Abstract
Modelling and simulation of recrystallization, grain growth, and related phenomena are important tools for the fundamental understanding of microstructural evolution that takes place during the annealing and thermomechanical processing of steel. It is also important for the prediction of engineering properties. In this paper, the evolution of mean grain radius and the recrystallized volume fraction of steel was modelled using the statistical theory of grain growth originally developed by Lücke [1] and here integrated to take into consideration the effect of recrystallization. In particular, the effect of one free input parameter (initial distribution of grain radii) of the model is analysed without taking into account the textures effect.
1 Introduction and description of the model
Grain size and chemical composition deeply affect the mechanical properties of steel and in recent years much efforts have been made to exploit the effect of these variables to improve mechanical and other properties of steels, these include: yield strength, ductility, fatigue behaviour, weldability, creep, and corrosion resistance [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9].
Recrystallization and grain growth are others aspect relevant to the mechanical properties of steel and there is a need for models which will predict the effect of the processing parameters on the materials that are produced [13]. There are micro models such as Monte Carlo simulation [14], cellular automata [15], molecular dynamics, vertex model [16] and the phase-field model [1718]. In this paper an analytical model is reported, that can predict most of the characteristic of microstructural evolution (i.e. grain size and grain size distribution) combining a recrystallization model that works simultaneously with a grain growth model (based on Hillert model and further developed by Abbruzzese and Lücke) [18, 19, 20]. The goal of the micro model is to generate snapshots of the evolving microstructure with time and the local and ensemble properties of the microstructure may be determined from these snapshot.
As it is well known from the basics of metallurgy theory, the driving force of primary recrystallization is the driving force of primary recrystallization is for the most part related to the system tendency to eliminate the deformation energy introduced by cold working. During the heat treatment, it occurs a release of the deformation energy that activates the movement of dislocation and sub-grain boundaries thus restoring a dislocation free microstructure. Once all the dislocation is eliminated and a complete recrystallized structure is created in the material, the larger grains begin to growth at the expenses of the smaller grains (secondary recrystallization).
As concerns grain growth, the statistical model is based on the assumption of [21]:
Super-position of average grain curvatures in individual grain boundaries.
Homogeneous surroundings of the grains. As a first approximation is assumed that for each grain v the individual neighbourhood of Nv individual grain can be replaced by a surrounding obtained by averaging over a neighbourhood of all grains of the same radius Rv. Since then all grains of the same radius would have the same surrounding, also their growth rate would be equal. This means that all grains could be collected in classes characterized by their radius and that the behaviour of only different classes has to be considered, instead of single grains.
A random array of the grains namely the probability of contact among the grains is only depending on their relative surface in the system.
The integration of all the above assumptions in the model leads to the following final form of the grain growth rate equation:
Where:
Ri [cm] – Radius of grain belonging to class i
Rj [cm] – Radius of grain belonging to class j
ni – Total number of grains in class i
nj – Total number of grains in class j
Where M = 2mγ is again the boundary diffusivity and in our case study m was evaluated according to the Stokes-Einstein relationship [22]:
Where:
D [cm/s] – Diffusion coefficient
kB [erg/K] - Boltzmann constant
ΔE [erg/mol K] – Activation energy
T [K] – Annealing temperature
D was chosen proportional to the diffusion coefficient of Fe in Fe-γ.
To describe the recrystallization process integrated with the grain growth, it is necessary to propose an extended growth equation that allows to analyse contemporarily and continuously the evolution of free nuclei in the matrix passing through partially impinged grains up to full contact. An “influence mean radius” that allow to evaluate the fraction of surface in contact between different grain [18] was introduced.
The final equation for recrystallization and grain growth can therefore be written as:
Where:
G [dyne/cm2] – Shear modulus b [cm] – Burger’s vector
Δρ [cm−2] – Difference of dislocation density for the deformed material and the recrystallized material.
Thanks to the previous equations, a calculus program that can predict the evolution over time of the grain size distribution, has been developed. The constitutive equation of plastic deformation has been introduced in the model to further reduce the free input parameters [23]:
Where:
ξ – Deformation of material (Reduction rate)
b [cm] – Burger’s vector
L [cm] – Free path of dislocation nuclei
2 Results
2.1 Effect of the initial grain distribution
One of the free input parameters of the statistical model is the initial grain size distribution. Three different distribution have been investigated: lognormal, normal and a uniform distribution (see figure 1). For the simulation, the other free input parameters namely, thereduction rate of steel, the total number of deformation nuclei and the dislocation density, have been maintained constant in the range values typical of industrially deformed steels.
