Abstract
C37H22N2O, monoclinic, P2/n (no. 13), a = 8.9663(3) Å, b = 9.1812(3) Å, c = 30.8083(9) Å, β = 93.714(3)°, Z = 4, V = 2530.86(14) Å3, R gt(F) = 0.0445, wR ref(F 2) = 0.1192, T = 150 K.
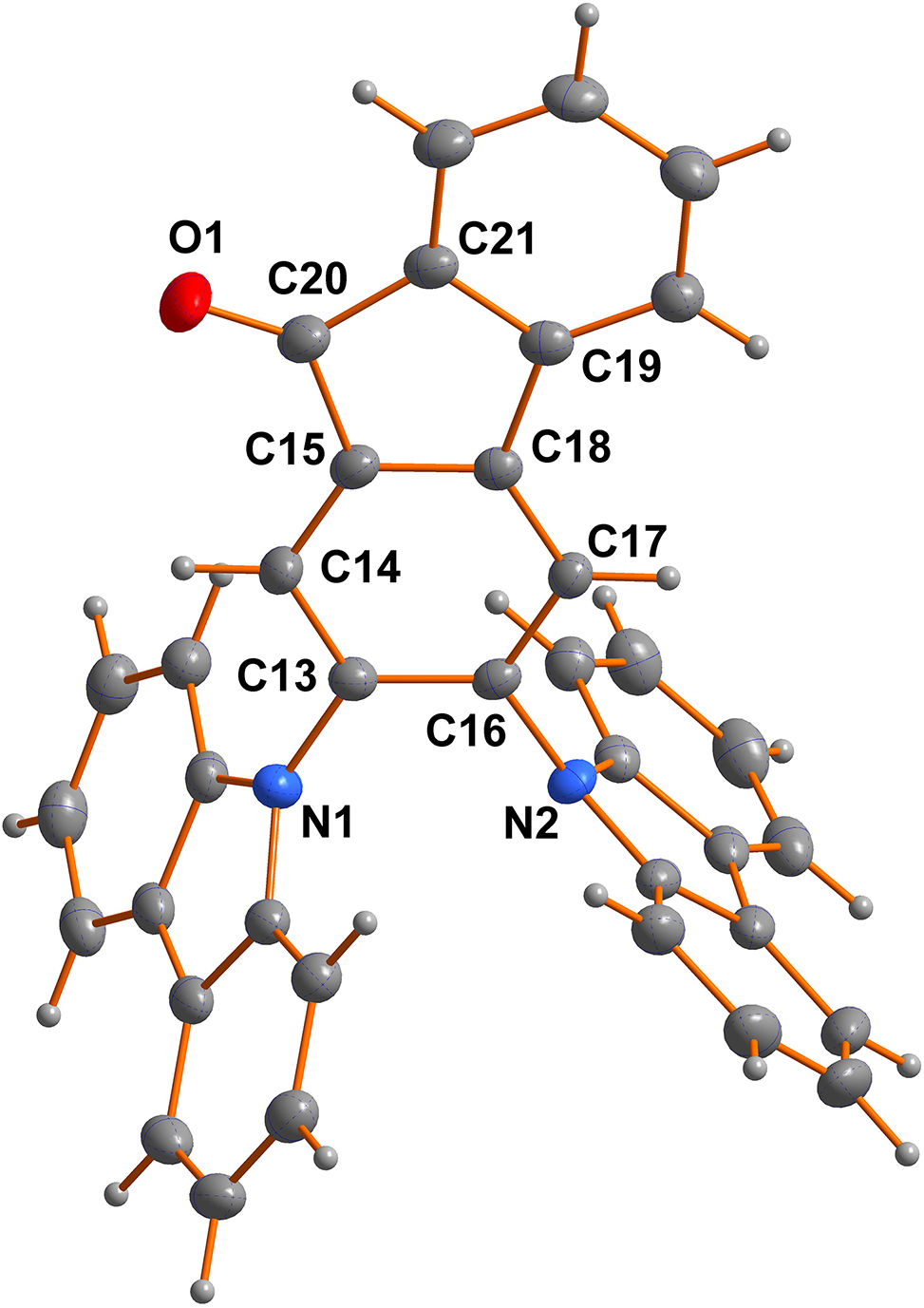
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contain the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.15 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | CuKα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 0.63 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 74.0°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 9905, 4986, 0.039 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 3982 |
| N(param)refined: | 361 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], Olex2 [2], Shelx [3, 4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | 1.02951 (17) | 0.52811 (16) | 0.24738 (5) | 0.0451 (4) |
| N1 | 0.65632 (16) | 0.32558 (15) | 0.36732 (5) | 0.0258 (3) |
| N2 | 0.56823 (15) | 0.59757 (15) | 0.40313 (4) | 0.0225 (3) |
| C1 | 0.51130 (19) | 0.27029 (18) | 0.36092 (5) | 0.0245 (3) |
| C2 | 0.3913 (2) | 0.32477 (19) | 0.33515 (5) | 0.0286 (4) |
| H2 | 0.399893 | 0.411425 | 0.318646 | 0.034* |
| C3 | 0.2584 (2) | 0.2475 (2) | 0.33450 (6) | 0.0321 (4) |
| H3 | 0.173639 | 0.283081 | 0.317655 | 0.039* |
| C4 | 0.2461 (2) | 0.1182 (2) | 0.35811 (6) | 0.0333 (4) |
| H4 | 0.153548 | 0.067583 | 0.357025 | 0.040* |
| C5 | 0.3669 (2) | 0.06333 (19) | 0.38292 (6) | 0.0309 (4) |
| H5 | 0.358323 | −0.024799 | 0.398725 | 0.037* |
| C6 | 0.50229 (19) | 0.13976 (18) | 0.38442 (5) | 0.0252 (3) |
| C7 | 0.6477 (2) | 0.11435 (18) | 0.40589 (5) | 0.0263 (4) |
| C8 | 0.7053 (2) | 0.00699 (19) | 0.43436 (6) | 0.0309 (4) |
| H8 | 0.643498 | −0.069954 | 0.443336 | 0.037* |
