Abstract
C23H20N20O3, monoclinic, C2/c (no. 15), a = 21.738(2) Å, b = 6.0988(9) Å, c = 24.229(3) Å, β = 114.396(4)°, V = 2,925.3(7) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.0533, wR ref (F2) = 0.1434, T = 170 K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.12 × 0.10 × 0.05 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.11 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 26.4°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 11,927, 2,945, 0.054 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1,978 |
| N(param)refined: | 217 |
| Programs: | Olex2, 1 SHELX, 2 , 3 Bruker 4 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.67157 (11) | 0.4163 (4) | 0.73264 (11) | 0.0323 (5) |
| C2 | 0.70122 (11) | 0.3454 (4) | 0.69247 (10) | 0.0313 (5) |
| C3 | 0.68488 (11) | 0.1616 (4) | 0.65693 (10) | 0.0313 (5) |
| C4 | 0.63782 (13) | −0.0079 (4) | 0.65031 (11) | 0.0368 (6) |
| C5 | 0.76419 (11) | 0.3498 (4) | 0.64570 (10) | 0.0303 (5) |
| C6 | 0.92554 (12) | 0.2379 (4) | 0.49950 (11) | 0.0343 (6) |
| C7 | 0.88132 (11) | 0.2200 (4) | 0.52903 (10) | 0.0298 (5) |
| C8 | 0.83496 (11) | 0.0622 (4) | 0.52438 (10) | 0.0297 (5) |
| C9 | 0.82047 (12) | −0.1274 (4) | 0.48685 (11) | 0.0336 (6) |
| C10 | 0.83010 (11) | 0.2982 (4) | 0.58628 (10) | 0.0298 (5) |
| C11 | 0.98614 (14) | 0.8603 (5) | 0.64197 (13) | 0.0532 (8) |
| H11A | 1.0118 | 0.9793 | 0.6342 | 0.080* |
| H11B | 1.0166 | 0.7705 | 0.6758 | 0.080* |
| H11C | 0.9507 | 0.9224 | 0.6523 | 0.080* |
| N1 | 0.64750 (10) | 0.4727 (4) | 0.76410 (10) | 0.0388 (5) |
| N2 | 0.59870 (12) | −0.1397 (4) | 0.64588 (12) | 0.0539 (7) |
| N3 | 0.72580 (9) | 0.1678 (3) | 0.62602 (8) | 0.0308 (5) |
| H3 | 0.7267 | 0.0728 | 0.5990 | 0.037* |
| N4 | 0.75134 (9) | 0.4644 (3) | 0.68592 (9) | 0.0333 (5) |
| N5 | 0.81237 (10) | 0.4150 (3) | 0.62595 (9) | 0.0355 (5) |
| N6 | 0.84711 (11) | 0.6146 (4) | 0.64618 (11) | 0.0433 (6) |
| H6A | 0.8178 | 0.7233 | 0.6355 | 0.052* |
| H6B | 0.8684 | 0.6105 | 0.6860 | 0.052* |
| N7 | 0.80248 (9) | 0.1103 (3) | 0.56099 (9) | 0.0309 (5) |
| N8 | 0.87794 (9) | 0.3720 (3) | 0.56936 (9) | 0.0307 (5) |
| H8 | 0.9020 | 0.4926 | 0.5816 | 0.037* |
| N9 | 0.95963 (12) | 0.2476 (4) | 0.47445 (11) | 0.0479 (6) |
| N10 | 0.80961 (11) | −0.2748 (4) | 0.45454 (10) | 0.0425 (6) |
| O1 | 0.95627 (8) | 0.7281 (3) | 0.58934 (8) | 0.0438 (5) |
| H1 | 0.9818 | 0.7239 | 0.5711 | 0.066* |
| O2a | 0.5482 (4) | 0.9200 (13) | 0.7450 (5) | 0.146 (3) |
| H2a | 0.5481 | 1.0461 | 0.7589 | 0.219* |
| C12 | 0.5000 | 0.8006 (10) | 0.7500 | 0.0811 (16) |
| H12Aa | 0.4587 | 0.8116 | 0.7125 | 0.122* |
| H12Ba | 0.4911 | 0.8545 | 0.7841 | 0.122* |
| H12Ca | 0.5145 | 0.6471 | 0.7571 | 0.122* |
-
aOccupancy: 0.5.