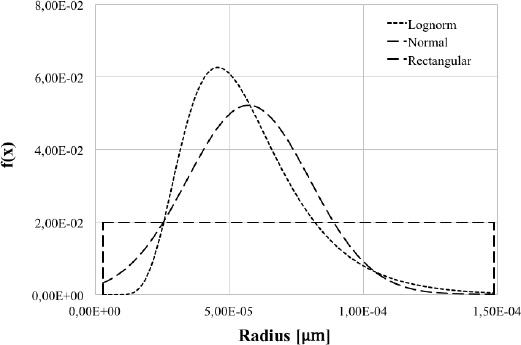
Initial grain size distribution
Input parameters used in the statistical model
| ε [reduction] | Ntot[cm−3] | Δρ[cm−2] | T [ ∘C] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.80 | 8.59e9 | 1.99e11 | 1100 |
The lognormal distribution is very important in the description of natural phenomena because numerous natural growth processes are driven by the accumulation of many small percentage changes [24]. Normal (or Gaussian) distribution is a continuous probability function very common and thanks to the central limit theorem when independent random variables are added (like grain dimension), their sum tends toward a normal distribution even if the original variables themselves are not normally distributed [25]. Unlike a normal distribution with a hump in the middle, a uniform distribution has no mode and every outcome is equally likely to occur and was tested as a case limit [26].
A simulation of an annealing process of 300 seconds at T=1100∘C resulted in a mean grain radius obtained from the uniform distribution bigger than the log-normal and normal distribution (respectively 29.25% bigger and 43.74%) and the difference for the three trends begin after the complete recrystallization of steel as can be seen in figure 2. The difference between the-log normal and normal distribution is less pronounced and the log-normal distribution leads to a 20 % larger grain.
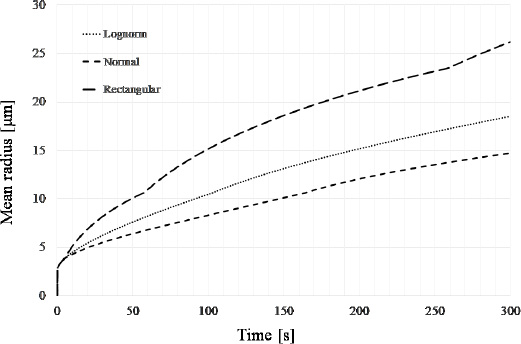
Mean radius over time for three different grain size distribution
With regards to the recrystallized volume fraction, all the three simulation leads the complete recrystallization at the same time (approximately at 4.5 second), as is shown in figure 3. The recrystallized volume fraction in figure 3 was calculated based on the same input parameters as in figure 2.
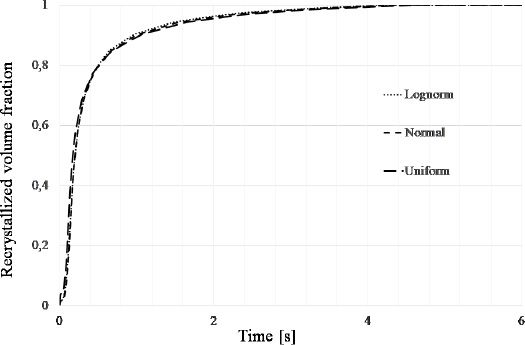
Recrystallized volume fraction, for the first seconds of simulation, for the three different distribution
3 Conclusion
Results from a recrystallization and grain growth model based on statistical assumption have been discussed here. In particular, the effect of the initial grain radii distribution has been analyzed. Results show that:
Final mean radius size is bigger for the uniform distribution than the log-normal and normal distribution;
The mean radius is almost the same size for the three different distribution before the complete recrystallization;
The complete recrystallization occurs at the same time for isothermal annealing process (even for different distribution).
The potential of this approach is a general purpose tool for thermo-mechanical treatment result prediction.
