Abstract
Background
Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (chRCC) has a favorable prognosis. Due to irregular nuclei and nuclear pleomorphism, chRCC has a high Fuhrman nuclear grade (FNG). The chromophobe tumor grade (CTG) is a novel three-tier grading system that has been reported to be a better prognosticator than the traditional FNG. We compared the two nuclear grading systems in terms of patients’ clinical outcomes.
Patients and Method
We performed this retrospective chart review of all patients with chRCC from 2000 to 2017. All pathologic features and CTG and FNG results were re-evaluated.
Result
Eighteen patients’ records were reviewed with a mean follow-up of 70.6 months. The nuclear grading distribution was as follows: FNG 2, 56%; FNG 3, 39%; FNG 4, 5%; CTG 1, 78%; CTG 2, 17%; and CTG 3, 6%. Only one patient died. This patient had adrenal invasion, lung metastasis, sarcomatoid change and tumor necrosis, and the tumor was graded as FNG 4 and CTG 3. Overall survival was associated with both FNG and CTG.
Conclusion
Chromophobe RCC was associated with a low rate of cancer-specific death and sarcomatoid differentiation. Both FNG and CTG were associated with overall survival.
1 Introduction
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) was diagnosed in 350,000 people worldwide in 2013 [1]. In the United States of America, about 65,000 new patients are diagnosed with RCC and almost 15,000 patients die each year [2]. Improvements in diagnostic tools have led to earlier diagnosis of RCC in recent years. Clear cell RCC is the most common type of RCC, and chromophobe RCC (chRCC) only accounts for 5% of all cases of RCC [3]. Use of the Fuhrman nuclear grade (FNG) is worldwide, and it categorizes tumors as grade 1 to grade 4 according to nuclei size, shape, presence of nucleoli, and nuclear pleomorphism [4]. However, new subtypes of RCC were defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2016, and the FNG has not yet been validated for these subtypes of RCC, and a proposed fourtier World Health Organization /International Society of Urological Pathology grading system is only applicable for clear cell RCC and papillary RCC [5].
Chromophobe RCC has a better prognostic outcome than clear cell RCC, with a 10-year survival rate of more than 80% [6, 7]. However, due to irregular nuclei and nuclear pleomorphism, chRCC’s high FNG can confuse physicians because of the inconsistency of a favorable prognosis and high grade. Delahunt et al. concluded that FNG was not suitable for chRCC [8], and{Delahunt, 2007 #7} Paner et al. proposed a three-tier grading scheme that was strongly associated with pathologic stage and was shown to be an independent predictive factor of outcomes [9]. This grading system has not been applied globally due to controversial conclusions between studies. In this study, we re-evaluated patients with chRCC at our hospital using the two grading systems and patient clinical outcomes.
2 Materials and methods
After institutional review board approval, charts of all patients with chRCC from January 2000 to May 2017 were reviewed retrospectively. Patients who did not receive surgical resection and those with no available pathologic slide reviews were excluded. Informed consent has been obtained from all individuals included in this study.
Clinical features included age at surgery, sex, laterality, location, symptoms at presentation, treatment methods, and performance status according to the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) class at surgery. The vital signs of each patient were also reviewed. Image surveys including computed tomography and ultrasound performed 3-6 months after surgery and then annually during follow-up. Adverse events including local recurrence, distance metastasis, and death owing to disease were recorded by clinic visit or telephone interview. Follow-up ended on September 30, 2017.
Pathologic features included tumor size, margin status, neurovascular invasion, lymph node status, cell type (classic or pale, eosinophilic, mixed cell types), broad alveolar growth, sarcomatoid change, necrosis, and pathologic TNM stage according to the 2016 American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC 8th edition, 2016). The nuclear characteristics were evaluated by FNG (grades 1, 2, 3, and 4) and the chromophobe tumor grade (CTG) three-tier grading system described by Paner et al. [9] (Table 1) The novel CTG system is based on nuclear crowding and anaplasia. Tumor slides were assessed at 100x and 400x magnification. Nuclear crowding was defined as high nuclear/cytoplasmic density at 100x magnification and some nuclei contact at 400x magnification. Anaplasia was defined as a ≥ three-fold variation in nuclear size and distinct nuclear chromatin irregularities. At least two areas were graded, and the highest grade was assigned to the tumor. A grade 1 tumor was defined as a classic chRCC pattern without nuclear crowding and anaplasia (Figure 1); grade 2 was defined as nuclear crowding and nuclear pleomorphism (Figure 2); and grade 3 was defined as frank anaplasia or sarcomatoid change (Figure 3). All pathologic features and tumor grading were reviewed by one pathologist (SHD).