1 Source of material
An appropriate amount of 2-amino-4,5-dicyan-imidazole, hydrochloric acid and potassium permanganate were added to the reactor. The temperature of the reactor was reduced to 273 K and the reactions are for 2 h. After the end of the reaction, the solids are removed and the filtrate is retained. The solvent in the filtrate is removed by a rotary evaporator to obtain white solid. The white solid was separated by column chromatography using petroleum ether and ethyl acetate as eluent. The solution obtained by column chromatography was evaporated at room temperature to obtain the colorless block shaped crystals.
2 Experimental details
Hydrogen atoms were placed in their geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms.
3 Comment
Azole heterocyclic compounds are a class of high-energy nitrogen-rich energetic materials. 5 , 6 Imidazole compounds are currently the focus of research on field of energetic materials due to good thermal stability and a large number of modification sites. 7 , 8 , 9
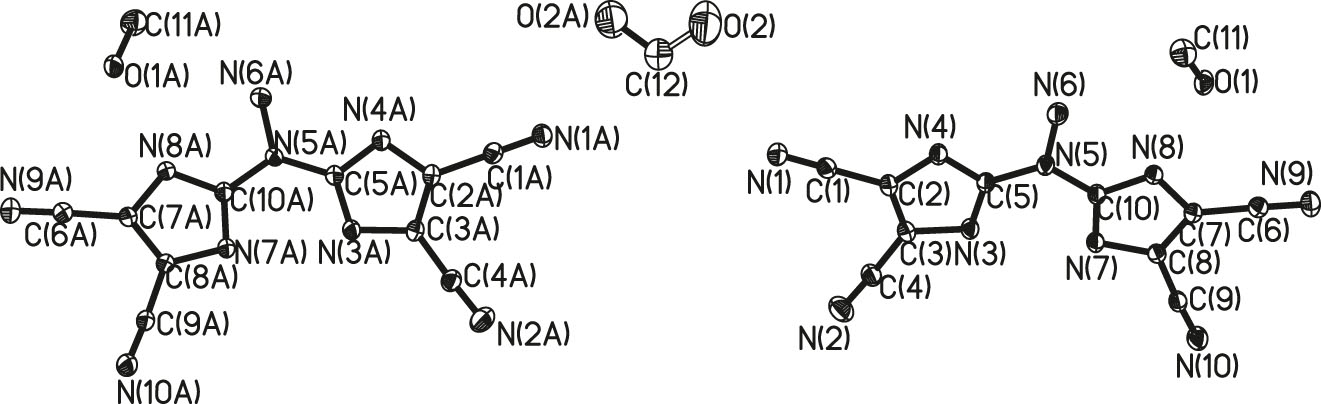
The title compound is cocrystal of two 2,2′-(hydrazine-1,1-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarbonitrile) molecules and three methanol molecules. The bond lengths and angles are in the expected ranges. 2,2′-(hydrazine-1,1-diyl)bis (1h-imidazole-4,5-dicarbonitrile) molecules are formed by connecting two imidazole planes by –N–NH2 structure. The two imidazole planes form a small angle and the dihedral angle is only 1.637°. Four hydrogen bonds are formed within 2,2′-(hydrazine-1,1-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarbonitrile) molecules. The bond lengths of hydrogen bonds are 2.696, 2.745, 2.441 and 2.207 respectively. The four carbon atoms of C2, C3, C7 and C8 are connected with four –CN groups and each –C–CN triatom structure is collinear. The above collinear structure is the same as the structure of 2-amino-4,5-dicyan-imidazole. 10
2,2′-(Hydrazine-1,1-diyl)bis(1h-imidazole-4,5-dicarbonitrile) is synthesized from two 2-amino-4,5-dicarbonitrile molecules. During the reaction, the amino group of one 2-amino-4,5-dicarbonitrile molecule is removed, and two hydrogen atoms of another 2-amino-4, 5-dicyanimidazole is removed. The two intermediates are connected by nitrogen atom and the free amino groups is attached to nitrogen atom, forming 2,2′-(hydrazine-1,1-diyl)bis(1h-imidazole-4,5-dicarbonitrile) molecule.