References
[1] Lücke K., Computer simulation of texture-controlled grain growth, Acta Metallurgica, 1988, 36, 818–82510.2355/isijinternational1966.28.818Search in Google Scholar
[2] Di Schino A., Guarnaschelli C., Microstructure and cleavage resistance of high strength steels. Materials Science Forum, 2010, 638–462, 3188–319310.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.638-642.3188Search in Google Scholar
[3] Di Schino A., Kenny J.M., Barteri M., High temperature resistance of a high nitrogen and low nickel austenitic stainless steel, Journal of Materials Science Letters, 2003, 22, 691–69310.1023/A:1023675212900Search in Google Scholar
[4] Di Schino A., Di Nunzio P.E., Effect of Nb microalloying on the heat affected zone microstructure of girth welded joints, Materials Letters, 2017, 186, 86–8910.1016/j.matlet.2016.09.092Search in Google Scholar
[5] Di Schino A., Analysis of heat treatment effect on microstructural features evolution in a micro-alloyed martensitic steel, Acta Metallurgica Slovaca, 2016, 22, 266–27010.12776/ams.v22i4.815Search in Google Scholar
[6] Di Schino A., Di Nunzio P.E., Metallurgical aspects related to contact fatigue phenomena in steels for back-up rolls, Acta Metallurgica Slovaca, 2017, 23, 62–7110.12776/ams.v23i1.852Search in Google Scholar
[7] Di Schino A., Richetta M., Effect of microalloying on quenching behaviour of steels for back-up rolls, Acta Metallurgica Slovaca, 2017, 23, 105–11010.12776/ams.v23i2.898Search in Google Scholar
[8] Püttgen W., Pant M., Bleck W., Seidl I., Rabitsch R., Testani C., Selection of suitable tool materials and development of tool concepts for the Thixoforging of steels, Steel Research International, 2006, 77, 342–34810.1002/srin.200606396Search in Google Scholar
[9] Gabrel J., Coussement C., Verelst K., Blum R., Chen Q., Testani C., Superheater materials testing for USC boilers: Steam side oxidation rate of 9 advanced materials in industrial conditions Materials Science Forum, 2001, 369–372, 931–93810.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.369-372.931Search in Google Scholar
[10] Di Schino A., Barteri M., Kenny J.M., Fatigue behaviour of a high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel as a function of its grain size, Journal of Materials Science Letters, 2003, 22, 1511–151310.1023/A:1026155215111Search in Google Scholar
[11] Raabe D., Computational materials science: the simulation of materials microstructures and properties Wiley-VHC,1998.10.1002/3527601945Search in Google Scholar
[12] Atkinson H.V., Theories of normal grain growth in pure single phase system, Acta Metallurgica, 1988,36, 469–49110.1016/0001-6160(88)90079-XSearch in Google Scholar
[13] Humphreys F.J., Hatherly M., Recrystallization and related annealing phenomena, Chapter 9, 1996, Pergamon Press.10.1016/B978-0-08-041884-1.50017-9Search in Google Scholar
[14] Rollett A.D., Srolovitz D.J., Anderson A.M., Doherty R.D., Computer simulation of recrystallization-III. Influence of a dispersion of fine particles, Acta Metallurgica, 1992, 40, 3475–3495.10.1016/0956-7151(92)90062-JSearch in Google Scholar
[15] Frost H., Thompson C.V., Walton D.T, Grain growth in polycrystalline materials, Trans Tech Publications, 1992.Search in Google Scholar
[16] K. Kawasaki, T. Nagai, K. Nakashima, Vertex models for two- dimensional grain growth Philosophical Magazine, 1989, 60, 399–42110.1080/13642818908205916Search in Google Scholar
[17] Krill C.E., Chen L.Q., Computer simulation of 3-D grain growth using a phase- field model Acta Materialia, 2002, 50, 3057–3073.10.1016/S1359-6454(02)00084-8Search in Google Scholar
[18] Di Schino A., Kenny J.M., Salvatori, I., Abbruzzese G., Modelling the primary recrystallization and grain growth in a low nickel austenitic stainless steel, Journal of materials science, 2001, 36, 593–60110.1023/A:1004856001632Search in Google Scholar
[19] M. Hillert. On the theory of normal and abnormal grain growth Acta Metallurgica, 1965, 13, 22710.1016/0001-6160(65)90200-2Search in Google Scholar
[20] Abbruzzese G., Heckelman I., Lücke K., Statistical theory of two-dimensional grain growth. kinetics of grain growth, Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1992, 40, 533–54210.1016/0956-7151(92)90402-ZSearch in Google Scholar
[21] Abbruzzese, G., Lücke K., A theory of texture controlled grain growth—I. Derivation and general discussion of the model, Acta Metallurgica, 1986, 34, 905–91410.1016/0001-6160(86)90064-7Search in Google Scholar
[22] Edward J.T., Molecular volumes and the Stokes-Einstein equation, Journal of Chemical Education, 1970, 40, 261–27010.1021/ed047p261Search in Google Scholar
[23] Di Schino A., Kenny J.M., Abbruzzese G., Analysis of the recrystallization and grain growth processes in AISI 316 stainless steel, Journal of Materials Science, 2002, 37, 5291–529810.1023/A:1021068806598Search in Google Scholar