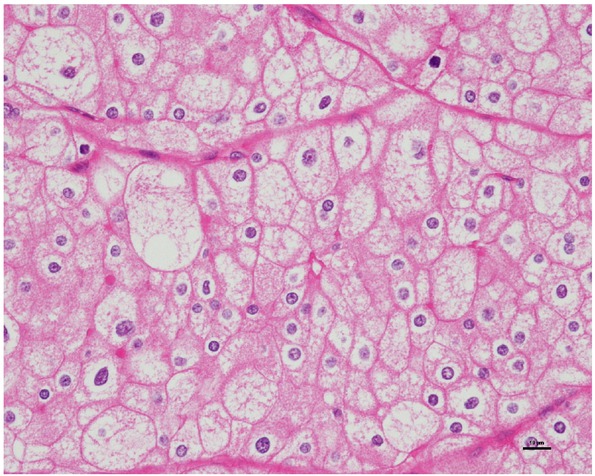
Classical chromophobe renal cell carcinoma pattern with wide constitutive nuclear range, without nuclear crowding and anaplasia (400x), CTG 1, FNG 3
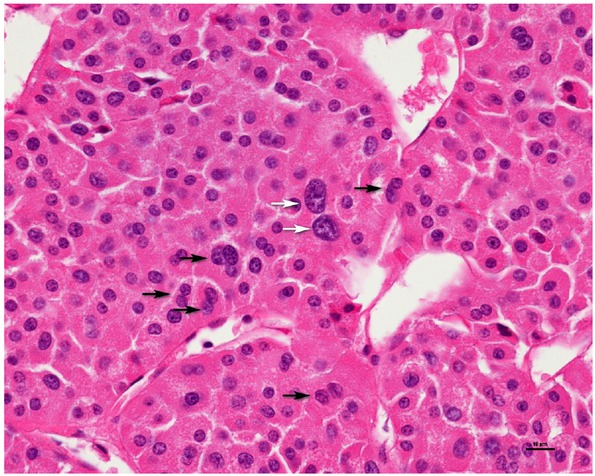
Nuclear crowding (black arrow) with pleomorphism (white arrow, three-fold variation in nuclear size and distinct nuclear chromatin irregularities) (400x), CTG 2, FNG 3
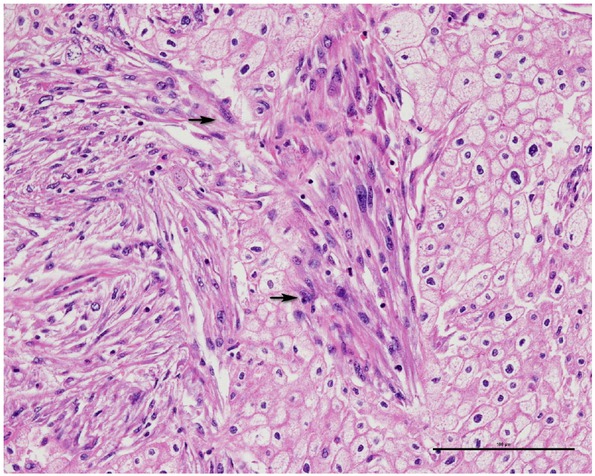
Tumor cells with sarcomatoid change (black arrow) (200x), CTG 3, FNG 4
Descriptive and analytic statistics of the data were computed using SPSS (version 21.0; IBM SPSS Statistics, IBM Corporation, Chicago, IL) for Windows. All tests were two-tailed, and the level of significance was set at p < 0.05. Fisher’s exact test and the t-test were used for comparisons of demographics including pathologic parameters and survival status. Associations between nuclear grade and pathologic stage were evaluated using Fisher’s exact test.
The criteria of two tumor grading system for chromophobe RCC
| Grade | Fuhrman nuclear grading | Chromophobe tumor grading |
|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Nucleoli are absent or inconspicuous and basophilic at 400x | Wide constitutive nuclear range but without nuclear crowding and anaplasia |
| Grade 2 | Nucleoli are conspicuous and eosinophilic at 400x and visible but not prominent at 100x | Geographic nuclear crowding and the presence of nuclear pleomorphism |
| Grade 3 | Nucleoli are conspicuous and eosinophilic at 100x | Presence of frank anaplasia (nuclear polylobation, tumor giant cells) or sarcomatoid change |
| Grade 4 | Extreme nuclear pleomorphism, mulitnucleate giant cells, and/or rhabdoid, sarcomatoid differentiation |
3 Results
A total of 20 patients were identified, of whom two were excluded due to having both clear cell and chromophobe cell types. The remaining 18 patients (eight men and ten women; median age 51.7 years, range 35 – 74 years) were enrolled into the analysis. The clinicopathologic and demographic characteristics are illustrated in Table 2. Fourteen patients received radical nephrectomy, and four patients received partial nephrectomy. Neither lymph node dissection nor venous thrombectomy was performed as there was no obvious lymph node enlargement or tumor thrombus. The patients’ performance status was assessed by ASA class; two cases were class I, eleven cases were class II, and five were class III. The average tumor size was 7.2 cm (range 2.5 – 14 cm), and 84% of the patients had a low stage (stage I – II) and 16% had a high stage (stage III – IV). Pathology showed that 44% of the cases were mixed type (classic and eosinophilic types) and 44% had tumor necrosis. One case had sarcomatoid change, and another case had neurovascular invasion. All of the cases had a broad alveolar growth pattern. The nuclear grading was as follows: FNG 2, 56%; FNG 3, 39%; FNG 4, 5%; CTG 1, 78%; CTG 2, 17%; and CTG 3, 6%. None of the cases had FNG 1 in this study. 9 cases in FNG 2 and 5 cases in FNG 3 downgrade to CTG 1, 2 cases in FNG 3 downgrade to CTG 2, and one case remained grade 2 in two grading systems. One case remained in the highest grade in pathologic finding.