| C9 | 0.8540 (2) | 0.0146 (2) | 0.44928 (6) | 0.0342 (4) |
| H9 | 0.894413 | −0.057917 | 0.468638 | 0.041* |
| C10 | 0.9456 (2) | 0.1275 (2) | 0.43628 (6) | 0.0340 (4) |
| H10 | 1.047918 | 0.128895 | 0.446430 | 0.041* |
| C11 | 0.8905 (2) | 0.23787 (19) | 0.40883 (6) | 0.0298 (4) |
| H11 | 0.952608 | 0.315322 | 0.400378 | 0.036* |
| C12 | 0.74075 (19) | 0.23022 (18) | 0.39425 (5) | 0.0250 (3) |
| C13 | 0.70628 (18) | 0.46012 (18) | 0.35058 (5) | 0.0232 (3) |
| C14 | 0.80629 (19) | 0.45846 (19) | 0.31750 (6) | 0.0279 (4) |
| H14 | 0.840770 | 0.368878 | 0.306403 | 0.034* |
| C15 | 0.85368 (18) | 0.58925 (19) | 0.30136 (5) | 0.0252 (3) |
| C16 | 0.65867 (17) | 0.59324 (18) | 0.36672 (5) | 0.0206 (3) |
| C17 | 0.70441 (18) | 0.72516 (18) | 0.34937 (5) | 0.0220 (3) |
| H17 | 0.668566 | 0.815142 | 0.359803 | 0.026* |
| C18 | 0.80329 (17) | 0.72205 (18) | 0.31657 (5) | 0.0210 (3) |
| C19 | 0.87574 (18) | 0.84156 (19) | 0.29338 (5) | 0.0238 (3) |
| C20 | 0.9616 (2) | 0.6177 (2) | 0.26712 (6) | 0.0293 (4) |
| C21 | 0.96905 (19) | 0.77980 (19) | 0.26369 (5) | 0.0260 (4) |
| C22 | 1.0510 (2) | 0.8647 (2) | 0.23692 (6) | 0.0321 (4) |
| H22 | 1.114640 | 0.821644 | 0.217042 | 0.038* |
| C23 | 1.0376 (2) | 1.0150 (2) | 0.23993 (6) | 0.0344 (4) |
| H23 | 1.091364 | 1.076015 | 0.221543 | 0.041* |
| C24 | 0.9464 (2) | 1.0764 (2) | 0.26955 (6) | 0.0355 (4) |
| H24 | 0.939505 | 1.179437 | 0.271264 | 0.043* |
| C25 | 0.8642 (2) | 0.99113 (19) | 0.29698 (6) | 0.0290 (4) |
| H25 | 0.802608 | 1.034389 | 0.317373 | 0.035* |
| C26 | 0.42219 (18) | 0.65095 (17) | 0.40215 (5) | 0.0239 (3) |
| C27 | 0.3186 (2) | 0.66548 (19) | 0.36691 (6) | 0.0302 (4) |
| H27 | 0.343108 | 0.641435 | 0.338236 | 0.036* |
