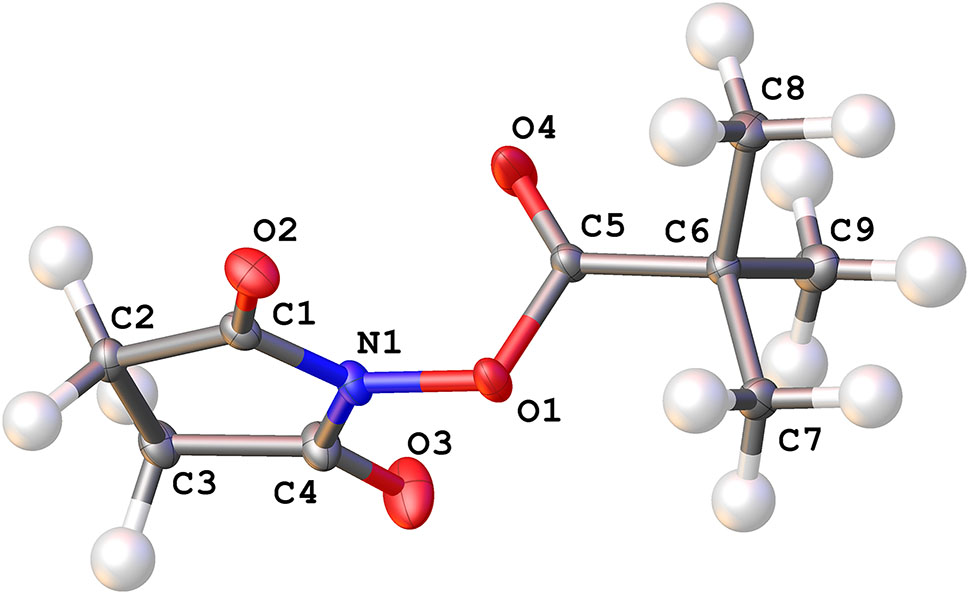
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless plate |
| Size: | 0.40 × 0.11 × 0.02 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 0.88 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 76.4°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 15,980, 2,117, 0.037 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs°>°2σ(Iobs), 2,101 |
| N(param)refined: | 180 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO, 1 Olex2, 2 , 5 SHELX 3 , 4 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | 0.46920 (7) | 0.38586 (6) | 0.380074 (18) | 0.01749 (10) |
| O2 | 0.31426 (7) | 0.49476 (6) | 0.275772 (19) | 0.02198 (10) |
| O3 | 0.40633 (10) | 0.00003 (7) | 0.39319 (2) | 0.03435 (13) |
| O4 | 0.81127 (8) | 0.30810 (8) | 0.34404 (2) | 0.02958 (12) |
| N1 | 0.37577 (9) | 0.26785 (6) | 0.34127 (2) | 0.01538 (11) |
| C1 | 0.29848 (9) | 0.33288 (8) | 0.29114 (2) | 0.01413 (11) |
| C2 | 0.19979 (10) | 0.16399 (8) | 0.26216 (2) | 0.01607 (12) |
| H2A | 0.3006 (16) | 0.1392 (14) | 0.2254 (4) | 0.038 (2)* |
| H2B | 0.0235 (16) | 0.1940 (13) | 0.2501 (4) | 0.033 (2)* |
| C3 | 0.21366 (10) | 0.00071 (8) | 0.30327 (2) | 0.01858 (12) |
| H3A | 0.3052 (17) | −0.1217 (13) | 0.2867 (4) | 0.035 (2)* |
| H3B | 0.0379 (18) | −0.0393 (15) | 0.3184 (4) | 0.039 (2)* |
| C4 | 0.34294 (10) | 0.07723 (8) | 0.35195 (2) | 0.01844 (12) |
| C5 | 0.70599 (9) | 0.39101 (8) | 0.37838 (2) | 0.01450 (11) |
| C6 | 0.80311 (9) | 0.51332 (7) | 0.42386 (2) | 0.01283 (11) |
| C7 | 0.61930 (10) | 0.60241 (8) | 0.46030 (2) | 0.01792 (12) |
| H7A | 0.5163 (17) | 0.4940 (15) | 0.4821 (4) | 0.038 (2)* |
| H7B | 0.7019 (17) | 0.6833 (14) | 0.4922 (4) | 0.038 (2)* |
| H7C | 0.5074 (18) | 0.6978 (15) | 0.4370 (4) | 0.040 (3)* |
| C8 | 0.94332 (11) | 0.66861 (9) | 0.39574 (2) | 0.01998 (13) |
| H8A | 1.0700 (17) | 0.6081 (14) | 0.3680 (4) | 0.043 (2)* |
| H8B | 0.8315 (19) | 0.7604 (15) | 0.3716 (4) | 0.044 (3)* |
| H8C | 1.0291 (18) | 0.7551 (14) | 0.4275 (4) | 0.038 (2)* |
| C9 | 0.95807 (11) | 0.38520 (9) | 0.45845 (3) | 0.02120 (13) |
| H9A | 0.859 (2) | 0.2683 (14) | 0.4770 (4) | 0.042 (3)* |
| H9B | 1.093 (2) | 0.3224 (16) | 0.4342 (4) | 0.049 (3)* |
| H9C | 1.0332 (19) | 0.4688 (16) | 0.4923 (4) | 0.047 (3)* |
1 Source of material