Clinicopathologic and demographic characteristics of patients. Associations between survival and parameters
| Mean (range) | p value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at surgery (years) | 51.7 (35-74) | 0.609 | |||
| Maximum tumor size (cm) | 7.2 (2.5-14) | 0.888 | |||
| Follow up time (months) | 70.6 (3-205) | ||||
| Number (%) | Survival (%) | Death (%) | p value | ||
| Sex | Female | 10 (56) | 10 (100) | 0 (0) | 0.183 |
| Male | 8 (44) | 6 (89) | 2 (11)* | ||
| ASA | I | 2 (11) | 2 (100) | 0 (0) | 0.137 |
| II | 11 (61) | 11 (100) | 0 (0) | ||
| III | 5 (28) | 3 (60) | 2 (40)* | ||
| Stage | I | 10 (56) | 9 (90) | 1 (10) | 0.379 |
| II | 5 (28) | 5 (100) | 0 (0) | ||
| III | 1 (5) | 1 (100) | 0 (0) | ||
| IV | 2 (11) | 1 (50) | 1 (50)* | ||
| Margin free status | 0.111 | ||||
| Yes | 17 (94) | 16 (94) | 1 (6) | ||
| No | 1 (6) | 0 (0) | 1 (100)* | ||
| Neurovascular invasion | >0.999 | ||||
| Yes | 1 (6) | 1 (100) | 0 (0) | ||
| No | 17 (94) | 15 (88) | 2 (12)* | ||
| Cell type | 1. classic (pale) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 1 (100)* | 0.176 |
| 2. eosinophilic | 5 (28) | 5 (100) | 0 (0) | ||
| 3. mixed cell types | 12 (67) | 11 (92) | 1 (8) | ||
| Sarcomatoid | Yes | 1 (6) | 0 (0) | 1 (100)* | 0.111 |
| No | 17 (94) | 16 (94) | 1 (6) | ||
| Necrosis | Yes | 8 (44) | 8 (80) | 2 (20)* | 0.477 |
| No | 10 (56) | 8 (100) | 0 (0) | ||
| Fuhrman nuclear | grade | 0.046 | |||
| 2 | 10 (56) | 10 (100) | 0 (0) | ||
| 3 | 7 (39) | 6 (86) | 1 (14) | ||
| 4 | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 1 (100)* | ||
| Chromophobe tumor grade | 0.039 | ||||
| 1 | 14 (78) | 14 (100) | 0 (0) | ||
| 2 | 3 (17) | 2 (67) | 1 (33) | ||
| 3 | 1 (6) | 0 (0) | 1 (100)* | ||
* represents the patient’s clinicopathologic characteristics who died due to chromophobe RCC
The mean follow-up period was 70.6 months (range 3 – 205 months). Two patients died. One of the patients died due to recurrence of colorectal cancer with multiple metastases, and the other died of chRCC. This patient had a tumor of 9.5 cm in size with adrenal gland invasion and lung metastasis and died 3 months after nephrectomy. Pathology revealed a pale cell type, sarcomatoid change, and tumor necrosis. The tumor grade was FNG 4 and CTG 3. None of the other patients had local recurrence or distant metastasis. The adverse event rate was 5.56%.
Risk factor analysis showed that neither FNG nor CTG were significantly associated with patient age, sex, surgical margin, cell type, neurovascular invasion, sarcomatoid changed, or necrosis. Both FNG and CTG were significantly associated with overall survival (Table 2), however there was no association with cancer-specific survival. In addition, there were no significant associations between survival and age, sex, tumor size, stage or other pathologic factors. There was also no significant relationship between overall survival with FNG (p=0.142) and CTG (p=0.176) in the nonsarcomatoid chRCC cohort. Pathologic stage was significantly associated with FNG (p = 0.005), but not with CTG (p = 0.064) (Table 3).
Associations between TNM stage and nuclear grade
| Stage I (%) | Stage II (%) | Stage III (%) | Stage IV (%) | Total n | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuhrman nuclear grade 2 | 30 | 50 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0.005 |
| Fuhrman nuclear grade 3 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | |
| Fuhrman nuclear grade 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 1 | |
| Chromophobe tumor grade 1 | 57 | 36 | 0 | 7 | 14 | 0.064 |
| Chromophobe tumor grade 2 | 67 | 0 | 33 | 0 | 3 | |
| Chromophobe tumor grade 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 1 |
4 Discussion
Previous studies have demonstrated the nuclear characteristics of chRCC according to FNG and CTG (Figure 4)
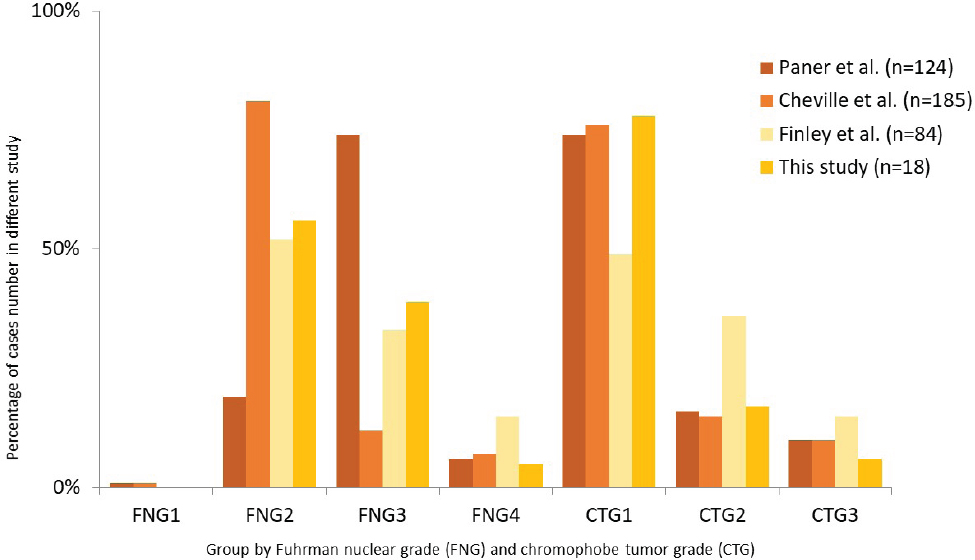
Comparison of FNG and CTG distributions in different studies Only two studies had 1% cases classified as FNG 1. Most cases were classified as FNG 2 or 3 and were classified as CTG 1
[9, 10, 11]. All of these studies and our data showed that approximately 0 to 1% of all cases were classified as FNG 1. Most cases were classified as FNG 2 or 3, and there were noticeable differences in each study. Most cases were classified as CTG 1, and it seemed to be more consistent in these four studies. As no lowest FNG grade is associated with a good prognosis, Finley et al. suggested that FNG cannot be used for chRCC [10]. Delahunt et al. reviewed 87 cases with chRCC and reported no associations between whole tumor and focal Fuhrman grade and adverse events. They suggested that chRCC often have an insignificant nucleolus, and unusual nuclear pattern. Because FNG relies on individual human observation of nuclear size, shape, and nucleolar prominence, interobserver error may have occurred and caused variations in previous studies. Delahunt concluded that the Fuhrman grading system is not appropriate for chRCC [8]. The fourth edition of the WHO classification also suggests that the Fuhrman system should not be used for chRCC, and that a new grading system for chRCC may be internationally accepted in the future [5]. In this study, FNG was significantly associated with overall survival, but not cancer-specific survival. This is consistent with previous studies in that the FNG system is not suitable for chRCC.