[24] Heintzenberg J., Properties of the Log-Normal Particle Size Distribution, Aerosol Science and Tecnology, 1994, 21, 46–4810.1080/02786829408959695Search in Google Scholar
[25] Rice J., Mathematical Statistics and Data Analysis second ed. , Duxbury Press, 1995.Search in Google Scholar
[26] Triola F.: Essential of statistics fifth ed., Pearson, 2005.Search in Google Scholar
© 2018 G. Napoli et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Article
- Real-scale comparison between simple and composite raw sewage sampling
- 10.1515/eng-2018-0017
- The risks associated with falling parts of glazed facades in case of fire
- Implementation of high speed machining in thin-walled aircraft integral elements
- Evaluating structural crashworthiness and progressive failure of double hull tanker under accidental grounding: bottom raking case
- Influence of Silica (SiO2) Loading on the Thermal and Swelling Properties of Hydrogenated-Nitrile-Butadiene-Rubber/Silica (HNBR/Silica) Composites
- Statistical Variations and New Correlation Models to Predict the Mechanical Behavior and Ultimate Shear Strength of Gypsum Rock
- Analytic approximate solutions to the chemically reactive solute transfer problem with partial slip in the flow of a viscous fluid over an exponentially stretching sheet with suction/blowing
- Thermo-mechanical behavior simulation coupled with the hydrostatic-pressure-dependent grain-scale fission gas swelling calculation for a monolithic UMo fuel plate under heterogeneous neutron irradiation
- Optimal Auxiliary Functions Method for viscous flow due to a stretching surface with partial slip
- Vibrations Analysis of Rectangular Plates with Clamped Corners
- Evaluating Lean Performance of Indian Small and Medium Sized Enterprises in Automotive Sector
- FPGA–implementation of PID-controller by differential evolution optimization
- Thermal properties and morphology of polypropylene based on exfoliated graphite nanoplatelets/nanomagnesium oxide
- A computer-based renewable resource management system for a construction company
- Hygrothermal Aging of Amine Epoxy: Reversible Static and Fatigue Properties
- The selected roof covering technologies in the aspect of their life cycle costs
- Influence of insulated glass units thickness and weight reduction on their functional properties
- Structural analysis of conditions determining the selection of construction technology for structures in the centres of urban agglomerations
- Selection of the optimal solution of acoustic screens in a graphical interpretation of biplot and radar charts method
- Subsidy Risk Related to Construction Projects: Seeking Causes
- Multidimensional sensitivity study of the fuzzy risk assessment module in the life cycle of building objects
- Planning repetitive construction projects considering technological constraints
- Identification of risk investment using the risk matrix on railway facilities
- Comparison of energy parameters of a centrifugal pump with a multi-piped impeller in cooperation either with an annular channel and a spiral channel
- Influence of the contractor’s payment method on the economic effectiveness of the construction project from the contractor’s point of view
- Special Issue Automation in Finland
- Diagnostics and Identification of Injection Duration of Common Rail Diesel Injectors
- An advanced teaching scheme for integrating problem-based learning in control education
- A survey of telerobotic surface finishing
- Wireless Light-Weight IEC 61850 Based Loss of Mains Protection for Smart Grid
- Smart Adaptive Big Data Analysis with Advanced Deep Learning
- Topical Issue Desktop Grids for High Performance Computing
- A Bitslice Implementation of Anderson’s Attack on A5/1
- Efficient Redundancy Techniques in Cloud and Desktop Grid Systems using MAP/G/c-type Queues
- Templet Web: the use of volunteer computing approach in PaaS-style cloud
- Using virtualization to protect the proprietary material science applications in volunteer computing
- Parallel Processing of Images in Mobile Devices using BOINC
- “XANSONS for COD”: a new small BOINC project in crystallography
- Special Issue on Sustainable Energy, Engineering, Materials and Environment
- An experimental study on premixed CNG/H2/CO2 mixture flames
- Tidal current energy potential of Nalón river estuary assessment using a high precision flow model
- Special Spring Issue 2017
- Context Analysis of Customer Requests using a Hybrid Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System and Hidden Markov Models in the Natural Language Call Routing Problem
- Special Issue on Non-ferrous metals and minerals
- Study of strength properties of semi-finished products from economically alloyed high-strength aluminium-scandium alloys for application in automobile transport and shipbuilding
