Abstract
C23H14Cl4N6O4, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 9.044(2) Å, b = 11.340(2) Å, c = 11.812(3) Å, α = 95.470(17)°, β = 105.46(2)°, γ = 90.084(18)°, V = 1161.8(5) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0914, wRref(F2) = 0.2547, T = 296 K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
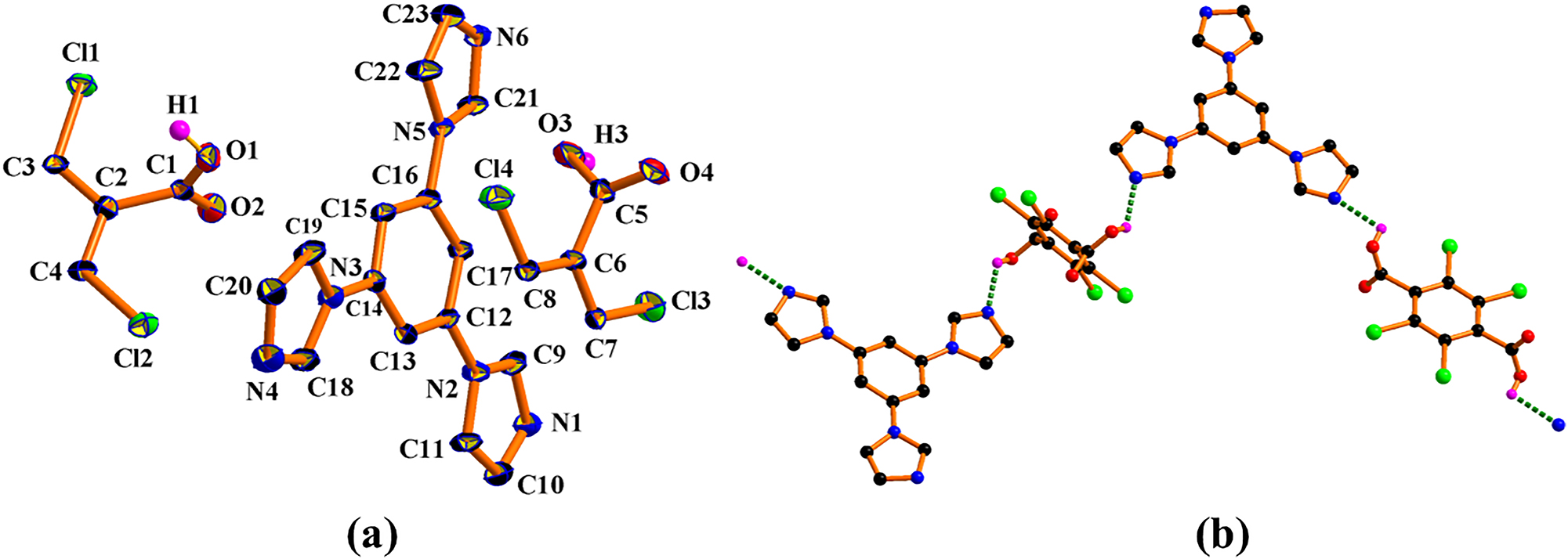
(a) The asymmetric unit structure of I, showing the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are shown at the 30 % probability level; (b) view of the 1D O–H⋯N hydrogen bonded framework in I. The dashed line shows the inter-molecular O–H⋯N hydrogen bond (symmetry codes: i −x, 2 − y, 1 − z; ii 3 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z).