Paner and colleagues first proposed the three-tier CTG tumor grading system for chRCC. In their study, all 12 CTG 3 tumors showed sarcomatoid changes, and tumors with sarcomatoid differentiation were excluded from their analysis. The pathologic stage was strongly positively associated with CTG, and according to multivariate Cox regression models, CTG and necrosis were independent predictors of adverse events [9]. Finley et al. reported a strong association between pathologic T stage and both grading systems. In ROC curve analysis, for RFS and OS, CTG provided slightly higher accuracy than FNG for the overall and non-sarcomatoid cohorts [10]. However, Cheville and colleagues reported different results. They collected data from only non-sarcomatoid and stage I and II cohorts, and found no association between CTG or FNG with cancer-specific survival. Therefore, they suggested that CTG did not provide more prognostic information [11]. In this study, pathologic stage was significantly associated with FNG, and tended to be associated with CTG in the patients overall. However, the number of cases was small.
Previous studies have reported that sarcomatoid differentiation ranges from 2% to 13% of all chRCC [7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13]. {Finley, 2011 #3} However, the number of cases varied greatly between these studies. Sarcomatoid differentiation was associated with adverse outcomes and the highest grade. The number of cases may have influenced the number of adverse events. In our study, only one tumor presented with sarcomatoid differentiation, and the patient died. There were no other cases of local recurrence or metastasis. Therefore, the association between survival and grading system may be affected by the small numbers of cases overall and those with sarcomatoid differentiation.
Weinzierl and colleagues reported that only pathologic stage CTG 3 was significantly associated with adverse events, and that CTG 1 and 2 did not have this association [12]. Xie et al reported 209 Chinese patients with chRCC, in whom multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that tumor stage and CTG were independent predictors of disease-free survival. They also compared CTG 1+2 with CTG 3 and reported that CTG3 was associated with significicantly worse disease-free survival, however, they did not find a significant difference between CTG 1 and 2 [7]. Cheville et al analyzed 185 patients with chRCC adjusted by TNM stage, and found that cancer-specific death was associated with CTG. With the reference set as CTG 1 compared with CTG 2, the p value was 0.13. This indicated that only CTG 3 compared with CTG 1 showed a significant difference in cancer-specific death [11]. In our study, nonsarcomatoid chRCC was also analyzed. Therefore, only CTG 1 and 2 were analyzed. FNG and CTG failed to show a significant relationship between the overall survival rate in the nonsarcomatoid chRCC cohort. This result is consistent with previous studies. As CTG 3 represents sarcomatoid change which in turn indicates poor survival, the authors concluded that CTG 3 may be an independent prognostic factor. However, the predictive value of CTG 1 and 2 was relatively weak, and further variables may be needed in this grading system to increase prognostic accuracy.
There are several limitations to this study. First, this was a retrospective study from a single center. Therefore, observation bias may be present. Second, the number of cases was small, and only one adverse event was found during a mean follow-up period of 70.6 months. Our study had relatively longer follow-up times than previous studies that compared both FNG and CTG. The only study that had a longer follow up time (126 months) was written by Cheville and college [11]. The other studies had follow up times shorter than 60 months. We reviewed all suspected cases, of which only 18 were compatible with chRCC, and we reviewed adverse events according to imaging findings and telephone interviews. Multivariate analysis cannot apply in our study due to fewer adverse events. The largest study of chRCC was by Volpe and colleagues, in which only 8.6% of the patients had disease recurrence and 6.2% of the patients died of the disease [6]. This shows that chRCC has a relatively good prognosis and low adverse event rate. Third, only one pathologist reviewed all pathological features in our study. Perez-Pedrosa et al. evaluated interobserver reproducibility of CTG, and found moderate discrete agreement between six participating observers [14]. Therefore, observer bias may have occurred in our study.
In conclusion, chRCC had low rates of cancer-specific death and sarcomatoid differentiation. Both FNG and CTG were associated with overall survival. Further studies are needed to evaluate the value of this system.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the staff at the Department of Urology of Mackay Memorial Hospital for their assistance.
- Abbreviations
- chRCC
Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma
- FNG
Fuhrman nuclear grade
- CTG
Chromophobe tumor grade
-
Conflict of interest
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest related to the subject matter or materials discussed in this article.