- Use of Humic Sorbent from Sapropel for Extraction of Palladium Ions from Chloride Solutions
- Topical Issue on Mathematical Modelling in Applied Sciences, II
- Numerical simulation of two-phase filtration in the near well bore zone
- Calculation of 3D Coordinates of a Point on the Basis of a Stereoscopic System
- The model of encryption algorithm based on non-positional polynomial notations and constructed on an SP-network
- A computational algorithm and the method of determining the temperature field along the length of the rod of variable cross section
- ICEUBI2017 - International Congress on Engineering-A Vision for the Future
- Use of condensed water from air conditioning systems
- Development of a 4 stroke spark ignition opposed piston engine
- Development of a Coreless Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for a Battery Electric Shell Eco Marathon Prototype Vehicle
- Removal of Cr, Cu and Zn from liquid effluents using the fine component of granitic residual soils
- A fuzzy reasoning approach to assess innovation risk in ecosystems
- Special Issue SEALCONF 2018
- Brush seal with thermo-regulating bimetal elements
- The CFD simulation of the flow structure in the sewage pump
- The investigation of the cavitation processes in the radial labyrinth pump
- Testing of the gaskets at liquid nitrogen and ambient temperature
- Probabilistic Approach to Determination of Dynamic Characteristics of Automatic Balancing Device
- The design method of rubber-metallic expansion joint
- The Specific Features of High-Velocity Magnetic Fluid Sealing Complexes
- Effect of contact pressure and sliding speed on the friction of polyurethane elastomer (EPUR) during sliding on steel under water wetting conditions
- Special Issue on Advance Material
- Effect of thermo-mechanical parameters on the mechanical properties of Eurofer97 steel for nuclear applications
- Failure prediction of axi-symmetric cup in deep drawing and expansion processes
- Characterization of cement composites based on recycled cellulosic waste paper fibres
- Innovative Soft Magnetic Composite Materials: Evaluation of magnetic and mechanical properties
- Statistical modelling of recrystallization and grain growth phenomena in stainless steels: effect of initial grain size distribution
- Annealing effect on microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-Al alloy subjected to Cryo-ECAP
- Influence of heat treatment on corrosion resistance of Mg-Al-Zn alloy processed by severe plastic deformation
- The mechanical properties of OFHC copper and CuCrZr alloys after asymmetric rolling at ambient and cryogenic temperatures
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Article
- Real-scale comparison between simple and composite raw sewage sampling
- 10.1515/eng-2018-0017
- The risks associated with falling parts of glazed facades in case of fire
- Implementation of high speed machining in thin-walled aircraft integral elements
- Evaluating structural crashworthiness and progressive failure of double hull tanker under accidental grounding: bottom raking case
- Influence of Silica (SiO2) Loading on the Thermal and Swelling Properties of Hydrogenated-Nitrile-Butadiene-Rubber/Silica (HNBR/Silica) Composites
- Statistical Variations and New Correlation Models to Predict the Mechanical Behavior and Ultimate Shear Strength of Gypsum Rock
- Analytic approximate solutions to the chemically reactive solute transfer problem with partial slip in the flow of a viscous fluid over an exponentially stretching sheet with suction/blowing
- Thermo-mechanical behavior simulation coupled with the hydrostatic-pressure-dependent grain-scale fission gas swelling calculation for a monolithic UMo fuel plate under heterogeneous neutron irradiation
- Optimal Auxiliary Functions Method for viscous flow due to a stretching surface with partial slip
- Vibrations Analysis of Rectangular Plates with Clamped Corners
- Evaluating Lean Performance of Indian Small and Medium Sized Enterprises in Automotive Sector
- FPGA–implementation of PID-controller by differential evolution optimization
- Thermal properties and morphology of polypropylene based on exfoliated graphite nanoplatelets/nanomagnesium oxide
- A computer-based renewable resource management system for a construction company
- Hygrothermal Aging of Amine Epoxy: Reversible Static and Fatigue Properties
- The selected roof covering technologies in the aspect of their life cycle costs
- Influence of insulated glass units thickness and weight reduction on their functional properties
- Structural analysis of conditions determining the selection of construction technology for structures in the centres of urban agglomerations
- Selection of the optimal solution of acoustic screens in a graphical interpretation of biplot and radar charts method