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.28 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.56 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB Mini (ROW), ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.1°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 6227, 4143, 0.068 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 2132 |
| N(param)refined: | 334 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO, 1 Olex2, 2 SHELX, 3 , 4 PLATON 5 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.2601 (7) | 0.1318 (6) | 0.4625 (6) | 0.0399 (16) |
| C2 | 0.1276 (7) | 0.0595 (5) | 0.4783 (6) | 0.0393 (16) |
| C3 | 0.1396 (7) | 0.0071 (5) | 0.5844 (6) | 0.0409 (16) |
| C4 | −0.0153 (7) | 0.0524 (5) | 0.3969 (6) | 0.0406 (16) |
| C5 | 0.8117 (7) | 0.4935 (6) | 0.1465 (6) | 0.0433 (16) |
| C6 | 0.6482 (7) | 0.4957 (6) | 0.0746 (5) | 0.0366 (15) |
| C7 | 0.5758 (7) | 0.6030 (6) | 0.0604 (6) | 0.0364 (14) |
| C8 | 0.5701 (7) | 0.3936 (5) | 0.0151 (6) | 0.0383 (15) |
| C9 | 0.3895 (8) | 0.7741 (5) | 0.3348 (7) | 0.0465 (17) |
| H9 | 0.484011 | 0.777099 | 0.390980 | 0.056* |
| C10 | 0.1724 (8) | 0.8249 (6) | 0.2209 (7) | 0.055 (2) |
| H10 | 0.091191 | 0.870569 | 0.185001 | 0.066* |
| C11 | 0.1851 (7) | 0.7086 (6) | 0.1947 (6) | 0.0478 (17) |
| H11 | 0.114834 | 0.658656 | 0.138749 | 0.057* |
| C12 | 0.3808 (6) | 0.5599 (5) | 0.2732 (5) | 0.0316 (14) |
| C13 | 0.2984 (7) | 0.4660 (5) | 0.2053 (6) | 0.0392 (15) |
| H13 | 0.206704 | 0.478422 | 0.149834 | 0.047* |
| C14 | 0.3504 (7) | 0.3514 (5) | 0.2185 (5) | 0.0345 (14) |
| C15 | 0.4843 (7) | 0.3320 (5) | 0.3033 (5) | 0.0356 (14) |
| H15 | 0.515977 | 0.255479 | 0.317313 | 0.043* |
| C16 | 0.5700 (6) | 0.4303 (5) | 0.3669 (5) | 0.0346 (14) |
| C17 | 0.5204 (6) | 0.5441 (5) | 0.3552 (5) | 0.0337 (14) |
| H17 | 0.577912 | 0.608367 | 0.400525 | 0.040* |
| C18 | 0.1165 (8) | 0.2535 (7) | 0.0817 (7) | 0.058 (2) |
| H18 | 0.054919 | 0.319395 | 0.077918 | 0.070* |
| C19 | 0.3142 (9) | 0.1409 (6) | 0.1294 (7) | 0.060 (2) |
| H19 | 0.410764 | 0.112316 | 0.162743 | 0.072* |
| C20 | 0.1947 (9) | 0.0802 (7) | 0.0526 (7) | 0.060 (2) |
| H20 | 0.196632 | 0.001220 | 0.023515 | 0.072* |
| C21 | 0.7959 (7) | 0.4920 (6) | 0.5350 (6) | 0.0403 (16) |
| H21 | 0.767351 | 0.569424 | 0.549933 | 0.048* |
| C22 | 0.7926 (8) | 0.3066 (6) | 0.4596 (7) | 0.055 (2) |
| H22 | 0.763093 | 0.234536 | 0.414356 | 0.066* |
| C23 | 0.9221 (8) | 0.3316 (6) | 0.5477 (7) | 0.0544 (19) |
| H23 | 0.998517 | 0.277746 | 0.572945 | 0.065* |
| Cl1 | 0.31573 (19) | 0.01128 (15) | 0.68752 (17) | 0.0559 (6) |
| Cl2 | −0.0326 (2) | 0.11624 (17) | 0.26641 (17) | 0.0578 (6) |
| Cl3 | 0.6689 (2) | 0.72942 (16) | 0.13764 (18) | 0.0629 (6) |
| Cl4 | 0.6587 (2) | 0.25842 (16) | 0.0385 (2) | 0.0647 (6) |
| N1 | 0.2990 (6) | 0.8658 (5) | 0.3093 (5) | 0.0511 (15) |
| N2 | 0.3234 (6) | 0.6772 (4) | 0.2673 (5) | 0.0396 (13) |
| N3 | 0.2641 (6) | 0.2535 (4) | 0.1483 (5) | 0.0438 (14) |
| N4 | 0.0708 (7) | 0.1505 (6) | 0.0235 (6) | 0.0655 (19) |
| N5 | 0.7133 (5) | 0.4115 (4) | 0.4511 (4) | 0.0339 (12) |
| N6 | 0.9252 (6) | 0.4441 (5) | 0.5936 (5) | 0.0427 (14) |
| O1 | 0.3517 (5) | 0.0822 (4) | 0.4144 (5) | 0.0559 (13) |
| H1 | 0.362444 | 0.013890 | 0.432089 | 0.084* |
| O2 | 0.2677 (5) | 0.2371 (4) | 0.5045 (5) | 0.0558 (13) |
| O3 | 0.8323 (5) | 0.4808 (5) | 0.2570 (4) | 0.0624 (14) |
| H3 | 0.841024 | 0.546181 | 0.294654 | 0.094* |
| O4 | 0.9149 (5) | 0.5000 (5) | 0.0983 (4) | 0.0591 (14) |
1 Source of materials
All chemicals were purchased from commercial sources and used as received. A mixture of Pr(NO3)3·6H2O (0.0870 g, 2 mmol), 2,3,5,6-tetrachlorobenzene-1,4-dicarboxylate (0.03050 g, 1 mmol), 1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene (0.0275 g, 1 mmol) and methanol/acetonitrile/H2O (2 mL/2 mL/10 mL) was added to a 25 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel reactor and heated at 413 K for 4 days. After cooling to room temperature at a rate of 283 K h−1, colorless block-shaped crystals of I were collected by filtration, washed with anhydrous ethanol and dried in air. Phase pure crystals were obtained by manual separation (Yield: 17.4 mg ca. 30 % based on 1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene). Anal. Calc. for I: C23H14Cl4N6O4 (%) (Mr = 580.20): C, 47.57; H, 2.41; N, 14.48. Found: C, 47.59; H, 2.38; N, 14.49 (CCDC number 2359934).