Funding source: National Natural Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 22105023
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22105023).
References
1. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. BRUKER. SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2016.Search in Google Scholar
5. Su, P.; Song, X.; Sun, R. Hydrogen Bonding in the Crystal Structure of the Molecular Salt of Pyrazole–Pyrazolium Picrate. Acta Crystallogr. 2016, E72, 861–863; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2056989016008215.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
6. Matuszek, K.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Forsyth, C. M. Pyrazolium Phase Change Materials for Solar-Thermal Energy Storage. ChemSusChem 2019, 13, 201902601; https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201902601.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Tan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H. High Energy Explosive with Low Sensitivity: A New Energetic Cocrystal Based on CL-20 and 1,4–DNI. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 4476–4482; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.9b00250.Search in Google Scholar
8. Windler, G. K.; Scott, B. L.; Tomson, N. C. Crystal Structure of 4,5-Dinitro-1H-Imidazole. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, E71, o634; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2056989015013432.Search in Google Scholar
9. Marcin, S.; Hines, C. C.; Reichert, W. M. Azolium Azolates from Reactions of Neutral Azoles with 1,3-Dimethyl-Imidazolium-2-Arboxylate, 1,2,3-Trimethyl-Imidazolium Hydrogen Carbonate, and N,N-Dimethyl-Pyrrolidinium Hydrogen Carbonate. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 1461–1469; https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nj00147d.Search in Google Scholar
10. Hardgrove, G. L. Jnr; Jons, S. D. Structure of 2-Amino-4,5-Dicyanoimidazole. Acta Crystallogr. 1991, C47, 337–339; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108270190004851.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Editorial
- Editorial 2024 – New developments and changes of Zeitschrift für Kristallographie – New Crystal Structures
- New Crystal Structures
- Hydrogen bonding and π⋅⋅⋅halogen interactions in the crystal structure of bis(theophyllinium) hexachloridoplatinate(IV) monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-2-carboxypyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C6H7ClN2O6
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-(3-amino-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 4 N:O:O':O')(1-methylpyrroldin-2-one-κ1O)dicopper(II)] – 1-methylpyrroldin-2-one (1/3), C40H48Cu2N12O12
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6-k6O6(2,4,5-trinitroimidazol-1-ido-k1O)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-bromoisophthalato-κ3O,O′:O″)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)dicadmium(II)] dihydrate
- Crystal structure of (5R,6S,E)-5-acetoxy-2-methyl-6-((2aR,3R,5aS,5bS,11aR,12aS)-2a,5a,8,8-tetramethyl-9-oxotetradecahydro-1H,12H-cyclopenta[a]cyclopropa[e]phenanthren-3-yl)hept-2-enoic acid, C32H48O5
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2 -thiocyanato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II) monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene–2,3,5,6-tetrachlorobenzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid (1/1)
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(1-[(2-ethyl-benzimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H–benzotriazole) cadmium(II), C32H32CdN10OCl2
- The crystal structure of N′-(tert-butyl)-N′-(3,5-dimethylbenzoyl)-3-methoxy-N,2-dimethylbenzohydrazide, C23H30N2O3
- Crystal stucture of 3-benzamido-N-(2-bromo-4-(perfluoropropan-2-yl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-fluorobenzamide
- Crystal structure of bis(μ-benzeneselenolato)-(tetracarbonyl)-{μ-[N-(diphenylphosphanyl)-N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-P,P-diphenylphosphinous amide]} diiron, C48H35Fe2NO4P2Se2
- The crystal structure of 2′-(p-tolyl)-4′H-spiro[isochromane-1,1′-naphthalene]-3,4′-dione, C25H18O3
- The crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-tetrakis(μ4-pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylate-κ5N: O: O′: O″: O‴)-bi(μ2-pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N: O: O′)-digadolinium(III)tricopper (II)], [Gd2Cu3(C7H3NO4)6(H2O)6] n