The title compound was obtained by an intermolecular arrangement reaction of pivaloyl chloride and 2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl glycine in acetonitrile (1:1 molar ratio) in the presence of diisopropylethylamine (Hünig’s base, DIPEA) as a base. The reaction occurs after 24 h under continuous stirring at room temperature. After completed reaction (TLC control: dichloromethane/methanol, 9:1, R f = 0.15) the mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure until a pale oil left. The crude material was dissolved in dichloromethane, washed three times with saturated sodium hydrogencarbonate and brine, and dried over sodium sulfate. The organic phase was filtered and evaporated to yield 107.7 mg (70 %) of a brownish oil, which was left to slowly to crystallize at ambient conditions. White crystals suitable for X-ray structure analysis were obtained after recrystallization from dichloromethane and crystallization over a period of several days at 295–297 K. The crystals were analyzed directly from the mother liquor at 100(1) K. The melting point of pyrrolidin-1-yl pivalate is 338.9–341.4 K.
2 Experimental details
A single crystal of the title compound was examined on a Rigaku Supernova diffractometer 1 using CuKα (λ = 1.54184 Å) radiation. The crystal was kept at 100.0(1) K during data collection. Using Olex2, 2 the structure was solved with the ShelXT 3 , 4 structure solution program using Intrinsic Phasing method and refined with the olex2.refine 5 , 6 refinement package using Gauss–Newton minimisation. Refinement using NoSpherA2, an implementation of NOn-SPHERical Atom-form-factors in Olex2. 7 NoSpherA2 implementation of HAR makes use of tailor-made aspherical atomic form factors calculated on-the-fly from a Hirshfeld-partitioned electron density (ED) – not from spherical-atom form factors. The ED is calculated from a Gaussian basis set single determinant SCF wavefunction – either Hartree–Fock or DFT using selected functionals – for a fragment of the crystal. This fragment can be embedded in an electrostatic crystal field by employing cluster charges or modelled using implicit solvatation models, depending on the software used. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50 % probability level. Hydrogen atoms were taken into account using a riding model. There is one molecule in the asymmetric unit. All bond lengths and angles are in the expected ranges. 8 , 9 , 10 , 11
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support by the Bulgarian National Science Found (BNSF) under grant number KP-06-COST/14 (from 22.05.2024, CA22105).