2 Experimental details
CrysAlisPro 1.171.39.46 (Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, 2018) empirical absorption correction using spherical harmonics, implemented in SCALE3 ABSPACK scaling algorithm. 1 Using Olex2, 2 the structure was solved with the ShelXT 3 structure solution program and refined with the ShelXL 4 refinement package. Carbon-bound hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions (d = 0.93 Å) for CH and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation, with Uiso(H) set to 1.2Ueq(C) for –CH. The H atoms of hydroxyl group in I were refined as rotating groups, with dO–H = 0.82 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(O). The structure was examined using the ADDSYM subroutine of PLATON 5 to ensure that no additional symmetry could be applied to the models.
3 Comment
Cocrystals are single-phase solid complexes, consisting of two or more neutral molecules that are solid under ambient conditions (called coformers) with a well-defined stoichiometric ratio, for which no charge transfer is observed in the resulting crystal structure. 6 Recently, the design and investigation of cocrystals have obtained considerable attention because of not only their different potential applications, but also their potential to enhance solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. 7 – 9 Cocrystal development is however limited by their poor thermodynamic stability in aqueous environments. 10 Cocrystallization is an attractive formulation tool for tuning the physicochemical properties of a compound while not altering its molecular structure and has gained interest from both industry and academia. 11 Although the design strategy for cocrystals has marked several milestones over the past few decades, a holistic approach that utilizes as much cocrystal data in the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD) as possible is still lacking. 12 To date, the halogen-containing carboxylic acids, such as 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid, 2,3,5,6-tetrachlorobenzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid, and 2,3,5,6- tetrabromobenzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid, have afforded great interset in the preparation of MOFs for their out-standing features of versatile coordination fashions as well as potential hydrogen-bonding donors (C and O) and acceptors (F, Cl, Br). 13 – 15 A cocrystals can be afforded with the metal ions reaction with the above mentioned halogen-containing ligands and multi-nitrogen containing neutral auxiliary ligands under appropriate conditions. Accordingly, C–H⋯F/Cl/Br, C–F/Cl/Br⋯π, C–H⋯π and π⋯π are excellent candidates for assembling different organic molecules to cocrystals in different ways, ranging from one-dimensional (1D) chains and two-dimensional (2D) sheets to three- dimensional (3D) porous structures. 16 – 18 Of further interest, 2,3,5,6-tetrachlorobenzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid featuring four chlorines in the 2,3,5,6-positions of the phenyl ring, as a derivative of terephthalic acid, remains largely unexplored hitherto in the field of cocrystals, compared with the well-studied ligands, terephthalic acid. 19 In this study, we seek to use 2,3,5,6-tetrachlorobenzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid and 1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene as organic ligands for Pr(III) centers. Unfortunately, these combinations were unexpectedly obtained a cocrystal, which has been synthesized by hydrothermal methods and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction and elemental analysis.
The asymmetric unit of the title structure contains a 1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene molecule, in a general position, and two halfs of a 2,3,5,6-tetrachlorobenzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid molecules, being situated about a centre of inversion. There are hydrogen-bonding and π-stack interactions calculated by PLATON software. 5 Two 2,3,5,6-tetrachlorobenzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid molecules firstly interact with 1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene to form a 1D chain by a pair of N–H⋯O [O1–H1⋯N1, length 2.625(7) Å, angle 123°; O3–H3⋯N6, length 2.509(7) Å, angle 105° hydrogen bonds. In particular, interchain hydrogen bonds C–H⋯Cl stabilized the crystal structure of I; these were formed between the chlorine of the tetrachlorobenzene (Cl1, Cl2, Cl3, and Cl4), which is the acceptor, and the carbon of the imidazole, which acts as the donor [length 2.937(8)–3.559(8) Å, angle 102.06–168.07°]. The two bond distances of C⋯Cl are 3.546(7) Å and 3.559(8) Å, which is slightly greater than the sum of the van der Waals radii of C and Cl (3.52 Å); and a bond angle of C–H⋯Cl is 102.06°, which exceeds the preferred minimum hydrogen bond angle of 110°. 