| C28 | 0.1778 (2) | 0.7165 (2) | 0.37531 (7) | 0.0382 (4) |
| H28 | 0.104553 | 0.727686 | 0.351867 | 0.046* |
| C29 | 0.1411 (2) | 0.7519 (2) | 0.41739 (7) | 0.0408 (5) |
| H29 | 0.043143 | 0.785207 | 0.422126 | 0.049* |
| C30 | 0.2454 (2) | 0.7391 (2) | 0.45223 (7) | 0.0357 (4) |
| H30 | 0.220116 | 0.764018 | 0.480771 | 0.043* |
| C31 | 0.38859 (19) | 0.68897 (18) | 0.44478 (6) | 0.0266 (4) |
| C32 | 0.5226 (2) | 0.66515 (17) | 0.47236 (5) | 0.0253 (3) |
| C33 | 0.5605 (2) | 0.6872 (2) | 0.51655 (6) | 0.0337 (4) |
| H33 | 0.487976 | 0.721648 | 0.535240 | 0.040* |
| C34 | 0.7039 (2) | 0.6583 (2) | 0.53267 (6) | 0.0366 (4) |
| H34 | 0.730146 | 0.672477 | 0.562745 | 0.044* |
| C35 | 0.8119 (2) | 0.6083 (2) | 0.50544 (6) | 0.0346 (4) |
| H35 | 0.910815 | 0.590812 | 0.517256 | 0.041* |
| C36 | 0.7773 (2) | 0.58380 (19) | 0.46150 (5) | 0.0278 (4) |
| H36 | 0.850261 | 0.549206 | 0.442986 | 0.033* |
| C37 | 0.63189 (19) | 0.61189 (17) | 0.44574 (5) | 0.0224 (3) |
1 Source of materials
A mixture of 2,3-difluoro-9H-fluoren-9-one (216 mg, 1 mmol), 9H-carbazole (367 mg, 2.2 mmol) and potassium carbonate (414 mg, 3 mmol) in 50 mL hydrofuran under nitrogen was refluxed for 12 h. After cooling down to room temperature, the product was extracted with dichloromethane and washed with water. The combined organic phase was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica gel using dichloromethane/petroleum to afford a yellow solid. Crystals were obtained by slow evaporation within 5 days.
2 Experimental details
Hydrogen atoms were included using riding models implemented in the Shelxl software [3, 4]. Using Olex2 [2], the structure was solved with the ShelXS [3] structure solution program and refined with the ShelXL [4] package.