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Bulgarian National Science Fund (BNSF), Grant No. KP-06-COST/14 (from 22.05.2024, CA22105).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Rigaku, O. D. CrysAlisPro 1.171.43.96a: Abingdon, Oxfordshire, England, 2023.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXT – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXL 2018; University of Göttingen: Germany, 2018.Search in Google Scholar
5. Bourhis, L. J.; Dolomanov, O. V.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. The Anatomy of a Comprehensive Constrained, Restrained Refinement Program for the Modern Computing Environment-Olex2 Dissected. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 59–75; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314022207.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
6. Hooft, R. W. W.; Straver, L. H.; Spek, A. L. Using the T-Distribution to Improve the Absolute Structure Assignment with Likelihood Calculations. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2010, 43, 665–668; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889810018601.Search in Google Scholar
7. Kleemiss, F.; Dolomanov, O. V.; Bodensteiner, M.; Peyerimhoff, N.; Midgley, M.; Bourhis, L. J.; Genoni, A.; Malaspina, L. A.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spencer, J. L.; White, F.; Grundkoetter-Stock, B.; Steinhauer, S.; Lentz, D.; Puschmann, H.; Grabowsky, S. Accurate Crystal Structures and Chemical Properties from NoSpherA2. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 1675–1692; https://doi.org/10.1039/d0sc05526c.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. Kolev, T.; Peeva, M. I.; Bogdanov, I. P.; Ognyanov, I. V.; Atanasov, A. G.; Tzvetkov, N. T. The Crystal Structure of Histidinium Hydrogensquarate, C10H11N3O6. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 601–603; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0181.Search in Google Scholar
9. Tzvetkov, N. T.; Peeva, M. I.; Tsakovska, I.; Milella, L.; Pajeva, I.; Stammler, H.-G. The Crystal Structure of (4SR)-7-(3,4-Dichlorobenzyl)-4,8,8-Trimethyl-7,8-Dihydroimidazo[5,1c] [1,2,4]triazine-3,6(2H,4H)-Dione, C15H16Cl2N4O215. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 319–321; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0016.Search in Google Scholar
10. Hermanson, G. T. The Reactions of Bioconjugates. Chapter 3, in Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd ed.; Academic Press, 2013; pp. 229–258.10.1016/B978-0-12-382239-0.00003-0Search in Google Scholar
11. Barre, A.; Tintas, M.-L.; Levacher, V.; Papamicael, C.; Gembus, V. An Overview of the Synthesis of Highly Versatile N-Hydroxysuccinimide Esters. Synthesis 2016, 48, A–L; https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1588607.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Editorial
- Editorial 2024 – New developments and changes of Zeitschrift für Kristallographie – New Crystal Structures
- New Crystal Structures
- Hydrogen bonding and π⋅⋅⋅halogen interactions in the crystal structure of bis(theophyllinium) hexachloridoplatinate(IV) monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-2-carboxypyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C6H7ClN2O6
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-(3-amino-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 4 N:O:O':O')(1-methylpyrroldin-2-one-κ1O)dicopper(II)] – 1-methylpyrroldin-2-one (1/3), C40H48Cu2N12O12
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6-k6O6(2,4,5-trinitroimidazol-1-ido-k1O)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-bromoisophthalato-κ3O,O′:O″)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)dicadmium(II)] dihydrate
- Crystal structure of (5R,6S,E)-5-acetoxy-2-methyl-6-((2aR,3R,5aS,5bS,11aR,12aS)-2a,5a,8,8-tetramethyl-9-oxotetradecahydro-1H,12H-cyclopenta[a]cyclopropa[e]phenanthren-3-yl)hept-2-enoic acid, C32H48O5
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2 -thiocyanato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II) monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene–2,3,5,6-tetrachlorobenzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid (1/1)
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(1-[(2-ethyl-benzimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H–benzotriazole) cadmium(II), C32H32CdN10OCl2
- The crystal structure of N′-(tert-butyl)-N′-(3,5-dimethylbenzoyl)-3-methoxy-N,2-dimethylbenzohydrazide, C23H30N2O3
- Crystal stucture of 3-benzamido-N-(2-bromo-4-(perfluoropropan-2-yl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-fluorobenzamide