20 Therefore, it belongs to a weak C–H⋯Cl hydrogen bond, compared with the reported literature. 21 – 23 In addition, the cocrystal has two types of π⋯π stacking interactions (Cg1/Cg3, Cg4/Cg6): between the imidazole rings (5-membered ring, Cg1: N1/C9/N2/C11/C10 and 5-membered ring, Cg3: N5/C21/N6/C23/C22) related to the (1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene compositions), and between the 1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene and the tetrachlorobenzene phenyl rings (6-membered ring, Cg4: C12/C13/C14/C15/C16/C17 and 6-membered ring, Cg6: C6/C7/C8 ii /C6 ii /C7 ii /C8). The dihedral angles between the Cg1/Cg3 iii or Cg3 iii /Cg1 (symmetry code: iii 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z) is 4.9(4)°, with centroid-to-centroid distance of 3.642(4) Å, and perpendicular distance of 3.443(3) or 3.362(3) Å. The dihedral angles between the Cg4/Cg6 (Cg4/Cg6 iv , symmetry code: 1 − x, 1 − y, −z) or Cg6/Cg4 (Cg6 iv /Cg4) is 7.1(3)°, with centroid-to-centroid distance of 3.698(4) Å, and perpendicular distance of 3.588(2) or 3.450(3) Å. Furthermore, three C–Cl⋯π (C4–Cl2⋯Cg2, C7–Cl3⋯Cg2 iv , C8–Cl4⋯Cg1 iv , 5-membered ring, Cg1: N1/C9/N2/C11/C10) interactions exist between the flanking imidazole rings and C–Cl of the tetrachlorobenzene with C4⋯Cg2, C7⋯Cg2 iv , and C8⋯Cg1 iv distances of 3.411(4), 3.479(4), and 3.783(4) Å, and the C4–Cl2⋯Cg2, C7–Cl3⋯Cg2 iv , and C8–Cl4⋯Cg1 iv angles of 138.4(2), 97.1(2), and 91.7(2)°, respectively. Thus, through hydrogen bonds O–H⋯N, C–H⋯O/N/Cl and π⋯π as well as with C–Cl⋯π interactions, the 2,3,5,6-tetrachlorobenzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid and 1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene in I, is expanded into a stable three-dimensional supramolecular architecture. PLATON 5 analysis shows that the whole framework is composed of voids of 1.5 % that represent 1161.8 Å3 per unit cell volume and 16.9 Å3 total potential solvent area volume.
Funding source: Guangxi Key Laboratory of Green Chemical Materials and Safety Technology, Beibu Gulf University
Award Identifier / Grant number: YCSW2024560
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This research was funded by the Guangxi Key Laboratory of Green Chemical Materials and Safety Technology, Beibu Gulf University (Grant No. 2023ZZKT01).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Oxford Diffraction Ltd, CrysAlisPRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Version 1.171.39.6a, England, 2018.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Spek, A. L. Structure Validation in Chemical Crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. 2009, D65, 148–155; https://doi.org/10.1107/s090744490804362x.Search in Google Scholar
6. Bond, A. D. What Is a Co-crystal? CrystEngComm 2007, 9, 833–834; https://doi.org/10.1039/b708112j.Search in Google Scholar
7. Li, J. X.; Lu, Y. J.; Quan, K. Y.; Wu, L. B.; Feng, X.; Wang, W. Z. One-pot Cocrystallization of Mononuclear and 1D Cobalt(II) Complexes Based on Flexible Triclopyr and 2,2′-Bipyridine Coligands: Structural Analyses, Conformation Comparison, Non-covalent Interactions and Magnetic Properties. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1297, 136830, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.136830.Search in Google Scholar
8. Li, J. X.; Liu, M. Y.; You, X.; Wang, J. Q.; Feng, X. One-pot Cocrystallization of 1D Linear and Zigzag Cobalt(II) Polymers Assembled by Triclopyr and 4,4′-Bipyridine: Structural Comparison, Conformational Analysis, Non-covalent Interactions as Well as the Magnetic Property of the Latter. Polyhedron 2024, 249, 116791, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2023.116791.Search in Google Scholar
9. Friŝĉić, T. Supramolecular Concepts and New Techniques in Mechanochemistry: Cocrystals, Cages, Rotaxanes, Open Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3493–3510; https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs15332g.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Wong, S. N.; Fu, M.; Li, S.; Kwok, W. T. C.; Chow, S.; Low, K.-H.; Chow, S. F. Discovery of New Cocrystals Beyond Serendipity: Lessons Learned from Successes and Failures. CrystEngComm 2024, 26, 1505–1526; https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ce00021h.Search in Google Scholar
11. Huanga, N.; Rodríguez-Hornedo, N. Engineering Cocrystal Thermodynamic Stability and Eutectic Points by Micellar Solubilization and Ionization. CrystEngComm 2011, 13, 5409–5422; https://doi.org/10.1039/c1ce05381g.Search in Google Scholar
12. Devogelaer, J.-J.; Brugman, S. J. T.; Meekes, H.; Tinnemans, P.; Vlieg, E.; Gelder de, R. Cocrystal Design by Network-Based Link Prediction. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 6875–6885; https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ce01110b.Search in Google Scholar