3 Comment
Thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) materials offer a promising avenue for future commercial organic light-emitting diode (OLED) applications as they efficiently harness both singlet (S1) and triplet (T1) excitons without relying on noble metals [5]. A general strategy in designing TADF molecules involve connecting the donor (D) and acceptor (A) components by σ bond. This arrangement ensures a wide separation of electron distribution and enables the realization of emission at various wavelengths by modulating the intensity of D–A pairs [6].
Herein, a TADF molecule with 9H-fluoren-9-one for yellow OLEDs, namely DCM, is reported. In the molecular structure, the bond length of O1–C20 is 1.210(2) Å, which belongs to the typical C=O double bonds. The C–N bond lengths of the aromatic rings were between 1.395(2) and 1.403(2) Å, while the one that connects the two rings were slightly longer, at 1.422(2) and 1.4265(18) Å, respectively. The angles of C12–N1–C1 and O1–C20–C15 were measured at 108.65(14)° and 127.14(17)° respectively. Other bond lengths and bond angles are all in the normal ranges [7, 8]. The groups O1–C20–C21–C22 and O1–C20–C21–C19 exhibit torsion angles with the value of 1.7(3)° and −178.1(2)°, respectively, which indicate that the 9H-fluoren-9-one rings are almost coplanar. It can be observed that there is a significant angle between the donor (carbazole) and acceptor (9H-fluoren-9-one) with the torsion angles of 70.4(2)°. The twisted configuration of the carbazoles and acceptor skeleton allows for efficient separation of the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO), leading to an effective reverse intersystem crossing (RISC) process.
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work is supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2022M710020), the Science and Technology Project of Shenzhen City (JSGG20210802154213040).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. Saint, Apex2 and Sadabs; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
5. Ma, W., Bin, Z. Y., Yang, G., Liu, J. J., You, J. S. Structurally nontraditional bipolar hosts for RGB phosphorescent OLEDs: boosted by a Butterfly-shaped medium ring acceptor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202116681; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202116681.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Sun, B. J., Tong, K. N., Chen, X., He, J. L., Liu, H., Fung, M. K., Fan, J. A universal thermally activated delayed fluorescence host with short triplet lifetime for highly efficient phosphorescent OLEDs with extremely low efficiency roll-off. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 7706–7712; https://doi.org/10.1039/d1tc01394g.Search in Google Scholar
7. Li, Y. L., Wang, X. Z. Crystal structure of 10-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-5H-dibenzo[a,d] [7]annelen-5-one, C27H17NO. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 111–112; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0495.Search in Google Scholar
8. Sreenivas, D. K., Nagarajan, R. Highly regioselective synthesis of indenocarbazolones via palladium-catalyzed intramolecular ortho arylation. Synlett 2012, 23, 1007–1012; https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0031-1290660.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Solvothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(p-acetamidobenzoate-κ2O,O′)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)terbium(III) - water - methanol (1/1/1)
- Crystal structure of hexaaquazinc(II) catena-poly[bis(1-(3-carboxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(μ2-1-(3-carboxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-κ2O:O′)trizinc(II)] hexahydrate C26H36N4O20Zn2
- The crystal structure of valinyl-N-ium-4-(5-(thiophen-2-yl)isoxazol-3-yl)phenyl trifluoroacetate
- Crystal structure of bis(3,5-diisopropyl-1H-pyrazol-4-ammonium) tetrafluoroterephthalate, 2[C9H18N3][C8F4O4]
- Crystal structure of aqua-octakis(μ3-salicylato)-(1,10-phenanthroline)-(acetonitrile)-dicobalt(II)-trititanium(IV), C70H45N3O25Co2Ti3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-4,4′-diimidazole diphenyl ether-κ2N:N′)-(sulfato-κ1O)-cobalt(II)] – dimethylformamide (2/1), C39H37CoN9O8S
- Crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R, 13R,14R,17S)-2-(E-3-fluorobenzylidene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C37H53FO3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-((4,5,6-trimethoxy-3-oxobenzofuran-2(3H)-ylidene)methyl)phenyl diphenylphosphinate, C30H25O7P