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(4-(4-(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)pyridin-1-ium-κ1N)-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ5O:O′: O″:O‴:O⁗)-(μ2-2,5-dicarboxyterephthalato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II)], C52H32N4O16Zn2
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-carboxy-6-nitrobenzoate monohydrate, C24H25FN4O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(1-((3,5-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-k1N)zinc(II), C22H24ZnN12Cl2
- The crystal structure of (3-chlorothiophene-2-carboxylato-κ2O, O′)-(2,2′-dipyridyl-κ2N,N′)lead(II), C20H12Cl2N2O4S2Pb
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (Z)-4-((1-(3-fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methylene)-5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one, C19H14FN5O
- The crystal structure of the coordination compound catena-poly[(18-crown-6-ether-κ6O6)(4,5-dinitroimidazolato-κ1O)potassium(I)]
- Crystal structure of 7-(diethylamino)-3-(trifluoroacetyl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H14F3NO3
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-1-[(2-ethylimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H–benzotriazole κ1N zinc(II), C24H26ZnN10Cl2
- Crystal and molecular structure of 5-bromopyridine-2,3-diamine
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-1-(3-carboxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-k3-O,O′:O″)hexaqua-dicobalt tetrahydrate], C26H36N4O20Co2
- Crystal structure of thiocyanate-κ1N-bis(μ1-2,6-diformyl-4-methylphenol oxime-κ2N,O)-manganese(III) acetonitrile solvate, C21H21MnN6O6S
- The crystal structure of pyrrolidin-1-yl pivalate, C9H13NO4
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-(2,2-diphenylethene-1,1-diyl)bis(1,4-dimethoxybenzene), C30H28O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzyltrimethylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), {(C6H5CH2)(CH3)3N}2[WS4]
- The crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-2-(ethoxymethylene)-3-oxobutanoate, C9H14O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-6-bromo-3,5-dimethyl-2-(1-phenylprop-1-en-2-yl)-3Himidazo[4,5b]pyridine, C17H16BrN3
- Crystal structure of (3S,3′S,4R,4′S)-3′-(furan-3-yl)-3-hydroxy-4′-methyl-3,5,6′,7′-tetrahydro-1H,3′H-4,5′-spirobi[isobenzofuran]-1,1′(4′H)-dione-methanol (1/1), C21H22O7
- Cocrystal structure of progesterone-isophthalic acid, C25H33O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(6-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-1-methylquinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C17H12FN3O
- Crystal structure of S-(4-carboxybutyl)- l -cysteine
- The cocrystal of 2,2′-(hydrazine-1,1-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarbonitrile)– methanol (2/3)
- Crystal structure of (1′R,2′S,4′R,6′S)-4,6-dihydroxy-1′,8′,8′-trimethyl-3-(3-methylbutanoyl)-4′,8′,6′,1′,7,2′-hexahydro-1H-4′,6′-methanoxanthene-8-carbaldehyde, C23H30O5
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-methylphenyl pyridazine-k 2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenyl-pyrazole-κ 2 C,N) iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C39H29F6IrN8P
- Crystal structure of 1,5-bis[(E)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene]thiocarbonohydrazide dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate, C17H18N4O2S·C2H6OS
- Crystal structure of (S)-4-(2-(4-(2-acetyl-5-chlorophenyl)-3-methoxy-6-oxopyridazin-1(6H)-yl)-3-phenylpropanamido)benzoic acid monohydrate, C29H26ClN3O7
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(2,4-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane
- Crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzyl (S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19ClO3
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-4-benzyl-1-(4-bromophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)ethan-1-one, C24H20BrN3O3
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3′-(2-(1-(3,4-dimethyl-phenyl)-3-methyl-5-oxo-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazol-4-ylidene)hydrazinyl)-2′-hydroxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3-carboxylicacid ─ methanol (1/1), C26H26N4O5
- Crystal structure of (S)-1-phenylpropan-1-aminium (S)-(1-phenylpropyl)carbamate C19H26N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-((5-bromo-4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)thio)acetate, C18H16BrN3O2S