13. Fujisawa, K.; Harakuni, S.; Ageishi, K.; Tiekink, E. R. T. Crystal Structure of Bis(3,5-Dimethyl-1h-Pyrazol-4-Ammonium) Tetrafluoroterephthate, 2[C5H10N3] [C8F4O4]. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 1017–1020; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0333.Search in Google Scholar
14. Fujisawa, K.; Harakuni, S.; Iwai, K.; Ageishi, K.; Tiekink, E. R. T. Crystal Structure of Bis(3,5-Diisopropyl-1h-Pyrazol-4-ammonium) Tetrafluoroterephthalate, 2[C9H18N3] [C8F4O4]. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239, 167–170; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0455.Search in Google Scholar
15. Mokoto, T. M. L.; Lemmerer, A.; Sayed, Y.; Smith, M. G. The Crystal Structure of the Host-Guest Complex: N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy)acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-Oxo-1,3-Diazinan-1-Yl)butanamide-Diethyl Ether (2/1). Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239, 261–264, https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0515.Search in Google Scholar
16. Zhu, H.; Li, Y.-H.; Xiao, Q.-Q.; Cui, G.-H. Three Luminescent Cd(II) Coordination Polymers Containing Aromatic Dicarboxylate and Flexible Bis(benzimidazole) Ligands as Highly Sensitive and Selective Sensors for Detection of Cr2O72− Oxoanions in Water. Polyhedron 2020, 187, 114648; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2020.114648.Search in Google Scholar
17. Chen, S.-C.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Huang, K.-L.; Chen, Q.; He, M.-Y.; Cui, A.-J.; Li, C.; Liu, Q.; Du, M. Solvent-controlled Assembly of Manganese(II) Tetrachloroterephthalates with 1D Chain, 2D Layer, and 3D Coordination Architectures. Cryst. Growth Des. 2008, 8, 3437–3445; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg8003905.Search in Google Scholar
18. Chen, S.-C.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Huang, K.-L.; Luo, H.-K.; He, M.-Y.; Du, M.; Chen, Q. Alkali-Metal-Regulated Construction of Superhydrophilic ZnII and CdII Coordination Polymers with Perhalogenated Terephthalate Ligands. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 9613–9622; https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ce41108g.Search in Google Scholar
19. Chen, X.-L.; Shen, Y.-J.; Gao, C.; Yang, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.-D.; Wei, G.-P.; Xiang, J.-F.; Sessler, J. L.; Gong, H.-Y. Regulating the Structures of Self-assembled Mechanically Interlocked Moleculecular Constructs via Dianion Precursor Substituent Effects. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 7443–7455; https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b13473.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
20. Arunan, E.; Desiraju, G. R.; Klein, R. A.; Sadlej, J.; Scheiner, S.; Alkorta, I.; Clary, D. C.; Crabtree, R. H.; Dannenberg, J. J.; Hobza, P.; Kjaergaard, H. G.; Legon, A. C.; Mennucci, B.; Nesbitt, D. J. Definition of the Hydrogen Bond (IUPAC Recommendations 2011). Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 1637–1641; https://doi.org/10.1351/pac-rec-10-01-02.Search in Google Scholar
21. Liu, M.; Yin, C.; Chen, P.; Zhang, M.; Parkin, S.; Zhou, P.; Li, T.; Yu, F.; Long, S. sp2C–H⋯Cl Hydrogen Bond in the ConFormational Polymorphism of 4-Chloro-Phenylanthranilic Acid. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 4345–4354; https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ce00772h.Search in Google Scholar
22. Tresca, B. W.; Zakharov, L. N.; Carroll, C. N.; Johnson, D. W.; Haley, M. M. Aryl C–H⋯Cl− Hydrogen Bonding in a Fluorescent Anion Sensor. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7240–7242; https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc44574g.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
23. Weng, Q.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Li, J.-M.; Ouyang, M. Construction of Two Stable Co(II)-Based Hydrogen-Bonded Organic Frameworks as a Luminescent Probe for Recognition of Fe3+ and Cr2O2−7 in H2O. Molecules 2021, 26, 5955; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26195955.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Editorial
- Editorial 2024 – New developments and changes of Zeitschrift für Kristallographie – New Crystal Structures
- New Crystal Structures
- Hydrogen bonding and π⋅⋅⋅halogen interactions in the crystal structure of bis(theophyllinium) hexachloridoplatinate(IV) monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-2-carboxypyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C6H7ClN2O6
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-(3-amino-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 4 N:O:O':O')(1-methylpyrroldin-2-one-κ1O)dicopper(II)] – 1-methylpyrroldin-2-one (1/3), C40H48Cu2N12O12
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6-k6O6(2,4,5-trinitroimidazol-1-ido-k1O)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-bromoisophthalato-κ3O,O′:O″)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)dicadmium(II)] dihydrate