References
[1] Capitanio U, Montorsi F. Renal cancer. Lancet (London, England). 2016;387(10021):894-906; DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(15)00046-x10.1016/s0140-6736(15)00046-xSuche in Google Scholar
[2] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2018;68(1):7-30; DOI: 10.3322/caac.2144210.3322/caac.21442Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Frees S, Kamal MM, Knoechlein L, Bell R, Ziesel C, Neisius A, et al. Differences in Overall and Cancer-specific Survival of Patients Presenting With Chromophobe Versus Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Matched Analysis. Urology. 2016;98:81-7; DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2016.05.04810.1016/j.urology.2016.05.048Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Fuhrman SA, Lasky LC, Limas C. Prognostic significance of morphologic parameters in renal cell carcinoma. The American journal of surgical pathology. 1982;6(7):655-66310.1097/00000478-198210000-00007Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Moch H, Cubilla AL, Humphrey PA, Reuter VE, Ulbright TM. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part A: Renal, Penile, and Testicular Tumours. European urology. 2016;70(1):93-105; DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.02.02910.1016/j.eururo.2016.02.029Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Volpe A, Novara G, Antonelli A, Bertini R, Billia M, Carmignani G, et al. Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (RCC): oncological outcomes and prognostic factors in a large multicentre series. BJU international. 2012;110(1):76-83, DOI: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10690.x10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10690.xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Xie Y, Ma X, Li H, Gao Y, Gu L, Chen L, et al. Prognostic Value of Clinical and Pathological Features in Chinese Patients with Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma: A 10-Year Single-Center Study. Journal of Cancer. 2017;8(17):3474-9; DOI: 10.7150/jca.1995310.7150/jca.19953Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Delahunt B, Sika-Paotonu D, Bethwaite PB, McCredie MR, Martignoni G, Eble JN, et al. Fuhrman grading is not appropriate for chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. The American journal of surgical pathology. 2007;31(6):957-60; DOI: 10.1097/01.pas.0000249446.28713.5310.1097/01.pas.0000249446.28713.53Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Paner GP, Amin MB, Alvarado-Cabrero I, Young AN, Stricker HJ, Moch H, et al. A novel tumor grading scheme for chromophobe renal cell carcinoma: prognostic utility and comparison with Fuhrman nuclear grade. The American journal of surgical pathology. 2010;34(9):1233-40; DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181e96f2a10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181e96f2aSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Finley DS, Shuch B, Said JW, Galliano G, Jeffries RA, Afifi AA, et al. The chromophobe tumor grading system is the preferred grading scheme for chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. The Journal of urology. 2011;186(6):2168-74; DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.07.06810.1016/j.juro.2011.07.068Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Sukov WR, Thompson RH, Leibovich BC. Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma: the impact of tumor grade on outcome. The American journal of surgical pathology. 2012;36(6):851-6; DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318249689510.1097/PAS.0b013e3182496895Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Weinzierl EP, Thong AE, McKenney JK, Jeon SH, Chung BI. Relating prognosis in chromophobe renal cell carcinoma to the chromophobe tumor grading system. Korean journal of urology. 2014;55(4):239-44; DOI: 10.4111/kju.2014.55.4.23910.4111/kju.2014.55.4.239Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Przybycin CG, Cronin AM, Darvishian F, Gopalan A, Al-Ahmadie HA, Fine SW, et al. Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma: a clinicopathologic study of 203 tumors in 200 patients with primary resection at a single institution. The American journal of surgical pathology. 2011;35(7):962-70; DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31821a455d10.1097/PAS.0b013e31821a455dSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Perez-Pedrosa A, Ortiz-Rey JA, Lorenzo-Mahia Y, Iglesias-Rodriguez B, Peteiro-Cancelo A, Gonzalez-Carrero J. Interobserver reproducibility of a grading system for chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Actas urologicas espanolas. 2013;37(6):338-41; DOI: 10.1016/j. acuro.2012.04.00510.1016/j.acuro.2012.04.005Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2019 Tsu-Feng Lin et al. published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Article
- Prostate Cancer-Specific of DD3-driven oncolytic virus-harboring mK5 gene
- Case Report
- Pediatric acute paradoxical cerebral embolism with pulmonary embolism caused by extremely small patent foramen ovale
- Research Article
- Associations between ambient temperature and acute myocardial infarction
- Case Report
- Discontinuation of imatinib mesylate could improve renal impairment in chronic myeloid leukemia
- Research Article
- METTL3 promotes the proliferation and mobility of gastric cancer cells
- The C677T polymorphism of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene and susceptibility to late-onset Alzheimer’s disease
- microRNA-1236-3p regulates DDP resistance in lung cancer cells
- Review Article
- The link between thyroid autoimmunity, depression and bipolar disorder
- Research Article
- Effects of miR-107 on the Chemo-drug sensitivity of breast cancer cells
- Analysis of pH dose-dependent growth of sulfate-reducing bacteria
- Review Article
- Musculoskeletal clinical and imaging manifestations in inflammatory bowel diseases
- Research Article
- Regional hyperthermia combined with chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer
- Analysis of hormone receptor status in primary and recurrent breast cancer via data mining pathology reports
- Morphological and isokinetic strength differences: bilateral and ipsilateral variation by different sport activity
- The reliability of adjusting stepped care based on FeNO monitoring for patients with chronic persistent asthma
- Comparison of the clinical outcomes of two physiological ischemic training methods in patients with coronary heart disease
- Analysis of ticagrelor’s cardio-protective effects on patients with ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome accompanied with diabetes
- Computed tomography findings in patients with Samter’s Triad: an observational study
- Case Report
- A spinal subdural hematoma induced by guidewire-based lumbar drainage in a patient with ruptured intracranial aneurysms
- Research Article
- High expression B3GAT3 is related with poor prognosis of liver cancer
- Effects of light touch on balance in patients with stroke