- The crystal structure of trichlorobis(pyridine-2,6-dithio-κS-carbomethylamido)antimony(III), [SbCl3(C9H11N3S2)2]
- Crystal structure of 1,8-dihydroxy-3-{[(triphenylstannyl)oxy]carbonyl} anthracene-9,10-dione, C33H22O6Sn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(2-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)hydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium-2-olate dihydrate, C12H14N4O4
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-pyridinium-2-carboxylate, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-nitrato-κ3O,O:O′′-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)sodium(I)], C24H18N6O7Na2
- Retractions
- Retraction of: Crystal structure of bis[diaquaisonicotinatosamarium(III)]-µ-isonicotinato-[diisonicotinatocopper(II)], CuSm2(C6H4NO2)8(H2O)4
- Retraction of: Crystal structure of aqua(2,2′-bipyridine-k 2 N:N′)(nitrato)-(4-aminobenzoato)cadmium(II) nitrate, [Cd(H2O)(NO3)(C10H8N2)(C7H7NO2)][NO3]
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Editorial
- Editorial 2024 – New developments and changes of Zeitschrift für Kristallographie – New Crystal Structures
- New Crystal Structures
- Hydrogen bonding and π⋅⋅⋅halogen interactions in the crystal structure of bis(theophyllinium) hexachloridoplatinate(IV) monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-2-carboxypyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C6H7ClN2O6
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-(3-amino-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 4 N:O:O':O')(1-methylpyrroldin-2-one-κ1O)dicopper(II)] – 1-methylpyrroldin-2-one (1/3), C40H48Cu2N12O12
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6-k6O6(2,4,5-trinitroimidazol-1-ido-k1O)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-bromoisophthalato-κ3O,O′:O″)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)dicadmium(II)] dihydrate
- Crystal structure of (5R,6S,E)-5-acetoxy-2-methyl-6-((2aR,3R,5aS,5bS,11aR,12aS)-2a,5a,8,8-tetramethyl-9-oxotetradecahydro-1H,12H-cyclopenta[a]cyclopropa[e]phenanthren-3-yl)hept-2-enoic acid, C32H48O5
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2 -thiocyanato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II) monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene–2,3,5,6-tetrachlorobenzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid (1/1)
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(1-[(2-ethyl-benzimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H–benzotriazole) cadmium(II), C32H32CdN10OCl2
- The crystal structure of N′-(tert-butyl)-N′-(3,5-dimethylbenzoyl)-3-methoxy-N,2-dimethylbenzohydrazide, C23H30N2O3
- Crystal stucture of 3-benzamido-N-(2-bromo-4-(perfluoropropan-2-yl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-fluorobenzamide
- Crystal structure of bis(μ-benzeneselenolato)-(tetracarbonyl)-{μ-[N-(diphenylphosphanyl)-N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-P,P-diphenylphosphinous amide]} diiron, C48H35Fe2NO4P2Se2
- The crystal structure of 2′-(p-tolyl)-4′H-spiro[isochromane-1,1′-naphthalene]-3,4′-dione, C25H18O3
- The crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-tetrakis(μ4-pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylate-κ5N: O: O′: O″: O‴)-bi(μ2-pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N: O: O′)-digadolinium(III)tricopper (II)], [Gd2Cu3(C7H3NO4)6(H2O)6] n
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(4-(4-(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)pyridin-1-ium-κ1N)-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ5O:O′: O″:O‴:O⁗)-(μ2-2,5-dicarboxyterephthalato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II)], C52H32N4O16Zn2
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-carboxy-6-nitrobenzoate monohydrate, C24H25FN4O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(1-((3,5-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-k1N)zinc(II), C22H24ZnN12Cl2
- The crystal structure of (3-chlorothiophene-2-carboxylato-κ2O, O′)-(2,2′-dipyridyl-κ2N,N′)lead(II), C20H12Cl2N2O4S2Pb
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (Z)-4-((1-(3-fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methylene)-5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one, C19H14FN5O
- The crystal structure of the coordination compound catena-poly[(18-crown-6-ether-κ6O6)(4,5-dinitroimidazolato-κ1O)potassium(I)]