- Crystal structure of (5R,6S,E)-5-acetoxy-2-methyl-6-((2aR,3R,5aS,5bS,11aR,12aS)-2a,5a,8,8-tetramethyl-9-oxotetradecahydro-1H,12H-cyclopenta[a]cyclopropa[e]phenanthren-3-yl)hept-2-enoic acid, C32H48O5
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2 -thiocyanato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II) monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene–2,3,5,6-tetrachlorobenzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid (1/1)
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(1-[(2-ethyl-benzimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H–benzotriazole) cadmium(II), C32H32CdN10OCl2
- The crystal structure of N′-(tert-butyl)-N′-(3,5-dimethylbenzoyl)-3-methoxy-N,2-dimethylbenzohydrazide, C23H30N2O3
- Crystal stucture of 3-benzamido-N-(2-bromo-4-(perfluoropropan-2-yl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-fluorobenzamide
- Crystal structure of bis(μ-benzeneselenolato)-(tetracarbonyl)-{μ-[N-(diphenylphosphanyl)-N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-P,P-diphenylphosphinous amide]} diiron, C48H35Fe2NO4P2Se2
- The crystal structure of 2′-(p-tolyl)-4′H-spiro[isochromane-1,1′-naphthalene]-3,4′-dione, C25H18O3
- The crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-tetrakis(μ4-pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylate-κ5N: O: O′: O″: O‴)-bi(μ2-pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N: O: O′)-digadolinium(III)tricopper (II)], [Gd2Cu3(C7H3NO4)6(H2O)6] n
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(4-(4-(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)pyridin-1-ium-κ1N)-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ5O:O′: O″:O‴:O⁗)-(μ2-2,5-dicarboxyterephthalato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II)], C52H32N4O16Zn2
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-carboxy-6-nitrobenzoate monohydrate, C24H25FN4O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(1-((3,5-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-k1N)zinc(II), C22H24ZnN12Cl2
- The crystal structure of (3-chlorothiophene-2-carboxylato-κ2O, O′)-(2,2′-dipyridyl-κ2N,N′)lead(II), C20H12Cl2N2O4S2Pb
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (Z)-4-((1-(3-fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methylene)-5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one, C19H14FN5O
- The crystal structure of the coordination compound catena-poly[(18-crown-6-ether-κ6O6)(4,5-dinitroimidazolato-κ1O)potassium(I)]
- Crystal structure of 7-(diethylamino)-3-(trifluoroacetyl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H14F3NO3
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-1-[(2-ethylimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H–benzotriazole κ1N zinc(II), C24H26ZnN10Cl2
- Crystal and molecular structure of 5-bromopyridine-2,3-diamine
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-1-(3-carboxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-k3-O,O′:O″)hexaqua-dicobalt tetrahydrate], C26H36N4O20Co2
- Crystal structure of thiocyanate-κ1N-bis(μ1-2,6-diformyl-4-methylphenol oxime-κ2N,O)-manganese(III) acetonitrile solvate, C21H21MnN6O6S
- The crystal structure of pyrrolidin-1-yl pivalate, C9H13NO4
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-(2,2-diphenylethene-1,1-diyl)bis(1,4-dimethoxybenzene), C30H28O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzyltrimethylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), {(C6H5CH2)(CH3)3N}2[WS4]
- The crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-2-(ethoxymethylene)-3-oxobutanoate, C9H14O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-6-bromo-3,5-dimethyl-2-(1-phenylprop-1-en-2-yl)-3Himidazo[4,5b]pyridine, C17H16BrN3
- Crystal structure of (3S,3′S,4R,4′S)-3′-(furan-3-yl)-3-hydroxy-4′-methyl-3,5,6′,7′-tetrahydro-1H,3′H-4,5′-spirobi[isobenzofuran]-1,1′(4′H)-dione-methanol (1/1), C21H22O7
- Cocrystal structure of progesterone-isophthalic acid, C25H33O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(6-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-1-methylquinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C17H12FN3O
- Crystal structure of S-(4-carboxybutyl)- l -cysteine
- The cocrystal of 2,2′-(hydrazine-1,1-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarbonitrile)– methanol (2/3)
- Crystal structure of (1′R,2′S,4′R,6′S)-4,6-dihydroxy-1′,8′,8′-trimethyl-3-(3-methylbutanoyl)-4′,8′,6′,1′,7,2′-hexahydro-1H-4′,6′-methanoxanthene-8-carbaldehyde, C23H30O5
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-methylphenyl pyridazine-k 2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenyl-pyrazole-κ 2 C,N) iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C39H29F6IrN8P
- Crystal structure of 1,5-bis[(E)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene]thiocarbonohydrazide dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate, C17H18N4O2S·C2H6OS