- Oncoprotein LAMTOR5 activates GLUT1 via upregulating NF-κB in liver cancer
- Effects of budesonide combined with noninvasive ventilation on PCT, sTREM-1, chest lung compliance, humoral immune function and quality of life in patients with AECOPD complicated with type II respiratory failure
- Prognostic significance of lymph node ratio in ovarian cancer
- Case Report
- Brainstem anaesthesia after retrobulbar block
- Review Article
- Treating infertility: current affairs of cross-border reproductive care
- Research Article
- Serum inflammatory cytokines comparison in gastric cancer therapy
- Behavioural and psychological symptoms in neurocognitive disorders: Specific patterns in dementia subtypes
- MRI and bone scintigraphy for breast cancer bone metastase: a meta-analysis
- Comparative study of back propagation artificial neural networks and logistic regression model in predicting poor prognosis after acute ischemic stroke
- Analysis of the factors affecting the prognosis of glioma patients
- Compare fuhrman nuclear and chromophobe tumor grade on chromophobe RCC
- Case Report
- Signet ring B cell lymphoma: A potential diagnostic pitfall
- Research Article
- Subparaneural injection in popliteal sciatic nerve blocks evaluated by MRI
- Loneliness in the context of quality of life of nursing home residents
- Biological characteristics of cervical precancerous cell proliferation
- Effects of Rehabilitation in Bankart Lesion in Non-athletes: A report of three cases
- Management of complications of first instance of hepatic trauma in a liver surgery unit: Portal vein ligation as a conservative therapeutic strategy
- Matrix metalloproteinase 2 knockdown suppresses the proliferation of HepG2 and Huh7 cells and enhances the cisplatin effect
- Comparison of laparoscopy and open radical nephrectomy of renal cell cancer
- Case Report
- A severe complication of myocardial dysfunction post radiofrequency ablation treatment of huge hepatic hemangioma: a case report and literature review
- Solar urticaria, a disease with many dark sides: is omalizumab the right therapeutic response? Reflections from a clinical case report
- Research Article
- Binge eating disorder and related features in bariatric surgery candidates
- Propofol versus 4-hydroxybutyric acid in pediatric cardiac catheterizations
- Nasointestinal tube in mechanical ventilation patients is more advantageous
- The change of endotracheal tube cuff pressure during laparoscopic surgery
- Correlation between iPTH levels on the first postoperative day after total thyroidectomy and permanent hypoparathyroidism: our experience
- Case Report
- Primary angiosarcoma of the kidney: case report and comprehensive literature review
- Research Article
- miR-107 enhances the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to paclitaxel
- Incidental findings in dental radiology are concerning for family doctors
- Suffering from cerebral small vessel disease with and without metabolic syndrome
- A meta-analysis of robot assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy versus laparoscopic radical prostatectomy
- Indications and outcomes of splenectomy for hematological disorders
- Expression of CENPE and its prognostic role in non-small cell lung cancer
- Barbed suture and gastrointestinal surgery. A retrospective analysis
- Using post transplant 1 week Tc-99m DTPA renal scan as another method for predicting renal graft failure
- The pseudogene PTTG3P promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Lymph node ratio versus TNM system as prognostic factor in colorectal cancer staging. A single Center experience
- Review Article
- Minimally invasive pilonidal sinus treatment: A narrative review
- Research Article
- Anatomical workspace study of Endonasal Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Approach
- Hounsfield Units on Lumbar Computed Tomography for Predicting Regional Bone Mineral Density
- Communication
- Aspirin, a potential GLUT1 inhibitor in a vascular endothelial cell line
- Research Article
- Osteopontin and fatty acid binding protein in ifosfamide-treated rats
- Familial polyposis coli: the management of desmoid tumor bleeding
- microRNA-27a-3p down-regulation inhibits malignant biological behaviors of ovarian cancer by targeting BTG1
- PYCR1 is associated with papillary renal cell carcinoma progression
- Prediction of recurrence-associated death from localized prostate cancer with a charlson comorbidity index–reinforced machine learning model
- Colorectal cancer in the elderly patient: the role of neo-adjuvant therapy
- Association between MTHFR genetic polymorphism and Parkinson’s disease susceptibility: a meta-analysis
- Metformin can alleviate the symptom of patient with diabetic nephropathy through reducing the serum level of Hcy and IL-33
- Case Report
- Severe craniofacial trauma after multiple pistol shots
- Research Article
- Echocardiography evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function in elderly women with metabolic syndrome
- Tailored surgery in inguinal hernia repair. The role of subarachnoid anesthesia: a retrospective study
- The factors affecting early death in newly diagnosed APL patients
- Review Article
- Oncological outcomes and quality of life after rectal cancer surgery
- Research Article
- MiR-638 repressed vascular smooth muscle cell glycolysis by targeting LDHA
- microRNA-16 via Twist1 inhibits EMT induced by PM2.5 exposure in human hepatocellular carcinoma
- Analyzing the semantic space of the Hippocratic Oath
- Fournier’s gangrene and intravenous drug abuse: an unusual case report and review of the literature
- Evaluation of surgical site infection in mini-invasive urological surgery
- Dihydromyricetin attenuates inflammation through TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway
- Clinico-pathological features of colon cancer patients undergoing emergency surgery: a comparison between elderly and non-elderly patients
- Case Report
- Appendix bleeding with painless bloody diarrhea: A case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Protective effects of specneuzhenide on renal injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy
- PBF, a proto-oncogene in esophageal carcinoma
- Use of rituximab in NHL malt type pregnant in I° trimester for two times
- Cancer- and non-cancer related chronic pain: from the physiopathological basics to management
- Case report
- Non-surgical removal of dens invaginatus in maxillary lateral incisor using CBCT: Two-year follow-up case report
- Research Article
- Risk factors and drug resistance of the MDR Acinetobacter baumannii in pneumonia patients in ICU
- Accuracy of tumor perfusion assessment in Rat C6 gliomas model with USPIO
- Lemann Index for Assessment of Crohn’s Disease: Correlation with the Quality of Life, Endoscopic Disease activity, Magnetic Resonance Index of Activity and C- Reactive Protein
- Case report
- Münchausen syndrome as an unusual cause of pseudo-resistant hypertension: a case report
- Research Article
- Renal artery embolization before radical nephrectomy for complex renal tumour: which are the true advantages?