- Crystal structure of bis(μ-benzeneselenolato)-(tetracarbonyl)-{μ-[N-(diphenylphosphanyl)-N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-P,P-diphenylphosphinous amide]} diiron, C48H35Fe2NO4P2Se2
- The crystal structure of 2′-(p-tolyl)-4′H-spiro[isochromane-1,1′-naphthalene]-3,4′-dione, C25H18O3
- The crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-tetrakis(μ4-pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylate-κ5N: O: O′: O″: O‴)-bi(μ2-pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N: O: O′)-digadolinium(III)tricopper (II)], [Gd2Cu3(C7H3NO4)6(H2O)6] n
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(4-(4-(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)pyridin-1-ium-κ1N)-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ5O:O′: O″:O‴:O⁗)-(μ2-2,5-dicarboxyterephthalato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II)], C52H32N4O16Zn2
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-carboxy-6-nitrobenzoate monohydrate, C24H25FN4O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(1-((3,5-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-k1N)zinc(II), C22H24ZnN12Cl2
- The crystal structure of (3-chlorothiophene-2-carboxylato-κ2O, O′)-(2,2′-dipyridyl-κ2N,N′)lead(II), C20H12Cl2N2O4S2Pb
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (Z)-4-((1-(3-fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methylene)-5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one, C19H14FN5O
- The crystal structure of the coordination compound catena-poly[(18-crown-6-ether-κ6O6)(4,5-dinitroimidazolato-κ1O)potassium(I)]
- Crystal structure of 7-(diethylamino)-3-(trifluoroacetyl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H14F3NO3
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-1-[(2-ethylimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H–benzotriazole κ1N zinc(II), C24H26ZnN10Cl2
- Crystal and molecular structure of 5-bromopyridine-2,3-diamine
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-1-(3-carboxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-k3-O,O′:O″)hexaqua-dicobalt tetrahydrate], C26H36N4O20Co2
- Crystal structure of thiocyanate-κ1N-bis(μ1-2,6-diformyl-4-methylphenol oxime-κ2N,O)-manganese(III) acetonitrile solvate, C21H21MnN6O6S
- The crystal structure of pyrrolidin-1-yl pivalate, C9H13NO4
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-(2,2-diphenylethene-1,1-diyl)bis(1,4-dimethoxybenzene), C30H28O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzyltrimethylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), {(C6H5CH2)(CH3)3N}2[WS4]
- The crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-2-(ethoxymethylene)-3-oxobutanoate, C9H14O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-6-bromo-3,5-dimethyl-2-(1-phenylprop-1-en-2-yl)-3Himidazo[4,5b]pyridine, C17H16BrN3
- Crystal structure of (3S,3′S,4R,4′S)-3′-(furan-3-yl)-3-hydroxy-4′-methyl-3,5,6′,7′-tetrahydro-1H,3′H-4,5′-spirobi[isobenzofuran]-1,1′(4′H)-dione-methanol (1/1), C21H22O7
- Cocrystal structure of progesterone-isophthalic acid, C25H33O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(6-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-1-methylquinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C17H12FN3O
- Crystal structure of S-(4-carboxybutyl)- l -cysteine
- The cocrystal of 2,2′-(hydrazine-1,1-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarbonitrile)– methanol (2/3)
- Crystal structure of (1′R,2′S,4′R,6′S)-4,6-dihydroxy-1′,8′,8′-trimethyl-3-(3-methylbutanoyl)-4′,8′,6′,1′,7,2′-hexahydro-1H-4′,6′-methanoxanthene-8-carbaldehyde, C23H30O5
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-methylphenyl pyridazine-k 2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenyl-pyrazole-κ 2 C,N) iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C39H29F6IrN8P
- Crystal structure of 1,5-bis[(E)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene]thiocarbonohydrazide dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate, C17H18N4O2S·C2H6OS
- Crystal structure of (S)-4-(2-(4-(2-acetyl-5-chlorophenyl)-3-methoxy-6-oxopyridazin-1(6H)-yl)-3-phenylpropanamido)benzoic acid monohydrate, C29H26ClN3O7
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(2,4-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane
- Crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzyl (S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19ClO3
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-4-benzyl-1-(4-bromophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)ethan-1-one, C24H20BrN3O3