- Subsidy Risk Related to Construction Projects: Seeking Causes
- Multidimensional sensitivity study of the fuzzy risk assessment module in the life cycle of building objects
- Planning repetitive construction projects considering technological constraints
- Identification of risk investment using the risk matrix on railway facilities
- Comparison of energy parameters of a centrifugal pump with a multi-piped impeller in cooperation either with an annular channel and a spiral channel
- Influence of the contractor’s payment method on the economic effectiveness of the construction project from the contractor’s point of view
- Special Issue Automation in Finland
- Diagnostics and Identification of Injection Duration of Common Rail Diesel Injectors
- An advanced teaching scheme for integrating problem-based learning in control education
- A survey of telerobotic surface finishing
- Wireless Light-Weight IEC 61850 Based Loss of Mains Protection for Smart Grid
- Smart Adaptive Big Data Analysis with Advanced Deep Learning
- Topical Issue Desktop Grids for High Performance Computing
- A Bitslice Implementation of Anderson’s Attack on A5/1
- Efficient Redundancy Techniques in Cloud and Desktop Grid Systems using MAP/G/c-type Queues
- Templet Web: the use of volunteer computing approach in PaaS-style cloud
- Using virtualization to protect the proprietary material science applications in volunteer computing
- Parallel Processing of Images in Mobile Devices using BOINC
- “XANSONS for COD”: a new small BOINC project in crystallography
- Special Issue on Sustainable Energy, Engineering, Materials and Environment
- An experimental study on premixed CNG/H2/CO2 mixture flames
- Tidal current energy potential of Nalón river estuary assessment using a high precision flow model
- Special Spring Issue 2017
- Context Analysis of Customer Requests using a Hybrid Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System and Hidden Markov Models in the Natural Language Call Routing Problem
- Special Issue on Non-ferrous metals and minerals
- Study of strength properties of semi-finished products from economically alloyed high-strength aluminium-scandium alloys for application in automobile transport and shipbuilding
- Use of Humic Sorbent from Sapropel for Extraction of Palladium Ions from Chloride Solutions
- Topical Issue on Mathematical Modelling in Applied Sciences, II
- Numerical simulation of two-phase filtration in the near well bore zone
- Calculation of 3D Coordinates of a Point on the Basis of a Stereoscopic System
- The model of encryption algorithm based on non-positional polynomial notations and constructed on an SP-network
- A computational algorithm and the method of determining the temperature field along the length of the rod of variable cross section
- ICEUBI2017 - International Congress on Engineering-A Vision for the Future
- Use of condensed water from air conditioning systems
- Development of a 4 stroke spark ignition opposed piston engine
- Development of a Coreless Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for a Battery Electric Shell Eco Marathon Prototype Vehicle
- Removal of Cr, Cu and Zn from liquid effluents using the fine component of granitic residual soils
- A fuzzy reasoning approach to assess innovation risk in ecosystems
- Special Issue SEALCONF 2018
- Brush seal with thermo-regulating bimetal elements
- The CFD simulation of the flow structure in the sewage pump
- The investigation of the cavitation processes in the radial labyrinth pump
- Testing of the gaskets at liquid nitrogen and ambient temperature
- Probabilistic Approach to Determination of Dynamic Characteristics of Automatic Balancing Device
- The design method of rubber-metallic expansion joint
- The Specific Features of High-Velocity Magnetic Fluid Sealing Complexes
- Effect of contact pressure and sliding speed on the friction of polyurethane elastomer (EPUR) during sliding on steel under water wetting conditions
- Special Issue on Advance Material
- Effect of thermo-mechanical parameters on the mechanical properties of Eurofer97 steel for nuclear applications
- Failure prediction of axi-symmetric cup in deep drawing and expansion processes
- Characterization of cement composites based on recycled cellulosic waste paper fibres
- Innovative Soft Magnetic Composite Materials: Evaluation of magnetic and mechanical properties
- Statistical modelling of recrystallization and grain growth phenomena in stainless steels: effect of initial grain size distribution
- Annealing effect on microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-Al alloy subjected to Cryo-ECAP
- Influence of heat treatment on corrosion resistance of Mg-Al-Zn alloy processed by severe plastic deformation
- The mechanical properties of OFHC copper and CuCrZr alloys after asymmetric rolling at ambient and cryogenic temperatures