- Prognostic significance of CD276 in non-small cell lung cancer
- Potential drug-drug interactions in acute ischemic stroke patients at the Neurological Intensive Care Unit
- Effect of vitamin D3 on lung damage induced by cigarette smoke in mice
- CircRNA-UCK2 increased TET1 inhibits proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer cells via sponge miRNA-767-5p
- Case report
- Partial hydatidiform mole and coexistent live fetus: a case report and review of the literature
- Research Article
- Effect of NGR1 on the atopic dermatitis model and its mechanisms
- Clinical features of infertile men carrying a chromosome 9 translocation
- Review Article
- Expression and role of microRNA-663b in childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia and its mechanism
- Case Report
- Mature cystic teratoma of the pancreas: A rare cystic neoplasm
- Research Article
- Application of exercised-based pre-rehabilitation in perioperative period of patients with gastric cancer
- Case Report
- Predictive factors of intestinal necrosis in acute mesenteric ischemia
- Research Article
- Application of exercised-based pre-rehabilitation in perioperative period of patients with gastric cancer
- Effects of dexmedetomidine on the RhoA /ROCK/ Nox4 signaling pathway in renal fibrosis of diabetic rats
- MicroRNA-181a-5p regulates inflammatory response of macrophages in sepsis
- Intraventricular pressure in non-communicating hydrocephalus patients before endoscopic third ventriculostomy
- CyclinD1 is a new target gene of tumor suppressor miR-520e in breast cancer
- CHL1 and NrCAM are primarily expressed in low grade pediatric neuroblastoma
- Epidemiological characteristics of postoperative sepsis
- Association between unstable angina and CXCL17: a new potential biomarker
- Cardiac strains as a tool for optimization of cardiac resynchronization therapy in non-responders: a pilot study
- Case Report
- Resuscitation following a bupivacaine injection for a cervical paravertebral block
- Research Article
- CGF treatment of leg ulcers: A randomized controlled trial
- Surgical versus sequential hybrid treatment of carotid body tumors
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Article
- Prostate Cancer-Specific of DD3-driven oncolytic virus-harboring mK5 gene
- Case Report
- Pediatric acute paradoxical cerebral embolism with pulmonary embolism caused by extremely small patent foramen ovale
- Research Article
- Associations between ambient temperature and acute myocardial infarction
- Case Report
- Discontinuation of imatinib mesylate could improve renal impairment in chronic myeloid leukemia
- Research Article
- METTL3 promotes the proliferation and mobility of gastric cancer cells
- The C677T polymorphism of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene and susceptibility to late-onset Alzheimer’s disease
- microRNA-1236-3p regulates DDP resistance in lung cancer cells
- Review Article
- The link between thyroid autoimmunity, depression and bipolar disorder
- Research Article
- Effects of miR-107 on the Chemo-drug sensitivity of breast cancer cells
- Analysis of pH dose-dependent growth of sulfate-reducing bacteria
- Review Article
- Musculoskeletal clinical and imaging manifestations in inflammatory bowel diseases
- Research Article
- Regional hyperthermia combined with chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer
- Analysis of hormone receptor status in primary and recurrent breast cancer via data mining pathology reports
- Morphological and isokinetic strength differences: bilateral and ipsilateral variation by different sport activity
- The reliability of adjusting stepped care based on FeNO monitoring for patients with chronic persistent asthma
- Comparison of the clinical outcomes of two physiological ischemic training methods in patients with coronary heart disease
- Analysis of ticagrelor’s cardio-protective effects on patients with ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome accompanied with diabetes
- Computed tomography findings in patients with Samter’s Triad: an observational study
- Case Report
- A spinal subdural hematoma induced by guidewire-based lumbar drainage in a patient with ruptured intracranial aneurysms
- Research Article
- High expression B3GAT3 is related with poor prognosis of liver cancer
- Effects of light touch on balance in patients with stroke
- Oncoprotein LAMTOR5 activates GLUT1 via upregulating NF-κB in liver cancer
- Effects of budesonide combined with noninvasive ventilation on PCT, sTREM-1, chest lung compliance, humoral immune function and quality of life in patients with AECOPD complicated with type II respiratory failure
- Prognostic significance of lymph node ratio in ovarian cancer
- Case Report
- Brainstem anaesthesia after retrobulbar block
- Review Article
- Treating infertility: current affairs of cross-border reproductive care
- Research Article
- Serum inflammatory cytokines comparison in gastric cancer therapy
- Behavioural and psychological symptoms in neurocognitive disorders: Specific patterns in dementia subtypes
- MRI and bone scintigraphy for breast cancer bone metastase: a meta-analysis
- Comparative study of back propagation artificial neural networks and logistic regression model in predicting poor prognosis after acute ischemic stroke
- Analysis of the factors affecting the prognosis of glioma patients
- Compare fuhrman nuclear and chromophobe tumor grade on chromophobe RCC
- Case Report
- Signet ring B cell lymphoma: A potential diagnostic pitfall
- Research Article
- Subparaneural injection in popliteal sciatic nerve blocks evaluated by MRI
- Loneliness in the context of quality of life of nursing home residents
- Biological characteristics of cervical precancerous cell proliferation
- Effects of Rehabilitation in Bankart Lesion in Non-athletes: A report of three cases
- Management of complications of first instance of hepatic trauma in a liver surgery unit: Portal vein ligation as a conservative therapeutic strategy
- Matrix metalloproteinase 2 knockdown suppresses the proliferation of HepG2 and Huh7 cells and enhances the cisplatin effect
- Comparison of laparoscopy and open radical nephrectomy of renal cell cancer
- Case Report
- A severe complication of myocardial dysfunction post radiofrequency ablation treatment of huge hepatic hemangioma: a case report and literature review
- Solar urticaria, a disease with many dark sides: is omalizumab the right therapeutic response? Reflections from a clinical case report
- Research Article
- Binge eating disorder and related features in bariatric surgery candidates
- Propofol versus 4-hydroxybutyric acid in pediatric cardiac catheterizations
- Nasointestinal tube in mechanical ventilation patients is more advantageous
- The change of endotracheal tube cuff pressure during laparoscopic surgery