- Crystal structure of 7-(diethylamino)-3-(trifluoroacetyl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H14F3NO3
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-1-[(2-ethylimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H–benzotriazole κ1N zinc(II), C24H26ZnN10Cl2
- Crystal and molecular structure of 5-bromopyridine-2,3-diamine
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-1-(3-carboxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-k3-O,O′:O″)hexaqua-dicobalt tetrahydrate], C26H36N4O20Co2
- Crystal structure of thiocyanate-κ1N-bis(μ1-2,6-diformyl-4-methylphenol oxime-κ2N,O)-manganese(III) acetonitrile solvate, C21H21MnN6O6S
- The crystal structure of pyrrolidin-1-yl pivalate, C9H13NO4
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-(2,2-diphenylethene-1,1-diyl)bis(1,4-dimethoxybenzene), C30H28O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzyltrimethylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), {(C6H5CH2)(CH3)3N}2[WS4]
- The crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-2-(ethoxymethylene)-3-oxobutanoate, C9H14O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-6-bromo-3,5-dimethyl-2-(1-phenylprop-1-en-2-yl)-3Himidazo[4,5b]pyridine, C17H16BrN3
- Crystal structure of (3S,3′S,4R,4′S)-3′-(furan-3-yl)-3-hydroxy-4′-methyl-3,5,6′,7′-tetrahydro-1H,3′H-4,5′-spirobi[isobenzofuran]-1,1′(4′H)-dione-methanol (1/1), C21H22O7
- Cocrystal structure of progesterone-isophthalic acid, C25H33O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(6-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-1-methylquinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C17H12FN3O
- Crystal structure of S-(4-carboxybutyl)- l -cysteine
- The cocrystal of 2,2′-(hydrazine-1,1-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarbonitrile)– methanol (2/3)
- Crystal structure of (1′R,2′S,4′R,6′S)-4,6-dihydroxy-1′,8′,8′-trimethyl-3-(3-methylbutanoyl)-4′,8′,6′,1′,7,2′-hexahydro-1H-4′,6′-methanoxanthene-8-carbaldehyde, C23H30O5
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-methylphenyl pyridazine-k 2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenyl-pyrazole-κ 2 C,N) iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C39H29F6IrN8P
- Crystal structure of 1,5-bis[(E)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene]thiocarbonohydrazide dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate, C17H18N4O2S·C2H6OS
- Crystal structure of (S)-4-(2-(4-(2-acetyl-5-chlorophenyl)-3-methoxy-6-oxopyridazin-1(6H)-yl)-3-phenylpropanamido)benzoic acid monohydrate, C29H26ClN3O7
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(2,4-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane
- Crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzyl (S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19ClO3
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-4-benzyl-1-(4-bromophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)ethan-1-one, C24H20BrN3O3
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3′-(2-(1-(3,4-dimethyl-phenyl)-3-methyl-5-oxo-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazol-4-ylidene)hydrazinyl)-2′-hydroxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3-carboxylicacid ─ methanol (1/1), C26H26N4O5
- Crystal structure of (S)-1-phenylpropan-1-aminium (S)-(1-phenylpropyl)carbamate C19H26N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-((5-bromo-4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)thio)acetate, C18H16BrN3O2S
- The crystal structure of trichlorobis(pyridine-2,6-dithio-κS-carbomethylamido)antimony(III), [SbCl3(C9H11N3S2)2]
- Crystal structure of 1,8-dihydroxy-3-{[(triphenylstannyl)oxy]carbonyl} anthracene-9,10-dione, C33H22O6Sn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(2-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)hydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium-2-olate dihydrate, C12H14N4O4
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-pyridinium-2-carboxylate, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-nitrato-κ3O,O:O′′-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)sodium(I)], C24H18N6O7Na2
- Retractions
- Retraction of: Crystal structure of bis[diaquaisonicotinatosamarium(III)]-µ-isonicotinato-[diisonicotinatocopper(II)], CuSm2(C6H4NO2)8(H2O)4
- Retraction of: Crystal structure of aqua(2,2′-bipyridine-k 2 N:N′)(nitrato)-(4-aminobenzoato)cadmium(II) nitrate, [Cd(H2O)(NO3)(C10H8N2)(C7H7NO2)][NO3]