- Crystal structure of 3-((5-methylpyridin-2-yl)amino)-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C15H16N2O
- The crystal structure of (R)-9-(5-methoxy-2-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]naphthalen-1-ylidene)-9H-thioxanthene, C28H22OS
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[1-(1-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ2N,O)] manganese(II), C16H20MnN10O8
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-[(methanesulfonyl)(methyl)amino]-6-(propan-2-yl)pyrimidin-5-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C26H36FN3O6S
- The crystal structure of samarium sulfate pentahydrate, Sm2(SO4)3(H2O)5
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ 4 N,O,O,O)-zinc(II)] monohydrate, C12H15NO9Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,3-difluoro-11H-benzo-[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoindol-11-one, C14H6F2N2O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-9H-fluoren-9-one, C37H22N2O
- The crystal structure of 5-(2-chloro-3-(3,6-di-tert-butyl-9H-carbazol-9-yl)phenyl)-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,f]azepine, C40H39ClN2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-1-hydroxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-enyloxy)-9H-xanthen-9-one, C18H15BrO4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-benzenesulfonato-κ2O:O′)-bis(μ2-6,6′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))-bis(2-methoxyphenolato-κ6O,O′:O′,N,N′,O′′:O′′,O′′′))disodium(I)dicopper(II)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1,2-bis(benzo[e][1,2]azaborinin-2(1H)-yl)ethene, C18H16B2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-benzyl ester, C37H52O3
- The crystal structure of ethyl (E)-1-chloro-3-(4-chloro-1-methyl-1H-indole-2-carbonyl)-4-oxo-2-phenylcyclooct-2-ene-1-carboxylate, C27H25Cl2NO4
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-((5-bromo-2-iodo-1,3-phenylene)bis(oxy))bis(tert-butylbenzene) ─ ethanol (2/1), C26H28BrIO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(benzyloxy)-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(dimethylamino)prop-2-en-1-one, C18H19NO3
- The crystal structure of N1,N3-bis(1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)\ propanediamide hydrate, C25H26N6O4, 2(H2O)
- The crystal structure of 2,5-bis[(1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)amino]cyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione, C28H26N6O4
- Crystal structure of 3,4-bis[2-(hydroxymethyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl] cyclobut-3-ene-1,2-dione hydrate, C14H22N2O5
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,4–dichlorobenzyl)-1H-benzimidazole, C14H10Cl2N2
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-((4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)oxy)phenyl)-4-(piperidin-1-yl)-5H-chromeno[2,3-d]pyrimidine, C28H27N5O4
- The crystal structure of 6-(benzofuran-2-yl)-2-oxo-4,5-diphenyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-3-carbonitrile, C26H17NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(4-bromobenzyl)-3-(difluoromethyl)-1-methyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide, C18H15BrF2N4O
- The crystal structure of the host-guest complex: N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy)acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide-diethyl ether (2/1)
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H17N3O2
- The crystal structure of diethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-cyanophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate, C20H22N2O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(5-((4-(difluoromethoxy)phenyl) sulfonyl)-3,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrol-2(1H)-yl) oxetane-3-carboxamide, C17H19F2N3O5S
- Crystal structure of 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)amino)-N-(2-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzamide hydrate, C25H37Cl2N5O6
- Crystal structure of 3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde, C14H8BrNO2S
- Crystal structure of 3-(difluoromethyl)-1-methyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide, C11H10F2N4O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-1-isopropyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate(V), C20H34F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dichloro-2-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1 H-benzo[d]imidazole-2-carboxylate, C11H12Cl2N2O2
- The crystal of structure of (OC-6-22)-pentakis(acetonitrile)bromidoruthenium(II)bromide monohydrate, C10H15Br2N5Ru