- Correlation between iPTH levels on the first postoperative day after total thyroidectomy and permanent hypoparathyroidism: our experience
- Case Report
- Primary angiosarcoma of the kidney: case report and comprehensive literature review
- Research Article
- miR-107 enhances the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to paclitaxel
- Incidental findings in dental radiology are concerning for family doctors
- Suffering from cerebral small vessel disease with and without metabolic syndrome
- A meta-analysis of robot assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy versus laparoscopic radical prostatectomy
- Indications and outcomes of splenectomy for hematological disorders
- Expression of CENPE and its prognostic role in non-small cell lung cancer
- Barbed suture and gastrointestinal surgery. A retrospective analysis
- Using post transplant 1 week Tc-99m DTPA renal scan as another method for predicting renal graft failure
- The pseudogene PTTG3P promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Lymph node ratio versus TNM system as prognostic factor in colorectal cancer staging. A single Center experience
- Review Article
- Minimally invasive pilonidal sinus treatment: A narrative review
- Research Article
- Anatomical workspace study of Endonasal Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Approach
- Hounsfield Units on Lumbar Computed Tomography for Predicting Regional Bone Mineral Density
- Communication
- Aspirin, a potential GLUT1 inhibitor in a vascular endothelial cell line
- Research Article
- Osteopontin and fatty acid binding protein in ifosfamide-treated rats
- Familial polyposis coli: the management of desmoid tumor bleeding
- microRNA-27a-3p down-regulation inhibits malignant biological behaviors of ovarian cancer by targeting BTG1
- PYCR1 is associated with papillary renal cell carcinoma progression
- Prediction of recurrence-associated death from localized prostate cancer with a charlson comorbidity index–reinforced machine learning model
- Colorectal cancer in the elderly patient: the role of neo-adjuvant therapy
- Association between MTHFR genetic polymorphism and Parkinson’s disease susceptibility: a meta-analysis
- Metformin can alleviate the symptom of patient with diabetic nephropathy through reducing the serum level of Hcy and IL-33
- Case Report
- Severe craniofacial trauma after multiple pistol shots
- Research Article
- Echocardiography evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function in elderly women with metabolic syndrome
- Tailored surgery in inguinal hernia repair. The role of subarachnoid anesthesia: a retrospective study
- The factors affecting early death in newly diagnosed APL patients
- Review Article
- Oncological outcomes and quality of life after rectal cancer surgery
- Research Article
- MiR-638 repressed vascular smooth muscle cell glycolysis by targeting LDHA
- microRNA-16 via Twist1 inhibits EMT induced by PM2.5 exposure in human hepatocellular carcinoma
- Analyzing the semantic space of the Hippocratic Oath
- Fournier’s gangrene and intravenous drug abuse: an unusual case report and review of the literature
- Evaluation of surgical site infection in mini-invasive urological surgery
- Dihydromyricetin attenuates inflammation through TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway
- Clinico-pathological features of colon cancer patients undergoing emergency surgery: a comparison between elderly and non-elderly patients
- Case Report
- Appendix bleeding with painless bloody diarrhea: A case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Protective effects of specneuzhenide on renal injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy
- PBF, a proto-oncogene in esophageal carcinoma
- Use of rituximab in NHL malt type pregnant in I° trimester for two times
- Cancer- and non-cancer related chronic pain: from the physiopathological basics to management
- Case report
- Non-surgical removal of dens invaginatus in maxillary lateral incisor using CBCT: Two-year follow-up case report
- Research Article
- Risk factors and drug resistance of the MDR Acinetobacter baumannii in pneumonia patients in ICU
- Accuracy of tumor perfusion assessment in Rat C6 gliomas model with USPIO
- Lemann Index for Assessment of Crohn’s Disease: Correlation with the Quality of Life, Endoscopic Disease activity, Magnetic Resonance Index of Activity and C- Reactive Protein
- Case report
- Münchausen syndrome as an unusual cause of pseudo-resistant hypertension: a case report
- Research Article
- Renal artery embolization before radical nephrectomy for complex renal tumour: which are the true advantages?
- Prognostic significance of CD276 in non-small cell lung cancer
- Potential drug-drug interactions in acute ischemic stroke patients at the Neurological Intensive Care Unit
- Effect of vitamin D3 on lung damage induced by cigarette smoke in mice
- CircRNA-UCK2 increased TET1 inhibits proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer cells via sponge miRNA-767-5p
- Case report
- Partial hydatidiform mole and coexistent live fetus: a case report and review of the literature
- Research Article
- Effect of NGR1 on the atopic dermatitis model and its mechanisms
- Clinical features of infertile men carrying a chromosome 9 translocation
- Review Article
- Expression and role of microRNA-663b in childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia and its mechanism
- Case Report
- Mature cystic teratoma of the pancreas: A rare cystic neoplasm
- Research Article
- Application of exercised-based pre-rehabilitation in perioperative period of patients with gastric cancer
- Case Report
- Predictive factors of intestinal necrosis in acute mesenteric ischemia
- Research Article
- Application of exercised-based pre-rehabilitation in perioperative period of patients with gastric cancer
- Effects of dexmedetomidine on the RhoA /ROCK/ Nox4 signaling pathway in renal fibrosis of diabetic rats
- MicroRNA-181a-5p regulates inflammatory response of macrophages in sepsis
- Intraventricular pressure in non-communicating hydrocephalus patients before endoscopic third ventriculostomy
- CyclinD1 is a new target gene of tumor suppressor miR-520e in breast cancer
- CHL1 and NrCAM are primarily expressed in low grade pediatric neuroblastoma
- Epidemiological characteristics of postoperative sepsis
- Association between unstable angina and CXCL17: a new potential biomarker
- Cardiac strains as a tool for optimization of cardiac resynchronization therapy in non-responders: a pilot study
- Case Report
- Resuscitation following a bupivacaine injection for a cervical paravertebral block
- Research Article
- CGF treatment of leg ulcers: A randomized controlled trial
- Surgical versus sequential hybrid treatment of carotid body tumors