- Crystal structure of (S)-4-(2-(4-(2-acetyl-5-chlorophenyl)-3-methoxy-6-oxopyridazin-1(6H)-yl)-3-phenylpropanamido)benzoic acid monohydrate, C29H26ClN3O7
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(2,4-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane
- Crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzyl (S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19ClO3
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-4-benzyl-1-(4-bromophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)ethan-1-one, C24H20BrN3O3
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3′-(2-(1-(3,4-dimethyl-phenyl)-3-methyl-5-oxo-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazol-4-ylidene)hydrazinyl)-2′-hydroxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3-carboxylicacid ─ methanol (1/1), C26H26N4O5
- Crystal structure of (S)-1-phenylpropan-1-aminium (S)-(1-phenylpropyl)carbamate C19H26N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-((5-bromo-4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)thio)acetate, C18H16BrN3O2S
- The crystal structure of trichlorobis(pyridine-2,6-dithio-κS-carbomethylamido)antimony(III), [SbCl3(C9H11N3S2)2]
- Crystal structure of 1,8-dihydroxy-3-{[(triphenylstannyl)oxy]carbonyl} anthracene-9,10-dione, C33H22O6Sn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(2-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)hydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium-2-olate dihydrate, C12H14N4O4
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-pyridinium-2-carboxylate, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-nitrato-κ3O,O:O′′-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)sodium(I)], C24H18N6O7Na2
- Retractions
- Retraction of: Crystal structure of bis[diaquaisonicotinatosamarium(III)]-µ-isonicotinato-[diisonicotinatocopper(II)], CuSm2(C6H4NO2)8(H2O)4
- Retraction of: Crystal structure of aqua(2,2′-bipyridine-k 2 N:N′)(nitrato)-(4-aminobenzoato)cadmium(II) nitrate, [Cd(H2O)(NO3)(C10H8N2)(C7H7NO2)][NO3]
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Editorial
- Editorial 2024 – New developments and changes of Zeitschrift für Kristallographie – New Crystal Structures
- New Crystal Structures
- Hydrogen bonding and π⋅⋅⋅halogen interactions in the crystal structure of bis(theophyllinium) hexachloridoplatinate(IV) monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-2-carboxypyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C6H7ClN2O6
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-(3-amino-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ 4 N:O:O':O')(1-methylpyrroldin-2-one-κ1O)dicopper(II)] – 1-methylpyrroldin-2-one (1/3), C40H48Cu2N12O12
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6-k6O6(2,4,5-trinitroimidazol-1-ido-k1O)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ2-5-bromoisophthalato-κ3O,O′:O″)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)dicadmium(II)] dihydrate
- Crystal structure of (5R,6S,E)-5-acetoxy-2-methyl-6-((2aR,3R,5aS,5bS,11aR,12aS)-2a,5a,8,8-tetramethyl-9-oxotetradecahydro-1H,12H-cyclopenta[a]cyclopropa[e]phenanthren-3-yl)hept-2-enoic acid, C32H48O5
- The crystal structure of poly[diaqua-bis(μ2 -thiocyanato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II) monohydrate
- The crystal structure of 1,3,5-tri(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene–2,3,5,6-tetrachlorobenzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid (1/1)
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(1-[(2-ethyl-benzimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H–benzotriazole) cadmium(II), C32H32CdN10OCl2
- The crystal structure of N′-(tert-butyl)-N′-(3,5-dimethylbenzoyl)-3-methoxy-N,2-dimethylbenzohydrazide, C23H30N2O3
- Crystal stucture of 3-benzamido-N-(2-bromo-4-(perfluoropropan-2-yl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-fluorobenzamide
- Crystal structure of bis(μ-benzeneselenolato)-(tetracarbonyl)-{μ-[N-(diphenylphosphanyl)-N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-P,P-diphenylphosphinous amide]} diiron, C48H35Fe2NO4P2Se2
- The crystal structure of 2′-(p-tolyl)-4′H-spiro[isochromane-1,1′-naphthalene]-3,4′-dione, C25H18O3
- The crystal structure of poly[hexaqua-tetrakis(μ4-pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylate-κ5N: O: O′: O″: O‴)-bi(μ2-pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylate-κ3N: O: O′)-digadolinium(III)tricopper (II)], [Gd2Cu3(C7H3NO4)6(H2O)6] n
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(4-(4-(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)pyridin-1-ium-κ1N)-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ5O:O′: O″:O‴:O⁗)-(μ2-2,5-dicarboxyterephthalato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II)], C52H32N4O16Zn2
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-carboxy-6-nitrobenzoate monohydrate, C24H25FN4O10