- Crystal structure of (2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(((4aS,5R,6S)-1-oxo-5-vinyl-4,4a,5,6-tetrahydro-1H,3H-pyrano[3,4-c]pyran-6-yl)oxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate hydrate, C23H26O12·H2O
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-amino-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16FN3O
- The crystal structure of 2′-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-[1,1′-binaphthalen]-2-amine, C32H22N2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ3-diiodido-[μ2-di(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methane-κ2N,N′)]dicopper(I)], C7H8Cu2I2N4
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-N′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 1,3-diacetyltetrahydroimidazo[4,5-d]imidazole-2,5(1H,3H)-dione, C8H10O4N4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane-k2N: N′)-bis(sorbato-κ1O)-copper(II), C18H28CuN2O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2 -1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-κ3O,O′:O′′)manganese(II)], C12H12N2O8Mn
- The crystal structure of [hexaaquamagnesium(II)] 4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalate trihydrate, C14H26N2O14Mg
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O3
- The crystal structure of bis(1,4,7,10,13-pentaoxacyclopentadecane)-potassium(I) dichloridocopper(I), C20H40Cl2CuKO10
- The crystal structure of tris(tetra-n-butylammonium) hexanitrato-κ2O,O′-lanthanium(III) C48H108N9O18La
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Solvothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(p-acetamidobenzoate-κ2O,O′)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)terbium(III) - water - methanol (1/1/1)
- Crystal structure of hexaaquazinc(II) catena-poly[bis(1-(3-carboxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(μ2-1-(3-carboxyphenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-κ2O:O′)trizinc(II)] hexahydrate C26H36N4O20Zn2
- The crystal structure of valinyl-N-ium-4-(5-(thiophen-2-yl)isoxazol-3-yl)phenyl trifluoroacetate
- Crystal structure of bis(3,5-diisopropyl-1H-pyrazol-4-ammonium) tetrafluoroterephthalate, 2[C9H18N3][C8F4O4]
- Crystal structure of aqua-octakis(μ3-salicylato)-(1,10-phenanthroline)-(acetonitrile)-dicobalt(II)-trititanium(IV), C70H45N3O25Co2Ti3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-4,4′-diimidazole diphenyl ether-κ2N:N′)-(sulfato-κ1O)-cobalt(II)] – dimethylformamide (2/1), C39H37CoN9O8S
- Crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R, 13R,14R,17S)-2-(E-3-fluorobenzylidene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C37H53FO3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-((4,5,6-trimethoxy-3-oxobenzofuran-2(3H)-ylidene)methyl)phenyl diphenylphosphinate, C30H25O7P
- Crystal structure of 3-((5-methylpyridin-2-yl)amino)-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C15H16N2O
- The crystal structure of (R)-9-(5-methoxy-2-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]naphthalen-1-ylidene)-9H-thioxanthene, C28H22OS
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis[1-(1-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylato-κ2N,O)] manganese(II), C16H20MnN10O8
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-[(methanesulfonyl)(methyl)amino]-6-(propan-2-yl)pyrimidin-5-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C26H36FN3O6S
- The crystal structure of samarium sulfate pentahydrate, Sm2(SO4)3(H2O)5
- The crystal structure of [triaqua-(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ 4 N,O,O,O)-zinc(II)] monohydrate, C12H15NO9Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,3-difluoro-11H-benzo-[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoindol-11-one, C14H6F2N2O
- The crystal structure of 2,3-di(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-9H-fluoren-9-one, C37H22N2O
- The crystal structure of 5-(2-chloro-3-(3,6-di-tert-butyl-9H-carbazol-9-yl)phenyl)-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,f]azepine, C40H39ClN2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-1-hydroxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-enyloxy)-9H-xanthen-9-one, C18H15BrO4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-benzenesulfonato-κ2O:O′)-bis(μ2-6,6′-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))-bis(2-methoxyphenolato-κ6O,O′:O′,N,N′,O′′:O′′,O′′′))disodium(I)dicopper(II)
- The crystal structure of (E)-1,2-bis(benzo[e][1,2]azaborinin-2(1H)-yl)ethene, C18H16B2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-benzyl ester, C37H52O3