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3′-(2-(1-(3,4-dimethyl-phenyl)-3-methyl-5-oxo-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazol-4-ylidene)hydrazinyl)-2′-hydroxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3-carboxylicacid ─ methanol (1/1), C26H26N4O5
- Crystal structure of (S)-1-phenylpropan-1-aminium (S)-(1-phenylpropyl)carbamate C19H26N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-((5-bromo-4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)thio)acetate, C18H16BrN3O2S
- The crystal structure of trichlorobis(pyridine-2,6-dithio-κS-carbomethylamido)antimony(III), [SbCl3(C9H11N3S2)2]
- Crystal structure of 1,8-dihydroxy-3-{[(triphenylstannyl)oxy]carbonyl} anthracene-9,10-dione, C33H22O6Sn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(2-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)hydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium-2-olate dihydrate, C12H14N4O4
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-pyridinium-2-carboxylate, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-nitrato-κ3O,O:O′′-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)sodium(I)], C24H18N6O7Na2
- Retractions
- Retraction of: Crystal structure of bis[diaquaisonicotinatosamarium(III)]-µ-isonicotinato-[diisonicotinatocopper(II)], CuSm2(C6H4NO2)8(H2O)4
- Retraction of: Crystal structure of aqua(2,2′-bipyridine-k 2 N:N′)(nitrato)-(4-aminobenzoato)cadmium(II) nitrate, [Cd(H2O)(NO3)(C10H8N2)(C7H7NO2)][NO3]
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Editorial
- Editorial 2024 – New developments and changes of Zeitschrift für Kristallographie – New Crystal Structures
- New Crystal Structures
- Hydrogen bonding and π⋅⋅⋅halogen interactions in the crystal structure of bis(theophyllinium) hexachloridoplatinate(IV) monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-2-carboxypyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C6H7ClN2O6
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-(3-amino-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 4 N:O:O':O')(1-methylpyrroldin-2-one-κ1O)dicopper(II)] – 1-methylpyrroldin-2-one (1/3), C40H48Cu2N12O12
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6-k6O6(2,4,5-trinitroimidazol-1-ido-k1O)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-bromoisophthalato-κ3O,O′:O″)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)dicadmium(II)] dihydrate
- Crystal structure of (5R,6S,E)-5-acetoxy-2-methyl-6-((2aR,3R,5aS,5bS,11aR,12aS)-2a,5a,8,8-tetramethyl-9-oxotetradecahydro-1H,12H-cyclopenta[a]cyclopropa[e]phenanthren-3-yl)hept-2-enoic acid, C32H48O5
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2 -thiocyanato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II) monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene–2,3,5,6-tetrachlorobenzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid (1/1)
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(1-[(2-ethyl-benzimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H–benzotriazole) cadmium(II), C32H32CdN10OCl2
- The crystal structure of N′-(tert-butyl)-N′-(3,5-dimethylbenzoyl)-3-methoxy-N,2-dimethylbenzohydrazide, C23H30N2O3
- Crystal stucture of 3-benzamido-N-(2-bromo-4-(perfluoropropan-2-yl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-fluorobenzamide
- Crystal structure of bis(μ-benzeneselenolato)-(tetracarbonyl)-{μ-[N-(diphenylphosphanyl)-N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-P,P-diphenylphosphinous amide]} diiron, C48H35Fe2NO4P2Se2
- The crystal structure of 2′-(p-tolyl)-4′H-spiro[isochromane-1,1′-naphthalene]-3,4′-dione, C25H18O3
- The crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-tetrakis(μ4-pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylate-κ5N: O: O′: O″: O‴)-bi(μ2-pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N: O: O′)-digadolinium(III)tricopper (II)], [Gd2Cu3(C7H3NO4)6(H2O)6] n
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(4-(4-(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)pyridin-1-ium-κ1N)-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ5O:O′: O″:O‴:O⁗)-(μ2-2,5-dicarboxyterephthalato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II)], C52H32N4O16Zn2
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-carboxy-6-nitrobenzoate monohydrate, C24H25FN4O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(1-((3,5-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-k1N)zinc(II), C22H24ZnN12Cl2
- The crystal structure of (3-chlorothiophene-2-carboxylato-κ2O, O′)-(2,2′-dipyridyl-κ2N,N′)lead(II), C20H12Cl2N2O4S2Pb
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (Z)-4-((1-(3-fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methylene)-5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one, C19H14FN5O