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(1-((3,5-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-k1N)zinc(II), C22H24ZnN12Cl2
- The crystal structure of (3-chlorothiophene-2-carboxylato-κ2O, O′)-(2,2′-dipyridyl-κ2N,N′)lead(II), C20H12Cl2N2O4S2Pb
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (Z)-4-((1-(3-fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methylene)-5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one, C19H14FN5O
- The crystal structure of the coordination compound catena-poly[(18-crown-6-ether-κ6O6)(4,5-dinitroimidazolato-κ1O)potassium(I)]
- Crystal structure of 7-(diethylamino)-3-(trifluoroacetyl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C15H14F3NO3
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-1-[(2-ethylimidazole-1-yl)methyl]-1H–benzotriazole κ1N zinc(II), C24H26ZnN10Cl2
- Crystal and molecular structure of 5-bromopyridine-2,3-diamine
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-1-(3-carboxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-k3-O,O′:O″)hexaqua-dicobalt tetrahydrate], C26H36N4O20Co2
- Crystal structure of thiocyanate-κ1N-bis(μ1-2,6-diformyl-4-methylphenol oxime-κ2N,O)-manganese(III) acetonitrile solvate, C21H21MnN6O6S
- The crystal structure of pyrrolidin-1-yl pivalate, C9H13NO4
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-(2,2-diphenylethene-1,1-diyl)bis(1,4-dimethoxybenzene), C30H28O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzyltrimethylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), {(C6H5CH2)(CH3)3N}2[WS4]
- The crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-2-(ethoxymethylene)-3-oxobutanoate, C9H14O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-6-bromo-3,5-dimethyl-2-(1-phenylprop-1-en-2-yl)-3Himidazo[4,5b]pyridine, C17H16BrN3
- Crystal structure of (3S,3′S,4R,4′S)-3′-(furan-3-yl)-3-hydroxy-4′-methyl-3,5,6′,7′-tetrahydro-1H,3′H-4,5′-spirobi[isobenzofuran]-1,1′(4′H)-dione-methanol (1/1), C21H22O7
- Cocrystal structure of progesterone-isophthalic acid, C25H33O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(6-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)-1-methylquinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C17H12FN3O
- Crystal structure of S-(4-carboxybutyl)- l -cysteine
- The cocrystal of 2,2′-(hydrazine-1,1-diyl)bis(1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarbonitrile)– methanol (2/3)
- Crystal structure of (1′R,2′S,4′R,6′S)-4,6-dihydroxy-1′,8′,8′-trimethyl-3-(3-methylbutanoyl)-4′,8′,6′,1′,7,2′-hexahydro-1H-4′,6′-methanoxanthene-8-carbaldehyde, C23H30O5
- Crystal structure of (3,6-di(2-pyridyl)-4-methylphenyl pyridazine-k 2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenyl-pyrazole-κ 2 C,N) iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C39H29F6IrN8P
- Crystal structure of 1,5-bis[(E)-1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene]thiocarbonohydrazide dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate, C17H18N4O2S·C2H6OS
- Crystal structure of (S)-4-(2-(4-(2-acetyl-5-chlorophenyl)-3-methoxy-6-oxopyridazin-1(6H)-yl)-3-phenylpropanamido)benzoic acid monohydrate, C29H26ClN3O7
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(2,4-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane
- Crystal structure of 4-chlorobenzyl (S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C21H19ClO3
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-4-benzyl-1-(4-bromophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)ethan-1-one, C24H20BrN3O3
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3′-(2-(1-(3,4-dimethyl-phenyl)-3-methyl-5-oxo-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazol-4-ylidene)hydrazinyl)-2′-hydroxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3-carboxylicacid ─ methanol (1/1), C26H26N4O5
- Crystal structure of (S)-1-phenylpropan-1-aminium (S)-(1-phenylpropyl)carbamate C19H26N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-((5-bromo-4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)thio)acetate, C18H16BrN3O2S
- The crystal structure of trichlorobis(pyridine-2,6-dithio-κS-carbomethylamido)antimony(III), [SbCl3(C9H11N3S2)2]
- Crystal structure of 1,8-dihydroxy-3-{[(triphenylstannyl)oxy]carbonyl} anthracene-9,10-dione, C33H22O6Sn
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-(2-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)hydrazine-1-carbonyl)pyridin-1-ium-2-olate dihydrate, C12H14N4O4
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-pyridinium-2-carboxylate, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-nitrato-κ3O,O:O′′-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)sodium(I)], C24H18N6O7Na2
- Retractions
- Retraction of: Crystal structure of bis[diaquaisonicotinatosamarium(III)]-µ-isonicotinato-[diisonicotinatocopper(II)], CuSm2(C6H4NO2)8(H2O)4
- Retraction of: Crystal structure of aqua(2,2′-bipyridine-k 2 N:N′)(nitrato)-(4-aminobenzoato)cadmium(II) nitrate, [Cd(H2O)(NO3)(C10H8N2)(C7H7NO2)][NO3]