- The crystal structure of ethyl (E)-1-chloro-3-(4-chloro-1-methyl-1H-indole-2-carbonyl)-4-oxo-2-phenylcyclooct-2-ene-1-carboxylate, C27H25Cl2NO4
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-((5-bromo-2-iodo-1,3-phenylene)bis(oxy))bis(tert-butylbenzene) ─ ethanol (2/1), C26H28BrIO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(benzyloxy)-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(dimethylamino)prop-2-en-1-one, C18H19NO3
- The crystal structure of N1,N3-bis(1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)\ propanediamide hydrate, C25H26N6O4, 2(H2O)
- The crystal structure of 2,5-bis[(1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)amino]cyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione, C28H26N6O4
- Crystal structure of 3,4-bis[2-(hydroxymethyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl] cyclobut-3-ene-1,2-dione hydrate, C14H22N2O5
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,4–dichlorobenzyl)-1H-benzimidazole, C14H10Cl2N2
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-((4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)oxy)phenyl)-4-(piperidin-1-yl)-5H-chromeno[2,3-d]pyrimidine, C28H27N5O4
- The crystal structure of 6-(benzofuran-2-yl)-2-oxo-4,5-diphenyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-3-carbonitrile, C26H17NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(4-bromobenzyl)-3-(difluoromethyl)-1-methyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide, C18H15BrF2N4O
- The crystal structure of the host-guest complex: N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy)acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide-diethyl ether (2/1)
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H17N3O2
- The crystal structure of diethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-cyanophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate, C20H22N2O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(5-((4-(difluoromethoxy)phenyl) sulfonyl)-3,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrol-2(1H)-yl) oxetane-3-carboxamide, C17H19F2N3O5S
- Crystal structure of 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dimethylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)amino)-N-(2-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl)benzamide hydrate, C25H37Cl2N5O6
- Crystal structure of 3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde, C14H8BrNO2S
- Crystal structure of 3-(difluoromethyl)-1-methyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide, C11H10F2N4O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-1-isopropyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate(V), C20H34F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 5,6-dichloro-2-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1 H-benzo[d]imidazole-2-carboxylate, C11H12Cl2N2O2
- The crystal of structure of (OC-6-22)-pentakis(acetonitrile)bromidoruthenium(II)bromide monohydrate, C10H15Br2N5Ru
- Crystal structure of (2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(((4aS,5R,6S)-1-oxo-5-vinyl-4,4a,5,6-tetrahydro-1H,3H-pyrano[3,4-c]pyran-6-yl)oxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate hydrate, C23H26O12·H2O
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-amino-N′-(1-(4-fluorophenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16FN3O
- The crystal structure of 2′-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-[1,1′-binaphthalen]-2-amine, C32H22N2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ3-diiodido-[μ2-di(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methane-κ2N,N′)]dicopper(I)], C7H8Cu2I2N4
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-N′-hydroxy-1H-pyrazole-4-carboximidamide, C4H7N5O
- The crystal structure of 1,3-diacetyltetrahydroimidazo[4,5-d]imidazole-2,5(1H,3H)-dione, C8H10O4N4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane-k2N: N′)-bis(sorbato-κ1O)-copper(II), C18H28CuN2O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ2 -1-(4-carboxylatophenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropyridazine-3-carboxylato-κ3O,O′:O′′)manganese(II)], C12H12N2O8Mn
- The crystal structure of [hexaaquamagnesium(II)] 4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalate trihydrate, C14H26N2O14Mg
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O3
- The crystal structure of bis(1,4,7,10,13-pentaoxacyclopentadecane)-potassium(I) dichloridocopper(I), C20H40Cl2CuKO10
- The crystal structure of tris(tetra-n-butylammonium) hexanitrato-κ2O,O′-lanthanium(III) C48H108N9O18La