- The crystal structure of the coordination compound catena-poly[(18-crown-6-ether-κ6O6)(4,5-dinitroimidazolato-κ1O)potassium(I)]
- Crystal structure of 7-(diethylamino)-3-(trifluoroacetyl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H14F3NO3
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-1-[(2-ethylimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H–benzotriazole κ1N zinc(II), C24H26ZnN10Cl2
- Crystal and molecular structure of 5-bromopyridine-2,3-diamine
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-1-(3-carboxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-k3-O,O′:O″)hexaqua-dicobalt tetrahydrate], C26H36N4O20Co2
- Crystal structure of thiocyanate-κ1N-bis(μ1-2,6-diformyl-4-methylphenol oxime-κ2N,O)-manganese(III) acetonitrile solvate, C21H21MnN6O6S
- The crystal structure of pyrrolidin-1-yl pivalate, C9H13NO4
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-(2,2-diphenylethene-1,1-diyl)bis(1,4-dimethoxybenzene), C30H28O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzyltrimethylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), {(C6H5CH2)(CH3)3N}2[WS4]
- The crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-2-(ethoxymethylene)-3-oxobutanoate, C9H14O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-6-bromo-3,5-dimethyl-2-(1-phenylprop-1-en-2-yl)-3Himidazo[4,5b]pyridine, C17H16BrN3
- Crystal structure of (3S,3′S,4R,4′S)-3′-(furan-3-yl)-3-hydroxy-4′-methyl-3,5,6′,7′-tetrahydro-1H,3′H-4,5′-spirobi[isobenzofuran]-1,1′(4′H)-dione-methanol (1/1), C21H22O7
- Cocrystal structure of progesterone-isophthalic acid, C25H33O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(6-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-1-methylquinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C17H12FN3O
- Crystal structure of S-(4-carboxybutyl)- l -cysteine
- The cocrystal of 2,2′-(hydrazine-1,1-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarbonitrile)– methanol (2/3)
- Crystal structure of (1′R,2′S,4′R,6′S)-4,6-dihydroxy-1′,8′,8′-trimethyl-3-(3-methylbutanoyl)-4′,8′,6′,1′,7,2′-hexahydro-1H-4′,6′-methanoxanthene-8-carbaldehyde, C23H30O5
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-methylphenyl pyridazine-k 2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenyl-pyrazole-κ 2 C,N) iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C39H29F6IrN8P
- Crystal structure of 1,5-bis[(E)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene]thiocarbonohydrazide dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate, C17H18N4O2S·C2H6OS
- Crystal structure of (S)-4-(2-(4-(2-acetyl-5-chlorophenyl)-3-methoxy-6-oxopyridazin-1(6H)-yl)-3-phenylpropanamido)benzoic acid monohydrate, C29H26ClN3O7
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(2,4-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane
- Crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzyl (S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19ClO3
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-4-benzyl-1-(4-bromophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)ethan-1-one, C24H20BrN3O3
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3′-(2-(1-(3,4-dimethyl-phenyl)-3-methyl-5-oxo-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazol-4-ylidene)hydrazinyl)-2′-hydroxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3-carboxylicacid ─ methanol (1/1), C26H26N4O5
- Crystal structure of (S)-1-phenylpropan-1-aminium (S)-(1-phenylpropyl)carbamate C19H26N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-((5-bromo-4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)thio)acetate, C18H16BrN3O2S
- The crystal structure of trichlorobis(pyridine-2,6-dithio-κS-carbomethylamido)antimony(III), [SbCl3(C9H11N3S2)2]
- Crystal structure of 1,8-dihydroxy-3-{[(triphenylstannyl)oxy]carbonyl} anthracene-9,10-dione, C33H22O6Sn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(2-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)hydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium-2-olate dihydrate, C12H14N4O4
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-pyridinium-2-carboxylate, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-nitrato-κ3O,O:O′′-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)sodium(I)], C24H18N6O7Na2
- Retractions
- Retraction of: Crystal structure of bis[diaquaisonicotinatosamarium(III)]-µ-isonicotinato-[diisonicotinatocopper(II)], CuSm2(C6H4NO2)8(H2O)4
- Retraction of: Crystal structure of aqua(2,2′-bipyridine-k 2 N:N′)(nitrato)-(4-aminobenzoato)cadmium(II) nitrate, [Cd(H2O)(NO3)(C10H8N2)(C7H7NO2)][NO3]

